Inversion Evaluation of Rare Earth Elements in Soil by Visible-Shortwave Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
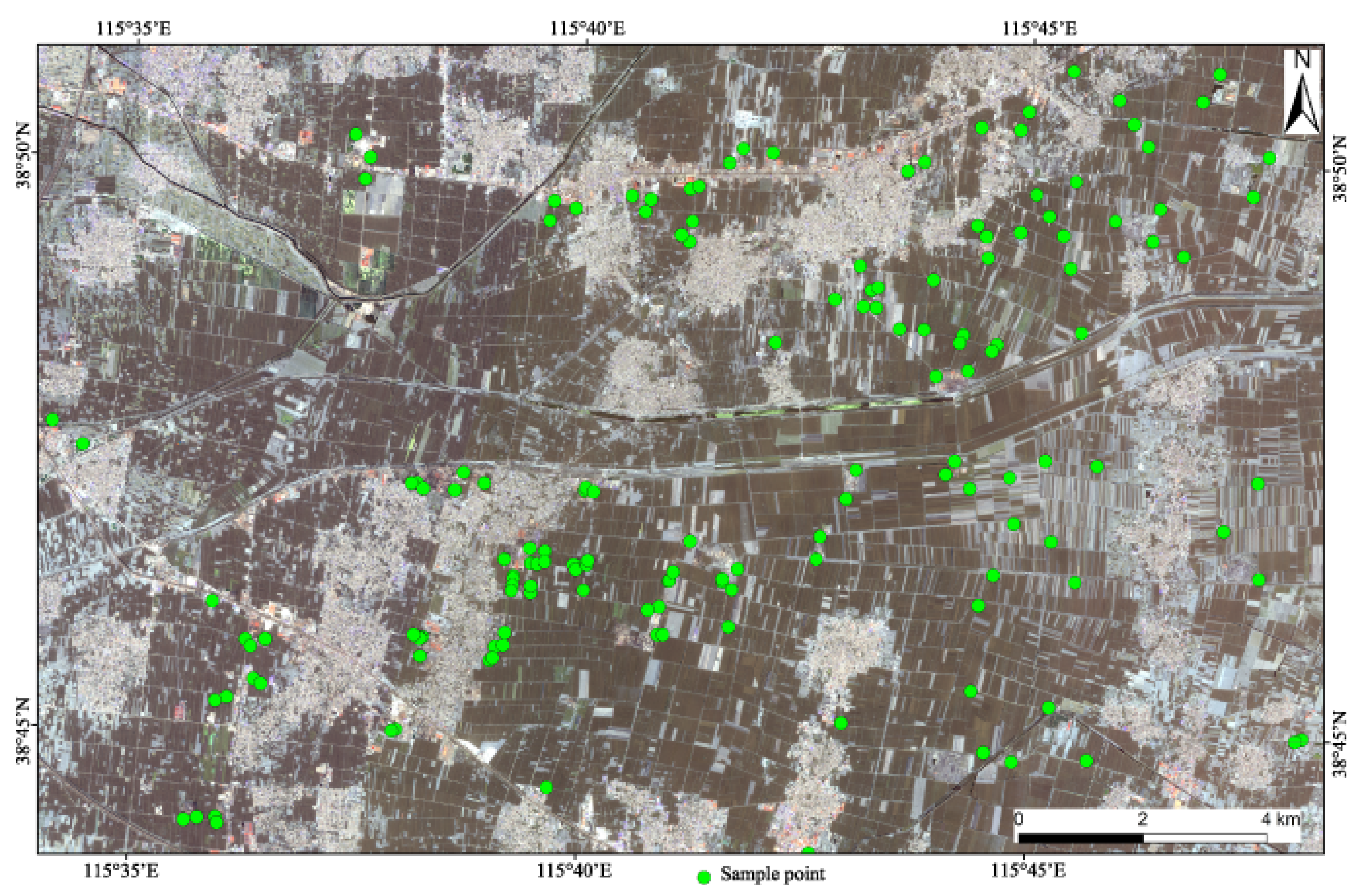
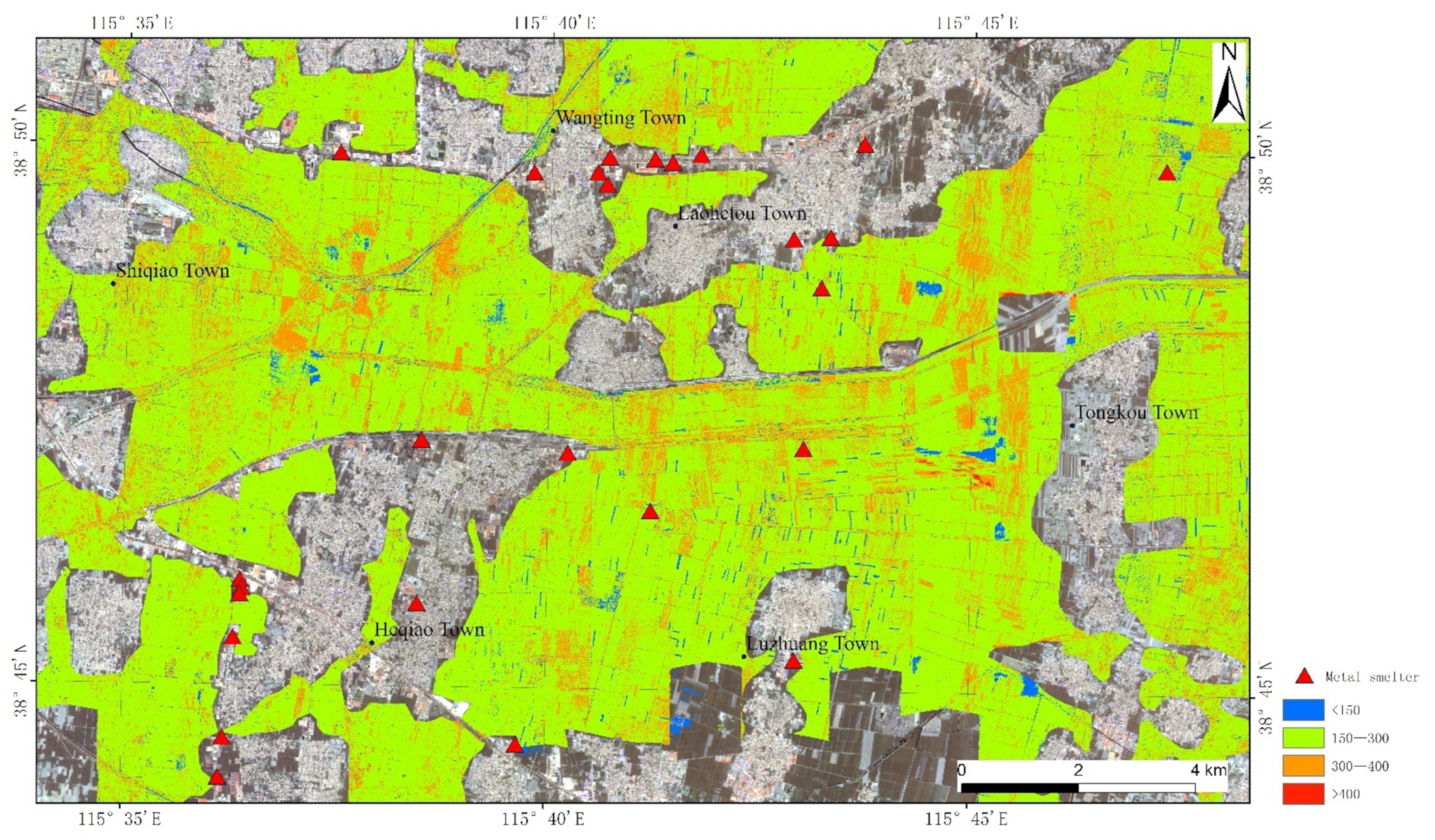
