Abstract
In solar cycle 24, the strongest geomagnetic storm took place on 17 March 2015, when the geomagnetic activity index was as high as −223 nT. To verify the impact that the storm had on the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)’s positioning accuracy and precision, we used 30-s observations from 15 reference stations located in Central Europe. For each of them, we applied kinematic precise point positioning (PPP) using gLAB software for the day of the storm and, for comparison, for a selected quiet day (13 March 2015). Based on the conducted analyses, we found out that the position root mean square (RMS) values on the day of the geomagnetic storm were significantly high and amounted to several dozen centimeters. The average RMS for the altitude coordinates was 0.58 m between 12:00 and 24:00 (GPS time), and 0.37 and 0.26 m for directions North and East, respectively. The compromised accuracy level was caused by a sudden decrease in the number of satellites used for calculations. This was due to a high number of cycle slips (CSs) detected during this period. The occurrence of these effects was strictly correlated with the appearance of traveling ionospheric disturbances (TIDs). This was proven by analyzing changes in the total electron content (TEC) estimated for each station–satellite pair.
1. Introduction
The ionosphere is a layer of the Earth’s atmosphere, wherein density distribution of free electrons is heterogeneous and is determined by the intensity of solar radiation, which stimulates ionization of atoms and gas particles. The density of free electrons and their variations significantly affects electromagnetic signals passing through the atmosphere. Along with the changes in the signal propagation velocity, irregularities of electron density may cause its diffraction and refraction. An assessment of the current state of the ionosphere can be made by analyzing the total electron content (TEC) parameter. The TEC, which represents the ionospheric refraction, depends on a given geographical location, the hour of a day and solar activity levels. Since the ionosphere is a dispersive region, refraction depends on the frequency of a signal. In case of the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), 1 TECU (TEC units) is responsible for approximately a 0.16 m delay in L1 band. For single frequency receivers, ionospheric delay can be reduced only by modelling its value. Users can apply Klobuchar model coefficients [1] broadcasted with a GPS navigation message, which allows them to reduce the root mean square (RMS) ionospheric range error by about 50%. With the launch of the Galileo system, the NeQuick model was introduced [2], characterized by better quality; it can mitigate the ionospheric delay up to 68% [3]. Nonetheless, these values are insufficient for high precision applications. Thus, differential measurements can be used. With a vector length not exceeding 10 km, ionospheric refraction may be neglected [4]. However, long-range measurements are affected by a decrease in accuracy [5]. The solution is to use an ionospheric-free linear combination, which can eliminate 99% of first-order ionospheric delay but requires double frequency receivers. The second- and third-order delay can be efficiently modeled [6]. Ionospheric-free linear combination is applied particularly in the precise point positioning (PPP) approach [7,8], where only one receiver is used. However, this combination increases observation noise and makes resolving ambiguities difficult. It is worth noting that the ionosphere can significantly affect signal receiver acquisition. This may cause scintillation by rapid fluctuations in the signal amplitude and phase [9,10]. The accidental or rare phenomena, such as traveling ionospheric disturbances (TIDs) [11], may also be a problem. TIDs are sudden changes in plasma density in the ionosphere causing interference in a radio signal by changing the refraction index. They can cause sudden and notable changes in TEC, which can result in the hindered acquisition of GNSS signals and decrease positioning accuracy and precision [12]. TIDs can be generated not only by solar activity, but also by other sources, e.g., earthquakes [13] or intense phenomena in the troposphere [14]. Luo et al. (2018) investigated the accuracy of PPP positioning during a selected geomagnetic storm in solar cycle 24. Their findings clearly show that the RMS of a 3D position can reach over 1.5 m during superstorms [15]. This decrease of the accuracy was mainly caused by the occurrence of cycle-slip (CS) effects, which is a confirmation of previous works [16]. Moreno et al. (2010) found PPP large variations during the periods when the large rate of TEC (ROT) was observed at equatorial latitudes between April 18 and 22, 2004 [17]. Similar results were obtained by Jacobsen and Andalsvik who noticed the rapid increasing of vertical position errors together with increasing ROT index (ROTI) for both PPP and real-time kinematic (RTK) techniques [18]. Lu et al. (2020), based on data from Hong Kong, showed that ionospheric scintillation events vastly decreased the PPP accuracy due to the negative impact of cycle slips on convergence time [19]. Additionally, small-scale ionospheric irregularities of auroral origin can cause a PPP positioning error of about 0.5 m [20].
Because GNSS signals are sensitive to an ionospheric state, they can be successfully used for the purpose of investigating it. The research concerns global and local TEC mapping [21,22], investigating TIDs [23,24], modeling vertical profiles [25], estimating the height of ionospheric disturbances [26], etc.
In this paper, we present the negative effect of medium-scale TIDs that occurred during a severe geomagnetic storm on St. Patrick’s Day in 2015 on kinematic PPP solutions. Our analyses were performed based on observations derived from a reference network in Poland. We focused on relative changes in TEC values and correlated them with the quality of the received signal. In Section 2, we briefly introduce the storm that took place on 17 March 2015. The data and the methodology are described in detail in Section 3. The results of the kinematic PPP positioning are show in Section 4. This is followed by a discussion in Section 5 where potential causes and effects of the obtained lower accuracy are analyzed. The article concludes in Section 6 with a summary of the obtained results.
2. The St. Patrick’s Day 2015 Geomagnetic Storm
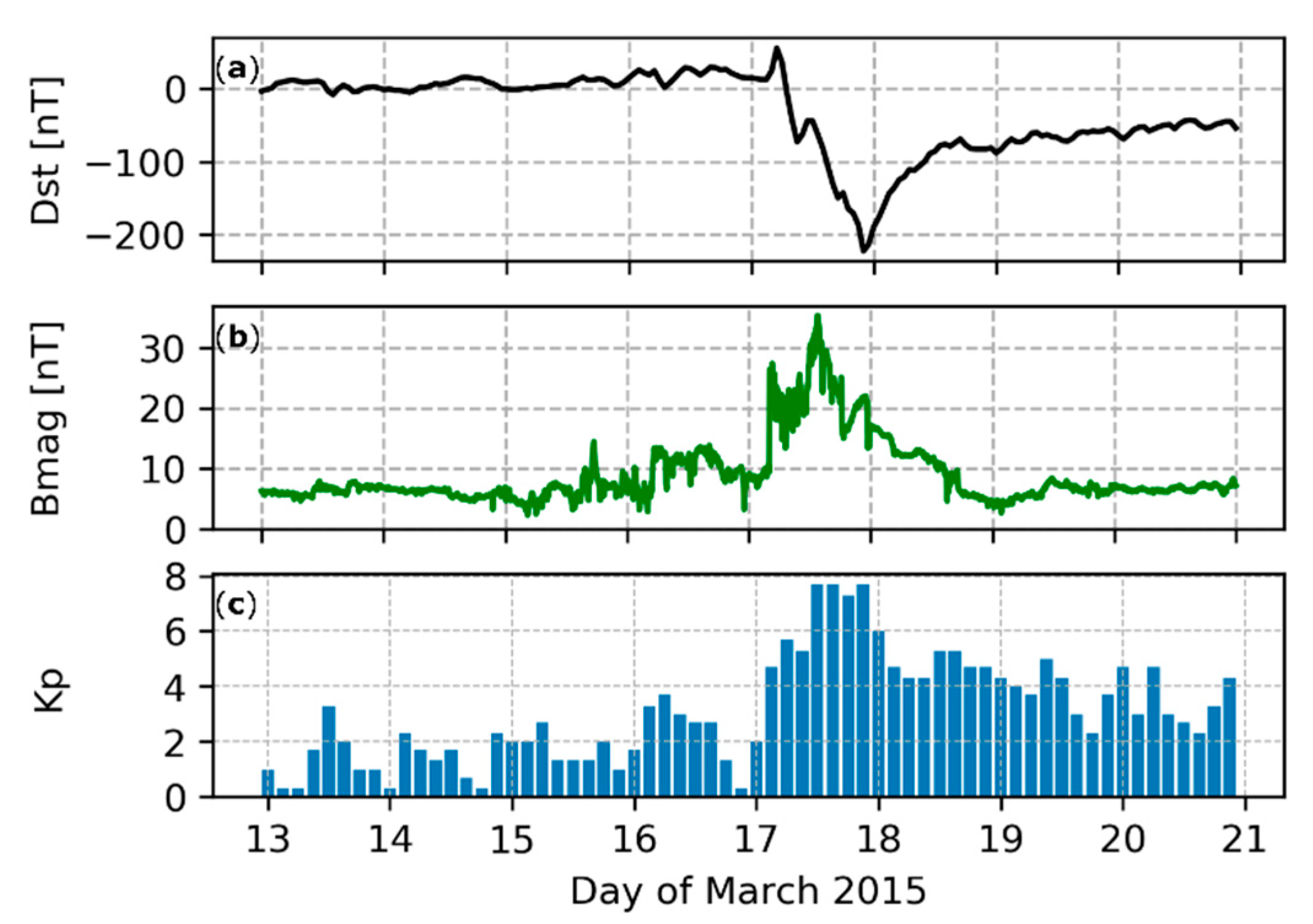
The source of the geomagnetic storm of 17–18 March 2015 (called the St. Patrick’s Day event) was the ejection of coronal mass from the Sun on March 15. The initial velocity of the coronal masses’ propagation in space was about 668 km/s, which made it possible for the magnetic cloud, formed during this phenomenon, to reach the area around the Earth on 17 March at 03:59 UT [27]. As a result of the interaction of echoes of coronal ejection with the magnetic field of the Earth, a geomagnetic storm was formed. The measurements conducted on that day showed a very low value of the disturbance storm time (Dst) parameter, which was −223 nT during the storm (Figure 1a). This allows it to be classified as a G4 (severe) geomagnetic storm [28]. This is also confirmed by a very strong total interplanetary magnetic field, which was over 35 nT about 13:30 UT on 15 March (Figure 1b). In Figure 1, we also present the planetary 3-h range Kp index to show the size of geomagnetic field variations caused by the system irregulars. All these parameters indicate that it was the most intense geomagnetic storm of the 24th solar cycle [29].
