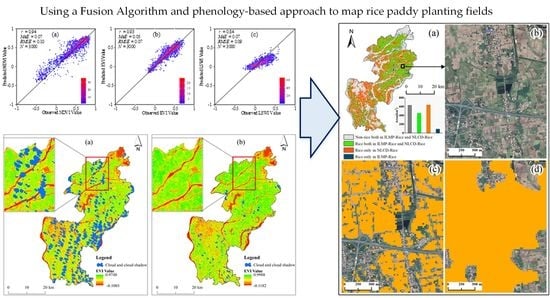
Phenology-Based Rice Paddy Mapping Using Multi-Source Satellite Imagery and a Fusion Algorithm Applied to the Poyang Lake Plain, Southern China
Abstract
Share and Cite
Ding, M.; Guan, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L. Phenology-Based Rice Paddy Mapping Using Multi-Source Satellite Imagery and a Fusion Algorithm Applied to the Poyang Lake Plain, Southern China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12061022
Ding M, Guan Q, Li L, Zhang H, Liu C, Zhang L. Phenology-Based Rice Paddy Mapping Using Multi-Source Satellite Imagery and a Fusion Algorithm Applied to the Poyang Lake Plain, Southern China. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(6):1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12061022
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Mingjun, Qihui Guan, Lanhui Li, Huamin Zhang, Chong Liu, and Le Zhang. 2020. "Phenology-Based Rice Paddy Mapping Using Multi-Source Satellite Imagery and a Fusion Algorithm Applied to the Poyang Lake Plain, Southern China" Remote Sensing 12, no. 6: 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12061022
APA StyleDing, M., Guan, Q., Li, L., Zhang, H., Liu, C., & Zhang, L. (2020). Phenology-Based Rice Paddy Mapping Using Multi-Source Satellite Imagery and a Fusion Algorithm Applied to the Poyang Lake Plain, Southern China. Remote Sensing, 12(6), 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12061022