Abstract
Lake ice, one of the most direct lake physical characteristics affected by climate change, can reflect small-scale environmental changes caused by the atmosphere and hydrology, as well as large-scale climate changes such as global warming. This study uses National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (NOAA AVHRR), MOD09GQ surface reflectance products, and Landsat surface reflectance Tier 1 products, which comprehensively used RS and GIS technology to study lake ice phenology (LIP) and changes in Qinghai Lake. Over the past 38 years, freeze-up start and freeze-up end dates were gradually delayed by a rate of 0.16 d/a and 0.19 d/a, respectively, with a total delay by 6.08 d and 7.22 d. The dates of break-up start and break-up end showed advancing trends by −0.36 d/a and −0.42 d/a, respectively, which shifted them earlier by 13.68 d and 15.96 d. Overall, ice coverage duration, freeze duration, and complete freeze duration showed decreasing trends of −0.58 d/a, −0.60 d/a, and −0.52 d/a, respectively, and overall decreased by 22.04 d, 22.81 d, and 9.76 d between 1980 and 2018. The spatial pattern in the freeze–thaw of Qinghai Lake can be divided into two areas; the west of the lake area has similar spatial patterns of freezing and ablation, while, in the east of the lake area, freezing and ablation patterns are opposite. Climate factors were closely related to LIP, especially the accumulated freezing degree-day (AFDD) from October to April of the following year. Furthermore, freeze-up start time was more sensitive to changes in wind speed and precipitation.
1. Introduction
Lakes, as an important component of the terrestrial hydrosphere, are the bonds connecting the cryosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere of the earth’s surface system. Lake periodic formation and decay of ice cover and the changes in its timing as a result of seasonal and interannual variations in climate are called lake ice phenology (LIP) [1]. Lake ice cover is defined as an essential climate variable (ECV) in the Global Climate Observation System (GCOS) [2]. The LIP is strongly influenced by variations in the air temperature, while consistent long-term records of lake ice change provide a sensitive climate change indicator [3,4,5]. Studies have shown that lake ecosystems with periodic temperatures below 0 °C in the northern hemisphere are very sensitive to climate change [6]. With global warming, the temperature of surface lakes has increased by an average rate of 0.34 °C/a [7], and the duration of lake freezing has been shortened by about 5 d for every 1 °C increase in average temperature [8]. The duration of lake ice cover on most lakes in the northern hemisphere showed a rapid shortening trend from 2002 to 2015, and similar changes were more obvious and widespread in lakes at higher latitudes [9]. For example, most studies of lake ice of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau have shown that ice duration has decreased as a result of both later lake ice freeze-up date and earlier break-up date [1,10,11,12]. Additionally, the freezing and thawing process of lakes reflects differences in lake water depth and salinity [12,13], and it can also have an important impact on lake ecosystems and weather by controlling lake reflectivity and the exchange of matter and energy between the lake and atmosphere [10,14,15]. For example, when a large air mass passes over the Laurentian Great Lakes in North America in winter, the warmer water surface and the lakeshore results in the formation of lake effect snow systems that can result in significant snowfall events [16].
Most plateau lakes lack field observation data due to harsh environments, the small number of meteorological stations, and poor accessibility. Since the 1970s, remote sensing technology has been applied to the extraction of lake ice parameters. At present, research on lake ice has focused on the LIP (including ice–water classification or lake ice frozen area, freeze–thaw time) and ice thickness. Active microwave (Sentinel-1, RADARSAT-2, and ASAR), passive microwave (AMSR-E, SMMR, and SSM/R), and multispectral (MODIS and AVHRR) datasets could be used to distinguish ice and water by reflectance, backscatter coefficient, and brightness temperature difference [13]. Remotely sensed images with high spatiotemporal resolution can be used for automatic (or semiautomatic) extraction of LIP characteristics and have become the main means of monitoring lake ice in recent years [1,17,18]. Some scholars detect lake ice using deep learning and machine learning. For example, [19] presented a lake ice monitoring system in 2020 based on the automatic analysis of Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data by a deep neural network. The authors of [20] also proposed a machine learning-based semantic segmentation approach in 2018 for lake ice detection using low spatial resolution (250 m–1000 m) optical satellite data (MODIS and VIIRS). There are also algorithms for classifying water and ice. The authors of [21] developed an automatic algorithm that analyzes dual-polarized RS2 SAR images to distinguish open water (rough and calm) and sea ice, achieving an average classification accuracy of (91 ± 4)%. The authors of [22] presented an automatic ice-mapping approach that integrates unsupervised segmentation from the Iterative Region Growing using Semantics (IRGS) algorithm with supervised random forest (RF) labeling. Lake ice thickness monitoring has become increasingly quantified with the development of microwave technology in recent years, mainly using radar and altimeter sensors. The authors of [23] extracted backscatter values from SAR images of floating and grounded ice from lakes in two regions in Alaska and statistically compared mean backscatter intensity between them. The authors of [24] derived arctic sea ice thickness from freeboard measurements acquired by ICESat satellite altimetry (2003–2008).
LIP is the most sensitive to temperature changes, researchers had found, based on mathematical models, that temperature is the main cause of the differences in freezing and thawing times of lakes in different regions [17]. In [5] it was found that freeze duration (FD) of lakes distributed in areas between 45° and 61°N gradually shortened with climate warming, and predicted that these lakes could evolve into ice-free lakes in the future. The authors of [8] studied changes in the phenological characteristics of lake ice and river ice in the northern hemisphere within 150 years and found that for every 1.2 °C increase in temperature, lakes froze over 0.57 d/10a later, and broke up 0.65 d/10a earlier. The duration of lake ice cover on most lakes in the northern hemisphere showed a rapid shortening trend from 2002 to 2015 in the context of continued warming, and similar changes were more obvious and widespread in lakes at higher latitudes [9]. Similar findings have been reported elsewhere [17,25,26]. Additionally, [27] predicted that air temperature warming will hasten break-up by 10–20 days, and delay freeze-up by 5–15 days, from 2041 to 2070 in North America.
The special transitional location of Qinghai Lake makes it sensitive to climate change [28]. As the largest inland saltwater lake in China, Qinghai Lake was listed as a national nature reserve as early as 1997. There are more than 200 species of birds in the lake and the surrounding area, and it has been listed by the United Nations as an internationally important wetland reserve. In recent years, Qinghai Lake’s winter tourism has gradually attracted people’s attention, especially hiking activities on the frozen lakes. The danger of doing ice activities in winter is increasing, due to the lack of understanding of the freezing conditions of Qinghai Lake. Many accidents that have caused people and vehicles to fall into the lake due to cracking ice have been reported in the news (http://www.qhnews.com). Therefore, it is particularly urgent to deeply investigate the spatial freezing and melting patterns of Qinghai Lake and the response of LIP to climate change. Unfortunately, no research has been done yet on the long-term sequence of LIP for Qinghai Lake, and the research on its spatial freeze–thaw process is still limited. The purpose of this study is to construct a long-term LIP dataset for Qinghai Lake, to clarify the freezing and melting process, and to explore its response to climate change.
2. Study Area
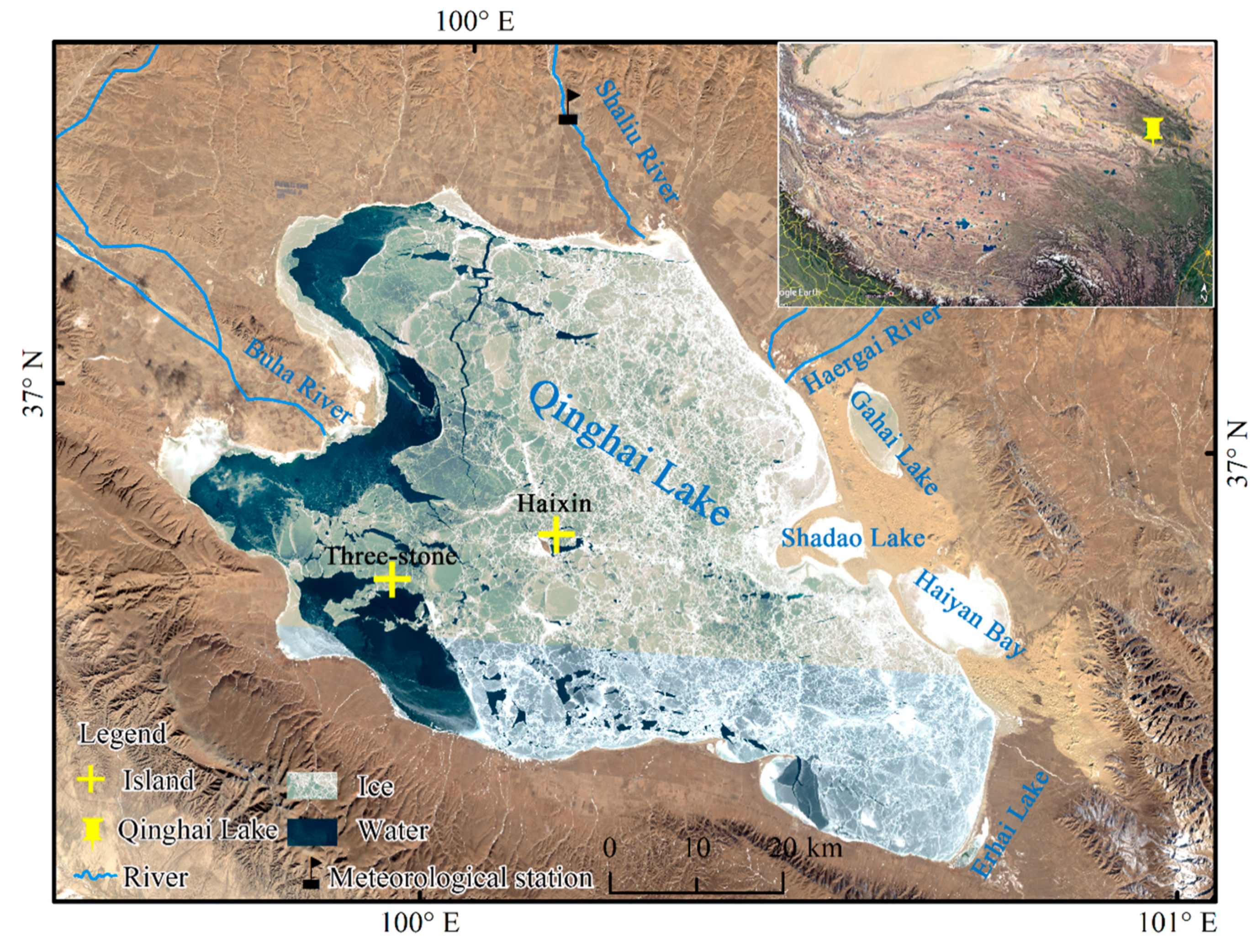
Qinghai Lake (36.53°–37.25°N, 99.60°–100.78°E) is located in the northeast of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau and is the largest salt lake in China (Figure 1). Qinghai Lake formed due to a stratigraphic fault depression, and the stratum development is relatively complete. There are two islands in the center of Qinghai Lake: Haixin Mountain and Three-stones. The lake is surrounded by sub-lakes: Gahai Lake, Shadao Lake, Haiyan Bay, and Erhai Lake are distributed in order from north to south in the east of the lake area. The average altitude of Qinghai Lake is 3200 m, and the length of the shoreline is 445 km. The coastline is tortuous; the lake is convex in shape and measures about 109 km from northwest to southeast and 80 km from west to east. The lake water is weakly alkaline. When the water level is 3193.8 m, the lake area is 4294 km2, the storage capacity is about 785.2 × 108 m3, the average water depth is 18.3 m, and the maximum depth is 26.6 m. In recent years, the water level of Qinghai Lake has continued to rise, and its area has gradually expanded due to the increase in precipitation in the basin [29].
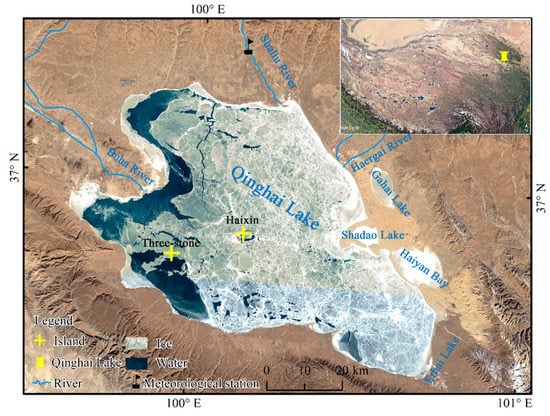
Figure 1.
Location and surroundings of Qinghai Lake (base map is Landsat-8 image of 21 January 2017, from the U.S. Geological Survey, and the composite band is 4-3-2).
