Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Pollution Monitoring with Sentinel-5P Satellite Imagery over Europe during the Coronavirus Pandemic Outbreak
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
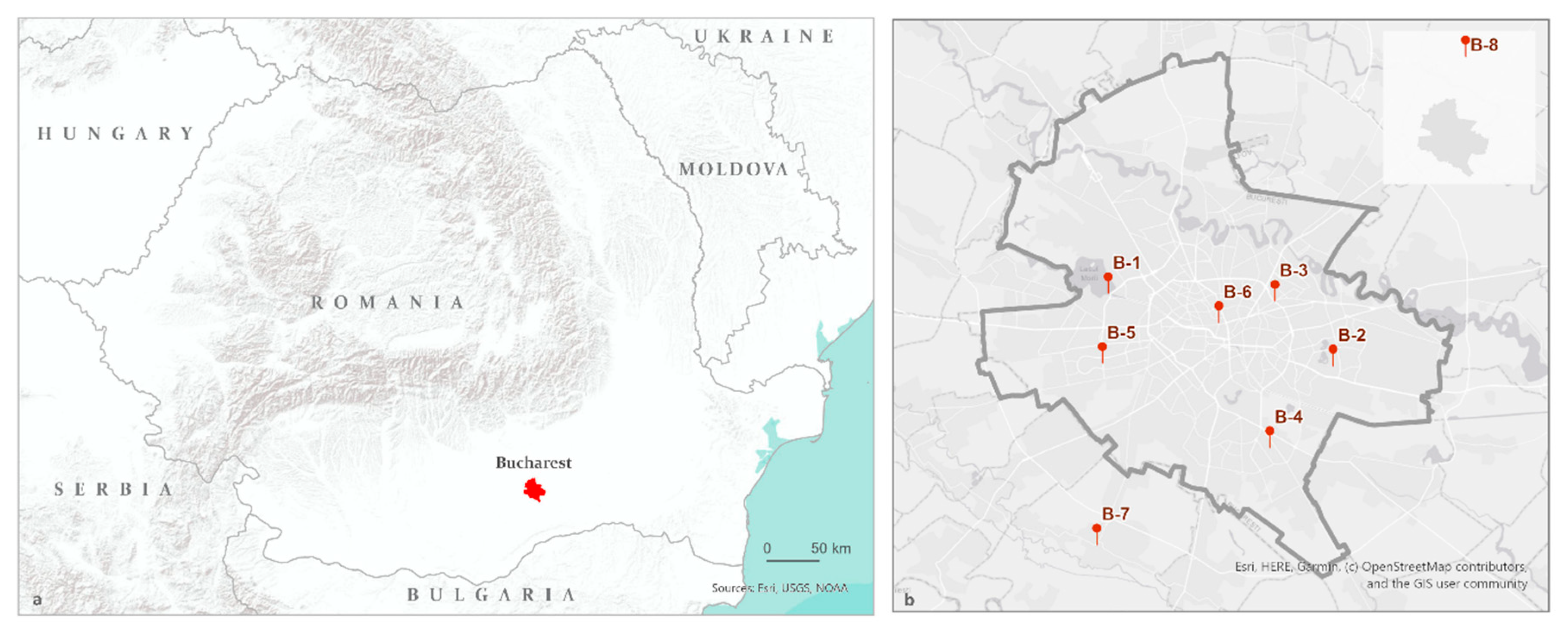
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Types and Sources
2.3. Data Processing Methodology
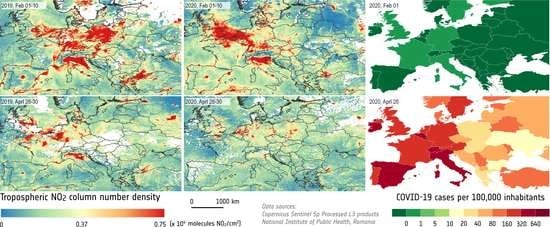
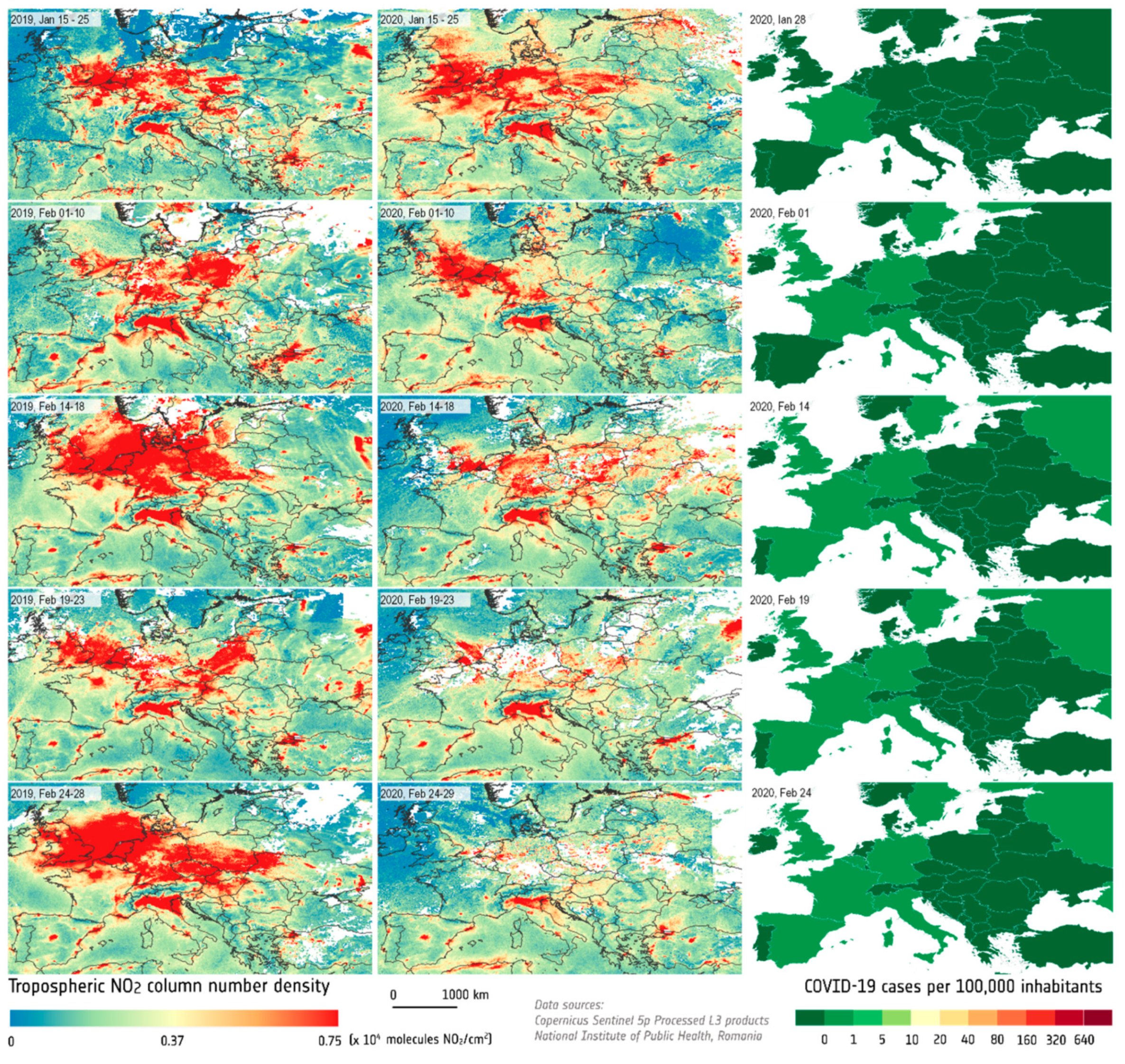
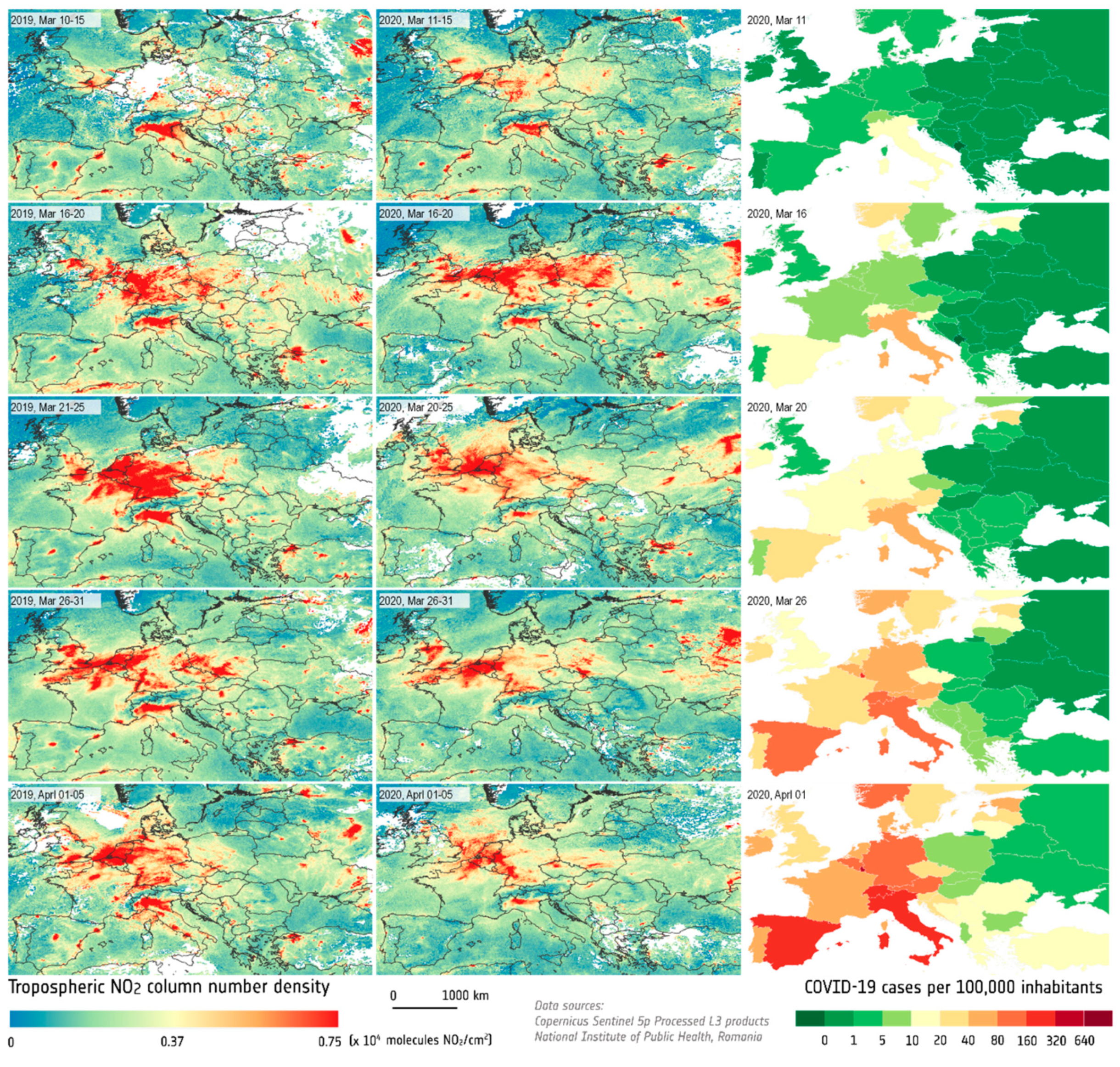
3. Results
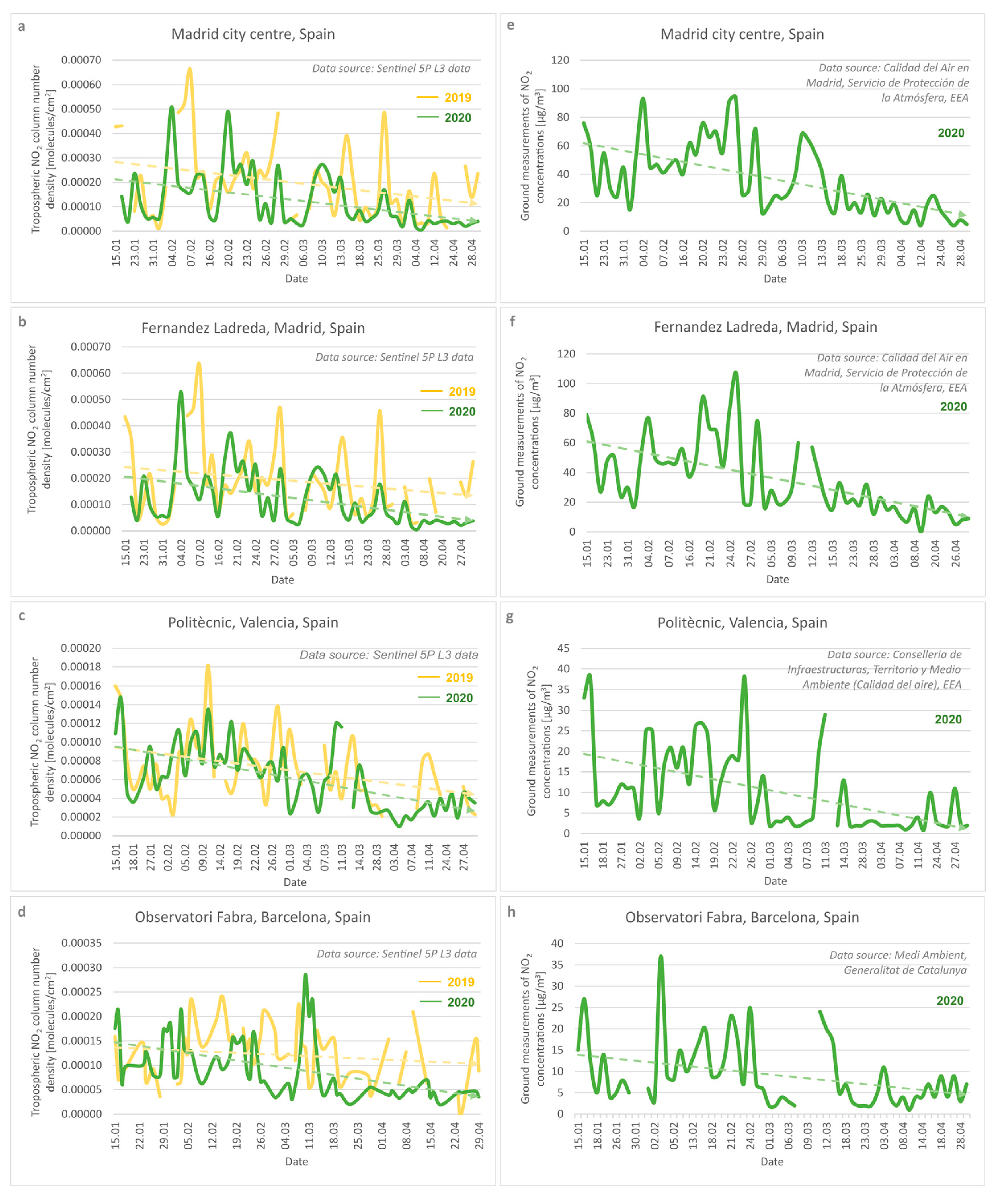
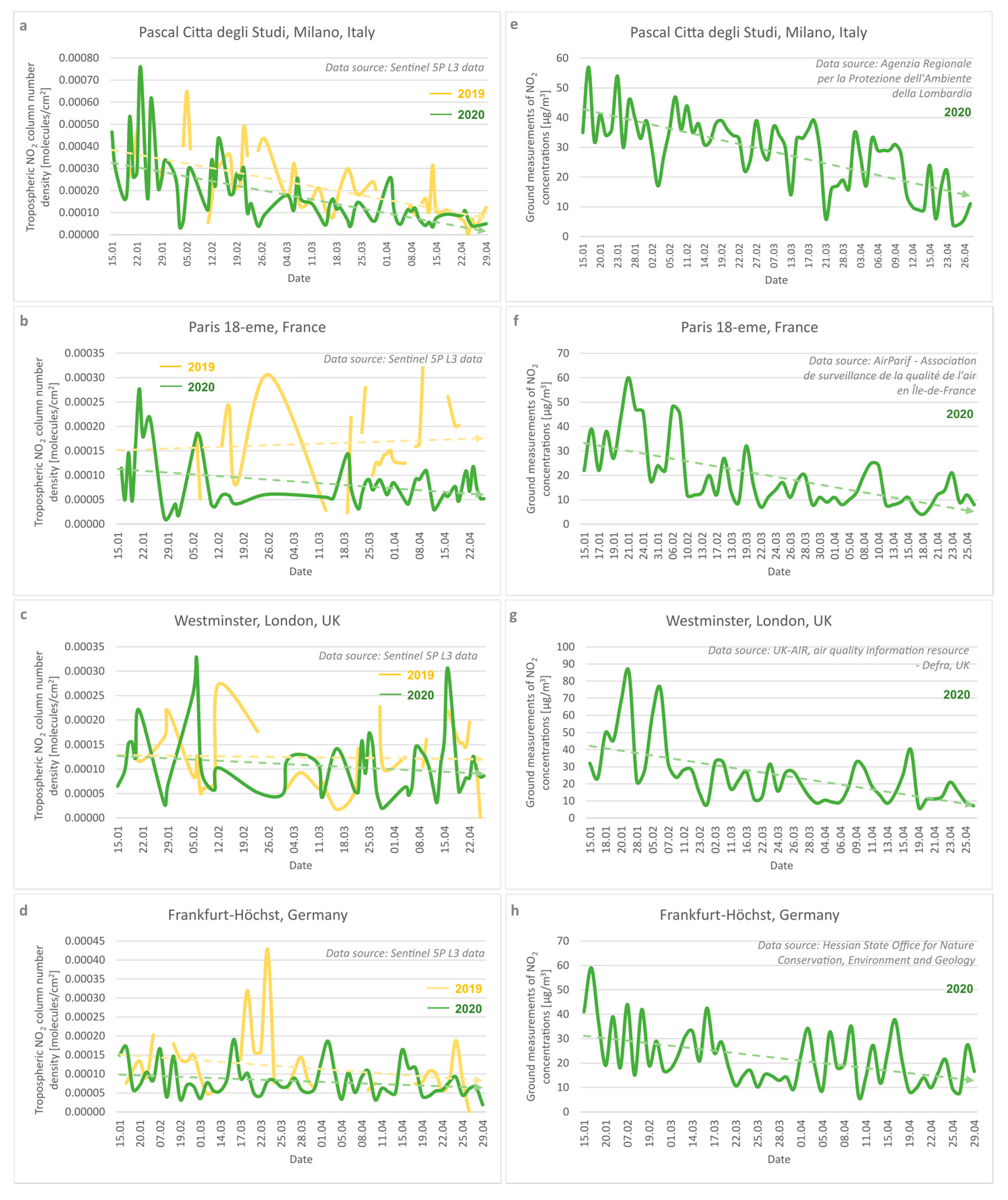
3.1. European Spatiotemporal Distribution of the NO2 Pollution
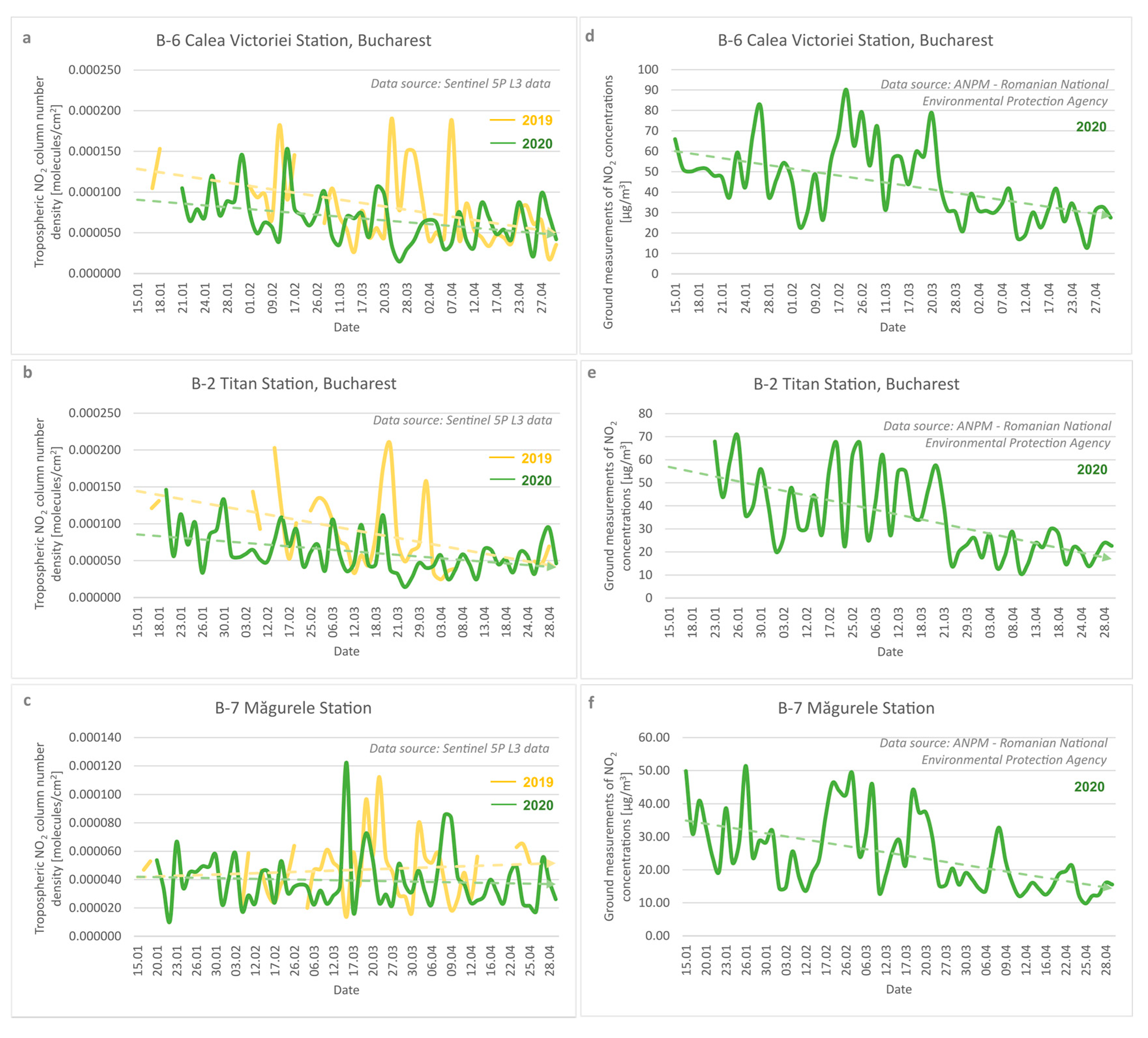
3.2. Local Scale NO2 Pollution Mapping and Assessment: A Case Study of Bucharest, Romania
3.3. Quantitative Spatiotemporal Differences of NO2 Pollution Hotspots during the Pandemic Lockdown
4. Discussion
4.1. Cross-Correlation between Tropospheric NO2 TROPOMI-Based Data and Ground-Based Air Quality Station Measurements
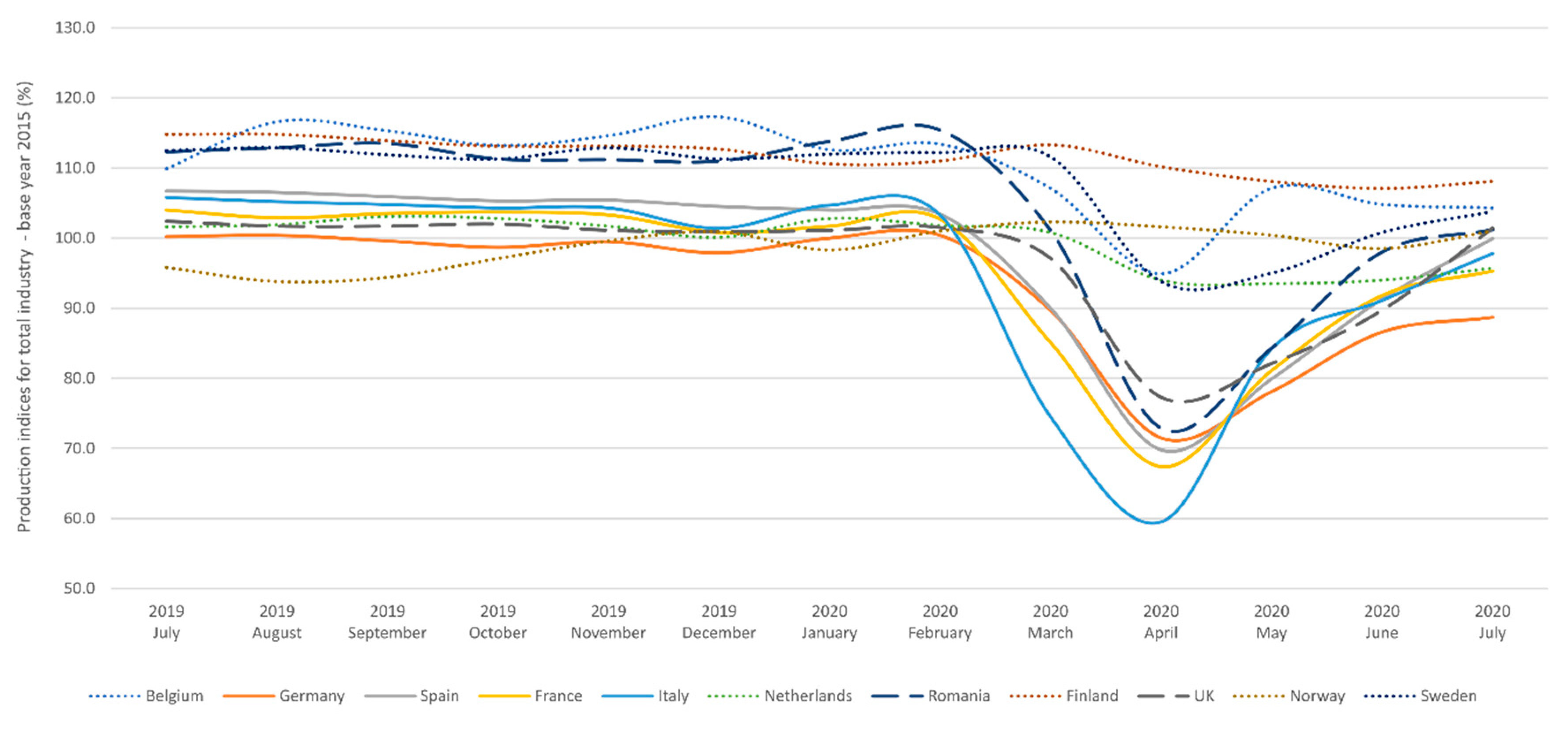
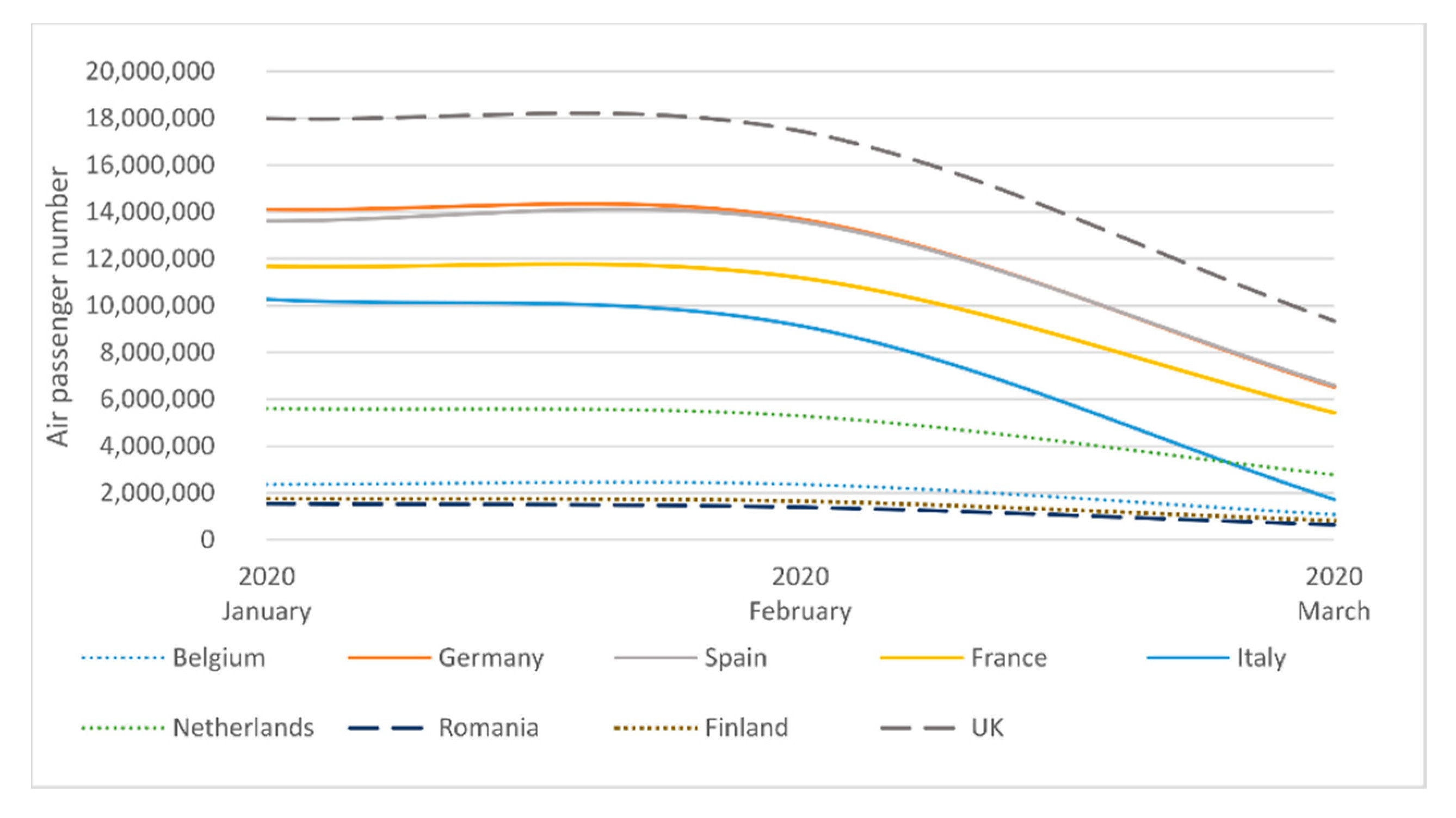
4.2. NO2 Pollution vs. COVID-19 Lockdown
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meetham, A.R.; Bottom, D.; Cayton, S. Atmospheric Pollution: Its History, Origins and Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Olmo, N.R.S.; Saldiva, P.; Braga, A.L.F.; Lin, C.A.; Santos, U.D.P.; Pereira, L.A. A review of low-level air pollution and adverse effects on human health: Implications for