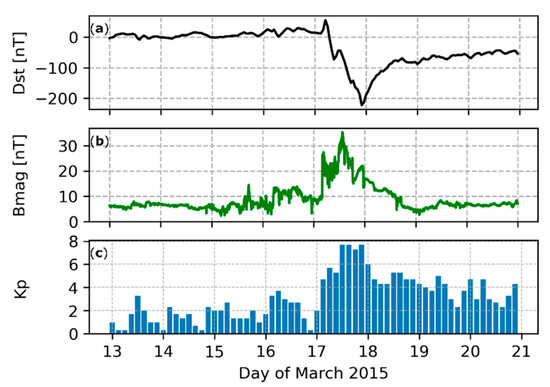
Figure 1.
The disturbance storm time (Dst) index (a), the total interplanetary magnetic field (Bmag, b), and planetary Kp index (c), between 13 and 21 March 2015. The occurrence of a very strong geomagnetic storm on 17 March 2015 is clearly visible.
3. Methodology and Data
In this study, we used 30-s GPS observations derived from 15 reference stations belonging to a national ASG-EUPOS network (Figure 2a). Calculations were performed for two days, i.e., the one on which the geomagnetic storm disturbance occurred (17 March 2015) and a quiet day as a reference (13 March 2015). The gLAB 5.4.4 software [30] was used for obtaining the kinematic PPP solution for each station with an interval equal to the data acquisition. The advantage of the gLAB software is epoch-by-epoch processing using the Kalman filter, which is very similar to the approach used in real-time processing. To ensure high accuracy and precision of the PPP solution, it is necessary that precise ephemeris and clocks of the satellites be used. In this study, products from the International GNSS Service were applied [31]. This allowed us to achieve a position with an accuracy of about 3 cm [32]. First-order ionospheric delays were reduced using dual-frequency observations, while tropospheric effects were eliminated by estimating correction to the a priori tropospheric delay. To reduce the multipath effect and remove signals passing low above the horizon, we adopted a 10° elevation mask. In addition, we considered satellites’ and receivers’ antenna phase center offsets and their variations, relativistic effects, as well as wind-up and solid-tide corrections. Cycle slips (CSs) were detected using two methods based on the Melbourne–Wübbena [33] and the geometry-free [34] linear combinations.
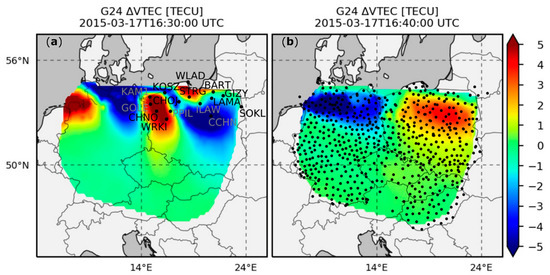
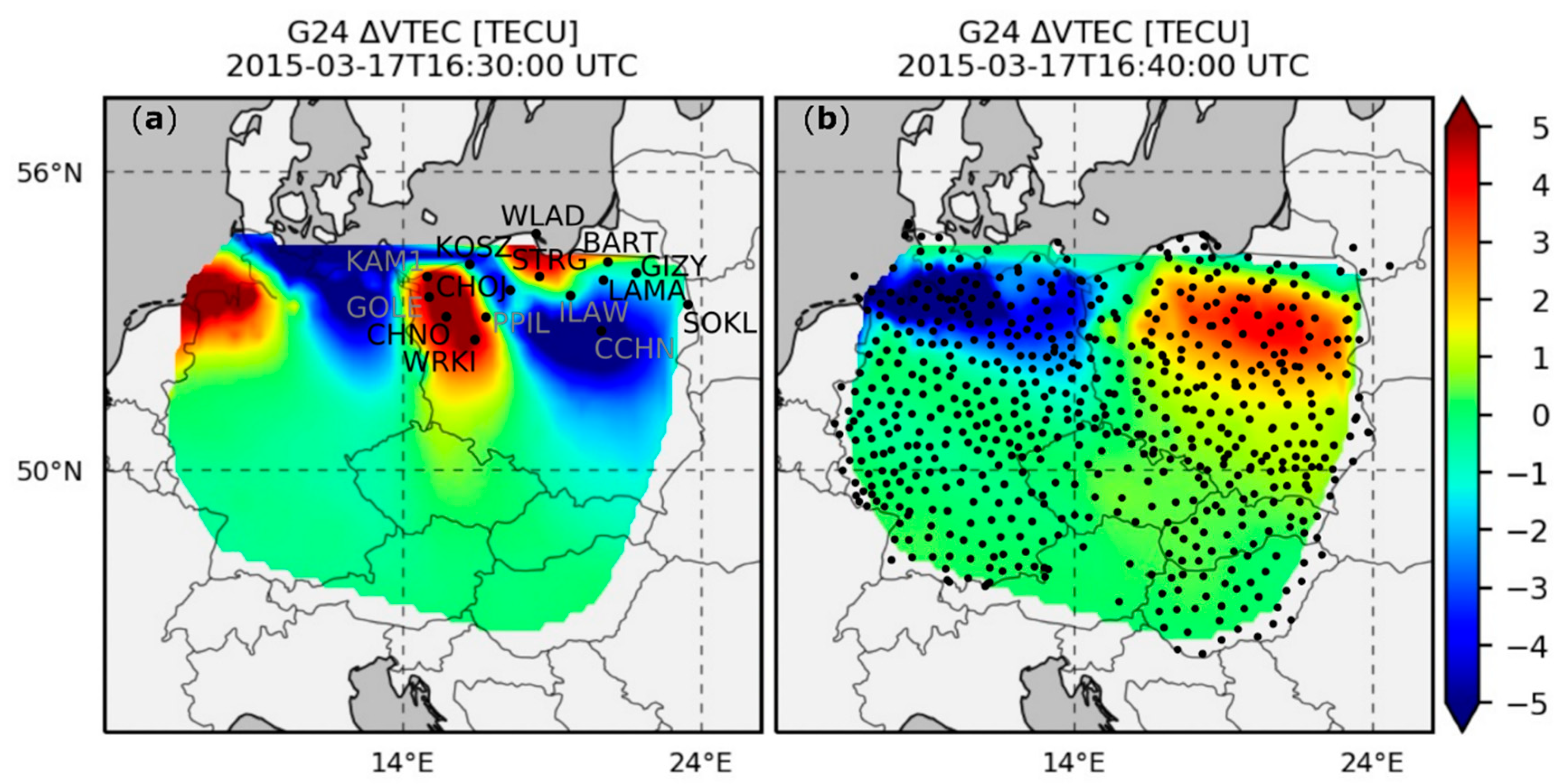
Figure 2.
Distribution of the stations analyzed in this study (a) and stations used for the estimation of traveling ionospheric disturbances (TIDs) (b) on the background of TIDs that occurred on 17 March 2015 at 16:30 (a) and 16:40 (b) UT.
In order to determine the impact of TIDs on the position, we estimated vertical total electron content (VTEC) variations (ΔVTEC) based on observations from 650 reference stations (Figure 2b; coordinates presented in Table A1 in the Appendix A). For each station–satellite pair, ΔVTEC time series were determined according to the methodology described by Nykiel et al. [24,26]. The use of a dense network of receivers allowed us to obtain maps for individual satellites. These maps are characterized by high 0.1° spatial resolution. The time resolution was consistent with the observation data (30 s), so it was possible to compare positioning results with ΔVTEC data explicitly. Examples of ΔVTEC maps showing the movement of TIDs determined from signals of GPS satellite number 24 are shown in Figure 2. As presented by Nykiel et al. [24], during the active phase of the storm (between 16:00 and 19:00 UTC) the RMS value of ΔVTEC maps amounted to more than 1 TECU, which is significantly higher than the average value estimated for quiet days (0.1 TECU). Moreover, at this time, the main direction of the motion of the inhomogeneities was from east to west with a velocity of about 1 km/s.
