Estimating PM2.5 Concentrations Using Spatially Local Xgboost Based on Full-Covered SARA AOD at the Urban Scale
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Ground-Level PM2.5 Measurements
2.2.2. Satellite-Based AOD
2.2.3. Meteorological Data
2.2.4. Geographical Data
2.2.5. Data Preparation
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) Regression
2.3.2. Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR)
2.3.3. Spatially Local XGBoost (SL-XGB)
2.3.4. Model Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. PM2.5 and AOD Data Set Description
3.2. Missing AOD Filling
3.3. PM2.5 Estimation Model Performance
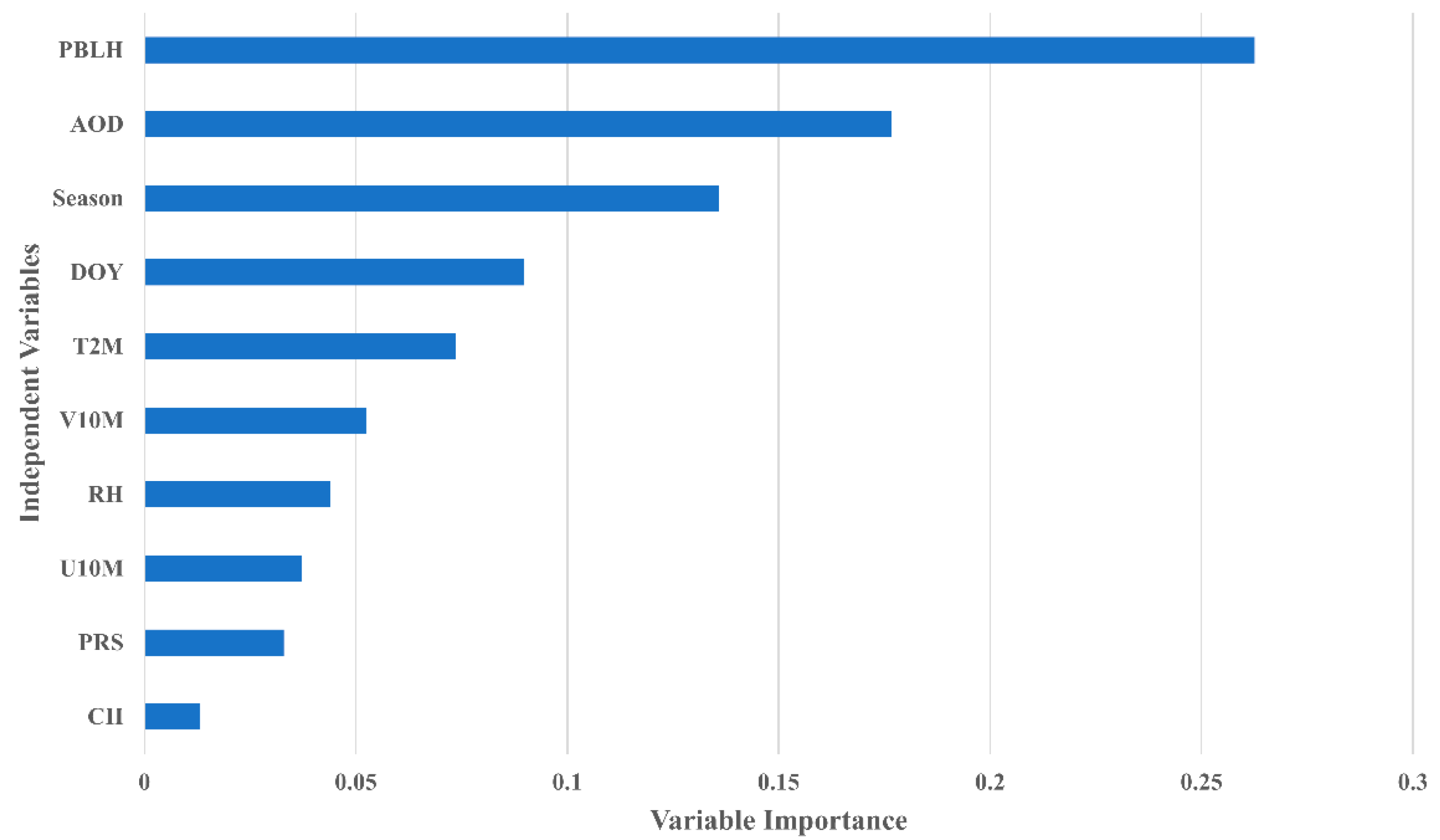
3.4. Variable Importance in SL-XGB
3.5. Seasonal and Annual PM2.5 Distribution
3.6. The Effect of the AOD Gap-Fill Process on PM2.5 Estimation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anenberg, S.C.; Horowitz, L.W.; Tong, D.Q.; West, J.J. An estimate of the global burden of anthropogenic ozone and fine particulate matter on premature human mortality using atmospheric modeling. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzati, M.; Lopez, A.D.; Rodgers, A.A.; Murray, C.J. Comparative Quantification of Health Risks: Global and Regional Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risk Factors; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; pp. 1353–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, M.; Millard, K.; Laurin, E. Big geospatial data analysis for Canada’s Air Pollutant Emissions Inventory (APEI): Using google earth engine to estimate particulate matter from exposed mine disturbance areas. Giscience Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, R.D.; Sanjay, R.; Arden, P.C.; Brook, J.R.; Aruni, B.; Diez-Roux, A.V.; Fernando, H.; Yuling, H.; Luepker, R.V.; Mittleman, M.A. Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease: An update to the scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 121, 2331–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arden, P.C.; Burnett, R.T.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Daniel, K.; Kazuhiko, I.; Thurston, G.D. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Francesca, D.; Peng, R.D.; Bell, M.L.; Luu, P.; Aidan, M.D.; Zeger, S.L.; Samet, J.M. Fine particulate air pollution and hospital admission for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. JAMA J. Am. Med Assoc. 2006, 295, 1127. [Google Scholar]
- Forouzanfar, M.H.; Afshin, A.; Alexander, L.T.; Anderson, H.R.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Biryukov, S.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Cercy, K.; Charlson, F.J. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1659–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lelieveld, J.; Evans, J.S.; Fnais, M.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chafe, Z.A.; Brauer, M.; Klimont, Z.; Van Dingenen, R.; Mehta, S.; Rao, S.; Riahi, K.; Dentener, F.; Smith, K.R. Household cooking with solid fuels contributes to ambient PM2.5 air pollution and the burden of disease. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, J.N.; Ma, G.X.; Zhang, Y.S. China tackles the health effects of air pollution. Lancet 2013, 382, 1959–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Li, L. Impact of urbanization level on urban air quality: A case of fine particles (PM2.5) in Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 194, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Wei, J.; Duan, D.; Guo, Y.; Yang, D.; Jia, C.; Mi, X. Impact of Land-Use and Land-Cover Change on urban air quality in representative cities of China. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2016, 142, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Huang, W.; Li, Z.; Xue, W.; Peng, Y.; Sun, L.; Cribb, M. Estimating 1-km-resolution PM2.5 concentrations across China using the space-time random forest approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel-Cox, J.A.; Holloman, C.H.; Coutant, B.W.; Hoff, R.M. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of MODIS satellite sensor data for regional and urban scale air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2495–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.P.; Zhang, X.Y.; Che, H.Z.; Gong, S.L.; An, X.; Cao, C.X.; Guang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.C. Correlation between PM concentrations and aerosol optical depth in eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5876–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Lau, A.K.; Li, C.; Fung, J.C. Using satellite remote sensing data to estimate the high-resolution distribution of ground-level PM2.5. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, M.; Holloway, T.; Choi, S.; O’Neill, S.M.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Jin, X.; Fiore, A.M.; Henze, D.K. Methods, availability, and applications of PM2.5 exposure estimates derived from ground measurements, satellite, and atmospheric models. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2019, 69, 1391–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Lee, J.; Im, J.; Song, C.K.; Choi, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Park, R.; Kim, S.M.; Yoon, J. Estimation of spatially continuous daytime particulate matter concentrations under all sky conditions through the synergistic use of satellite-based AOD and numerical models. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Waller, L.A.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Crosson, W.L.; Estes Jr, M.G.; Estes, S.M.; Quattrochi, D.A.; Sarnat, J.A.; Liu, Y. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in the southeastern US using geographically weighted regression. Environ. Res. 2013, 121, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zeng, C.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, L. Point-surface fusion of station measurements and satellite observations for mapping PM2.5 distribution in China: Methods and assessment. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 152, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, W.; Jia, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y. A satellite-based geographically weighted regression model for regional PM2.5 estimation over the Pearl River Delta region in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Mao, F.; Du, L.; Pan, Z.; Gong, W.; Fang, S. Deriving hourly PM2.5 concentrations from himawari-8 aods over beijing–tianjin–hebei in China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, Z.; Gong, W.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, K.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Mao, F.; Shen, H.; Li, Z. Estimation of ultrahigh resolution PM2.5 concentrations in urban areas using 160 m Gaofen-1 AOD retrievals. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bilal, M.; Dong, W. Mapping daily PM2.5 at 500 m resolution over Beijing with improved hazy day performance. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.; Wu, J.; Li, W.; Peng, J. Estimating Daily PM2.5 Concentrations in Beijing Using 750-M VIIRS IP AOD Retrievals and a Nested Spatiotemporal Statistical Model. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.; Di Girolamo, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Statistical evaluation of the feasibility of satellite-retrieved cloud parameters as indicators of PM2.5 levels. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unnithan, S.K.; Gnanappazham, L. Spatiotemporal mixed effects modeling for the estimation of PM2.5 from MODIS AOD over the Indian subcontinent. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloog, I.; Koutrakis, P.; Coull, B.A.; Lee, H.J.; Schwartz, J. Assessing temporally and spatially resolved PM2.5 exposures for epidemiological studies using satellite aerosol optical depth measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6267–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chang, H.H.; Meng, X.; Geng, G.; Lyapustin, A.; Liu, Y. Full-coverage high-resolution daily PM2.5 estimation using MAIAC AOD in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Di, B.; Luo, Y.; Deng, X.; Grieneisen, M.L.; Wang, Z.; Yao, G.; Zhan, Y. A nonparametric approach to filling gaps in satellite-retrieved aerosol optical depth for estimating ambient PM2.5 levels. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ban, J.; Chen, N.X.; Li, T. High-resolution daily AOD estimated to full coverage using the random forest model approach in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 203, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.A.; Kaufman, Y.; Zibordi, G.; Chern, J.; Mao, J.; Li, C.; Holben, B. Global monitoring of air pollution over land from the Earth Observing System-Terra Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Christopher, S.A. Particulate matter air quality assessment using integrated surface, satellite, and meteorological products: Multiple regression approach. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Spurr, R.J.; Burnett, R.T. High-resolution satellite-derived PM2.5 from optimal estimation and geographically weighted regression over North America. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10482–10491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, W.; Zang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, W. National-scale estimates of ground-level PM2.5 concentration in China using geographically weighted regression based on 3 km resolution MODIS AOD. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Q.; Chang, H.H.; Geng, G.; Liu, Y. An ensemble machine-learning model to predict historical PM2.5 concentrations in China from satellite data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13260–13269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ho, H.C.; Wong, M.S.; Deng, C.; Shi, Y.; Chan, T.-C.; Knudby, A. Evaluation of machine learning techniques with multiple remote sensing datasets in estimating monthly concentrations of ground-level PM2.5. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E.; Bleiweiss, M.P.; Dubois, D. A Simplified high resolution MODIS Aerosol Retrieval Algorithm (SARA) for use over mixed surfaces. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E. Evaluation of MODIS aerosol retrieval algorithms over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region during low to very high pollution events. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 7941–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E.; Chan, P.W. Validation and accuracy assessment of a Simplified Aerosol Retrieval Algorithm (SARA) over Beijing under low and high aerosol loadings and dust storms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 153, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Q.; Amini, H.; Shi, L.; Kloog, I.; Silvern, R.; Kelly, J.; Sabath, M.B.; Choirat, C.; Koutrakis, P.; Lyapustin, A. An ensemble-based model of PM2.5 concentration across the contiguous United States with high spatiotemporal resolution. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Sbihi, H.; Pan, X.; Brauer, M. Local variation of PM2.5 and NO2 concentrations within metropolitan Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 200, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Just, A.; De Carli, M.; Shtein, A.; Dorman, M.; Lyapustin, A.; Kloog, I. Correcting Measurement Error in Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth with Machine Learning for Modeling PM2.5 in the Northeastern USA. