Robust Object Tracking Algorithm for Autonomous Vehicles in Complex Scenes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
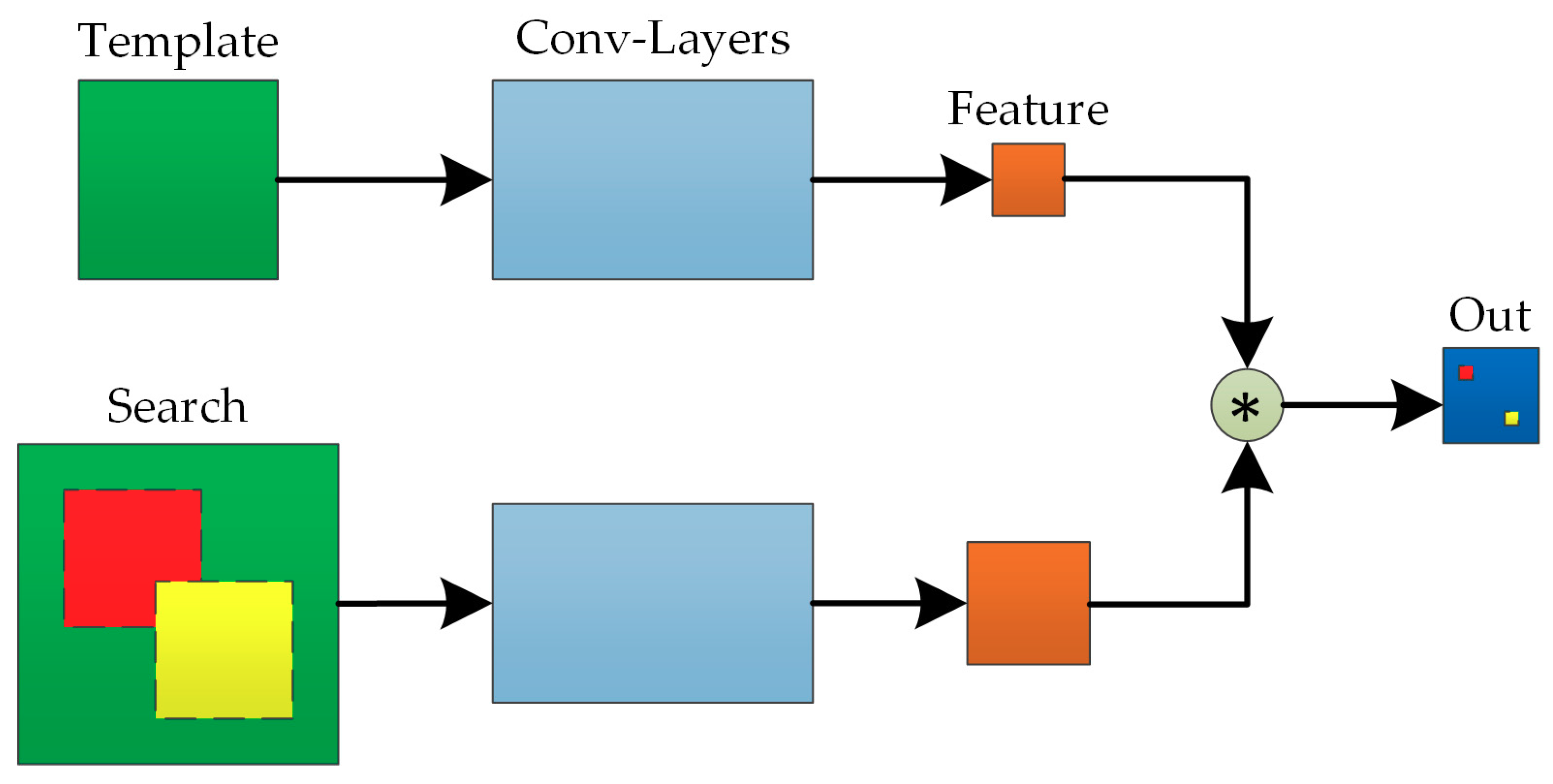
2.1. Siam-FC Network
2.2. Algorithms Related to Siam-FC
2.3. Limitations of Existing Algorithms
- (1)
- The adopted feature extraction backbone network has insufficient ability to extract deep features, cannot identify the exact location of the tracking object in the search area, and has poor tracking accuracy;
- (2)
- The network model only performs object recognition based on deep features, ignoring the detailed information of shallow features. When the scale of the tracking object changes greatly, the object can be lost easily;
- (3)
- The balance of tracking speed and tracking accuracy cannot be guaranteed. There are too many training parameters and redundant features are prone to occur, and the tracking efficiency is relatively low.
