Abstract
Land-use/land cover change (LUCC) is an important problem in developing and under-developing countries with regard to global climatic changes and urban morphological distribution. Since the 1900s, urbanization has become an underlying cause of LUCC, and more than 55% of the world’s population resides in cities. The speedy growth, development and expansion of urban centers, rapid inhabitant’s growth, land insufficiency, the necessity for more manufacture, advancement of technologies remain among the several drivers of LUCC around the globe at present. In this study, the urban expansion or sprawl, together with spatial dynamics of Hyderabad, Pakistan over the last four decades were investigated and reviewed, based on remotely sensed Landsat images from 1979 to 2020. In particular, radiometric and atmospheric corrections were applied to these raw images, then the Gaussian-based Radial Basis Function (RBF) kernel was used for training, within the 10-fold support vector machine (SVM) supervised classification framework. After spatial LUCC maps were retrieved, different metrics like Producer’s Accuracy (PA), User’s Accuracy (UA) and KAPPA coefficient (KC) were adopted for spatial accuracy assessment to ensure the reliability of the proposed satellite-based retrieval mechanism. Landsat-derived results showed that there was an increase in the amount of built-up area and a decrease in vegetation and agricultural lands. Built-up area in 1979 only covered 30.69% of the total area, while it has increased and reached 65.04% after four decades. In contrast, continuous reduction of agricultural land, vegetation, waterbody, and barren land was observed. Overall, throughout the four-decade period, the portions of agricultural land, vegetation, waterbody, and barren land have decreased by 13.74%, 46.41%, 49.64% and 85.27%, respectively. These remotely observed changes highlight and symbolize the spatial characteristics of “rural to urban transition” and socioeconomic development within a modernized city, Hyderabad, which open new windows for detecting potential land-use changes and laying down feasible future urban development and planning strategies.
1. Introduction
Urbanization symbolizes the development and modernization of cities and highlights the movement of residents from rural to urban areas. Currently, more than half of the total world population resides in cities [1]. Due to the increase in population, cities are rapidly expanding in terms of physical infrastructures, and advancing in technological levels during the recent few decades [2,3], with an attempt to create sustainable communities in long run [4]. Although these urbanization pathways have motivated the technological breakthrough of modern societies and have led to transitions and variations of landscape patterns and land covers of the individual city and spatial area [5,6,7], it also triggers various devastating environmental effects, for example, environmental degradation in city areas, the loss of agriculture land and groundwater depletion [8,9].
Overall, rapid urbanization observed worldwide can be categorized by demographic attention and urban expansion [10], while urban expansion can further be categorized by the form of land use; cross-land-use patterns; commercial development along highways; and development of public service and culture [10,11], because urbanization processes are usually closely interconnected with the economic, cultural, and political development of a city, where the modifications and updating of local structures or landscapes could possibly be in line with national or regional planning missions, as well as changes in land use regulations [12,13,14]. For modernized regions, whenever urban economic development is insufficient to maintain or support the employment and housing demands of new residents, slums will be created, thus a series of large-scale settlements were established. During the process, land use/land cover change (LUCC) must take place. Here, LUCC refers to the impact of anthropogenic activities and disturbances on Earth’s surface, and the corresponding human transformation could serve as the most direct indicator for characterizing changes and modifications of natural features, as well as global environmental and climatic changes [15,16]. Despite better use of available land for satisfying different human needs, traditional landscape features and natural sceneries could have become worsened, via the disintegration and heterogeneity of 3-dimensional structures [17,18], and this could also affect the biodiversity and sustainable development of a city in both short and long terms [19]. In particular, for developed countries like the United States, an urban expansion that occurred at the expense of forests or woodlands in The San Antonio River Basin, i.e., LUCC processes have imposed significant impacts on its ecosystem service values [20], while the increase of urban land expansion has led to the losses of farmland as stated in [2]. Further, the changes in land use in Dongtan (i.e., Chongming Island of China) have imposed ecological impacts on the surrounding environment, and the construction processes were not environmentally friendly nor sustainable [21]. Therefore, it is essential to enumerate LUCC, for excavating indulgence of urban expansion, associated spatial dynamics, and potential impacts to the country or city development in different perspectives. In particular, the most prominent indicator that could be traced is the excessive urban land use and sprawl, which will likely expand in both qualitative and spatial extents [14,22].
With today’s rapid economic development and increased population, urbanization-induced LUCC has dramatically increased and attracted public’s attention, thus relevant studies have become hotspots particularly for future city planning [23]. As for developing countries or cities, urbanization or LUCC usually take place around the central regions of individual cities [24], thus wrinkle and induce long-lasting spatial discrepancies between rural and urban areas. Such difference will be more obvious among space and time [10], therefore, the study of LUCC and associated socio-economic impacts in developing and under-developing countries or cities is of great significance. In this study, the changes of spatial features within Pakistan, the 5th most populous country, are of paramount interest [25]. In particular, changes in Hyderabad, the 2nd largest city of Sindh, which is the most urbanized province of Pakistan are investigated and explored. This city has undergone huge and continuous socio-cultural transitions since the past, and because of the accelerated phase of industrialization, it has observed rapid and dynamic growth in population and significant features of urban expansion [26]. Despite the achievement of accelerated city development, excess urbanization and uneven urban growth patterns within Hyderabad have also led to hastened and significant conversion of agricultural practices and enhancement in vehicular traffic, which cause cultivated land loss, increased noise, dust and air pollution within the neighborhood environment [27,28].
Due to the lack of long-term strategic planning, the absence of resources and proper statistical centers for conducting spatial analyses in many developing cities like Hyderabad [29], LUCC and associated spatial updates can only be effectively quantified via change detection approaches. Some commonly adopted assessment procedures include transformation, post-classification and direct comparison, for example, by comparing the difference in magnitude, nominal ratio, or regressive factors of time series plots retrieved from multispectral channels [30], in a remote manner. Although some of these techniques can expediently simplify the operational processes and supply change/non-change statistics, they cannot provide information regarding the land cover categories, as well as the detailed mechanism of these changes. Nevertheless, the post-classification approach can remedy such deficiency, by classifying the desired attributes within two periods, then conducting overlaying operations. However, errors in classification could proliferate and magnify with aggregate processing steps [31]. Thus, a consistent, comprehensive and continuous monitoring framework, remotely sensed datasets, and a relevant statistical machine learning algorithm that can effectively govern the changes of land-use patterns are particularly important for related studies and assessments.
Remote sensing (RS) approaches obtain data from the earth surface without involving any direct contacts, and have shown capable performance in examining the land cover changes, assessing urban LUCC and sustainability features within different spatial regions [32,33,34,35], and even outlying future environmental and development policies [36]. Generally speaking, RS is a better means of extracting LUCC attributes because of the higher frequency, wider field of view, and the availability of multi-spectral characteristics [37], especially after the United States allowed public access and downloading of Landsat datasets, as well as the corresponding time series retrieved by different algorithms [38]. Commonly and freely available earth observing moderate-resolution Landsat equipment, like Landsat 1/2/3 Multi-Spectral Scanner (MSS), Landsat 5 MSS and Thematic Mapper (TM), Landsat 7 Enhanced Thematic Mapper plus (ETM), and Landsat 8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) [39], are all suitable for LUCC assessment, via retrieving land-use characteristics based on the reflection of electromagnetic waves or eminence from ground objects, then obtaining long-term monitoring through repeated and continuous remote measurements, and eventually conducting data analyses and storage processes. All these tools have enabled researchers to put emphasis on image-texturing and performing contextual and statistical analyses of neighboring pixels in available datasets, thus enlightened the accuracies of image classification [40,41,42]. In recent decades, many research studies have combined medium resolution imageries obtained from remote sensing technologies, together with numerical and statistical algorithms to conduct a spatial and temporal assessment of land cover changes, for example, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) [43], Maximum Likelihood Classifier (MLC) and Support Vector Machine (SVM) [44], as well as Random Forest (RF) approaches [45]. The estimated outputs are proficient in identifying the spatial variabilities related to morphological structures of towns, such as volume, density, and range of urbanized or rural areas [46,47].
So far, there is still very little research that highlights the processes and mechanisms of changing land-use patterns, and land cover dynamics within South Asian countries in recent decades, while only some qualitative conclusions have been reached. In particular, the complicated spatial patterns of physical and social infrastructures within different metropolitan cities of India, together with potential challenges of urban development were well-remarked in [48], while geospatial techniques and supervised classification have been employed to detect and assess the LUCC in Sikkim Himalaya, India, and revealed that the proportion of impervious surface/built-up areas has increased during 1988–2017, and was accompanied by the reduction of cropland and barren land within the spatial region [49]. Moreover, a case study conducted on Margallah Hills National Park, Islamabad has shown that there was a decline in vegetation cover due to exotic species like paper mulberry [50], while another recent study has investigated the land-use changes of Islamabad from 1992 to 2012 [51]. The conclusions are quite similar, that the proportions of cropland, built-up areas and waterbodies have increased, and can be attributed to the decrease in forest and barren land within the city [51]. Similar deduction has also been acquired in the Multan district of Pakistan, via the use of RS and GIS techniques [52]. Due to the aforementioned spatial research gaps, and the fact that all anthropogenic processes are still taking place in different municipalities of Pakistan, it is crucial to obtain fine-scale spatial changing patterns in under-developing cities like Hyderabad. In this paper, Section 2 provides a brief overview of the study area, processing of different Landsat images, and the retrieval of spatial dynamics (i.e., LUCC), via the combination of remote sensing, SVM and geoprocessing techniques. Then, the classification of land covers and respective numerical accuracies, temporal transitions and trends of land use during 1979–2020, together with underlying geographical and historical reasons are provided in Section 3. The discussion of spatial dynamics and relation with population changes, potential future connections with meteorological changes and local air quality, comparison with similar studies, together with some recommendations of future urban development of Hyderabad or similar developing cities, are outlined in Section 4. Finally, Section 5 outlines the potential extension, outlook, and the summary of this study.
2. Study Area, Datasets and Methodologies
2.1. Study Area
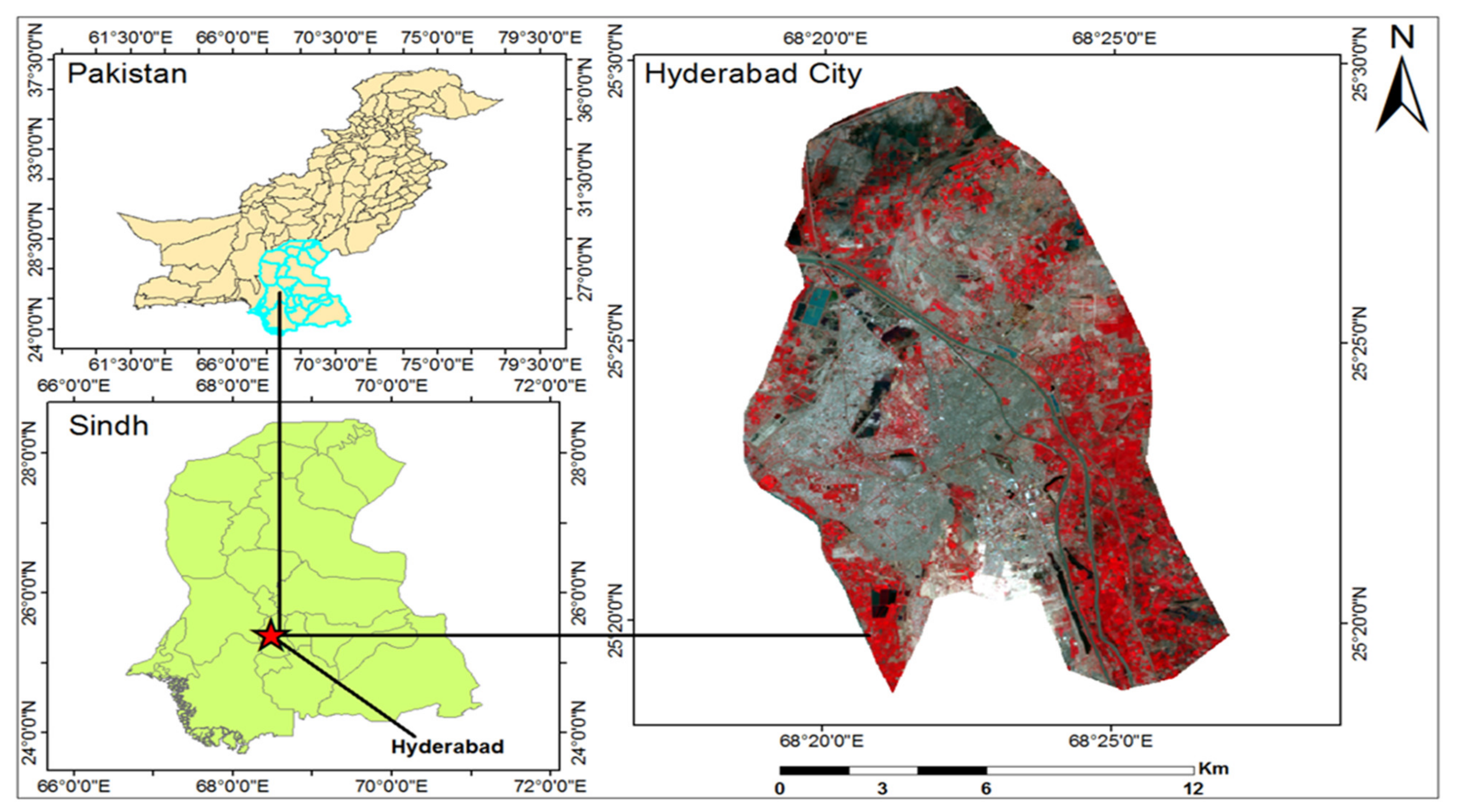
Hyderabad is the second-largest city in Sindh province, right after Karachi. The city was founded in 1768, because the river Indus of Pakistan was changing course in 1757, thus resulted in periodic flooding. Afterwards, the king Mian Ghulam Shah Kalhoro of the Kalhora Dynasty has decided to shift the capital from Khudabad to a new one, which was named “Hyderabad” [53]. In terms of geographical location, the city is situated at the latitude of 25°23′33″N and longitude of 68°22′25″E, with an elevation of 13 m above sea level (as shown in Figure 1 below). The city has a warm desert climate (Köppen BWh), with hot environmental conditions throughout the entire year. The hottest duration of the year is usually from mid-April to late June, before the onset of monsoons, and the corresponding temperature in 2016 and 2017 reached 43 °C, as compared to its historical record of 43.3 °C in 1973 [54]. Such high temperature and rapid increase in urban heat island (UHI) could be attributed to the urban sprawl and transitions, as validated in many studies [55,56,57]. In terms of social context, Hyderabad has main transportation junctions, in particular, the two largest highways of Pakistan, namely the Indus Highway and National Highway join exactly at Hyderabad. The industries of Hyderabad include textiles, sugar, soap, ice, paper, pottery, cement, manufacturing of mirrors, plastics, tanneries, and hosiery mills. In addition, the ornamental glass industry of Hyderabad is also very popular among the Pakistan population [58,59], while the city itself also acts as the main commercial hub for agricultural production of the contiguous zone.