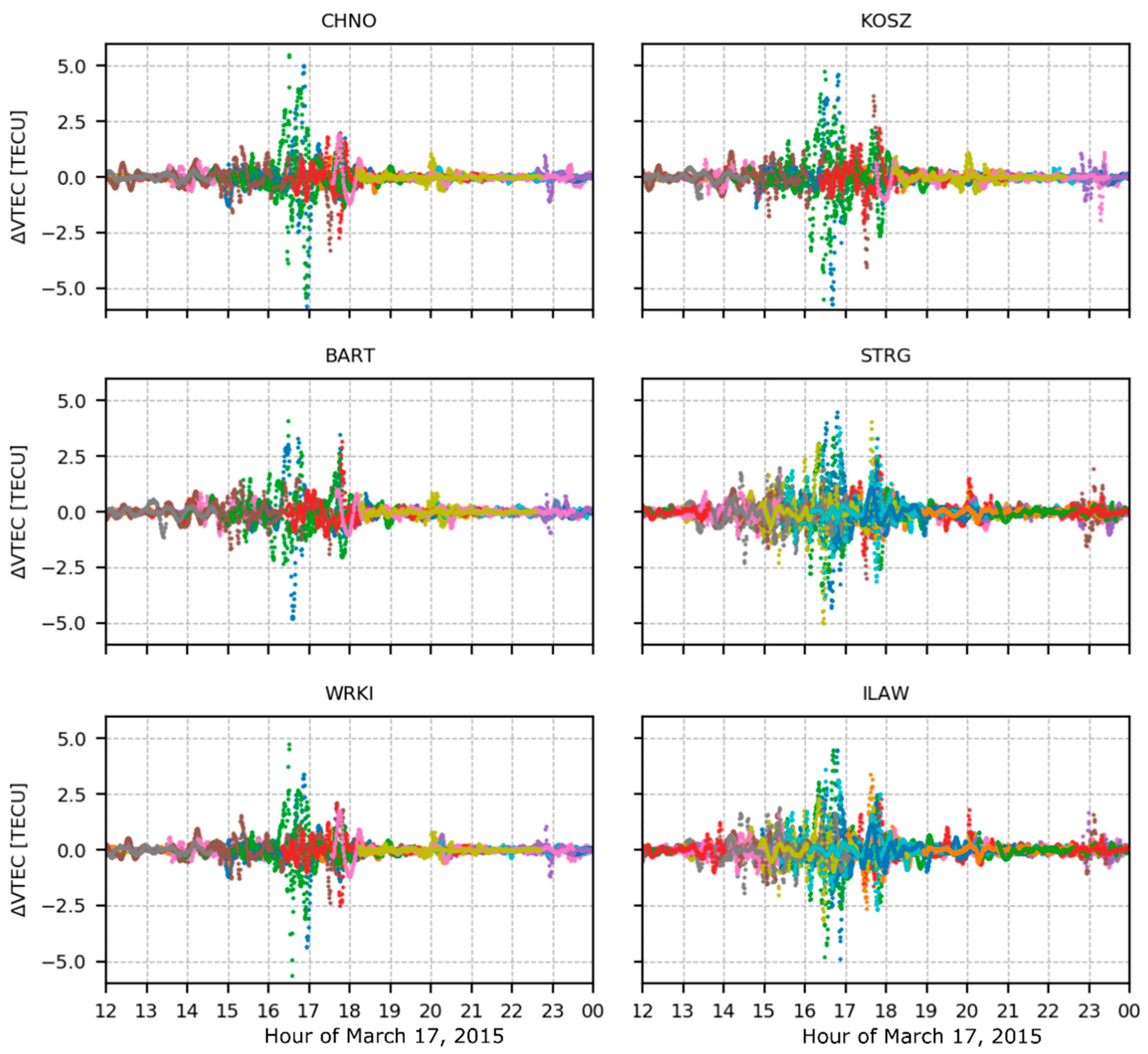
Figure 3 shows ΔVTEC results of GPS/GLONASS satellites for selected stations analyzed in this study. The TIDs between 16 and 18 UT, causing VTEC disturbances of up to ±5 TECU, are clearly visible. They translate into signal delays of about 0.8 m on L1 frequency. Such sudden and considerable ΔVTEC jumps can affect the quality of satellite tracking and, consequently, positioning results.
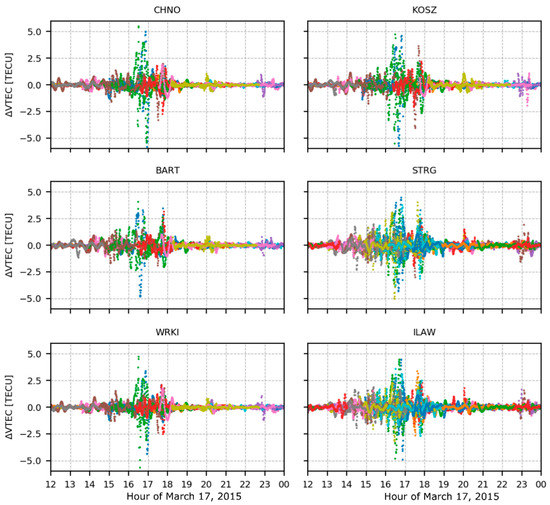
Figure 3.
Variations of vertical total electron content (VTEC) derived from GPS/GLONASS measurements observed by the selected stations. TIDs induced by the geomagnetic storm are clearly visible between 16 and 18 UT of 17 March 2015. Different colors represent data for different observed satellites.
4. Results
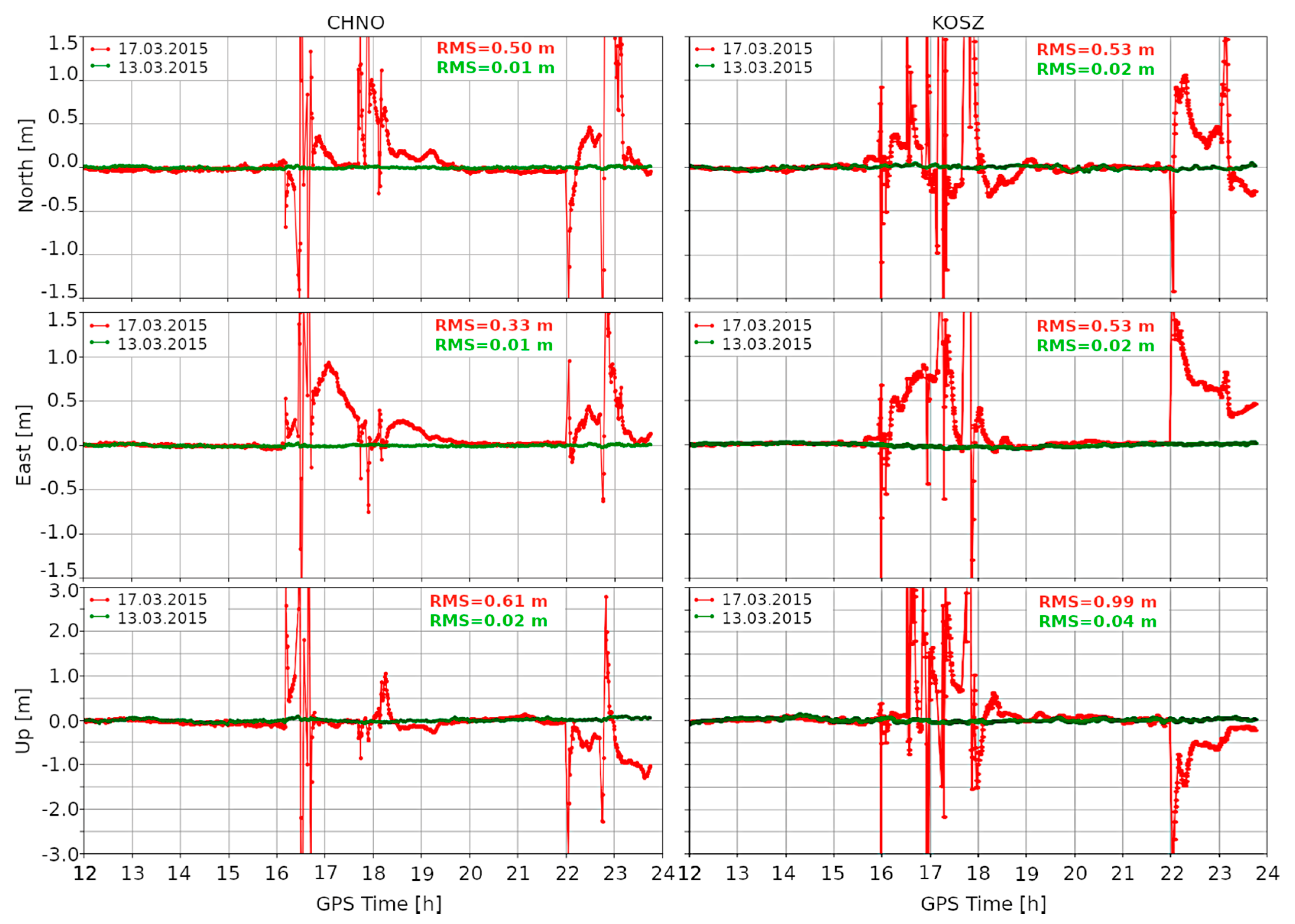
In this section, we present results of the coordinates’ estimation conducted for the quiet (13 March) and the stormy (17 March) days. For the example of the CHNO (Figure 4, left) and KOSZ (Figure 4, right) stations, it can be observed how the position was changing depending on the ionospheric conditions. In both these cases, time series of topocentric coordinates clearly varied during the day with ionospheric disturbances (the red line) compared to the quiet day (the green line). The position variations can be observed in two main episodes. The first episode started around 16:00 and lasted until 19:00, while the second one started around 22:00 and lasted until the end of the day. The occurrence of position degradation is consistent with TIDs’ appearance presented in Figure 3. In Figure 4, a slight delay between the disturbances in the KOSZ and CHNO stations is visible, which is due to the TIDs’ movement.
