Building Extraction Based on U-Net with an Attention Block and Multiple Losses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
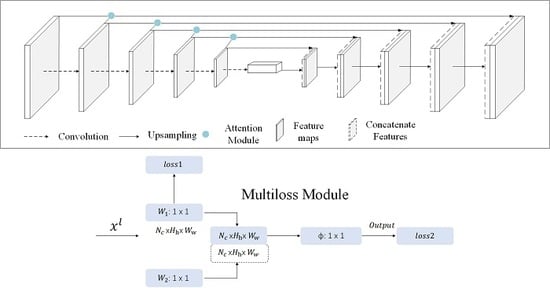
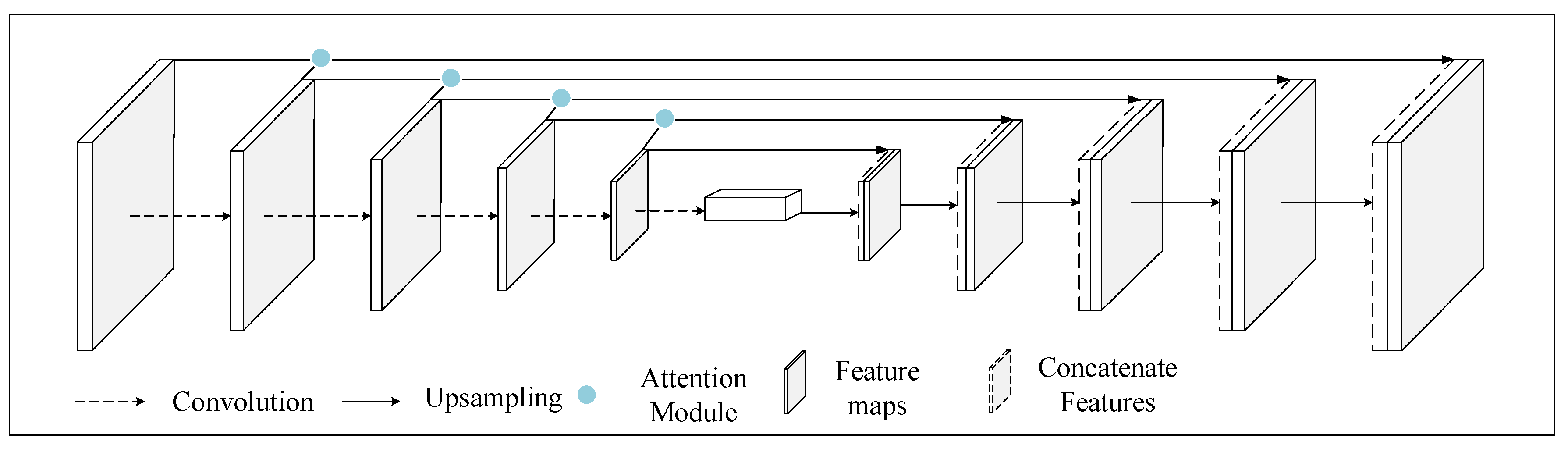
2. Methodology
2.1. Gate Control Based on the Attention Mechanism
2.1.1. Merging of Features at Different Scales
2.1.2. Gate Control
2.2. Multiloss Approach Based on Pixels
3. Materials and Results
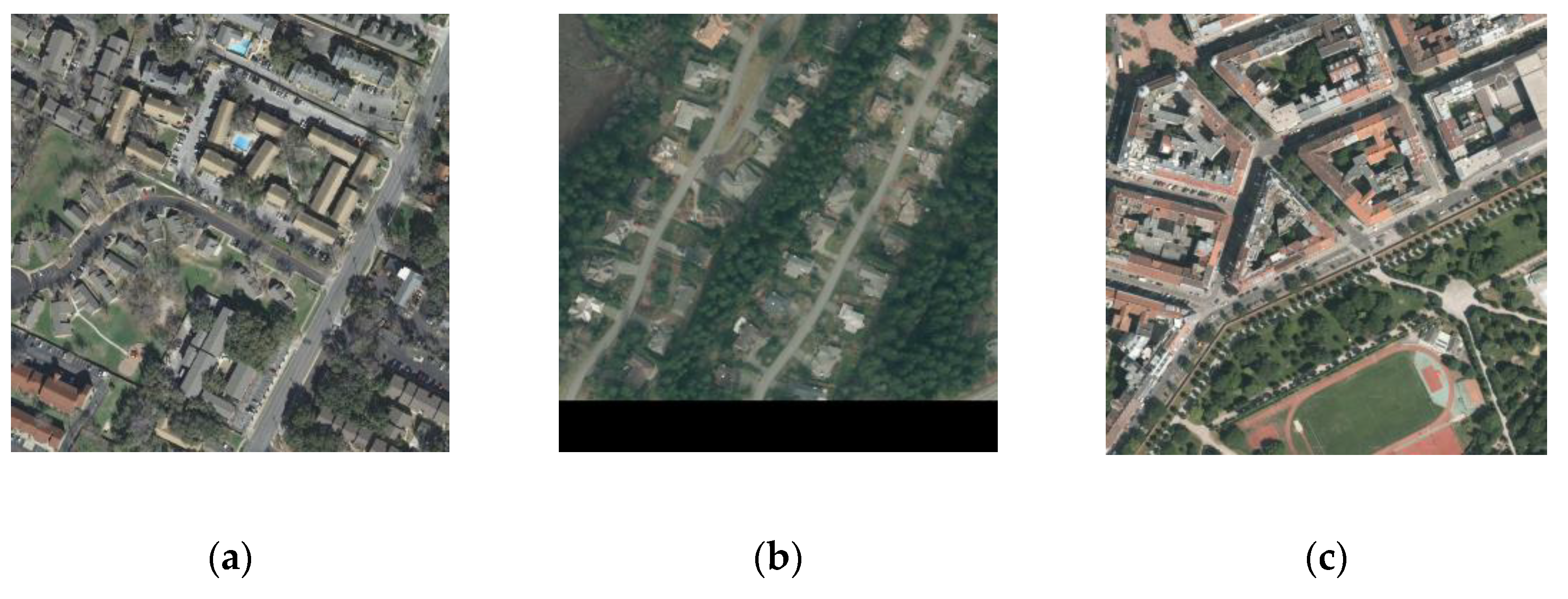
3.1. Datasets
3.1.1. Inria Aerial Image Labeling Dataset
3.1.2. Aerial Imagery for Roof Segmentation Dataset
3.2. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison to State-of-the-Art Methods
4.2. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rees, W.G. Physical Principles of Remote Sensing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wu, L. Quality assessment of building footprint data using a deep autoencoder network. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 1929–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Minh Nguyen, D.; Deligiannis, N.; Ding, W.; Munteanu, A. Hourglass-shapenetwork based semantic segmentation for high resolution aerial imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Piramanayagam, S.; Monteiro, S.T.; Saber, E. Dense semantic labeling of very-high-resolution aerial imagery and lidar with fully-convolutional neural networks and higher-order CRFs. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW 2017), Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Gao, L.; Marinoni, A.; Zhang, B.; Yang, F.; Gamba, P. Semantic labeling of high resolution aerial imagery and LiDAR data with fine segmentation network. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, L.; Xie, Z.; Chen, Z. Building extraction in very high resolution remote sensing imagery using deep learning and guided filters. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 3213–3223. [Google Scholar]
- Sirmacek, B.; Unsalan, C. Urban-Area and Building Detection Using SIFT Keypoints and Graph Theory. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2009, 47, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L. Morphological Building/Shadow Index for Building Extraction from High-Resolution Imagery over Urban Areas. IEEE J.-Stars 2012, 5, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G. A Morphological Building Detection Framework for High-Resolution Optical Imagery over Urban Areas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Zoej, M.J.V.; Ebadi, H.; Moghaddam, H.A.; Mohammadzadeh, A. Automatic urban building boundary extraction from high resolution aerial images using an innovative model of active contours. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2010, 12, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liasis, G.; Stavrou, S. Building extraction in satellite images using active contours and colour features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 1127–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Xu, S.; Meng, W.; Zhang, X. Building Extraction from Remotely Sensed Images by Integrating Saliency Cue. IEEE J.