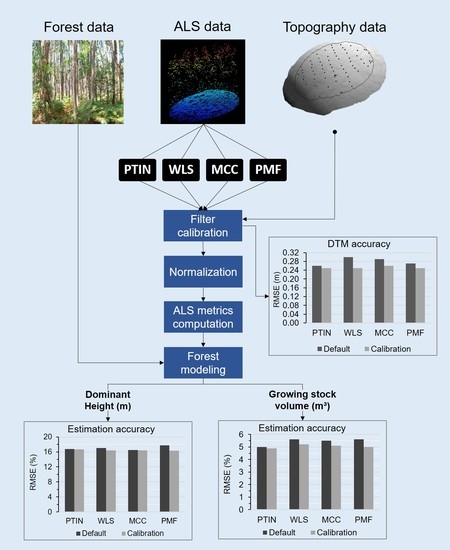
Impact of Calibrating Filtering Algorithms on the Quality of LiDAR-Derived DTM and on Forest Attribute Estimation through Area-Based Approach
Abstract
Share and Cite
Cosenza, D.N.; Gomes Pereira, L.; Guerra-Hernández, J.; Pascual, A.; Soares, P.; Tomé, M. Impact of Calibrating Filtering Algorithms on the Quality of LiDAR-Derived DTM and on Forest Attribute Estimation through Area-Based Approach. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12060918
Cosenza DN, Gomes Pereira L, Guerra-Hernández J, Pascual A, Soares P, Tomé M. Impact of Calibrating Filtering Algorithms on the Quality of LiDAR-Derived DTM and on Forest Attribute Estimation through Area-Based Approach. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(6):918. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12060918
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosenza, Diogo N., Luísa Gomes Pereira, Juan Guerra-Hernández, Adrián Pascual, Paula Soares, and Margarida Tomé. 2020. "Impact of Calibrating Filtering Algorithms on the Quality of LiDAR-Derived DTM and on Forest Attribute Estimation through Area-Based Approach" Remote Sensing 12, no. 6: 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12060918
APA StyleCosenza, D. N., Gomes Pereira, L., Guerra-Hernández, J., Pascual, A., Soares, P., & Tomé, M. (2020). Impact of Calibrating Filtering Algorithms on the Quality of LiDAR-Derived DTM and on Forest Attribute Estimation through Area-Based Approach. Remote Sensing, 12(6), 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12060918