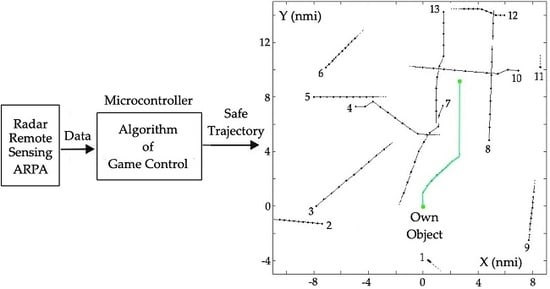
Game Control Methods Comparison when Avoiding Collisions with Multiple Objects Using Radar Remote Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
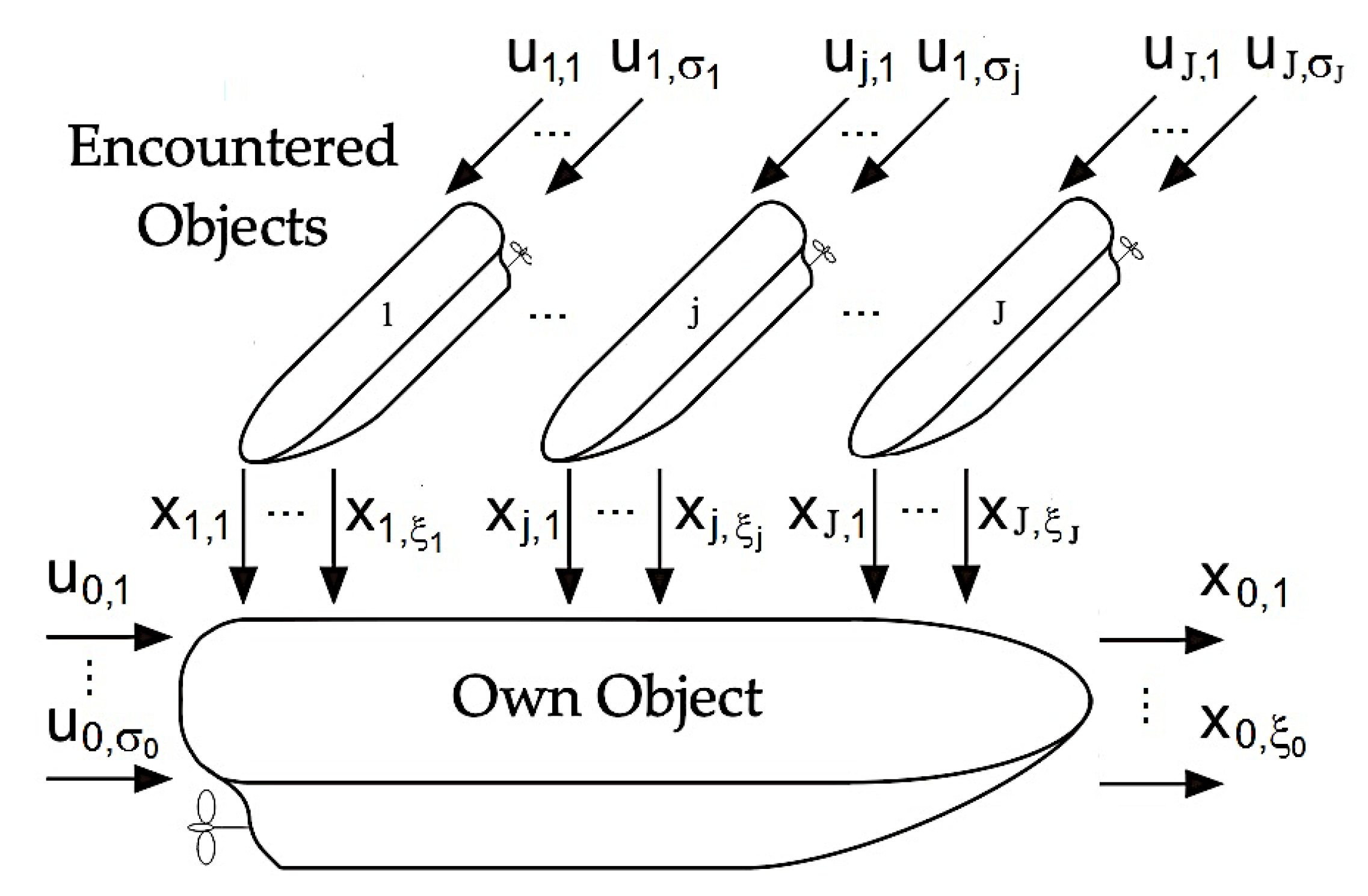
2. Game Control Process of Multiple Objects Movement
2.1. General Description
2.2. Types of Object Traffic Game Control
- —leads to the shortest distance between subjects, often during the dangerous objects approach or when transferring cargo at sea.
