Seasonal Variability of Retroflection Structures and Transports in the Atlantic Ocean as Inferred from Satellite-Derived Salinity Maps
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. HYCOM Simulation
2.2. SMOS Data
2.3. Argo Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sea Surface Salinity Variability
3.1.1. North Brazil Current Retroflection
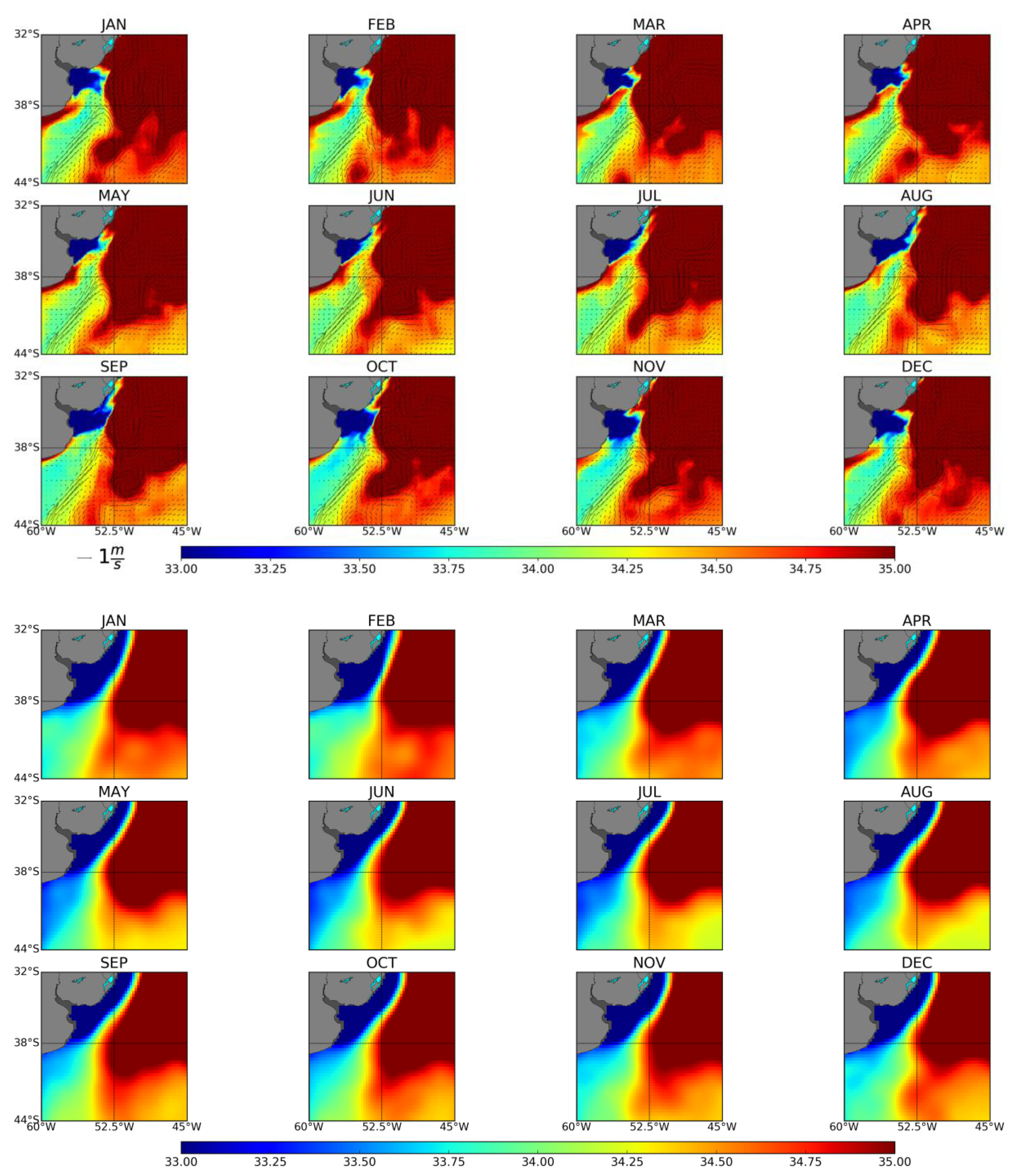
3.1.2. Brazil-Malvinas Confluence
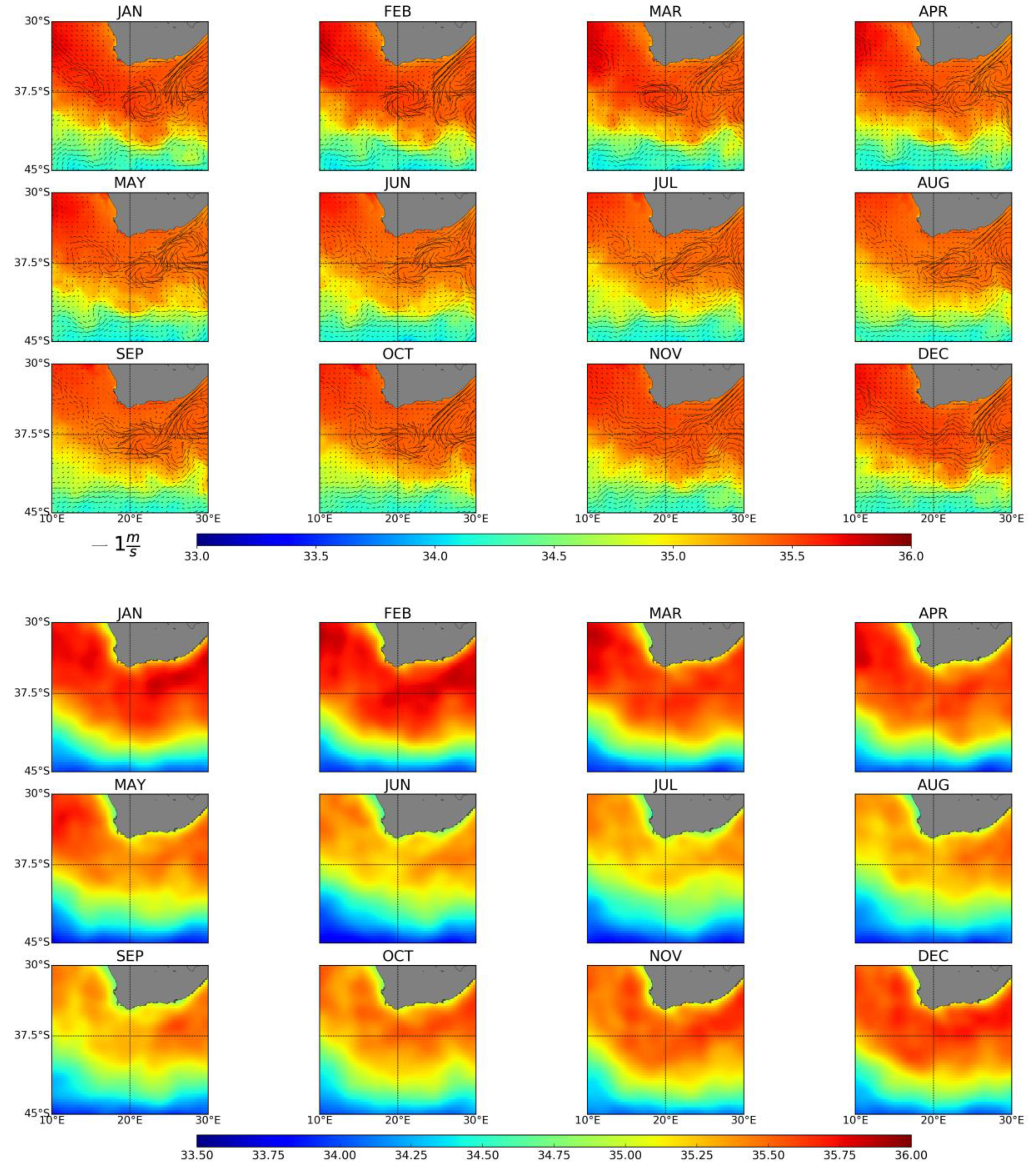
3.1.3. Agulhas Leakage
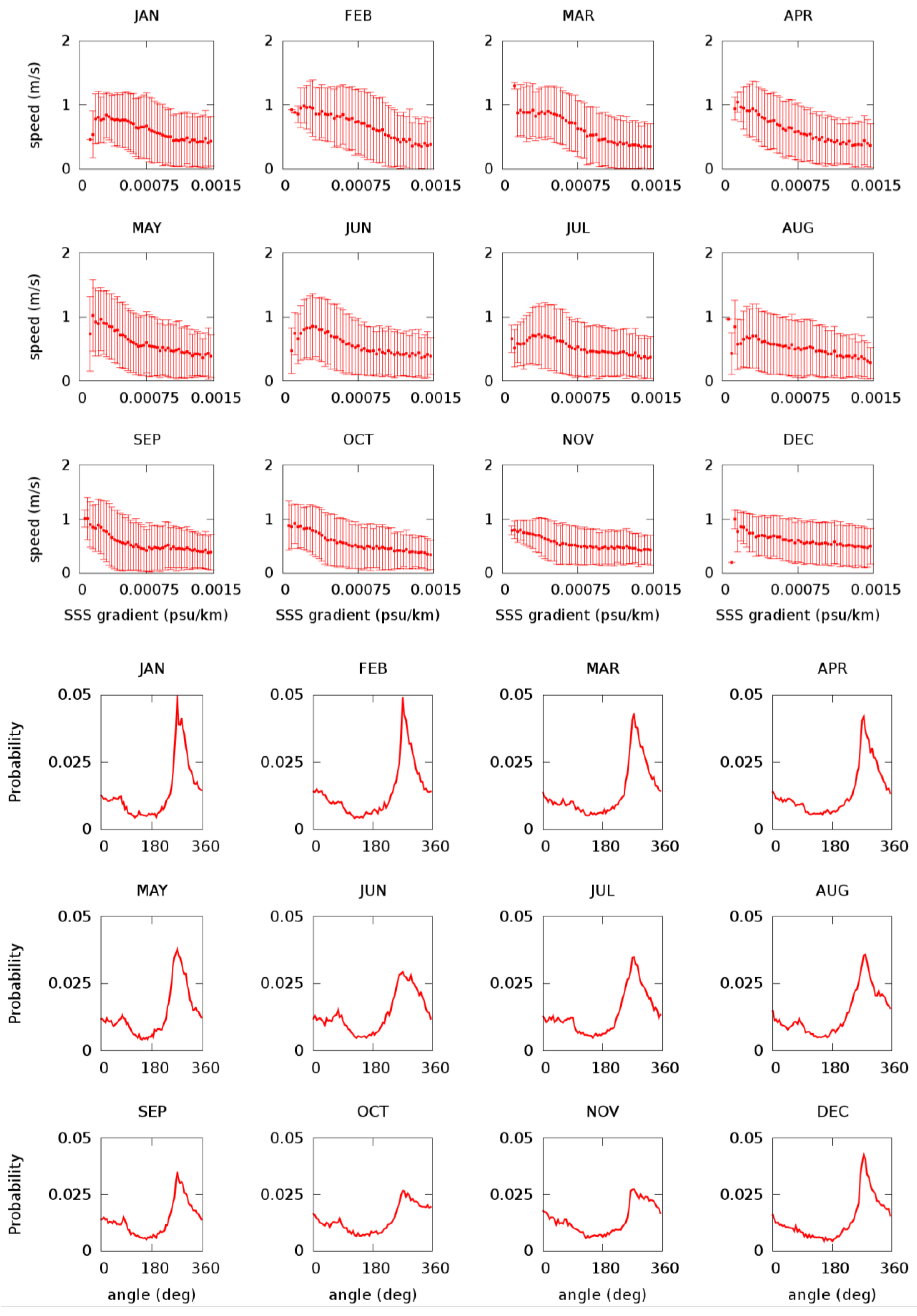
3.2. Relation Between the Surface Salinity and Velocity Fields
3.3. Salt Transport Variability
3.3.1. North Brazil Current Retroflection
3.3.2. Brazil-Malvinas Confluence
3.3.3. Agulhas Leakage
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haarsma, R.J.; Campos, E.; Hazeleger, W. Influence of the meridional overturning circulation on tropical Atlantic climate and variability. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 1403–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, S.E.; Toom, M.; Dijkstra, H.A.; Drijfhout, S. An indicator of the multiple equilibria regime of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 40, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzoli, S.L.; Matano, R. The South Atlantic and the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation. Deep Sea Res. II 2011, 58, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, L.D. Shallow, intermediate and deep overturning components of the global heat budget. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2003, 33, 530–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.L. The brawniest retroflection. Nature 2003, 421, 904–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos, P.; Pelegrí, J.L.; Campos, E.D.; Rosell-Fieschi, M.; Gasser, M. Response of the surface tropical Atlantic Ocean to wind forcing. Progr. Oceanogr. 2015, 134, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell-Fieschi, M.; Pelegrí, J.L.; Gourrion, J. Zonal jets in the equatorial Atlantic Ocean. Progr. Oceanogr. 2015, 130, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, G.R.J. Simulation of North Atlantic decadal/multidecadal winter SST anomalies driven by basin-scale atmospheric circulation anomalies. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1998, 28, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleck, R. An oceanic general circulation model framed in hybrid isopycnic-Cartesian coordinates. Ocean Model. 2002, 4, 55–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc 1996, 77, 437–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, P.; Campos, E.J.D.; Giddy, I.; Santis, W. Inter-comparison studies between high- resolution HYCOM simulation and observational data: The South Atlantic and the Agulhas leakage system. J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 159, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, J.; Camps, A.; Borges, A.; Martin-Neira, M.; Boutin, J.; Reul, N.; Kerr, Y.; Hahne, A.; Mechlenburg, S. SMOS: The challenging sea surface salinity measurement from space. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Delwart, S.; Cabot, F.; Boutin, J.; Escorihuela, M.-J.; Font, J.; Reul, N.; Gruhier, C.; et al. The SMOS mission: New tool for monitoring key elements of the global water cycle. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 666–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullan, K.D.; Brown, M.; Martin-Neira, M.; Rits, W.; Ekholm, S.; Marti, J.; Lemanczyk, J. SMOS: The payload. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, E.; Martínez, J.; Turiel, A.; Ballabrera-Poy, J.; Portabella, M. Debiased non-Bayesian retrieval: A novel approach to SMOS sea surface salinity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 193, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, S.; Delecluse, P. Amazon River runoff on the tropical Atlantic. Phys. Chem. Earth B 2001, 26, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodsky, S.A.; Carton, J.A.; Bryan, F.O. A curious local surface salinity maximum in the northwestern tropical Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 2014, 119, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltman, R.E. Reconnaissance Investigations of the Discharge and Water Quality of the Amazon River; Geological Survey Circular 552; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1968; 16p.
- Campos, E.J.D.; Olson, D.B. Stationary Rossby Waves in western boundary current extensions. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1991, 21, 1202–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matano, R. On the separation of the Brazil Current from the coast. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1992, 23, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, E.; Pascual, A.; Gaube, P.; Ruiz, S.; Pelegrí, J.L.; Delepoulle, A. Subregional characterization of mesoscale eddies across the Brazil-Malvinas Confluence. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 3329–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraceno, M.; Provost, C.; Piola, A.R.; Bava, J.; Gagliardini, A. Brazil Malvinas Frontal System as seen from 9 years of advanced very high resolution radiometer data. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2004, 109, C05027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borús, J.; Giacosa, J. Evaluación de caudales diarios descargados por los grandes ríos del Sistema del Plata al Río de la Plata; Dirección de Sistemas de Información y Alerta Hidrológico Instituto Nacional del Agua: Ezeiza, Argentina, 2014.