epidemiological studies and public policy. Clinics 2011, 66, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sokhi, R.; Kitwiroon, N. Air pollution in urban areas. In World Atlas of Atmospheric Pollution; Anthem Press: London, UK, 2011; pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lavaine, E. An Econometric Analysis of Atmospheric Pollution, Environmental Disparities and Mortality Rates. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2014, 60, 215–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Air Pollution. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/air-pollution#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 14 August 2020).
- Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Andersen, Z.J.; Beelen, R.; Samoli, E.; Stafoggia, M.; Weinmayr, G.; Hoffmann, B.; Fischer, P.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Air pollution and lung cancer incidence in 17 European cohorts: Prospective analyses from the European Study of Cohorts for Air Pollution Effects (ESCAPE). Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, L.; Declercq, C.; Iñiguez, C.; Aguilera, I.; Badaloni, C.; Ballester, F.; Bouland, C.; Chanel, O.; Cirarda, F.B.; Forastiere, F.; et al. Chronic burden of near-roadway traffic pollution in 10 European cities (APHEKOM network). Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cesaroni, G.; Forastiere, F.; Stafoggia, M.; Andersen, Z.J.; Badaloni, C.; Beelen, R.; Caracciolo, B.; De Faire, U.; Erbel, R.; Eriksen, K.T.; et al. Long term exposure to ambient air pollution and incidence of acute coronary events: Prospective cohort study and meta-analysis in 11 European cohorts from the ESCAPE Project. BMJ 2014, 348, f7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slama, R.; Bottagisi, S.; Solansky, I.; Lepeule, J.; Giorgis-Allemand, L.; Sram, R. Short-Term Impact of Atmospheric Pollution on Fecundability. Epidemiology 2013, 24, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidotto, J.P.; Pereira, L.A.A.; Braga, A.L.F.; Silva, C.A.; Sallum, A.M.; Campos, L.M.; Martins, L.C.; Farhat, S.C.L. Atmospheric pollution: Influence on hospital admissions in paediatric rheumatic diseases. Lupus 2012, 21, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldasano, J.M. COVID-19 lockdown effects on air quality by NO2 in the cities of Barcelona and Madrid (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Health Aspects of Air Pollution with Particulate Matter, Ozone and Nitrogen Dioxide; WHO: Bonn, Germany, 2003; p. 98. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Rui, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Zuo, J.; Tong, Y. Sources of atmospheric pollution: A bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 2017, 112, 1025–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WAKI. Available online: https://waqi.info/ (accessed on 29 July 2020).
- AIRINDEX. Available online: https://airindex.eea.europa.eu/Map/AQI/Viewer/ (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- EC. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/air/quality/standards.htm (accessed on 18 May 2020).
- EEA. Air Quality in Europe; European Environment Agency, Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019; p. 99. [Google Scholar]
- Gentner, D.R.; Jathar, S.H.; Gordon, T.D.; Bahreini, R.; Day, D.A.; El Haddad, I.; Hayes, P.L.; Pieber, S.M.; Platt, S.M.; De Gouw, J.; et al. Review of Urban Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation from Gasoline and Diesel Motor Vehicle Emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1074–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, P.; Artiñano, B.; Viana, M.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Gonzalez–Fernandez, I.; Alonso, R. Spatial and temporal variations in PM10 and PM2.5 across Madrid metropolitan area in 1999–2008. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagpure, A.S.; Gurjar, B.R.; Martel, J. Human health risks in national capital territory of Delhi due to air pollution. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2014, 5, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sindhwani, R.; Goyal, P. Assessment of traffic-generated gaseous and particulate matter emissions and trends over Delhi (2000–2010). Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2014, 5, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Environment Agency. Available online: http://www.eea.europa.eu/ (accessed on 16 December 2011).