Qinghai Lake is a closed lake based on precipitation replenishment. The average annual rainfall is 319 to 395 mm and is concentrated in June to September each year. The year-round temperature is low, and the daily temperature difference is large, the annual average temperature is between −1.0 and 1.5 °C. About 50 rivers enter the lake, and these are mostly seasonal rivers concentrated in the west and north of the lake. The Buha River has the largest flow, accounting for about 60% of the total flow into the lake [30]. The freezing temperature of Qinghai Lake is slightly lower than 0 °C. It usually freezes in mid-December each year and completely freezes in early January of the following year. The frozen Qinghai Lake begins to melt in mid- to late March and is completely melted by early April [31]. Ice thickness is on average 50 cm, and the maximum ice thickness is 70 cm [32].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data and Processing
The data used in this study mainly included MOD09GQ surface reflectance products, NOAA AVHRR, and Landsat surface reflectance Tier 1 products, the details and purpose of which are shown in Table 1. Because the available NOAA AVHRR reflectivity products masked the water body information on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform [33], we used Python language processing on the Integrated Development and Learning Environment (IDLE) platform to analyze data, and the rest of the data preprocessing and information extraction was implemented on the GEE platform. The remote sensing data and applications used in this paper are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Main data and their purpose used in this study.
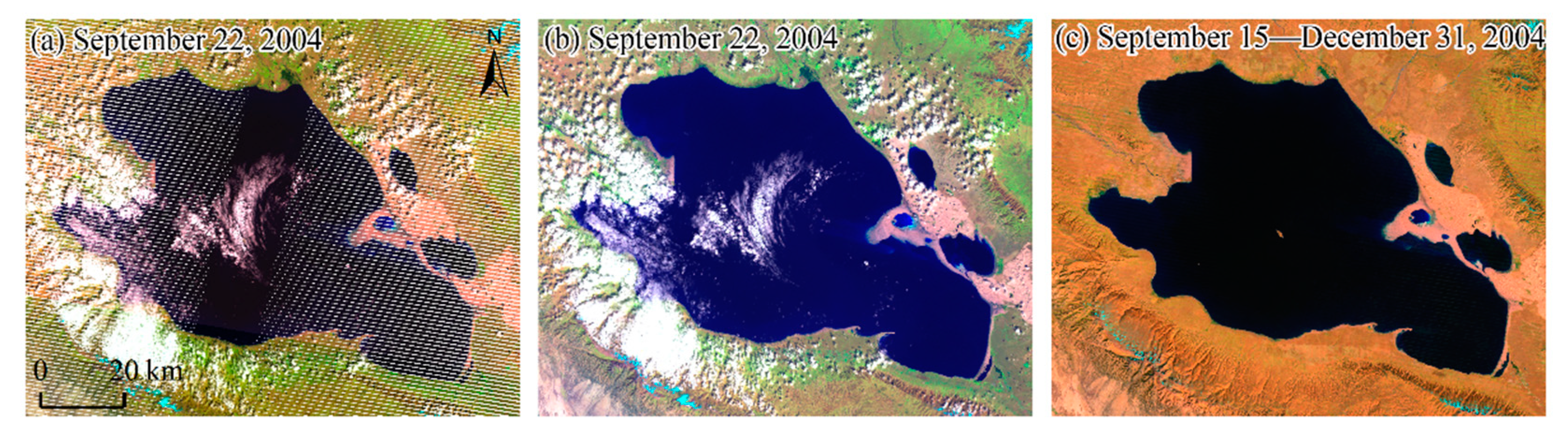
The study area is located across two Landsat scenes (Path/Row: 133/035 and 133/034). A total of 71 Landsat images (2 MSS, 51 TM, 12 ETM+, and 6 OLI) from the 1980s to 2018 were requested through GEE in this study. As the scan line corrector (SLC) of the Landsat7 ETM+ sensor malfunctioned in 2003, gaps were filled by linear histogram matching using available images from previous and subsequent times, as shown in Figure 2a–c. This algorithm was developed by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) Earth Resources Observation Systems (EROS) Data Center (https://www.usgs.gov/media/files/landsat-7-slc-gap-filled-products-phase-two-methodology). All Landsat data were initially masked to exclude pixels contaminated by clouds and cloud shadows using the pixel quality attributes generated from the CFMASK algorithm, and a cloud-free image was synthesized by calculating the mean of all values at each pixel across the stack of all matching bands. Finally, the annual lake boundary was mapped via normalized difference water index (NDWI) [34] followed by strict visual quality assurance and case-by-case manual inspection.
where BGreen and BNIR represent reflectance in the green and near-infrared bands, respectively.
Figure 2.
Landsat surface reflectance product preprocessing on the GEE platform. (a) Original Landsat 7 ETM+image; (b) repaired Landsat 7 ETM+image; (c) composite image after removing the cloud.
The NOAA satellite is one of the most successful and widely used meteorological satellites. NOAA/AVHRR 1B data are divided into four data types. Among them, High Rate Picture Transmission (HRPT) has a resolution of 1.1 km. For this study, we selected the AVHRR HRPT 1 B data from 1980 to 2018. Previous studies have shown that Channels 1, 2, and 4 have better sensitivity to clouds, ice and snow (visible light), water–land boundaries (near-infrared), and ice surface temperature (thermal infrared), respectively, and better monitor lake ice [32]. We collected the images from NOAA official website (https://www.bou.class.noaa.gov) and the National Satellite Meteorological Center Data (https://www.nsmc.org.cn). After Channels 1 and 2 data of NOAA AVHRR were corrected using the atmosphere and the bidirectional reflection model, their reflectivity reflected the true situation at the surface.
To verify the accuracy of ice phenology information on Qinghai Lake based on NOAA AVHRR, we selected the MOD09GQ terra surface reflectance daily product, which provides an estimate of the surface spectral reflectance as it would be measured at ground level in the absence of atmospheric scattering or absorption [35]. Its high temporal resolution (1 d) and spatial resolution (250 m) are quite beneficial for the study of ground features that change rapidly over time. We selected corrected products produced at an ideal quality, especially the reflectance products of the red and near-infrared bands, which were not affected by the deep sea and clouds, according to the surface reflectivity quality assurance band (QC_250m).
In addition, the meteorological data used were obtained from China Meteorological Forcing Dataset (CMFD) and China Meteorological Data Service Center (CMDSC) (http://data.cma.cn). The CMFD data are a near-surface meteorological and environmental factor reanalysis dataset developed by the Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research Chinese Academy of Sciences. With a temporal resolution of 3 h and a spatial resolution of 0.1°, these data were obtained from the Cold and Arid Regions Scientific Data Center (http://westdc.westgis.ac.cn).
3.2. Lake Ice Extraction
Typical methods of lake ice extraction include the index method and the threshold method. Previous research has shown that the threshold method can eliminate certain atmospheric effects and system errors, and can more accurately identify the time when the lake starts to freeze and starts to melt [36]. Therefore, the threshold method was used to extract the lake ice area. Then, the extraction results were visually interpreted for inspection and correction. The calculation method is as follows [37]:
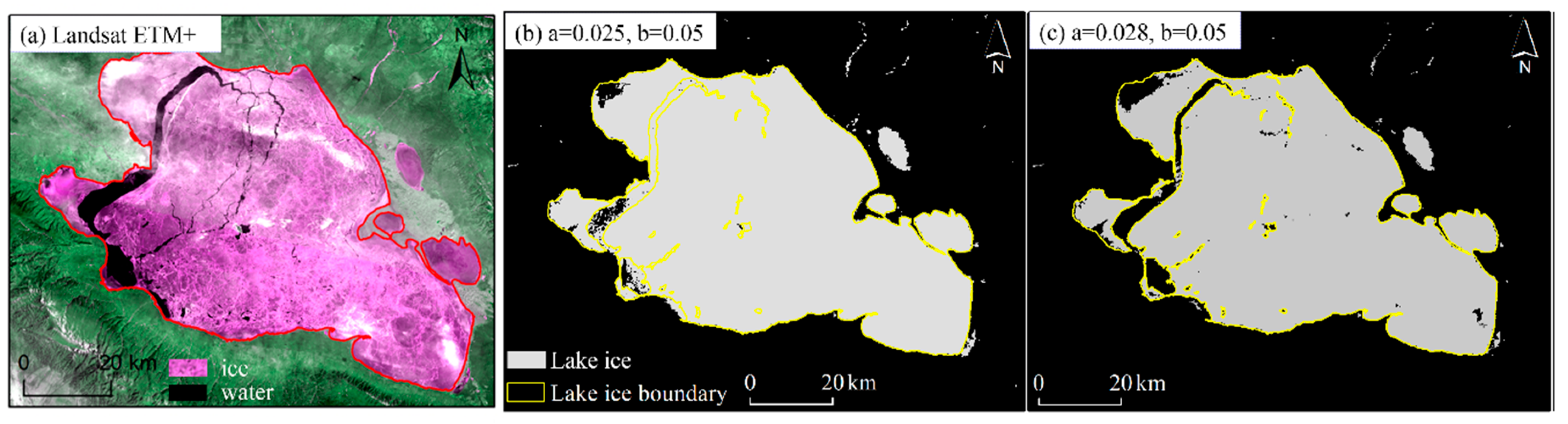
In this expression, and denote the reflectance of the red and near-infrared bands, respectively. The parameters a and b are thresholds, and it is worth noting that the thresholds of different lakes are not the same. When the difference between the red-light reflectance and the near-infrared reflectance is greater than a, and the red-light reflectance value is greater than b, the lake ice area can be accurately extracted. In order to determine the appropriate threshold for identifying lake ice in Qinghai Lake, we have referred to other scholars’ [37] methods and thresholds for lake ice extraction. First, we chose a Landsat remote sensing image of Qinghai Lake that was not completely frozen, and manually digitized the ice range (Figure 3a). Then, we chose the MODIS image for the same day as the Landsat image and used the Band Math Tool to perform band calculation based on Equation (2) (Figure 3b). We refer to the above process as human–computer interaction testing. We repeated this process until the result of the band calculation and the digital ice vector range achieved the maximal coincidence; under this condition, the values of a and b are optimized. Figure 3 shows the results of the digital ice range and the results of the recognition of different thresholds. Finally, we determined that a was 0.028, and b was 0.05 (Figure 3c). It is worth noting that the MODIS and AVHRR data are affected by the cloud, and the resolution of MODIS is a bit higher than AVHRR, so we only list visualized results of MODIS images in this study. Additionally, we checked both the extraction results of AVHRR and MODIS one by one.
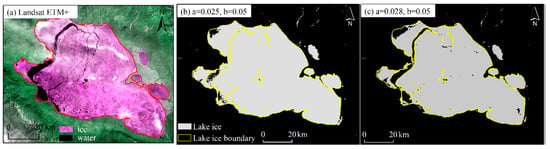
Figure 3.
Result of human–computer interaction tests in ENVI 5.3 software. (a) Landsat -7 image of February 22, 2014, after a gap filled, from the U.S. Geological Survey, and the composite band is 3-4-3. (b) The result is obtained after band calculation when a is 0.025 and b is 0.05 in ENVI 5.3 software. (c) The best result is obtained after multiple band calculations.
3.3. TheLake Ice Phenology Extraction
The four time nodes, being lake freeze-up start (FUS) and freeze-up end (FUE), ice break-up start (BUS), and break-up end (BUE), reflect the periodicity of lake ice change. In this study, the FUS date was defined as the time point when the lake ice area was continuously greater than or equal to 10% of the lake area. When the lake ice area was greater than or equal to 90% of the lake area, the date of this day was determined as FUE. If the lake ice area was stable at less than or equal to 90% of the lake area, the date of this day was determined as BUS, while BUE was defined as the time point when the ice was less than or equal to 10% of the total cover [38]. Some scholars have different understandings of a lake’s FD. For example, Gou [11] defined FD as the period from FUE to BUE, and [36] defined it as the period from FUE to BUE. However, Kropáček [1] considered it to be the duration from FUS to BUE and proposed the concept of complete freeze duration (CFD), that is, the time interval from FUE of the lake to BUS. To facilitate the comparison of existing research, this paper selected FD as proposed by Reed [38] and CFD as proposed by Kropáček [1] for the analysis of Qinghai Lake ice conditions. Additionally, to better understand the response of the Qinghai Lake LIP to climate change, this study defined the concepts of complete ice coverage duration (ICD) and ablation duration (AD). The ICD of this research was defined as the number of days between FUS and BUE, and AD encompasses the period between BUS and BUE. The ice phenology timings and an associated definition are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Different ice phenology timings and an associated definition used in this study.
