Real-Time Estimation of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellite Clock Based on Ground Tracking Stations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Constellation and Observation Simulation
2.1. Constellation Design
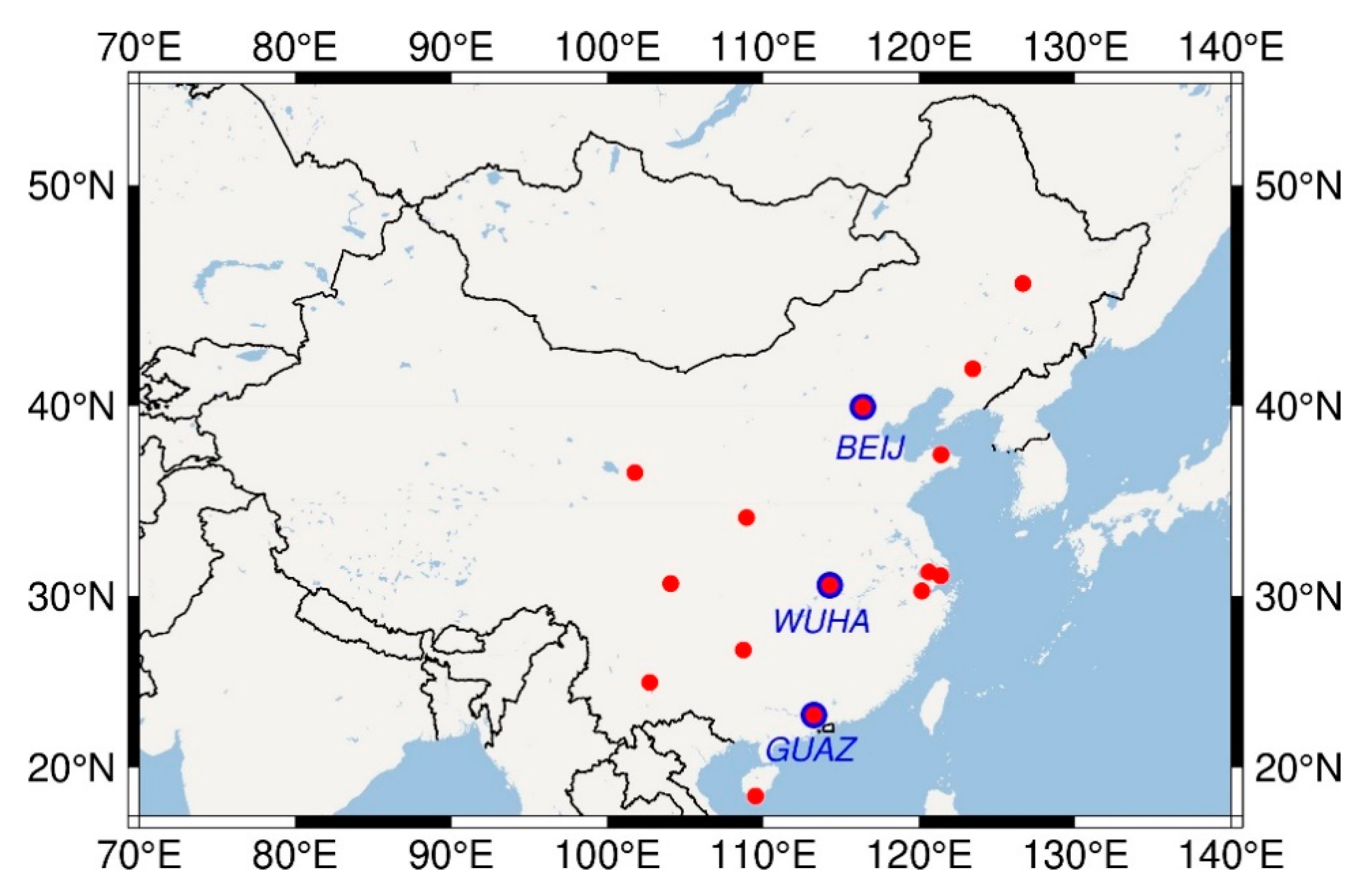
2.2. Observation Simulation
3. Methods
3.1. LEO Satellite Clock Estimation
3.2. LEO-Augmented GNSS PPP
3.3. Data Processing Strategy
4. Analysis of Results
4.1. Analysis of LEO Satellite Clock
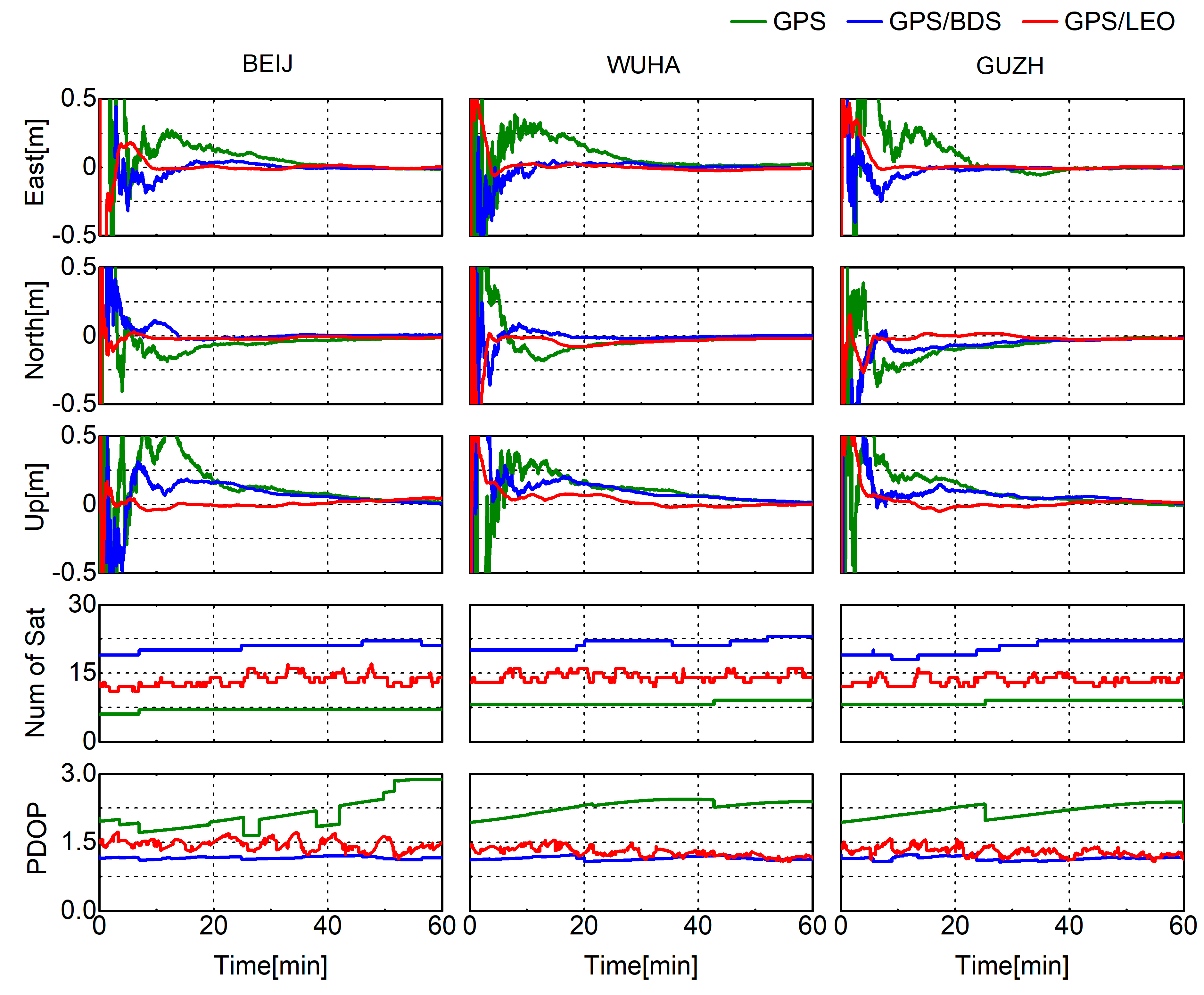
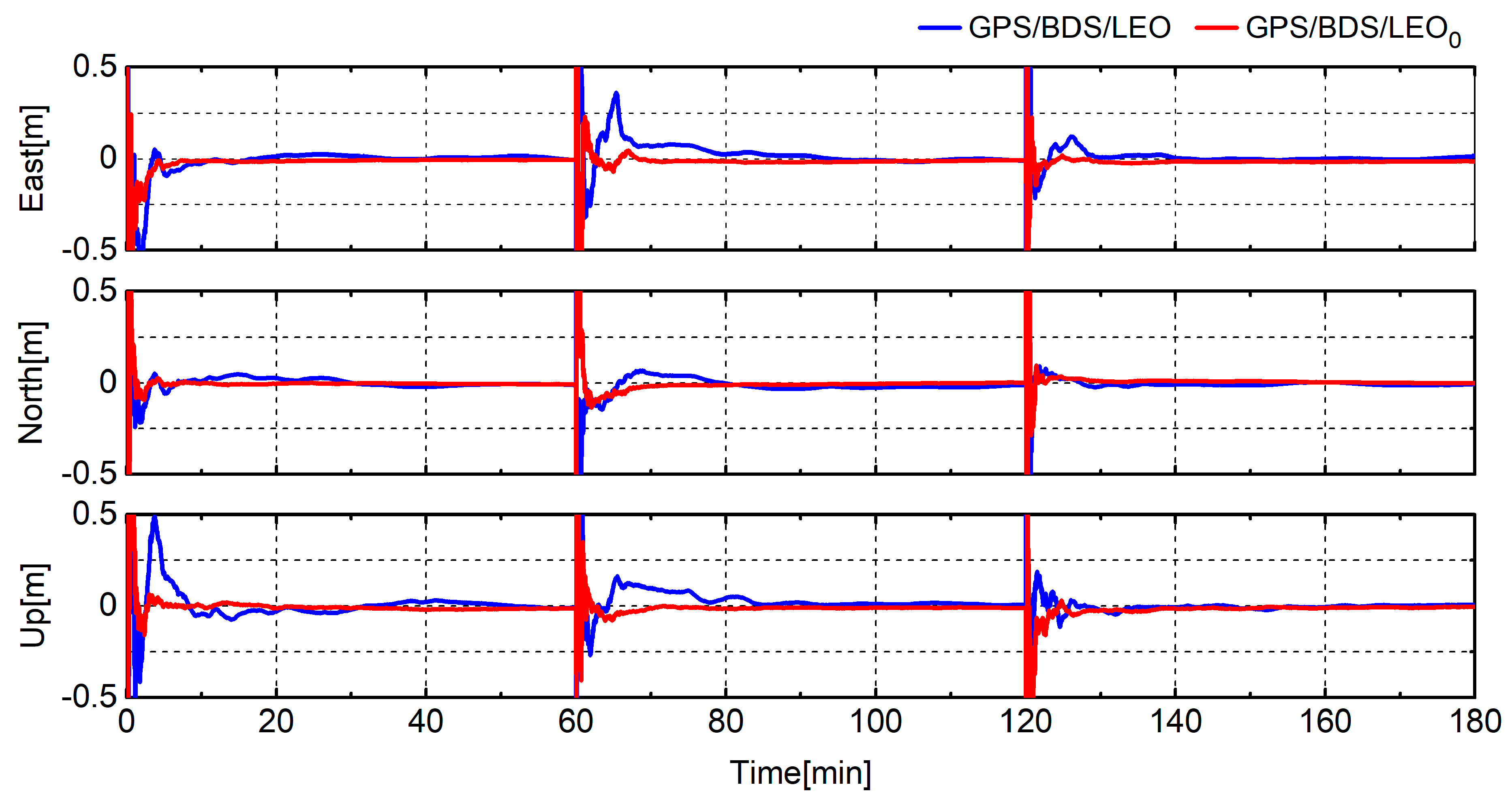
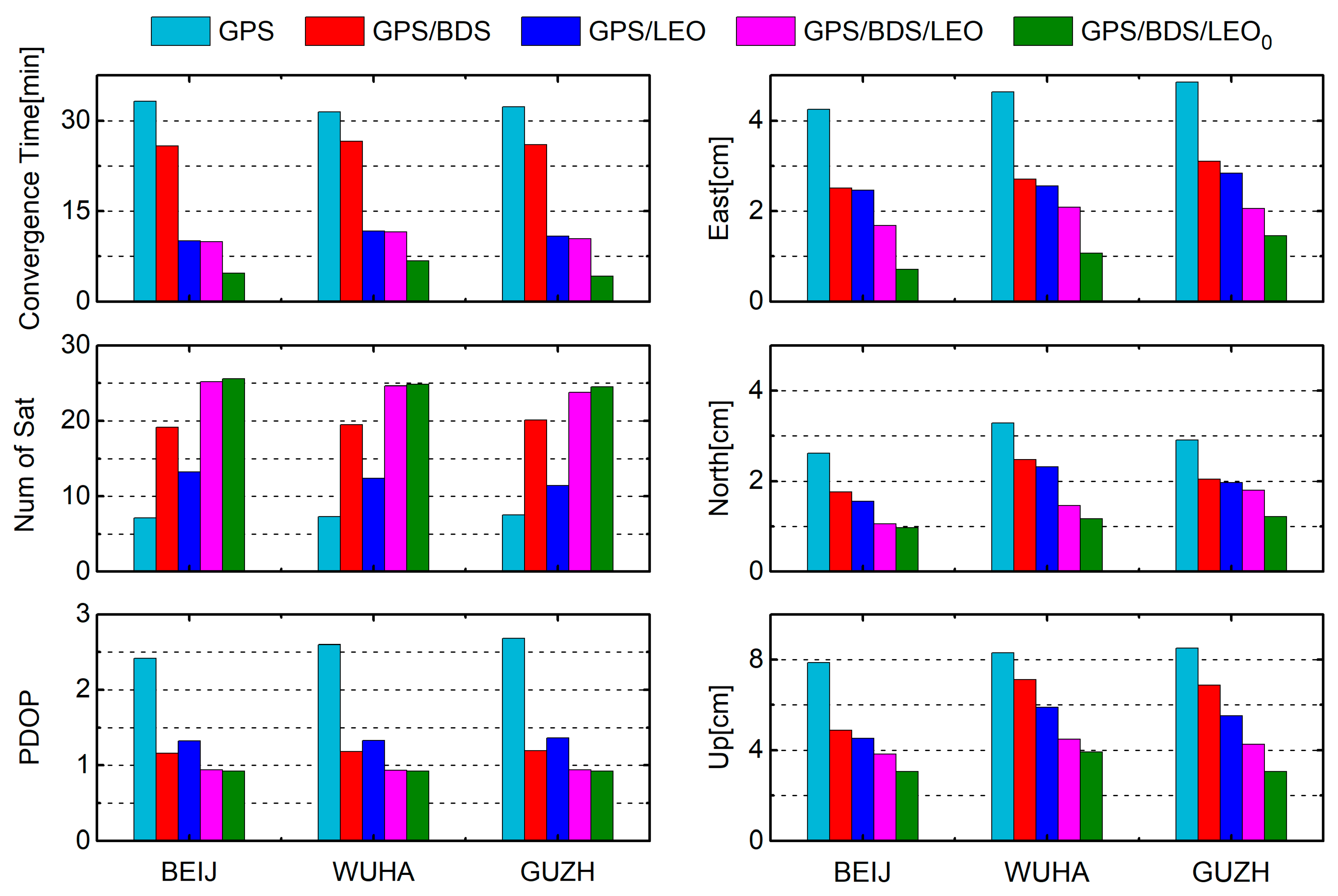
4.2. Analysis of LEO-Augmented GNSS PPP
