Recognition of Water Colour Anomaly by Using Hue Angle and Sentinel 2 Image
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.2.1. In Situ Remote-Sensing Reflectance
2.2.2. Sentinel-2 Image Data and Pre-Processing
3. Study Methods
3.1. Accuracy Evaluation of Indices
3.2. Water Body Extraction
10.8ND(3,8) + 6.1ND(3,11) + 13.6ND(3,12) − 0.28ND(4,8) − 3.9ND(4,11) − 2.1ND(4,12) −
5.3ND(8,11) − 5.3ND(11,12) − 0.33
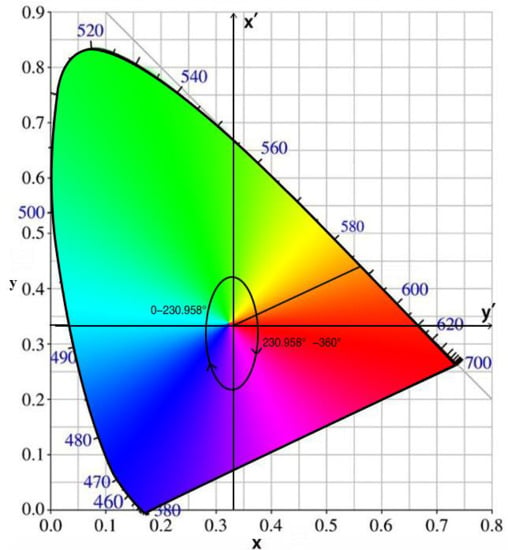
3.3. Calculation of the Hue Angle of the Water Body
Y = 1.0000R + 4.5907G + 0.0601B
Z = 0.0000R + 0.0565G + 5.5934B
y = Y/(X+Y+Z)
z = Z/(X+Y+Z)
3.4. Recognition of Water Colour Anomaly by Using the Hue Angle of the Water Body
4. Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Verification of the Hue Angle Threshold of a Water Body
5.2. Recognition of Water Colour Anomalies in the Xiong’an New Area
5.3. Reasonability Evaluation of the Proposed Recognition Method for Water Colour Anomaly
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xi, J. To Win the Great Victory of Socialism with Chinese Characteristics in the New Era by Building a Well-off Society in an All-round Way: A Report at the Nineteenth National Congress of the Communist Party of China. In October 2017. Available online: http://www.xinhuanet.com/2017-10/27/c_1121867529.htm (accessed on 27 October 2017).
- Xi, J. We Will Resolutely Fight Against Pollution and Promote the Construction of Ecological Civilization to a New Level. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2018-05/19/content_5292116.htm (accessed on 19 May 2018).
- The Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council. Opinions on Enhancing the Protection of Ecological Environment in an All-round Way and Fighting the Strong Battle of Pollution Prevention and Controlresolutely on 24 June 2018. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2018-06/24/content_5300953.htm (accessed on 24 June 2018).