4. Results
4.1. Temporal Characteristics of Ice Phenology in Qinghai Lake
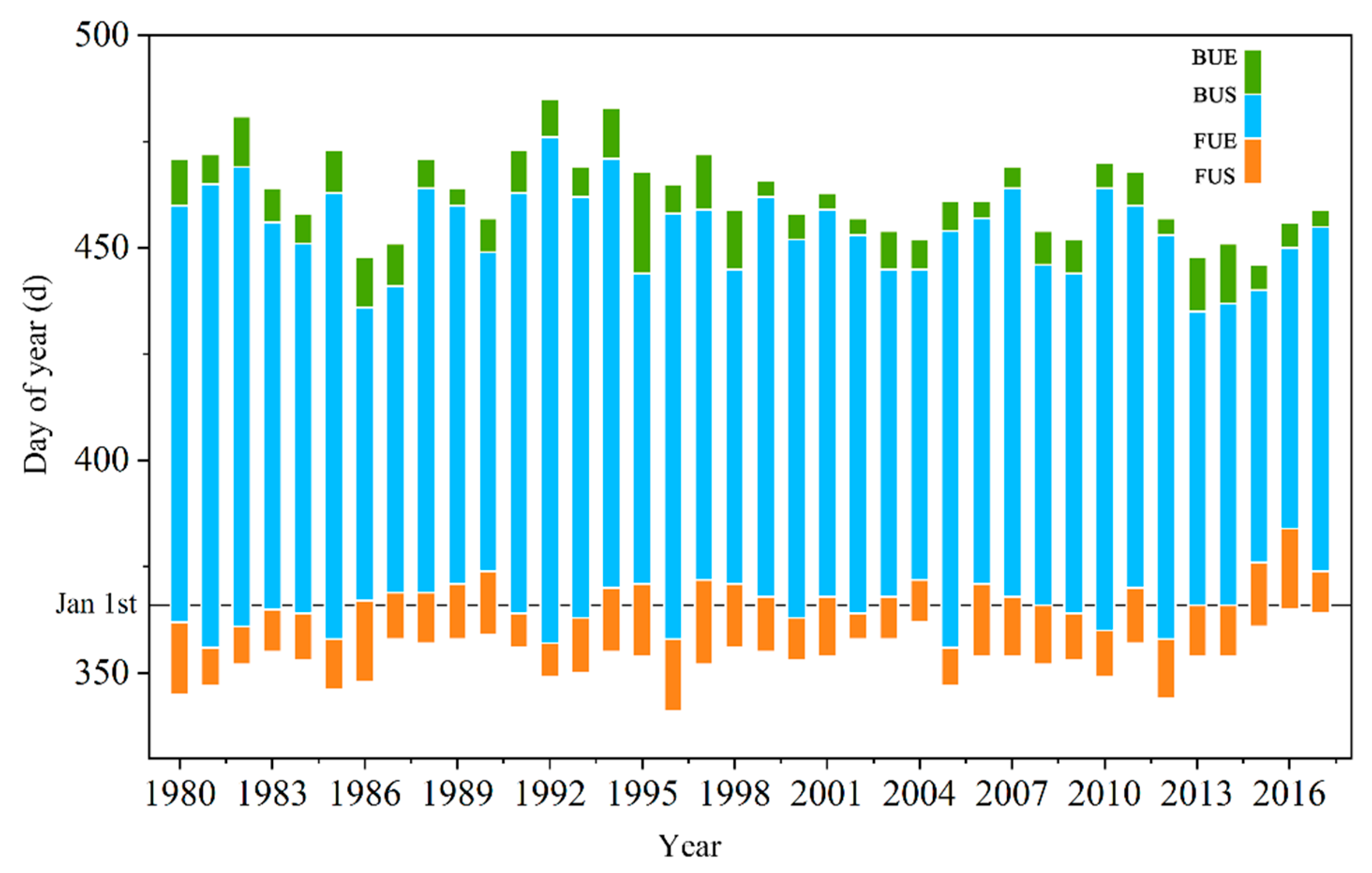
Figure 4 shows the temporal characteristics of LIP of Qinghai Lake from 1980 to 2018 based on AVHRR HRPT data extraction. As shown in Figure 4, the freeze–thaw situation of Qinghai Lake varied between different years. In the past 40 years, the average FUS of Qinghai Lake was 20 December, and the earliest and latest FUS appeared on 7 December 1996, and 31 December 2016, respectively. After about 13 d of freezing, Qinghai Lake was completely covered by ice at the end of December or early January each year. The average FUE appeared on 1 January, and the earliest and latest FUE appeared on 22 December 1981, and 19 January 2017, respectively. The freeze lasted until late March, and the ice layer that was completely frozen began to melt gradually as the temperature increased. The average BUS was 30 March, and 11 March 2014, and 21 April 1993, were the earliest and latest BUS, respectively. After about 8 d of ablation, the ice layer had completely disappeared. The average BUE was April 8. The earliest and latest BUE appeared on 22 March 2016, and 30 April 1993.
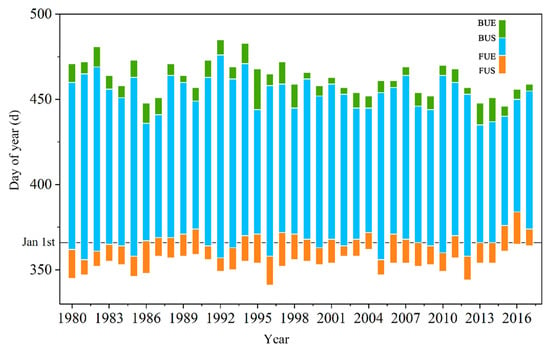
Figure 4.
The lake ice phenology (LIP) characteristics of Qinghai Lake from 1980 to 2018 (day) (Abscissa denotes the day of the year of the ice phenology, in which numbers larger than 365 indicate dates in the following year).
From 1980 to 2018, FD (between BUE and FUE) and CFD (between BUS and FUE) of Qinghai Lake differed greatly from year to year. The average FD was 96 d, the shortest was 70 d (from 2015 to 2016), and the longest was 128 d (from 1992 to 1993). The average CFD was 88 d, and the shortest and longest durations were 64 d and 119 d, respectively. The extreme values of CFD and FD appear in the same year. In recent years, the average ICD of Qinghai Lake was 109 d, the shortest was 85 d (from 2015 to 2016), and the longest was 136 d (from 1992 to 1993); The average FD of lake ice was 8 d, the shortest was 4 d (seven years, such as from 2002 to 2003, 2017 to 2018, etc.), and the longest was 24 d (from 1995 to 1996).
4.2. Verify the Accuracy of Lake Ice Phenology Extracted from AVHRR Data
To verify LIP accuracy extracted from AVHRR HRPT data, we extracted LIP from 2000 to 2018 based on the MODIS MOD09GQ data. It is worth noting that MODIS and AVHRR data were affected by clouds, but this did not influence the determination of the four freeze–thaw dates of Qinghai Lake. Because we only need to confirm the dates when the lake ice area percent is 10% and 90% each year, which is relatively easy to confirm. We can also check date accuracy via monitoring the ice conditions for 2–3 d before and after freezing or ablation, and the biggest error was not more than a week. According to the results from the same period of extraction based on the AVHRR and MODIS data, we introduced the mean absolute error (MAE) and relative error (RE) to compare and analyze these results [39], as shown in Table 3 and Figure 5. The results show that, on the whole, the four time nodes (FUS, FUE, BUS, and BUE) of Qinghai Lake freeze–thaw extracted from AVHRR and MODIS data have high consistency (R2 > 0.9), and their MAE is 2.66, 2.38, 2.05, and 1.11 d, respectively. According to the MAE, the maximum errors of ICD, AD, FD, and CFD during the study period are calculated as 7, 7, 8, and 12 d, respectively. Compared with the results of MODIS data monitoring, FUS and BUS dates extracted based on AVHRR data were usually later, while the FUE date appeared earlier. The above differences may be due to crushed ice that had been scattered by the wind during the freezing stage, difficult for sensors to identify, and hence increasing the overall difficulty of identification.

Table 3.
Errors of the four freeze–thaw dates and ice coverage duration derived from AVHRR and MODIS data (in days).
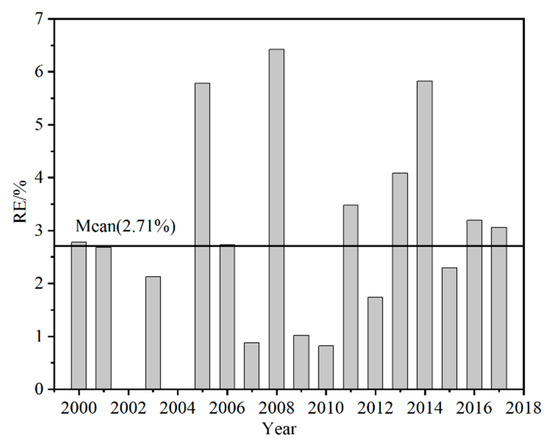
Figure 5.
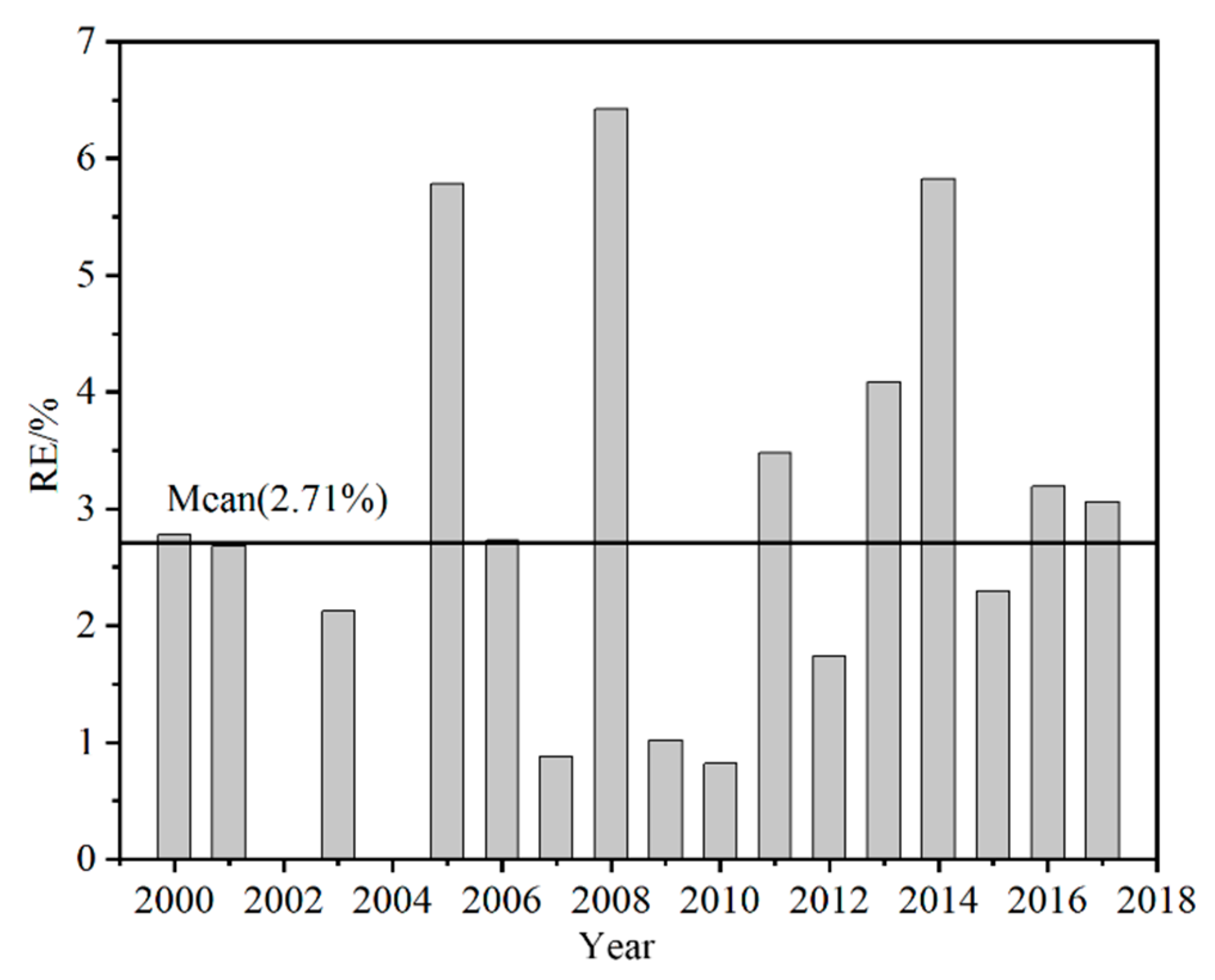
The relative error of ice cover duration (ICD) calculated from AVHRR and MODIS data between 2000 and 2018. (The line represents the mean relative error for the 18 years).