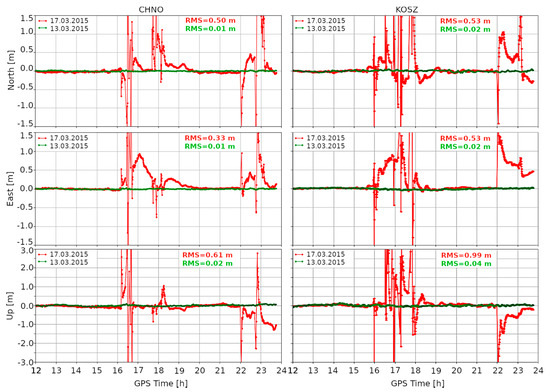
Figure 4.
Topocentric coordinates for the quiet (13 March 2015, the green line) and the stormy (17 March 2015, the red line) days; for example, the ASG-EUPOS reference stations of CHNO and KOSZ. The horizontal axis is shown for hours between 12 and 24 (GPS time) to better highlight the differences.
The position degradation is evidenced in RMS values. During the quiet day, the RMS of horizontal coordinates was in the range of 0.01 and 0.02 m for the CHNO and KOSZ stations, respectively. At the same time, the RMS of the vertical component was only slightly higher and amounted to 0.03 and 0.04 m. Significantly higher values were obtained during the stormy day. For the CHNO station, they were 0.50, 0.32, and 0.63 m for North, East, and Up components, respectively, whereas for KOSZ they were 0.53, 0.53, and 0.99 m, respectively.
The detailed information regarding the impact of ionospheric disturbances on the position quality can be found in Appendix A, which contains differences in North (Figure A1), East (Figure A2), and Up (Figure A3) components, between the stormy day and the reference day. To underline the impact of the geomagnetic storm itself, the time span of the analyzed data was reduced to the 12:00–24:00 GPS period. For the North component, it was observed that ionospheric anomalies did not equally affect all stations. It is clearly visible that each station is represented by slightly different variations. Although, for most of them, the first episode of coordinate variations started around 16:00 and lasted three hours, for three stations (CCHN, ILAW, and WRKI) it started around 17:30 and lasted only half an hour. Similar discrepancies were found for the second episode. For most of the stations, it occurred between 22:00 and 24:00, while three stations (CCHN, GIZY, ILAW) were not clearly affected by the second ionospheric event. In the case of the East component, the distribution of the occurrence of both episodes was similar to the case of the North component differences. The exceptions here were the STRG and CHOJ stations, for which the variations obtained in the second episode were almost negligible. Variations in the vertical coordinates during both ionospheric episodes were similar to those found for horizontal components. The ionospheric storm had the least impact on the position quality at the ILAW and CCHN stations, while the WLAD station seems to have been affected the most.
The RMS positions obtained for the topocentric coordinates are summarized in Table 1. They were calculated for both the quiet day and the stormy day between 12:00 and 24:00 GPS time. While the quiet day was characterized by the average RMS equal to 0.02, 0.02, and 0.03 m, for the North, the East, and the Up components, respectively, the maximum RMS value did not exceed 0.05 m in any case. In contrast to this, much greater discrepancies between the coordinates took place in the occurrence of ionospheric disturbances. This can be observed, among others, in the average RMS that was equal to 0.37, 0.26, and 0.58 m for the North, the East, and the Up components, respectively. For the northern coordinate, the RMS varied from 0.13 m (ILAW) to 0.69 m (WLAD), and for most of the stations it ranged from 0.20 m to 0.50 m. Slightly lower values were observed for the eastern coordinate. In this case, the RMS varied from 0.06 m (CCHN, ILAW) to 0.53 m (KOSZ), and for most of the stations it ranged from 0.20 m to 0.30 m. A similar distribution of the lowest and the highest RMS was observed for the Up component, for which it varied from 0.06 m (ILAW) up to 1.37 m (WLAD). Although, in general, the vertical coordinate is characterized by lower-quality GNSS processing compared to the horizontal ones, three stations (CCHN, ILAW, and SOKL) obtained RMS values of the Up component lower than those of the North or the East components. It is worth noting that the high RMS value does not fully reflect position quality. Based on the presented results, it is clear that during the main phase of the geomagnetic storm it was impossible to determine the precise position correctly. For all the analyzed stations, the accuracy was exceptionally low and, in many cases, far worse than 1.5 m for all the components. Moreover, for several times, the position was not estimated at all.

Table 1.
Summary of the root mean square (RMS) values for the analyzed Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) stations on the quiet day (13 March 2015) and the stormy day (17 March 2015) for the hour range 12:00–24:00 GPS time.
5. Discussion
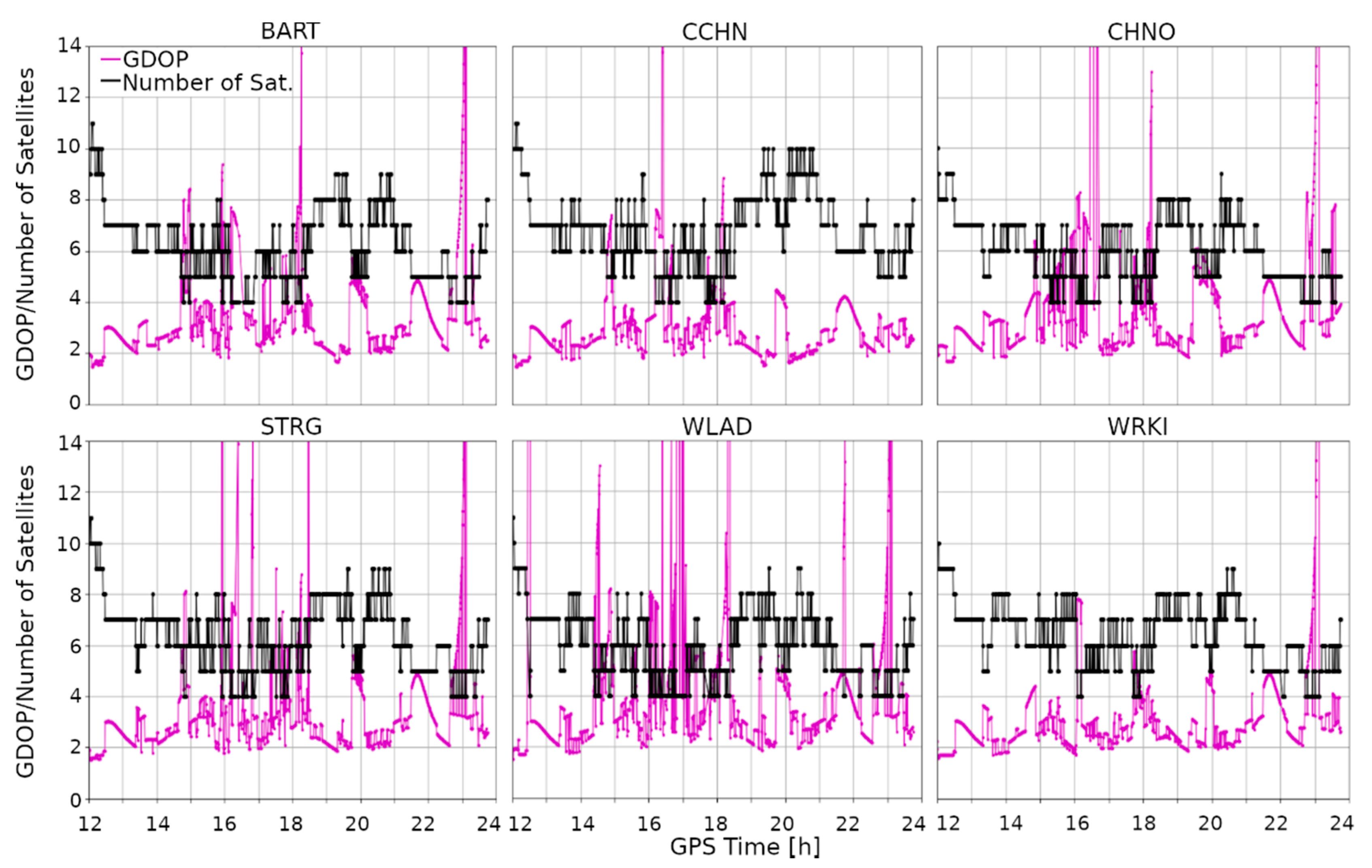
Above, we presented results for the kinematic PPP determination. Clearly, ionospheric disturbances had a considerable negative impact on solution accuracy. In this section, we discuss why this decreased accuracy is so significant. In Figure 5, the number of satellites used for position estimation is shown for each of the analyzed stations. It can be seen that, during the geomagnetic storm, the number of the used satellites falls significantly to 4, which directly translates to the value of the geometrical dilution of precision (GDOP) factor (Figure 5, the magenta line). Its value is inversely proportional to the number of satellites. Here, we can observe high GDOP values, which at some moments were even greater than 14. This means that the estimated position was characterized by a low confidence level. High GDOP values are strictly correlated with compromised accuracy, which is clearly noticeable in the presented results (Figure A1, Figure A2 and Figure A3). Above, we show epochs when the positions were estimated. However, it is worth noting that, in some cases, the number of observed satellites was so low that the position equations could not be resolved. Such data breaks occurred most often for the WLAD (23 breaks) and KOSZ (17 breaks) stations. The average number of missing epochs was 10.
