Stratified Particle Filter Monocular SLAM
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Motion Model
3.2. Sensor Model
3.3. Sequential Importance Resampling (SIR) Particle Filter
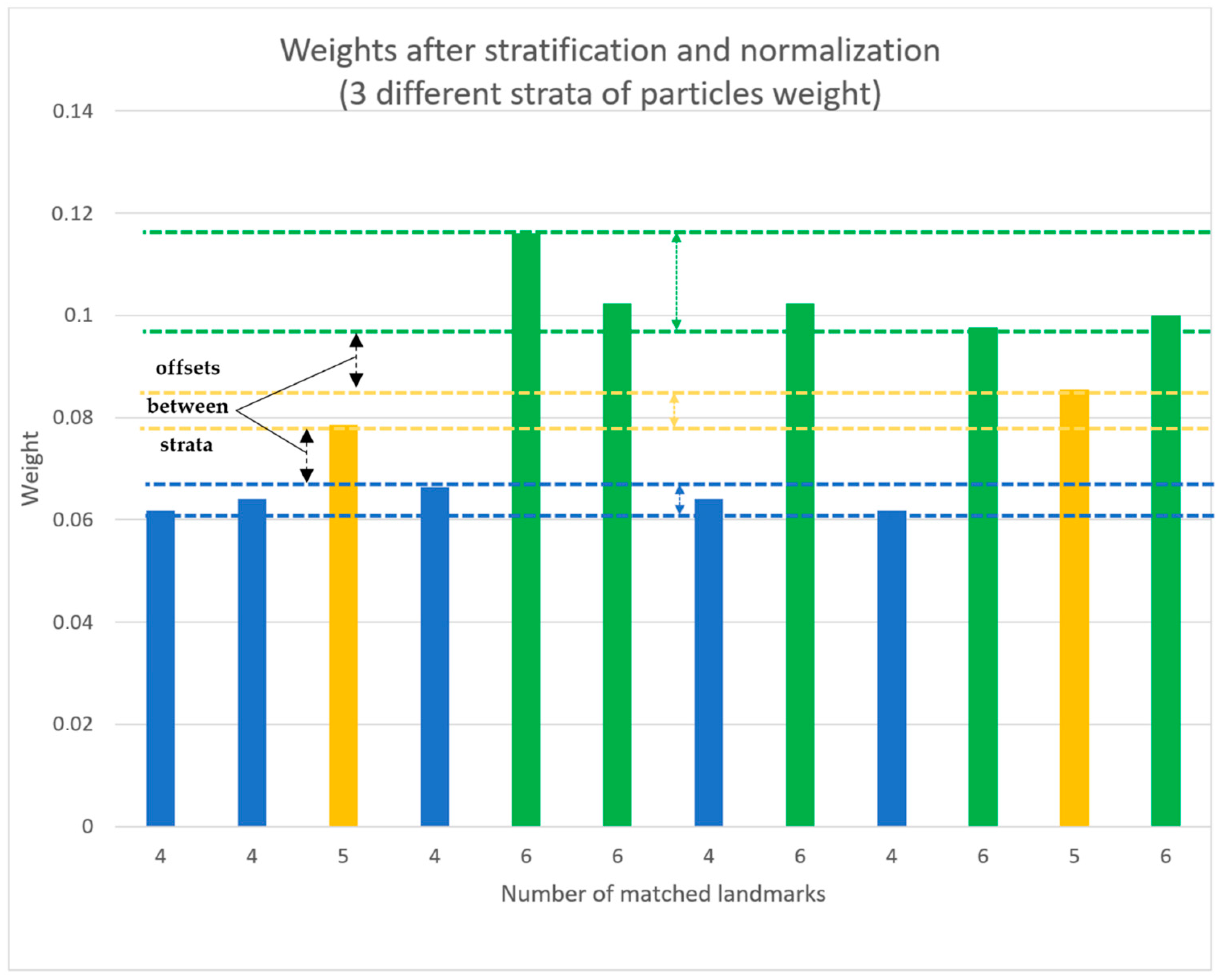
3.4. Weighting Approach
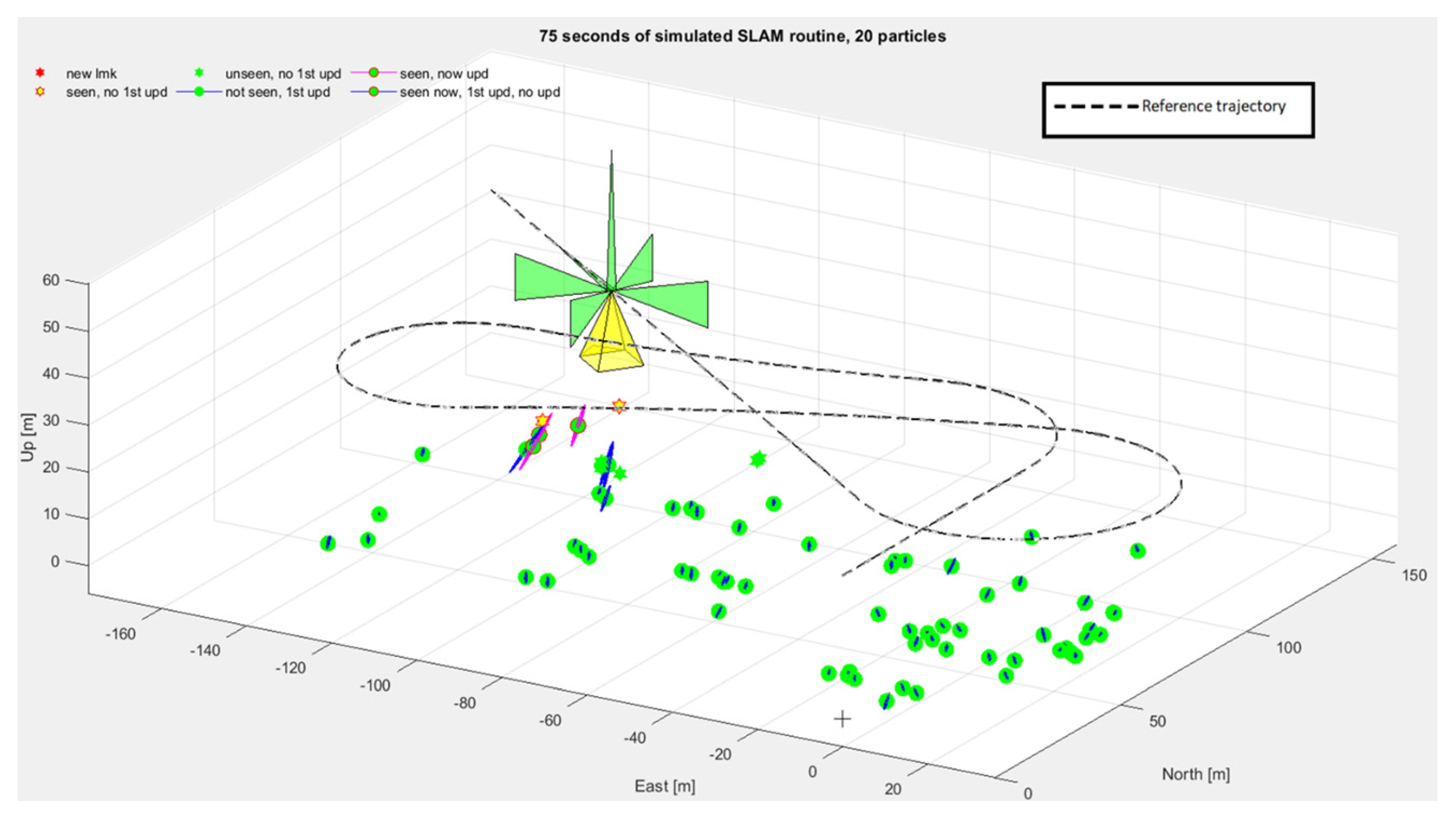
3.5. Landmark Management
4. Results
- Our novel weights stratification.
- Adding a penalty for unmatched landmarks, in accordance to the Equation (24).
- Weighting particles using only the lowest number of matched landmarks (so that all the samples are evaluated using an equal number of landmarks).
- Using no gating, as in [33].
- Gating without addressing the issue of difference in the number of matched landmarks between particles.
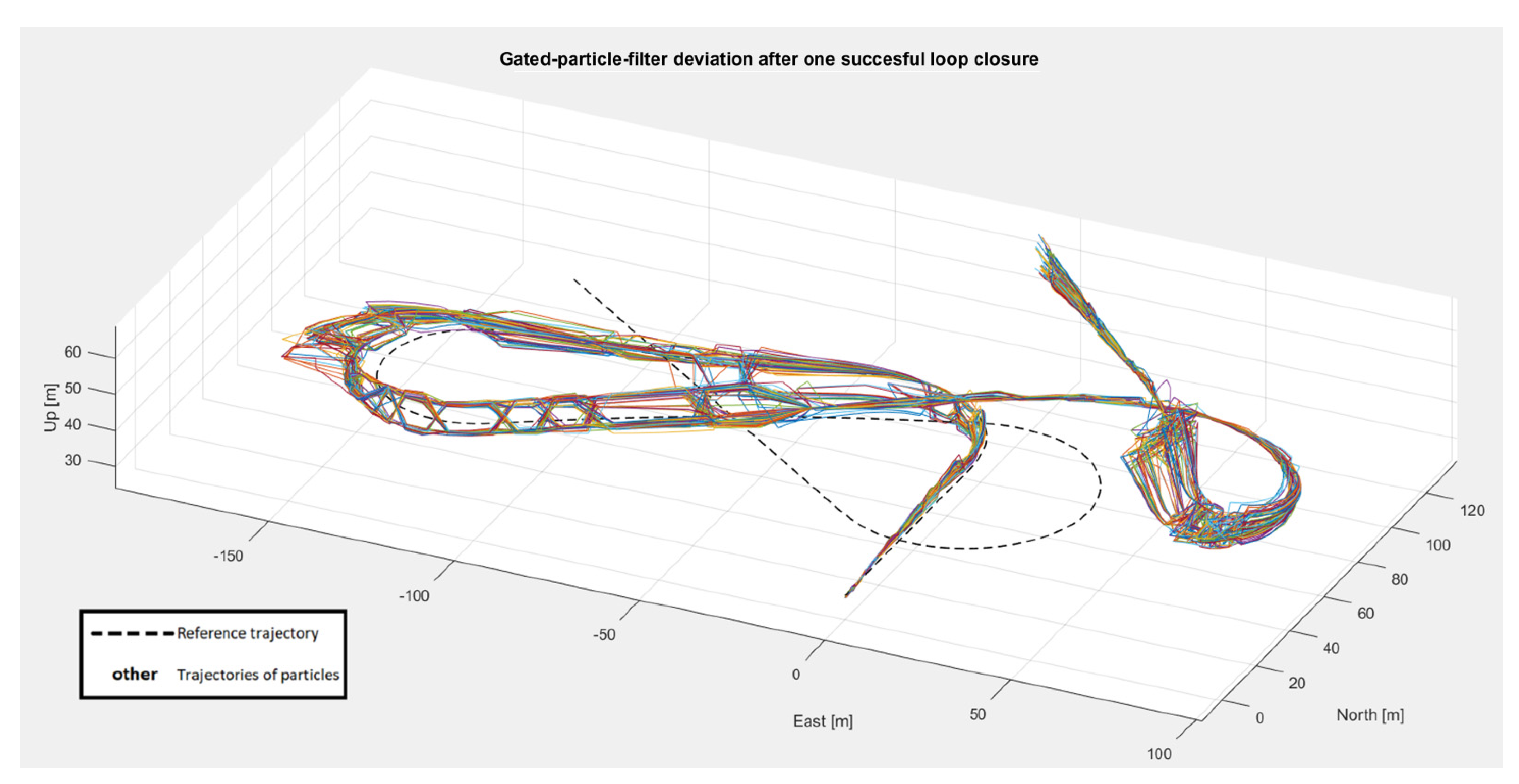
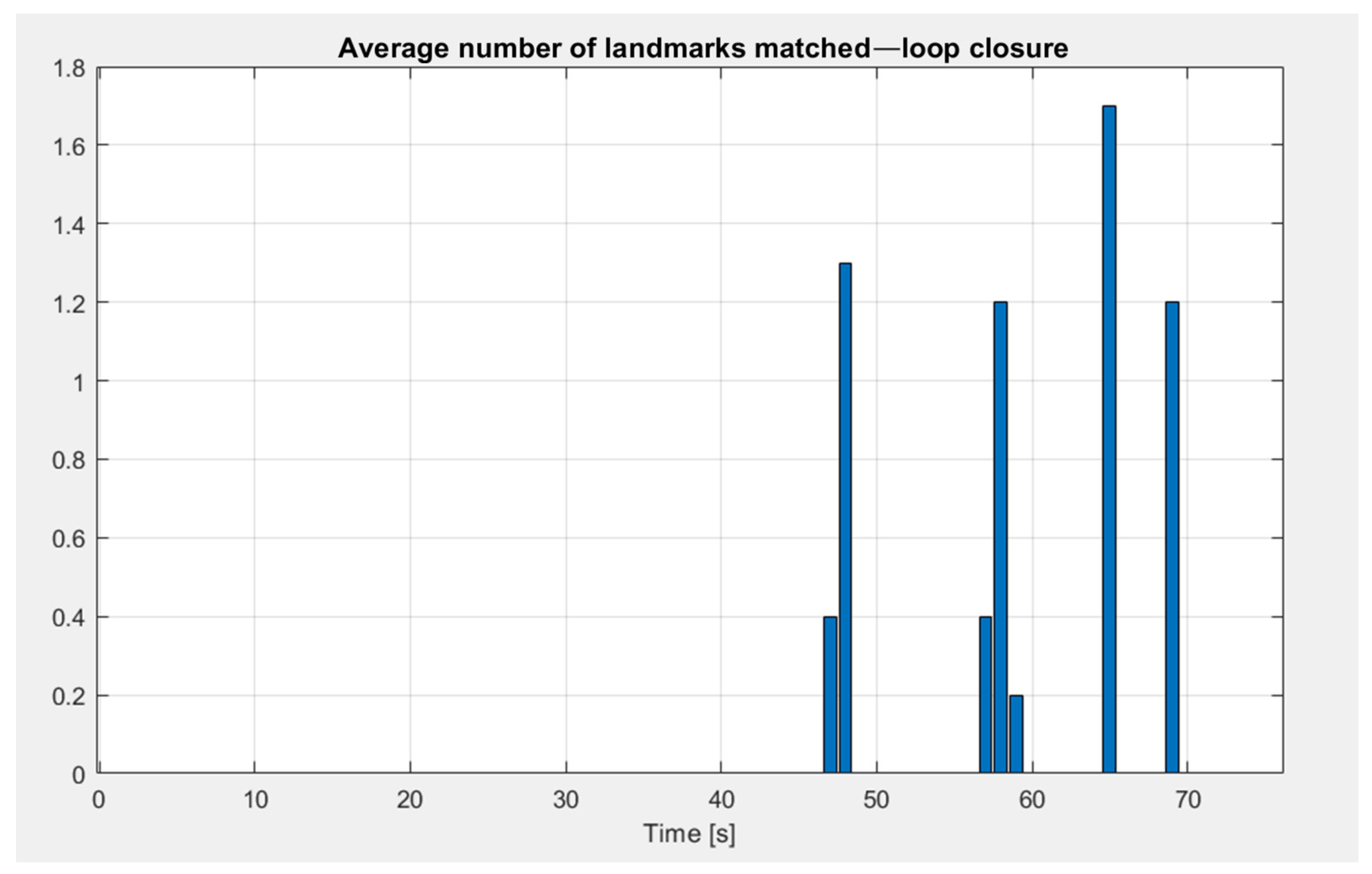
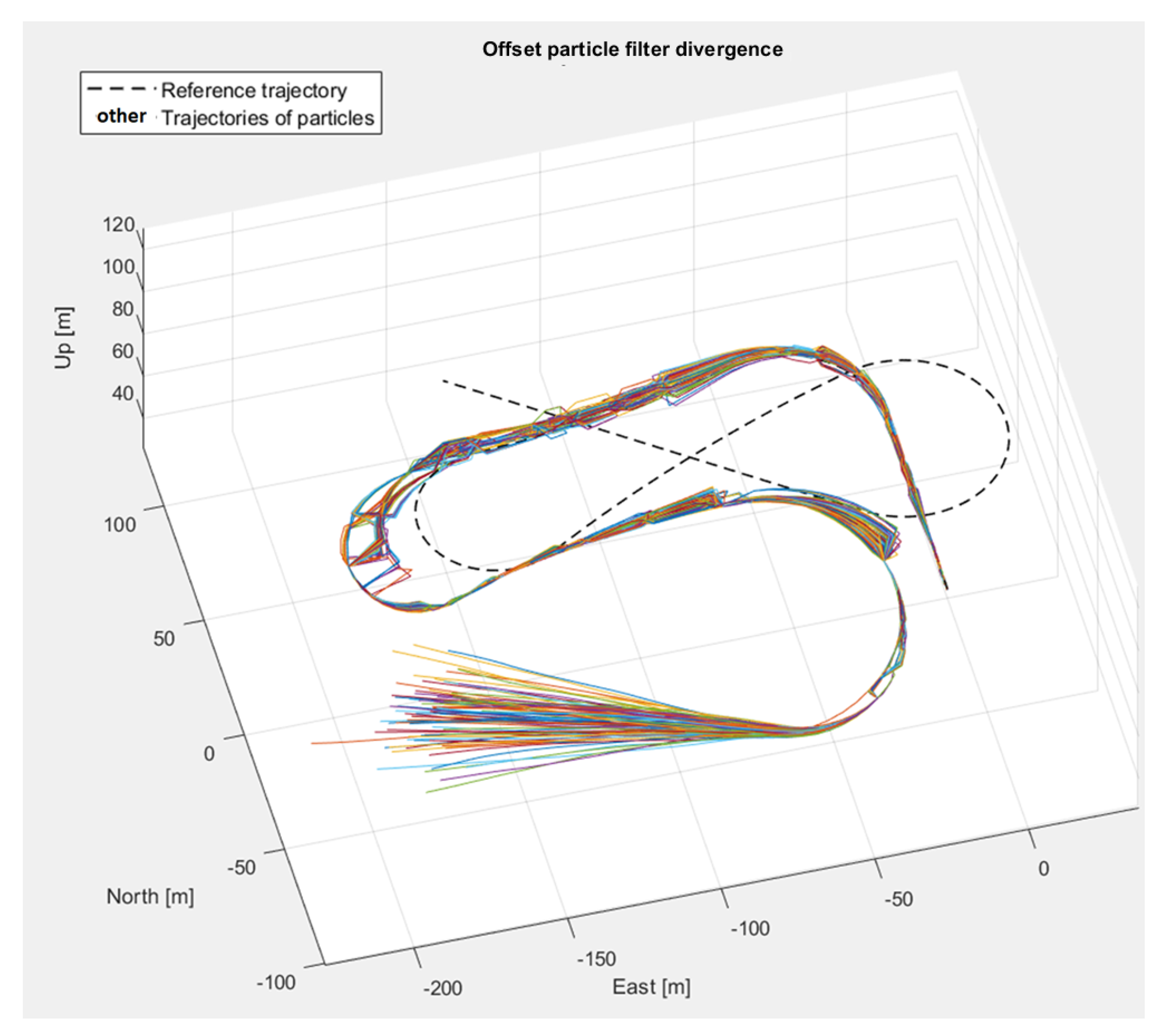
4.1. Simulation
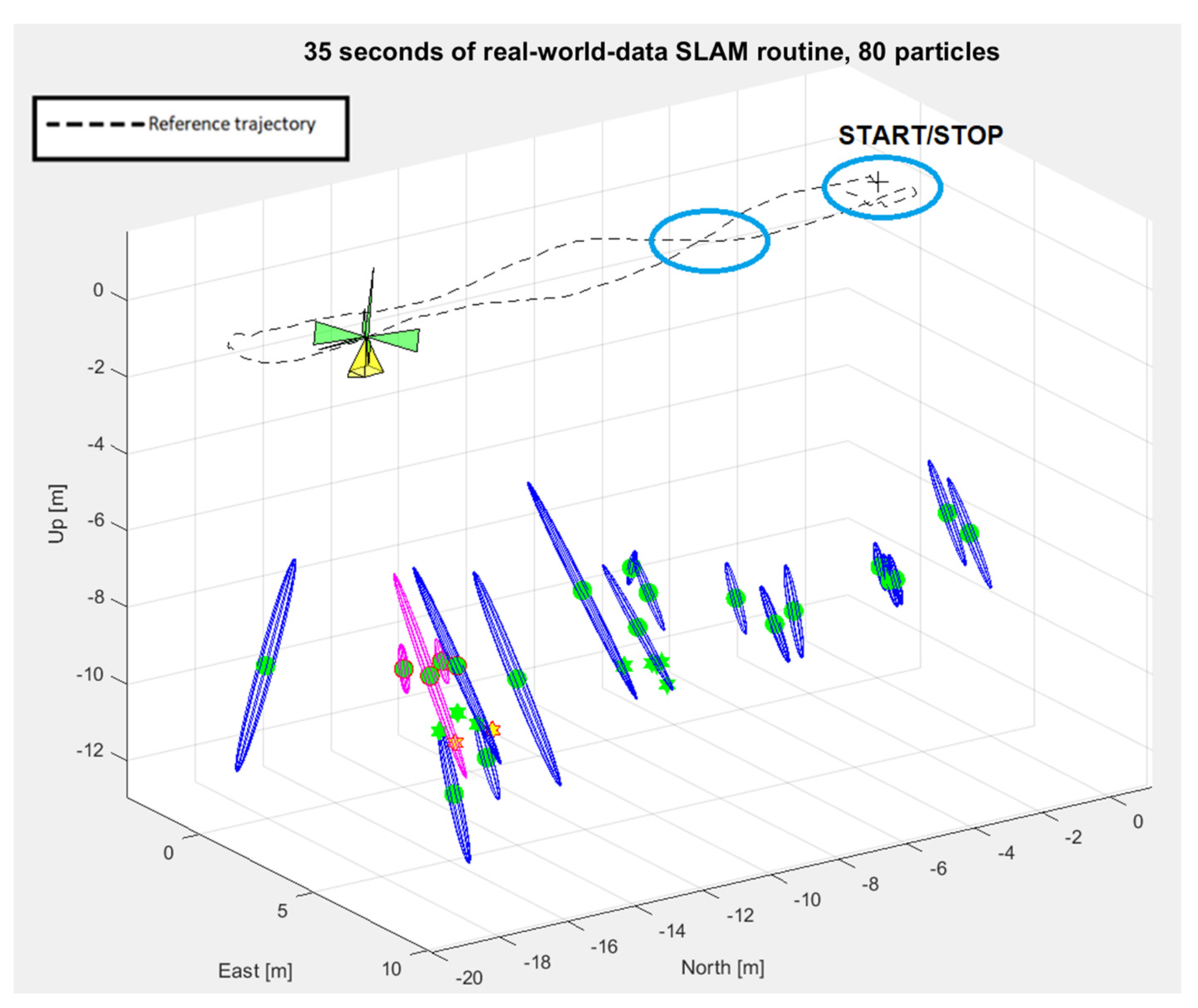
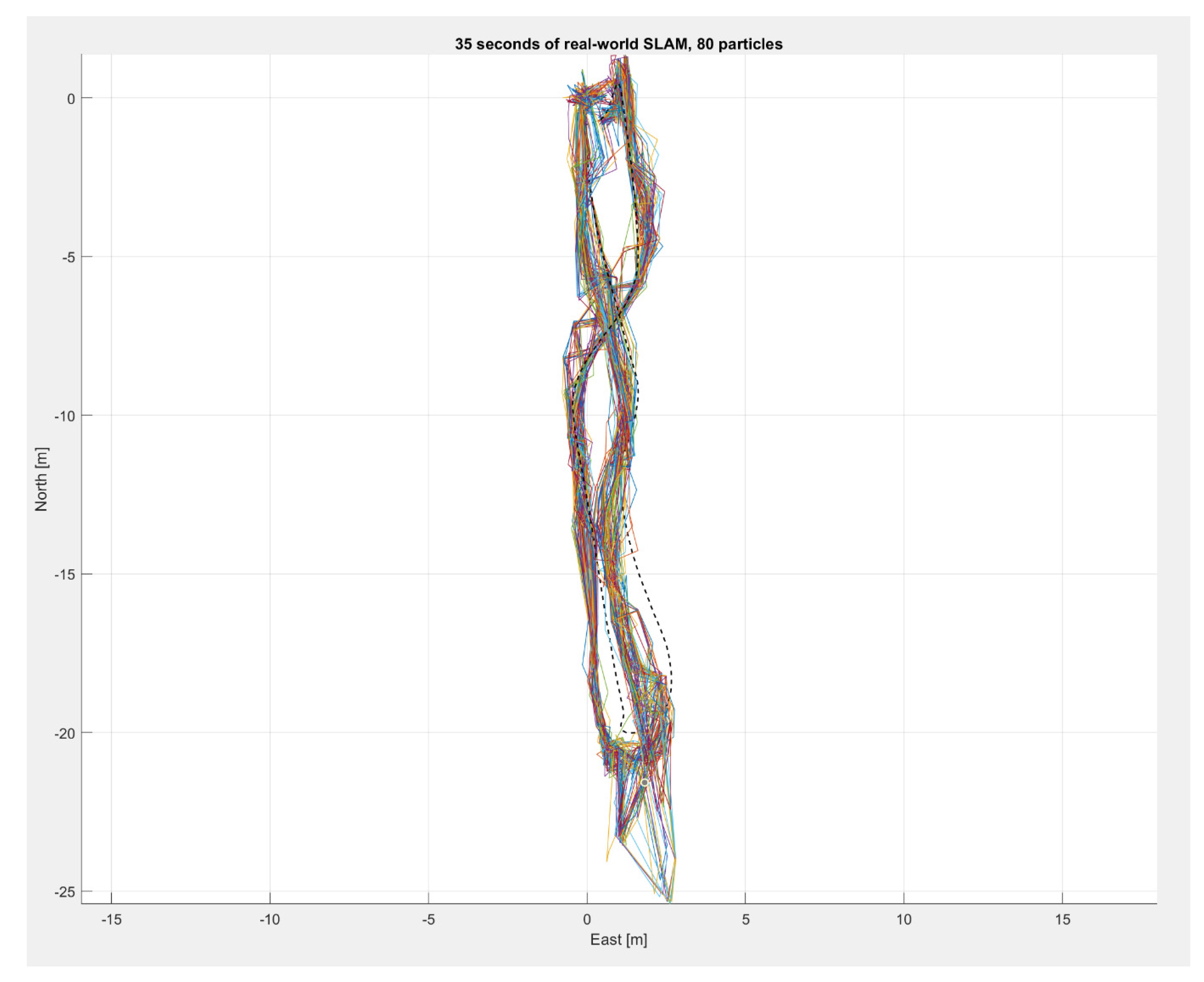
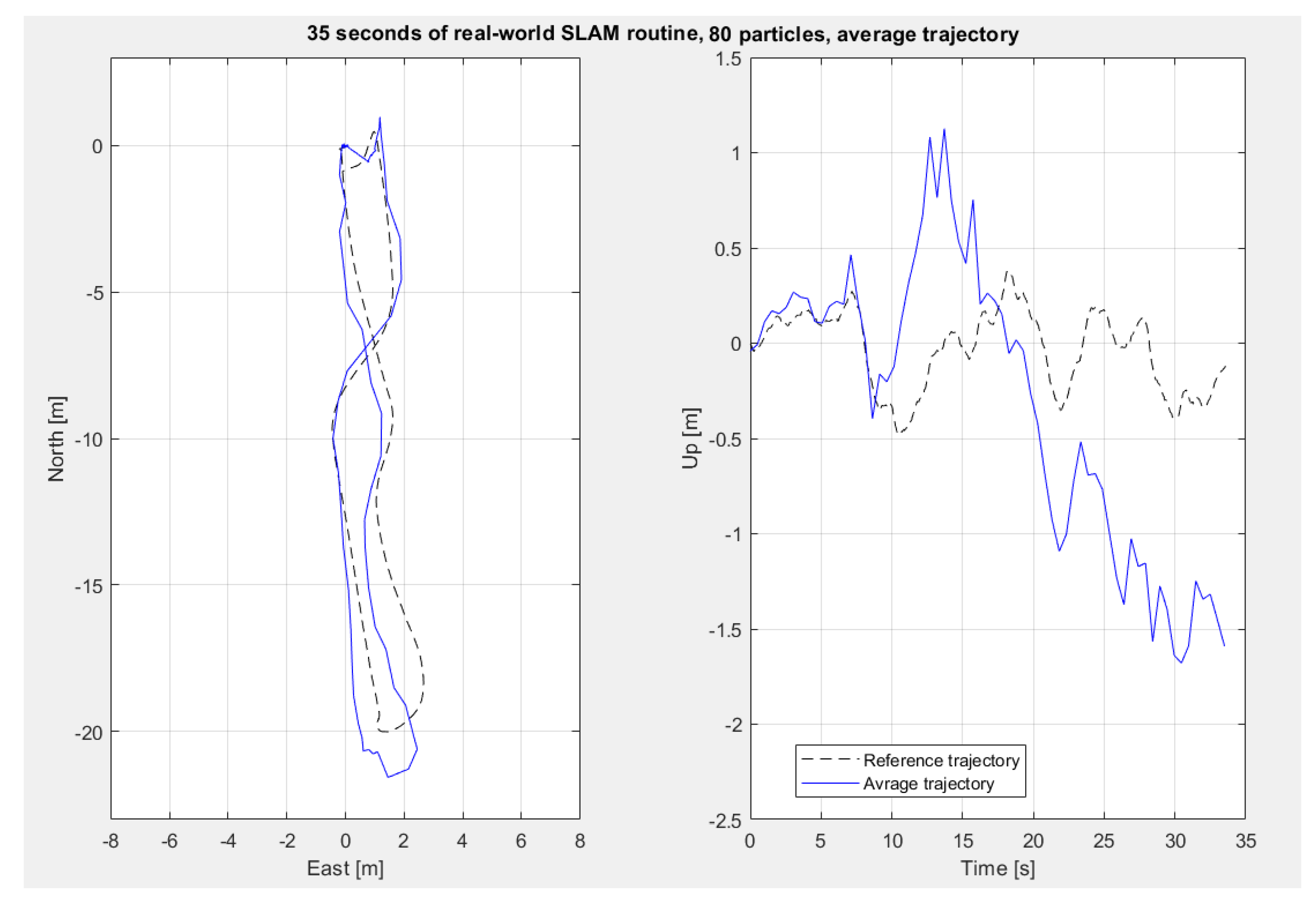
4.2. Real-World Data
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cadena, C.; Carlone, L.; Carrillo, H.; Latif, Y.; Scaramuzza, D.; Neira, J.; Reid, I.; Leonard, J.J. Past, present, and future of simultaneous localization and mapping: Toward the robust-perception age. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 32, 1309–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Younes, G.; Asmar, D.; Shammas, E.; Zelek, J. Keyframe-based monocular SLAM: Design, survey, and future directions. Rob. Auton. Syst. 2017, 98, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solà, J.; Vidal-Calleja, T.; Civera, J.; Montiel, J.M.M. Impact of landmark parametrization on monocular EKF-SLAM with points and lines. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2012, 97, 339–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant-Whyte, H.; Bailey, T. Simultaneous localization and mapping: Part I. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2006, 13, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Fu, G.; Li, J.; Yan, Z.; Bian, X. An Adaptive UKF Based SLAM Method for Unmanned Underwater Vehicle. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 605981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montemerlo, M.; Thrun, S.; Koller, D.; Wegbreit, B. FastSLAM: A factored solution to the simultaneous localization and mapping problem. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 28 July–1 August 2002; pp. 593–598. [Google Scholar]
- Thrun, S.; Montemerlo, M.; Koller, D.; Wegbreit, B.; Nieto, J.; Nebot, E. Fastslam: An efficient solution to the simultaneous localization and mapping problem with unknown data association. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2004, 4, 380–407. [Google Scholar]
- Grisetti, G.; Kummerle, R.; Stachniss, C.; Burgard, W. A Tutorial on Graph-Based SLAM. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2010, 2, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasdat, H.; Montiel, J.M.M.; Davison, A.J. Real-time monocular SLAM: Why filter? In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010; pp. 2657–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minkler, G.; Minkler, J. Theory and Application of Kalman Filtering; Magellan Book Co.: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 1993; ISBN 0962161829. [Google Scholar]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Montiel, J.M.M.; Tardos, J.D. ORB-SLAM: A Versatile and Accurate Monocular SLAM System. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1147–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altermatt, M.; Martinelli, A.; Tomatis, N.; Siegwart, R. SLAM with comer features based on a relative map. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37566), Sendai, Japan, 28 September–2 October 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1053–1058. [Google Scholar]
