Magnetic Survey at the Roman Military Camp of el Benian in Mauretania Tingitana (Morocco): Results and Implications
Abstract
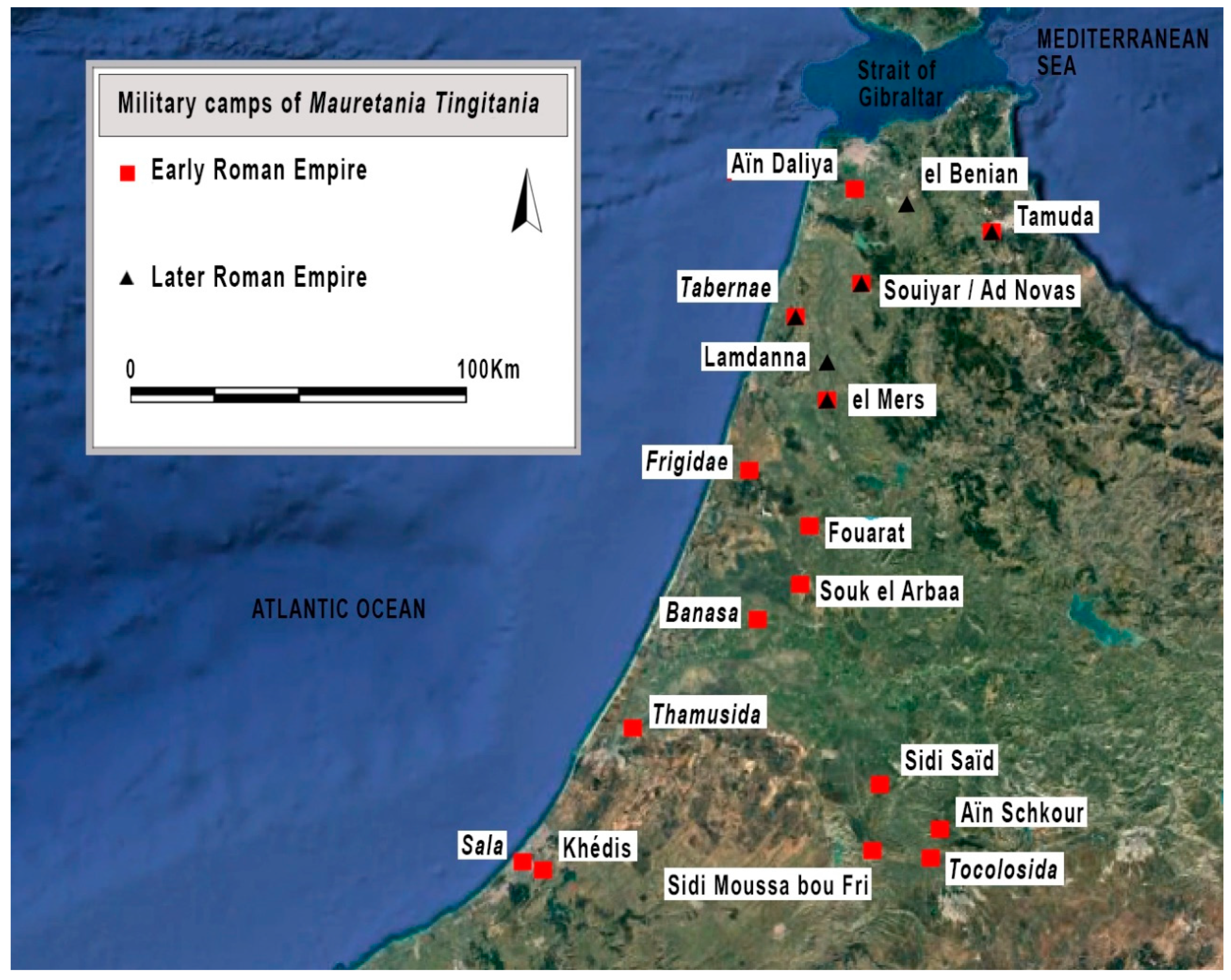
:1. Introduction
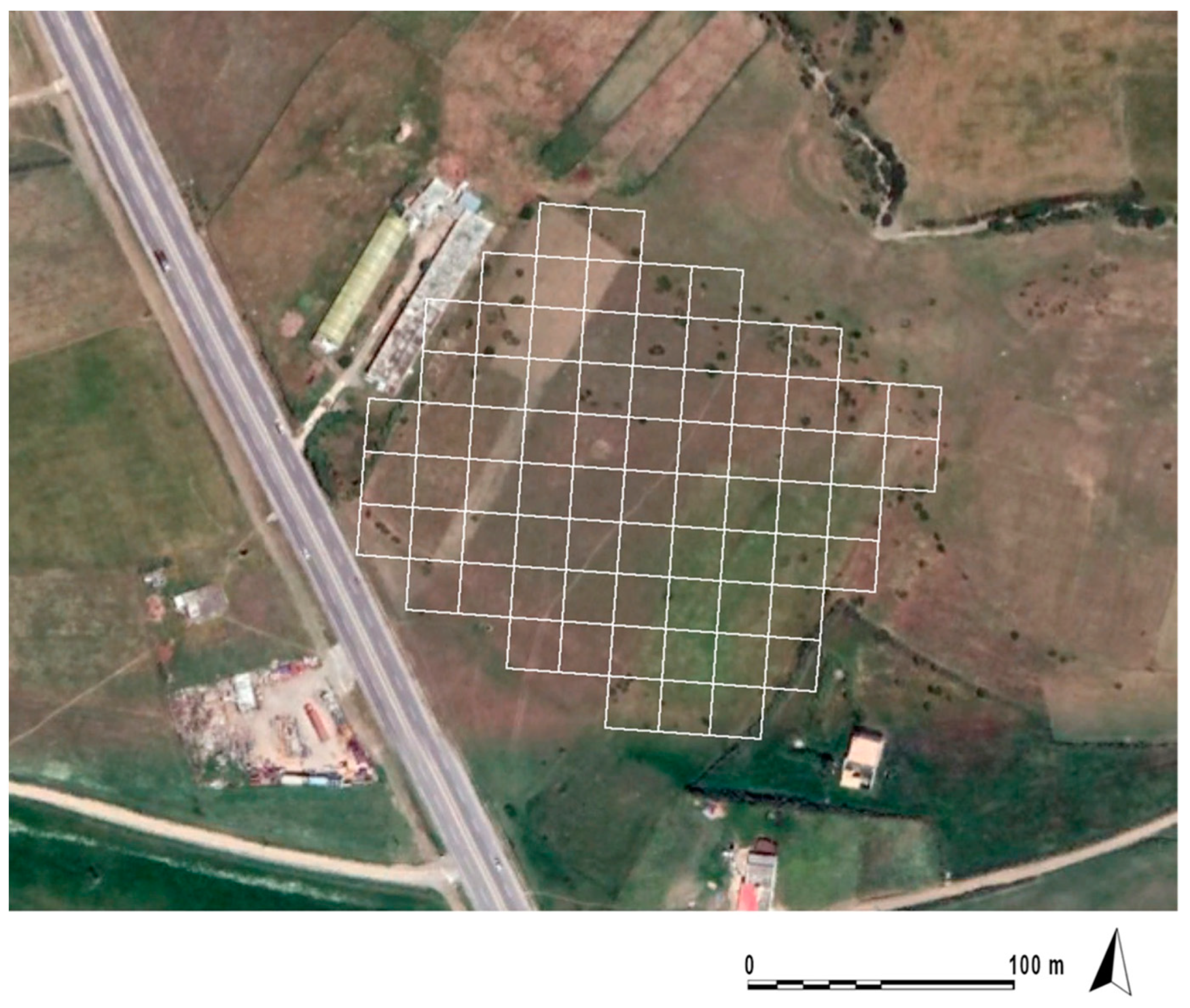
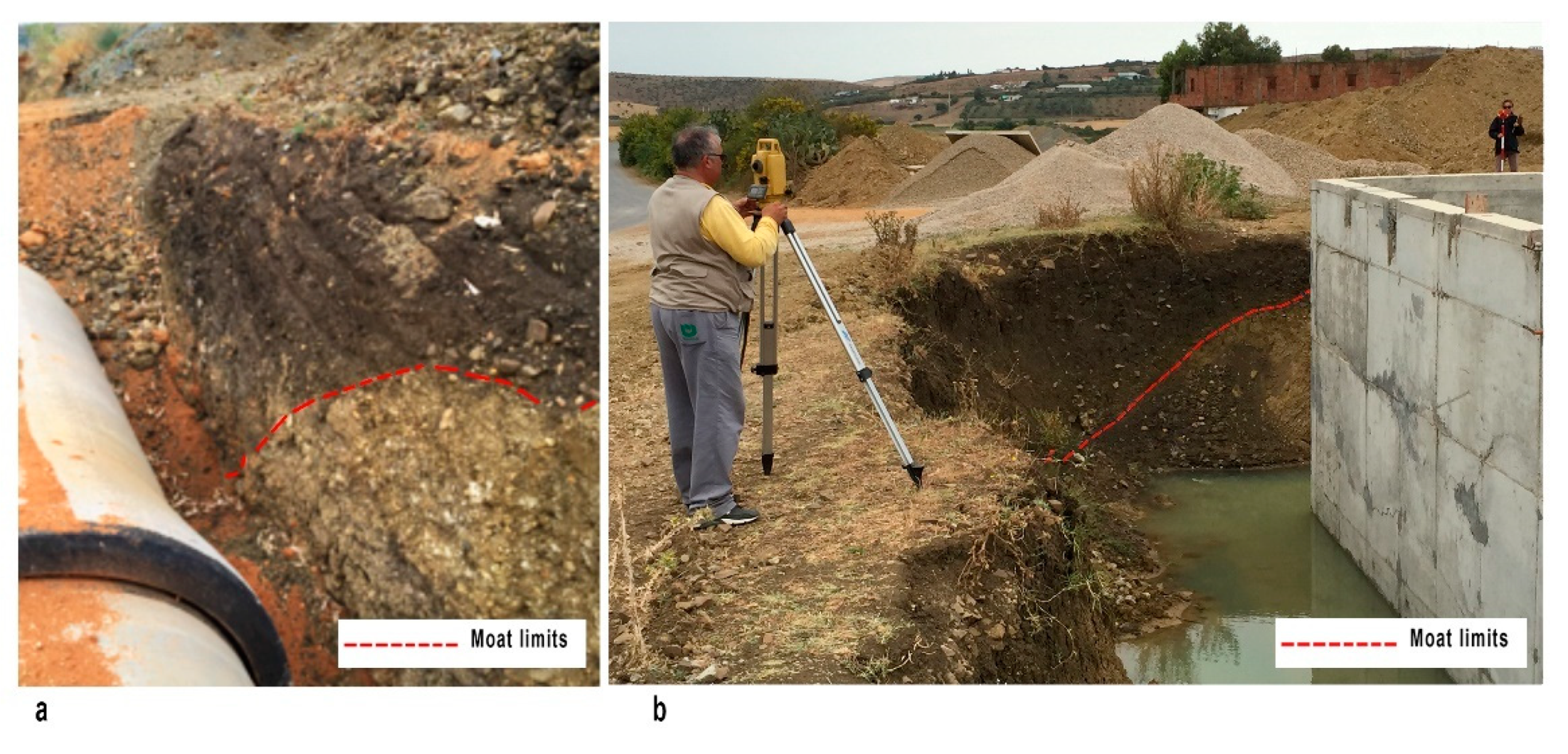
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
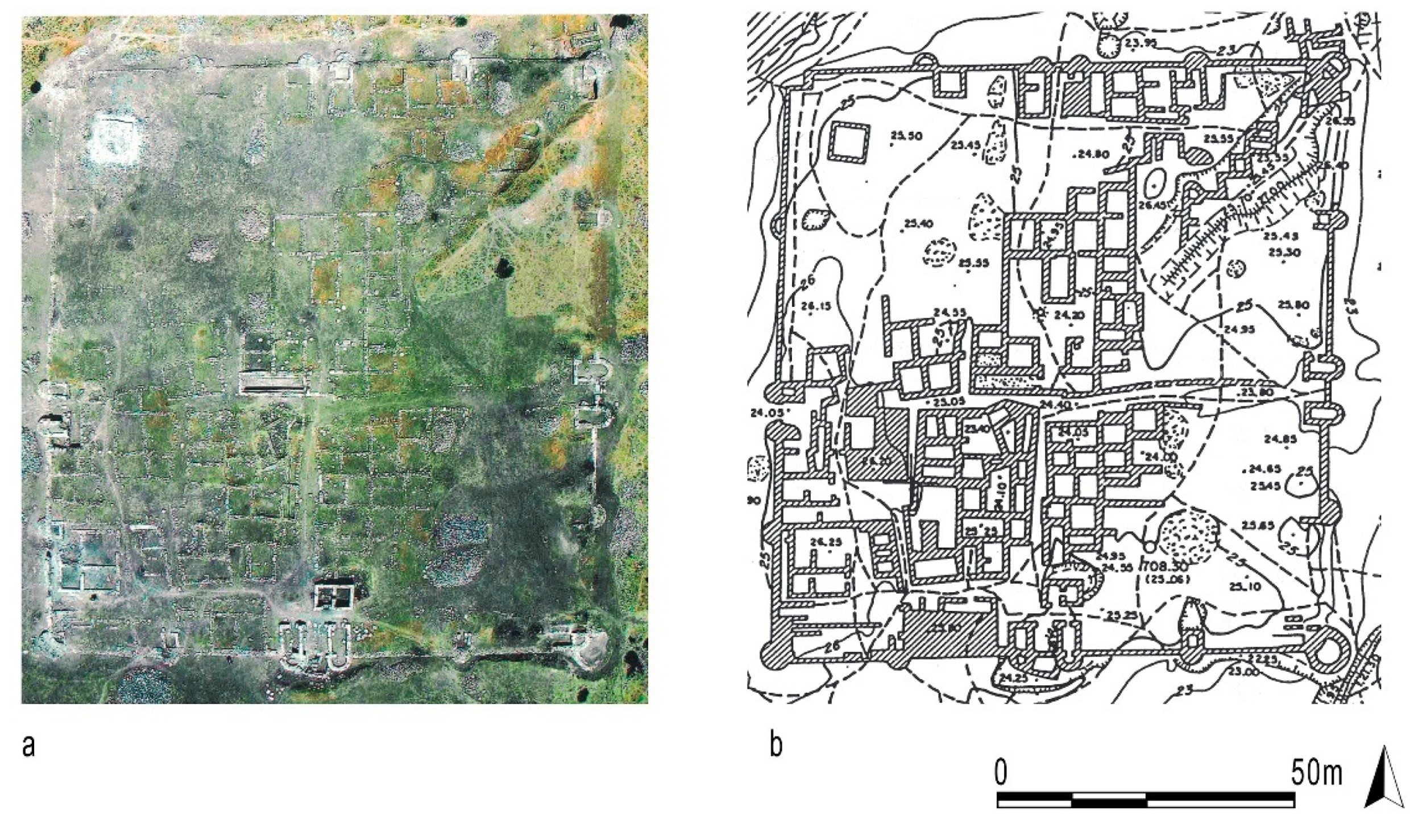
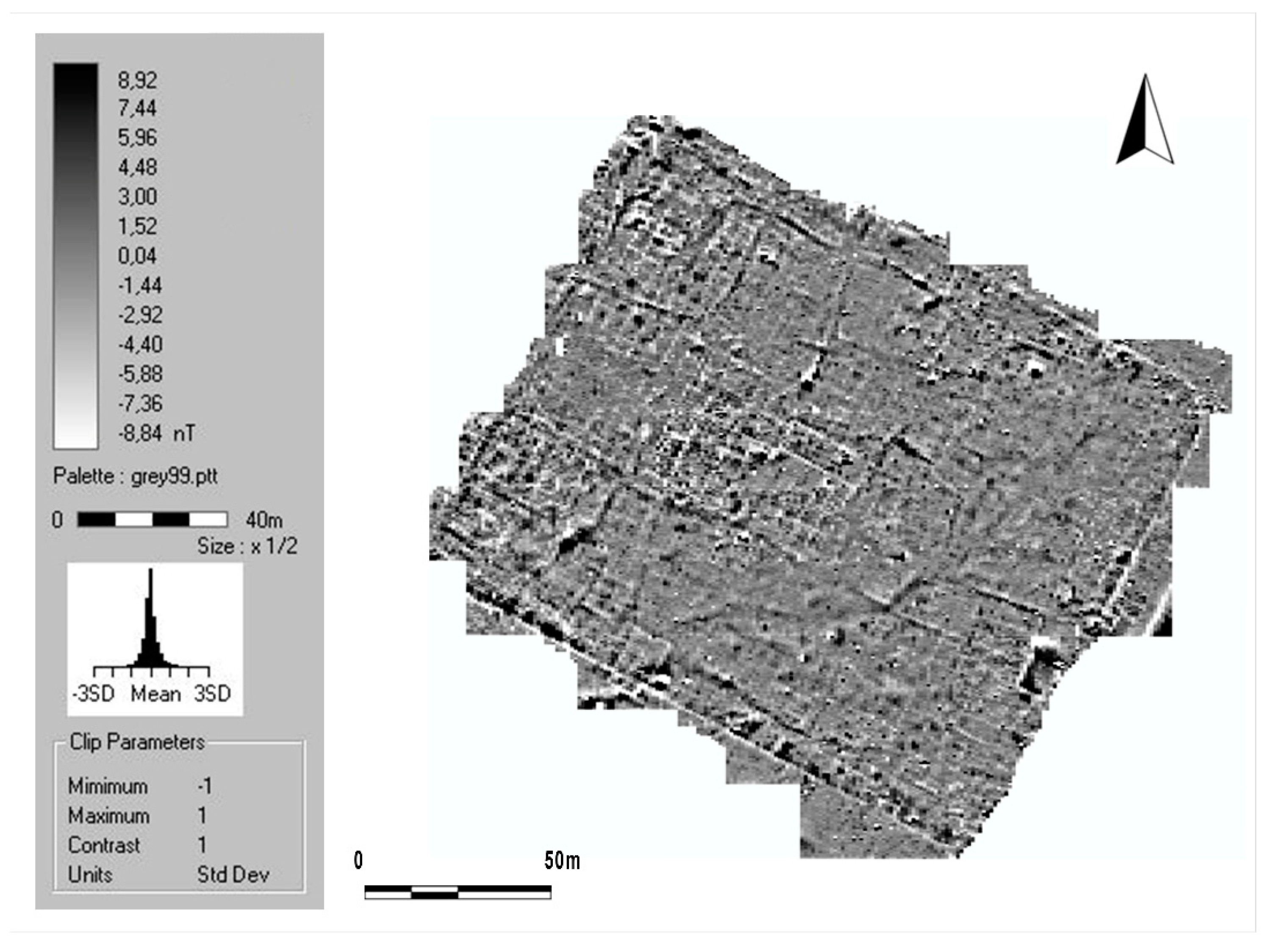
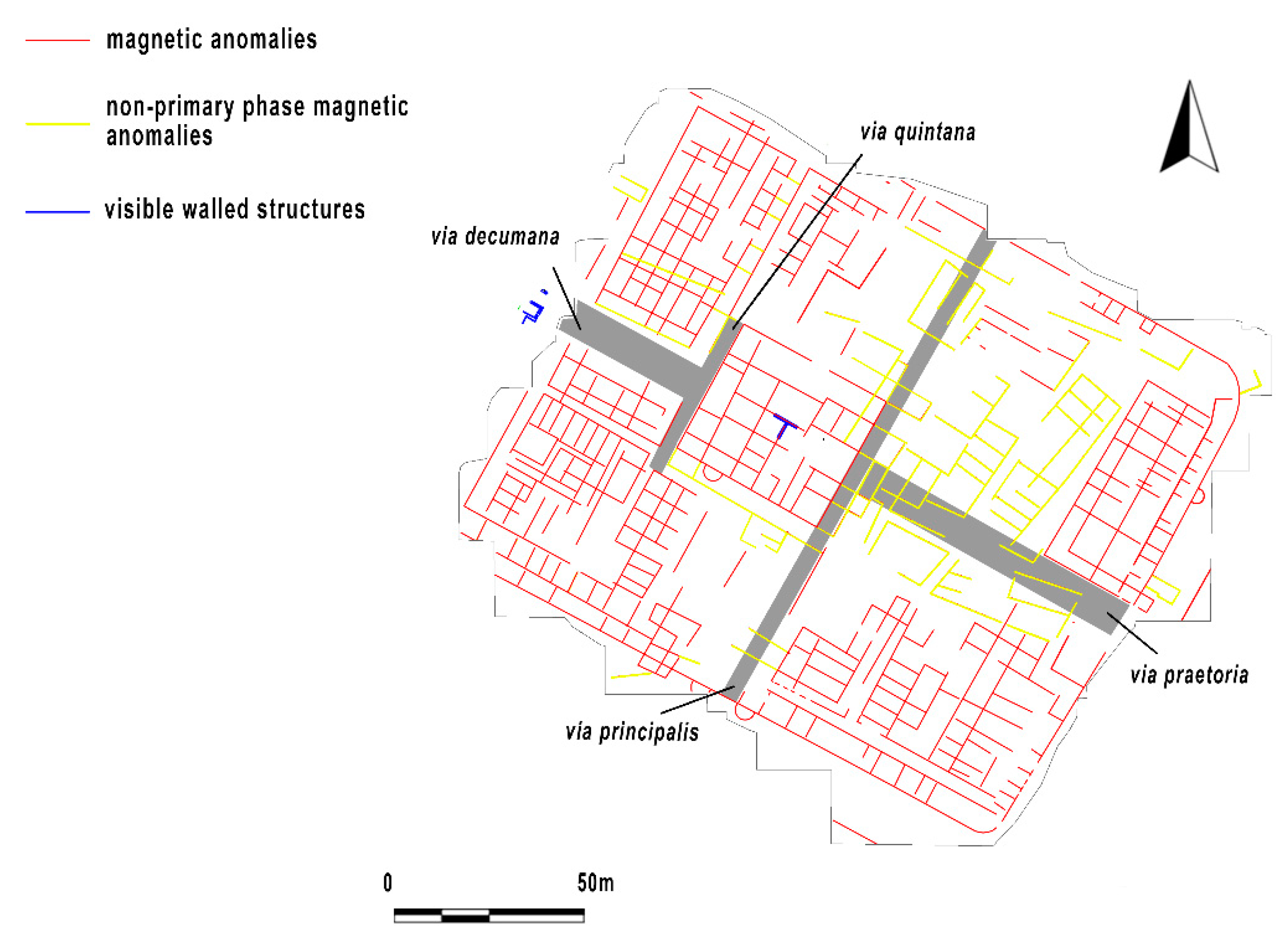