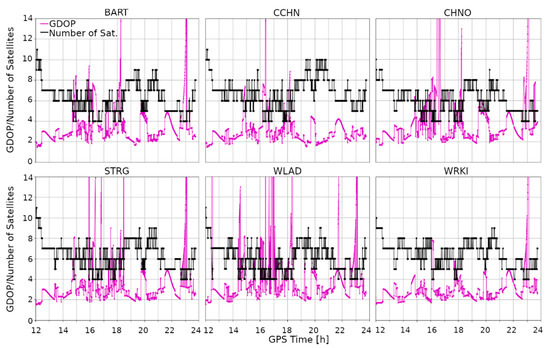
Figure 5.
The number of satellites used for calculations (the black line) and the value of the geometrical dilution of precision (GDOP) (the magenta line) on 17 March 2015 for the hour range 12:00–24:00 for the analyzed stations.
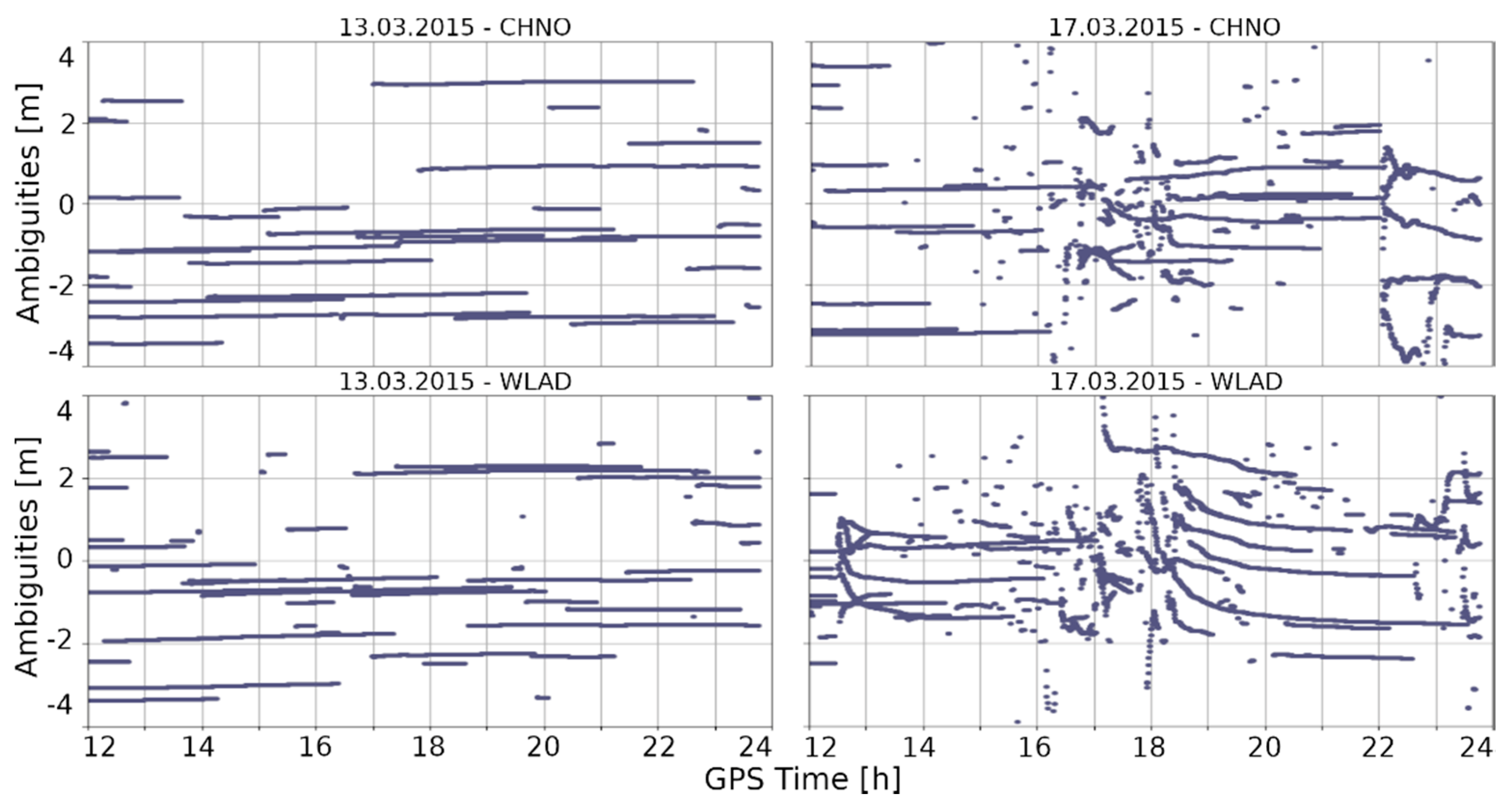
We determined the cause of these drops in the number of satellites. In Figure 6, we present the values of the estimated phase ambiguities. Clearly, no significant deterioration in ambiguity resolution was observed during calm ionospheric conditions (Figure 6, left). In contrast to this, the occurrence of ionospheric disturbances resulted in a clear degradation of ambiguity resolution at each of the analyzed stations (Figure 6, right). In most cases, this took place during two episodes, namely, at 16:00–19:00 and 22:00–24:00 GPS time, exactly at the same time as in the case of the previously analyzed disorders. The effect characterized by a leap in the phase of the signal received from the satellite is called a cycle slip (CS). As a result of a CS, a given satellite cannot be used for solving the position. When this situation occurs for many satellites, determining the high accuracy position proves impossible. Moreover, here we can observe that ambiguities estimated during the main phase of the storm are very dispersed, which makes it difficult to apply CS repairing methods.
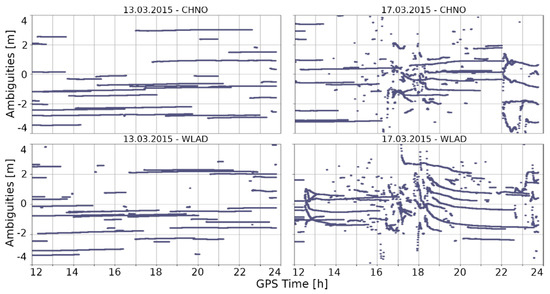
Figure 6.
Results of ambiguity estimations on the quiet day (13 March 2015 and on the stormy day (17 March 2015). A significant number of CSs is visible in the main phase of the geomagnetic storm.