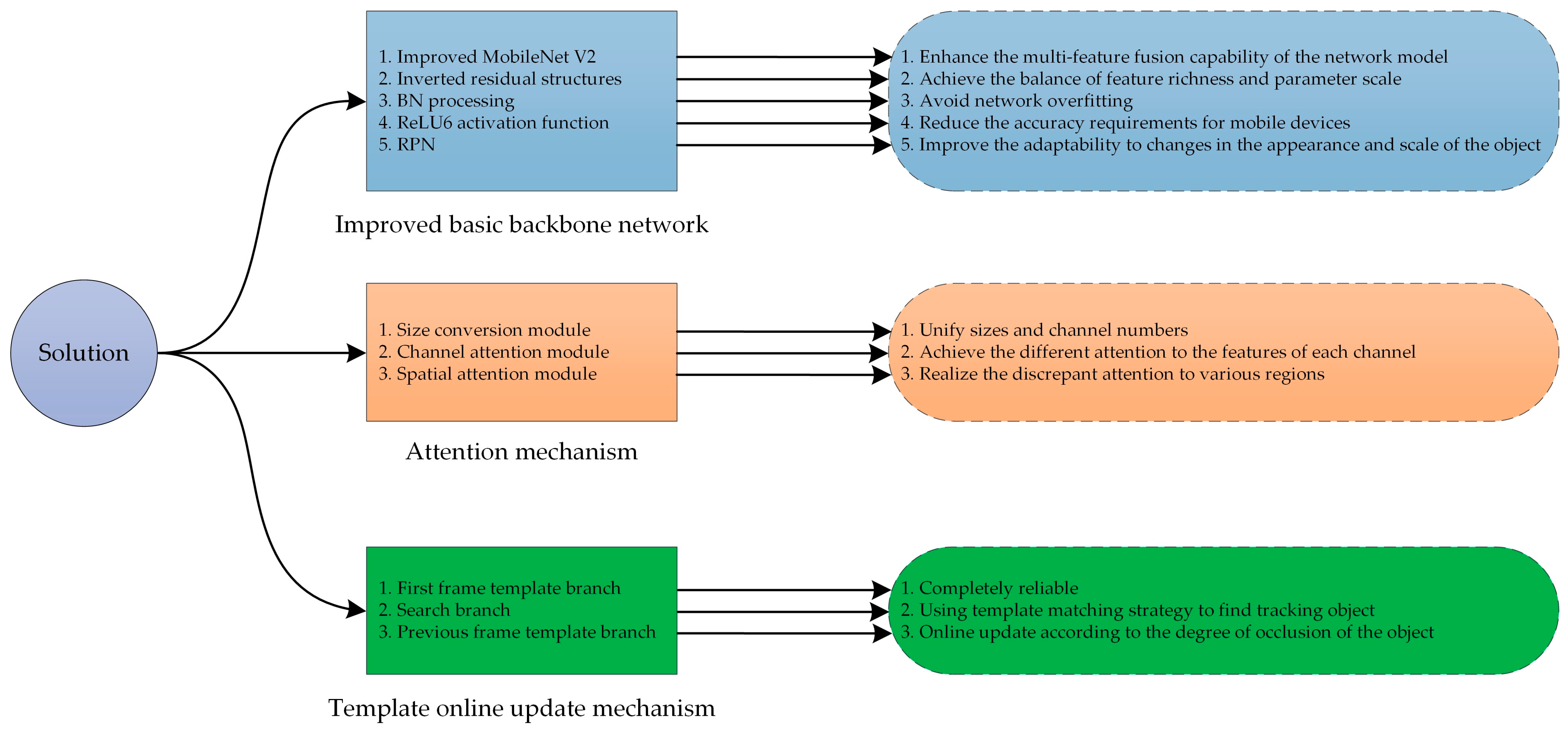
3. Network Model
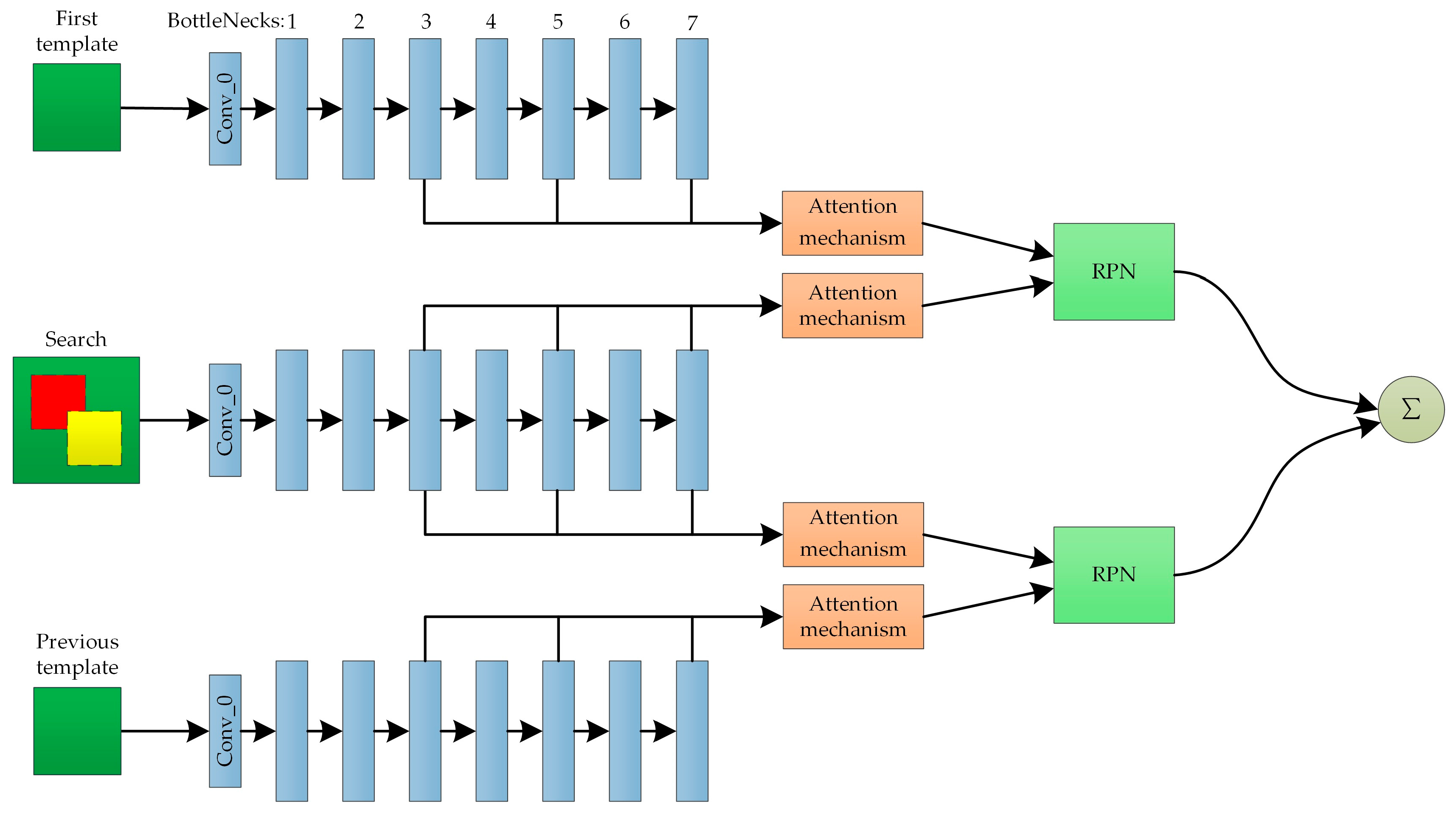
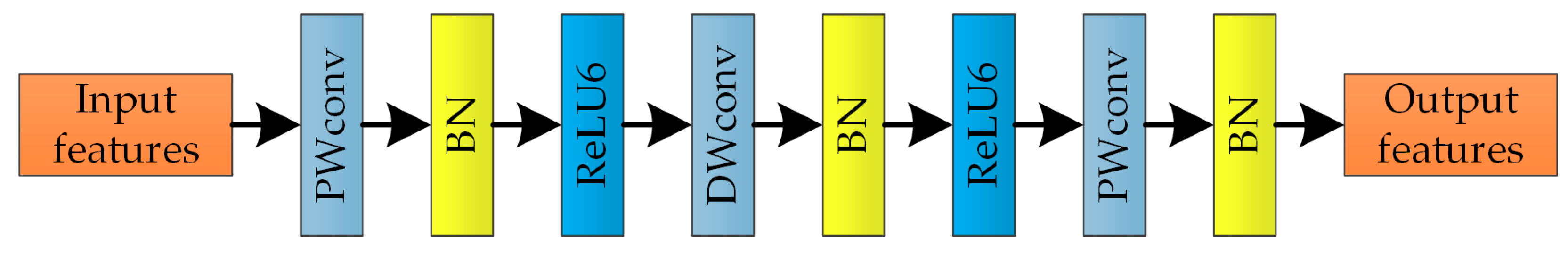
3.1. Double-Template Siamese Network Model Based on Multi-Feature Fusion
