Using Training Samples Retrieved from a Topographic Map and Unsupervised Segmentation for the Classification of Airborne Laser Scanning Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
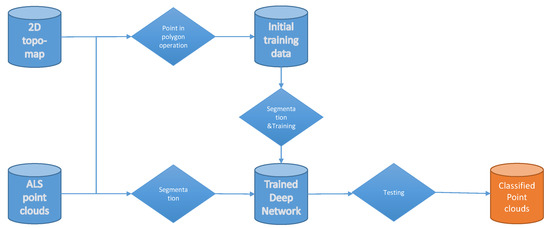
- We propose a point-in-polygon operation using a 2D topographic map to generate the initial training samples automatically;
- We modify the initial training samples using an unsupervised segmentation method; the unsupervised strategy reduces the noisy effect and improves the accuracy of our point-in-polygon training samples;
- We use the intensity value to improve the segmentation performance on small categories and use a graph convolutional neural network for the training and testing work.
2. Related Work
3. Methodology
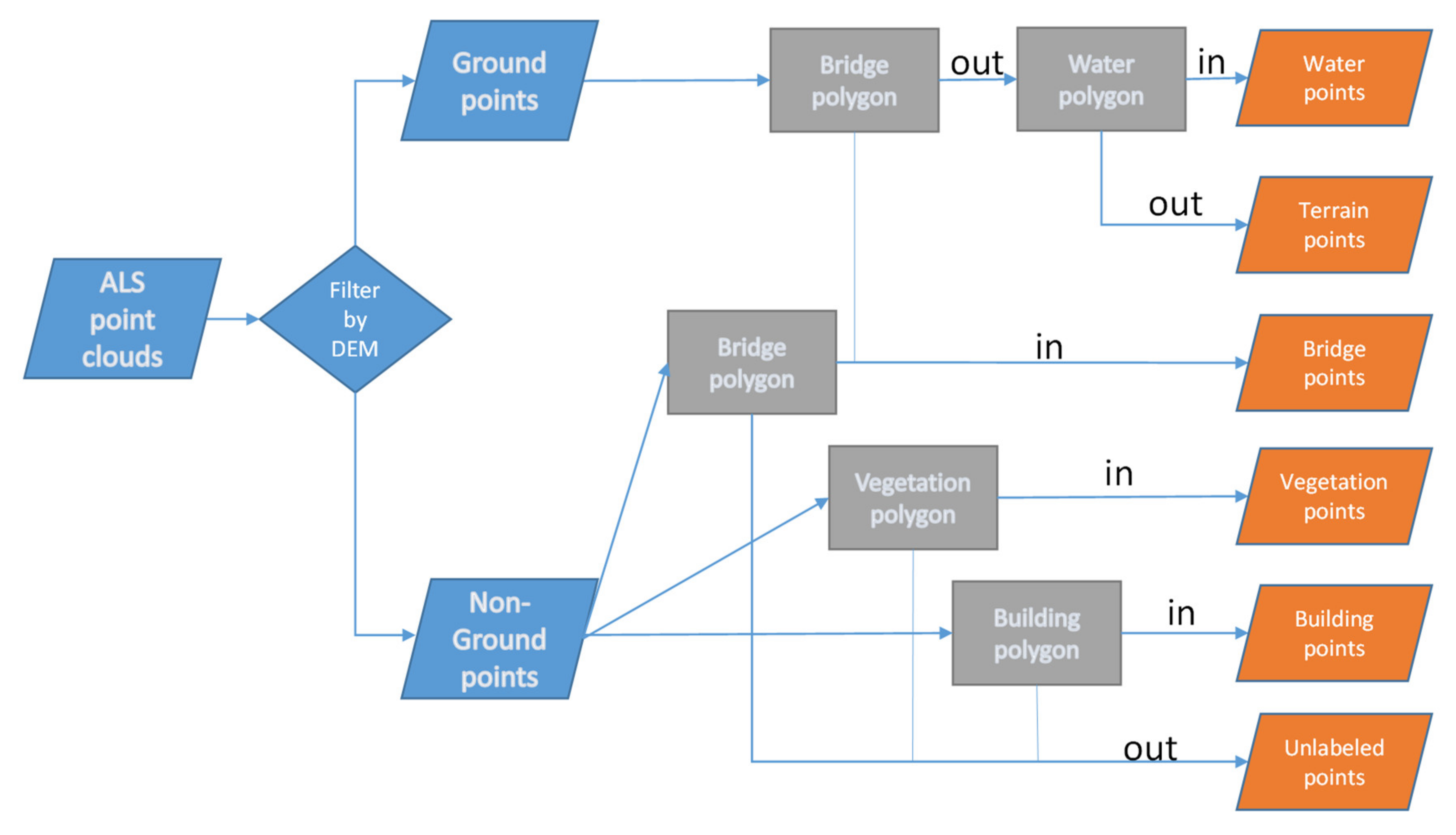
3.1. Point-in-Polygon Operation
3.2. Unsupervised Segmentation
3.3. Super Point Graph
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Dataset
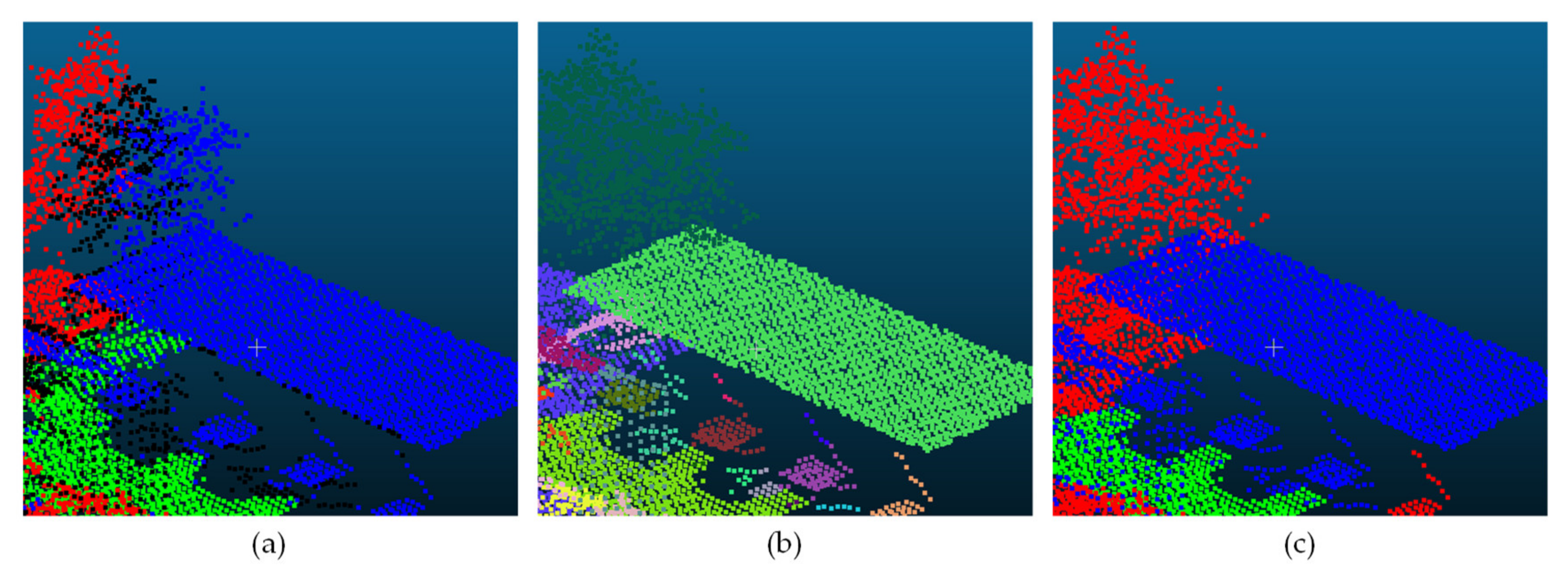
4.2. Influence of the Unsupervised Segmentation
4.3. Influence of the Intensity
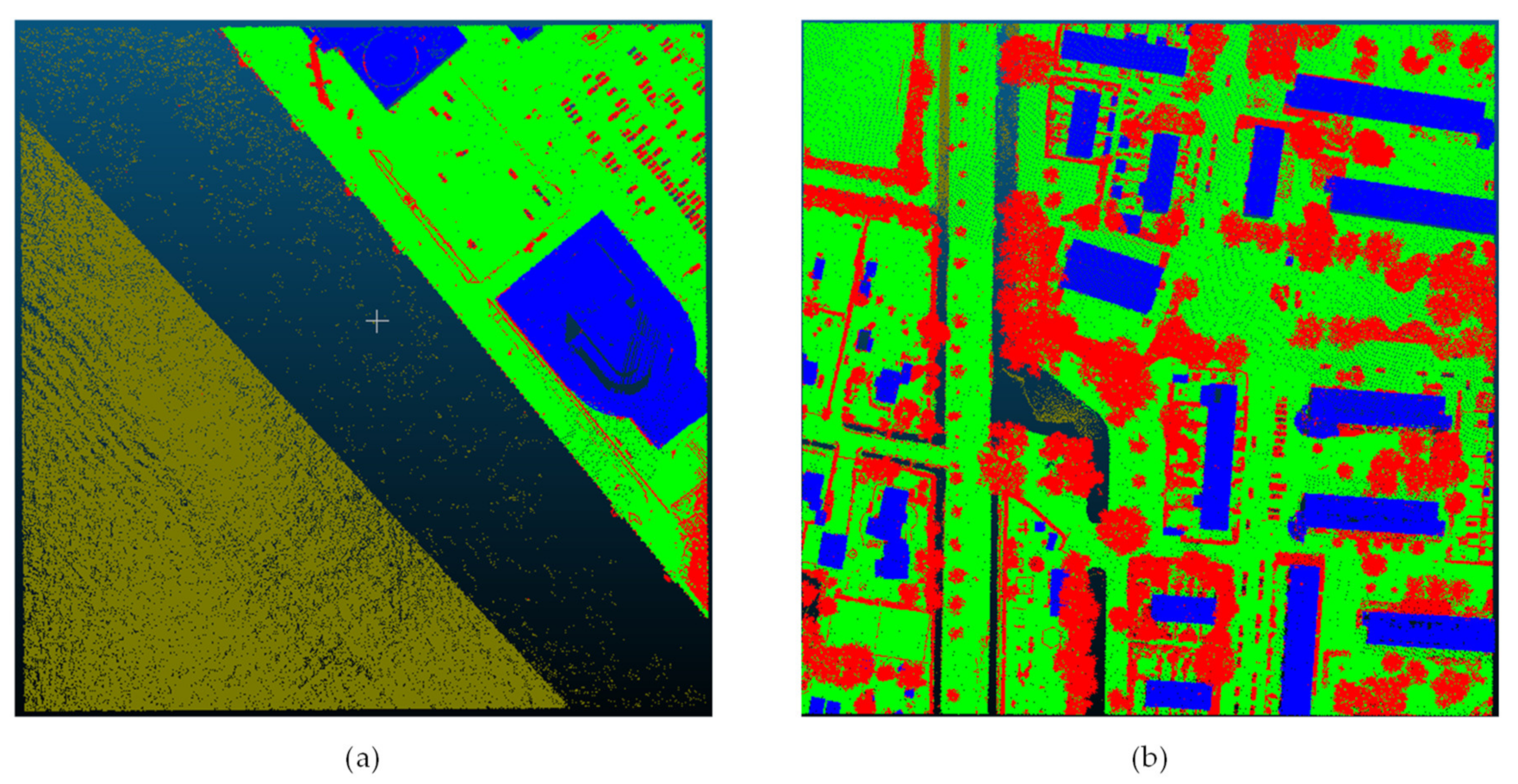
4.4. Comparison of the Result on Different Training Samples
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Endres, F.; Plagemann, C.; Stachniss, C.; Burgard, W. Unsupervised discovery of object classes from range data using latent Dirichlet allocation. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA, 28 June–1 July 2009; pp. 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Poux, F.; Billen, R. Voxel-based 3D point cloud semantic segmentation: Unsupervised geometric and relationship featuring vs deep learning methods. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vosselman, G. Slope based filtering of laser altimetry data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2000, 33, 935–942. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Deng, H. A mathematical morphology-based multi-level filter of LiDAR data for generating DTMs. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2013, 56, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutzinger, M.; Höfle, B.; Hollaus, M.; Pfeifer, N. Object-based point cloud analysis of full-waveform airborne laser scanning data for urban vegetation classification. Sensors 2008, 8, 4505–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lafarge, F.; Mallet, C. Creating