- Beal, L.M.; De Ruijter, W.P.M.; Biastoch, A.; Zhan, R. On the role of the Agulhas system in ocean circulation and climate. Nature 2011, 472, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutjeharms, J.R.E.; Van Ballegooyen, R.C. The retroflection of the Agulhas Current. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1988, 18, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boebel, O.; Lutjeharms, J.; Schmid, C.; Zenk, W.; Rossby, T.; Barron, C. The Cape Cauldron: A regime of turbulent inter-ocean exchange. Deep Sea Res II 2003, 50, 57–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piola, A.R.; Campos, E.J.; Möller, O.O.; Charo, M.; Martínez, C. Subtropical Shelf Front off eastern South America. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2000, 105, 6565–6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dencausse, G.; Arhan, M.; Speich, S. Spatio-temporal characteristics of the Agulhas Current retroflection. Deep Sea Res. I 2010, 57, 1392–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, D.L.; Ferrari, R. Compensation of horizontal temperature and salinity gradient in the ocean mixed layer. Science 1999, 283, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, C.A.; Goni, G.J.; Johns, W.E.; Campos, E.J.D. Investigation of the North Brazil Current retroflection and North Equatorial Countercurrent variability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L21304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artana, C.; Ferrari, R.; Koenig, Z.; Sennéchael, N.; Saraceno, M.; Piola, A.R.; Provost, C. Malvinas Current volume transport at 41°S: A 24 yearlong time series consistent with mooring data from 3 decades and satellite altimetry. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 378–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.; Stramma, L. Upper-level circulation in the South Atlantic Ocean. Progr. Oceanogr. 1991, 26, 1–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matano, R.; Schlax, M.; Chelton, D. Seasonal variability in the Southwestern Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 027–035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valla, D.; Piola, A.R.; Meinen, C.S.; Campos, E. Strong mixing and recirculation in the northwestern Argentine Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 4624–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orúe-Echevarría, D.; Pelegrí, J.L.; Machín, F.; Hernández-Guerra, A.; Emelianov, M. Inverse modeling the Brazil-Malvinas Confluence. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2019, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, H.; de Ruijter, W.P.M. On the physics of the Agulhas Current: Steady retroflection regimes. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 2971–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Putrasahan, D.; Beal, L.; Kirtman, B. Quantifying Agulhas Leakage in a high-resolution climate model. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 6881–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castellanos, P.; Olmedo, E.; Pelegrí, J.L.; Turiel, A.; Campos, E.J.D. Seasonal Variability of Retroflection Structures and Transports in the Atlantic Ocean as Inferred from Satellite-Derived Salinity Maps. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070802
Castellanos P, Olmedo E, Pelegrí JL, Turiel A, Campos EJD. Seasonal Variability of Retroflection Structures and Transports in the Atlantic Ocean as Inferred from Satellite-Derived Salinity Maps. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(7):802. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070802
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastellanos, Paola, Estrella Olmedo, Josep Lluis Pelegrí, Antonio Turiel, and Edmo J. D. Campos. 2019. "Seasonal Variability of Retroflection Structures and Transports in the Atlantic Ocean as Inferred from Satellite-Derived Salinity Maps" Remote Sensing 11, no. 7: 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070802
APA StyleCastellanos, P., Olmedo, E., Pelegrí, J. L., Turiel, A., & Campos, E. J. D. (2019). Seasonal Variability of Retroflection Structures and Transports in the Atlantic Ocean as Inferred from Satellite-Derived Salinity Maps. Remote Sensing, 11(7), 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070802