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zumberge, J.; Heflin, M.; Jefferson, D.; Watkins, M.; Webb, F. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Dai, X.; Ren, X.; Fritsche, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Accuracy and reliability of multi-GNSS real-time precise positioning: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 607–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Fritsche, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Precise positioning with current multi-constellation global navigation satellite systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and BeiDou. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Li, M. Real-Time Precise Point Positioning (RTPPP) with raw observations and its application in real-time regional ionospheric VTEC modeling. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 1267–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Gao, Y. Modeling and assessment of combined GPS/GLONASS precise point positioning. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggrey, J.; Bisnath, S. Improving GNSS PPP convergence: The case of atmospheric-constrained, multi-GNSS PPP-AR. Sensors 2019, 19, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Gao, Y.; Pan, L.; Zhu, J. Precise point positioning with quad-constellations: GPS, BeiDou, GLONASS and Galileo. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 56, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisnath, S.; Gao, Y. Current state of precise point positioning and future prospects and limitations. In Observing Our Changing Earth; Sideris, M.G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 133, pp. 615–623. [Google Scholar]
- De Selding, P.B. Signs of a Satellite Internet Gold Rush in Burst of ITU Filings. Available online: https://spacenews.com/signs-of-satellite-internet-gold-rush/ (accessed on 19 November 2018).