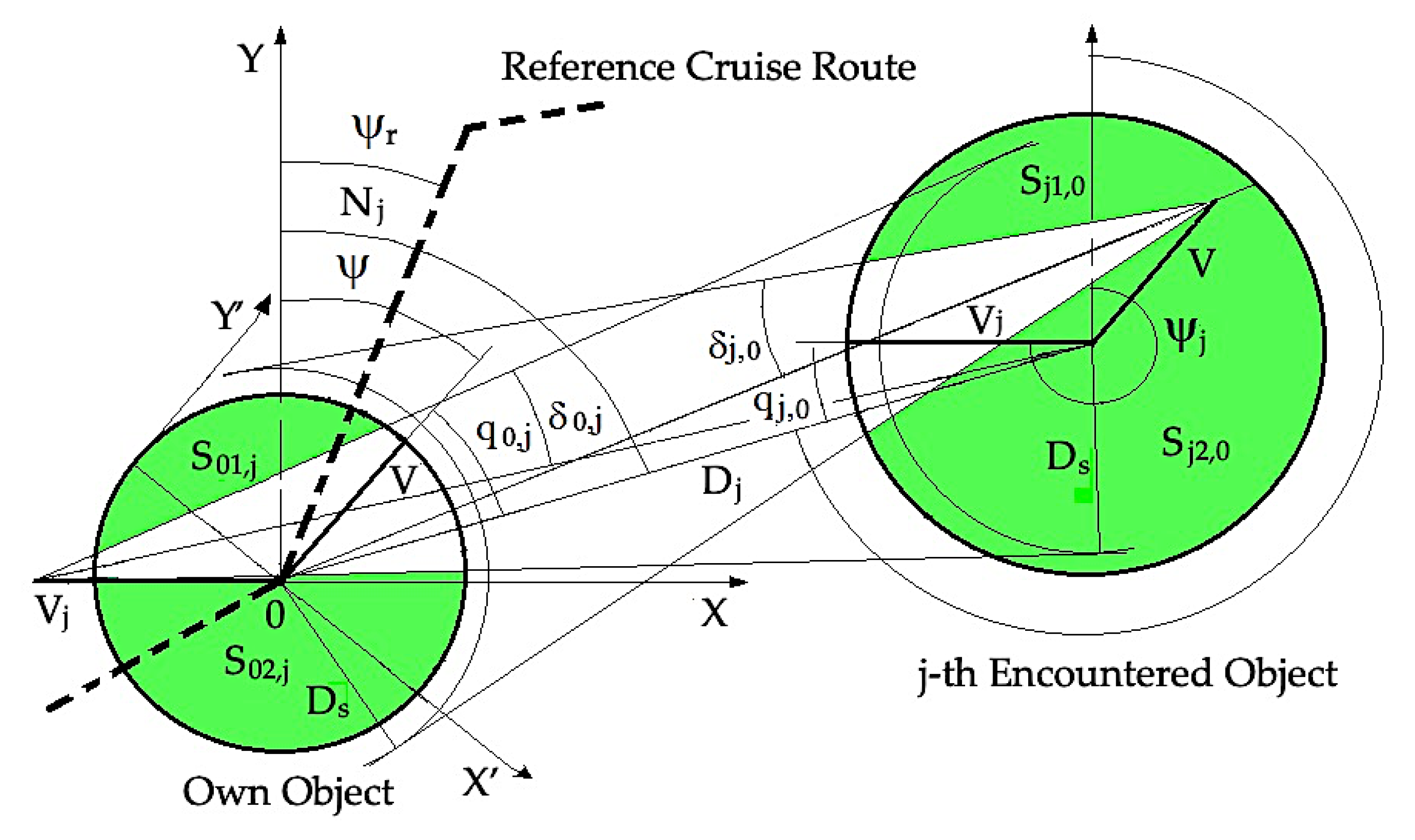
- —this means an anti-collision maneuver to achieve the value of the smallest distance to j-th object, which is greater than the apparent safety distance Ds that is determined under the given conditions:where Dj min is the distance of the closest point of approach; Dj is the distance to the encountered j-th object; Ds is the safe distance of approach.