- Ministry of Environmental Protection. Notice on the Investigation and Renovation of Pollutant Ponds. In EIO Environmental Supervision Letter [2017] 616; Ministry of Environmental Protection: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- National Development and Reform Commission. Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Cooperative Development of Eco-Environmental Protection Planning; National Development and Reform Commission: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Forel, F.A. Le Leman: Monographie limnologique; Rouge, F., Ed.; University of Michigan Library: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1892; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Novoa, S.; Wernand, M.R.; Van der Woerd, H.J. The Forel-Ule scale revisited spectrally: Preparation protocol, transmission measurements and chromaticity. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Rapid Publ. 2013, 8, 13057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfold, T.; Munday, J. Water Quality Analysis by Digital Chromaticity Mapping of Landsat Data. Canad. J. Remote Sens. 1978, 4, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernand, M.R.; Van der Woerd, H.J. Spectral analysis of the Forel-Ule Ocean colour comparator scale. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Rapid Publ. 2010, 5, 10014s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaquet, J.M.; Zand, B. Colour Analysis of Inland Waters Using Landsat TM Data. ESA SP 1989, 1102, 57–67. [Google Scholar]
- Bukata, R.P.; Bruton, J.E.; Jerome, J.H. Use of Chromaticity in Remote Measurement of Water Quality. Remote Sens. Environ. 1983, 13, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukata, R.P.; Jerome, J.H.; Kondatyev, K.Y.; Pozdnyokov, D.V.; Kotykhov, A.A. Modelling the Radiometric Colour of Inland Waters: Implications to a) Remote Sensing and b) Limnological Colour Scales. J. Great Lakes Res. 1997, 23, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörnhöfer, K.; Scholze, J.; Stelzer, K.; Oppelt, N. Water Colour Analysis of Lake Kummerow Using Time Series of Remote Sensing and In Situ Data. PFG J. Photogram. Remote Sens. Geoinform. Sci. 2018, 86, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, F.; Lu, Z. MODIS-Based Radiometric Colour Extraction and Classification of Inland Water with the Forel-Ule Scale: A Case Study of Lake Taihu. IEEE J. Select. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernand, M.R.; Hommersom, A.; van der Woerd, H.J. MERIS-based ocean colour classification with the discrete Forel–Ule scale. Ocean Sci. 2013, 9, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garaba, S.P.; Friedrichs, A.; Voß, D.; Zielinski, O. Classifying natural waters with the forel-ule colour index system: Results, applications, correlations and crowdsourcing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Pub. Health 2015, 12, 16096–16109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Shen, Q.; Peng, D.; Tian, L. MODIS observations of water colour of the largest 10 lakes in China between 2000 and 2012. Int. J. Dig. Earth 2016, 9, 788–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Ye, H.; Zhang, B. A CIE Colour Purity Algorithm to Detect Black and Odorous Water in Urban Rivers Using High-Resolution Multispectral Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6577–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudorff, N.; Rudorff, C.M.; Kampel, M.; Ortiz, G. Remote sensing monitoring of the impact of a major mining wastewater disaster on the turbidity of the Doce River plume off the eastern Brazilian coast. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 2018, 145, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oron, G.; Gitelson, A. Real-time quality monitoring by remote sensing of contaminated water-bodies: Waste stabilization pond effluent. Water Res. 1996, 30, 3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Tang, Z.; Li, J.; Lv, J.; Chen, Z.; Jia, K. Spatio-Temporal Change of Lake Water Extent in Wuhan Urban Agglomeration Based on Landsat Images from 1987 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wernand, M.R.; van der Woerd, H.J.; Gieskes, W.W. Trends in ocean colour and chlorophyll concentration from 1889 to 2000. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernand, M.R.; Hommersom, A.; van der Woerd, H.J. MERIS-based ocean colour classification with the discrete Forel–Ule scale. Ocean Sci. Discuss. 2012, 9, 2817–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed image. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcfeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated water extraction index: A new technique for surface water mapping using Landsat image. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanga, X.; Xiea, S.; Zhanga, X.; Chend, C.; Guoe, H. A robust Multi-Band Water Index (MBWI) for automated extraction of surface water from Landsat 8 OLI image. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinform. 2018, 68, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.D. Multi-Spectral Water Index (MuWI): A Native 10-m Multi-Spectral Water Index for Accurate Water Mapping on Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhan, W.; Sun, C.; Duan, Y. Landsat 8 OLI image based terrestrial water extraction from heterogeneous backgrounds using a reflectance homogenization approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, C.; White, J.C.; Wulder, M.A. Optical remotely sensed time series data for land cover classification: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 116, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Changming, Z.; Xin, Z.; Jiancheng, L.; Wanqing, L.I.; Jiwei, Y. Automatic extraction of coastline by remote sensing technology based on svm and auto-selection of training samples. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2013, 25, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, J. Study on the automatic extraction of water body from tm image using decision tree algorithm. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2008, 6625, 662502. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://k.sina.com.cn/article_5044281310_12ca99fde02000i5gp.html (accessed on 5 July 2018).