- Li, D.; Shen, X.; Li, D.; Li, S. On civil-military integrated space-based real-time information service system. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2017, 42, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaohong, Z.; Fujian, M. Review of the development of LEO navigation-augmented GNSS. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2019, 48, 1073. [Google Scholar]
- De Selding, P.B. SpaceX To Build 4000 Broadband Satellites in Seattle. Available online: https://spacenews.com/spacex-opening-seattle-plant-to-build-4000-broadband-satellites/ (accessed on 23 October 2018).
- De Selding, P.B. Virgin, Qualcomm Invest in OneWeb Satellite Internet Venture. Available online: https://spacenews.com/virgin-qualcomm-invest-in-global-satellite-internet-plan/ (accessed on 28 January 2019).
- Magan, V. Samsung Exec Envisions LEO Constellation for Satellite Internet Connectivity. Available online: https://www.satellitetoday.com/telecom/2015/08/18/samsung-exec-envisions-leo-constellation-for-satellite-internet-connectivity/ (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- De Selding, P.B. Boeing Proposes Big Satellite Constellations in V- and C-bands. Available online: https://spacenews.com/boeing-proposes-big-satellite-constellations-in-v-and-c-bands/ (accessed on 21 April 2019).
- De Selding, P.B. Telesat: LEO Gives More User Bandwidth than GEO HTS. Available online: https://www.spaceintelreport.com/telesat-leo-gives-more-user-bandwidth-than-geo-hts/ (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- Reid, T.G.; Neish, A.M.; Walter, T.F.; Enge, P.K. Leveraging commercial broadband LEO constellations for navigation. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS 2016, Portland, OR, USA, 12–16 September 2016; pp. 2300–2314. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, M.; Lv, J.; Chang, J.; Dai, W.; Tong, K.; Zhu, M. Integrating GPS and LEO to accelerate convergence time of precise point positioning. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Wireless Communications & Signal Processing (WCSP), Nanjing, China, 15–17 October 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ma, F.; Li, X.; Lv, H.; Bian, L.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, X. LEO constellation-augmented multi-GNSS for rapid PPP convergence. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Li, B.; Ge, M.; Zang, N.; Nie, L.; Shen, Y.; Schuh, H. Initial assessment of precise point positioning with LEO enhanced global navigation satellite systems (LeGNSS). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Ma, F.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, X. Improved PPP ambiguity resolution with the assistance of multiple LEO constellations and signals. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ge, H.; Ge, M.; Nie, L.; Shen, Y.; Schuh, H. LEO enhanced Global Navigation Satellite System (LeGNSS) for real-time precise positioning services. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Su, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. BeiDou augmented navigation from low earth orbit satellites. Sensors 2019, 19, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Design for LEO satellite navigation augmentation system based on integrated communication and navigation. In Proceedings of the 11th China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC), Chengdu, China, 23 May 2020; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, J.G. Satellite constellations. J. Br. Interplanet. Soc. 1984, 37, 559–572. [Google Scholar]
- DOD SPS. Global Positioning System Standard Positioning Service Performance Standard, 4th ed.; Department of Defense USA: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- China Satellite Navigation Office (CSNO). BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document: Open Service Signal, Version 2.1; China Satellite Navigation Office: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, R.; Dach, R.; Collilieux, X.; Jäggi, A.; Schmitz, M.; Dilssner, F. Absolute IGS antenna phase center model igs08. atx: Status and potential improvements. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J. Atmospheric correction for the troposphere and stratosphere in radio ranging satellites. Use Artif. Satell. Geod. 1972, 15, 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Böhm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y. GNSS biases, their effect and calibration. In Proceedings of the IGS Workshop, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 2–6 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, M.; Douša, J.; Gendt, G.; Wickert, J. A computationally efficient approach for estimating high-rate satellite clock corrections in realtime. Gps Solut. 2012, 16, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enge, P.; Ferrell, B.; Bennet, J.; Whelan, D.; Gutt, G.; Lawrence, D. Orbital diversity for satellite navigation. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS 2012, Nashville, TN, USA, 17–21 September 2012; pp. 3834–3845. [Google Scholar]







| System | Satellite Number | Constellation | Inclination [deg] | Altitude [km] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEO A | 132 | Walker (132/12/1) | 50 | 800 |
| LEO B | 36 | Walker (36/3/0) | 85 | 820 |
| GPS | 24 | Six planes | 56 | 20,180 |
| BDS MEO | 24 | Walker (24/3/1) | 55 | 21,528 |
| BDS GEO | 3 | Placed at 80° E, 110.5° E, 140° E | 0 | 35,786 |
| BDS IGSO | 3 | RAAN of 118° E | 55 | 35,786 |
| Items | Description |
|---|---|
| Satellites | 168 LEO + 24 GPS + 30 BDS |
| Estimator | LSQ in sequential mode |
| Observations | Undifferenced code and phase observations |
| Signal selection | GPS: L1/L2; BDS: B1C/B2a; LEO: L1/L2 |
| Elevation mask | 7° |
| Sampling interval | 5 s for PCE and 1 s for PPP |
| Weighting | Priori precision 5 mm for phase and 1.0 m for code; Elevation-dependent weight |
| Relativistic effect | IERS Conventions 2010 |
| Tropospheric delay | Initial model (Saastamoinen [29] and GMF [30]) and random-walk process |
| Ionospheric delay | IF combination |
| Station displacement | Solid Earth tide, pole tide, ocean loading tide |
| Satellite antenna phase center | PCO and PCV corrected for GPS and BDS using igs08.atx [28]; none for LEO |
| Receiver antenna phase center | PCO and PCV corrected for GPS and only PCO corrected for BDS using igs08.atx [28]; none for LEO |
| Phase wind-up | Corrected |
| ISB | Estimated as constant |
| Station coordinate | Fixed for PCE; Estimated in static mode for PPP |
| Satellite orbit | Fixed with the simulated precise orbit products from STK software |
| Satellite clocks | Estimated with white noise for PCE; Fixed with the products from PCE for LEO PPP; Fixed with the simulated precise clock products for GPS and BDS PPP |
| Receiver clocks | Estimated with white noise |
| Ambiguities | Constant for each arc |
| System | Convergence Times [min] | RMS [ns] | STD [ns] |
|---|---|---|---|
| LEO | 2.86 | 0.71 | 0.39 |
| GPS | 31.21 | 0.31 | 0.13 |
| System | Station Numbers | Satellite TDOP | Delta TDOP |
|---|---|---|---|
| LEO | 7.19 | 19.13 | 0.10 |
| GPS | 11.46 | 1294.70 | 0.10 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Qian, C.; Shu, B.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lou, Y. Real-Time Estimation of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellite Clock Based on Ground Tracking Stations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12122050
Yang Z, Liu H, Qian C, Shu B, Zhang L, Xu X, Zhang Y, Lou Y. Real-Time Estimation of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellite Clock Based on Ground Tracking Stations. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(12):2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12122050
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhixin, Hui Liu, Chuang Qian, Bao Shu, Linjie Zhang, Xintong Xu, Yi Zhang, and Yidong Lou. 2020. "Real-Time Estimation of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellite Clock Based on Ground Tracking Stations" Remote Sensing 12, no. 12: 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12122050
APA StyleYang, Z., Liu, H., Qian, C., Shu, B., Zhang, L., Xu, X., Zhang, Y., & Lou, Y. (2020). Real-Time Estimation of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellite Clock Based on Ground Tracking Stations. Remote Sensing, 12(12), 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12122050