Compared with the freeze–thaw date, the ICD can better reflect the overall ice situation of Qinghai Lake [40]. As shown in Figure 5, except for an ICD RE greater than 5% in 2005, 2008, and 2014, the rest of the years are less than 5%, and the average RE is 2.71%, while the MAE is 2.66 d. According to the Global Climate Observing System (GCOS) recommendation for ice-on (FUS, FUE) and ice-off (BUS, BUE) dates are +/-2 days; the consistency of LIP results based on AVHRR and MODIS data extraction is not very high. Nevertheless, this does not affect the overall trend in LIP.
4.3. Changes in Ice Phenology of Qinghai Lake
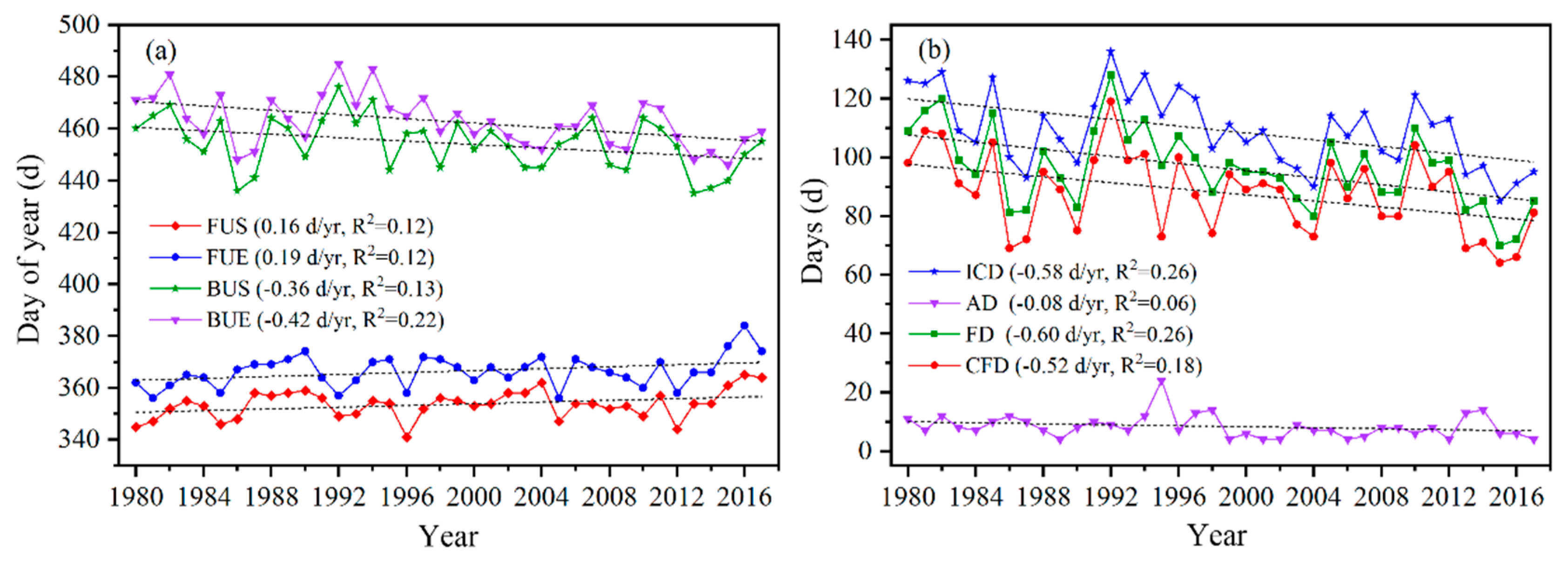
To investigate the interannual variation of LIP in Qinghai Lake, a trend analysis was conducted by linear regression. The changes in LIP observed over the 38 years are all significant at the 95% level except for changes in AD. From 1980 to 2018, FUS and FUE of Qinghai Lake showed a gradually delayed change trend over time (Figure 5), with change rates of 0.16 d/a and 0.19 d/a, respectively. Both BUS and BUE dates showed advancing trends (Figure 6a), with change rates by −0.36 d/a and −0.42 d/a, respectively. Over the past 38 years, FUS and FUE were delayed by 6.08 d and 7.22 d. However, BUS and BUE were shifted earlier by 13.68 d and 15.96 d, respectively. This directly resulted in the duration of ICD, FD, and CFD varying greatly over different periods, and the overall shortening trend was obvious (Figure 6b). In general, the change rates of ICD, FD, and CFD were all greater than 0.5 d/a, and overall decreased by 22.04 d, 22.81 d, and 9.76 d between 1980 and 2018. The changing trend of AD was not obvious; except for a long duration (24 d) from 1995 to 1996, the remaining years were stable at about 8 to 10 d.
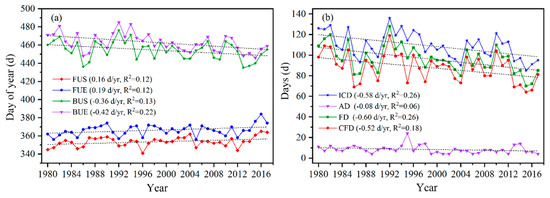
Figure 6.
The LIP characteristics change for Qinghai Lake from 1980 to 2018. (a) Changes in the freezing (FUS and FUE) and melting time (BUS and BUE). (b) Changes in the ice cover duration (ICD, AD, FD and CFD).
To investigate the interannual variation of LIP in Qinghai Lake, a trend analysis was conducted by linear regression. The changes in LIP observed over the 38 years are all significant at the 95% level except for changes in AD. From 1980 to 2018, FUS and FUE of Qinghai Lake showed a gradually delayed change trend over time (Figure 5), with change rates of 0.16 d/a and 0.19 d/a, respectively. Both BUS and BUE dates showed advancing trends (Figure 6a), with change rates by −0.36 d/a and −0.42 d/a, respectively. Over the past 38 years, FUS and FUE were delayed by 6.08 d and 7.22 d. However, BUS and BUE were shifted earlier by 13.68 d and 15.96 d, respectively. This directly resulted in the duration of ICD, FD, and CFD varying greatly over different periods, and the overall shortening trend was obvious (Figure 6b). In general, the change rates of ICD, FD, and CFD were all greater than 0.5 d/a, and overall decreased by 22.04 d, 22.81 d, and 9.76 d between 1980 and 2018. The changing trend of AD was not obvious; except for a long duration (24 d) from 1995 to 1996, the remaining years were stable at about 8 to 10 d.
In general, the LIP record for Qinghai Lake, 1980 to 2018, has shown that ice cover durations (ICD, FD, and CFD) have decreased as a result of later lake ice freeze-up dates and earlier break-up dates. This change is consistent with changes in ice phenology in other regions of the world. For example, the duration of lake ice cover on most lakes in the northern hemisphere showed a rapid shortening trend from 2002 to 2015, and similar changes were more obvious and widespread in lakes at higher latitudes [9]. The authors of [8] found that 39 lakes in the northern hemisphere showed consistent changes in ice phenology over the past 150 years with later FUS and earlier BUS; [41] reached the same conclusion on the study of lake ice phenology characteristics in the middle and high northern latitudes (north of 40°N). Against the background of climate warming, the LIP is the same, but different lakes show different rates of change. For example, [17] analyzed the LIP trend in Canada from 1950 to 2004, showed that lakes froze over 1.2 d/decade later by the end of the period, and that lake ice broke up 1.8 d/decade earlier over the same timespan. The authors of [42] studied the freezing of lakes in North America (the USA and Canada) and Europe (Sweden and Finland) and found that the average BUS shifted 1.9 d/decade earlier, and the average ICD decreased by 1.87 d/decade. Compared with the above results, although the timespan is different, the ice phenology of Qinghai Lake between 1980 and 2018 showed larger trends, i.e., FUS shifted 1.6 d/decade later, and BUS shifted 3.6 d/decade earlier.
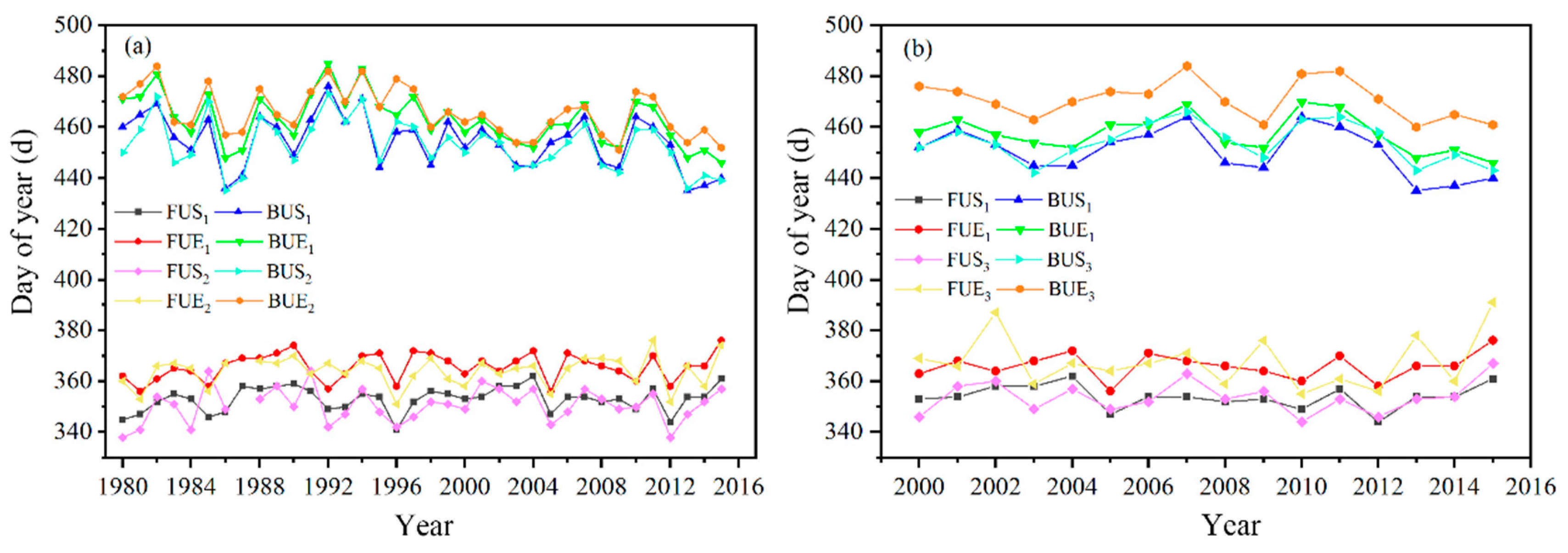
Compared with existing studies [39,43], the results of this study show better consistency. In Figure 7, the subscript one (in the legend) indicates the extraction result of this study, and two and three indicate the result from [39] and [43], respectively. Compared with the study by [39], the changing trend of LIP characteristics extracted from this study is the same, while the specific dates of the lake FUS, FUE, BUS, and BUE differ from year to year (Figure 7a). The comparison results show that the maximum differences between the four freeze–thaw dates (FUS, FUE, BUS, and BUE) are 18 d (1985–1986), 10 d (1992–1993), 10 d (1983–1984), and 14 d (1996–1997). Further research showed that FUS, FUE, and BUS dates extracted based on AVHRR data were generally delayed compared with the results of passive microwave data extraction during the same period, with the average delay being 2 d, and BUE appeared earlier. This is related to the different data sources and methods for extracting LIP. For example, the former used SMMR and SSM/I passive microwave data (resolution was 25 km) with low spatial resolution. Although the theoretical time resolution of the data was 1 d, the actual data obtained was not continuous due to the lack of orbital spacing and data. Furthermore, the brightness temperature data on Qinghai Lake was obtained approximately every 6 d due to the influence of the track interval, and the error caused by the data itself was about 2–6 d. According to the difference between ice/snow and water reflectance, [43] extracted LIP of Qinghai Lake based on the 500 m resolution MODIS data. As shown in Figure 7b, both our results and Guo’s also show high consistency during the same study period. It was worth noting that FUE, BUS, and BUE dates extracted by MODIS were earlier than the results of the AVHRR data extraction, especially BUE date with an average difference of 13 d, while the average difference between FUE and BUS dates were 2 d and 3 d, respectively. In summary, the LIP of Qinghai Lake extracted based on different data sources showed high consistency.
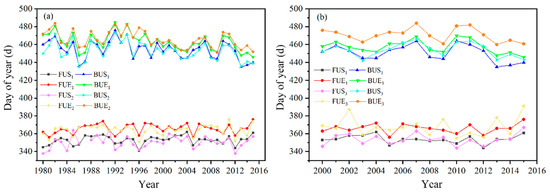
Figure 7.