- Amann, M.; Bertok, I.; Borken-Kleefeld, J.; Cofala, J.; Heyes, C.; Höglund-Isaksson, L.; Klimont, Z.; Nguyen, B.; Posch, M.; Rafaj, P.; et al. Cost-effective control of air quality and greenhouse gases in Europe: Modeling and policy applications. Environ. Model. Softw. 2011, 26, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; Lesne, O.; Alexandre, N.; Mangin, A.; Collomp, R. Air quality trends and potential health effects—Development of an aggregate risk index. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; Talbot, C.; Lesne, O.; Mangin, A.; Alexandre, N.; Collomp, R. The Aggregate Risk Index: An intuitive tool providing the health risks of air pollution to health care community and public. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, M.; Lozano, A.; Hierro, J.; Tapia, O.; Del Valle, J.; Alastuey, A.; Moreno, T.; Anzano, J.; Querol, X. Assessment of the variability of atmospheric pollution in National Parks of mainland Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 132, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fotourehchi, Z. Health effects of air pollution: An empirical analysis for developing countries. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougoudis, I.; Demertzis, K.; Iliadis, L.; Anezakis, V.-D.; Papaleonidas, A. Semi-supervised Hybrid Modeling of Atmospheric Pollution in Urban Centers. In International Conference on Engineering Applications of Neural Networks; Springer: Cham, Switherlands, 2016; pp. 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Bougoudis, I.; Demertzis, K.; Iliadis, L. HISYCOL a hybrid computational intelligence system for combined machine learning: The case of air pollution modeling in Athens. Neural Comput. Appl. 2015, 27, 1191–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulia, S.; Nagendra, S.S.; Khare, M.; Khanna, I. Urban air quality management-A review. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 286–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, J.; Mathur, R.; Pleim, J.; Hogrefe, C.; Gan, C.-M.; Wong, D.C.; Wei, C.; Gilliam, R.; Pouliot, G. Observations and modeling of air quality trends over 1990–2010 across the Northern Hemisphere: China, the United States and Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2015, 15, 2723–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vardoulakis, S.; Solazzo, E.; Lumbreras, J. Intra-urban and street scale variability of BTEX, NO2 and O3 in Birmingham, UK: Implications for exposure assessment. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5069–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.; Lloyd, C.; McKinley, J. Increasing the accuracy of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) pollution mapping using geographically weighted regression (GWR) and geostatistics. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 21, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menut, L.; Bessagnet, B.; Khvorostyanov, D.; Beekmann, M.; Blond, N.; Colette, A.; Coll, I.; Curci, G.; Foret, G.; Hodzic, A.; et al. CHIMERE 2013: A model for regional atmospheric composition modelling. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 981–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Dentener, F.; Muntean, M.; Pouliot, G.; Keating, T.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.; Wankmüller, R.; et al. HTAP_v2.2: A mosaic of regional and global emission grid maps for 2008 and 2010 to study hemispheric transport of air pollution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2015, 15, 11411–11432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beelen, R.; Hoek, G.; Vienneau, D.; Eeftens, M.; Dimakopoulou, K.; Pedeli, X.; Tsai, M.-Y.; Künzli, N.; Schikowski, T.; Marcon, A.; et al. Development of NO2 and NOx land use regression models for estimating air pollution exposure in 36 study areas in Europe—The ESCAPE project. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 72, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckerman, B.; Jerrett, M.; Martin, R.V.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Ross, Z.; Burnett, R.T. Application of the deletion/substitution/addition algorithm to selecting land use regression models for interpolating air pollution measurements in California. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Beirle, S.; Jin, J.; Shaiganfar, R.; Yan, P.; Wagner, T. Tropospheric NO2 vertical column densities over Beijing: Results of the first three years of ground-based MAX-DOAS measurements (2008–2011) and satellite validation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1547–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, W.T.; Allan, J.D.; Bower, K.; Highwood, E.J.; Liu, D.; Mcmeeking, G.R.; Northway, M.J.; Williams, P.I.; Krejci, R.; Coe, H. Airborne measurements of the spatial distribution of aerosol chemical composition across Europe and evolution of the organic fraction. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2010, 10, 4065–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novotny, E.V.; Bechle, M.J.; Millet, D.B.; Marshall, J.D. National satellite-based land-use regression: NO2 in the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4407–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colette, A.; Granier, C.; Hodnebrog, Ø.; Jakobs, H.; Maurizi, A.; Nyiri, A.; Bessagnet, B.; d’Angiola, A.; d’Isidoro, M.; Gauss, M. Air quality trends in Europe over the past decade: A first multi-model assessment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 11657–11678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pouliot, G.; Pierce, T.; Van Der Gon, H.D.; Schaap, M.; Moran, M.; Nopmongcol, U. Comparing emission inventories and model-ready emission datasets between Europe and North America for the AQMEII project. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 53, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Hoogh, K.; Gulliver, J.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Marshall, J.D.; Bechle, M.J.; Cesaroni, G.; Pradas, M.C.; Dedele, A.; Eeftens, M. Development of West-European PM2.5 and NO2 land use regression models incorporating satellite-derived and chemical transport modelling data. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, G.; León, T.; Liang, J.; Huang, G.; Gao, Z.; Jiao, S.; He, X.; et al. Land use regression models coupled with meteorology to model spatial and temporal variability of NO2 and PM10 in Changsha, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 116, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, J.; Silver, J.; Frohn, L.; Geels, C.; Gross, A.; Hansen, A.; Hansen, K.M.; Hedegaard, G.; Skjoth, C.A.; Villadsen, H.; et al. An integrated model study for Europe and North America using the Danish Eulerian Hemispheric Model with focus on intercontinental transport of air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 53, 156–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.; Monteiro, A.; Solman, S.; Miranda, A.I.; Borrego, C. Climate-driven changes in air quality over Europe by the end of the 21st century, with special reference to Portugal. Environ. Sci. Policy 2010, 13, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, U.; Jain, V.K. ARIMA forecasting of ambient air pollutants (O3, NO, NO2 and CO). Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2009, 24, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Lam, N.S. Spatial disaggregation of carbon dioxide emissions from road traffic based on multiple linear regression model. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Hammingh, P.; Colette, A.; Querol, X.; Degraeuwe, B.; De Vlieger, I.; Van Aardenne, J. Impact of maritime transport emissions on coastal air quality in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 90, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Jiang, Y.; Han, X.; Liu, L.; Xu, X.; Qiao, Z.; Sun, W. Spatiotemporal Relationships between Air Quality and Multiple Meteorological Parameters in 221 Chinese Cities. Complexity 2020, 2020, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.W.; Amram, O.; Wheeler, A.J.; Brauer, M. The transferability of NO and NO2 land use regression models between cities and pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, B.N.; Prados, A.I.; Lamsal, L.N.; Liu, Y.; Streets, D.G.; Gupta, P.; Hilsenrath, E.; Kahn, R.A.; Nielsen, J.E.; Beyersdorf, A.J.; et al. Satellite data of atmospheric pollution for U.S. air quality applications: Examples of applications, summary of data end-user resources, answers to FAQs, and common mistakes to avoid. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J. Pollution Trends in China from 2000 to 2017: A Multi-Sensor View from Space. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popp, T.; Hegglin, M.I.; Hollmann, R.; Ardhuin, F.; Bartsch, A.; Bastos, A.; Bennett, V.; Boutin, J.; Brockmann, C.; Buchwitz, M.; et al. Consistency of satellite climate data records for Earth system monitoring. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Canty, T.; Carmichael, G.R.; De Foy, B.; Dickerson, R.R.; Duncan, B.N.; Edwards, D.P.; Haynes, J.A.; Henze, D.K.; Houyoux, M.R.; et al. Emissions estimation from satellite retrievals: A review of current capability. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 1011–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Kahn, R.; Levy, R.; Verduzco, C.; Villeneuve, P.J. Global Estimates of Ambient Fine Particulate Matter Concentrations from Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Depth: Development and Application. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chudnovsky, A.A.; Kostinski, A.; Lyapustin, A.; Koutrakis, P. Spatial scales of pollution from variable resolution satellite imaging. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 172, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Geng, G.; He, K. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations over three megalopolises in China using satellite-derived aerosol optical depth measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, C.; Lau, A.K.H.; Liao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, W.; Li, C.; Fung, J.C.; Tse, T.K.T. Assessing Long-Term Trend of Particulate Matter Pollution in the Pearl River Delta Region Using Satellite Remote Sensing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11670–11678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, K.; Ma, M.; Chang, N.-B.; Gao, W. Spatiotemporal trend analysis for fine particulate matter concentrations in China using high-resolution satellite-derived and ground-measured PM2.5 data. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Cao, D.; Wang, X.; Ye, D. Long-term trend and spatiotemporal variations of haze over China by satellite observations from 1979 to 2013. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 119, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Remote sensing of atmospheric fine particulate matter (PM2.5) mass concentration near the ground from satellite observation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konovalov, I.B.; Beekmann, M.; Kuznetsova, I.N.; Yurova, A.Y.; Zvyagintsev, A.M. Atmospheric impacts of the 2010 Russian wildfires: Integrating modelling and measurements of an extreme air pollution episode in the Moscow region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2011, 11, 10031–10056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vadrevu, K.P.; Lasko, K. Intercomparison of MODIS AQUA and VIIRS I-Band Fires and Emissions in an Agricultural Landscape—Implications for Air Pollution Research. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheel, V.; Lal, S.; Richter, A.; Burrows, J.P. Comparison of satellite observed tropospheric NO2 over India with model simulations. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3314–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.M. Temporal Analysis of OMI-Observed Tropospheric NO2 Columns over East Asia during 2006–2015. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bechle, M.J.; Millet, D.B.; Marshall, J.D. Remote sensing of exposure to NO2: Satellite versus ground-based measurement in a large urban area. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 69, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vienneau, D.; De Hoogh, K.; Bechle, M.J.; Beelen, R.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Millet, D.B.; Hoek, G.; Marshall, J.D. Western European Land Use Regression Incorporating Satellite- and Ground-Based Measurements of NO2 and PM10. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13555–13564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsal, L.N.; Martin, R.V.; Parrish, D.D.; Krotkov, N.A. Scaling Relationship for NO2 Pollution and Urban Population Size: A Satellite Perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7855–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingmann, P.; Veihelmann, B.; Langen, J.; Lamarre, D.; Stark, H.; Courrèges-Lacoste, G.B. Requirements for the GMES Atmosphere Service and ESA’s implementation concept: Sentinels-4/-5 and -5p. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veefkind, J.; Aben, E.; McMullan, K.; Förster, H.; De Vries, J.; Otter, G.; Claas, J.; Eskes, H.; De Haan, J.; Kleipool, Q.; et al. TROPOMI on the ESA Sentinel-5 Precursor: A GMES mission for global observations of the atmospheric composition for climate, air quality and ozone layer applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, J.; Voors, R.; Ording, B.; Dingjan, J.; Veefkind, P.; Ludewig, A.; Kleipool, Q.; Hoogeveen, R.; Aben, I. TROPOMI on ESA’s Sentinel 5p ready for launch and use. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment, Paphos, Cyprus, 4–8 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kleipool, Q.; Ludewig, A.; Babić, L.; Bartstra, R.; Braak, R.; Dierssen, W.; Dewitte, P.-J.; Kenter, P.; Landzaat, R.; Leloux, J.; et al. Pre-launch calibration results of the TROPOMI payload on-board the Sentinel-5 Precursor satellite. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 6439–6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, J.; Vollmer, B.; Ostrenga, D.; Gerasimov, I. Air Quality Satellite Monitoring by TROPOMI on Sentinel-5P. Earth Space Sci. Open Arch. 2019, 33, 3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beirle, S.; Borger, C.; Dörner, S.; Li, A.; Hu, Z.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Wagner, T. Pinpointing nitrogen oxide emissions from space. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loyola, D.G.; Xu, J.; Heue, K.-P.; Zimmer, W. Applying FP_ILM to the retrieval of geometry-dependent effective Lambertian equivalent reflectivity (GE_LER) daily maps from UVN satellite measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Marinello, F. Spatial Variation of NO2 and Its Impact Factors in China: An Application of Sentinel-5P Products. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quesada-Ruiz, S.; Attié, J.-L.; Lahoz, W.A.; Abida, R.; Ricaud, P.; El Amraoui, L.; Zbinden, R.; Piacentini, A.; Joly, M.; Eskes, H.; et al. Benefit of ozone observations from Sentinel-5P and future Sentinel-4 missions on tropospheric composition. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borsdorff, T.; De Brugh, J.A.; Hu, H.; Hasekamp, O.; Sussmann, R.; Rettinger, M.; Hase, F.; Gross, J.; Schneider, M.; Garcia, O.; et al. Mapping carbon monoxide pollution from space down to city scales with daily global coverage. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5507–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theys, N.; Hedelt, P.; De Smedt, I.; Lerot, C.; Yu, H.; Vlietinck, J.; Pedergnana, M.; Arellano, S.; Galle, B.; Fernandez, D.; et al. Global monitoring of volcanic SO2 degassing with unprecedented resolution from TROPOMI onboard Sentinel-5 Precursor. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioletov, V.; McLinden, C.A.; Griffin, D.; Theys, N.; Loyola, D.G.; Hedelt, P.; Krotkov, N.A.; Li, C. Anthropogenic and volcanic point source SO2 emissions derived from TROPOMI on board Sentinel-5 Precursor: First results. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, 20, 5591–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Landgraf, J.; Detmers, R.; Borsdorff, T.; De Brugh, J.A.; Aben, I.; Butz, A.; Hasekamp, O. Toward Global Mapping of Methane With TROPOMI: First Results and Intersatellite Comparison to GOSAT. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3682–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geffen, J.; Boersma, K.F.; Eskes, H.; Sneep, M.; Ter Linden, M.; Zara, M.; Veefkind, J.P. S5P TROPOMI NO2 slant column retrieval: Method, stability, uncertainties and comparisons with OMI. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 1315–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, L.; Tao, J.; Valks, P.; Yu, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L. NO2 Retrieval from the Environmental Trace Gases Monitoring Instrument (EMI): Preliminary Results and Intercomparison with OMI and TROPOMI. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omrani, H.; Omrani, B.; Parmentier, B.; Helbich, M. Spatio-temporal data on the air pollutant nitrogen dioxide derived from Sentinel satellite for France. Data Brief 2020, 28, 105089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorente, A.; Boersma, K.F.; Eskes, H.J.; Veefkind, J.P.; Van Geffen, J.; De Zeeuw, M.B.; Van Der Gon, H.A.C.D.; Beirle, S.; Krol, M.C. Quantification of nitrogen oxides emissions from build-up of pollution over Paris with TROPOMI. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ialongo, I.; Virta, H.; Eskes, H.; Hovila, J.; Douros, J. Comparison of TROPOMI/Sentinel-5 Precursor NO2 observations with ground-based measurements in Helsinki. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexandri, F.; Zyrichidou, I.; Balis, D.; Poupkou, A.; Melas, D. Inference Of Surface Nitrogen Dioxide Concentrations From Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) Tropospheric NO2 Column Observations over South-Eastern Europe. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328477825_Inference_of_surface_nitrogen_dioxide_concentrations_from_Ozone_Monitoring_Instrument_OMI_tropospheric_NO2_column_observations_over_South-Eastern_Europe (accessed on 26 October 2020).
