Exploiting High-Resolution Remote Sensing Soil Moisture to Estimate Irrigation Water Amounts over a Mediterranean Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Remote Sensing Data
3.2. Meteorological Data
3.3. Benchmark Irrigation Volumes
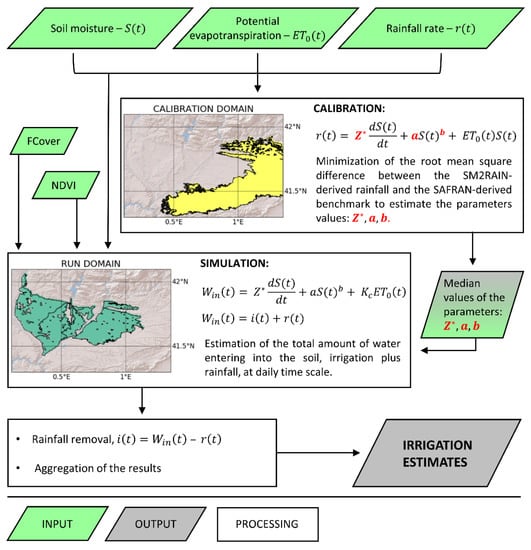
3.4. The SM2RAIN Algorithm
3.4.1. Calibration
3.4.2. Irrigation Estimates
3.4.3. Assessment of the Parameters Uncertainty
3.5. Remote Sensing and Meteorological Data Preparation
4. Results
4.1. Experiment with SMAP at 1 km Soil Moisture
4.1.1. Irrigation Estimates
4.1.2. Estimate of the Model Parameters Uncertainty
4.2. Experiment with SMOS at 1 km Soil Moisture
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- the proposed method is able to quantitatively estimate the irrigation that actually occurred over the study area, at least for four of the five irrigation districts considered;
- the method proved to be suitable not only to estimate the long-term irrigation magnitudes, but also to represent the spatial distribution and the timing of irrigation events;
- over semi-arid regions, the evapotranspiration process plays the leading role in determining the total amount of water entering into the soil according to the SM2RAIN equation if compared to the direct contribution of soil moisture, which, however, plays additional indirect roles;
- the method presented in this study is less sensitive to the SM2RAIN parameters , , and when irrigation mainly occurs. Conversely, uncertainties linked to the p parameter are at maximum during the highest irrigation intensity periods;
- the comparable performances of the DISPATCH downscaled SMAP and SMOS data sets in detecting the irrigation signal over the pilot area ensure the reliability of the extension back to 2011, thus allowing the quantitative estimation of irrigation for a 7 year period.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbot, B.W.; Bishop, K.; Zarnetske, J.P.; Minaudo, C.; Chapin, F.S., III; Krause, S.; Hannah, D.M.; Conner, L.; Ellison, D.; Godsey, S.E.; et al. Human domination of the global water cycle absent from depictions and perceptions. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Rosegrant, M.W. Global Water Demand and Supply Projections: Part 1. A Modeling Approach. Water Int. 2002, 27, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; Ramankutty, N.; Brauman, K.A.; Cassidy, E.S.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Nathaniel, D.M.; O’Connell, C.; Ray, D.K.; West, P.C.; et al. Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature 2011, 478, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Green, P.; Salisbury, J.; Lammers, R.B. Global water resources vulnerability from climate change and population growth. Science 2000, 289, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rockström, J.; Falkenmark, M.; Lannerstad, M.; Karlberg, L. The planetary water drama: Dual task of feeding humanity and curbing climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L15401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummu, M.; Guillaume, J.; De Moel, H.; Eisner, S.; Flörke, M.; Porkka, M.; Siebert, S.; Veldkamp, T.; Ward, P. The world’s road to water scarcity: Shortage and stress in the 20th century and pathways towards sustainability. Sci. Rep. UK 2016, 6, 38495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kharrou, M.; Page, M.L.; Chehbouni, A.; Simonneaux, V.; Er-Raki, S.; Jarlan, L.; Ouzine, L.; Khabba, S.; Chehbouni, G. Assessment of Equity and Adequacy of Water Delivery in Irrigation Systems Using Remote Sensing-Based Indicators in Semi-Arid Region, Morocco. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 4697–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalasmeh, A.A.; Gharaibeh, M.A.; Alghzawi, M.Z.; Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C.; Ghezzehei, T.A.; Flammini, A. Using wastewater in irrigation: The effects on infiltration process in a clayey soil. Water 2020, 12, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Döll, P.; Siebert, S. Global modelling of irrigation water requirements. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 81–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Wisser, D.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Global modelling of withdrawal, allocation and consumptive use of surface water and groundwater resources. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2014, 5, 15–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Moramarco, T.; Hahn, S.; Hasenauer, S.; Kidd, R.; Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W.; Levizzani, V. Soil as a natural rain gauge: Estimating global rainfall from satellite soil moisture data. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 5128–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Tarpanelli, A.; Filippucci, P.; Dorigo, W.; Zaussinger, F.; Gruber, A.; Fernández-Prieto, D. How much water is used for irrigation? A new approach exploiting coarse resolution satellite soil moisture products. Int. J. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilvand, E.; Tairishy, M.; Hashemi, S.A.G.; Brocca, L. Quantification of irrigation water using remote sensing of soil moisture in a semi-arid region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippucci, P.; Tarpanelli, A.; Massari, C.; Serafini, A.; Strati, V.; Alberi, M.; Raptis, K.G.C.; Mantovani, F.; Brocca, L. Soil moisture as a potential variable for tracking and quantifying irrigation: A case study with proximal gamma-ray spectroscopy data. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 136, 103502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaussinger, F.; Dorigo, W.; Gruber, A.; Tarpanelli, A.; Filippucci, P.; Brocca, L. Estimating irrigation water use over the contiguos United States by combining satellite and reanalysis soil moisture data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 897–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zohaib, M.; Choi, M. Satellite-based global-scale irrigation water use and its contemporary trends. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaguera, M.; Krol, M.; Salama, M.; Su, Z.; Hoekstra, A. Application of a remote sensing method for estimating monthly blue water evapotranspiration in irrigated agriculture. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10033–10050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peña-Arancibia, J.L.; Mainuddin, M.; Kirby, J.M.; Chiew, F.H.S.; McVicar, T.R.; Vaze, J. Assessing irrigated agriculture’s surface water and groundwater consumption by combining satellite remote sensing and hydrologic modelling. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, M.J.; Quintana-Seguí, P. Comparison of remote sensing and simulated soil moisture datasets in Mediterranean landscapes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fontanet, M.; Fernàndez-Garcia, D.; Ferrer, F. The value of satellite remote sensing soil moisture data and the DISPATCH algorithm in irrigation fields. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 5889–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Q.; Zribi, M.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Baghdadi, N.; Quintana-Seguí, P. Irrigation mapping using Sentinel-1 time series at field scale. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazzi, H.; Baghdadi, N.; Ienco, D.; El Hajj, M.; Zribi, M.; Belhouchette, H.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Demarez, V. Mapping Irrigated Areas Using Sentinel-1 Time Series in Catalonia, Spain. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dari, J.; Quintana-Seguí, P.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Stefan, V.; Brocca, L.; Morbidelli, R. Detecting and mapping irrigated areas in a Mediterranean environment using remote sensing soil moisture and a land surface model. Remote Sens. Environ. in press.