3.2. Attention Mechanism
3.2.1. Size Conversion Module
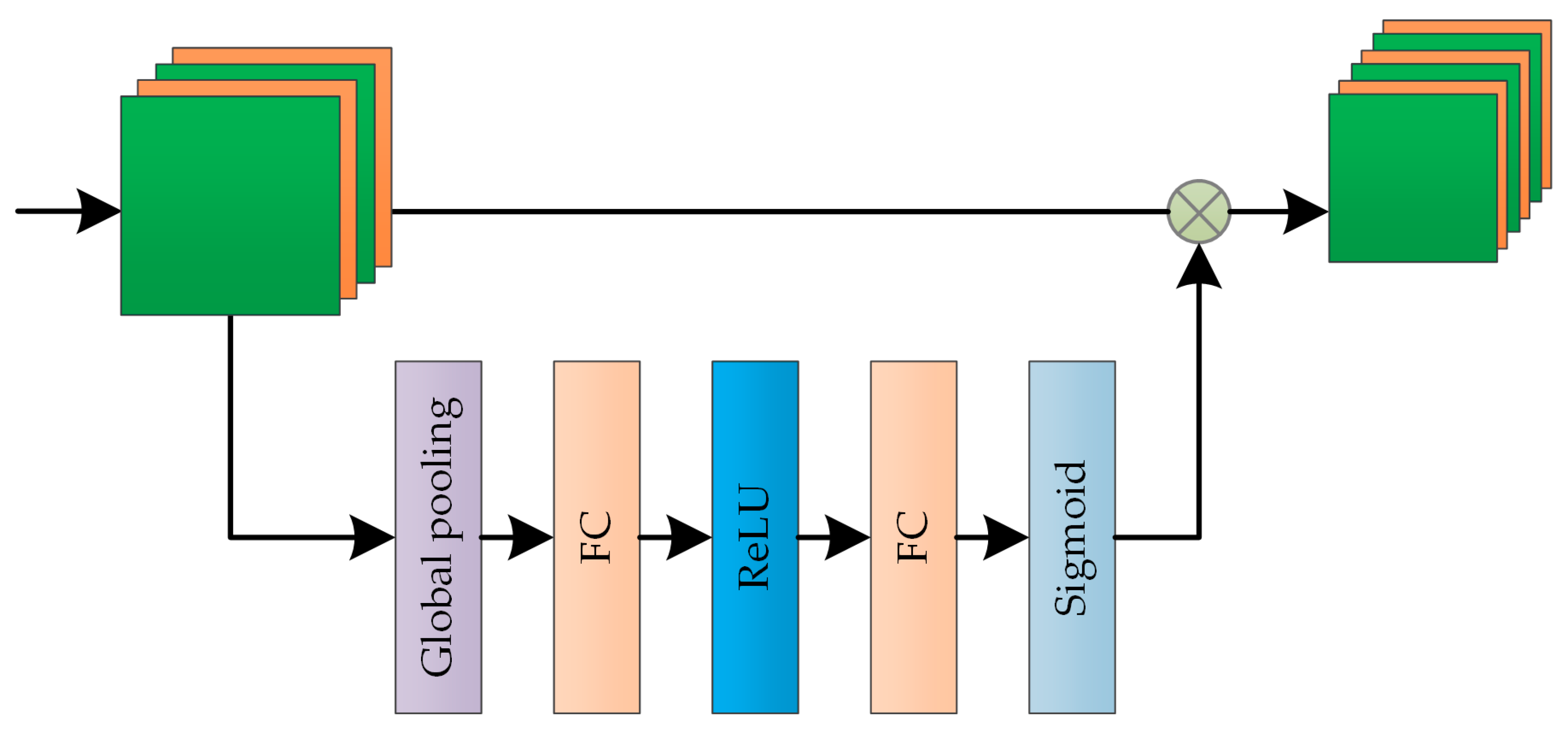
3.2.2. Channel Attention Module
3.2.3. Spatial Attention Module
3.3. Template Online Update
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Environment
4.2. Object Tracking Experiment Based on Public Datasets
4.2.1. Public Datasets
4.2.2. Training Settings and Evaluation Indicators
4.2.3. Analysis and Discussion of Testing Results
- 1.