Comparison of four freeze–thaw dates and existing research results (Note: the subscript 1 indicates the extraction result of this article, and two and three indicate the results of [39] and [43], respectively). (a) Comparison with the research results of [39]. (b) Comparison with the research results of [43].
4.4. Spatial Patterns in the Freeze–thaw Cycle of Qinghai Lake
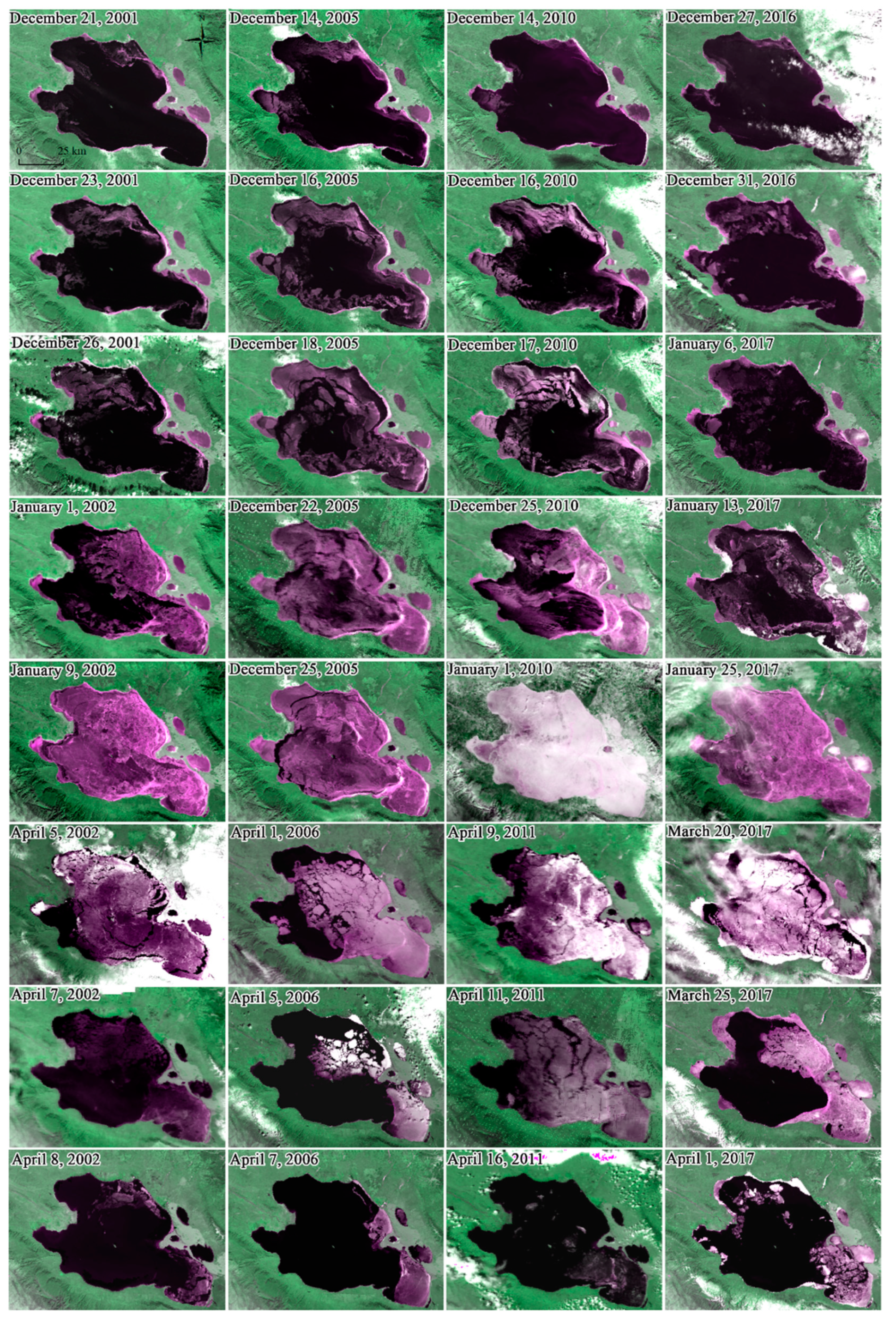
Patterns in lake freeze-ablation reflect differences in lake water depth to a certain extent. For example, the seven lakes in the northern Hoh Xil region and Namco had all frozen from the shallow lake shores and expanded to the center of the lake [11,12]. Figure 8 shows the freeze–thaw status of Qinghai Lake at different periods. It can be seen that Haiyan Bay, Gahai Lake, Shadao Lake, the northern part of the Lake, and the vicinity of Tiebuka Bay began to form crushed ice first and then gradually expanded from the waterfront to the center of the lake. The newly appeared ice layer could disappear easily during the freezing process due to a sudden rise in temperature or a change in the wind speed, resulting in repeated freezing-thawing phenomena in the freezing process of lakes. As shown in Figure 7, from 31 December 2016, to 6 January 2017, a similar phenomenon appeared on the lake. Judging from the physical processes of lake ice generation and degeneration, in the case of differences between the water and land heat capacity, primary ice in the form of ice crystals and thin ice first appeared in the coastal region. With the gradual expansion of the range of broken ice, wind and waves quickly cracked the thinner lake ice at the beginning of the freezing and blew it to the lakeshore to form a thin and transparent ice belt—shore ice. The time for the formation of continuous fixed ice along the coast is mainly related to the shape of the shoreline and the prevailing wind direction [44]. Areas with complicated coastlines (such as Haiyan Bay, Gahai Lake, Shadao Lake, and Tiebuka Bay) first showed shore ice, and then formed continuous fixed ice.
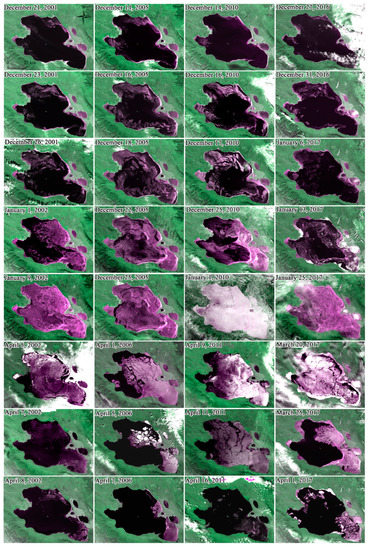
Figure 8.
Freezing and melting process of Qinghai Lake (base map is Landsat remote sensing image from the U.S. Geological Survey (the composite band is 3-4-3), the color of purple or white over the lake denotes lake ice, and the black represents water body).
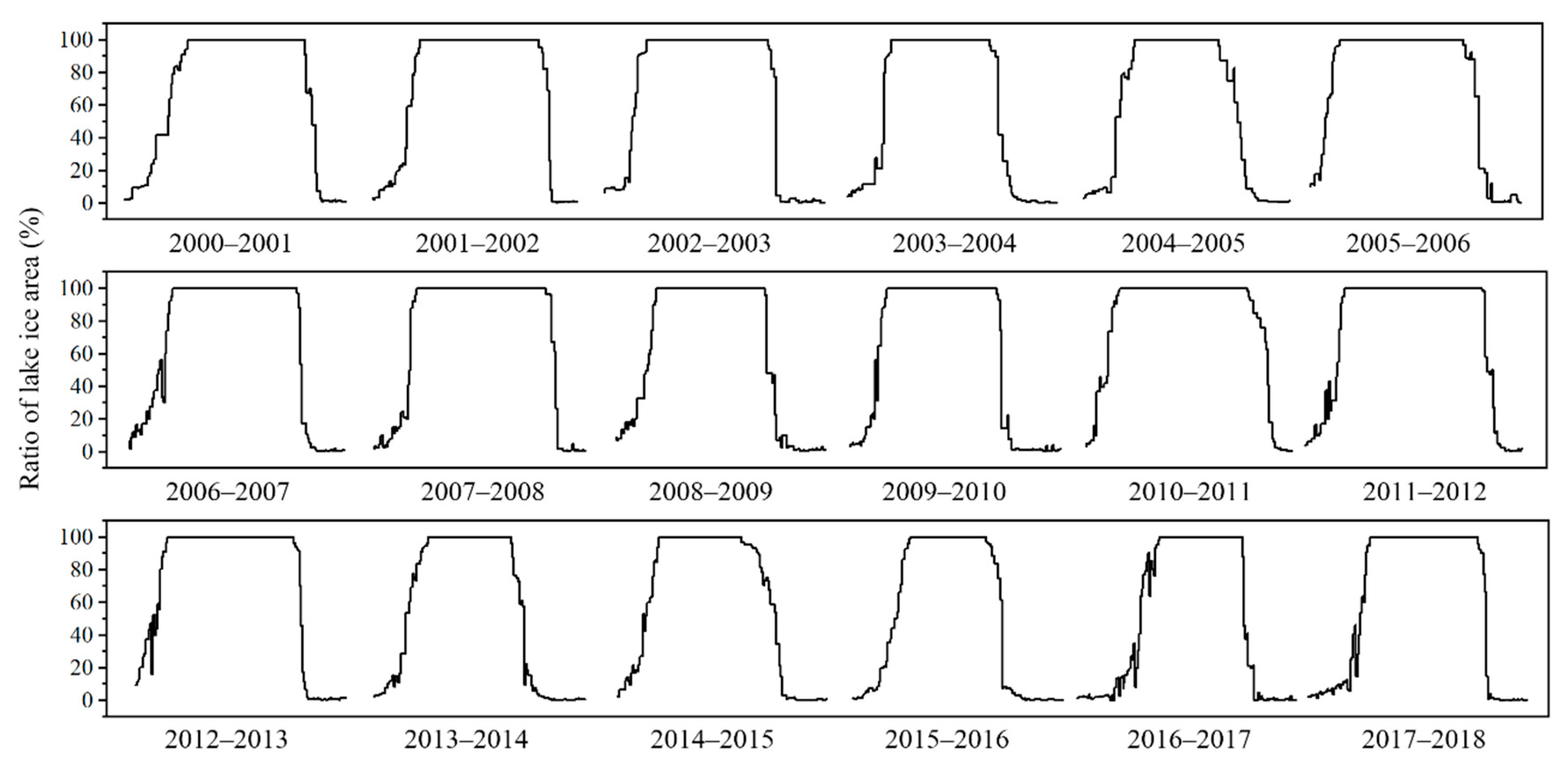
As the temperature continued to decrease, the intensity of the lake’s heat dissipation increased, and the range of shore ice began to expand toward the center of the lake, and the open water surface of the lake gradually decreased. At the same time, the impact of the wind on the ice layer also weakened, and the lake began to freeze and formed a complete ice cover. At this time, the lake also relied on thermal conductivity to freeze to the deep, the freezing speed accelerated, and the thickness increased. Qinghai Lake was a completely frozen lake. The entire freezing process was relatively slow and required a continuous low temperature. Near the end of March or early April, as the temperature increased, part with the ice surface of the Qinghai Lake ruptured, especially at the mouth of the Buha River in the northwestern part of the lake, where a large crack appeared in the ice surface (as shown in Figure 8, 25 December 2005). The possibility of the continued existence of lake ice depended largely on the vertical transmission of energy in the lake area. Under the influence of heat flow and temperature rise, the ice layer on the lake surface began to melt, and the factors that break the ice layer (increasing water level and wind force) promoted an increase in the contact between the ice and the surrounding environment and accelerated the melting of the lake ice [45,46]. Qinghai Lake usually begins to ablate in the north and west of the lake area, and the ablation rate is fast. Melting started at the latest in the southeastern part of the lake area and areas adjacent to Haiyan Bay, Gahai Lake, and Shadao Lake. As far as the Qinghai Lake freeze-ablation process is concerned, the ablation process is relatively rapid. Figure 9 shows the change curve with the time of the ice area percentage for Qinghai Lake since 2000. There are six complete freeze–thaw periods on the abscissa, and the ordinate represents the percentage of lake ice area. Statistics showed that the average duration of the freezing process (13 d) was generally longer than the ablation process (8 d) and the difference between the two was about 5 d. The maximum number of days of difference in the study period was 13 d, which occurred in 2006–2007.
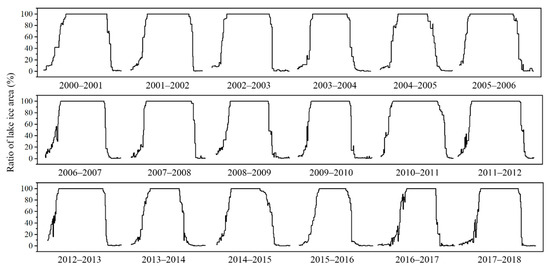
Figure 9.
The ratio of lake ice area on Qinghai Lake in different years.