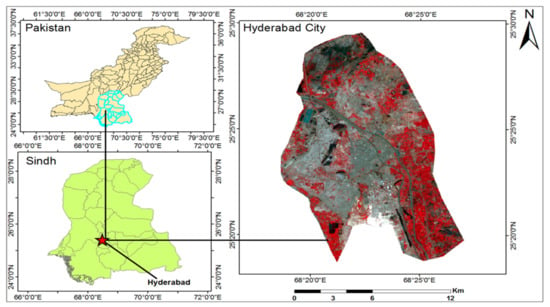
Figure 1.
Geographical location of the study area—Hyderabad, Pakistan, together with the latest land-use distribution, based on false color combination of Landsat datasets.
2.2. Datasets
In this study, remotely sensed Landsat datasets were acquired from the United States of Geological Survey (USGS, Reston, Virginia) [60]. Detailed descriptions of different types of Landsat images, together with the acquisition time, and corresponding resolutions are as shown in Table 1. Overall, 5 types of images were acquired from Multispectral Scanner System (MSS) sensor [61], Operational Land Imager (OLI) [62,63], and The Landsat Thematic Mapper (TM) sensor [64] of USGS, where the 151st path and the 42nd row pass through Hyderabad. Images of different periods, i.e., 1979, 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020 were retrieved, which serve as objective representations of spatial land-use patterns within the concerned decades. The acquisition time was sometime in September, when winter or spring crops are usually the most vigorous. This is conducive and particularly useful in distinguishing built-up areas from other land cover types. The Landsat sensors are usually repeating its cycle on earth every 16 days, which is fine enough for observing long-term land-use changes within a spatial region.

Table 1.
Details of remote sensing datasets obtained from Landsat, their acquisition time, and corresponding resolutions of images adopted in this study.
To avoid being affected by cloudy scenes, there was no cloud coverage within all images obtained from sensors onboard Landsat 3, 5 and 8. Thus, the changes observed via Landsat roughly correspond to realistic environmental conditions and changes in land-use patterns. Upon the acquisition of relevant datasets, the Fast Line-of-sight Atmospheric Analysis of Hypercubes (FLAASH) algorithm developed by Exelis Visual Information Solutions Inc., Boulder, CO, USA [65] was adopted to perform radiometric calibrations and atmospheric correction, which can enhance data quality. A detailed user guide of FLAASH can be found in [66].
Landsat datasets were commonly adopted in conducting studies related to urban expansion and LUCC, because of its long-term and comprehensive digital record, together with a medium spatial resolution, and comparatively consistent spectral and radiometric resolutions, as illustrated in [67,68,69]. Spatial homogenization was conducted by projecting all available Landsat datasets of the interested area onto a common mesh produced and pre-set within the ArcGIS platform, so that all datasets will eventually share similar spatial resolutions for a fair comparison. Further, radiometric correction and cross-track illumination tools of ENVI were adopted for radiometric homogenization [70]. Overall, the use of Landsat datasets is particularly beneficial and practical to detect any changes within developing cities. Moreover, the urban environment is usually characterized by highly heterogeneous surface covers, and the presence of substantial inter- and intra-pixel changes. Thus, the competencies of change detection can essentially be explained and traced, due to the sufficiently fine spatial resolution of digital images acquired in urban areas [71].
2.3. Overview of Methodologies
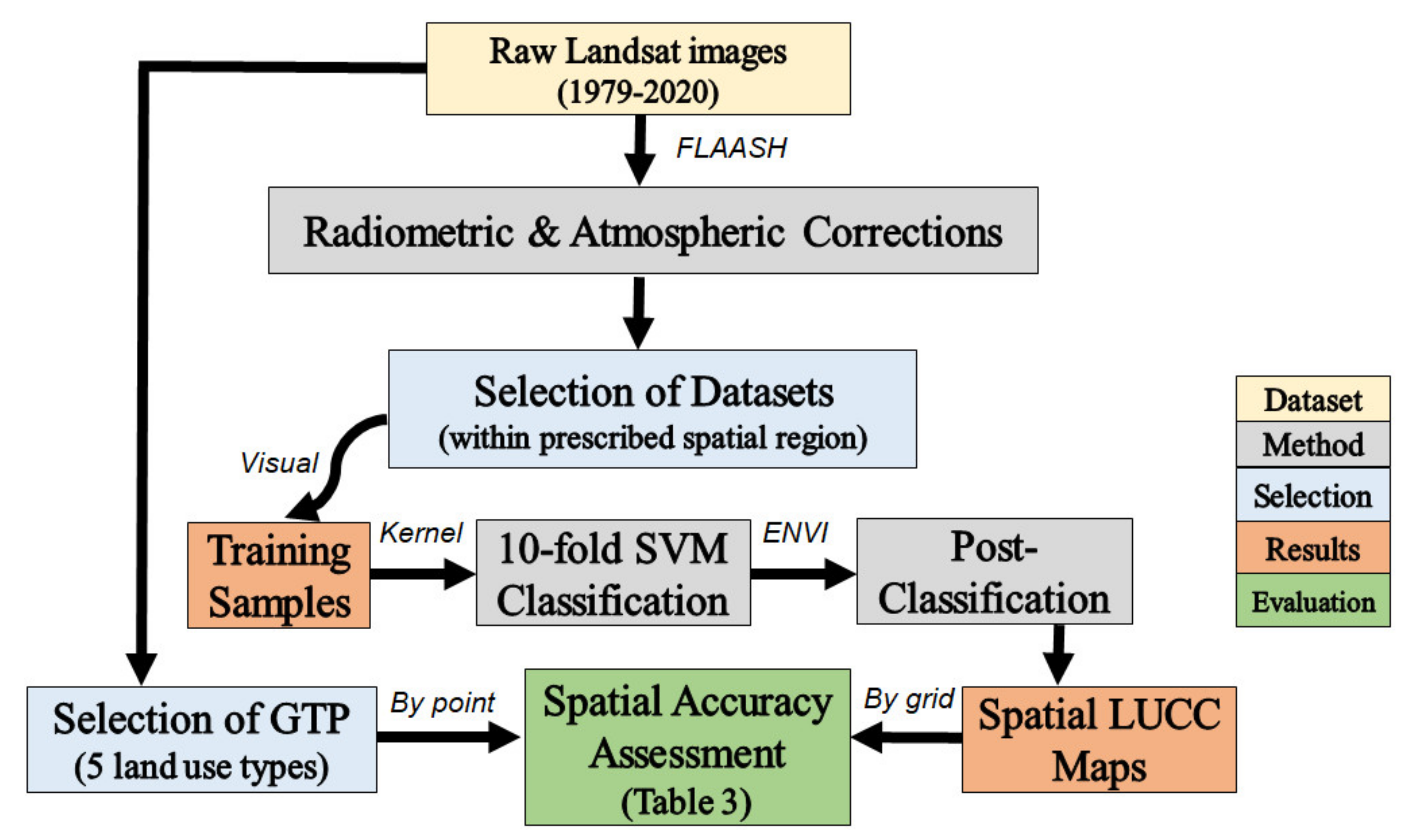
Figure 2 below shows the overall flowchart and framework of this study, starting from the acquisition of Landsat datasets (in Section 2.2), to image processing (Section 2.3.1), the application of statistical classification algorithms (Section 2.3.2), post-classification procedures (Section 2.3.2), then finally the approaches of conducting spatial LUCC assessments (Section 2.3.3).
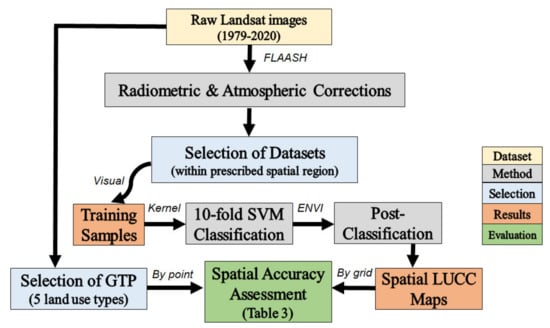
Figure 2.
Overall Flowchart of this study—for LUCC spatial assessment in Hyderabad, with different components labelled in different colors, and intermediate connection stated on top of arrows. FLAASH: Fast Line-of-sight Atmospheric Analysis of Spectral Hypercubes; SVM: Support Vector Machine; ENVI: The Environment for Visualizing Images; GTP: Ground Truth Points; LUCC: Land-use/Land Cover Change.
2.3.1. Image and Land-Use Classification Algorithms
In history, Level 1 of the Anderson classification system [72] was usually adopted for interpreting Landsat-based data, because it can effectively reduce the potential errors of misclassification, and the classification of different land-use categories can become more trustworthy [73,74]. Land-use and land cover types here are divided into 5 key types, namely built-up area (as indicated by impervious surface), agricultural land, vegetation, waterbodies, and barren land [75], via remote sensing (RS) image classification techniques. RS has been the most cost-effective and convenient manner for developing and analyzing LUCC information, because attributes can be obtained without directly getting in touch with the ground surface, therefore it has been used in many developing cities [32,71,76], where sensors are always absent or insufficient in these places. In particular, Landsat 8 OLI RS-based datasets have been adopted to retrieve a total of 8 land cover classes in Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, and other Southeast Asia countries with high accuracies [77], while SPOT-VEGETATION satellite data from 1998–2000 have also been used to derive regional land-cover maps within South and Southeast Asia [78]. Normally, the classification mechanism can either be supervised or unsupervised, or a combination of both, for example, the pre-processing of Landsat images via ISODATA unsupervised classification [79], maximum likelihood supervised classification [75], and iterative hybrid-classification approaches [80].
In this study, land-use features were categorized into 5 key types, namely built-up area, agricultural land, vegetation, waterbody and barren land. In principle, further categorization into more detailed counterparts like different kinds of agricultural features could be conducted, but it is not necessary here. First, our study area, Hyderabad, is only a small city of the Sindh Province, there is not much agricultural nor cultivation concept within most city areas of Pakistan, therefore 5 land-use types are more than sufficient for identifying LUCC. Second, built-up areas or impervious surfaces are mainly associated with artificial structures like concrete, stone and rooftops, while barren land mostly refers to places with thin soil, sand or rocks, for example, deserts and beaches, which are particularly important in quantifying land-use changes of developing cities like Hyderabad. Therefore, one could easily distinguish each type of more important land use within this city from another. The use of “built-up area/impervious surface” and “barren land” have been well adopted in recent LUCC studies, like in [81,82,83]. As for the classification of land use, one may either refer to the peaks obtained from histograms of different acquired Landsat images (see Table 1), which precisely categorized pixels into either land area and waterbody [84], or determine from the spectral reflectance shown on the pixel spectral curve of different bands, where built-up areas show high reflectance values in each band, as compared to the relatively lower reflectance of agricultural land, vegetation, waterbodies, and barren land pixels. An index called “Enhanced Normalized Difference Impervious Surfaces index” has also been designed in [85] to distinguish different land-use types.
Apart from the comparison of reflectance values, the supervised statistical learning algorithm, namely the Support Vector Machine (SVM) was applied in this study to identify each land-use type to its highest accuracy. In recent years, the capabilities of SVM and associated statistical analyses have been shown practical and useful in different applications and scenarios [84,86,87,88]. For each land-use type, sufficient number of training samples was first collected by visual interpretation. As aforementioned, a reasonable spectral signature is the one such that the confusion between any mapped land covers is minimal [89], then the acquired Landsat datasets were classified using SVM, with the appropriately selected statistical kernel, based on respective mathematical properties. Details of the use of SVM are described in Section 2.3.2.