- intense urban planning activities that were performed at open spaces and free areas initially filled by main roads (Figure 12);
- confirmation of the presence of internal quadrangular towers and external semicircular towers leaning against the walls of the military camp.
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akerraz, A. Les fortifications de la Maurétanie tingitane. Comptes Rendus l’Académie Inscriptions Belles Lett. 2010, 154, 539–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradez, J. Fossatum Africae, Recherches aeriennes sur l’organisation des confins sahariens à l’epoque romaine. Am. J. Archaeol. 1951, 55, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benseddik, N. Les Troupes Auxiliaires en Mauritanie Cesarienne sous le Haut Empire; Publication autorisée par le jury: Alger, Italy, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Cagnat, R. L’armée Romaine d’Afrique et L’occupation Militaire de l’Afrique sous les Empereurs, Paris; Erdkamp, P., Ed.; A Companion to the Roman Army: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Euzennat, M. La frontière d’Afrique 1976–1983, Studien zu den Militärgrenzen Roms III, 13. Int. Limeskongress 1986, 13, 573–583. [Google Scholar]
- Fentress, E.W.B. Numidia and the Roman Army. In Social, Military and Economic Aspects of the Frontier Zone; BAR International Series 53; BAR: Oxford, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Laporte, J.-P. Rapidum. Le Camp de la Cohorte des Sardes en Maurétanie Césarienne; Sassari, Italy, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Le Bohec, Y. Les unités auxiliaires de l’Armée romaine en Afrique proconsulaire et Numidie sous le Haut Empire. 1989. Available online: https://www.persee.fr/doc/etaf_0768-2352_1989_mon_3_1 (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Le Bohec, Y. La troisième légion Auguste; Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS): Paris, France, 1989.