- Zhao, X.; Griffin, D.; Fioletov, V.E.; McLinden, C.A.; Cede, A.; Tiefengraber, M.; Müller, M.; Bognar, K.; Strong, K.; Boersma, K.F.; et al. Assessment of the quality of TROPOMI high-spatial-resolution NO2 data products in the Greater Toronto Area. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 2131–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikwambana, L.; Mhangara, P.; Mbatha, N. Trend analysis and first time observations of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide in South Africa using TROPOMI/Sentinel-5 P data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 91, 102130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.; Zhao, X.; McLinden, C.A.; Boersma, F.; Bourassa, A.; Dammers, E.; Degenstein, D.; Eskes, H.; Fehr, L.; Fioletov, V.E.; et al. High-Resolution Mapping of Nitrogen Dioxide With TROPOMI: First Results and Validation Over the Canadian Oil Sands. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaplan, G.; Avdan, Z.Y. Space-borne air pollution observation from sentinel-5p tropomi: Relationship between pollutants, geographical and demographic data. Int. J. Eng. Geosci. 2020, 5, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, M.; Alsafi, Z.; Sohrabi, C.; Kerwan, A.; Al-Jabir, A.; Iosifidis, C.; Agha, M.; Agha, R. The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19): A review. Int. J. Surg. 2020, 78, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brickell, K.; Picchioni, F.; Natarajan, N.; Guermond, V.; Parsons, L.; Zanello, G.; Bateman, M. Compounding crises of social reproduction: Microfinance, over-indebtedness and the COVID-19 pandemic. World Dev. 2020, 136, 105087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldekop, J.A.; Horner, R.; Hulme, D.; Adhikari, R.; Agarwal, B.; Alford, M.; Bakewell, O.; Banks, N.; Barrientos, S.; Bastia, T.; et al. COVID-19 and the case for global development. World Dev. 2020, 134, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodell, J.W. COVID-19 and finance: Agendas for future research. Financ. Res. Lett. 2020, 35, 101512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, A.; Aloui, C.; Yarovaya, L. COVID-19 pandemic, oil prices, stock market, geopolitical risk and policy uncertainty nexus in the US economy: Fresh evidence from the wavelet-based approach. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2020, 70, 101496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiang, S.; Allen, D.; Annan-Phan, S.; Bell, K.; Bolliger, I.; Chong, T.; Druckenmiller, H.; Huang, L.Y.; Hultgren, A.; Krasovich, E.; et al. The effect of large-scale anti-contagion policies on the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 584, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Chen, X.; Shi, W. Impacts of social and economic factors on the transmission of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China. J. Popul. Econ. 2020, 33, 1127–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Heo, K.; Seo, Y. COVID-19 in South Korea: Lessons for developing countries. World Dev. 2020, 135, 105057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorsi, G.; Pierri, F.; Cinelli, M.; Flori, A.; Galeazzi, A.; Porcelli, F.; Schmidt, A.L.; Valensise, C.M.; Scala, A.; Quattrociocchi, W.; et al. Economic and social consequences of human mobility restrictions under COVID-19. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 15530–15535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.; Kramer, K.Z. The potential impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on occupational status, work from home, and occupational mobility. J. Vocat. Behav. 2020, 119, 103442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.J.; Hensher, D.A.; Wei, E. Slowly coming out of COVID-19 restrictions in Australia: Implications for working from home and commuting trips by car and public transport. J. Transp. Geogr. 2020, 88, 102846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, S.; Long, X.; Salman, M. COVID-19 pandemic and environmental pollution: A blessing in disguise? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, J. Short-Run Environmental Effects of COVID-19: Evidence from Forest Fires. SSRN Electron. J. 2020, 105120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conticini, E.; Frediani, B.; Caro, D. Can atmospheric pollution be considered a co-factor in extremely high level of SARS-CoV-2 lethality in Northern Italy? Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Chang, R. Air quality changes and Grey relational analysis of pollutants exceeding standards during the COVID-19 pandemic in Wuhan. Res. Sq. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Yung, Y.L.; Li, G.; Seinfeld, J.H. Unexpected air pollution with marked emission reductions during the COVID-19 outbreak in China. Science 2020, 369, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutheil, F.; Baker, J.S.; Navel, V. COVID-19 as a factor influencing air pollution? Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, K.; Sarfraz, M.; Shah, S.G.M. The impact of COVID-19 as a necessary evil on air pollution in India during the lockdown. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, T.; Rothman, K.J.; Goffi, A.; Ferrari, F.; Maffeis, G.; Orsini, N.; Vinceti, M. Satellite-detected tropospheric nitrogen dioxide and spread of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Northern Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 140278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, B.; Carvalho, G.; Da Silva, C.M.; Arbilla, G. The Impact of COVID-19 Partial Lockdown on Primary Pollutant Concentrations in the Atmosphere of Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo Megacities (Brazil). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 105, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESA. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Applications/Observing_the_Earth/Copernicus/Sentinel-5P/COVID-19_nitrogen_dioxide_over_China (accessed on 18 July 2020).
- Bauwens, M.; Compernolle, S.; Stavrakou, T.; Müller, J.; Van Gent, J.; Eskes, H.; Levelt, P.F.; Van Der A, R.; Veefkind, J.P.; Vlietinck, J.; et al. Impact of Coronavirus Outbreak on NO 2 Pollution Assessed Using TROPOMI and OMI Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekmoudi, I.; Khomsi, K.; Faieq, S.; Idrissi, L. Covid-19 lockdown improves air quality in Morocco. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.05417. [Google Scholar]
- Stratoulias, D.; Nuthammachot, N. Air quality development during the COVID-19 pandemic over a medium-sized urban area in Thailand. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogen, Y. Assessing nitrogen dioxide (NO2) levels as a contributing factor to coronavirus (COVID-19) fatality. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameletti, M. The Effect of Corona Virus Lockdown on Air Pollution: Evidence from the City of Brescia in Lombardia Region (Italy). Atmos. Environ. 2020, 239, 117794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesas-Carrascosa, F.; Porras, F.P.; Triviño-Tarradas, P.; García-Ferrer, A.; Meroño, J. Effect of Lockdown Measures on Atmospheric Nitrogen Dioxide during SARS-CoV-2 in Spain. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worldometer. World Population Prospects: The 2019 Revision; United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Available online: https://population.un.org/wpp/ (accessed on 26 October 2020).
- Kotzeva, M.; Brandmüller, T.; Lupu, I.; Önnerfors, Å. EUROSTAT Urban Europe Statistics on Cities, Towns and Suburbs; Publications office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- TROPOMI. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/user-guides/sentinel-5p-tropomi (accessed on 18 March 2020).
- Van Geffen, J.H.G.M.; Eskes, H.J.; Boersma, H.F.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Veefkind, J.P. TROPOMI ATBD of he Total and Thropospheric NO2 Data Products; ESA: Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute: De Bilt, The Netherlands, 2019.
- SCIHUB. Available online: https://scihub.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Guzzonato, E.; Mora, B.; Remondière, S.; Palazzo, F. RUS Copernicus: An Expert Service for New Sentinel Data Users. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 509, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, F.; Šmejkalová, T.; Castro-Gomez, M.; Rémondière, S.; Scarda, B.; Bonneval, B.; Gilles, C.; Guzzonato, E.; Mora, B. RUS: A New Expert Service for Sentinel Users. Multidiscip. Digit. Publ. Inst. Proc. 2018, 2, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- RUS. Available online: https://rus-copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 14 March 2020).
- Richmond-Bryant, J.; Snyder, M.; Owen, R.; Kimbrough, S. Factors associated with NO2 and NOX concentration gradients near a highway. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 174, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorga, G.; Raicu, C.B.; Stefan, S.; Iorga, G. Annual air pollution level of major primary pollutants in Greater Area of Bucharest. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras Ochando, L.; Font Julian, C.I.; Contreras Ochando, F.; Ferri, C. Airvlc: An application for real-time forecasting urban air pollution. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Mining Urban, Lille, France, 11 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras, L.; Ferri, C. Wind-sensitive Interpolation of Urban Air Pollution Forecasts. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 80, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, J.; Brauer, M.; Ainslie, B.; Steyn, U.; Larson, T.; Buzzelli, M. An innovative land use regression model incorporating meteorology for exposure analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorai, A.K.; Tuluri, F.; Tchounwou, P.B.; Ambinakudige, S. Influence of local meteorology and NO2 conditions on ground-level ozone concentrations in the eastern part of Texas, USA. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2015, 8, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buontempo, C.; Thépaut, J.-N.; Bergeron, C. Copernicus Climate Change Service. Available online: https://climate.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 18 October 2020).