In general, there were two areas of spatial pattern in the freeze–thaw of Qinghai Lake; the earliest region that started to freeze west of the lake was the earliest region to begin ablation, indicating that the spatial patterns of freezing and ablation are similar; while in the east of the lake area, freezing and ablation patterns are opposite, and the earliest areas to freeze were the latest areas that started to ablate. This is different from the freeze–thaw spatial pattern of other lakes in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, such as the lakes in the Hoh Xil region [12], and Namco [11], and this may be related to the geographical location, water depth, lake morphology, salinity, or mineralization of the lake [47]. Freeze–thaw patterns and processes of the lake are also closely related to the spatial distribution of lake ice thickness. The results of this study have certain reference values for the future simulation of lake ice thickness and winter tourism in Qinghai Lake.
4.5. Impact of Climate Change on Lake Ice Phenology of Qinghai Lake
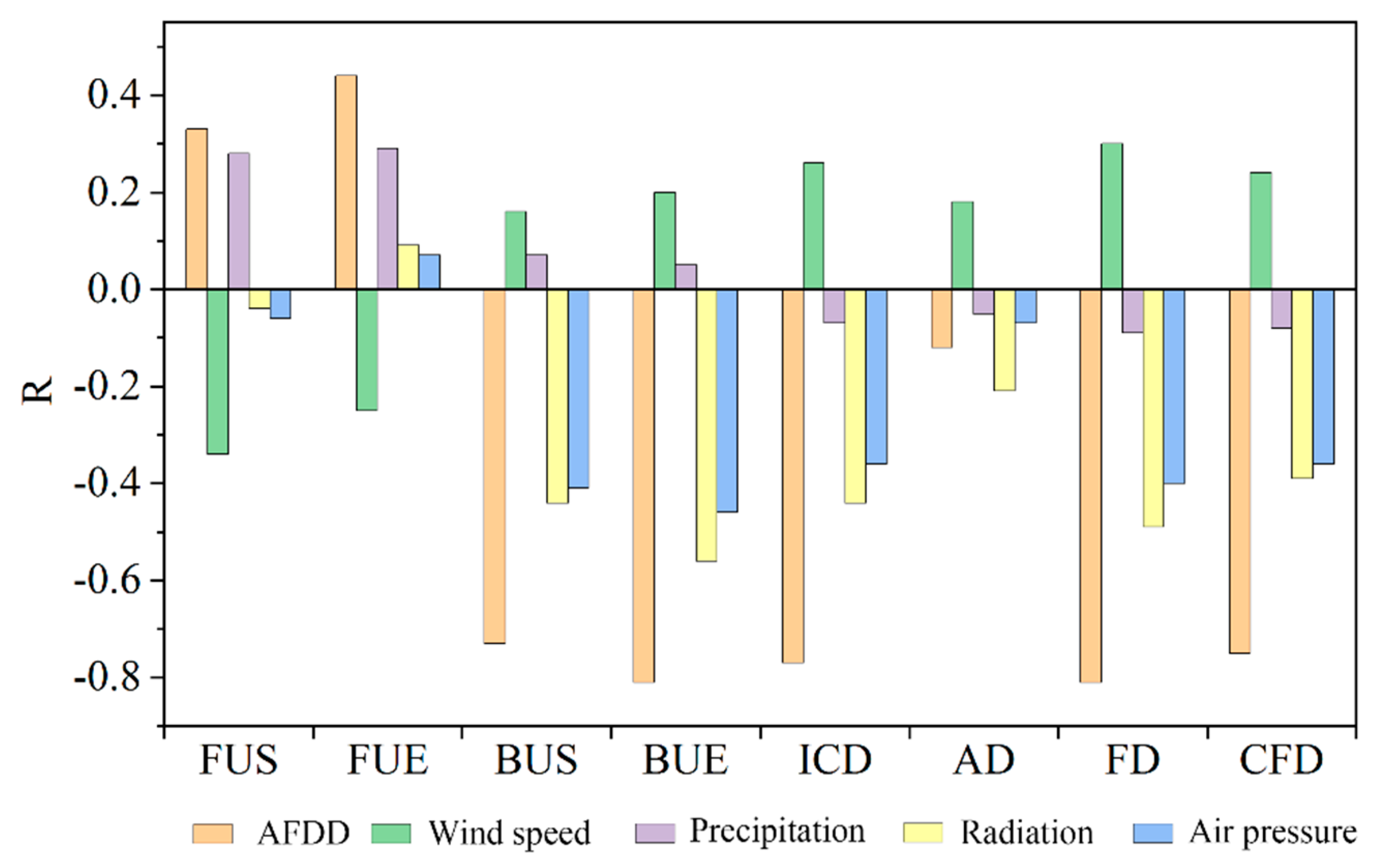
The main factors affecting the changes in LIP include meteorological factors such as temperature, solar radiation, humidity, and snowfall, and geographical factors such as lake shape and geographical location. The process of lake ice development and disappearance is mainly determined by the vertical energy transfer in the lake and meteorological factors [44]. To study the influence of meteorological factors on the freeze–thaw process of Qinghai Lake, this study collated and calculated the correlation between LIP and climate variables (temperature, wind speed, precipitation, radiation, and barometric pressure) (Figure 10). Here, it is necessary to explain that the temperature refers to accumulated freezing degree-day (AFDD)—calculated as the sum of mean daily temperature departures below the freezing point (0 °C) from October to April of the following year. AFDD is an important cold season weather–climate variable, which measures the thickness and phenology of winter ice cover [48]. Wind speeds correspond to the average wind speed in the 5 d before the freeze–thaw of Qinghai Lake (corresponding to FUS, FUE, BUS, and BUE) or the winter half-year (corresponding to ICD, CFD, AD, and FD); precipitation refers to the sum of precipitation in the Qinghai Lake Basin in the winter; radiation and air pressure are average values in the winter.
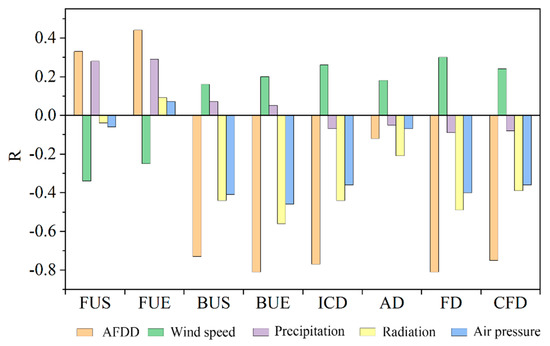
Figure 10.
Relationship between LIP and climate variables.
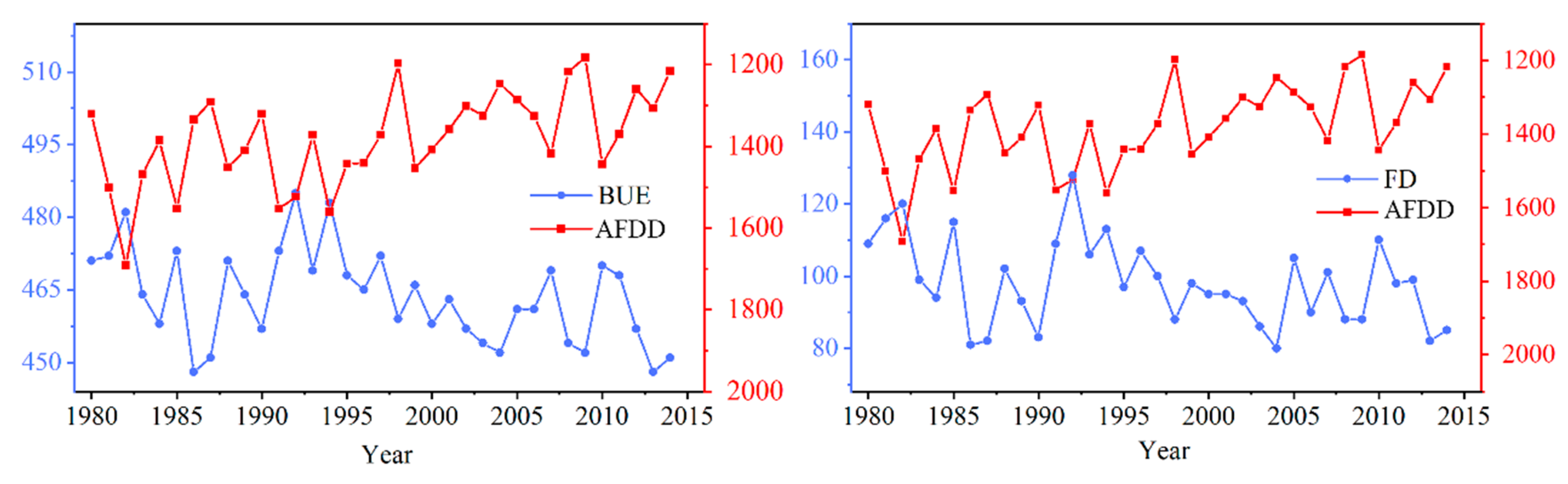
Among the eight phenological indicators, FUS and FUE were positively correlated with AFDD (correlation coefficients were 0.33 and 0.44, respectively), and the other indicators were negatively correlated with it (Figure 10). This indicated that in years with a smaller AFDD, ICD has shortened as a result of later FUS and earlier BUS. At a confidence level of 0.05, the correlation between each of BUE and AFDD, and between FD and AFDD in winter were all −−0.81. The changing trend is shown in Figure 11. BUE and FD show the same change trend, indicating that they were the most sensitive to changes in winter temperature. Additionally, ICD, CFD, and BUS were very sensitive to changes in AFDD, and their correlation coefficients are −0.77, −0.75, and −0.73, respectively. These calculation results show that a smaller AFDD would correspond to delayed FUS, earlier BUS, and shorter ICD, CFD, and FD. Conversely, ICD, CFD, and FD will lengthen when AFDD is larger.
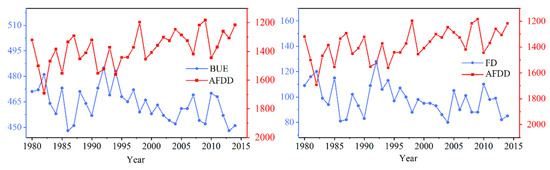
Figure 11.
Relationship between accumulated freezing degree-day (AFDD), break-up end (BUE), and freeze duration (FD) of Qinghai Lake from 1980 to 2018.
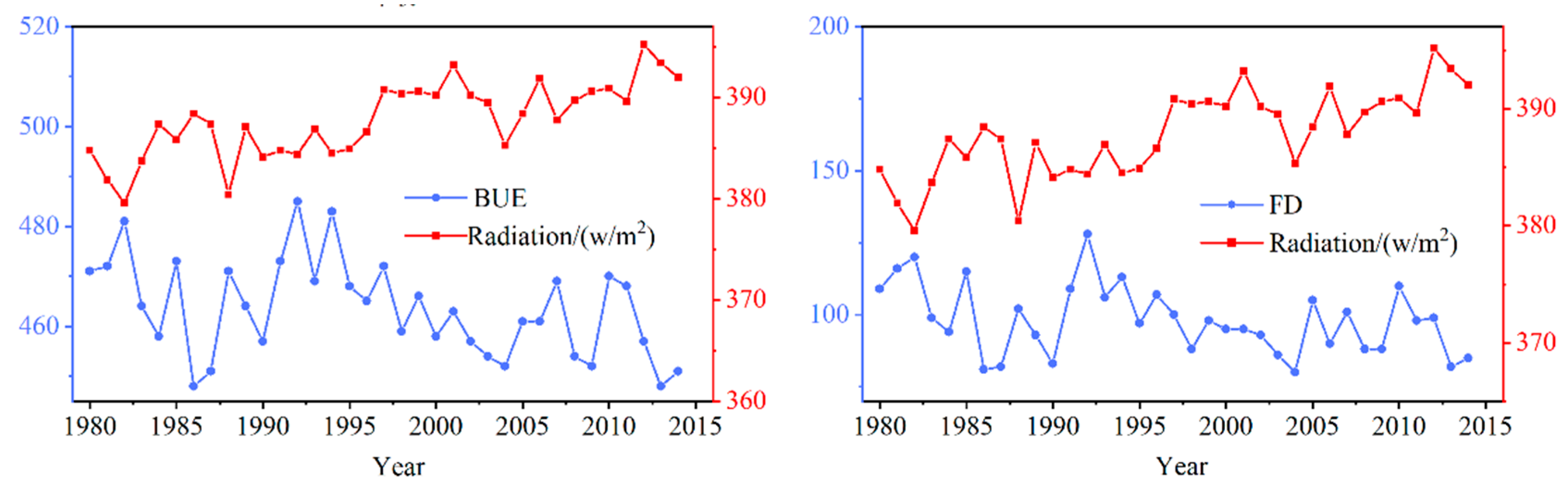
Radiation is one of the important climate variables affecting LIP. The results of this paper showed that only FUE and radiation (total of shortwave and longwave) were positively correlated, and the rest of the indicators were negatively correlated with radiation. With the lessening of solar radiation in autumn and winter, when the temperature was lower than 0 °C, ice crystals were generated in the lake, and broken ice gradually formed. When the water on the lake froze, the albedo of the ice (70%) was much larger than the albedo of the water (8%), which reduced the solar radiation and heat flux absorbed into the lake. In this case, it would intensify the further development of lake ice [49] In the same way, if the solar radiation were small, the ablation of lake ice would be inhibited by the lake ablation process, thereby delaying BUS and prolonging ICD. Of all the indicators, BUE and FD were the most sensitive to radiation changes, and their correlation coefficients with radiation were −0.56 and −0.49, respectively. As shown in Figure 12, the radiation values in winter show an upward trend. BUE and FD trends show an opposite state to radiation during the corresponding period, indicating that larger radiation values accelerate the melting of lake ice and shorten FD.