- Qualitative analysis and discussion
- 2.
- Quantitative analysis and discussion
4.3. Object Tracking Experiment Based on Actual Driving Videos
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, F.; Shao, L.; Han, J. Robust and long-term object tracking with an application to vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 3387–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Moving vehicle detection and tracking based on video sequences. Trait. Signal 2020, 37, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavda, H.K.; Dhamecha, M. Moving object tracking using PTZ camera in video surveillance system. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Energy, Communication, Data Analytics and Soft Computing (ICECDS), Chennai, India, 1–2 August 2017; pp. 263–266. [Google Scholar]
- Granstrom, K.; Renter, S.; Fatemi, M.; Svensson, L. Pedestrian tracking using Velodyne data-Stochastic optimization for extended object tracking. In Proceedings of the 28th IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Redondo Beach, CA, USA, 11–14 June 2017; pp. 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Choi, Y.; Park, M.; Lee, S.; Kim, S. Multi-sensor-based detection and tracking of moving objects for relative position estimation in autonomous driving conditions. J. Supercomput. 2020, 76, 8225–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Li, Y. An improved moving object tracking method based on meanshift algorithm. ICIC Express Lett. Part B Appl. 2016, 7, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, C.; Yao, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, H.; Zha, H. On-road vehicle tracking using part-based particle filter. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 20, 4538–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, L.; Zhang, R.; Lv, L.; Wang, D.; Li, J. Object tracking in video sequence based on kalman filter. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Intelligent Control (ICCEIC), Chongqing, China, 6–8 November 2020; pp. 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, D.A.; Lim, J.; Lin, R.S.; Yang, M.H. Incremental learning for robust visual tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 77, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arróspide, J.; Salgado, L.; Nieto, M. Multiple object tracking using an automatic variable-dimension particle filter. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Hong Kong, China, 26–29 September 2010; pp. 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Du, K.; Ju, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, G.; Qian, S.; Li, Y. MeanShift tracking algorithm with adaptive block color histogram. In Proceedings of the 2012 2nd International Conference on Consumer Electronics, Communications and Networks (CECNet), Three Gorges, Yichang, China, 21–23 April 2012; pp. 2692–2695. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, H.; Nagai, Y.; Tasaka, K.; Yanagihara, H. Object tracking by branched correlation filters and particle filter. In Proceedings of the 4th Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR), Nanjing, China, 26–29 November 2017; pp. 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Liu, X.; Su, X.; Zhang, B. Robust kernelized correlation filter with scale adaption for real-time single object tracking. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2018, 15, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, D. A multiple feature fused model for visual object tracking via correlation filters. J. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 27271–27290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danelljan, M.; Häger, G.; Fahad Shahbaz, K.; Felsberg, M. Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking. In Proceedings of the 25th British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Nottingham, UK, 1–5 September 2014; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Henriques, J.F.; Caseiro, R.; Martins, P.; Batista, J. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Wang, G.; Yang, Q. Real-time part-based visual tracking via adaptive correlation filters. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2014; pp. 4902–4912. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, X.; Lu, H. Visual tracking with fully convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 15th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 11–18 December 2015; pp. 3119–3127. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, H.; Han, B. Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the 29th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 4293–4302. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Ma, C.; Wu, X.; Gong, L.; Bao, L.; Zuo, W.; Shen, C.; Lau, R.W.H.; Yang, M.H. Vital: Visual tracking via adversarial learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8990–8999. [Google Scholar]