2.3.2. Support Vector Machine (SVM) Algorithm and Post-Classification
Adopting SVM approaches for multisource classification is convenient and accurate especially in remote sensing applications [90]. It pursues to find out an optimal hyperplane between different classes of data via a minimal number of training samples. Such hyperplane maximizes the boundaries in between classes, and “support vectors” are regarded as the data points that lie closest to the hyperplane, and are treated as the training dataset [91,92]. These data are then projected from the input space to another higher dimensional feature space, so that a linearly separable output dataset can be obtained. Such projection process relies on the use of an appropriate kernel function, introduction of a penalty or regularization parameter for data fitting purposes [84]. Detailed mathematical formulation of SVM is as explained in [93]. In our study, the Gaussian-based Radial Basis Function (RBF) was adopted for training in the SVM algorithm. RBF works well in all applications, as validated in [94], while “Gaussian” distribution possesses nice and symmetrical mathematical properties, and the width of individual basis function is relatively easier to control [95], as compared to other options, like multiquadratic or inverse kernels.
The non-linear RBF model can be fully described by 4 parameters, namely (1) basis function ; (2) center of basis function ; (3) width of basis function ; and (4) weight associated with the respective basis function . Assuming that there are N n-tuple (i.e., an input vector x of dimension n − 1, and the corresponding output scalar y), and basis functions in overall, the functional form of RBF is as shown in Equation (1) below.
Here, any input vector x is transformed into another K-dimensional vector, i.e., through the RBF model, and represents the estimate of output, which is expressed as the linear combination of all available K basis functions, with individual weights . It should be noted that except weights, other parameters would constitute the non-linearity of the RBF model. The mathematical formulation of the basis function of Gaussian RBF is as shown in Equation (2). Corrected definitions of the parameters in this equation will increase the accuracy of SVM classification; in particular, the categorization of land cover types in this study.
Although SVM was originally developed for binary classifications, multi-class problems are often encountered in our daily lives, especially in applications related to environmental retrievals. Thus, scientists have extended the basic binary SVM methodology to form a multi-class classifier, as illustrated in [96,97]. Thus, it is applicable for the classification of land-use types, as well as detecting temporal and spatial changes of land covers, which are of practical interest within the study, especially for developing cities.
In this study, SVM with 10-fold cross-validation was applied, i.e., all pixels of every original Landsat image were randomly partitioned into 10 equal sized subsets of pixels. Nine of these subsets were used for training, and the output was being validated by the remaining subset. The entire process was repeated for 10 times, and results were averaged to retrieve the outputs.
Afterwards, in the post-classification stage, majority analysis and the process of dividing clump classes and sieve classes have been performed in ENVI Classic 5.3, with the aim of obtaining statistical advancement. Following the approach of [75], polygon layers of land-use characteristics and categorization were converted into raster layers via the GIS platform, and data were also resampled to respective Landsat resolutions (as shown in Table 1). Thus, the categorization of land cover types can be processed for temporal and spatial assessments, and the historical advancement of a developing city can also be traced and monitored, based on remotely sensed approaches.
2.3.3. Accuracy Assessment of LUCC Classification
As a whole, a number of polygons were selected in ArcGIS, from the processed remotely sensed Landsat datasets during each of the 5 acquisition periods. Then, the land cover classification maps of 1979, 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020 were retrieved, via the combination of supervised classification and SVM approach.
To conduct an objective accuracy assessment of SVM approach in LUCC classification, selected Ground Truth Points (GTP) within the region of interest (ROI) (i.e., Hyderabad, Pakistan) were obtained from all 5 Landsat images (see Table 1) via stratified random sampling [75], with the respective number of GTP of each land-use type stated in Table 2. In this study, we name agricultural land as “A”, vegetation as “V”, built-up area as “BU”, waterbody as “W”, and barren land as “B”. To ensure the reliability of all these GTPs, the Google Earth Engine has been used for conducting ground verification within Hyderabad.

Table 2.
The number of Ground Truth Points (GTP) of each land-use type selected from each Landsat image. The numerical figures inside the bracket represent the year of attainment of datasets.
The selection of GTP within image samples was conducted in ENVI Classic 5.3, based on each unclassified Landsat image, and the confusion matrix derived from post-classification processing of previously classified images. Throughout this process, several metrics have been adopted to conduct overall accuracy assessment with respect to land-use categorization, namely (1) Producer’s Accuracy (PA); (2) User’s Accuracy (UA); (3) Overall Accuracy (OA); and (4) KAPPA coefficient (KC). These metrics have been widely acceptable and applicable in previous studies [98,99,100]. Selected results and conclusions obtained from previous studies of Pakistan, based on satellite derivation and image processing retrieval, were also used for temporal comparison and will be discussed in Section 4.2 of this paper.
Next, to better illustrate the concepts of PA, UA and OA respectively, Table 3 and the 3 mathematical formulas thereafter (i.e., Equation (3)) show the representations and calculations of these metrics. Notations in each of these equations are in line with that shown in Table 3. In particular, based on [98], a producer is interested to know how well the desired land-use characteristics is being classified, thus PA can serve as the probability that a reference pixel could be correctly classified, i.e., expressed as the total number of correct pixels of a specific land-use type divided by the total number of pixels within that land-use type, as derived from the referenced dataset. Next, UA is a representative figure of reliability, and can be expressed as the ratio of total number of correct pixels of a specific land-use type to the total number of pixels being classified within that land-use type [101]. OA can simply be obtained by dividing the total number of pixels that are being accurately classified by the total number of pixels within the entire study.

Table 3.
An illustration of how Producer’s Accuracy (PA), User’s Accuracy (UA), and Overall Accuracy (OA) are obtained from the classification of land use types in this study.
For example, the PA and UA of the classification of agricultural land in Hyderabad, Pakistan are and , respectively. Using the same table, another discrete multivariate mathematical approach of accuracy assessment is named KAPPA [102]. The KAPPA coefficient (KC) based on the notations of Table 3 is expressed as in the first equal sign of Equation (4), where represents the total number of observations, and are the total number of data in the row and the column respectively [103]. If KC is being interpreted in a probabilistic manner, such quantity can simply be expressed as in the second half of Equation (4), where and are the proportion (or probability) of pixels being correctly classified, in which the agreement of classification is of expected value [104]. Having a KC of higher than 0.8 could be interpreted as “almost perfect” in classification, because around 64%–100% of data are reliable, while a value of 0.61–0.79 implicates “substantial” accuracy. In contrast, for KC values below 0.2, the classification approach can be described as “poor”, because only at most 4% of data are considered as reliable [100].
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy Assessment of Land Cover Classification Maps from 1979–2020
To evaluate the applicability of SVM classification and post-classification techniques for retrieving reasonably accurate LUCC maps, a number of training samples were selected from the Landsat datasets in each of the 5 years. The parameters introduced in Section 2.3.3 (i.e., PA, UA, OA, and KC) were adopted for accuracy assessments, upon the comparison with selected GTPs. Table 4 shows the PA and UA of each of the five land-use types during each year within this study, together with respective OA and KC. Overall, the spatial retrieval framework (shown in Figure 2) is highly reliable and could provide insights with regard to the changes of land use during recent decades. In particular, the PA and UA of all land-use types in 1979 were above 80%, while for all other years, the respective accuracies were all higher than 90%. The discrepancy among accuracies of these years can mainly be attributed to the much smaller number of GTPs (of mainly vegetation, built-up area, and waterbody) in 1979, as compared with any of the other 4 years. Further numerical information has been illustrated in Table 2. Moreover, as indicated by the high PAs and UAs, the retrievals of all land-use types were very accurate, especially for built-up areas and barren land, with all numerical figures from 1990 onwards exceeding 95%. Despite the high accuracies obtained among all land-use types, the PA of waterbody in 2010 was only 92.65%; while PAs and UAs of agricultural land (95.69% and 92.33%) and vegetation (92.65% and 90.37%) in 1990 were also relatively lower, especially when compared with corresponding retrieval of built-up areas, waterbody and barren land within the same year. This may again be caused by the sharp increase in the number of GTP selected as built-up areas, for 1990 and 2010 Landsat images (shown in Table 2), while barren land, vegetation and waterbody have less GTP in general.

Table 4.
Accuracy Assessment of retrieved LUCC Maps in 1979, 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020 respectively, based on selected Ground Truth Points (GTP) from Landsat images, and the framework as outlined in Figure 2. The numerical figures of Producer Accuracy (PA) and User Accuracy (UA) are categorized according to the 5 key land-use types in this study.
In terms of OA and Kappa index agreement, the performance in 1990, 2000, 2010 and 2020 were almost the same, with a consistently high numerical value. As for 1979, although the respective OA and KC were relatively lower, with values of 87.45% and 0.81, the accuracy of our newly established retrieval algorithm, in particular, the use of the SVM approach and associated kernels, can actually be guaranteed, after taking into account that the number of GTP from the 1979 dataset is much lower than all the other four retrieved periods. To summarize, the OA and KC of all 5 years are around 96.10% and 0.94 respectively, which further provide confidence in using this remotely sensed and statistical framework for detecting future changes of urban land-use patterns and morphologies.
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Trends of Land Cover from 1979–2020
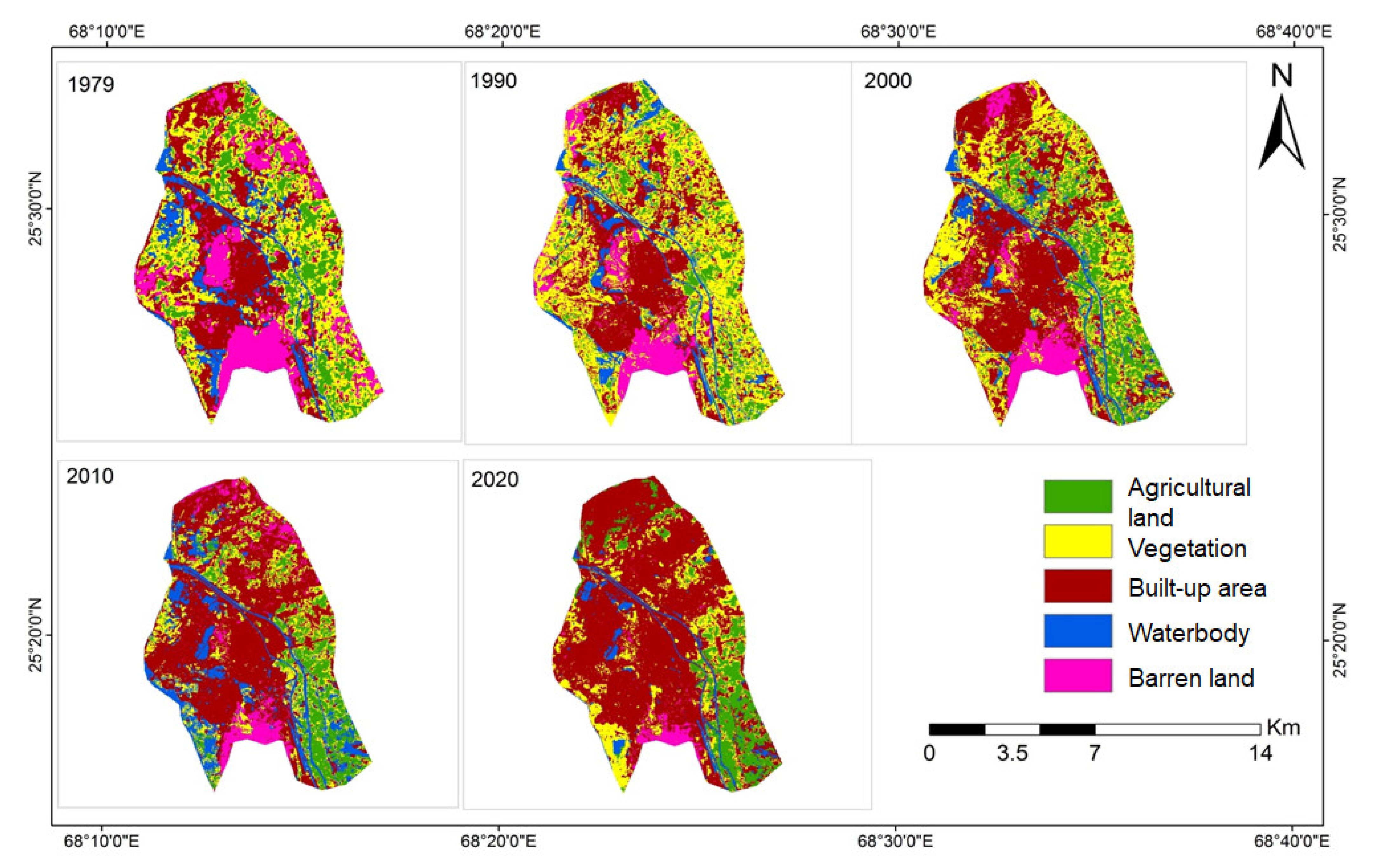
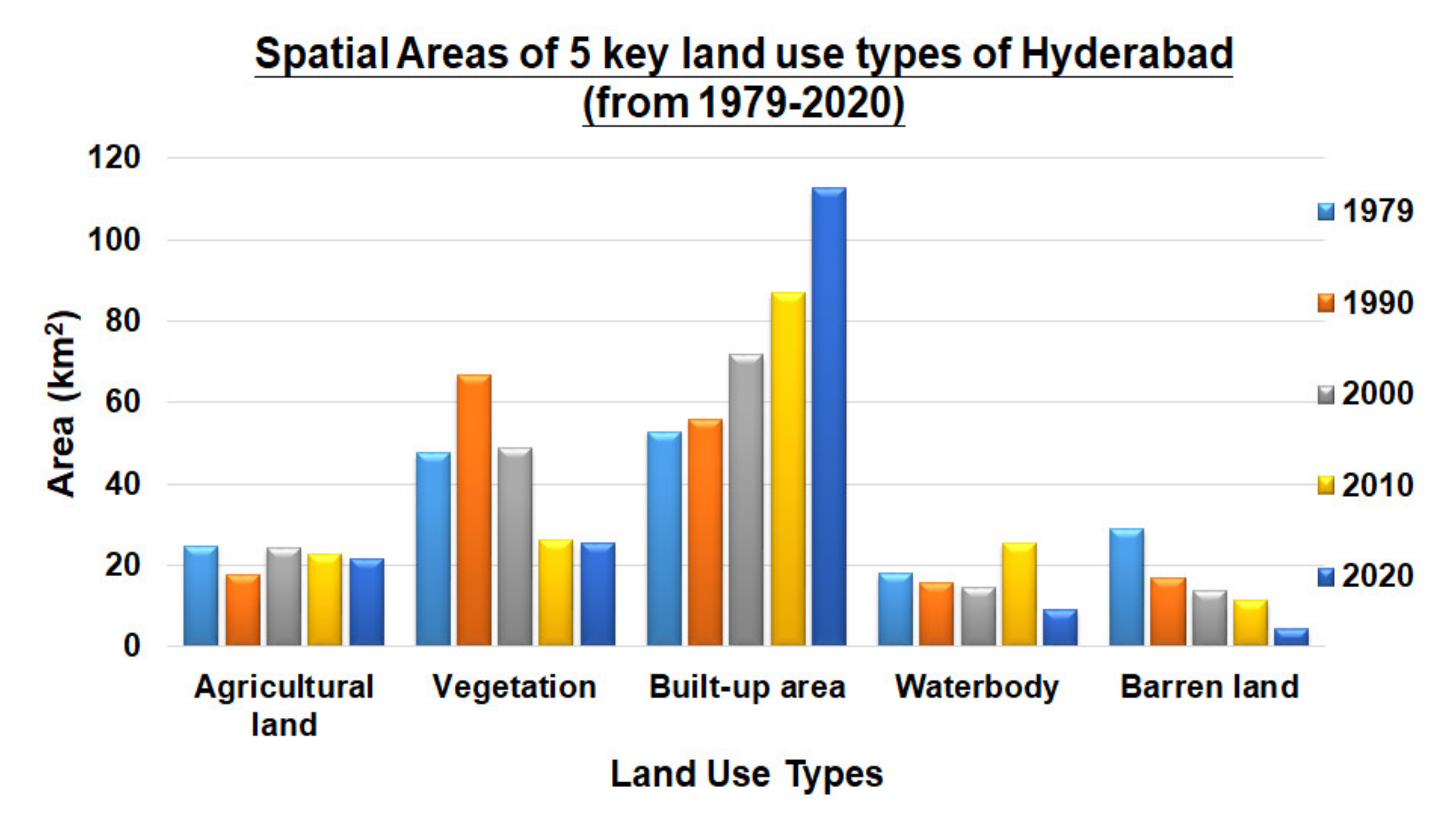
Figure 3 illustrates the spatial land cover classification maps of Hyderabad in 1979, 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020 respectively, with each land-use type indicated in different colors, while Figure 4 shows the corresponding areas of each land-use type in each of the 5 investigated years, with the temporal changes clearly indicated by the bar charts.