- Kendrick, C.M.; Koonce, P.; George, L.A. Diurnal and seasonal variations of NO, NO2 and PM 2.5 mass as a function of traffic volumes alongside an urban arterial. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cersosimo, A.; Serio, C.; Masiello, G. TROPOMI NO2 Tropospheric Column Data: Regridding to 1 km Grid-Resolution and Assessment of their Consistency with in Situ Surface Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




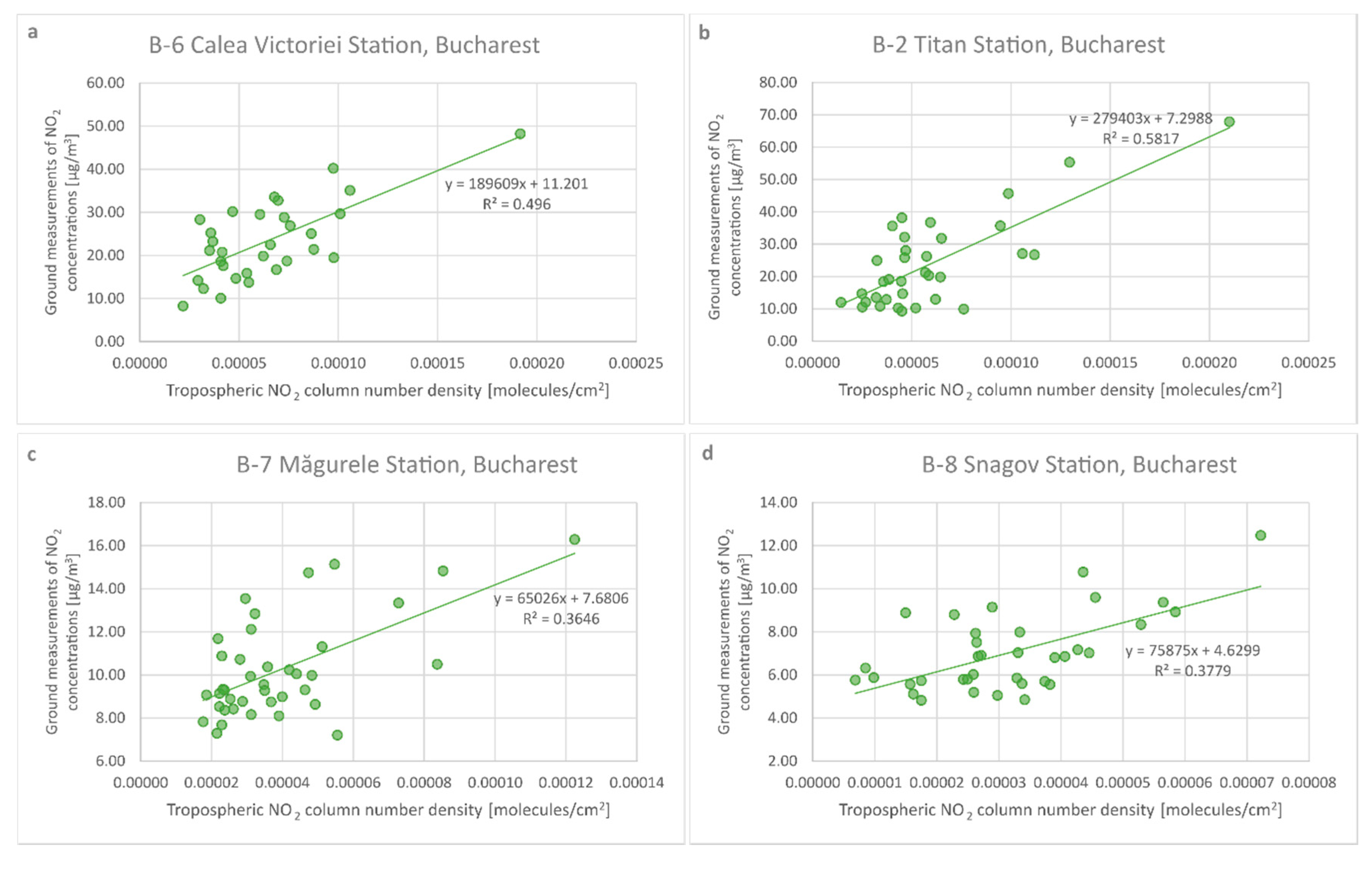
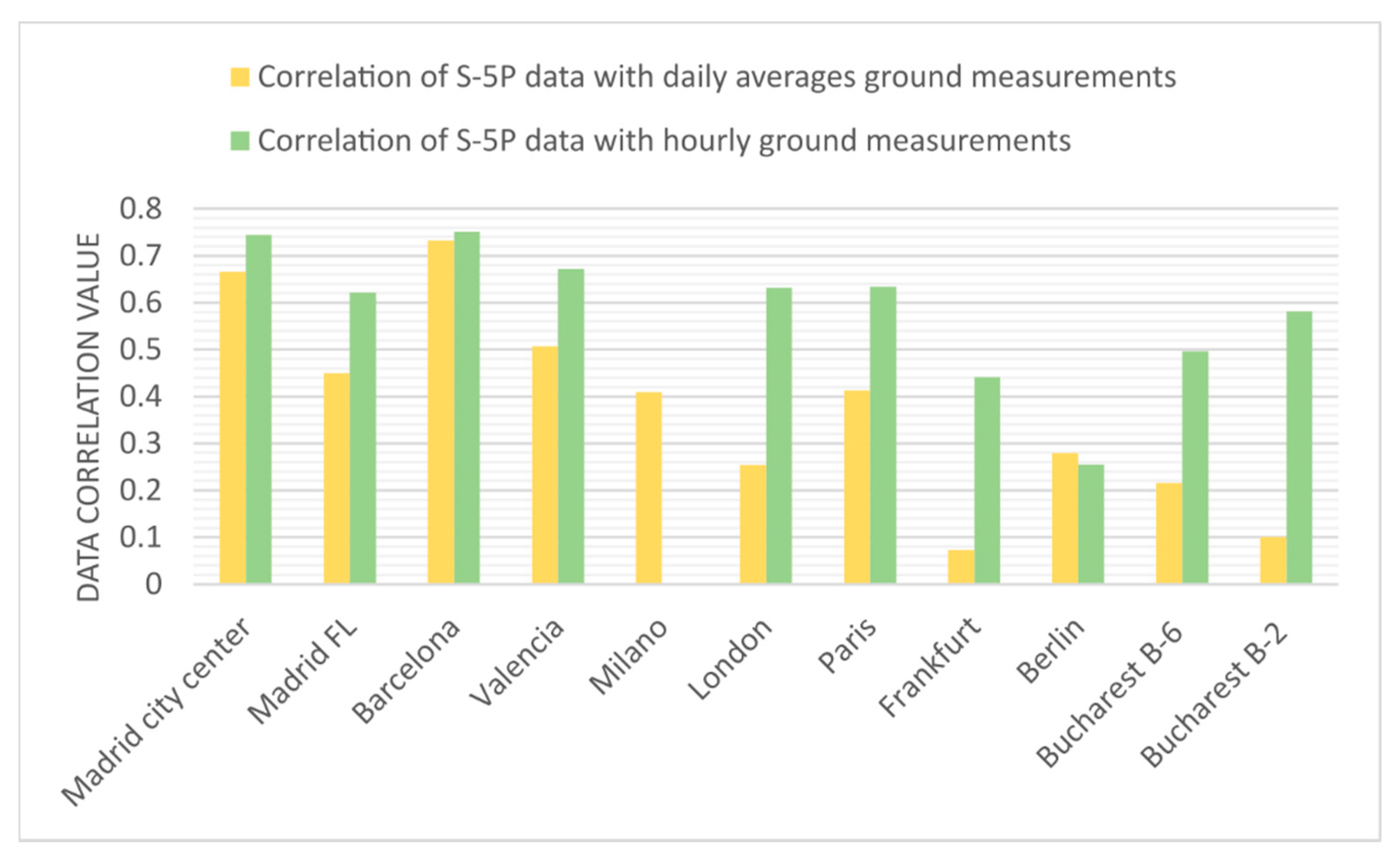

| Ground Station Location | Correlation Significance Level (by p-Value) | Pearson Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| Madrid city center | <5% significant | 0.862543989 |
| Fernandez Ladreda, Madrid, Spain | <5% significant | 0.7872871252 |
| Politècnic, Valencia, Spain | <5% significant | 0.818251168 |
| Observatori Fabra, Barcelona, Spain | <5% significant | 0.865555982 |
| Pascal Citta degli Studi, Milano, Italy | <5% significant | 0.635701473 |
| Paris 18-eme, France | <5% significant | 0.802355165 |
| Westminster, London, UK | <5% significant | 0.78950097 |
| Frankfurt-Höchst, Germany | <5% significant | 0.669374336 |
| B-6 Bucharest, Romania | <5% significant | 0.698194842 |
| B-2 Bucharest, Romania | <5% significant | 0.762701866 |
| B-7 Bucharest, Romania | <5% significant | 0.60324087 |
| B-8 Bucharest, Romania | <5% significant | 0.597572962 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vîrghileanu, M.; Săvulescu, I.; Mihai, B.-A.; Nistor, C.; Dobre, R. Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Pollution Monitoring with Sentinel-5P Satellite Imagery over Europe during the Coronavirus Pandemic Outbreak. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3575. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213575
Vîrghileanu M, Săvulescu I, Mihai B-A, Nistor C, Dobre R. Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Pollution Monitoring with Sentinel-5P Satellite Imagery over Europe during the Coronavirus Pandemic Outbreak. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(21):3575. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213575
Chicago/Turabian StyleVîrghileanu, Marina, Ionuț Săvulescu, Bogdan-Andrei Mihai, Constantin Nistor, and Robert Dobre. 2020. "Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Pollution Monitoring with Sentinel-5P Satellite Imagery over Europe during the Coronavirus Pandemic Outbreak" Remote Sensing 12, no. 21: 3575. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213575
APA StyleVîrghileanu, M., Săvulescu, I., Mihai, B.-A., Nistor, C., & Dobre, R. (2020). Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Pollution Monitoring with Sentinel-5P Satellite Imagery over Europe during the Coronavirus Pandemic Outbreak. Remote Sensing, 12(21), 3575. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213575