-Stars 2017, 10, 906–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, A.O. Automated detection of buildings from single VHR multispectral images using shadow information and graph cuts. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 86, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X. Semantic classification of urban buildings combining VHR image and GIS data: An improved random forest approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turker, M.; Koc-San, D. Building extraction from high-resolution optical spaceborne images using the integration of support vector machine (SVM) classification, Hough transformation and perceptual grouping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2015, 34, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglada, J. Automatic recognition of man-made objects in high resolution optical remote sensing images by SVM classification of geometric image features. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2007, 62, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, G.; Liu, N.; Xu, D. Advanced Deep-Learning Techniques for Salient and Category-Specific Object Detection: A Survey. IEEE Signal Proc. Mag. 2018, 35, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehhi, R.; Marpu, P.R.; Woon, W.L.; Mura, M.D. Simultaneous extraction of roads and buildings in remote sensing imagery with convolutional neural networks. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Maggiori, E.; Tarabalka, Y.; Charpiat, G.; Alliez, P. High-Resolution Aerial Image Labeling with Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2017, 55, 7092–7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, S.; Vanneschi, L. Improved fully convolutional network with conditional random fields for building extraction. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Song, Z. A Convergence Theory for Deep Learning via over-Parameterization. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Stockholm, Sweden, 10 July–15 July 2018; pp. 242–252. [Google Scholar]
- Itti, L.; Koch, C.; Niebur, E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intel. 1998, 20, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itti, L.; Koch, C. Computational modelling of visual attention. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Z. Road extraction from high-resolution remote sensing imagery using deep learning. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, P.O.; Lin, T.; Collobert, R.; Dollár, P. Learning to Refine Object Segments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 75–91. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Hawaii Convention Center, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Liu, Y. Scene Segmentation and Semantic Representation for High-Level Retrieval. IEEE Signal Proc. Lett. 2008, 15, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intel. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, C.; Xu, W.; et al. Look and Think Twice: Capturing Top-down Visual Attention with Feedback Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2956–2964. [Google Scholar]