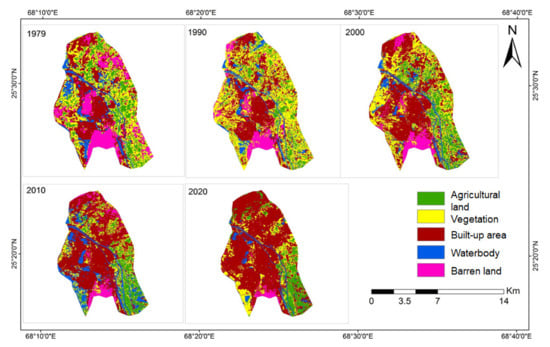
Figure 3.
Land cover classification maps of Hyderabad during 1979, 1990, 2000, 2010 and 2020, respectively, as retrieved from Landsat images, and via the statistical and data analytic framework illustrated in Figure 2.
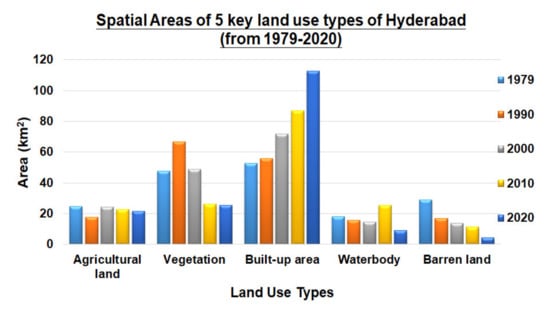
Figure 4.
Spatial areas allocated for each of the 5 key land-use types of Hyderabad during 1979, 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020. Exact spatial areas are represented as bars.
As observed from the spatial plot back in 1979, a similar number of pixels retrieved from Landsat was classified as built-up area and vegetation respectively, followed by barren land and agricultural land, then eventually waterbody. Extreme urban expansion in different places of north-eastern, central and west Hyderabad took place during the 1979–1990 and 1990–2000 periods. As a result, the built-up area has become the major land-use type starting from 2000 onwards. In particular, barren land in central and north-eastern Hyderabad, together with vegetation in eastern areas, were gradually replaced by built-up areas. The proportion of pixels being classified as “agricultural land” and “waterbody” have decreased during the two 10-year periods as well. During the 1990–2000 period, built-up area has formally replaced vegetation, and has become the majority land-use type of Hyderabad, while the spatial coverage of barren land and waterbody continued to decrease, at the same time accompanied by the slight increment of agricultural land pixels. Starting from 2010 onwards, the amount of barren land pixels has become negligible, and only remained in the southernmost areas of Hyderabad, however the amount of waterbody increased by 74.6% when compared to the quantity in 2000. The coverage of built-up area continued to increase, as accompanied by the obvious decrement of vegetation pixels upon retrieval. As of 2020, almost two-thirds of the pixels were classified as “built-up area”, as compared to less than one-third back in 1979. The temporal transition and temporal trend observed can be considered as a proper evidence of urban land expansion during the recent decades, which took place within different parts of Hyderabad, particularly in the central, central-west and north-eastern parts of the city.
To acquire a better understanding of the inter-conversion and temporal transition of land-use types within the past few decades, the corresponding transition matrix that includes the conversion rates in between any two out of the five major land-use types is as shown in Table 5. The numerical figures further reveal the increase of coverage of built-up area during the past four decades, from 52.88 km2 in 1979 to 112.28 km2 in 2020. The observed increase in built-up area was originated from all other four land-use types—agricultural land (11.39 km2), vegetation (28.00 km2), waterbody (10.19 km2), and barren land (20.21 km2). In contrast, 2.77 km2, 4.79 km2, 2.43 km2 and 0.17 km2 of built-up area have been converted into agricultural land, vegetation, waterbody, and barren land respectively during the last four decades, based on the SVM-based retrieval algorithm in this study. Within the same temporal period, the proportion of vegetation area has decreased from 47.51 km2 to 25.45 km2, with 8.42 km2, 28.00 km2, 1.07 km2 and 0.16 km2 areas being converted into agricultural land, built-up area, waterbody, and barren land throughout all years. Further, part of the built-up land area was converted into other four land-use types. This implicates that the exchange between land use for different practical purposes has actually taken place from time to time, while the increase of built-up area in 2020 was not totally comprised of the transition from vegetation, but rather the combined effects of all other four land-use types, for the purpose of urban development and expansion, human settlements, and gradual transition to a modernized city in the long run.

Table 5.
Transition Matrix of 5 Land Cover Types in Hyderabad from 1979 to 2020.
Further, the area being allocated as waterbody also decreased during the 1979–2020 period, based on the SVM-based retrieval, from 17.95 km2 to 9.04 km2. The majority of these regions (10.19 km2) were being converted into built-up areas as expected, while on the other hand, not many other land-use types were converted into waterbodies after 40 years. This may be due to the booming of real estates, and the construction of different infrastructures within Hyderabad throughout recent years, for example, a new international airport, electronic and manufacturing hubs were built [105]. As a result, environmental and hydrological degradation of water bodies took place, especially within urban areas of the city [105]. As for the barren land area, it decreased from 29.13 km2 to 4.19 km2 during the past 40 years. Most of them were converted into built-up areas, while the increment of barren land was minimal (i.e., 0.08 km2, 0.16 km2, 0.17 km2 and 0.03 km2 constituted from the other four land-use types respectively) in reality, i.e., almost no agricultural land, vegetation, built-up area and waterbody areas were converted into barren land during the 1979–2000 period. The reduction of agricultural land in the Indus Plains of Pakistan due to environmental and socioeconomic changes has also been confirmed and well-validated in [106].
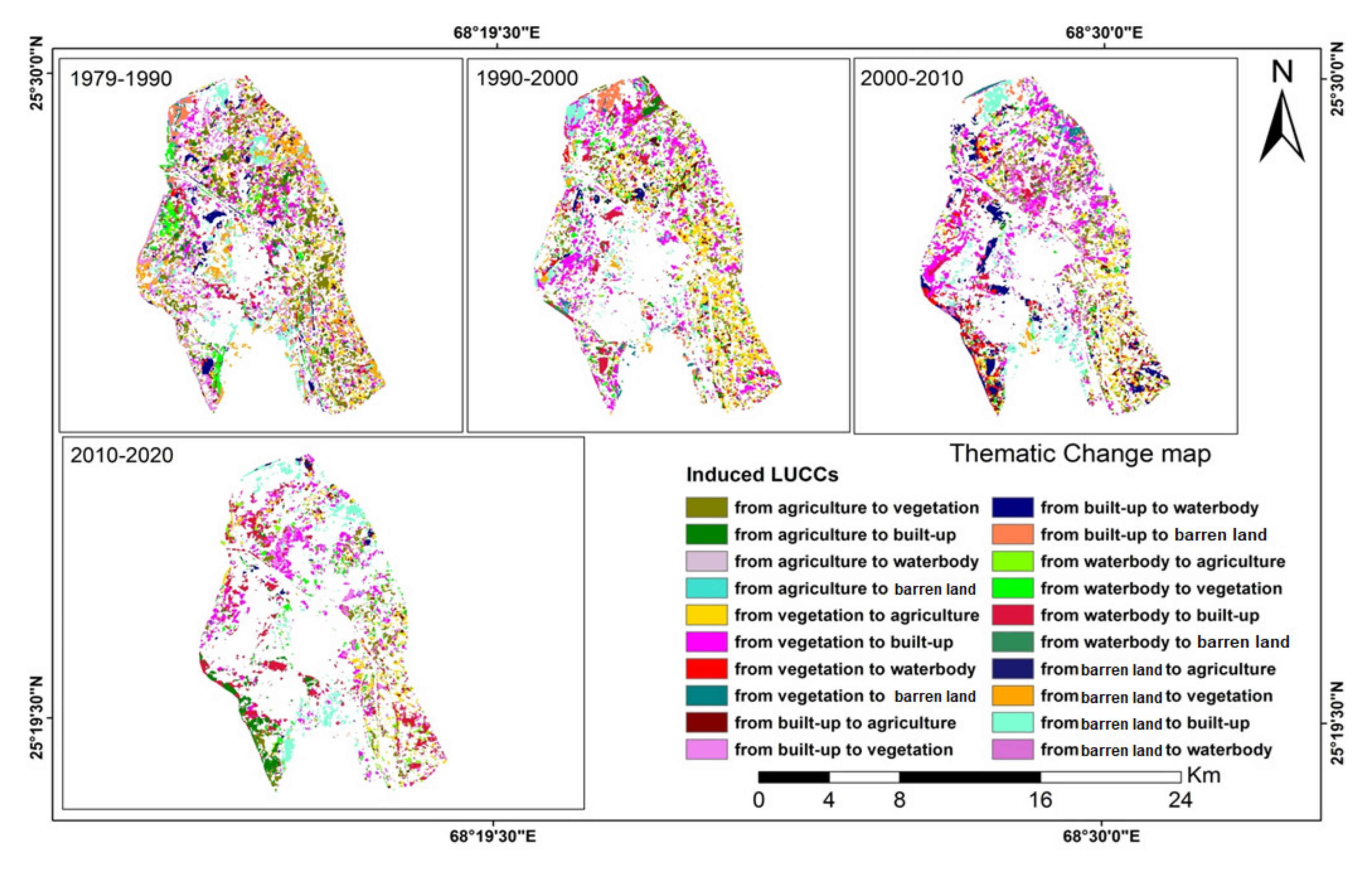
Figure 5 shows the thematic change maps of induced LUCCs throughout each of these four periods, with 10 or 11 years being considered in each analyzed period. Based on the spatial retrieval results obtained via SVM and post-processing, the numbers of vegetation and built-up area pixels during 1979–1990 were similar, and far exceeded the other three land-use types. The southern part of Hyderabad remained as barren land, while the trajectory of waterbody was obvious, joining from the northern west end to the southern east end, and was accompanied by some scattered waterbody in the far northern end of the city. However, such scattered waterbody area has gradually been developed into agricultural land and vegetation during the 1979–1990 period, then to the built-up area starting from 2000 onwards. Moreover, from 1990 onwards, most parts of Hyderabad were classified as built-up areas; while the barren land in its southern-most area was first converted into waterbody during the 1990–2000 period, then either remained as waterbody, or further converted into the built-up area from 2000 onwards. It is interesting to note that during 2000–2010, many pixels in the northern end changed from barren land to built-up area, while pixels right above the waterbody trajectory were converting from waterbody to built-up area, which clearly showcased the urban development within these areas. Afterwards, some pixels on the southern west that were classified as agricultural land in 2010 were also transformed into built-up area during the 2010–2020 period. Overall, as of 2020, most parts of Hyderabad were classified as “built-up or impervious surface”, together with the allocation of some vegetation areas in the south-eastern part of the city. The use of the waterbody “lane” remained until now, while very few pixels have converted back from built-up area to vegetation use, which were scattered in different parts of the city without prescribed spatial patterns.