large-scale city models from 3D-point clouds: A robust approach with hybrid representation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2012, 99, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerke, M.; Xiao, J. Fusion of airborne laserscanning point clouds and images for supervised and unsupervised scene classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 87, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Salvaggio, C. Aerial 3D building detection and modeling from airborne LiDAR point clouds. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, J.-Y.; Jhan, J.-P.; Hsu, Y.-C. Analysis of oblique aerial images for land cover and point cloud classification in an urban environment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 1304–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Vosselman, G.; Elberink, S.O. Multiple-entity based classification of airborne laser scanning data in urban areas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 88, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, R.; Fang, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z. Classification of urban point clouds: A robust supervised approach with automatically generating training data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodha, S.K.; Fitzpatrick, D.M.; Helmbold, D.P. Aerial lidar data classification using adaboost. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling 3DIM’07, Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–23 August 2007; pp. 435–442. [Google Scholar]
- Chehata, N.; Li, G.; Mallet, C. Airborne LIDAR feature selection for urban classification using random forests. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2009, 38, 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Mallet, C.; Bretar, F.; Roux, M.; Soergel, U.; Heipke, C. Relevance assessment of full-waveform lidar data for urban area classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, S71–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinmann, M.; Jutzi, B.; Hinz, S.; Mallet, C. Semantic point cloud interpretation based on optimal neighborhoods, relevant features and efficient classifiers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 286–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, J.; Rottensteiner, F.; Soergel, U. Contextual classification of lidar data and building object detection in urban areas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 87, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Sohn, G. Scene-layout compatible conditional random field for classifying terrestrial laser point clouds. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 2, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, X.; Munoz, D.; Bagnell, J.A.; Hebert, M. 3-d scene analysis via sequenced predictions over points and regions. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 2609–2616. [Google Scholar]
- Tosteberg, P. Semantic Segmentation of Point Clouds Using Deep Learning. 2017. Available online: https://liu.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1091059/FULLTEXT01.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- Boulch, A.; Saux, B.L.; Audebert, N. Unstructured point cloud semantic labeling using deep segmentation networks. In Proceedings of the Eurographics Workshop on 3D Object Retrieval, Lyon, France, 23–24 April 2017; Volume 2, pp. 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Xu, B.; Zhu, Q.; Jiang, S.; Huang, W. A convolutional neural network-based 3D semantic labeling method for ALS point clouds. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, H.; Qi, C.R.; Deschaud, J.-E.; Marcotegui, B.; Goulette, F.; Guibas, L.J. KPConv: Flexible and Deformable Convolution for Point Clouds. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.08889. [Google Scholar]
- Charles, R.Q.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann, F.; Kontogianni, T.; Hermans, A.; Leibe, B. Exploring spatial context for 3d semantic segmentation of point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Serna, A.; Marcotegui, B. Detection, segmentation and classification of 3D urban objects using mathematical morphology and supervised learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 93, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.-M.; Cai, J.-X.; Lai, Y.-K. Semantic labeling and instance segmentation of 3D point clouds using patch context analysis and multiscale processing. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2018, 18, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niemeyer, J.; Rottensteiner, F.; Sörgel, U.; Heipke, C. Hierarchical higher order crf for the classification of airborne lidar point clouds in urban areas. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. ISPRS Arch. 2016, 41, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vosselman, G.; Coenen, M.; Rottensteiner, F. Contextual segment-based classification of airborne laser scanner data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 128, 354–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Tan, B.; Pei, H.; Jiang, W. Segmentation and multi-scale convolutional neural network-based classification of airborne laser scanner data. Sensors 2018, 18, 3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engelmann, F.; Kontogianni, T.; Schult, J.; Leibe, B. Know what your neighbors do: 3D semantic segmentation of point clouds. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Landrieu, L.; Simonovsky, M. Large-scale Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation with Superpoint Graphs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Guinard, S.; Landrieu, L. Weakly supervised segmentation-aided classification of urban scenes from 3D LiDAR point clouds. In Proceedings of the ISPRS, Hannover, Germany, 6–9 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- LAStools–Efficient LiDAR Processing Software, Version 141017, Unlicensed. Available online: https://rapidlasso.com/lastools/ (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- Landrieu, L.; Obozinski, G. Cut pursuit: Fast algorithms to learn piecewise constant functions on general weighted graphs. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2017, 10, 1724–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaromczyk, J.W.; Toussaint, G.T. Relative neighborhood graphs and their relatives. Proc. IEEE 1992, 80, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar]
- Simonovsky, M.; Komodakis, N. Dynamic edge-conditioned filters in convolutional neural networks on graphs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- PODK-AHN3 Downloads. Available online: https://downloads.pdok.nl/ahn3-downloadpage/ (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- Downloads-PODK Dataset: Basisregistratie Grootschalige Topografie (BGT). Available online: https://www.pdok.nl/downloads/-/article/basisregistratie-grootschalige-topografie-bgt- (accessed on 14 October 2019).










| PiP | Tree | Terrain | Building | Water | Bridge | None | Num | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT | ||||||||