- —this means stabilizing the course or trajectory.
- Maneuvers of own object , for example, by changing a course Δψ and/or speed ΔV,
- Maneuvers of the j-th object ,
- Cooperating maneuvers .
2.3. Computer-Aided Object Safe Control in the Game Environment
3. Basic Model of Differential Game
3.1. State Equations
3.2. Limits of Control and State
3.3. Control Criterion
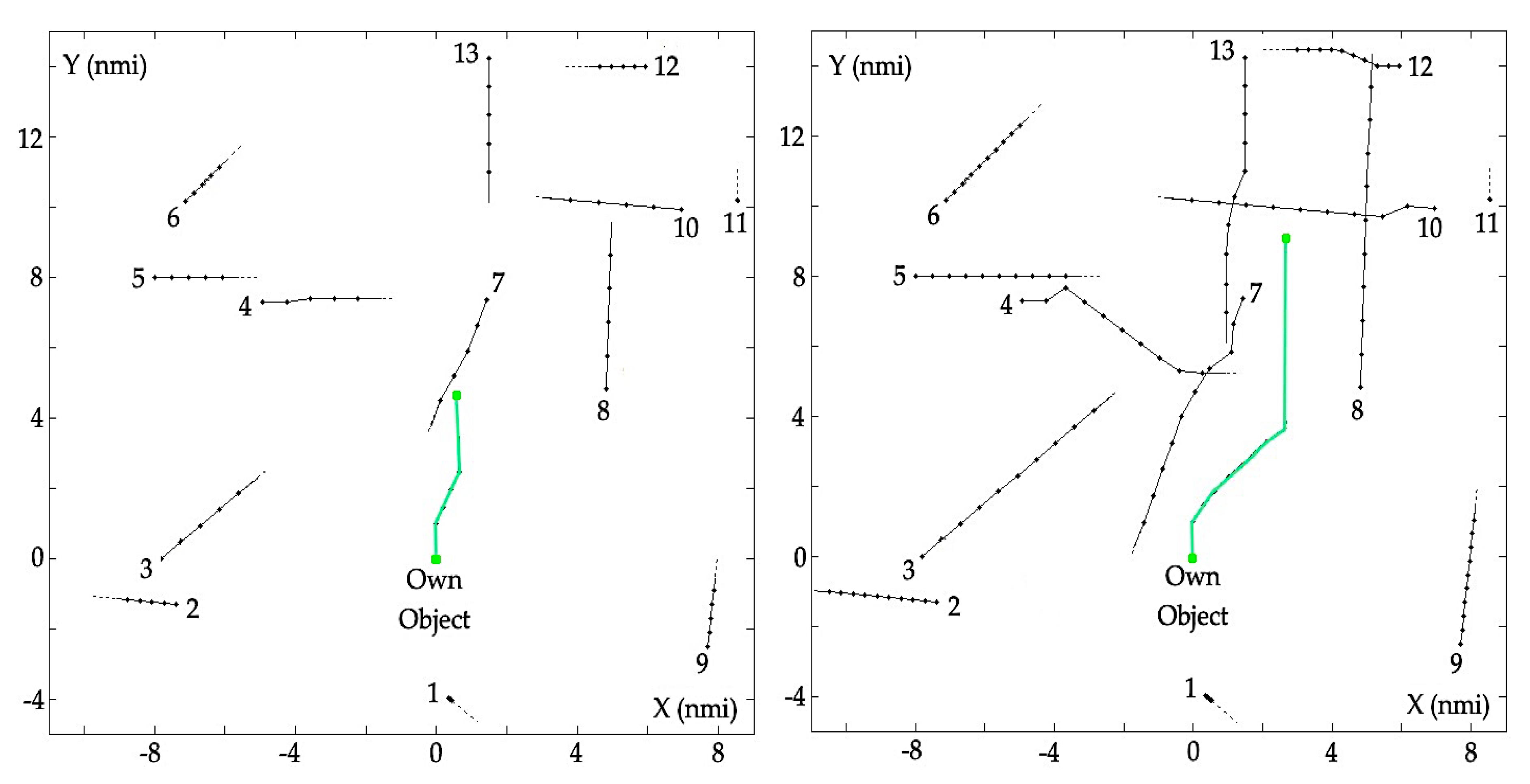
3.4. Computer Simulation
4. Surrogate Models of Differential Game
4.1. Positional Game Model
4.1.1. Sets of Object Safe Strategies
- A—encounter of the ship from bow or from any other direction,
- B—approaching or moving away of the ship,
- C—passing the ship astern or ahead,
- D—approaching of the ship from the bow or from the stern,
4.1.2. Positional Game Control
4.1.3. Computer Simulation
4.2. Matrix Game Model
4.2.1. Matrix of Risk Collision
4.2.2. Matrix Game Control
4.2.3. Computer Simulation of the Matrix Game Model
5. Comparison of Game Object Control Methods
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bist, D.S. Safety and Security at Sea. In A Guide to Safer Voyages; Butter Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2000; ISBN 0-75064-774-4. [Google Scholar]
- Cahill, R.A. Collisions and Their Causes; The Nautical Institute: London, UK, 2002; ISBN 1-87077-60-1. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, C.; Bucknall, R.; Greig, A. Review of Collision Avoidance and Path Planning Methods for Ships in Close Range Encounters. J. Navig. 2009, 62, 455–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, P.; Negenborn, R.R.; van Gelder, P.H.A.J.M. Ship Collision Avoidance Methods: State-of-the-art. Saf. Sci. 2020, 121, 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulakov, M.A.; Korh, M.V. Choice of Optimum Maneuver of Divergence by the Regions of Impermissible Values of Parameters. Sci. Educ. New Dimens. 2020, 27, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, T.A.; Perez, T.; Cristofaro, A. Ship Collision Avoidance and COLREGs Compliance using Simulation-based Control Behavior Selection with Predictive Hazard Assessment. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melhaoui, Y.; Ait Allal, A.; Kamil, A.; Mansouri, K.; Rachik, M. Toward an overview of ship collision avoidance maneuvers approaches in compliance with COLREG convention. In Proceedings of the IEEE 5th International Conference on Optimization and Applications, Kenitra, Morocco, 25–26 April 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwata, Y.; Wolf, M.; Zarzhitsky, D.; Huntsberger, T.L. Safe maritime autonomous navigation with COLREGS, using velocity obstacles. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2014, 39, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miele, A.; Wang, T. Optimal trajectories and guidance schemes for ship collision avoidance. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2006, 129, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statheros, T.; Howells, G.; Maier, K.M. Autonomous ship collision avoidance navigation concepts, technologies and techniques. J. Navig. 2008, 61, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, Y.-J.; Rhee, K.-P.; Ahn, J.-H. A method of inferring collision ratio based on maneuverability of own ship under critical collision conditions. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean Eng. 2013, 5, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perera, L.P.; Carvalho, J.P.; Soares, C.G. Bayesian Network based sequential collision avoidance action execution for an Ocean Navigational System. In Proceedings of the 8th IFAC Conference on Control Applications in Marine Systems, Rostock, Germany, 15–17 September 2010; pp. 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, Z. A novel framework for regional collision risk identification based on AIS data. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2019, 89, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Han, J.; Kim, J.; Son, N. Probabilistic quantification of ship collision risk considering trajectory uncertainties. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaich, M.; Kohler, S.; Reuter, S.; Hahn, A. Probabilistic Collision Avoidance for Vessels. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2015, 48, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarowska, A. Safe Ship Trajectory Planning Based on the Ant Algorithm—The Development of the Method. Act. Navig. Mar. Navig. Saf. Sea Transp. 2015, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomera, M. Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm Applied to Ship Steering Control. 18th Annual International Conference on Knowledge-Based and Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems KES, Gdynia, Poland. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 35, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn, J.-H.; Rhee, K.-P.; You, Y.-J. A study on the collision avoidance of a ship using neural networks and fuzzy logic. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2012, 37, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, B. Motion of maritime autonomous surface ships by dynamic programming for collision avoidance and speed optimization. Sensors 2019, 19, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebkowski, A. Evolutionary methods in the management of vessel traffic. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation, Gdynia, Poland, 17–19 June 2015; pp. 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Dinh, G.H.; Im, N.K. Study on the Construction of Stage Discrimination Model and Consecutive Waypoints Generation Method for Ship’s Automatic Avoiding Action. Int. J. Fuzzy Log. Intell. Syst. 2017, 17, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyu, H.; Yin, Y. COLREGS-Constrained Real-time Path Planning for Autonomous Ships Using Modified Artificial Potential Fields. J. Navig. 2019, 72, 588–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.I.; Chae, S.H.; Kim, D.; Jung, H.S. Application of Artificial Neural Networks to Ship Detection from X-Band Kompsat-5 Imagery. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Ji, K.; Leng, X.; Lin, Z. Contextual Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network with Multilayer Fusion for SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collingwood, A.; Treitz, P.; Charbonneau, F.; Atkinson, D.M. Artificial Neural Network Modeling of High Arctic Phytomass Using Synthetic Aperture Radar and Multispectral Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2134–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hertz, J.; Krogh, A.; Palmer, R.G. Introduction to the Theory of Neural Computation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-0-201-51560-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hinostroza, M.A.; Xu, H.; Soares, C.G. Cooperative operation of autonomous surface vehicles for maintaining formation in complex marine environment. Ocean Eng. 2019, 183, 132–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, Z. A cooperative game approach for assessing the collision risk in multi-vessel encountering. Ocean Eng. 2019, 187, 106175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, I.B.; Kufoalor, K.M.; Brekke, E.F.; Johansen, T.A. MPC-based collision avoidance strategy for existing marine vessel guidance systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Georgiou, T.T.; Pavon, M. Covariance steering in zero-sum linear-quadratic two-player differential games. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.05468v1. [Google Scholar]
- Gronbaek, L.; Lindroos, M.; Munro, G.; Pintassilgo, P. Cooperative Games in Fisheries with More than Two Players. In Game Theory and Fisheries Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 81–105. ISBN 978-3-030-40112-2. [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs, R. Differential Games; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1965; ISBN 0-48640-682-2. [Google Scholar]
- Gluver, H.; Olsen, D. Ship Collision Analysis; August Aimé Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; ISBN 90-5410-962-9. [Google Scholar]
- Perera, L.P.; Carvalho, J.P.; Soares, C.G. Autonomous guidance and navigation based on the COLREGs rules and regulations of collision avoidance. In Proceedings of the International Workshop “Avoidance Ship Design for Pollution Prevention”, Split, Croatia, 23–24 November 2009; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, D.H. The mathematics of collision avoidance at sea. J. Navig. 2010, 10, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dockner, E.; Feichtinger, G.; Mehlmann, A. Noncooperative solutions for a differential game model of the fishery. J. Econ. Dyn. Control. 1989, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, N.; Jain, L.C. Computational Intelligence in Games; Physica-Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; ISBN 978-3-662-00369-5. [Google Scholar]