- An, S.-Y.; Kang, J.-G.; Lee, L.-K.; Oh, S.-Y. SLAM with salient line feature extraction in indoor environments. In Proceedings of the 2010 11th International Conference on Control Automation Robotics & Vision, Singapore, 7–10 December 2010; pp. 410–416. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, S.; Leonard, J. Monocular SLAM Supported Object Recognition. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems XI, Rome, Italy, 13–17 July 2015; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Eade, E.; Drummond, T. Scalable Monocular SLAM Simultaneous Localization and Mapping. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; pp. 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civera, J.; Lee, S.H. RGB-D Odometry and SLAM. In Advances in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 117–144. ISBN 9783030286033. [Google Scholar]
- Bresson, G.; Alsayed, Z.; Yu, L.; Glaser, S. Simultaneous Localization and Mapping: A Survey of Current Trends in Autonomous Driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2017, 2, 194–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saeedi, S.; Trentini, M.; Li, H.; Seto, M. Multiple-robot Simultaneous Localization and Mapping-A Review 1 Introduction 2 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping: Problem statement. J. F. Robot. 2016, 33, 3–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniewski, P.; Słowak, P. Simulation and Analysis of Particle Filter Based Slam System. Annu. Navig. 2019, 25, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, K.P. Bayesian map learning in dynamic environments. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 1015–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, K.; Ma, X.; Dai, X.; Fang, F. Improved Rao-Blackwellized particle filter for simultaneous robot localization and person-tracking with single mobile sensor. J. Control Theory Appl. 2011, 9, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlone, L.; Kaouk Ng, M.; Du, J.; Bona, B.; Indri, M. Simultaneous localization and mapping using rao-blackwellized particle filters in multi robot systems. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. Theory Appl. 2011, 63, 283–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xuexi, Z.; Guokun, L.; Genping, F.; Dongliang, X.; Shiliu, L. SLAM algorithm analysis of mobile robot based on lidar. In Proceedings of the 2019 Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Guangzhou, China, 27–30 July 2019; pp. 4739–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, N.M.; Dissanayake, G. Bearing-only SLAM in indoor environments using a modified particle filter. In Proceedings of the Australasian Conference on Robotics Automation 2003, Brisbane, Australia, 1–3 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pupilli, M.L.; Calway, A.D. Real-Time Camera Tracking Using a Particle Filter. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, Oxford, UK, 5–8 September 2005; British Machine Vision Association: Durham, UK, 2005; pp. 519–528. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, R.; Elinas, P.; Griffin, M.; Little, J.J. Vision-based SLAM using the rao-blackwellised particle filter. In Proceedings of the IJCAI-05 Workshop Reasoning with Uncertainty in Robotics (RUR-05), Edinburgh, UK, 30 July 2005; Volume 14, pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; Volume 2, pp. 1150–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire, T.; Lacroix, S.; Sola, J. A practical 3D bearing-only SLAM algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2–6 August 2005; pp. 2449–2454. [Google Scholar]