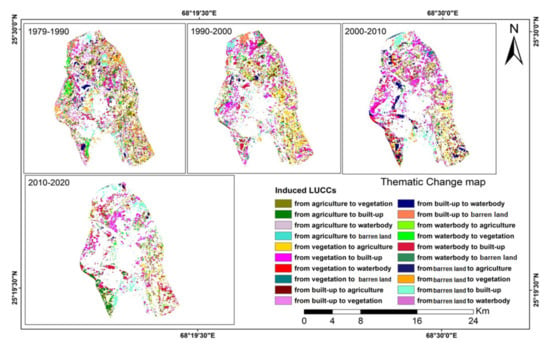
Figure 5.
The thematic change maps of land-use patterns in Hyderabad throughout four different periods, namely 1979–1990, 1990–2000, 2000–2010 and 2010–2020, as retrieved from remote sensing approaches. Each color shown on the maps indicates the respective changes of LUCC.
3.3. Reasons for Spatial Transitions of LUCC in Hyderabad
From the spatial classification results of LUCC during different stages of the 1979–2020 period, it has been properly justified and illustrated that significant changes of land-use types have actually taken place in different parts of Hyderabad (as highlighted in Section 3.2). Generally, the prompt increase with regard to the area of built-up land was accompanied by the corresponding reduction of agricultural land, vegetation, waterbody, and barren land areas during various transitional stages. The key spatial changes of built-up area were eminent and obvious during the last 40 years, which has increased by more than twice in terms of the original area. Such rapid development and spatial expansion took place because of several reasons: (1) Hyderabad is the second largest city of the Sindh Province, and Sindh is the most urbanized province in Pakistan. The city itself consists of a very historical background and is comprised of many commercial and industrial units. Thus, people living in the interior of the city are always directly linked with Hyderabad, and they travelled from their rural hometown to the city for acquiring daily life goods and necessities; (2) Better employment opportunities were provided in Hyderabad in recent years, and the city was equipped with a well-established education system and the provision of better health facilities, thus leading to higher living standard around the entire community. The migration ratio from rural to city region has also been continuously increasing, in an exponential manner, because of the more convenient geographical position and better liveability conditions around central Hyderabad. The majority of these migrants aim to strive for better financial and socio-economic status, and get benefited from the more comprehensive health facilities; (3) The continued increase of population within Hyderabad and surrounding areas led to increased demands of new human settlements. Thus, urban planning and the constructions of new residential housings, industrial and commercial hubs have converted different flat land components and other land-use types into built-up areas. In particular, agricultural land and vegetation area declined from 24.84 km2 and 47.51 km2 in 1979 to 21.43 km2 and 25.45 km2, respectively, within the investigated 40-year period; barren land area covered 29.13 km2 of the total area of Hyderabad back in 1979 according to Landsat retrieved results, but suffered from a sharp decline to only 4.19 km2 in 2020. These are accompanied by the decreasing trend of waterbody areas within Hyderabad, where significant reduction (from 17.95 km2 in 1979 to 8.96 km2 in 2020) could be observed and detected via remotely sensed means and the SVM-based retrieval algorithm proposed in this study. All these took place as a kind of government’s response to cope with different demands and spatial flow patterns, for example, the increased demand of new settlements from citizens, and the movement of humans and service centers of necessities from rural to urban regions that “build up” the entire city, which also indirectly boost up its economic development. This “undesirable but modernized” phenomenon could actually be reflected from the increase in Urban Sprawl Index (USI) during 2011–2015 (i.e., 48.1), as compared with the value of 10.0 during 1991–2001, as obtained via pattern analysis of urban sprawl effects within consistent time intervals [107]. The expansion of the city and the transition of land-use or land cover types have actually constituted the prompt increment of built-up area, and are generally in line with the trends observed in other developed cities [108,109]. The major driving forces are again to acquire better living qualities, more sustainable environmental conditions, and more importantly, children can receive education under a more established system, while adults can gain better and wider employment scopes in the long run.
4. Discussions
4.1. Urban Growth and Spatial Dynamics of Hyderabad and Neighboring Cities in Recent Decades
Hyderabad attained its unique spatial dynamics during its urban expansion processes. According to traditional analyses of urban expansion, urban growth types or development patterns of a city can generally be categorized into three quantitative manners, namely infilling, edge expansion, and leapfrog expansion [110]. As illustrated in Section 3.2, spatial expansion mainly took place within the central areas of Hyderabad, and more land covers along the mainstream were converted into built-up areas throughout different temporal periods. Previous studies have also shown that there were sharp contrasts in spatial dynamics in different cities of Pakistan, based on respective economic and geographical conditions [111,112]. In particular, infilling and leapfrog were the main urban growth patterns in polycentric development cities like Karachi and Lahore [113], whereas leapfrog was the prominent form of urban expansion in medium development cities like Multan [114]. In addition to these historical observations, it is also noticed that the spatial expansion patterns surrounding the urban center of Hyderabad were generally dominated by infilling, for example, the tower market and Gari Khata; while for neighboring areas of central Hyderabad like Latifabad and Qasimabad, leapfrog dominates throughout all years.
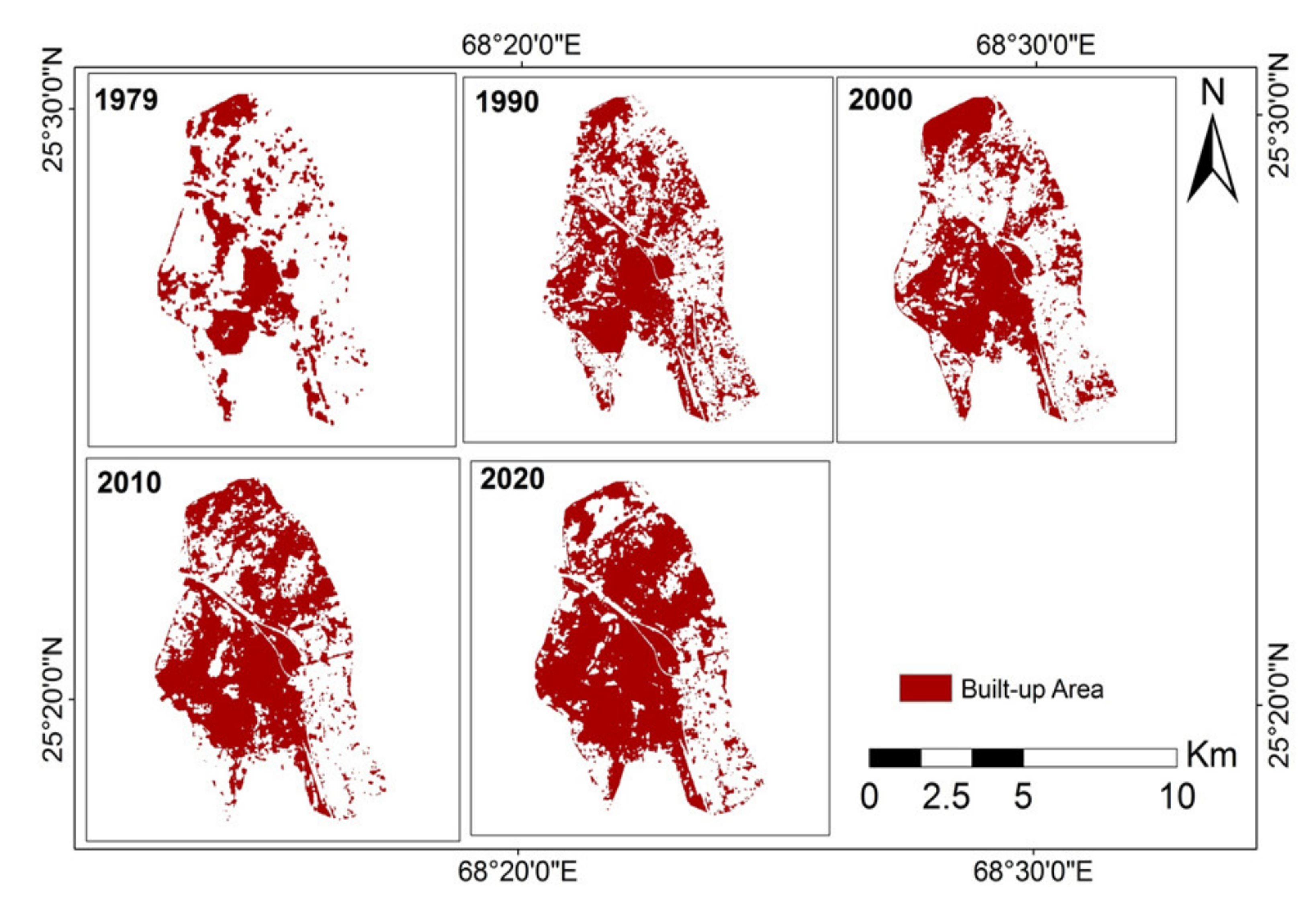
The discrepancies of urban expansion modes and the formation of impervious surface or built-up area were attributed to historical reasons [115]. In the early 1980s, the transportation network and some other basic infrastructures have already been built in the neighboring areas of the central Hyderabad, then the infrastructural development in the next 40 years has filled this piece of the land with roads, connecting junctions between roads, and various types of groundworks. Overall, the general urban growth patterns of Hyderabad itself are mainly comprising of both infilling and expansion, while the leapfrog tracts shown are indicators of land development processes of selected neighboring regions. All these urban expansion and transition work were compelled and coordinated by the local government and real estate enterprises [48]. Figure 6 shows the changes in the spatial distribution of built-up area within Hyderabad from 1979 to 2020, which shows that the majority of development processes could actually be traced back to two different periods, namely, 1979–1990 and 2000–2010. In particular, the amount of built-up area had a tremendous increase in central Hyderabad in 1990, as compared with the spatial plot in 1979, but was still scattered in nature. During the 1990–2000 period, the built-up areas were concentrated at both northern, central and southern Hyderabad of Pakistan. For the 2000–2010 period, major construction and expansion groundwork took place and were implemented in the north-eastern Hyderabad, while some built-up area in the south-eastern Hyderabad were recovered as vegetation, as observed in the 2010’s plot of both Figure 3 and Figure 5. As of 2020, two-thirds of the pixels of the Hyderabad region were considered as “built-up area”. The dotted blue lines in Figure 7 show the corresponding time-trend of amount of built-up area retrieved from Landsat images, which again verifies that major city expansion processes actually took place at different stages in the previous four decades, to fulfill different human and society needs, and such process is continuous in nature.
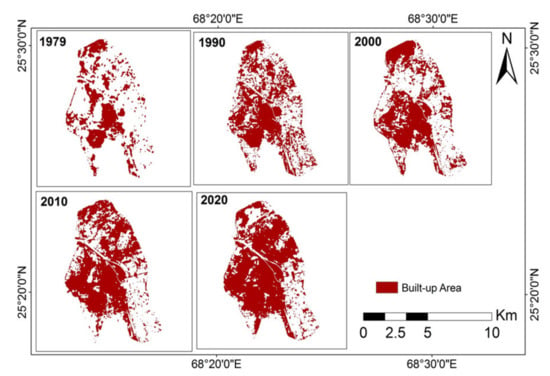
Figure 6.
Spatial Distribution of built-up area from 1979–2020, within major parts of Hyderabad, Pakistan. The figures are retrieved and computed via remote sensing and SVM approaches.