- Amamra, A.; Aouf, N. Real-time multiview data fusion for object tracking with RGBD sensors. Robotica 2016, 34, 1855–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashbaugh, J.; Kitts, C. Vision-based object tracking using an optimally positioned cluster of mobile tracking stations. IEEE Syst. J. 2018, 12, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimanitaleb, Z.; Keyvanrad, M.A.; Jafari, A. Object tracking methods: A review. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer and Knowledge Engineering (ICCKE), Mashhad, Iran, 24–25 October 2019; pp. 282–288. [Google Scholar]
- Dewangan, D.K.; Sahu, S.P. Real time object tracking for intelligent vehicle. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Power, Control and Computing Technologies (ICPC2T), Chhattisgarh, India, 3–5 January 2020; pp. 134–138. [Google Scholar]
- Ravindran, R.; Santora, M.J.; Jamali, M.M. Multi-object detection and tracking, based on DNN, for autonomous vehicles: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 5668–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avola, D.; Cinque, L.; Diko, A.; Fagioli, A.; Foresti, G.L.; Mecca, A.; Pannone, D.; Piciarelli, C. MS-Faster R-CNN: Multi-stream backbone for improved Faster R-CNN object detection and aerial tracking from UAV images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Cai, B.G. An intelligent vehicle tracking technology based on SURF feature and Mean-shift algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (IEEE ROBIO), Bali, Indonesia, 5–10 December 2014; pp. 1224–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Harada, H. Object tracking using virtual particles driven by optical flow and Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), Jeju, Korea, 15–18 October 2019; pp. 1064–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, J.; Nanda, P.K. Video object-tracking using particle filtering and feature fusion. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Electrical Control and Signal Systems (AECSS), Bhubaneswar, India, 8–9 November 2019; pp. 945–957. [Google Scholar]
- Judy, M.; Poore, N.C.; Liu, P.; Yang, T.; Britton, C.; Bolme, D.S.; Mikkilineni, A.K.; Holleman, J. A digitally interfaced analog correlation filter system for object tracking applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 2764–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Yoo, H.J. A low-power deep neural network online learning processor for real-time object tracking application. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2019, 66, 1794–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, B.; Mei, Z.; Cui, Z.; Gao, G. Visual object tracking with discriminative correlation filtering and hybrid color feature. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 34725–34744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, E.; Deng, M.; Tong, J.; Jia, C.; Du, S. Moving vehicle tracking based on improved tracking-learning-detection algorithm. IET Comput. Vis. 2019, 13, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Li, D.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J. Multiple-object-tracking algorithm based on dense trajectory voting in aerial videos. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Wang, B.; Su, Y. Object detection-tracking algorithm for unmanned surface vehicles based on a radar-photoelectric system. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 57529–57541. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, J.; Chen, J.; Li, N.; Chan, J.C.-W.; Kong, S.G. Object tracking in hyperspectral-oriented video with fast spatial-spectral features. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Tan, X.; Liao, P.; Wu, H.; Cui, X.; Zuo, Y.; Lv, Z. Single object tracking in satellite videos: Deep Siamese network incorporating an interframe difference centroid inertia motion model. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertinetto, L.; Valmadre, J.; Henriques, J.F.; Vedaldi, A.; Torr, P.H.S. Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 850–865. [Google Scholar]
- Valmadre, J.; Bertinetto, L.; Henriques, J.; Vedaldi, A.; Torr, P.H.S. End-to-end representation learning for Correlation Filter based tracking. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5000–5008. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Feng, W.; Zhou, C.; Huang, R.; Wan, L.; Wang, S. Learning dynamic siamese network for visual object tracking. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1781–1789. [Google Scholar]
- He, A.; Luo, C.; Tian, X.; Zeng, W. A twofold siamese network for real-time object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4834–4843. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Yan, J.; Wu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Hu, X. High performance visual tracking with siamese region proposal network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8971–8980. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks: Mobile Networks for Classification, Detection and Segmentation. Available online: http://202.113.61.185/xc-ftp/Paper2/Deep_Learning/mobilenetv2.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2018).