- Le Bohec, Y. Un Nouveau type D’unité Connu par L’epigraphie Africaine; Hanson, W.S., Keppie, L.J.F., Eds.; Roman Frontier Studie: Oxford, UK, 1979; pp. 931–942. [Google Scholar]
- Le Bohec, Y. L’ala Flavia ou ala I Flavia Numidica. Lib. Ant 1978, 15, 139–151. [Google Scholar]
- Le Bohec, Y. L’Armée Romaine en Afrique et en Gaule; Franz Steiner Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Le Bohec, Y. La recherche récente sur l’armée romaine d’Afrique (1977–1989). AntAfr 1991, 27, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bohec, Y. La stratégie de Rome en Afrique de 238 à 284, Histoire et Archeologie du l’Afrique du Nord. 110e Congrés national des Sociétes Savantes (Montpellier 1985); Comité des travaux historiques et scientifiques (C.T.H.S.): Paris, France, 1987; pp. 377–381. [Google Scholar]
- Le Bohec, Y. Le pseudo “camp des auxiliaires” à Lambèse. Armée Romaine Prov. 1977, 2, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Rebuffat, R. Au-delà des camps romains d’Afrique mineure: Renseignement, contrôle, penetration. ANRW 1982, II.10.2, 474–513. [Google Scholar]
- Rebuffat, R. Bu Njem 1972. Libya Antiqua 1977, 13, 37–77. [Google Scholar]
- Rebuffat, R. La frontière de la Tingitane. In Hommages à Pierre Salama; Publications de la Sorbonne: Paris, France, 1999; pp. 265–286. [Google Scholar]
- Erdkamp, P. The Corn Supply of the Roman Armies during the Principate (27 BC—235 AD). In The Roman Army and the Economy; Erdkamp, P., Ed.; Gieben: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 47–69. [Google Scholar]
- Erdkamp, P. The Grain Market. In the Roman Empire; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Le Bohec, Y. L’armée e l’organisation de l’espace urbain dans l’Afrique Romaine d’haut empire. L’Africa Romana 1992, 11, 313–320. [Google Scholar]
- Martorella, F. La conservazione delle derrate Nuove metodologie di indagine applicate allo studio di due magazzini di età imperiale (I-III d.C.) nelle città di Thamusida e Banasa (Mauretania Tingitana, marocco). HEROM J. Hell. Rom. Mater. Cult. 2020, 9, 233–251. [Google Scholar]
- Morizot, P. Impact de l’armée romaine sur l’économie de l’Afrique. In The Roman Army and the Economy; Erdkamp, P., Ed.; Gieben: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 345–374. [Google Scholar]
- Garnsey, P.; Saller, R. The Roman Empire: Economy, Society and Culture; University of California Press: Richmond, VA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Papi, E.; Martorella, F.; della Tingitana, I.G.; Papi, E. (Eds.) Supplying Rome and the Empire. J. Rom. Archaeol. Suppl Portsm. 2007, 69, 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Rickman, G. Roman Granaries and Store Buildings, Cambridge; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Salido Dominguez, J. Horrea Militaria. In El Aprovisionamiento de Grano al Ejército en el Occidente del Imperio Romano; Ediciones Polifemo: Madrid, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Akerraz, A.; Lenoir, E.; Rebuffat, R. Plaine et montagne en Tingitane méridionale, Histoire et archeologie du Nord., Actes du IIIe Colloque Internationale (Montpellier, 1–5 avril 1985); Comité des travaux historiques et scientifiques (C.T.H.S.): Paris, France, 1986; pp. 219–255. [Google Scholar]
- Akerraz, A.; Lenoir, E. Volubilis et son territoire au Ier siècle de notre ère, dans L’Afrique dans l’Occident romain, Actes du Colloque (Rome, 3–5 décembre 1987); École Française de Rome: Rome, Italy, 1990; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Carcopino, J. Le Maroc Antique; Gallimard: Paris, France, 1943. [Google Scholar]
- Colin, J. L’occupation romaine du Maroc; Cours Préparatoire au Service des Affaires Indigenes (Direction Génerale des Affaires Indigènes): Rabat, Morocco, 1925. [Google Scholar]
- Di Vita-Evrard, G. L’édit de Banasa: Un document exceptionelle? In Proceedings of the L’Africa romana 5, Atti del V Convegno di Studio, Sassari, Italy, 11–13 December 1987; Mastino, A., Ed.; Volume 5, pp. 287–304. [Google Scholar]
- Euzennat, M. Le limes de Tingitane: La Frontière Méridonale, Études D’antiquités Africaines; Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS): Paris, France, 1989.