- Larochelle, H.; Hinton, G.E. Learning to combine foveal glimpses with a third-order Boltzmann machine. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1243–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Heess, N.; Graves, A. Recurrent models of visual attention. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 2204–2212. [Google Scholar]
- Sountsov, P.; Santucci, D.M.; Lisman, J.E. A biologically plausible transform for visual recognition that is invariant to translation, scale, and rotation. Front. Comput. Neurosc. 2011, 5, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Spatial transformer networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 2017–2025. [Google Scholar]
- Bluche, T. Joint line segmentation and transcription for end-to-end handwritten paragraph recognition. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 838–846. [Google Scholar]
- Miech, A.; Laptev, I.; Sivic, J. Learnable pooling with context gating for video classification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.06905. [Google Scholar]
- Stollenga, M.F.; Masci, J.; Gomez, F.; Schmidhuber, J. Deep networks with internal selective attention through feedback connections. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 3545–3553. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Caballero, J.; Huszár, F.; Totz, J.; Aitken, A.P.; Bishop, R.; Rueckert, D.; Wang, Z. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 1874–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21 July–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; He, K.; Sun, J. Convolutional feature masking for joint object and stuff segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3992–4000. [Google Scholar]
- Unnikrishnan, R.; Pantofaru, C.; Hebert, M. Toward Objective Evaluation of Image Segmentation Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 929–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fowlkes, E.B.; Mallows, C.L. A method for comparing two hierarchical clusterings. J. Am. Stat Assoc. 1983, 78, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Marti, C.; Irniger, C.; Bunke, H. Distance measures for image segmentation evaluation. EURASIP J. Appl. Signal Proc. 2006, 2006, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unnikrishnan, R.; Hebert, M. Measures of similarity. In Proceedings of the 2005 Seventh IEEE Workshops on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV/MOTION’05)-Volume 1, Breckenridge, CO, USA, 5–7 January 2005; p. 394. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Yang, F.; Gao, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, B.; Fan, H.; Ren, J. Building Extraction from High-Resolution Aerial Imagery Using a Generative Adversarial Network with Spatial and Channel Attention Mechanisms. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bischke, B.; Helber, P.; Folz, J.; Borth, D.; Dengel, A. Multi-task learning for segmentation of building footprints with deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 1480–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Khalel, A.; El-Saban, M. Automatic pixelwise object labeling for aerial imagery using stacked u-nets. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.04953. [Google Scholar]