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reid, C.E.; Jerrett, M.; Petersen, M.L.; Pfister, G.G.; Morefield, P.E.; Tager, I.B.; Raffuse, S.M.; Balmes, J.R. Spatiotemporal prediction of fine particulate matter during the 2008 Northern California wildfires using machine learning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3887–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, B.; Chen, J. Development of a stacked ensemble model for forecasting and analyzing daily average PM2.5 concentrations in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.E. Geographically weighted regression: A method for exploring spatial nonstationarity. Geogr. Anal. 1996, 28, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J. Applied Regression Analysis and Generalized Linear Models; Sage Publications: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 341–358. [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M. Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 27–65. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, J.D.; Perez, A.; Lozano, J.A. Sensitivity analysis of k-fold cross validation in prediction error estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 32, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China, M. Ambient Air Quality Standards; GB 3095-2012; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, L.; Qin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, Y. A geographically and temporally weighted regression model for ground-level PM2.5 estimation from satellite-derived 500 m resolution AOD. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, K.; Xu, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, P. Satellite-based high-resolution mapping of ground-level PM2.5 concentrations over East China using a spatiotemporal regression kriging model. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hu, M. Filling the missing data gaps of daily MODIS AOD using spatiotemporal interpolation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, T.; Guo, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, T. Quantifying the relationship between PM2.5 concentration, visibility and planetary boundary layer height for long-lasting haze and fog–haze mixed events in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Tang, Q.; Gong, D.Y.; Zhang, Z. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in Beijing using a satellite-based geographically and temporally weighted regression model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Dong, W.; Lv, B.; Bai, Y. Daily estimation of ground-level PM2.5 concentrations over Beijing using 3 km resolution MODIS AOD. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12280–12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, F.; Jia, H.; Hu, Y. Can MODIS AOD be employed to derive PM2.5 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei over China? Atmos. Res. 2016, 181, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xu, H.; Yu, S. Estimating PM2.5 concentrations in Yangtze River Delta region of China using random forest model and the Top-of-Atmosphere reflectance. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 272, 111061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Huang, B. Satellite-based high-resolution PM2.5 estimation over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of China using an improved geographically and temporally weighted regression model. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, D.L.; Gupta, P.; Wang, K.; Jena, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G. Using gap-filled MAIAC AOD and WRF-Chem to estimate daily PM2.5 concentrations at 1 km resolution in the Eastern United States. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Hu, Y.; Chang, H.H.; Russell, A.G.; Bai, Y. Improving the accuracy of daily PM2.5 distributions derived from the fusion of ground-level measurements with aerosol optical depth observations, a case study in North China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4752–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Li, S.; Zou, B.; Sang, H.; Fang, X.; Xu, S. An improved geographically weighted regression model for PM2.5 concentration estimation in large areas. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 181, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Belle, J.H.; Meng, X.; Wildani, A.; Waller, L.A.; Strickland, M.J.; Liu, Y. Estimating PM2.5 concentrations in the conterminous United States using the random forest approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6936–6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, W. Meteorological parameters and gaseous pollutant concentrations as predictors of daily continuous PM2.5 concentrations using deep neural network in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 211, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Q.; Ban, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Li, S.; Li, T. Estimating the daily PM2.5 concentration in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region using a random forest model with a 0.01° × 0.01° spatial resolution. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Zou, B.; Wang, J. Spatial variations of PM2.5 in Chinese cities for the joint impacts of human activities and natural conditions: A global and local regression perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, K.; Li, K.; Chang, N.-B.; Gao, W. Advancing the prediction accuracy of satellite-based PM2.5 concentration mapping: A perspective of data mining through in situ PM2.5 measurements. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Huang, B. Satellite-based mapping of daily high-resolution ground PM2.5 in China via space-time regression modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Period | N | R2 | RMSE | MPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | 6578061 | 0.93 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| Summer | 5663296 | 0.90 | 0.15 | 0.09 |
| Autumn | 4763970 | 0.94 | 0.10 | 0.06 |
| Winter | 4624431 | 0.92 | 0.07 | 0.04 |
| Annual | 21629758 | 0.86 | 0.15 | 0.10 |
| Method | R2 | RMSE (μg/m3) | MPE (μg/m3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fitting | CV | Fitting | CV | Fitting | CV | |
| GWR | 0.81 | 0.71 | 30.74 | 33.67 | 19.86 | 21.79 |
| XGBoost | 0.89 | 0.85 | 21.71 | 27.01 | 15.87 | 19.52 |
| SL-XGB | 0.93 | 0.88 | 18.09 | 24.08 | 13.24 | 16.90 |
| Source | Year | Model | Resolution | Study Area | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ours | - | Spatially local XGBoost (SL-XGB) | 500 m | Beijing | sample-based CV R2 0.88, site-based CV R2 0.86, |
| Xie et al. [57] | 2015 | Mixed-effects model | 3 km | Beijing | site-based CV R2 0.83 |
| He and Huang [60] | 2018 | Improved geographically and temporally weighted regression | 3 km | BTH | sample-based CV R2 0.84 |
| Xie et al. [24] | 2019 | Mixed-effects model with cloud screen | 500 m | Beijing | site-based CV R2 0.82 |
| Yao et al. [25] | 2019 | Nested spatiotemporal Statistical model | 750 m | Beijing | sample-based CV R2 0.85 |
| Wang et al. [65] | 2019 | Deep neural network | 10 km | BTH | sample-based CV R2 0.87 |
| Zhao et al. [66] | 2020 | Random forest considering meteorological lag effects | 0.01° | BTH | sample-based CV R2 0.83 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Z.; Zhan, Q.; Yang, C.; Liu, H.; Bilal, M. Estimating PM2.5 Concentrations Using Spatially Local Xgboost Based on Full-Covered SARA AOD at the Urban Scale. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203368
Fan Z, Zhan Q, Yang C, Liu H, Bilal M. Estimating PM2.5 Concentrations Using Spatially Local Xgboost Based on Full-Covered SARA AOD at the Urban Scale. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(20):3368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203368
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Zhiyu, Qingming Zhan, Chen Yang, Huimin Liu, and Muhammad Bilal. 2020. "Estimating PM2.5 Concentrations Using Spatially Local Xgboost Based on Full-Covered SARA AOD at the Urban Scale" Remote Sensing 12, no. 20: 3368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203368
APA StyleFan, Z., Zhan, Q., Yang, C., Liu, H., & Bilal, M. (2020). Estimating PM2.5 Concentrations Using Spatially Local Xgboost Based on Full-Covered SARA AOD at the Urban Scale. Remote Sensing, 12(20), 3368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203368