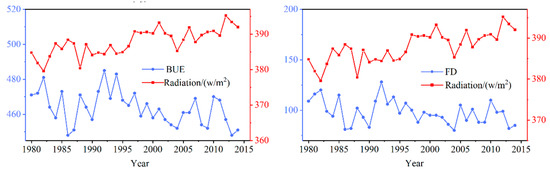
Figure 12.
Relationship between BUE and FD of Qinghai Lake and radiation from 1980 to 2018.
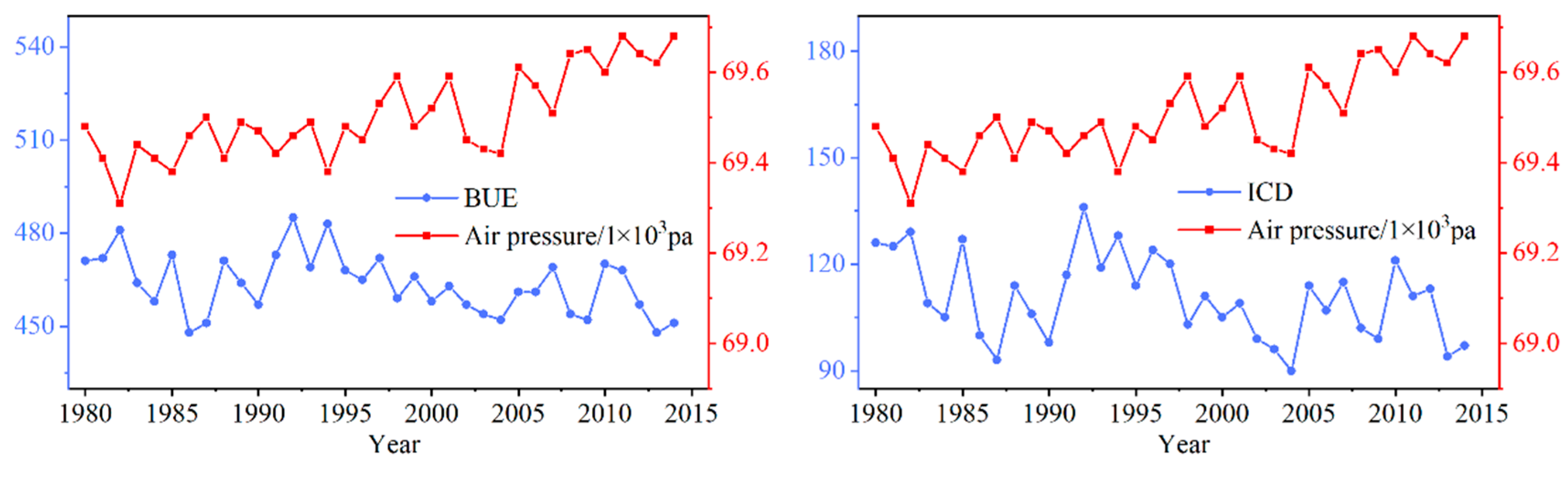
Air pressure also had a tremendous impact on lake ice conditions. Except for FUE, the indicators were negatively related to air pressure (Figure 10). This showed that high average pressure delays the freezing time of the lake. Furthermore, it promotes the melting of the ice layer during a thaw. This may be because of the higher the pressure, the lower the freezing point of the water, which delays the freezing time of the lake [43]. BUS, BUE, and FD were the most closely related to air pressure, which indicated that the melting time and FD of lakes were sensitive to changes in air pressure. In years with higher air pressure, later FUS and earlier BUS will decrease FD. As shown in Figure 13, the pressure increased significantly from 1980 to 2018, and the changing trend of BUE for Qinghai Lake was the opposite. Besides, the correlation between lake ICD and CFD and air pressure was not low, and their correlation coefficients were both -0.36, indicating that an increase in the air pressure shortened ICD and CFD (Figure 12). In the corresponding period, pressure and ICD showed an obvious opposite relationship.
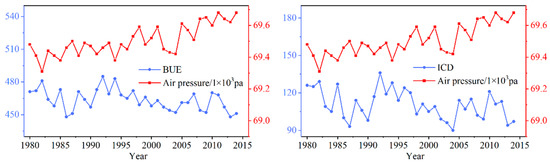
Figure 13.
Relationship between BUE and ICD of Qinghai Lake and air pressure from 1980 to 2018.
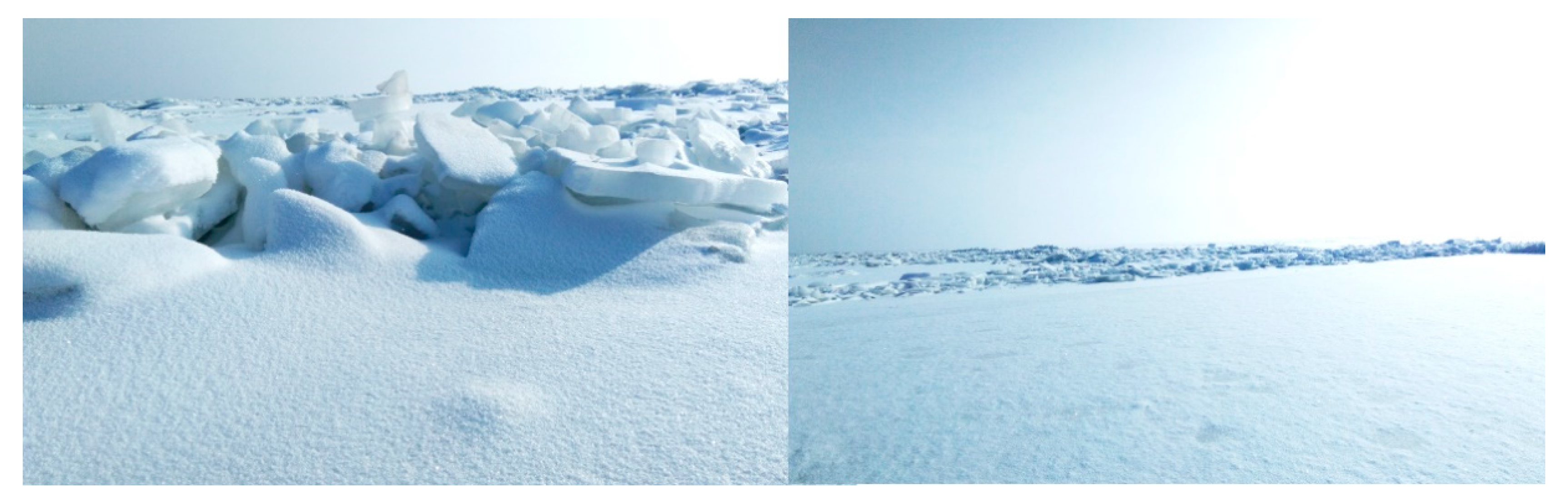
Wind speed was one of the factors affecting the freezing and thawing process of the lake. As shown in Figure 10, both FUS and FUE were negatively correlated with wind speed, and the remaining indicators were positively correlated with wind speed. In the early stage of lake ice formation, the greater the wind speed, the earlier Qinghai Lake froze, while in the early stage of lake ice melting, the greater the wind speed, the later the lake’s melting time. This is because, in the initial stage of the formation of lake ice, large wind speeds can accelerate air convection on the lake surface, bringing cold air to the lake surface, so that the heat dissipation intensity at the surface of the lake quickly reaches the freezing temperature, which accelerates the freezing process and delays the melting time [44]. However, sometimes larger wind speeds can also destroy thin ice, causing thinner ice on the lake surface to accumulate under the influence of wind during the initial freezing period, thereby extending the freezing time of the lake. As shown in Figure 14, the thin ice formed in the early stage under a high wind speed formed crushed ice and accumulated due to the wind (the wind was not the only reason for the accumulation of crushed ice).

Figure 14.
Crushed ice accumulated during the freeze in the north of Qinghai Lake.
Precipitation or snowfall also played a different role in freezing and thawing the lake. Precipitation/snowfall was positively correlated with the four dates of lake freezing and thawing, and negatively correlated with other indicators (Figure 10). Compared with BUS and BUE, the correlation between precipitation and FUS and FUE was higher. When the lake started to freeze, the surface water temperature continued to stay below 0 °C, that is, precipitation/snowfall at this time caused crystal nuclei to enter the water, in addition to cooling the water. These crystal nuclei were the basis of freezing, and the precipitation increased. As the number of crystal nuclei increased, the icing process accelerated [44,50]. Additionally, increased precipitation/snowfall also reduced the lake’s air temperature, making the freezing date earlier, and at the same time, precipitation/snowfall destroyed the formed lake ice and delayed the freezing time of the lake [51]. It was worth noting that precipitation/snowfall had a more significant blocking effect on lake ice than promoting effect. Precipitation/snowfall delays the melting of ice during the ablation of lakes, which may because precipitation/snowfall, on the one hand, reduces the temperature of the lake. On the other hand, in terms of the physical reasons for lake ice formation and elimination, snow accumulation in the lake ice area is an important factor affecting the energy balance of the ice layer. Lake area snow can slow the lake ice ablation process by reducing the heat exchange of ice and air and the luminous flux in and under the ice [3]. It can also affect the albedo through its thickness and snow surface characteristics, thereby determining the lake’s surface budget of solar radiation. We speculated that atmospheric suspended matter caused by precipitation/snowfall would also cause vertical differences in the optical properties of the ice layer, which would play a role in the freeze–thaw process of the lake. We need further research in the future.
5. Discussion and Expectation
To verify the accuracy of the lake ice area extracted by the threshold method of this study, we artificially interpreted the lake ice area of Qinghai Lake on 22 February 2014, using Landsat remote sensing images. At the same time, the threshold ice method was used to automatically extract the lake ice area on the same day, based on MOD09GQ surface reflectance daily data, and the error between the two was 0.8%. This showed that the threshold method used in this study to extract lake ice was reliable, and the results of MODIS extraction could be approximated to true values to verify the results based on AVHRR data extraction.
There were also inevitable problems with the data during the research process. Both MODIS and AVHRR data are affected by clouds, and the west bank of Qinghai Lake in particular was often shrouded in clouds. Therefore, the freeze–thaw dates of Qinghai Lake in some years could not be accurate to the daily scale during the automatic extraction of the lake ice area. Additionally, there was some crushed ice that was scattered by the wind during the freezing stage of the lake, and crushed ice that was not completely covered by the ice layer. These scattered ice distribution areas may be small and difficult to be identified by sensors, which increases the difficulty of identification. The presence of clouds and crushed ice will cause some errors in the results obtained from different data sources. Meteorological factors such as air temperature, solar radiation, humidity, and snowfall, as well as geographical factors such as lake shape and geographic location affect the changes in the phenological characteristics of lake ice. This study only discussed the correlation between climate variables and lake ice conditions, which limited further understanding of the influencing factors of lake ice phenological characteristics to a certain extent.
Lake ice is a sensitive indicator of regional climate change, and the current research was relatively incomplete. As the largest lake on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau in China, Qinghai Lake cannot meet the needs of comprehensive observations by relying only on data from surface observation stations. Free, long-term serial, and high spatiotemporal resolution remote sensing data play an important role in studying LIP response to climate change.