- Lasala Navarro, I. Caelestia animalia Mauretaniae: Una breve reflexion a proposito del edicto de Banasa. Ktema 2008, 33, 413–420. [Google Scholar]
- Martorella, F. An urban warehouse for foodstuffs in the Iulia Valentia Banasa colony (Mauretania Tingitana, Morocco). Antiquités Afr. 2020, 56, 61–77. [Google Scholar]
- Rebuffat, R. L’implantation militaire romaine en Maurétanie Tingitane. In Proceedings of the L’Africa romana 4, Atti del IV Convegno di Studio, Sassari, Italy, 12–14 December 1986; Volume 4, pp. 31–78. [Google Scholar]
- Rebuffat, R.; et Limane, H. Carte archeologique du Maroc antique. 1. In Le bassin du Sebou; Imprimerie El Maarif Al Jadida: Rabat, Morocco, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rebuffat, R. L’armée romaine de Maurétanie tingitane. Mélanges l’École Française Rome Antiquité 1998, 110-1, 193–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebuffat, R. Le discours oral du prince, Mélanges de l’École française de Rome. Antiquité 2002, 114-2, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Villaverde Vega, N. El ejército romano en la provincia de Mauretania Tingitana entre Diocleciano y Valentiniano I. In Proceedings of the L’armée romaine de Diocletien à Valentinien Ier, Lyon, Italy, 12–14 September 2002; Le Bohec, Y., et Wolff, C., Eds.; pp. 299–305. [Google Scholar]
- Villaverde Vega, N. Tingitana en la Antigüedad Tardía (siglos III-VII): Autoctonía y Romanidad en el Extremo Occidente Mediterráneo; R.A.H. Biblioteca Archaeologica Hispana: Madrid, Spain, 2001; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Lenoir, M. Le Camp Romain. Proche-Orient et Afrique du Nord; Bibliothèque des École françaises d’Athènes et de Rome; École française de Rome: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tissot, C. Recherches sur la géographie comparée de la Maurétanie tingitane. In Mémoires Présentés par Divers Savants à l’Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres; 1e sér., t.9; Imprimerie Nationale: Paris, France, 1878; pp. 307–308. [Google Scholar]
- Ponsich, M. Recherches archéologiques à Tanger et dans sa région; Éditions du Centre national de la recherche scientifique: Greensboro, NC, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Villaverde Vega, N. Recherches sur les camps romains du Maroc, campagne 1991. La stratégie militaire du Bas-Empire en Maurétanie tingitane. In Actes du VIe Colloque International sur l’histoire et l’archéologie de l’Afrique du Nord. Antique et Médiévale, Pau, october 1993; CTHS: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 343–364. [Google Scholar]
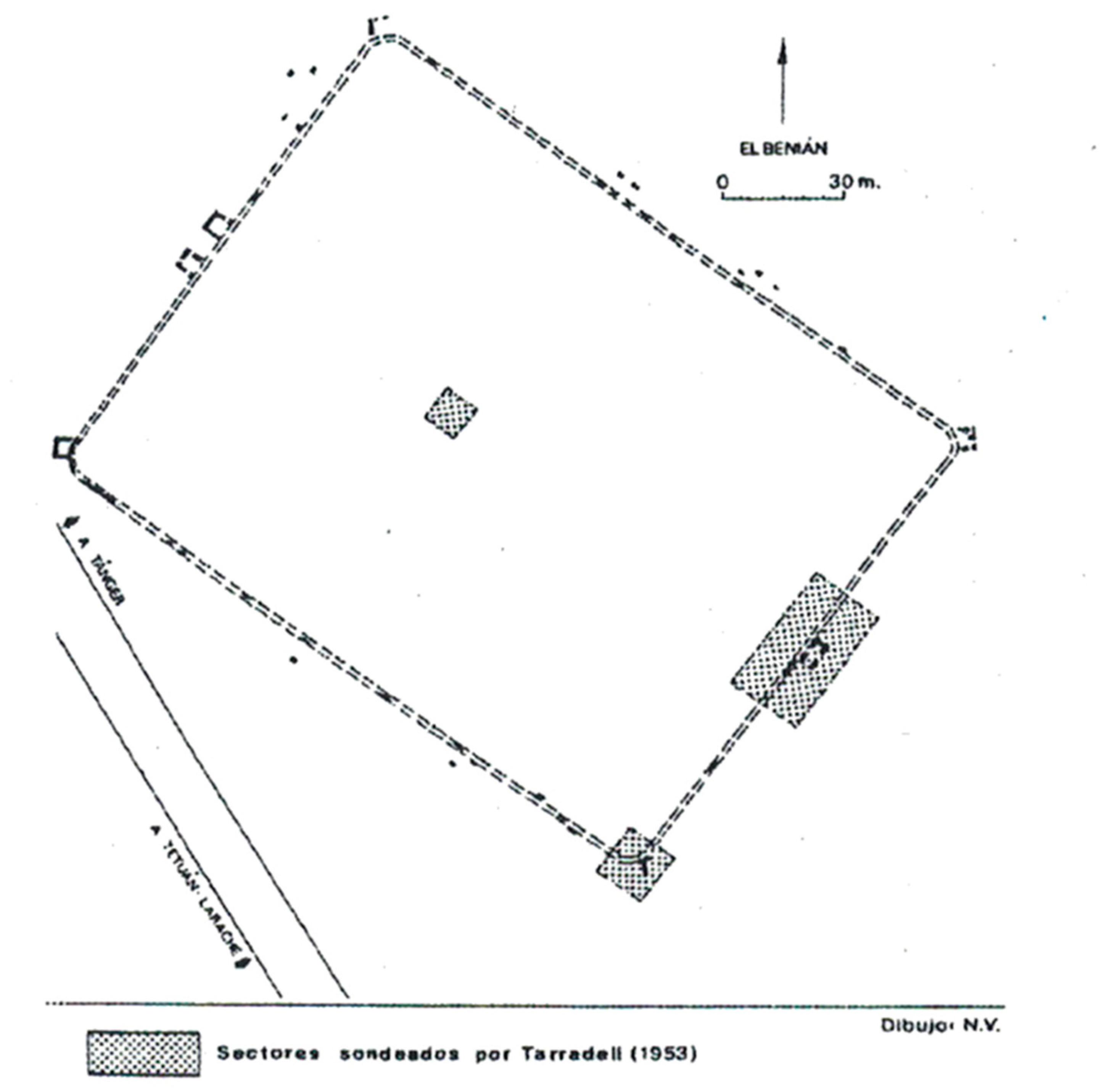
- Tarradell, M. El Benian, castellum romano entre Tetouan y Tanger, Tamuda 1; Tetuán, Spain, 1953; pp. 302–309. [Google Scholar]
- Fedi, M.; Cella, F.; Florio, G.; La Manna, M.; Paoletti, V. Geomagnetometry for Archaeology. In Sensing the Past; Masini, N., Soldovieri, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 203–230. [Google Scholar]
- Aitken, M.J. Magnetic prospecting. I. The Water Newton Survey; Archaeometry 1; Oxford University: Oxford, UK, 1958; pp. 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Florio, G.; Cella, S.F.; Castaldo, L.; Pierobon-Benoit, R.; Palermo, R. Multiscale techniques for 3D imaging of magnetic data for archaeo-geophysical investigations in the Middle East: The case of Tell Barri (Syria). Archaeol. Prospect. 2019, 26, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, E.; Chianese, D.; Lapenna, V. Magnetic, GPR and geoelectrical measurements for studying the archaeological site of ‘Masseria Nigro’ (Viggiano, southern Italy). Near Surf. Geophys. 