- Marcu, A.; Costea, D.; Slusanschi, E.; Leordeanu, M. A multi-stage multi-task neural network for aerial scene interpretation and geolocalization. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.01322. [Google Scholar]











| Austin | Chicago | Kitsap | Tyrol-w | Vienna | Overall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNet IoU | 79.95 | 70.18 | 68.56 | 49.38 | 54.82 | 49.69 |
| UNet accuracy | 97.10 | 92.67 | 99.31 | 84.44 | 96.11 | 93.07 |
| Attention UNet IoU | 64.58 | 63.54 | 66.17 | 68.44 | 70.69 | 67.18 |
| Attention UNet accuracy | 96.29 | 96.45 | 95.83 | 89.83 | 97.28 | 95.05 |
| AMUNet IoU | 84.43 | 81.22 | 68.13 | 79.97 | 85.05 | 79.76 |
| AMUNet accuracy | 97.29 | 96.45 | 93.83 | 98.83 | 97.28 | 96.73 |
| Austin | Chicago | Kitsap | Tyrol-w | Vienna | Overall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SegNet + multitask loss [54], IoU | 76.76 | 67.06 | 73.30 | 76.68 | 66.91 | 73 |
| SegNet + multitask loss accuracy | 93.21 | 99.25 | 97.84 | 91.71 | 96.61 | 93.07 |
| 2-level UNet IoU [55], | 77.29 | 68.52 | 72.84 | 75.38 | 78.72 | 74.55 |
| 2-level UNet accuracy | 96.69 | 92.4 | 99.25 | 98.11 | 93.79 | 96.05 |
| MSMT [56], IoU | 75.39 | 67.93 | 66.35 | 74.07 | 77.12 | 73.31 |
| MSMT accuracy | 95.99 | 92.02 | 99.24 | 97.78 | 92.49 | 96.06 |
| GAN-SCA [53], IoU | 81.01 | 71.73 | 68.54 | 78.62 | 81.62 | 77.75 |
| GAN-SCA accuracy | 97.26 | 93.32 | 99.30 | 98.32 | 94.84 | 96.61 |
| AMUNet IoU | 84.43 | 81.22 | 54.13 | 79.97 | 85.05 | 76.96 |
| AMUNet accuracy | 97.29 | 96.45 | 93.83 | 98.83 | 97.28 | 96.73 |
| Bellingham | Bloomington | Innsbruck | SFO | Tyrol-e | Overall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNet IoU | 56.77 | 49.16 | 55.90 | 59.16 | 59.78 | 57.10 |
| UNet accuracy | 95.71 | 95.25 | 94.89 | 86.67 | 96.41 | 93.79 |
| Attention UNet IoU | 58.03 | 53.81 | 62.86 | 61.22 | 64.13 | 60.47 |
| Attention UNet accuracy | 95.56 | 95.62 | 95.45 | 87.29 | 96.57 | 94.10 |
| AMUNet IoU | 64.46 | 54.59 | 68.75 | 70.78 | 71.38 | 67.69 |
| AMUNet accuracy | 96.33 | 95.69 | 96.20 | 90.29 | 97.39 | 95.18 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, M.; Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y. Building Extraction Based on U-Net with an Attention Block and Multiple Losses. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091400
Guo M, Liu H, Xu Y, Huang Y. Building Extraction Based on U-Net with an Attention Block and Multiple Losses. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(9):1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091400
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Mingqiang, Heng Liu, Yongyang Xu, and Ying Huang. 2020. "Building Extraction Based on U-Net with an Attention Block and Multiple Losses" Remote Sensing 12, no. 9: 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091400
APA StyleGuo, M., Liu, H., Xu, Y., & Huang, Y. (2020). Building Extraction Based on U-Net with an Attention Block and Multiple Losses. Remote Sensing, 12(9), 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091400