We can carry out further research in the following respects in the future based on the above deficiencies and the current research progress of LIP. (1) The existence of mixed pixels in remote sensing images limits the scope of application of data. In the future, mixed pixel processing can be used as a research direction to improve the data utilization rate; (2) In terms of extracting LIP characteristic data, we should introduce more datasets during different periods, use multiple methods, and comprehensively analyze the freeze–thaw status of lakes to improve the reliability of conclusions. In terms of LIP characteristics extraction methods, we can gradually achieve full quantitative monitoring in large regions. (3) The freezing and thawing process of lakes is closely related to the spatial distribution of lake ice thickness. In future research, the freezing and thawing process of lakes can be discussed in-depth in terms of the mechanism of ice layer generation and disappearance, and the factors affecting different freeze and thaw modes in Qinghai Lake can be studied. (4) In the context of climate warming, it is very important to use mathematical models to simulate the evolution of lake ice. At present, foreign countries have successfully simulated LIP and trends in North America from 2041 to 2071 based on energy transfer models (such as the MyLake model). As the “third pole” of the world, the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau has many lakes and is an outpost of climate change. Lake ice prediction models suitable for plateau areas should be developed to simulate future changes in lake ice conditions and provide evidence and references for climate change and basic research.
6. Conclusions
Qinghai Lake usually begins to freeze from mid-December to early January and is completely covered by ice at the end of December or early January. The complete ice layer will gradually melt away and disappear completely in early or mid-April. In the past 38 years, FD and CFD of Qinghai Lake averaged 96 d and 88 d, and ICD and AD averaged 109 d and 8 d. FUS and FUE were gradually delayed at a rate of 0.16 d/a and 0.19 d/a, respectively, with a total delay of 6.08 d and 7.22 d. BUS and BUE showed advancing trends by −0.36 d/a and −0.42 d/a, respectively, which shifted them earlier by 13.68 d and 15.96 d. Overall, ICD, FD, and CFD showed decreasing trends of −0.58 d/a, −0.60 d/a, and −0.52 d/a, respectively, and overall decreased by 22.04 d, 22.81 d, and 9.76 d between 1980 and 2018.
The spatial pattern in the freeze–thaw of Qinghai Lake can reflect the difference in lake water depth to a certain extent. When Qinghai Lake started to freeze, the northern part of the Lake began forming crushed ice first, and then gradually expanded from the waterfront to the center of the lake. When it began to melt, it usually started to ablate in the north and west of the lake area, and the ablation rate was fast. Therefore, the spatial pattern in the freeze–thaw of Qinghai Lake can be divided into two areas; the west of the lake area had similar spatial patterns for freezing and ablation, while in the east of the lake area, freezing and ablation patterns are opposite. Climate factors were closely related to LIP, especially AFDD from October to April of the following year. A smaller AFDD would correspond to delayed FUS, earlier BUS, and shorter ICD, CFD, and FD. The influence of radiation and air pressure on lake ice was also important. When the average radiation or atmospheric pressure was high in winter, which would lead to later FUS and earlier BUS. Additionally, wind speed and precipitation played different roles in the process of lake freezing and ablation, and FUS was more sensitive to changes in wind speed and precipitation.
Author Contributions
M.Q. delineated and analyzed fundamental data and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. S.L. and X.Y. supervised the study and edited the manuscript, they contributed equally to this work. F.X. and Y.G. provided material and technical support during the data processing process. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.41761144075 and Grant No. 41861013), the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (STEP) (Grant No. 2019QZKK0208), the Research Fund for Introducing Talents of Yunnan University (Grant No. YJRC3201702), the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Fund Project (Grant No. 41801052), was also supported by the Innovation Fund Designated for Graduate Students of Yunnan University (Grant No. 2019226).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Google Earth Engine Science team for the freely available cloud-computing platform, and We also would like to thank the CMFD used in this study was developed by the Data Assimilation and Modeling Center for Tibetan Multi-spheres, Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research of Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://westdc.westgis.ac.cn/). Other temperature data of the meteorological station was from the CMDSC (http://data.cma.cn/).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kropáček, J.; Maussion, F.; Chen, F.; Hoerz, S.; Hochschild, V. Analysis of ice phenology of lakes on the Tibetan Plateau from MODIS data. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GCOS-107. Systematic Observation Requirements for Satellite-Based Products for Climate; GCOS, WMO/TD; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Volume 1338, p. 103. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, L.C.; Duguay, C.R. The response and role of ice cover in lake-climate interactions. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2010, 34, 671–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenckner, T.; Jarvinen, M.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A. Atmospheric circulation and its impact on ice phenology in Scandinavia. Boreal Environ. Res. 2004, 9, 371–380. [Google Scholar]
- Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Livingstone, D.M.; Meili, M.; Jensen, O.; Benson, B.; Magnuson, J.J. Large geographical differences in the sensitivity of ice-covered lakes and rivers in the Northern Hemisphere to temperature changes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, J.R.; Kamenik, C. Validation of a chrysophyte stomatocyst-based cold-season climate reconstruction from high-alpine Lake Silvaplana Switzerland. J. Quat. Sci. 2011, 26, 268–275. [Google Scholar]
- Oreilly, C.; Sharma, S.; Gray, D.; Hampton, S.E. Rapid and highly variable warming of lake surface waters around the globe. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 42, 10773–10781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, J.J.; Roberton, D.M.; Benson, B.J.; Wynne, R.H.; Livingstone, D.M.; Arai, T.; Assel, R.A.; Barry, R.G.; Card, V.V.; Kuusisto, E.; et al. Historical trends in lake and river ice cover in the Northern Hemisphere. Science 2000, 289, 1743–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Kimball, J.S.; Duguay, C.; Kim, Y.; Watts, J.D. Satellite microwave assessment of Northern Hemisphere lake ice phenology from 2002 to 2015. Cryosphere 2017, 11, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.Q.; Tao, A.Q.; Jin, X. Variability in the ice phenology of Nam Co Lake in central Tibet from scanning multichannel microwave radiometer and special sensor microwave/imager: 1978 to 2013. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2013, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, P.; Ye, Q.h.; Wei, Q.F. Lake ice change at the Namco Lake on the Tibetan Plateau during 2000–2013 and influencing factors. Prog. Geogr. 2015, 34, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.J.; Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Sun, M.P.; Li, J. Spatial-temporal variations of lake ice in the Hoh Xil region from 2000 to 2011. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.F.; Ye, Q.H. Review of lake ice monitoring by remote sensing. Prog. Geog. 2010, 29, 803–810. [Google Scholar]
- Rouse, W.R.; Oswald, C.J.; Binyamin, J.; Spence, C.; Schertzer, W.H.; Blanken, P.D.; Bussières, N.; Duguay, C.R. The role of northern lakes in a regional energy balance. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugaste, R.; Haberman, J.; Blank, K. Cool winters versus mild winters: Effects on spring plankton in Lake Peipsi. Est. J. Ecol. 2010, 59, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenlaub, V.L. Lake effect snowfall to the lee of the great lakes: Its role in Michigan. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1970, 51, 403–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifovic, R.; Pouliot, D. Analysis of climate change impacts on LIP in Canada using the historical satellite data record. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Duguay, C.R.; Clausi, D.A. Semi-automated classification of Lake Ice Cover using dual polarization RADARSAT-2 imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom, M.; Aguilar, R.; Imhof, P.; Leinss, S.; Baltsavias, E.; Schindler, K. Lake Ice Detection from Sentinel-1 SAR with Deep Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.07040. [Google Scholar]
- Tom, M.; Kälin, U.; Sütterlin, M.; Baltsavias, E.; Schindler, K. Lake ice detection in low-resolution optical satellite images. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inform. Sci. 2018, IV, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalia, Z.; Anton, K.; Stefan, M.; Stein, S.; Mohamed, B. Operational algorithm for ice–water classification on dual-polarized RADARSAT-2 images. Cryosphere 2017, 11, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra, M.; Jiang, M.; Clausi, D.A.; Duguay, D. Lake Ice-Water Classification of RADARSAT-2 Images by Integrating IRGS Segmentation with Pixel-Based Random Forest Labeling. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engram, M.; Anthony, K.W.; Meyer, F.J.; Grosse, G. Characterization of L-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR) backscatter from floating and grounded thermokarst lake ice in Arctic Alaska. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.B.; Huang, H.J.; Su, Q.; Yan, L.W.; Liu, Y.X.; Xu, X.L. An Arctic sea ice thickness variability revealed from satellite altimetric measurements. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2014, 33, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, S.E.; Brown, L.C.; Kang, K.K.; Duguay, C.R. Variability in ice phenology on Great Bear Lake and Great Slave Lake, Northwest Territories, Canada, from SeaWinds/QuickSCAT: 2000–2006. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 816–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, D.; Rouzbeh, N.; Peter, R.; Key, G.R. Development of a Mid-Infrared Sea and Lake Ice Index (MISI) using the GOES imager. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 1015. [Google Scholar]
- Dibike, Y.; Prowse, T.; Bonsal, B.; Rham, D.L.; Saloranta, T. Simulation of North American lake-ice cover characteristics under contemporary and future climate conditions. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 32, 695–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.H.; Shi, Y.F. Impact of climate change on the water regime of Qinghai Lake—Ⅰ. Analysis of the past 30 years. Sci. Sin. 1992, 22, 537–542. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.M.; Song, Y.G. Shrinkage history of Lake Qinghai and causes during the last 52 years. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Water Resource & Environmental Protection (ISWREP), Xi’an, China, 20–22 May 2011; pp. 446–449. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.M.; Han, B.; Wang, L.L.; Fu, X.Y. Analysis on the Correlation Between Total Phosphorus, Water Temperature, Mineralization and Chlorophyll-a in Qinghai Lake, China. J. Agr. Environ. Sci. 2013, 32, 333–337. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, M.M.; Yao, X.J.; Li, X.F.; Duan, H.Y.; Gao, Y.P.; Liu, J. Spatial-temporal characteristics of ice phenology of Qinghai Lake from 2000 to 2016. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Z.; Wang, G.Y.; Li, W.J.; Zeng, Q.Z.; Jin, D.H.; Wang, L.H. Lake ice and its remote sensing monitoring in the Tibetan Plateau. J. Glac. Geocryol. 1995, 17, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Mutanga, O.; Kumar, L. Google Earth Engine Applications. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcfeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Wolfe, R. MOD09GQ MODIS/Terra Surface Reflectance Daily L2G Global 250 m SIN Grid V006 [Data Set]. NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC. 2015. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5067/MODIS/MOD09GQ.006 (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- Tao, A.Q. Research on the Variation of Namco Lake ice by Passive Microwave Remote Sensing. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q.J.; Yang, Y.L. Remote sensing monitoring of Qinghai Lake based on EOS/MODIS data. J. Lake Sci. 2005, 17, 356–360. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, B.; Budde, M.; Spencer, P.; Eiller, A.E. Integration of MODIS-derived metrics to assess interannual variability in snowpack, lake ice, and NDVI in southwest Alaska. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ke, C.Q.; Duan, Z. Monitoring ice variations in Qinghai Lake from 1979 to 2016 using passive microwave remote sensing data. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrian, R.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Zagarese, H.; Baines, S.B.; Hessen, D.O.; Keller, W.; Livingstone, D.M.; Sommaruga, R.; Straile, D.; Donk, E.V.; et al. Lakes as sentinels of climate change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, S.E.; Vavrus, S.J.; Foley, J.A.; Fisher, V.A.; Wynne, R.H.; Lenters, J.D. Global patterns of lake ice phenology and climate: Model simulations and observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 28825–28837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, B.J.; Magnuson, J.J.; Jensen, O.P.; Card, V.M.; Hodgkins, G.; Korhonen, J.; Livingstone, D.M.; Stewart, K.M.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Granin, N.G. Extreme events, trends, and variability in Northern Hemisphere lake-ice phenology (1855–2005). Clim. Chang. 2012, 112, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.N.; Wu, Y.H.; Zheng, H.X.; Zhang, B. Uncertainty and variation of remotely sensed lake cie phenology across the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1534–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R.B.; Li, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Chen, Y.F. Comparisons of thermodynamic processes between lake ice and landfast sea ice around Zhongshan Station, East Antarctica. Chin. J. Pol. Res. 2011, 23, 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, H.; Riffler, M.; Nõges, T.; Wunderle, S. Lake ice phenology from AVHRR data for European lakes: An automated two-step extraction method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, A.M.; Xiao, Z.X.; Wu, G.X. Characteristics of climate change over the Tibetan Plateau under the global warming during 1979–2014. Clim. Chang. Res. 2016, 12, 374–381. [Google Scholar]
- Krakow, B.D. Introduction to Lake Science, 1st ed.; The Commercial Press: Beijing, China, 1963; pp. 315–360. [Google Scholar]
- Beyene, M.T.; Jain, S. Freezing degree-day thresholds and Lake ice-out dates: Understanding the role of El Niño conditions. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 4335–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.H. Introduction to Cryospheric Science, 1st ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 114–115. [Google Scholar]
- Oveisy, A.; Boegman, L.; Imberger, J. One-dimensional simulation of lake and ice dynamics during winter. J. Limnol. 2014, 73, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolerski, T.; Shen, H.T. Possible effects of the 1984 St. Clair River ice jam on bed changes. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2015, 42, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).