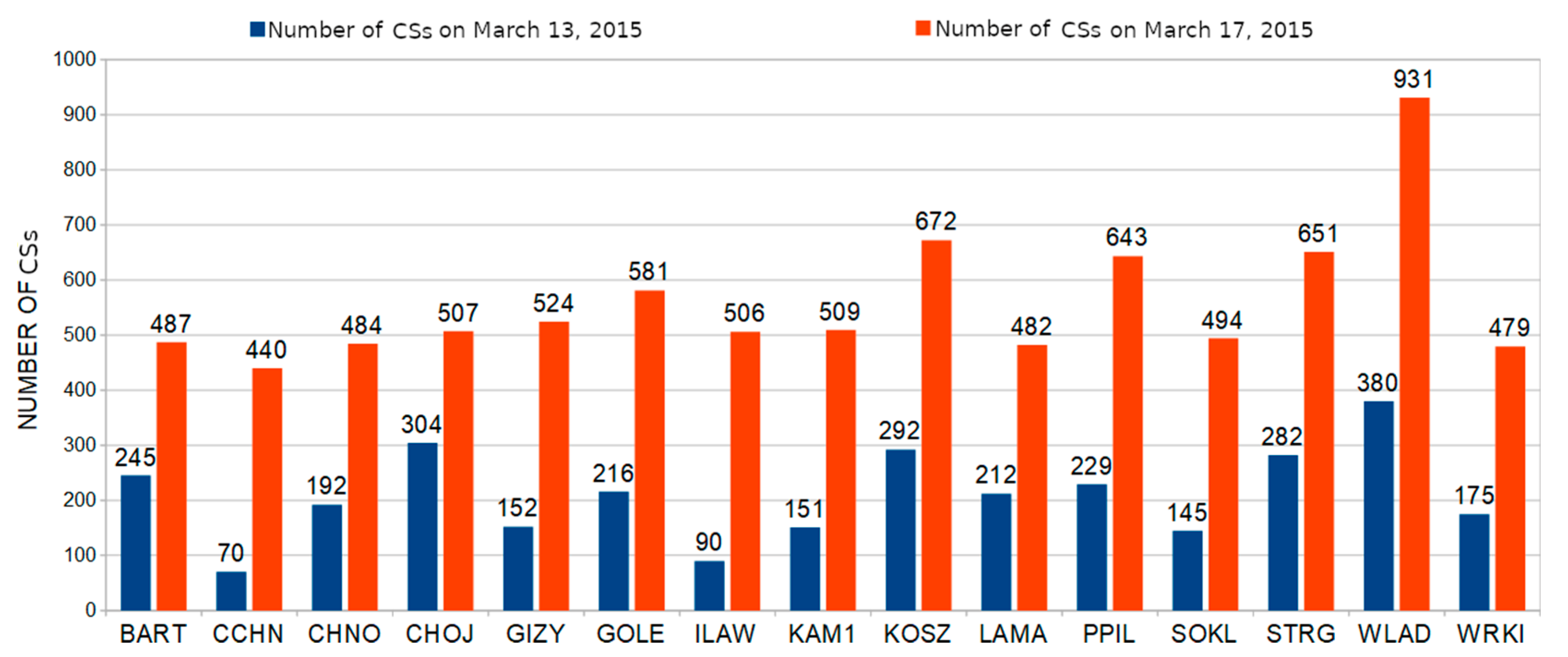
In Figure 7, the total number of CSs that occurred is shown for each of the analyzed stations. As can be seen, on the stormy day there were significantly more CSs than on the quiet day. The highest number of CSs occurred for the measurements at the WLAD station and amounted to 931 between 12:00 and 24:00 GPS time. This result is over twice as high as that observed for this station on the calm day. The second largest difference was recorded for the ILAW station, where the difference between the number of CSs for these two days was 416, meaning that the number of CSs observed on the stormy day was five times higher. Similar results were obtained for the CCHN station, where the number of the CSs observed during the stormy day was six times higher than that recorded on the calm day. The average number of CSs on the quiet day was 209, while on the stormy day it was estimated at 559, which is about 2.5 times more.
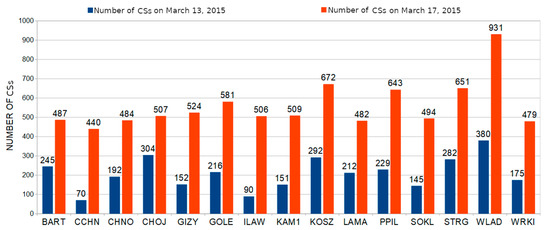
Figure 7.
Number of the cycle slips (CSs) that occurred on the quiet day (13 March 2015, in blue) and on the stormy day (17 March 2015, in red) for the hours between 12:00 and 24:00 GPS time.
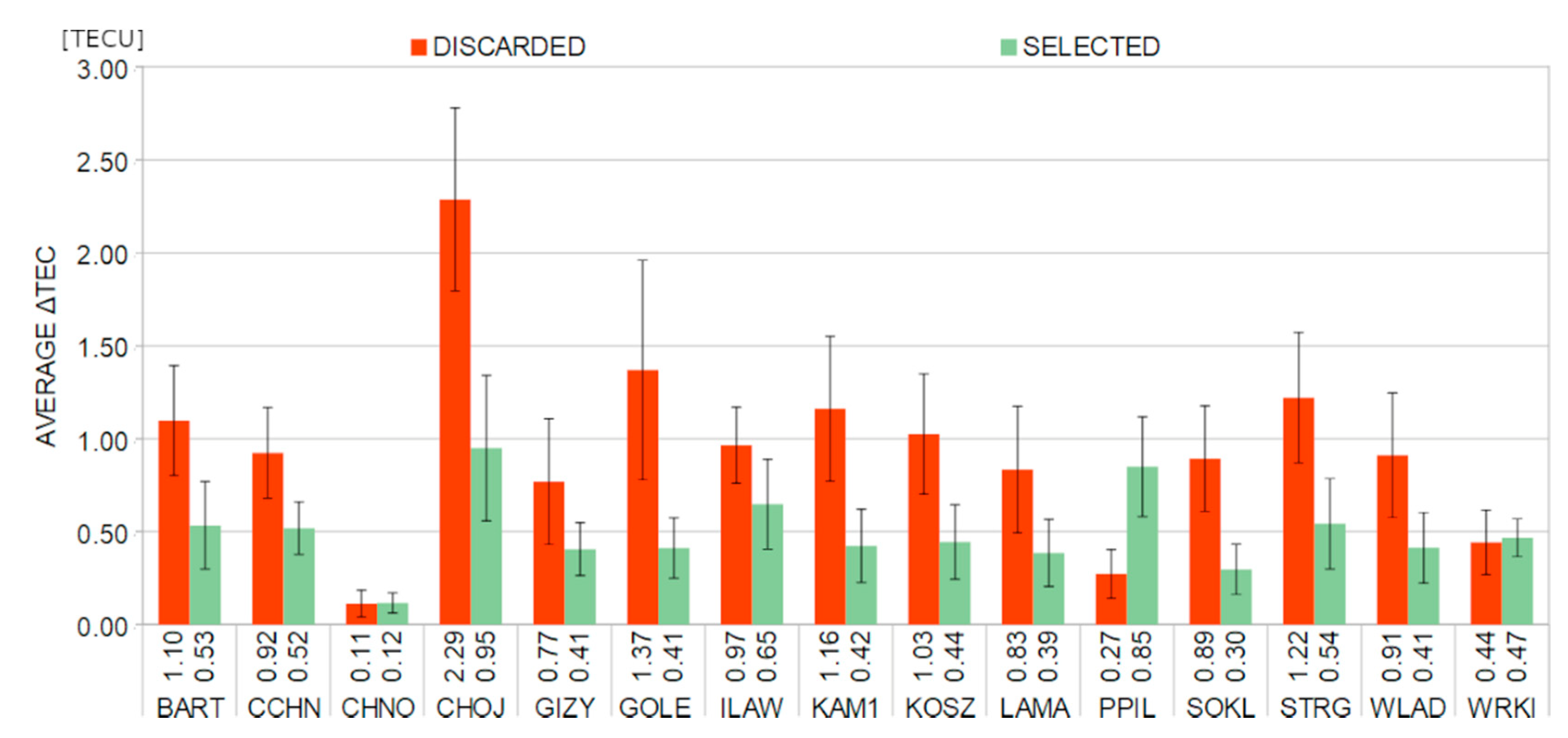
To clearly show the impact of TIDs on discarded satellites from positioning, we estimated the average ΔVTEC for each station. Figure 8 presents the values of ΔVTEC for selected (included in positioning) and discarded satellites. In general, for discarded observations the ΔVTEC was about 0.95 ± 0.49 TECU, which is twice as high as the value for the selected measurements (0.49 ± 0.20 TECU). In most cases, the ΔVTEC for excluded observations is significantly higher. The highest value was observed at the CHOJ station and amounted to 2.29±1.48 TECU, which is over twice as high as the result for the selected observations (0.95 ± 1.17 TECU). The three stations (CHNO, PPIL, and WRKI) are the exceptions. In these cases, the ΔVTEC of discarded observations is similar (WRKI and CHNO) or lower (PPIL) compared to the considered ones. This is due to the fact that the occurrence of CSs is determined not solely by the average value of ΔVTEC but also by the rapidity of its changes.