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Requirements, Irrigation and Drainage Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Merlin, O.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Mayoral, M.A.; Hagolle, O.; Al Bitar, A.; Kerr, Y. Self-calibrated evaporation-based disaggregationof SMOS soil moisture: An evaluation study at 3 km and 100 m resolution in Catalunya, Spain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Martinuzzi, J.M.; Font, J.; Berger, M. Soil moisture retrieval from space: The Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Richaume, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Mahmoodi, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Cabot, F.; Gruhier, C.; Juglea, S.E.; et al. The SMOS soil moisture retrieval algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1384–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Nioku, E.G.; Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J.; et al. The soil moisture activa passive (SMAP) mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliander, A.; Jackson, T.J.; Bindlish, R.; Chan, S.; Das, N.; Kim, S.B.; Cosh, M.H.; Dunbar, R.S.; Dang, L.; Pashaian, L.; et al. Validation of SMAP surface soil moisture products with core validation sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.N.; Entekhabi, D.; Dunbar, R.S.; Chaubell, M.J.; Colliander, A.; Yueh, S.; Jagdhuber, T.; Chen, F.; Crow, W.; O’Neill, P.E.; et al. The SMAP and Copernicus Sentinel 1A/B microwave active-passive high resolution surface soil moisture product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, O.; Walker, J.P.; Chehbouni, A.; Kerr, Y. Towards deterministic downscaling of SMOS soil moisture using MODIS derived soil evaporative efficiency. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3935–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, J.; Loew, A.; Merlin, O.; Verhoest, N.E.C. A review of spatial downscaling of satellite remotely sensed soil moisture. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 341–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, O.; Rüdiger, C.; Al Bitar, A.; Richaume, P.; Walker, J.; Kerr, Y. Disaggregation of SMOS soil moisture in Southeastern Australia. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1556–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merlin, O.; Chehbouni, A.; Walker, J.P.; Panciera, R.; Kerr, Y.H. A simple method to disaggregate passive microwave-based soil moisture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djamai, N.; Magagi, R.; Goita, K.; Merlin, O.; Kerr, Y.; Walker, A. Disaggregation of SMOS soil moisture over the Canadian Prairies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djamai, N.; Magagi, R.; Goita, K.; Merlin, O.; Kerr, Y.; Walker, A.; Roy, A. A combination of DISPATCH downscaling algorithm with CLASS land surface scheme for soil moisture estimation at fine scale during cloudy days. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbéteau, Y.; Merlin, O.; Molero, B.; Rüdiger, C.; Bacon, S. DisPATCh as a tool to evaluate coarse.scale remotely sensed soil moisture using localized in situ measurements: Application to SMOS and AMSR.E data in Southeastern Australia. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 45, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molero, B.; Merlin, O.; Malbéteau, Y.; Al Bitar, A.; Cabot, F.; Stefan, V.; Kerr, Y.; Bacon, S.; Cosh, M.H.; Bindlish, R.; et al. SMOS disaggregated soil moisture product at 1 km resolution: Processor overview and first validation results. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierckx, W.; Sterckx, S.; Benhadj, I.; Livens, S.; Duhoux, G.; Van Achteren, T.; Francois, M.; Mellab, K.; Saint, G. PROBA-V mission for global vegetation monitoring: Standard products and image quality. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 2589–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterckx, S.; Benhadj, I.; Duhoux, G.; Livens, S.; Dierckx, W.; Goor, E.; Adriaensen, S.; Heyns, W.; Van Hoof, K.; Strackx, G.; et al. The PROBA-V mission: Image processing and calibration. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 2565–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, Y.; Brun, E.; Merindol, L.; Guyomarc’h, G.; Lesaffre, B.; Martin, E. A meteorological estimation of relevant parameters for snow models. Ann. Glaciol. 1993, 18, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quintana-Seguí, P. SAFRAN analysis over Spain. ESPRI/IPSL 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana-Seguí, P.; Turco, M.; Herrera, S.; Miguez-Macho, G. Validation of a new SAFRAN-based gridded precipitation product for Spain and comparisons to Spain02 and ERA-Interim. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 2187–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quintana-Seguí, P.; Le Moigne, P.; Durand, Y.; Martin, E.; Habets, F.; Baillon, M.; Canellas, C.; Franchisteguy, L.; Morel, S. The SAFRAN atmospheric analysis: Description and validation. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.P.; Martin, E.; Franchistéguy, L.; Baillon, M.; Soubeyroux, J.M. A 50-year high-resolution atmospheric reanalysis over France with the Safran system. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 1627–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hersbach, H.; Dee, D. ERA-5 reanalysis is in production. In ECMWF Newsletter; Spring: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 147, p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Ll, C.; Barragán, J.; Montserrat, J. Evaluación del riego por tablares en la colectividad de Linyola Canal de Urgell (Lleida). Riegos y Drenayes 1991, 50, 24–48. [Google Scholar]
- Cots, L.; Montserrat, J.; Borrás, E.; Barragán, J. Evaluación del uso del agua en la zona de “Les Planes” (430 ha) del término municipal de Arbeca (Colectividad n. 13 de los Canales de Urgell, Lleida). In Proceedings of the XI Jornadas Técnicas sobre Riegos, Valladolid, Spain, 2–4 June 1993; pp. 178–185. [Google Scholar]
- Maté, L.; Cruz, J.; Cruz, L.M. Evaluación de la Eficiencia de un Polígono de Riego en la Zona del Canal de Aragón y Cataluña y Estimación del Ahorro Potencial de Agua de Riego Debido a la Aplicación de la Técnica de Refino Láser y al Aumento del Módulo de Agua Disponible; Centro de Estudios y Experimentación de Obras Públicas: Madrid, Spain, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Brocca, L.; Massari, C.; Ciabatta, L.; Moramarco, T.; Penna, D.; Zuecco, G.; Pianezzola, L.; Borga, M.; Matgen, P.; Martínez-Fernández, J. Rainfall estimation from in situ soil moisture observations at several sites in Europe: An evaluation of SM2RAIN algorithm. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2015, 63, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brocca, L.; Pellarin, T.; Crow, W.T.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Ryu, D.; Su, C.-H.; Rudiger, C.; Kerr, Y. Rainfall estimation by inverting SMOS soil moisture estimates: A comparison of different methods over Australia. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 12062–12079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penman, H.L. Natural evaporation from open water, bare soil, and grass. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1948, 193, 120–146. [Google Scholar]
- Monteith, J.L. Evaporation and environment. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol 1965, 19, 205–233. [Google Scholar]