- Available online: http://www.baiyangdian.gov.cn/zhuanti/axhbj/zhengwuxinxi/2017/1129/3877.html (accessed on 29 October 2017).
- Mueller, J.L.; Fargion, G.S.; Mcclain, C.R. Ocean Optics Protocols for Satellite Ocean Colour Sensor Validation, Revision 4, Volume III: Radiometric Measurements and Data Analysis Protocols; NASA/TM-2003-21621/Rev-Vol III; National Aeronautical and Sapce Adminsitration: Washington, DC, USA, 2003.
- Jun, T.; Guo, T.; Xiao, W.; Xiao, W.; Qing, S. The Methods of water Spectral Measurement and Analysis I: Above Water Method. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 8, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghi, M.; Babaeian, E.; Tuller, M.; Jones, S.B. The optical trapezoid model: A novel approach to remote sensing of soil moisture applied to Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veloso, A.; Mermoz, S.; Bouvet, A.; Le Toan, T.; Planells, M.; Dejoux, J.F.; Ceschia, E. Understanding the temporal behavior of crops using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2-like data for agricultural applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Sarkar, S.; Franz, B.A.; Balasubramanian, S.V.; He, J. Sentinel-2 MultiSpectral Instrument (MSI) data processing for aquatic science applications: Demonstrations and validations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puliti, S.; Saarela, S.; Gobakken, T.; Ståhl, G.; Næsset, E. Combining UAV and Sentinel-2 auxiliary data for forest growing stock volume estimation through hierarchical model-based inference. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakimow, B.; Griffiths, P.; Sebastian, V.D.L.; Hostert, P. Mapping pasture management in the Brazilian Amazon from dense Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezonik, P.L.; Olmanson, L.G.; Finlay, J.C.; Bauer, M.E. Factors affecting the measurement of CDOM by remote sensing of optically complex inland waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascon, F.; Bouzinac, C.; Thépaut, O.; Jung, M.; Francesconi, B.; Louis, J.; Lonjou, V.; Lafrance, B.; Massera, S.; Gaudel-Vacaresse, A.; et al. Copernicus Sentinel-2A calibration and products validation status. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capóa, M.; Péreza, A.; Lozanoa, J.A. An efficient approximation to the K-means clustering for Massive Data. Knowl. Based Sys. 2017, 117, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rishikeshan, C.A.; Ramesh, H. An automated mathematical morphology driven algorithm for water body extraction from remotely sensed images. ISPRS J. Photo. Remote Sens. 2018, 146, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIE. Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage Proceedings 1931; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1932; pp. 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- Bukata, R.P.; Pozdnyakov, D.V.; Jerome, J.H.; Tanis, F.J. Validation of a radiometric colour model applicable to optically complex water bodies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 77, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenglei, W.; Bing, Z.; Junsheng, L.; Andrew, N.T. Large-Scale and Long-time Water Quality Remote Sensing Monitoring over Lakes Based on Water Colour Index. Ph.D. Thesis, Universtiy of Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]















© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yang, F.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Yao, Y. Recognition of Water Colour Anomaly by Using Hue Angle and Sentinel 2 Image. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040716
Zhao Y, Shen Q, Wang Q, Yang F, Wang S, Li J, Zhang F, Yao Y. Recognition of Water Colour Anomaly by Using Hue Angle and Sentinel 2 Image. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(4):716. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040716
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yelong, Qian Shen, Qian Wang, Fan Yang, Shenglei Wang, Junsheng Li, Fangfang Zhang, and Yue Yao. 2020. "Recognition of Water Colour Anomaly by Using Hue Angle and Sentinel 2 Image" Remote Sensing 12, no. 4: 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040716
APA StyleZhao, Y., Shen, Q., Wang, Q., Yang, F., Wang, S., Li, J., Zhang, F., & Yao, Y. (2020). Recognition of Water Colour Anomaly by Using Hue Angle and Sentinel 2 Image. Remote Sensing, 12(4), 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040716