Reversal of Aerosol Properties in Eastern China with Rapid Decline of Anthropogenic Emissions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Satellite Aerosol Products
2.2. AERONET Observations and Air Quality Monitoring Network
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. General Trends of the Aerosol Loading since Emission Reduction in 2013
3.2. The Transition of Aerosol Optical and Microphysical Properties
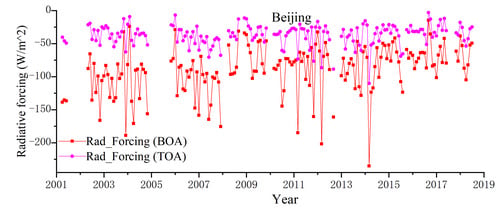
3.3. Influence and Implication of Drastic Changes in Aerosol Properties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramanathan, V.; Crutzen, P.J.; Kiehl, J.T.; Rosenfeld, D. Aerosols, Climate, and the Hydrological Cycle. Science 2001, 294, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pope, I.C.; Burnett, R.T.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.D. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IPCC. Climate Change: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.K., Tignor, M.M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M.P.M., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; 1535p. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanre, D.; Boucher, O. A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature 2002, 419, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G. Sulfur dioxide and primary carbonaceous aerosol emissions in China and India, 1996–2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9839–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Su, L.; Tao, J. Satellite observation of regional haze pollution over the North China Plain. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D12203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhao, H.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N.; Goloub, P.; Cuevas-Agulló, E.; Estelles, V.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; et al. Spatial distribution of aerosol microphysical and optical properties and direct radiative effect from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11843–11864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Li, C.; Chen, H.; Tsay, S.C.; Holben, B.; Huang, J.; Li, B.; Maring, H.; Qian, Y.; Shi, G.; et al. East Asian Studies of Tropospheric Aerosols and their Impact on Regional Climate (EAST-AIRC): An overview. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D00K34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Lau, W.M.; Ramanathan, V.; Wu, G.; Ding, Y.; Manoj, M.G.; Liu, J.; Qian, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, T.; et al. Aerosol and monsoon climate interactions over Asia. Rev Geophys. 2016, 54, 866–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Xia, X.; Tao, M.; Zhu, L. Modeling the feedback between aerosol and meteorological variables in the atmospheric boundary layer during a severe fog–haze event over the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 4279–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Guo, X.; Zhao, T.; An, X.; Zhao, Y.; Quan, J.; Mao, F.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, W.; et al. Are precipitation anomalies associated with aerosol variations over eastern China? Atmosp. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 8011–8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Su, T.; Li, Z.; Miao, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Cribb, M.; Zhai, P. Declining frequency of summertime local-scale precipitation over eastern China from 1970 to 2010 and its potential link to aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 5700–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Ding, A.; Liao, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Xue, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, B. Aerosol and boundary-layer interactions and impact on air quality. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 810–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, X.; Shao, M.; Hu, M.; Zeng, L.; Wu, Y.; Tan, T. The impact of aerosols on photolysis frequencies and ozone production in Beijing during the 4-year period 2012–2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 9413–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Tao, J.; Wang, X. Did the widespread haze pollution over China increase during the last decade? A satellite view from space. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 054019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonchyk, M.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Li, Y. Combined use of satellite and surface observations to study aerosol optical depth in different regions of China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; Geng, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhai, S.; Jacob, D.J.; Wang, X.; Shen, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Gui, K.; Zhao, T.; Liao, H. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) trends in China, 2013–2018: Separating contributions from anthropogenic emissions and meteorology. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11031–11041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, G.; He, K. Rapid transition in winter aerosol composition in Beijing from 2014 to 2017: Response to clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11485–11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Bates, K.H. Anthropogenic drivers of 2013–2017 trends in summer surface ozone in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, M.