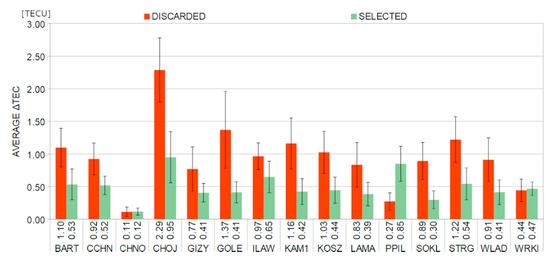
Figure 8.
Average values of ΔVTEC for the discarded (red bars) and selected (green bars) measurements during the main phase of the St. Patrick’s Day geomagnetic storm. The average values were calculated using the absolute values of ΔTEC. The error bars are given on a 1:3 ratio.
6. Conclusions
The analyzed geomagnetic storm was the result of coronal masses ejected from the Sun that reached the Earth’s atmosphere on 17 March 2015. The ionospheric disturbances it caused clearly affected the quality of position determination based on the GNSS technique. Based on the measurements derived from the 15 reference stations of the ASG-EUPOS network, a position with an interval of 30 s was estimated using the kinematic PPP method.
In this paper, we showed the impact of the St. Patrick’s Day storm on position. We observed a clear decrease in position accuracy in the main phase of the storm, during which high-intensity medium-scale TIDs occurred. Decreased accuracy was observed at all the analyzed stations and was caused by a fall in the number of satellites considered in positioning. We showed that the sudden drop in their number was caused by numerous occurrences of CSs, which made the satellites discarded in specific epochs. By analyzing the values of and changes in ΔVTEC over time for each of the receiver–satellite pairs, we proved that the occurrence of CSs was caused by TIDs. Moreover, in some cases, the decrease in the number of satellites was so severe that determining the position was impossible. On the day when the geomagnetic storm occurred, the RMS of the position was 0.37 ± 0.16, 0.26 ± 0.12, 0.58 ± 0.33 m on average for the North, East, Up topocentric components, respectively. For comparison, for the quiet day these values ranged from 0.02 to 0.03 m. We showed that, during the TIDs’ transition, the CS occurrences were several times greater than during the quiet day. Furthermore, given the determined ambiguities, we claim that, during the storm, correct tracking of the phase of the signal proved troublesome for the receivers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.N.; methodology, M.P. and G.N.; software, M.P.; validation, M.P.; formal analysis, M.P. and G.N.; investigation, M.P.; writing—original draft preparation, M.P.; writing—review and editing, G.N.; visualization, M.P. and G.N.; supervision, G.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The Kp index data used in this study were provided by the GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences, Potsdam, Germany. The authors would like to thank the Polish Head Office of Geodesy and Cartography, Warsaw, Poland, for the data from the ASG-EUPOS network.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Coordinates of the GNSS stations used in this study.
Table A1.
Coordinates of the GNSS stations used in this study.
| Station Name | Latitude | Longitude | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BART | 54°15″02.52′ | 20°48″55.57′ | 93.2 |
| CCHN | 52°52″58.03′ | 20°35″52.18′ | 167.7 |
| CHNO | 53°09″50.58′ | 15°24″50.54′ | 105.4 |
| CHOJ | 53°41″42.65′ | 17°33″08.47′ | 204.1 |
| GIZY | 54°02″08.81′ | 20°10″02.53′ | 166.8 |
| GOLE | 53°33″31.36′ | 14°50″16.81′ | 68.8 |
| ILAW | 53°35″13.64′ | 19°34″04.66′ | 162.8 |
| KAM1 | 53°57″47.01′ | 14°46″38.61′ | 57.8 |
| KOSZ | 54°12″12.19′ | 16°11″51.79′ | 123.2 |
| LAMA | 53°53″32.63′ | 20°40″11.77′ | 187.0 |
| PPIL | 53°09″25.11′ | 16°44″17.73′ | 121.7 |
| SOKL | 53°24″30.75′ | 23°29″44.66′ | 222.2 |
| STRG | 53°57″58.70′ | 18°31″47.96′ | 136.3 |
| WLAD | 54°47″48.32′ | 18°25″07.49′ | 34.7 |
| WRKI | 52°42″19.98′ | 16°22″15.87′ | 95.3 |
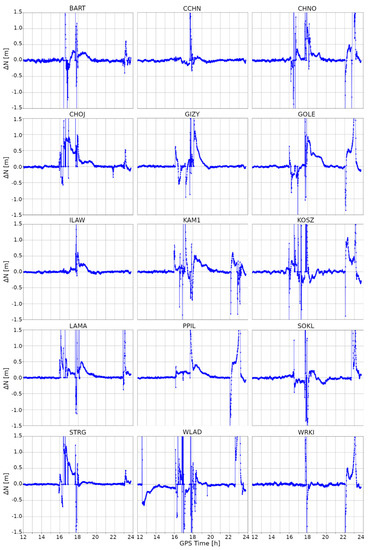
Figure A1.
Difference of North component between kinematic PPP solutions obtained for a quiet day (13 March 2015) and a stormy day (17 March 2015).
Figure A1.
Difference of North component between kinematic PPP solutions obtained for a quiet day (13 March 2015) and a stormy day (17 March 2015).
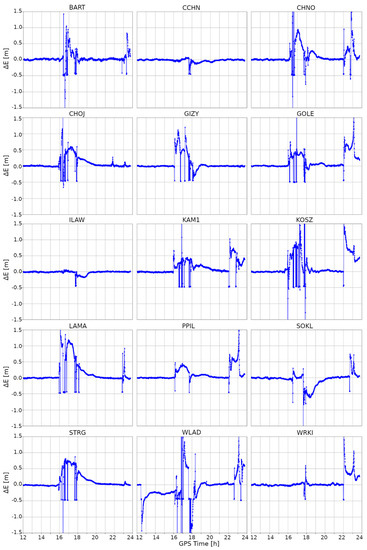
Figure A2.
Difference of East component between kinematic PPP solutions obtained for a quiet day (13 March 2015) and a stormy day (17 March 2015).
Figure A2.
Difference of East component between kinematic PPP solutions obtained for a quiet day (13 March 2015) and a stormy day (17 March 2015).
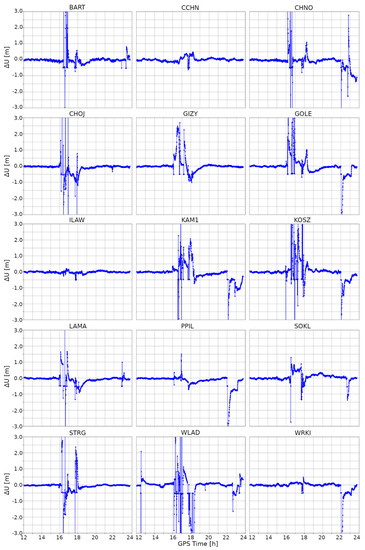
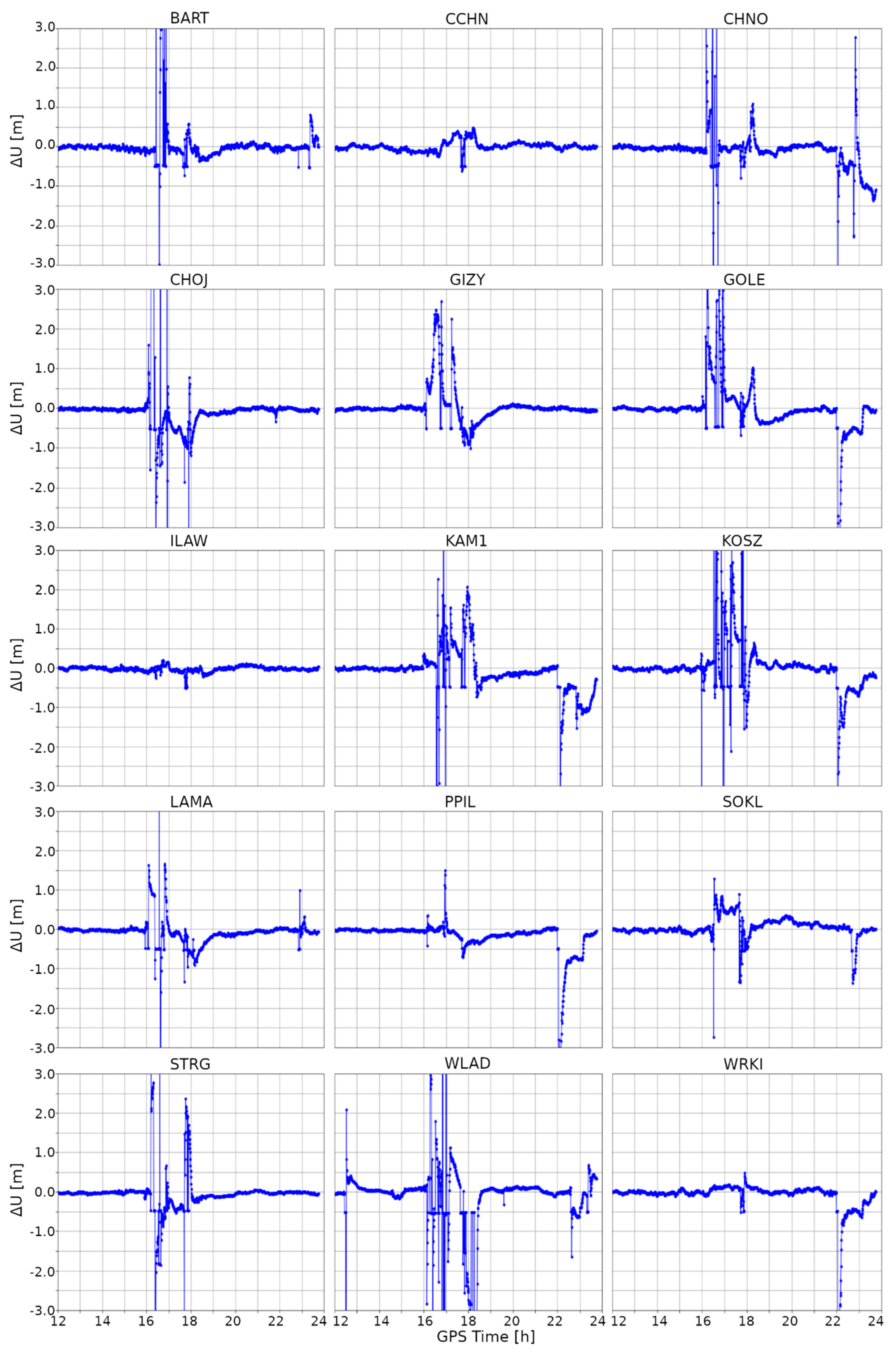
Figure A3.