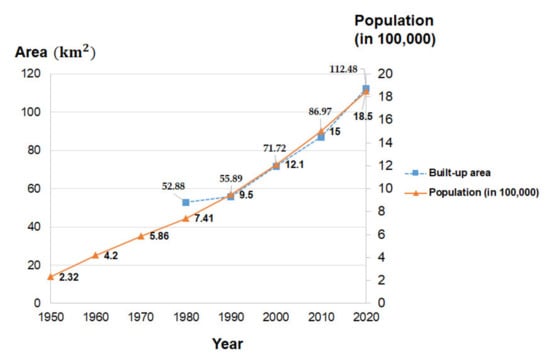
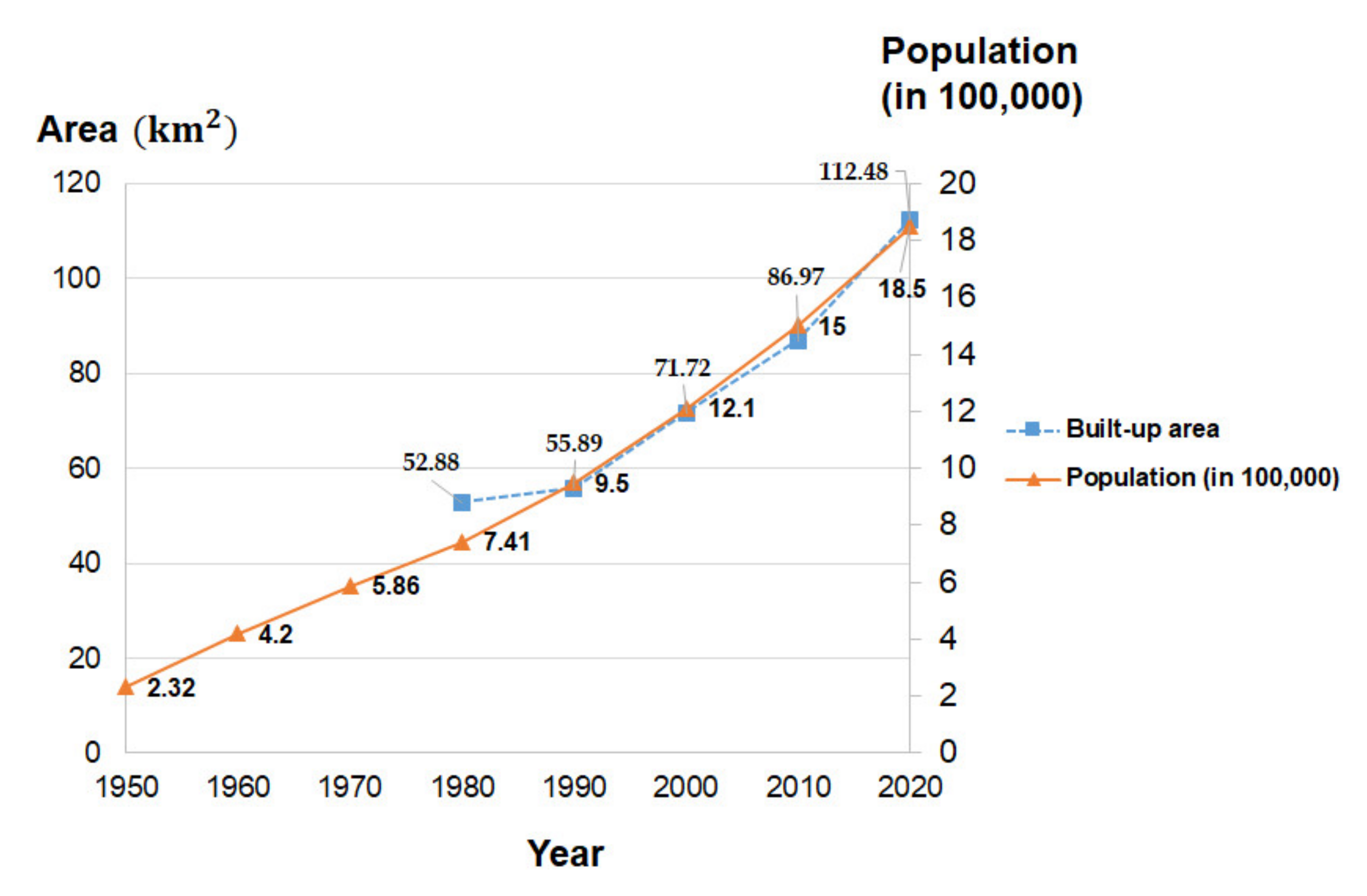
Figure 7.
Area of built-up land (left) and Population figures (right) in Hyderabad throughout the 1979–2020 and 1950–2020 periods, respectively. Population figures were obtained from Pakistan Bureau of Statistics [118], and both the blue and oranges lines are obtained based on the assumption that the amount of built-up area and population figures increase uniformly during each 10-year period.
Urban expansion of Hyderabad, Pakistan during the recent 40 years could actually be attributed to many different socio-economic factors, for example, population changes, economic and financial developments, industrialization, availability of transportation network, and physiography of the concerned spatial region [116,117,118]. Nevertheless, increase in population is the foremost and the most crucial reason, which took place because of two major reasons, namely (1) the natural increase in population that cannot be controlled; and (2) rural-to-urban migration caused by different push and pull factors, for example, the lack of economic security, unemployment, and political persecution in rural regions, as compared with the prosperity and ample employment opportunities in urbanized areas of Hyderabad. Figure 7 also shows the population changes of the city from 1950 to now, based on official statistical figures obtained from the local government website [119], as indicated by orange solid lines. It was observed that the population was only 232,000 in 1950, but increased by more than seven times by 2020, to 1,850,000, and a consistent increase in population could be found throughout all recent seven decades, and the increment starting from 1980 was faster than previous decades, which indirectly explains the spatial expansion of built-up areas in Hyderabad, Pakistan.
Apart from population increase, industrial development has also played a dynamic role in the urban expansion of Hyderabad. 75% of the industrial area in Sindh is located in the Karachi and Hyderabad regions [120], and more than 250 industrial units established under the Sindh industrial trading estate in 1950 were situated at the outskirts of Hyderabad [121]. These industrial units focused on the production and selling of textiles, sugar, soap, ice, pottery and cement, as well as the manufacturing of mirrors, tanneries and hosiery mills. Moreover, Hyderabad is also very famous for its ornamental glass industry, and is the main commercial hub of agricultural production within Pakistan. Economic growth, together with the increase in GDP per capita and working population, generate huge demands for new settlements of individuals. As a result, transportation routes were constructed and operated, so that citizens can easily travel to and from city areas and countryside, thus contribute to the linear urban expansion of Hyderabad. Further, the addition of roads in these geographical areas is actually a remarkable indicator of urban expansion, and can be effectively projected and displayed, via remotely sensed approaches, as shown in other case studies [122,123]. Nevertheless, due to the imperfect and deficient political administration, and the shortage of robust strategies for future planning, there is no rigorous and permissible agenda laid down in terms of city development. On top, many local developers will simply retain their properties and utilize their possession and land for making more profits, while businessmen will look for suitable speculation opportunities, thus the transformation of land-use types in Hyderabad has taken place in an abandoned but hostile manner.
4.2. Comparison with Previous Studies and Connection with Local Environmental Changes
Despite very few studies have focused on LUCC of Hyderabad, our satellite-based retrieved land cover maps are generally in line with previous studies. For example, based on our study, the amount of agricultural land retrieved from Landsat images in 2020 was 21.43 km2, as compared to 24.84 km2 in 1979, and 11.39 km2 of vegetation area have been converted into built-up area, while similar spatial transformation trend was obtained for vegetation areas (see Table 5). Such observation is in line with the conclusion obtained in [106,124], where [124] shows that 70% of agricultural land in Hyderabad district have been sold out, and converted into urbanized areas during 1981–2017; and [106] verified that the amount of agricultural land in Indus Plains has reduced by 9% in past 20 years, mainly due to socioeconomic and environmental factors like land ownership, lack of basic facilities, and the transition of the city to urbanized use and commercial purposes. Landsat datasets, together with geospatial and image processing techniques, have also been adopted for detecting land-use changes within different time periods. In particular, a study in Faisalabad, Pakistan has observed a tremendous increase in urban built-up area (i.e., impervious surface) during two highlighted periods, from 1980 to 2000 (by 30%), and from 2000 to 2005 (by 12%) respectively, and these built-up land have continuously engulfed agricultural land from 1980 to 2010 [125]; while another study that combines Landsat-5 TM multispectral image, Landsat-8 OLI multispectral image and Markov model produced LUCC maps of District Lahore, Pakistan during 1988–2016, at 30 m spatial resolution, and verified that the reduction of agricultural land, vegetation, waterbodies and barren land, have indirectly constituted the increase of built-up areas during the entire period [126]. All these temporal trends and conclusions of previous studies exactly match with results obtained in this research, although some of these studies emphasized on detecting LUCC in neighboring cities of Pakistan.
Further, a possible future extension of the current study is to evaluate the impacts of urbanization on meteorological changes within our atmosphere, in particular, the changes in temperature and urban heat island (UHI) effects induced. Numerous research studies have obtained a promising correlation between the two quantities, for example, every 10% increase in the impervious surface area detected via Landsat in Xiamen city, China has been associated with an increase in land surface temperature of 0.41–0.91 K during summers [81]; maximum increase in temperature (of 1 °C) was found over regions of the greatest urbanization in the Greater Phoenix region from 1973–2001, based on Landsat images and Regional Atmospheric Modelling System of 2-km grid spacing, as compared to the mean regional temperature increase of 0.12 °C within the entire region [127]. On top, based on the simulation results of the Weather Research and Forecasting Model (WRF) in arid Phoenix, AZ, USA, metropolitan area, urban development and construction of built-up areas could lead to an increase of nighttime temperatures by up to 10 K, while maximum temperature increase during the daytime could reach 2–4 K when vegetation areas were gradually converted into built-up areas [128]. Urban forms could also impact future thermal environment, where a dispersed city is capable of reducing mean UHI intensity, but at the same time imposes larger thermal loading within regional scale, as compared with more compact spatial areas [129]. Thus, corresponding assessments of temperature change caused by urbanization processes are important, because associated climatic variations could easily reduce thermal comfort, and trap pollutants within street canyons, especially in metropolitan cities, as a result causing devastating health impacts to residents. Therefore, on top of monitoring temperature changes within urbanized areas, one should also focus on evaluating how changing land-use patterns, local traffic and mobility conditions, and meteorological conditions could affect pollutant distributions at fine spatial resolutions, via satellite remote sensing techniques and modelling approaches [130,131,132].
4.3. Recommendations of Future Urban Planning in Hyderabad
Urban expansion, on one side, satisfies human needs and provides more available space for human settlements, which likely alleviates public health challenges, enhances environmental sustainability and economic productivity [133] in the long run; but on another side, the phenomenon of urban expansion and fragmentation can potentially cause different ecological and environmental problems, for example, the severe loss of natural grassland, cropland and prairie [134], trapping of CO2 and heat energy within urban environment, atmospheric pollution problems [135] and human discomfort [136]. Thus, it is of paramount importance to improve the resilience and sustainability of urban land-use planning and related implementations at an earlier stage, with the aim of maintaining spatial equities within the rural and urban counterparts of developing cities, overcoming associated socio-economic challenges in an innovative manner, and promoting smart city development in long run. The connections between different perspectives of neighborhood environmental conditions and health impacts could also be effectively quantified based on prescribed city-based indices [137].
First, the key approach of monitoring urban expansion lies in reducing spatial discrepancies of any construction projects. In particular, land-use strategies should aim at minimizing urban-rural inequalities, preventing the loss of open countryside, and maintaining urban-rural unity. One could learn experience from more developed cities like Singapore, Japan and Hong Kong, by promoting mixed land-use within a single building (e.g., with commercial zones downstairs, and residential zones situated upstairs [138]), implementing the revitalization of shrinking cities and communities, or even aging districts, buildings, and heritages [139,140]. In addition, upgrading local economies and provision of all service to neighboring rural regions could also achieve spatial equity, in terms of regional development, land administration, and the uniformity of policies.
Second, for developing cities like Hyderabad, and many other cities of Pakistan, many socio-economic problems have arisen due to the continuous and rapid increase in population, especially in areas situated near the town center. This includes housing shortages, suffering from unemployment, and even water and energy crises. The local administration committees and governmental departments should take immediate actions to resolve all these problems. Some potential approaches include the selection of appropriate venues for housing construction, or for infrastructural development. The desired area should be kept away from existing industrial zones to avoid any potential environmental threats, but has to be situated near the capital territory to cope with the shortfall of housing in Hyderabad. On top, raw materials allied industries should also be positioned around the desired housing areas, with the aim of creating sufficient employment opportunities and reducing poverty.
To integrate better technologies and construction standards from developed cities, Hyderabad could also encourage more foreign and local investors to support its housing development projects, as well as the construction of bridges, roads, and public facilities. With these, more advanced technologies and innovative ideas can be incorporated into building a more sustainable and universally compatible city [4]. Environmental impact assessment (EIA) should regularly be conducted in different parts of Hyderabad, or in any neighboring cities and towns, so that the actual environmental and social impacts of each large-scale construction or infrastructural project can be better reviewed and monitored [141]. With such environmental information on hand, mitigation measures can be effectively implemented to minimize associated health risks. More importantly, respective environmental informatics should be delivered to the general public based on the open data initiatives, with the aim of enhancing sustainability of the city in foreseeable future [142].