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Hou, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhu, H. How Do Aerosol Properties Affect the Temporal Variation of MODIS AOD Bias in Eastern China? Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, N.C.; Jeong, M.J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Hansell, A.M.; Seftor, C.S.; Huang, J.; Tsay, S.C. Enhanced Deep Blue aerosol retrieval algorithm: the second generation. J. Geohys. Res. 2013, 118, 9296–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Che, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Comparison and evaluation of the MODIS Collection 6 aerosol data in China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 6992–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garay, M.J.; Kalashnikova, O.V.; Bull, M.A. Development and assessment of a higher-spatial-resolution (4.4 km) MISR aerosol optical depth product using AERONET-DRAGON data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahn, R.A.; Gaitley, B.J.; Garay, M.J.; Diner, D.J.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N. Multiangle Imaging SpectroRadiometer global aerosol product assessment by comparison with the Aerosol Robotic Network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kahn, R.; Chin, M.; Garay, M.J.; Liu, Y. Improving satellite-retrieved aerosol microphysical properties using GOCART data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1157–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahn, R.A.; Gaitley, B.J. An analysis of global aerosol type as retrieved by MISR. J. Geohys. Res. 2015, 120, 4248–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanre′, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; King, M.D. A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 20673–20696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; King, M.D.; Tanré, D.; Slutsker, I. Variability of Absorption and Optical Properties of Key Aerosol Types Observed in Worldwide Locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 database—Automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for Sun photometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, J.Y.; Shen, X.J.; Zhang, Y.M.; Che, H.; Ma, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ogren, J.A. Observations of relative humidity effects on aerosol light scattering in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8439–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.T.; McElroy, M.B. Detection from space of a reduction in anthropogenic emissions of nitrogen oxides during the Chinese economic downturn. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8171–8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Ma, P.; Tao, J.; Jia, S. A study of urban pollution and haze clouds over northern China during the dusty season based on satellite and surface observations. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 82, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, B.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Lin, J.; Fu, T.M.; Zhang, Q. Exploring 2016–2017 surface ozone pollution over China: Source contributions and meteorological influences. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8339–8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matus, A.V.; L’Ecuyer, T.S.; Henderson, D.S. New Estimates of Aerosol Direct Radiative Effects and Forcing From A-Train Satellite Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 8338–8346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Site | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 85.1 ± 64.5 | 85.3 ± 69.1 | 79.1 ± 70.9 | 71.1 ± 69.1 | 57.0 ± 54.4 | 49.5 ± 42.7 |
| Shijiazhuang | 149.3 ± 110.9 | 125.6 ± 97.4 | 86.9 ± 65.5 | 94.6 ± 88.4 | 81.4 ± 62.6 | 69.5 ± 49.5 |
| Xuzhou | 73.8 ± 43.2 | 67.0 ± 43.2 | 63.6 ± 37.9 | 59.7 ± 40.2 | 67.2 ± 42.0 | 66.2 ± 47.8 |
| Zhengzhou | 109.0 ± 72.3 | 87.9 ± 50.2 | 94.9 ± 59.4 | 77.7 ± 68.7 | 70.7 ± 53.4 | 64.1 ± 49.9 |
| Nanjing | 77.3 ± 49.5 | 73.9 ± 40.5 | 56.6 ± 35.8 | 47.5 ± 31.4 | 40.7 ± 28.9 | 43.1 ± 32.6 |
| Wuhan | 92.2 ± 64.9 | 80.7 ± 50.3 | 69.2 ± 42.5 | 56.2 ± 35.5 | 51.9 ± 34.8 | 47.9 ± 29.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J. Reversal of Aerosol Properties in Eastern China with Rapid Decline of Anthropogenic Emissions. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030523
Tao M, Wang L, Chen L, Wang Z, Tao J. Reversal of Aerosol Properties in Eastern China with Rapid Decline of Anthropogenic Emissions. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(3):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030523
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Minghui, Lili Wang, Liangfu Chen, Zifeng Wang, and Jinhua Tao. 2020. "Reversal of Aerosol Properties in Eastern China with Rapid Decline of Anthropogenic Emissions" Remote Sensing 12, no. 3: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030523
APA StyleTao, M., Wang, L., Chen, L., Wang, Z., & Tao, J. (2020). Reversal of Aerosol Properties in Eastern China with Rapid Decline of Anthropogenic Emissions. Remote Sensing, 12(3), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030523