- Strasdat, H.; Stachniss, C.; Bennewitz, M.; Burgard, W. Visual Bearing-Only Simultaneous Localization and Mapping with Improved Feature Matching. In Proceedings of the Autonome Mobile Systeme 2007, 20. Fachgespräch, Kaiserslautern, Germany, 18–19 October 2007; pp. 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bay, H.; Ess, A.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Speeded-Up Robust Features (SURF). Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.; Lee, K.M. Monocular SLAM with locally planar landmarks via geometric rao-blackwellized particle filtering on Lie groups. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 1522–1529. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-H. Real-time camera tracking using a particle filter combined with unscented Kalman filters. J. Electron. Imaging 2014, 23, 013029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ababsa, F.; Mallem, M. Robust camera pose tracking for augmented reality using particle filtering framework. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2011, 22, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.; Stephens, M. A Combined Corner and Edge Detector. In Proceedings of the Alvey Vision Conference, Manchester, UK, 31 August–2 September 1988; pp. 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Çelik, K.; Somani, A.K. Monocular Vision SLAM for Indoor Aerial Vehicles. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2013, 2013, 374165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vidal, F.S.; Barcelos, A.D.O.P.; Rosa, P.F.F. SLAM solution based on particle filter with outliers filtering in dynamic environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE 24th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Buzios, Brazil, 3–5 June 2015; pp. 