| Tree | 48.0 | 0.3 | 4.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 47.2 | 103286913 | |
| Terrain | 0.3 | 97.5 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 134736757 | |
| Building | 0.6 | 0.3 | 92.9 | 0 | 0.1 | 6.1 | 150055441 | |
| Water | 0.1 | 1.4 | 0 | 98.4 | 0 | 0.1 | 23445286 | |
| Bridge | 4.9 | 16.8 | 5.7 | 0.6 | 60.5 | 11.5 | 5613662 | |
| Class | μ0.1 | μ0.2 | μ0.3 | μ0.4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tree | 87.8 | 85.7 | 86.1 | 86.8 |
| Terrain | 92.3 | 92.0 | 91.3 | 90.5 |
| Building | 91.1 | 89.2 | 87.7 | 88.5 |
| Water | 5.8 | 2.0 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
| Bridge | 43.0 | 59.2 | 28.2 | 35.7 |
| Overall Accuracy | 90.0 | 88.6 | 88.1 | 88.3 |
| Average F1 | 64.0 | 65.6 | 58.9 | 60.5 |
| Class | μ0.1 | μ0.2 | μ0.3 | μ0.4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tree | 89.0 | 85.8 | 88.6 | 87.3 |
| Terrain | 92.8 | 90.3 | 91.6 | 91.4 |
| Building | 93.2 | 92.2 | 91.4 | 89.4 |
| Water | 20.6 | 25.4 | 39.7 | 41.6 |
| Bridge | 39.0 | 48.3 | 62.7 | 44.8 |
| Overall Accuracy | 91.1 | 88.9 | 90.2 | 89.0 |
| Average F1 | 66.9 | 68.4 | 74.8 | 70.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Lin, Y.; Elberink, S.O. Using Training Samples Retrieved from a Topographic Map and Unsupervised Segmentation for the Classification of Airborne Laser Scanning Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050877
Yang Z, Jiang W, Lin Y, Elberink SO. Using Training Samples Retrieved from a Topographic Map and Unsupervised Segmentation for the Classification of Airborne Laser Scanning Data. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(5):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050877
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhishuang, Wanshou Jiang, Yaping Lin, and Sander Oude Elberink. 2020. "Using Training Samples Retrieved from a Topographic Map and Unsupervised Segmentation for the Classification of Airborne Laser Scanning Data" Remote Sensing 12, no. 5: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050877
APA StyleYang, Z., Jiang, W., Lin, Y., & Elberink, S. O. (2020). Using Training Samples Retrieved from a Topographic Map and Unsupervised Segmentation for the Classification of Airborne Laser Scanning Data. Remote Sensing, 12(5), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050877