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Real, E.; Shlens, J.; Mazzocchi, S.; Pan, X.; Vanhoucke, V. YouTube-BoundingBoxes: A large high-precision human-annotated data set for object detection in video. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7464–7473. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Lim, J.; Yang, M.H. Object tracking benchmark. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1834–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danelljan, M.; Hager, G.; Khan, F.S.; Felsberg, M. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the 15th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 11–18 December 2015; pp. 4310–4318. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Zhou, W.; Tian, Q.; Hong, R.; Wang, M.; Li, H. Multi-cue correlation filters for robust visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4844–4853. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Xing, J.; Gao, J.; Peng, P.; Hu, W.; Maybank, S. Visual tracking via spatially aligned correlation filters network. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 484–500. [Google Scholar]
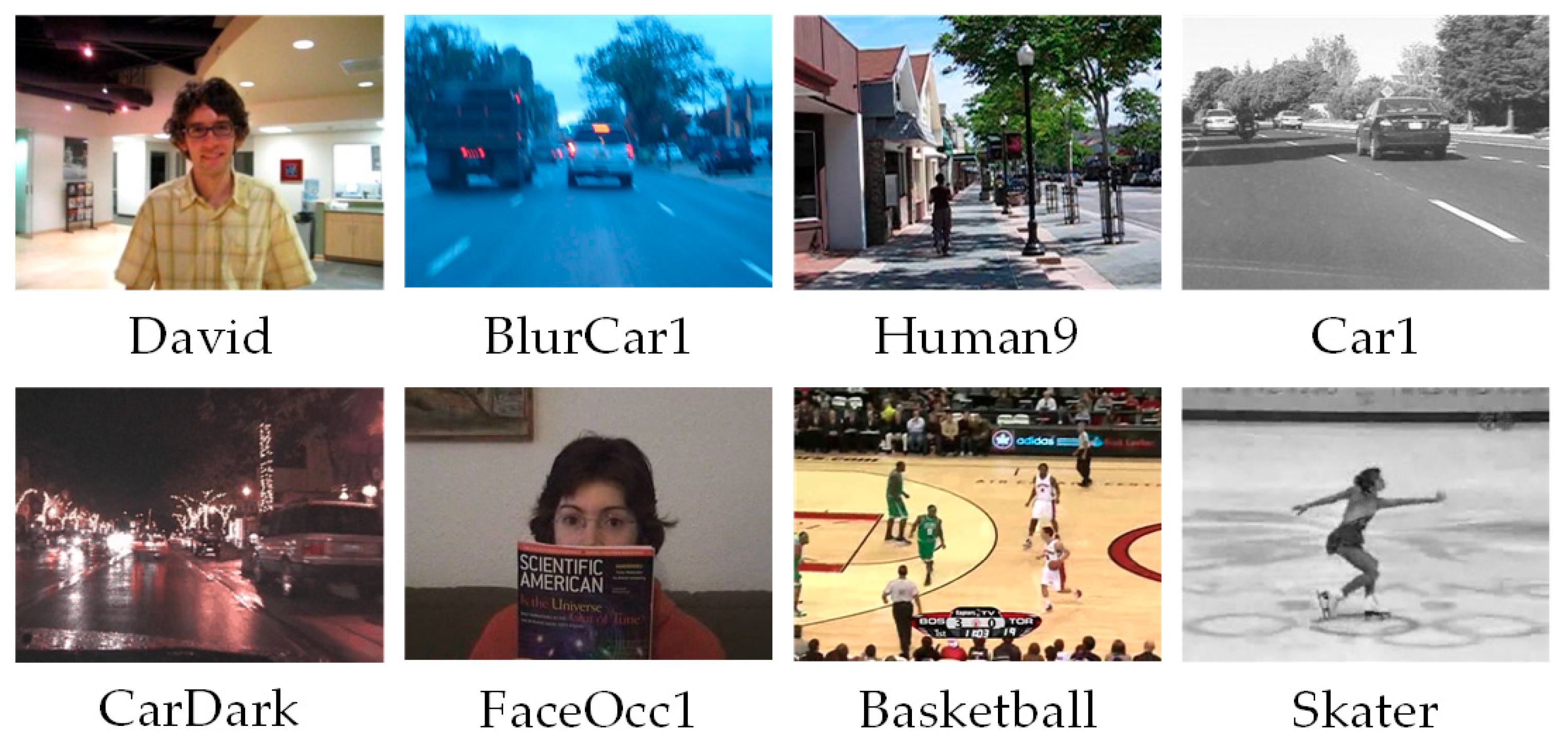




| CFNet | DSiam | SA-Siam | SiamRPN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Release date | July 2017 | October 2017 | June 2018 | June 2018 |
| Developers | Valmadre et al. [39] | Guo et al. [40] | He et al. [41] | Li et al. [42] |
| Training datasets | ILSVRC 2015-VID dataset | ILSVRC 2015-VID dataset | Color images in the ILSVRC 2015-VID dataset | ILSVRC 2015-VID dataset and YouTube-BoundingBoxes dataset |
| Outstanding feature | The correlation filtering operation is integrated into a single network layer and embedded into the network | Addition of the object appearance change conversion layer and background suppression conversion layer in the x and z branches, respectively | Use of two branch networks to obtain semantic features and appearance features, respectively | Application of the RPN module to the tracking task and transformation of the similarity measurement calculation into classification and regression |
| Video Sequence | Challenging Aspects |
|---|---|
| CarDark | IV, BC |
| Human4 | IV, SV, OCC, DEF |
| BlurCar1 | MB, FM |
| MotorRolling | IV, SV, MB, FM, IPR, BC, LR |
| Suv | OCC, IPR, OV |
| Biker | SV, OCC, MB, FM, OPR, OV, LR |
| Video Sequence | SRDCF | MCCT | SACF | CFNet | SA-Siam | SiamRPN | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CarDark | 58.9 | 68.5 | 69.2 | 64.3 | 74.1 | 78.4 | 82.5 |