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, S.; Kabiri, P. A Novel Feature-Based Approach for Indoor Monocular SLAM. Electronics 2018, 7, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Maskell, S. RB2-PF: A novel filter-based monocular visual odometry algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference on Information Fusion (Fusion), Xi’an, China, 10–13 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Lu, H.; Xiao, J.; Qiu, Q.; Li, Y. Robust SLAM system based on monocular vision and LiDAR for robotic urban search and rescue. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Safety, Security and Rescue Robotics (SSRR), Shanghai, China, 11–13 October 2017; pp. 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ravankar, A.A.; Ravankar, A.; Emaru, T. A Novel Approach for Lidar-Based Robot Localization in a Scale-Drifted Map Constructed Using Monocular SLAM. Sensors 2019, 19, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acevedo, J.J.; Messias, J.; Capitan, J.; Ventura, R.; Merino, L.; Lima, P.U. A Dynamic Weighted Area Assignment Based on a Particle Filter for Active Cooperative Perception. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Mousavian, A.; Xiang, Y.; Xia, F.; Bretl, T.; Fox, D. PoseRBPF: A Rao–Blackwellized Particle Filter for 6-D Object Pose Tracking. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Lu, X.; Li, D.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X. Particle filter re-detection for visual tracking via correlation filters. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 14277–14301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z. An improved particle filter for mobile robot localization based on particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 135, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel, J.M.M.; Civera, J.; Davison, A.J. Unified inverse depth parametrization for monocular SLAM. Robot. Sci. Syst. 2007, 2, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tareen, S.A.K.; Saleem, Z. A comparative analysis of SIFT, SURF, KAZE, AKAZE, ORB, and BRISK. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (iCoMET), Sukkur, Pakistan, 3–4 March 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, N.; Howard, A. Design and use paradigms for gazebo, an open-source multi-robot simulator. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37566), Sendai, Japan, 28 September–2 October 2004; Volume 3, pp. 2149–2154. [Google Scholar]
- Ivaldi, S.; Peters, J.; Padois, V.; Nori, F. Tools for simulating humanoid robot dynamics: A survey based on user feedback. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Madrid, Spain, 18–20 November 2014; pp. 842–849. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Z.; Liang, P.; Feng, L.; Cai, T.; Xu, W. Comparative Analysis Between Gazebo and V-REP Robotic Simulators. In Proceedings of the ICMREE 2011 International Conference on Materials for Renewable Energy and Environment, Shanghai, China, 20–22 May 2011; Volume 2, pp. 1678–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körber, M.; Lange, J.; Rediske, S.; Steinmann, S.; Glück, R. Comparing Popular Simulation Environments in the Scope of Robotics and Reinforcement Learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.04616. [Google Scholar]











| Number of particles | 20 | 40 | 80 | |||||||