5. Conclusions
In this study, the assessment of urban expansion and changing land-use types in Hyderabad in recent decades were conducted via remote sensing, image processing and statistical machine learning approaches. Temporal variations and spatial maps of different LUCC types from 1979–2020 were retrieved, in every 10-year period interval. In particular, the amount of built-up area was rapidly increasing during the 1979–2000 and 2000–2010 periods, from 52.88 km2 (account for 30.69% of areas in Hyderabad) in 1979 to 112.28 km2 (account for 65.04% of areas in Hyderabad) in 2020; while areas allocated for agricultural land, vegetation, waterbody, and barren land purposes continuously decreased, by a total of 13.74%, 46.41%, 49.64%, and 85.27%. Such conclusion is supported by several previous research of LUCC in Hyderabad, or in neighboring cities and towns of Pakistan. Further, an average of exceeding 90% accuracy in terms of Producer Accuracy (PA), User Accuracy (UA), Overall Accuracy (OA), and Kappa coefficient (KC) was obtained during all five time periods when Ground Truth Points (GTP) were adopted for validation.
Till now, very little research has been conducted with regard to the spatial dynamics and mechanism of LUCC changes in cities of Hyderabad; however, the continued increase of population, rural-to-urban migration, as well as industrial and socioeconomic developments could lead to many potential social and environmental problems, like rural-urban inequalities, excessive traffic emission, air and noise pollution, huge meteorological fluctuations, and improper use of existing available land. This study has opened a new window of detecting LUCC changes in developing cities via remotely sensed and pixel-based classification approaches, and can provide insights for conducting impact assessments, for better urban planning and environmental control. Further, the pixel-based image analytic framework of this study could also allow the integration of historical imageries and ancillary GIS data layers, for facilitating improved land-use classifications, monitoring change detection outputs, and making wiser infrastructural decisions. As a result, gaining a better overview of the historical and potential future development of the city could introduce a new milestone, in terms of technological advancement and smart urban governance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.U.D. and H.W.L.M.; methodology, H.W.L.M. and S.U.D.; software, S.U.D.; validation, H.W.L.M.; formal analysis, S.U.D. and H.W.L.M.; investigation, H.W.L.M. and S.U.D.; data curation, S.U.D.; writing—original draft preparation, H.W.L.M. and S.U.D.; supervision, H.W.L.M.; funding acquisition, H.W.L.M. Both authors have read and agreed to the published version of the paper.
Funding
This research was partially funded by HKU Seed Fund for Basic Research for New Staff, grant number 104005930.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to prescribed guidelines, and approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC) of HKU (Code: EA200004, approved on 6 August 2020).
Data Availability Statement
The remotely sensed datasets in this study were obtained from Landsat images, as cited in Reference [38]. Details of each Landsat dataset are also described in [61,63,64].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest, and no competing financial interest that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Angel, S.; Parent, J.; Civco, D.L.; Blei, A.; Potere, D. The dimensions of global urban expansion: Estimates and projections for all countries, 2000–2050. Prog. Plan. 2011, 75, 53–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güneralp, B.; Reba, M.; Hales, B.U.; Wentz, E.A.; Seto, K.C. Trends in urban land expansion, density, and land transitions from 1970 to 2010: A global synthesis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 044015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, R. Smart Cities: An Overview of the Technology Trends Driving Smart Cities. IEEE. 2017. Available online: www.ieee.org/content/dam/ieee-org/ieee/web/org/about/corporate/ieee-industry-advisory-board/ieee-smart-cities-trend-paper-2017.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2021).
- Goi, C.L. The impact of technological innovation on building a sustainable city. Int. J. Qual. Innov. 2017, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagan, H.; Yamagata, Y. Land-cover change analysis in 50 global cities by using a combination of Landsat data and analysis of grid cells. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 064015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tong, X. Spatiotemporal variation of landscape patterns and their spatial determinants in Shanghai, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 87, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y. Impact of Land-Use and Land-Cover Change on Meteorology in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region from 1990 to 2010. Sustainability 2018, 10, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patra, S.; Sahoo, S.; Mishra, P.; Mahapatra, S.C. Impacts of urbanization on land use /cover changes and its probable implications on local climate and groundwater level. J. Urban Manag. 2018, 7, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakode, H.B.; Baier, K.; Jha, R.; Azzam, R. Impact of urbanization on groundwater recharge and urban water balance for the city of Hyderabad, India. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Yamamoto, K. Population concentration, urbanization, and demographic transition. J. Urban Econ. 2005, 58, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Ma, H.; Wang, J. A Regional Categorization for “New-Type Urbanization” in China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Chen, C.; Hu, B. Governing urbanization and the New Urbanization Plan in China. Environ. Urban 2016, 28, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, E.; van der Zwet, A. Sustainable and Integrated Urban Planning and Governance in Metropolitan and Medium-Sized Cities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhan, J.; Deng, X. Spatio-temporal patterns and driving forces of urban land expansion in China during the economic reform era. Ambio 2005, 34, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Gallego, M.E.; Quintero-Angel, M.; Vila-Ortega, J.J. Exploring land use/land cover change and drivers in Andean mountains in Colombia: A case in rural Quindio. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 1288–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenkert, A.L.; Malone, E.L. Modeling Vulnerability and Resilience to Climate Change: A Case Study of India and Indian States. Clim. Chang. 2005, 72, 57–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, E.G.; Bockstael, N.E. The evolution of urban sprawl: Evidence of spatial heterogeneity and increasing land fragmentation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20672–20677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leyk, S.; Bulk, D.; Jones, B.; Montgomery, M.R.; Engin, H. The heterogeneity and change in the urban structure of metropolitan areas in the United States, 1990–2010. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Güneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, H.; Güneralp, B.; Filippi, A.M.; Kreuter, U.P.; Güneralp, I. Impacts of Land Change on Ecosystem Services in the San Antonio River Basin, Texas, from 1984 to 2010. Ecol Econ. 2017, 135, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Kreuter, U.P.; Li, B.; Ma, Z.; Chen, J.; Nakagoshi, N. An ecosystem service value assessment of land-use change on Chongming Island, China. Land Use Policy 2004, 21, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibia, S.; Asadib, N. 2011 International Conference on Green Buildings and Sustainable Cities: Causes, results and methods of controlling urban sprawl. Procedia Eng. 2011, 21, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X. A review of the international researches on land use/land cover change. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1996, 6, 553–558. [Google Scholar]
- Güneralp, B.; Lwasa, S.; Masundire, H.; Parnell, S.; Seto, K.C. Urbanization in Africa: Challenges and opportunities for conservation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 13, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Asia. Pakistan Surpasses Brazil to Become World’s 5th Most Populous Country. Available online: https://gulfnews.com/world/asia/pakistan/pakistan-surpasses-brazil-to-become-worlds-5th-most-populous-country-1.72557051 (accessed on 12 May 2021).
- Vani, M.; Kamraju, M. A Study on Growth and Distribution of Population in Hyderabad city. In Sustainable Development: A Dynamic Perspective, 1st ed.; Anjan Publisher: Kolkata, India, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gumma, M.K.; Mohammad, I.; Nedumaran, S.; Whitbread, A.; Lagerkvist, C.J. Urban Sprawl and Adverse Impacts on Agricultural Land: A Case Study on Hyderabad, India. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Kharol, S.; Badarinath, K.V.S. Influence of vehicular traffic on urban air quality—A case study of Hyderabad, India. Transp. Res. Part. D Transport. Environ. 2010, 15, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M. Urban Planning: Challenges in Developing Countries. I International Congress on Human Development. Madrid 2006. Available online: www.reduniversitaria.es/ficheros/Mila%20Freire(i).pdf (accessed on 12 May 2021).
- Tewkesbury, A.P.; Comber, A.J.; Tate, N.J.; Lamb, A.; Fisher, P.F. A critical synthesis of remotely sensed optical image change detection techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burrough, P.A.; McDonnell, R.A.; Lloyd, C.D. Principles of Geographical Information Systems for Land Resources Assessment, 3rd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Wang, Q. Urban Classification Using Full Spectral Information of Landsat ETM+ Imagery in Marion County, Indiana. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2005, 71, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myint, S.W.; Gober, P.; Brazel, A.; Grossman-Clarke, S.; Weng, Q. Per-pixel vs. object-based classification of urban land cover extraction using high spatial resolution imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 115, 1145–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochon, G.L.; Johannsen, C.J.; Landgrebe, D.A.; Engel, B.A.; Harbor, J.M.; Majumder, S.; Biehi, L.L. Remote Sensing as a Tool for Achieving and Monitoring Progress Toward Sustainability. In Technological Choices for Sustainability; Sikdar, S.K., Glavic, P., Jain, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 415–428. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, A.; Friedl, M.A.; Woodcock, C.E. Mapping urban areas by fusing multiple sources of coarse resolution remotely sensed data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 2623–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alphan, H. Land Use Change and Urbanization in Adana, Turkey. Land Degrad. Dev. 2003, 14, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vali, A.; Comai, S.; Matteucci, M. Deep Learning for Land Use and Land Cover Classification Based on Hyperspectral and Multispectral Earth Observation Data: A Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Landsat Missions: Landsat Data Access. Available online: www.usgs.gov/core-science-systems/nli/landsat/landsat-data-access?qt-science_support_page_related_con=0#qt-science_support_page_related_con (accessed on 12 May 2021).
- Hansen, M.C.; Loveland, T.R. A review of large area monitoring of land cover change using Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, G.J.; Niemann, K.O. Visualizing 3-D Texture: A Three Dimensional Structural Approach to Model Forest Texture. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 20, 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hay, G.J.; Niemann, K.O.; McLean, G. An Object-Specific Image-Texture Analysis of H-Resolution Forest Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 55, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, D.J.; Howarth, P.J.; Dubois, J.M.M.; Gratton, D.J. Evaluation of the Grey-Level Co-Occurrence Matrix Method for Land-Cover Classification Using SPOT Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1990, 28, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yeh, G.O. Principal component analysis of stacked multi-temporal images for the monitoring of rapid urban expansion in the Pearl River Delta. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 1501–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimal, B.; Rijal, S.; Kunwar, R. Comparing Support Vector Machines and Maximum Likelihood Classifiers for Mapping of Urbanization. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2020, 48, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.V.; Tuohy, M.; Irwin, M.; Tuan, P.V. Monitoring and mapping rural urbanization and land use changes using Landsat data in the northeast subtropical region of Vietnam. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2020, 23, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiß, C.; Leichtle, T.; Wurm, M.; Pelizari, P.A.; Standfuß, I.; Zhu, X.X.; So, E.; Siedentop, S.; Esch, T.; Taubenböck, H. Large-Area Characterization of Urban Morphology—Mapping of Built-Up Height and Density Using TanDEM-X and Sentinel-2 Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 99, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mesev, T.V.; Longley, P.A.; Batty, M.; Xie, Y. Morphology from Imagery: Detecting and Measuring the Density of Urban Land Use. Environ. Plan. A Environ. Plan. 1995, 27, 759–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadchan, J.; Shankar, R. An analysis of urban growth trends in the post-economic reforms period in India. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2012, 1, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, P.K.; Rai, A.; Rai, S.C. Land use and land cover change detection using geospatial techniques in the Sikkim Himalaya, India. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2020, 23, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.M. Spatio-temporal analysis of land cover/land use changes using geoinformatics (A Case Study of Margallah Hills National Park). Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 7, 1832–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Z.; Shabbir, R.; Ahmad, S.S.; Malik, A.H.; Aziz, N.; Butt, A.; Erum, S. Dynamics of land use and land cover change (LULCC) using geospatial techniques: A case study of Islamabad Pakistan. Springerplus 2016, 5, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, S.; Mubeen, M.; Akram, W.; Ahmad, A.; Habib-Ur-Rahman, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Amin, A.; Awais, M.; Farid, H.U.; Farooq, A.; et al. Study of land cover/land use changes using RS and GIS: A case study of Multan district, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 192, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talpur, M.A.M. The Vanishing Glory of Hyderabad (Sindh, Pakistan). UNIOR Web Journals. 2008. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.628.7661&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- Telangana Today. For Hyderabad, This April Was Coolest in 5 Years. Available online: https://telanganatoday.com/for-hyderabad-this-april-was-coolest-in-5-years (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- Son, N.T.; Chen, C.F.; Chen, C.R. Urban expansion and its impacts on local temperature in San Salvador, El Salvador. Urban Clim. 2020, 32, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Cai, H.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, L.; Jin, C.; Ge, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, F. Impacts of park landscape structure on thermal environment using QuickBird and Landsat images. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cai, H.; Qiao, Z.; Xu, X. Influence of urban expansion on the urban heat island effect in Shanghai. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2016, 30, 2421–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia. Hyderabad, Sindh. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyderabad,_Sindh (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- Mills, M.A. South Asian Folklore: An Encyclopedia, 1st ed.; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- United States Geological Survey (USGS). Earth Explorer. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- United States Geological Survey (USGS). USGS EROS Archive–Landsat Archives–Landsat 1–5 Multispectral Scanner (MSS) Level-1 Data Products. Available online: www.usgs.gov/centers/eros/science/usgs-eros-archive-landsat-archives-landsat-1-5-multispectral-scanner-mss-level?qt-science_center_objects=0#qt-science_center_objects (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- NASA—Landsat Science. Operational Land Imager. Available online: https://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/landsat-8/operational-land-imager (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- United States Geological Survey (USGS). Landsat Missions—Landsat 8. Available online: www.usgs.gov/core-science-systems/nli/landsat/landsat-8?qt-science_support_page_related_con=0#qt-science_support_page_related_con (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- United States Geological Survey (USGS). USGS EROS Archive–Landsat Archives–Landsat 4–5 Thematic Mapper (TM) Level-1 Data Products. Available online: www.usgs.gov/centers/eros/science/usgs-eros-archive-landsat-archives-landsat-4-5-thematic-mapper-tm-level-1-data?qt-science_center_objects=0#qt-science_center_objects (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- L3HARRISTM. Geospatial. Fast Line-of-sight Atmospheric Analysis of Hypercubes (FLAASH). Available online: www.l3harrisgeospatial.com/docs/flaash.html (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- ENVI. Atmospheric Correction Module: QUAC and FLAASH User’s Guide. Available online: www.l3harrisgeospatial.com/portals/0/pdfs/envi/Flaash_Module.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- Almazroui, M.; Mashat, A.; Assiri, M.E.; Butt, M.J. Application of Landsat Data for Urban Growth Monitoring in Jeddah. Earth Syst. Environ. 2017, 1, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mundia, C.N.; Aniya, M. Analysis of land use/cover changes and urban expansion of Nairobi city using remote sensing and GIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2831–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, Q.; Ding, H.; Liang, H. Detection of urban expansion and land surface temperature change using multi-temporal landsat images. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 128, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L3HARRIS. Geospatial Other Radiometric Correction Tools. Available online: www.l3harrisgeospatial.com/docs/otherradiometriccorrectiontools.html (accessed on 26 July 2021).