| Human4 | 79.5 | 80.6 | 87.1 | 68.4 | 82.5 | 84.6 | 85.8 |
| BlurCar1 | 58.2 | 59.0 | 65.4 | 55.8 | 72.3 | 76.5 | 80.6 |
| MotorRolling | 57.9 | 58.8 | 62.7 | 54.7 | 72.5 | 77.4 | 80.1 |
| Suv | 58.6 | 57.7 | 63.5 | 52.3 | 76.1 | 77.8 | 79.4 |
| Biker | 80.1 | 83.4 | 85.2 | 75.7 | 82.8 | 85.6 | 86.5 |
| Average | 65.5 | 68.0 | 72.2 | 61.9 | 76.7 | 80.1 | 82.5 |
| Video Sequence | SRDCF | MCCT | SACF | CFNet | SA-Siam | SiamRPN | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CarDark | 16.3 | 14.4 | 13.6 | 21.1 | 12.5 | 11.3 | 9.1 |
| Human4 | 6.4 | 6.2 | 5.5 | 10.6 | 6.0 | 5.9 | 5.7 |
| BlurCar1 | 21.7 | 19.5 | 16.6 | 23.8 | 14.5 | 12.8 | 10.4 |
| MotorRolling | 16.6 | 16.3 | 15.9 | 24.2 | 14.8 | 11.6 | 10.5 |
| Suv | 16.9 | 18.2 | 15.1 | 21.4 | 12.8 | 12.2 | 11.2 |
| Biker | 6.2 | 5.0 | 4.5 | 10.1 | 5.3 | 4.2 | 3.8 |
| Average | 14.0 | 13.3 | 11.9 | 18.5 | 11.0 | 9.7 | 8.5 |
| Algorithm | SRDCF | MCCT | SACF | CFNet | SA-Siam | SiamRPN | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPS | 24 | 40 | 42 | 67 | 52 | 58 | 56 |
| Real time | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Sequence Number | Object Type | Average OR (%) | Average CLE (Pixels) | FPS | Frame |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Car | 85.8 | 6.5 | 59 | 2849 |
| 2 | Pedestrian | 88.1 | 4.8 | 62 | 2670 |
| 3 | Bus | 80.7 | 10.2 | 53 | 2282 |
| 4 | Bicycle | 85.5 | 5.7 | 60 | 1795 |
| 5 | Motorbike | 83.4 | 7.1 | 56 | 1564 |
| Mean | - | 84.7 | 6.9 | 58 | 2232 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, J.; Song, C.; Song, S.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Ang, M.H., Jr. Robust Object Tracking Algorithm for Autonomous Vehicles in Complex Scenes. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163234
Cao J, Song C, Song S, Xiao F, Zhang X, Liu Z, Ang MH Jr. Robust Object Tracking Algorithm for Autonomous Vehicles in Complex Scenes. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(16):3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163234
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Jingwei, Chuanxue Song, Shixin Song, Feng Xiao, Xu Zhang, Zhiyang Liu, and Marcelo H. Ang, Jr. 2021. "Robust Object Tracking Algorithm for Autonomous Vehicles in Complex Scenes" Remote Sensing 13, no. 16: 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163234
APA StyleCao, J., Song, C., Song, S., Xiao, F., Zhang, X., Liu, Z., & Ang, M. H., Jr. (2021). Robust Object Tracking Algorithm for Autonomous Vehicles in Complex Scenes. Remote Sensing, 13(16), 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163234