- Simonneaux, V.; Duchemin, B.; Helson, D.; Er-Raki, S.; Olioso, A.; Chehboun, A.G. The use of high-resolution image time series for crop classification and evapotranspiration estimate over an irrigated area in central Morocco. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ray, S.S.; Dadhwal, V.K. Estimation of crop evapotranspiration of irrigation command area using remote sensing and GIS. Agric. Water Manag. 2001, 49, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calera-Belmonte, A.; Jochu, A.; Cuesta Garcia, A.; Montoro ROdriguez, A.; Lopez Fuster, P. Irrigation management from space: Towards user-friendly products. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2005, 19, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchemin, B.; Hadria, R.; Er-Raki, S.; Boulet, G.; Maisongrande, P.; Chehbouni, A.; Escadafal, R.; Ezzahar, J.; Hoedjes, J.; Karroui, H.; et al. Monitoring wheat phenology and irrigation in center of Morocco: On the use of relationship between evapotranspiration, crops coefficients, leaf area index and remotely sensed vegetation indices. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 79, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er-Raki, S.; Chehbouni, A.; Guemouria, N.; Duchemin, B.; Ezzahar, J.; Hadria, R. Combining FAO-56 model and ground-based remote sensing to estimate water consumptions of wheat crops in a semi-arid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 87, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toureiro, C.; Serralheiro, R.; Shahidian, S.; Sousa, A. Irrigation management with remote sensing: Evaluating irrigation requirements for maize under Mediterranean climate condition. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 184, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajj, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Zribi, M.; Rodríguez-Fernández, N.; Wigneron, J.P.; Al-Yaari, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Albergel, C.; Calvet, J.C. Evaluation of SMOS, SMAP, ASCAT and Sentinel-1 Soil Moisture Products at Sites in Southwestern France. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

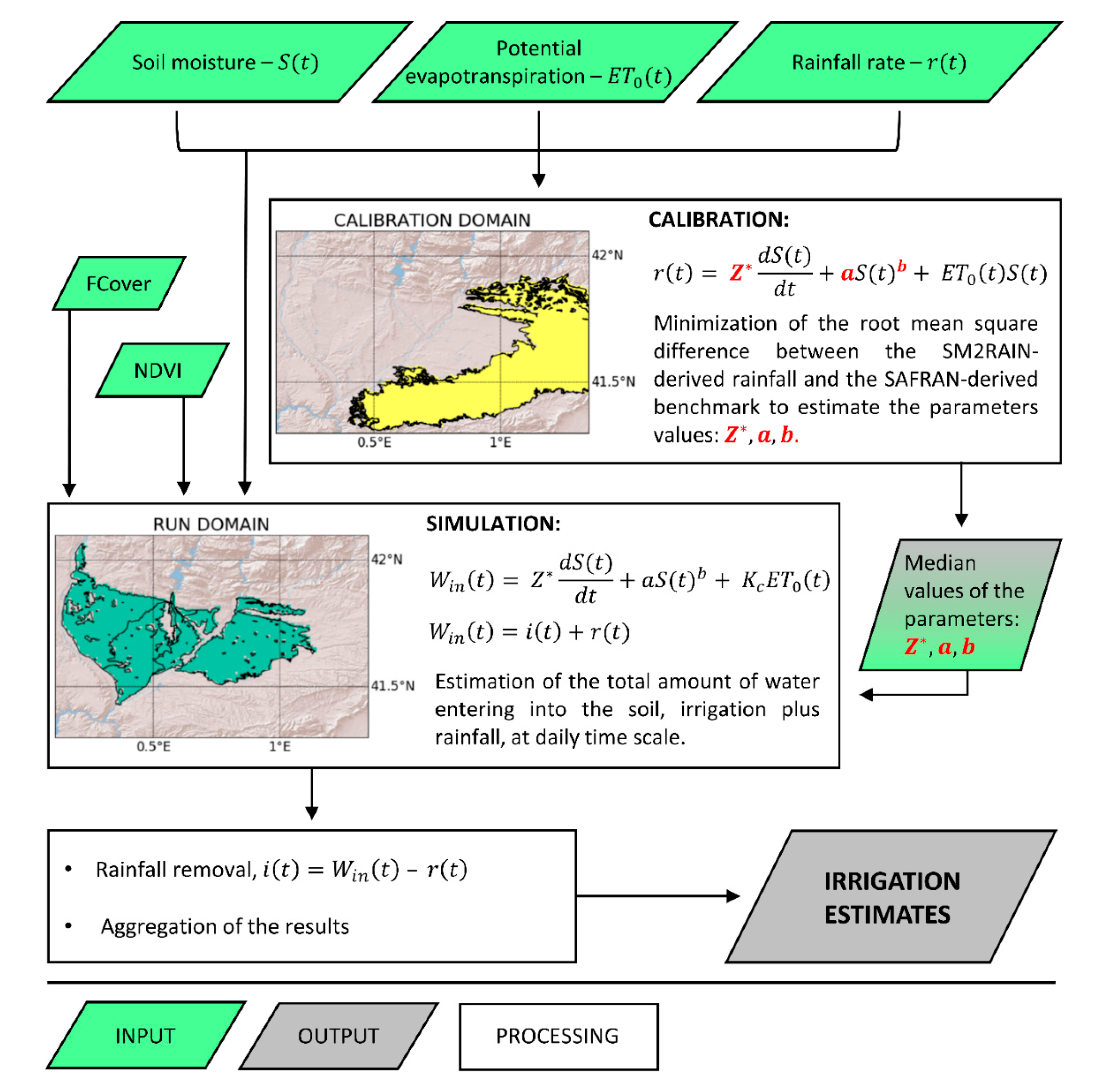







| District | Area [km2] | Irrigation Benchmark Source | Losses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urgell | 811.67 | Ebro Hydrological Plan/Water flowing through the irrigation canals (SAIH Ebro, stations C116 and C117) | 30% |
| Catalan and Aragonese—North | 657.04 | Water flowing through the irrigation canals (SAIH Ebro, station C081) | 15% |
| Catalan and Aragonese—South | 504.48 | Water flowing through the irrigation canals (SAIH Ebro, station C101) | 15% |
| Algerri Balaguer | 70.79 | Water pumped to the district (SAIH Ebro, station E271) | 10% |
| Pinyana | 149.74 | Data furnished by the canal’s technical office | 30% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dari, J.; Brocca, L.; Quintana-Seguí, P.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Stefan, V.; Morbidelli, R. Exploiting High-Resolution Remote Sensing Soil Moisture to Estimate Irrigation Water Amounts over a Mediterranean Region. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162593
Dari J, Brocca L, Quintana-Seguí P, Escorihuela MJ, Stefan V, Morbidelli R. Exploiting High-Resolution Remote Sensing Soil Moisture to Estimate Irrigation Water Amounts over a Mediterranean Region. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(16):2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162593
Chicago/Turabian StyleDari, Jacopo, Luca Brocca, Pere Quintana-Seguí, María José Escorihuela, Vivien Stefan, and Renato Morbidelli. 2020. "Exploiting High-Resolution Remote Sensing Soil Moisture to Estimate Irrigation Water Amounts over a Mediterranean Region" Remote Sensing 12, no. 16: 2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162593
APA StyleDari, J., Brocca, L., Quintana-Seguí, P., Escorihuela, M. J., Stefan, V., & Morbidelli, R. (2020). Exploiting High-Resolution Remote Sensing Soil Moisture to Estimate Irrigation Water Amounts over a Mediterranean Region. Remote Sensing, 12(16), 2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162593