2005, 3, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asăndulesei, A. Inside a Cucuteni Settlement: Remote Sensing Techniques for Documenting an Unexplored Eneolithic Site from Northeastern Romania. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paoletti, V.; Secomandi, M.; Piromallo, M.; Giordano, F.; Fedi, M.; Rapolla, A. Magnetic survey at the submerged archaeological site of Baia, Naples, Southern Italy. Archaeol. Prospect. 2005, 12, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo Meléndez, J. Los sistemas defensivos del castellum de Tamuda. ¿torres de planta en abanico? Gladius 2014, 34, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campos Carrasco, J.M.; Bermejo Meléndez, J.; Fernández Sutilo, L.; Toscano Pérez, C.; Salvador Delgado, A.; Gómez Rodríguez, A.; Verdugo Santos, J.; Ghottes, M. El castellum de Tamuda. Análisis Arqueoarquitectónico, Arqueología y turismo en el Círculo del Estrecho: Estrategias para la Puesta en Valor de los recursos patrimoniales del Norte de Marruecos, Actas del III Seminario Hispano-Marroquí (Algeciras, abril de 2011), Colección de Monografías del Museo Arqueológico de Tetuán (III); Servicio de Publicaciones de la Universidad de Cádiz: Cádiz, Spain, 2011; pp. 507–528. [Google Scholar]
- Fassbinder, J.W.E. Geophysical Prospection of the Frontiers of the Roman Empire in Southern Germany, UNESCO World Heritage Site. Archaeol. Prospect. 2010, 17, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugl, C.; Neubauer, W.; Nau, E.; Jernej, R. New Evidence for a Roman Military Camp at Virunum (Noricum). Archaeol. Pol. 2015, 53, 289–292. [Google Scholar]
- Pisz, M.; Tomas, A.; Hegyi, A. Non-destructive research in the surroundings of the Roman Fort Tibiscum (today Romania). Archaeol. Prospect. 2020, 27, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, R.; Gaffney, C.; Gater, J.; Wood, E. Fluxgate Gradiometry and Square Array Resistance Survey at Drumlanrig, Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. Archaeol. Prospect. 2005, 12, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerri, L. La prospezione magnetica: L’abitato antico. In Sidi Ali Ben Ahmed 1; Papi, E., Akerraz, A., Eds.; Quasar: Roma, Italy, 2008; pp. 31–50. [Google Scholar]
- Papi, E. Diploma militare da Thamusida (Mauretania Tingitana). 103/4. Zeitschrift für Papyrologie und Epigraphik 2004, 146, 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Papi, E.; e Akerraz, A. (Eds.) Sidi Ali Ben Ahmed—Thamusida 1; Quasar: Roma, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Akerraz, A.; Gliozzo, E.; Turbanti Memmi, I. (Eds.) Sidi Ali ben Ahmed—Thamusida 2. L’archeometria; Quasar: Roma, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Akerraz, A.; Camporeale, S.; Papi, E. Sidi Ali ben Ahmed—Thamusida 3. I Material; Quasar: Roma, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martorella, F. Magnetic Survey at the Roman Military Camp of el Benian in Mauretania Tingitana (Morocco): Results and Implications. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010028
Martorella F. Magnetic Survey at the Roman Military Camp of el Benian in Mauretania Tingitana (Morocco): Results and Implications. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartorella, Francesco. 2021. "Magnetic Survey at the Roman Military Camp of el Benian in Mauretania Tingitana (Morocco): Results and Implications" Remote Sensing 13, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010028
APA StyleMartorella, F. (2021). Magnetic Survey at the Roman Military Camp of el Benian in Mauretania Tingitana (Morocco): Results and Implications. Remote Sensing, 13(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010028