- Lu, D.; Mausel, P.; Brondizio, E.; Moran, E. Change detection techniques. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 2365–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.F.; Hardy, E.E.; Roach, J.T.; Witmer, R.E. A land use and land cover classification system for use with remote sensor data. U.S. Geol. Surv. Prof. Paper. 1976, 964, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Mallinis, G.; Emmanoloudis, D.; Giannakopoulos, V.; Maris, F.; Koutsias, N. Mapping and interpreting historical land cover/land use changes in a Natura 2000 site using earth observational data: The case of Nestos delta, Greece. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomeni, M.; Tzanopoulous, J.; Pantis, J.D. Historical analysis of landscape change using remote sensing techniques: An explanatory tool for agricultural transformation in Greek rural areas. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2008, 86, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenstein, O.; Karnieli, A. Comparison of methods for land-use classification incorporating remote sensing and GIS inputs. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadeel, A.; Jabbar, M.; Chen, X. Application of remote sensing and GIS to the study of land use/cover change and urbanization expansion in Basrah province, southern Iraq. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2009, 12, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukesh, S.B.; Choudhary, K.; Kupriyanov, A. 2019 Land Cover Map of Southeast Asia at 30 m Spatial Resolution with Changes Since 2010. Opt. Mem. Neural Netw. 2020, 29, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stibig, H.J.; Belward, A.S.; Roy, P.S.; Wasrin, U.R.; Agrawal, S.; Joshi, P.K.; Hildanus Beuchle, R.; Fritz, R.S.; Mubareka, S.; Giri, C. A Land-Cover Map for South and Southeast Asia Derived from SPOT-VEGETATION Data. J. Biogeogr. 2007, 34, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhodhi, M.K.; Saghri, J.A.; Ahmad, I.; Ul-Mustafa, R. D-ISODATA: A Distributed Algorithm for Unsupervised Classification of Remotely Sensed Data on Network of Workstations. J. Parallel Distr. Com. 1999, 59, 280–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakr, N.; Weindorf, D.C.; Bahnassy, M.H.; Marei, S.M.; El-Badawi, M.M. Monitoring land cover changes in a newly reclaimed area of Egypt using multi-temporal Landsat data. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Zhang, X.; Nie, Q.; Sun, F.; Tang, L. The Impacts of the Expansion of Urban Impervious Surfaces on Urban Heat Islands in a Coastal City in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q. Use of impervious surface in urban land-use classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, C. Impacts of impervious surface expansion on soil organic carbon—A spatially explicit study. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarp, G.; Ozcelik, M. Water body extraction and change detection using time series: A case study of Lake Burdur, Turkey. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2017, 11, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Yang, K.; Chen, S.; Yang, C.; Zhang, S.; He, L. Enhanced normalized difference index for impervious surface area estimation at the plateau basin scale. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2019, 13, 016502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adam, E.; Mutanga, O.; Odindi, J.; Abdel-Rahman, E.M. Land-use/cover classification in a heterogeneous coastal landscape using RapidEye imagery: Evaluating the performance of random forest and support vector machines classifiers. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 3440–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; David, L.S.; Townshend, J.R.G. An assessment of support vector machines for land cover classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 725–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, A.; Foody, G.M. Crop classification by support vector machine with intelligently selected training data for an operational application. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 2227–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Liu, Y. Determination of land degradation causes in Tongyu County, Northeast China via land cover change detection. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geo-Inf. 2010, 12, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanachaturaporn, P.; Arora, M.; Varshney, P.K. Multisource Classification Using Support Vector Machines. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2008, 74, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boser, B.E.; Guyon, I.M.; Vapnik, V.N. A Training Algorithm for Optimal Margin Classifiers. In Proceedings of the 5th Annual Workshop on Computational Learning Theory (COLT’92), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 27–29 July 1992; pp. 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Foody, G.M.; Boyd, D.S.; Sanchez-Hernandez, C. Mapping a specific class with an ensemble of classifiers. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1733–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burges, C.J. A Tutorial on Support Vector Machines for Pattern Recognition. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 1998, 2, 121–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENVI. ENVI’s User Guide. Version 4.1 September 2004 Edition. Available online: http://aviris.gl.fcen.uba.ar/Curso_SR/biblio_sr/ENVI_userguid.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- Shin, M.; Park, C. A Radial Basis Function Approach to Pattern Recognition and Its Applications. ETRI J. 2000, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, C.K. Classification of multiple cancer types by multicategory support vector machines using gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Cruz, F.; Artés-Rodríguez, A. Puncturing Multi-class Support Vector Machines. In Artificial Neural Networks—ICANN 2002. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Dorronsoro, J.R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; Volume 2415. [Google Scholar]
- Congalton, R.G. A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Status of land cover classification accuracy assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Story, M.; Congalton, R. Accuracy assessment: A user’s perspective. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1986, 52, 397–399. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, Y.; Fienberg, S.; Holland, P. Discrete Multivariate Analysis—Theory and Practice; MIT Press: Cambridge, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Purchell, G.P.; Rennels, G.D. Development and Evaluation of a Context-Based Document Representation for Searching the Medical Literature. Int. J. Digit. Libr. 1997, 1, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamraju, M. Impact of Urbanisation on Lakes: A Case Study of Hyderabad. 05. 2016. Available online: www.researchgate.net/publication/342916988_IMPACT_OF_URBANISATION_ON_LAKES_A_Case_Study_of_Hyderabad (accessed on 4 June 2021).
- Rajpar, H.; Zhang, A.; Razzaq, A.; Mehmood, K.; Pirzado, M.B.; Hu, W. Agricultural Land Abandonment and Farmers’ Perceptions of Land Use Change in the Indus Plains of Pakistan: A Case Study of Sindh Province. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franco, S.; Mandla, V.R.; Rao, K.R.M. Trajectory of Urban Growth and Its Socioeconomic Impact on a Rapidly Emerging Megacity. J. Urban. Plan. Dev. 2017, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Land Use and Land Cover Change in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh: Using Remote Sensing to Promote Sustainable Urbanization. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, S.; Chaudhary, P.; Thapa, L. Land Use/Land Cover Change Detection in Pokhara Metropolitan, Nepal Using Remote Sensing. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2020, 8, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dytham, C.; Forman, R.T.T. Land Mosaics: The Ecology of Landscapes and Regions. J. Ecol. 1996, 84, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboob, M.; Atif, I.; Iqbal, J. Remote Sensing and GIS Applications for Assessment of Urban Sprawl in Karachi, Pakistan. Inf. Technol. Dev. 2015, 34, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butt, A.; Shabbir, R.; Ahmad, S.S.; Aziz, N. Land use change mapping and analysis using Remote Sensing and GIS: A case study of Simly watershed, Islamabad, Pakistan. Egypt J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butt, M.S.; Naz, L.; Jaffery, N.B. City Dynamics in Pakistan 2015 (Thematic Research Report Series); Applied Economics Research Centre, University of Karachi: Karachi, Pakistan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Akhter, S.T.; Noon, M.H. Modeling spillover effects of leapfrog development and urban sprawl upon institutional delinquencies: A case for Pakistan. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 216, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, D. Hyderabad: Visioning, restructuring and making of a high-tech city. Cities 2015, 43, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, B. Analysis of Urban. Growth and Sprawl from Remote Sensing Data, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, R.O.; Clark, W.A.V. The Nature and Economics of Urban Sprawl. Land Econ. 1965, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, G.D. Urban Sprawl Causes, Consequences and Policy Responses, 1st ed.; Urban Institute Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Pakistan. Pakistan Bureau of Statistics (PBS). Available online: www.pbs.gov.pk/ (accessed on 6 June 2021).
- Memon, N. Tackling Unemployment in Rural Sindh. Political Economy. 2017. Available online: www.thenews.com.pk/tns/detail/563621-tackling-unemployment-rural-sindh (accessed on 6 June 2021).
- Parmar, V.; Jalbani, A.A. Investment Trends in Hyderabad, Pakistan. J. Indep. Stud. Res. 2005, 3, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.; Masser, I. Urban growth pattern modeling: A case study of Wuhan city, PR China. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2003, 62, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lo, C.P. Modelling urban growth and landscape changes in the Atlanta metropolitan area. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2003, 17, 463–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerzado, M.B.; Magsi, H.; Sheikh, M.J. Land use conflicts and urban sprawl: Conversion of agriculture lands into urbanization in Hyderabad, Pakistan. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2019, 18, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalli, M.N.; Ghaffar, A.; Shirazai, S.A.; Parveen, N.; Anwar, M.M. Change Detection Analysis of Land Use by using Geospatial Techniques: A case study of Faisalabad-Pakistan. Sci. Int. 2012, 24, 539–546. [Google Scholar]
- Akbar, T.A.; Hassan, Q.K.; Ishaq, S.; Batool, M.; Butt, H.J.; Jabbar, H. Investigative Spatial Distribution and Modelling of Existing and Future Urban Land Changes and Its Impact on Urbanization and Economy. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgescu, M.; Miguez-Macho, G.; Steyaert, L.T.; Weaver, C.P. Climatic effects of 30 years of landscape change over the Greater Phoenix, Arizona, region: 1. Surface energy budget changes. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2009, 114, D05110. [Google Scholar]
- Grossman-Clarke, S.; Zehnder, J.A.; Loridan, T.; Grimmond, C.S.B. Contribution of Land Use Changes to Near-Surface Air Temperatures during Recent Summer Extreme Heat Events in the Phoenix Metropolitan Area. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 1649–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Niyogil, D.; Tewari, M.; Aliaga, D.; Chen, F.; Tian, F.; Ni, G. Contrasting impacts of urban forms on the future thermal environment: Example of Beijing metropolitan area. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 034018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mak, H.W.L.; Laughner, J.L.; Fung, J.C.H.; Zhu, Q.; Cohen, R.C. Improved Satellite Retrieval of Tropospheric NO2 Column Density via Updating of Air Mass Factor (AMF): Case Study of Southern China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mak, H.W.L.; Ng, D.C.Y. Spatial and Socio-Classification of Traffic Pollutant Emissions and Associated Mortality Rates in High-Density Hong Kong via Improved Data Analytic Approaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.; Lv, X.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, H.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Ma, F. Study on Land-use Changes and Their Impacts on Air Pollution in Chengdu. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montejano, J.; Monkkonen, P.; Guerra, E.; Caudillo, C. The Costs and Benefits of Urban Expansion, Evidence from Mexico, 1990–2010. Lincoln Institute of Land Policy. Available online: www.lincolninst.edu/publications/working-papers/costs-benefits-urban-expansion (accessed on 6 June 2021).
- Zubair, O.A.; Ji, W.; Festus, O. Urban Expansion and the Loss of Prairie and Agricultural Lands: A Satellite Remote-Sensing Based Analysis at a Sub-Watershed Scale. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seto, K.C.; Marshall, J.S. Global urban land-use trends and climate impacts. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2009, 1, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argüeso, D.; Evans, J.P.; Pitman, A.J.; Di Luca, A. Effects of City Expansion on Heat Stress under Climate Change Conditions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.L.; Mak, H.W.L. From Comparative and Statistical Assessments of Liveability and Health Conditions of Districts in Hong Kong towards Future City Development. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Planning Department (PlanD). Appendix F: Zoning to Achieve Mixed Use Developments. Available online: www.pland.gov.hk/pland_en/p_study/comp_s/metroplan/metro_finalreport/appendix_f.htm (accessed on 6 June 2021).
- Wang, Y.; Fukuda, H. Sustainable Urban Regeneration for Shrinking Cities: A Case from Japan. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cities of Migration. Heritage and Modernity in Singapore’s Urban Renewal: Urban Redevelopment Authority. Available online: https://citiesofmigration.ca/good_idea/heritage-and-modernity-in-singapores-urban-renewal/ (accessed on 6 June 2021).
- Momtaz, S.; Kabir, Z. Evaluating Environmental and Social Impact Assessment in Developing Countries, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, H.W.L.; Lam, Y.F. Comparative assessments and insights of data openness of 50 smart cities in air quality aspects. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).