| Weighting and gating approach | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Percent of correct loop closures | loop 4 | 90 | 0 | 20 | 80 | 10 | 30 | 90 | 30 | 30 |
| loop 3 | 90 | 0 | 20 | 80 | 10 | 30 | 100 | 60 | 30 | |
| loop 2 | 100 | 0 | 30 | 100 | 10 | 30 | 100 | 60 | 40 | |
| loop 1 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 100 | 20 | 60 | 100 | 80 | 70 | |
| Number of resamplings | 62.11 | - | 37.5 | 68.5 | 29 | 50.33 | 68.22 | 63.67 | 53 | |
| Root mean squared error [m] | 20.34 | - | 34.23 | 13.545 | 29.95 | 28.68 | 7.80 | 17.33 | 15.97 | |
| Number of particles | 20 | 40 | 80 | |||||||
| Weighting and gating approach | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Percent of correct loop closures | loop 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | - | 30 | 60 | 0 | 40 |
| loop 1 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 50 | - | 40 | 90 | 0 | 70 | |
| Number of resamplings | - | - | - | 85.5 | - | 72.5 | 76.25 | - | 67.17 | |
| Root-mean-square error [m] | - | - | - | 10.44 | - | 12.28 | 5.94 | - | 7.16 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Slowak, P.; Kaniewski, P. Stratified Particle Filter Monocular SLAM. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3233. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163233
Slowak P, Kaniewski P. Stratified Particle Filter Monocular SLAM. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(16):3233. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163233
Chicago/Turabian StyleSlowak, Pawel, and Piotr Kaniewski. 2021. "Stratified Particle Filter Monocular SLAM" Remote Sensing 13, no. 16: 3233. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163233
APA StyleSlowak, P., & Kaniewski, P. (2021). Stratified Particle Filter Monocular SLAM. Remote Sensing, 13(16), 3233. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163233