Difference of Up component between kinematic PPP solutions obtained for a quiet day (13 March 2015) and a stormy day (17 March 2015).
Figure A3.
Difference of Up component between kinematic PPP solutions obtained for a quiet day (13 March 2015) and a stormy day (17 March 2015).
References
- Klobuchar, J.A. Ionospheric Time-Delay Algorithm for Single-Frequency GPS Users. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1987, 3, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. European GNSS (Galileo) Open Service—Ionospheric Correction Algorithm for Galileo Single Frequency Users; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2016; Issue 1.2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Zishen, L.; Li, M.; Yuan, Y.; Huo, X. GPS, BDS and Galileo ionospheric correction models: An evaluation in range delay and position domain. J. Atmospheric Solar-Terrestrial Phys. 2018, 170, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, E.D.; Hegarty, C.J. Characterisation of GNSS Space Service Volume. In Understanding GPS: Principles and Applications, 2nd ed.; Artech House Inc.: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wielgosz, P.; Kashani, I.; Grejner-Brzezinska, D. Analysis of long-range network RTK during a severe ionospheric storm. J. Geod. 2005, 79, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Pajares, M.; Juan, J.M.; Sanz, J.; Orús, R. Second-order ionospheric term in GPS: Implementation and impact on geodetic estimates. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, B08417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J.; Héroux, P. Precise point positioning using IGS orbit and clock products. GPS Solutions 2001, 5, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Gendt, G.; Rothacher, M.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Resolution of GPS carrier-phase ambiguities in Precise Point Positioning (PPP) with daily observations. J. Geod. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veettil, S.V.; Aquino, M.; Marques, H.A.; Moraes, A. Mitigation of ionospheric scintillation effects on GNSS precise point positioning (PPP) at low latitudes. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, H.A.; Marques, H.A.S.; Aquino, M.; Veettil, S.V.; Monico, J.F.G. Accuracy assessment of Precise Point Positioning with multi-constellation GNSS data under ionospheric scintillation effects. J. Space Weather. Space Clim. 2018, 8, A15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, G.; Azeem, I. Extreme Ionospheric Storms and Their Effects on GPS Systems. Extreme Events Geospace 2018, 555–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, D.; Shengyue, J.; Wu, C.; Zhizhao, L. Assessment and Mitigation of Ionospheric Disturbance Effects on GPS Accuracy and Integrity. J. Navig. 2014, 67, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Crowley, G.; Azeem, I.; Reynolds, A.; Duly, T.M.; McBride, P.; Winkler, C.; Hunton, D. Analysis of traveling ionospheric disturbances (TIDs) in GPS TEC launched by the 2011 Tohoku earthquake. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Yao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Kuo, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhai, C. A clear link connecting the troposphere and ionosphere: Ionospheric reponses to the 2015 Typhoon Dujuan. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Gu, S.; Lou, Y.; Xiong, C.; Chen, B.; Jin, X. Assessing the Performance of GPS Precise Point Positioning Under Different Geomagnetic Storm Conditions during Solar Cycle 24. Sensors 2018, 18, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.V.S.R.; Krishna, S.G.; Prasad, J.V.; Prasad, S.N.V.S.; Prasad, D.S.V.V.D.; Niranjan, K. Geomagnetic storm effects on GPS based navigation. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, B.; Radicella, S.; de Lacy, M.C.; Herraiz, M.; Rodriguez-Caderot, G. On the effects of the ionospheric disturbances on precise point positioning at equatorial latitudes. GPS Solutions 2011, 15, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, K.S.; Andalsvik, Y.L. Overview of the 2015 St. Patrick’s day storm and its consequences for RTK and PPP positioning in Norway. J. Space Weather. Space Clim. 2016, 6, A9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ji, S.; Chen, W. Assessing the positioning performance under the effects of strong ionospheric anomalies with multi-GNSS in Hong Kong. Radio Sci. 2020, 55, e2019RS007004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasyukevich, Y.; Vasilyev, R.; Ratovsky, K.; Setov, A.; Globa, M.; Syrovatskii, S.; Yasyukevich, A.; Kiselev, A.; Vesnin, A. Small-Scale Ionospheric Irregularities of Auroral Origin at Mid-latitudes during the 22 June 2015 Magnetic Storm and Their Effect on GPS Positioning. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Pajares, M.; Juan, J.; Sanz, J.; Orus, R.; Garcia-Rigo, A.; Feltens, J.; Komjathy, A.; Schaer, S.; Krankowski, A. The IGS VTEC maps: A reliable source of ionospheric information since 1998. J. Geodesy 2009, 83, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krypiak-Gregorczyk, A.; Wielgosz, P.; Gosciewski, D.; Paziewski, J. Validation of approximation techniques for local total electron content mapping. Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2013, 10, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, C.; Wrasse, C.; Takahashi, H.; Otsuka, Y.; Shiokawa, K.; Barros, D. Large-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances observed by GPS dTEC maps over North and South America on Saint Patrick’s day storm in 2015. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 4755–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nykiel, G.; Zanimonskiy, Y.M.; Yampolski, Y.M.; Figurski, M. Efficient Usage of Dense GNSS Networks in Central Europe for the Visualization and Investigation of Ionospheric TEC Variations. Sensors 2017, 17, 2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yizengaw, E.; Moldwin, M. The altitude extension of the mid-latitude trough and its correlation with plasmapause position. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L09105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nykiel, G.; Zanimonskiy, Y.; Koloskov, A.; Figurski, M. The possibility of estimating the height of the ionospheric inhomogeneities based on TEC variations maps obtained from dense GPS network. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 64, 2002–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liou, K.; Lepping, R.P.; Hutting, L.; Plunkett, S.; Russ, A.H.; Socker, D. The first super geomagnetic storm of solar cycle 24: “The St. Patrick’s day event (17 March 2015)”. Earth Planets Space 2016, 68, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamide, Y.; Kusano, K. No Major Solar Flares but the Largest Geomagnetic Storm in the Present Solar Cycle. Space Weather 2015, 13, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watari, S. Geomagnetic storms of cycle 24 and their solar sources. Earth Planets Space 2017, 69, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, D.; Rovira-García, A.; Sanz, J.; Juan, J.M.; Gonzalez-Casado, G.; Jimenez-Baños, D.; López-Echazarreta, C.; Lapin, I. The GNSS Laboratory Tool Suite (gLAB) updates: SBAS, DGNSS and Global Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the 9th ESA Workshop on Satellite Navigation Technologies (NAVITEC 2018), Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 5–7 December 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, G.; Riddell, A.; Hausler, G. The International GNSS Service. In Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems, 1st ed.; Teunissen, P.J.G., Montenbruck, O., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 967–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliszek, D.; Szolucha, M.; Kroszczyński, K. Accuracy of Precise Point Positioning (PPP) with the use of different International GNSS Service (IGS) products and stochastic modelling. Geod. Cartography 2018, 67, 207–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewitt, G. An Automatic Editing Algorithms for GPS Data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann-Wellenhof, B.; Lichtenegger, H.K.; Wasle, E. GNSS-Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Springer: Wien, Austria, 2008. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).