- Breton, M.; Szajowski, K. Advances in Dynamic Games: Theory, Applications and Numerical Methods for Differential and Stochastic Games; Birkhauser: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-8176-8089-3. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Soriano, J. An overview of game theory applications to engineering. Int. Game Theory Rev. 2013, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haurie, A.; Krawczyk, J.B.; Zaccour, G. Games and Dynamic Games, Subtle Connections; University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-9814401265. [Google Scholar]
- Mesterton-Gibbons, M. An. Introduction to Game Theoretic Modelling; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-82-181929-6. [Google Scholar]
- Osborne, M.J. An. Introduction to Game Theory; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-19512895-6. [Google Scholar]
- Broek, W.A.; Engwerda, J.C.; Schumacher, J.M. Robust equilibria in indefinite linear-quadratic differential games. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2003, 119, 565–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basar, T.; Olsder, G.J. Dynamic Non-Cooperative Game Theory; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-898-714-29-6. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.F. Non-cooperative games. Ann. Math. 1951, 54, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloh, T. Determination of Critical Maneuvres for Collision Avoidance Using the Theory of Differential Games; Bericht: Hamburg, Germany, 1975; ISBN 10.15480/882.666. [Google Scholar]
- Olsder, G.J.; Walter, J.L. A Differential Game Approach to Collision Avoidance of Ships. Optim. Technol. 1977, 6, 264–271. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, D. Games and Mathematics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-1-107-02460-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bressan, A.; Nguyen, K.T. Stability of feedback solutions for infinite horizon noncooperative differential games. Dyn. Games Appl. 2018, 8, 42–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromova, E.V.; Petrosyan, L.A. On an approach to constructing a characteristic function in cooperative differential games. Autom. Remote Control. 2017, 78, 1680–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, G. Stabilizability, Controllability, and Optimal Strategies of Linear and Nonlinear Dynamical Games. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen, Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, T. Ship Motion Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; ISBN 978-1-84628-157-0. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, P.V.; Zaccour, G. Feedback Nash equilibria in linear-quadratic difference games with constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2016, 62, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basar, T.; Bernhard, P. H-Infinity Optimal Control and Related Mini-Max Design Problems: A Dynamic Game Approach; Birkhauser: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-8176-4757-5. [Google Scholar]
- Engwerda, J.C. LQ Dynamic Optimization and Differential Games; John Wiley & Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2005; ISBN 978-0-470-01524-7. [Google Scholar]
- Millington, I.; Funge, J. Artificial Intelligence for Games; Elsevier: Burlington, MA, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-12-374731-0. [Google Scholar]
- Nisan, N.; Roughgarden, T.; Tardos, E.; Vazirani, V. Algorithmic Game Theory; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-0-521-87282-9. [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft, C.; Lameijer, J. A Guide to the Collision Avoidance Rules; Butterworth-Heinemann Publication: Oxford, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-0-080-97170-4. [Google Scholar]
- COLREGs Course. Available online: https://ecolregs.com/index.php?option=com_k2&view=item&layout=item&id=51&Itemid=383&lang=en (accessed on 15 February 2020).
- Modarres, M. Risk Analysis in Engineering, Techniques, Tools and Trends; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; ISBN 1-574444-794-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Naeem, W.; Rajabally, E.; Watson, G.; Mills, T.; Bhuiyan, Z.; Raeburn, C.; Salter, I.; Pekcan, C. A multi-objective optimization approach for COLREGs-compliant path planning of autonomous surface vehicles verified on networked bridge simulators. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, S.; Naeem, W. A rule-based heuristic method for COLREGs-compliant collision avoidance for an unmanned surface vehicle. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2012, 45, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravankar, A.; Ravankar, A.A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hoshino, Y.; Peng, C.C. Path smoothing techniques in robot navigation: State-of-art, current and future challenges. Sensors 2018, 18, 3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Variable | Means | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| own object state ξ0—dimensional vector | ||
| x0,1 | own object course | ψ |
| x0,2 | angular speed of the own object of return | |
| x0,3 | own object speed | V |
| x0,4 | own object drift angle | β |
| x0,5 | own object main drive screw rotational speed | n |
| x0,6 | own object main drive propeller pitch | H |
| j-th object state ξj—dimensional vector | ||
| xj,1 | distance to the j-th object | Dj |
| xj,2 | bearing to the j-th object | Nj |
| xj,3 | course of the j-th object | ψj |
| xj,4 | speed of the j-th object | Vj |
| own object control σ0 - dimensional vector | ||
| u0,1 | own object rudder deflection reference angle | αr |
| u0,2 | own object main propeller reference rotational speed | nr |
| u0,3 | own object main drive screw reference stroke | Hr |
| j-th object control σj—dimensional vector | ||
| uj,1 | angular speed of the j-th object of return | |
| uj,2 | thrust force of the propeller of the j-th object | Ftj |
| Bearing Nj (o) | DistanceDj (nmi) | Speed Vj (kn) | Course ψj (o) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Own Object | - | - | 20 | 0 |
| Object 1 | 175 | 4.0 | 0.5 | 130 |
| Object 2 | 260 | 7.5 | 6.9 | 275 |
| Object 3 | 270 | 7.8 | 14.3 | 50 |
| Object 4 | 315 | 11.3 | 9.6 | 90 |
| Object 5 | 326 | 8.8 | 13.5 | 90 |
| Object 6 | 325 | 12.4 | 6.7 | 45 |
| Object 7 | 11 | 7.5 | 16.0 | 200 |
| Object 8 | 45 | 6.8 | 19.1 | 2 |
| Object 9 | 108 | 8.1 | 7.9 | 6 |
| Object 10 | 35 | 12.1 | 15.7 | 275 |
| Object 11 | 40 | 13.3 | 0 | 0 |
| Object 12 | 23 | 15.2 | 6.5 | 270 |
| Object 13 | 6 | 14.3 | 16.2 | 180 |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lisowski, J. Game Control Methods Comparison when Avoiding Collisions with Multiple Objects Using Radar Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101573
Lisowski J. Game Control Methods Comparison when Avoiding Collisions with Multiple Objects Using Radar Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(10):1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101573
Chicago/Turabian StyleLisowski, Józef. 2020. "Game Control Methods Comparison when Avoiding Collisions with Multiple Objects Using Radar Remote Sensing" Remote Sensing 12, no. 10: 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101573
APA StyleLisowski, J. (2020). Game Control Methods Comparison when Avoiding Collisions with Multiple Objects Using Radar Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing, 12(10), 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101573