2.1. Soil Sampling
2.2. Chemical Analyses
2.3. Spectral Measurements and Transformations
2.3.1. SNV Transformation
2.3.2. FD Transformation
2.3.3. SD Transformation
2.3.4. MSC Transformation
2.3.5. CR Transformation
2.4. Modeling for Prediction
2.4.1. PLS
2.4.2. RF
2.4.3. BPNN
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of REEs in Soil
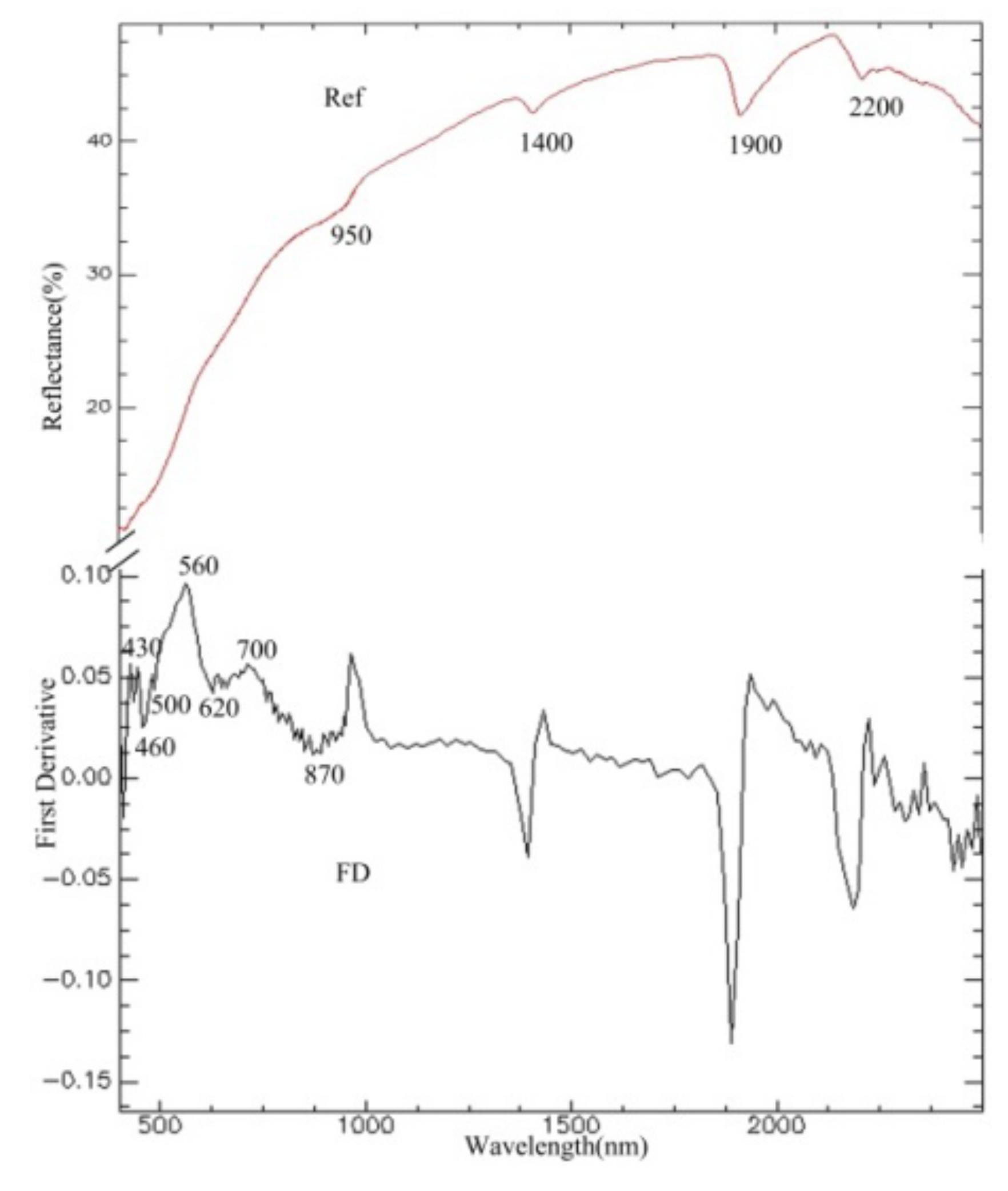
3.2. Analysis of Soil Spectra
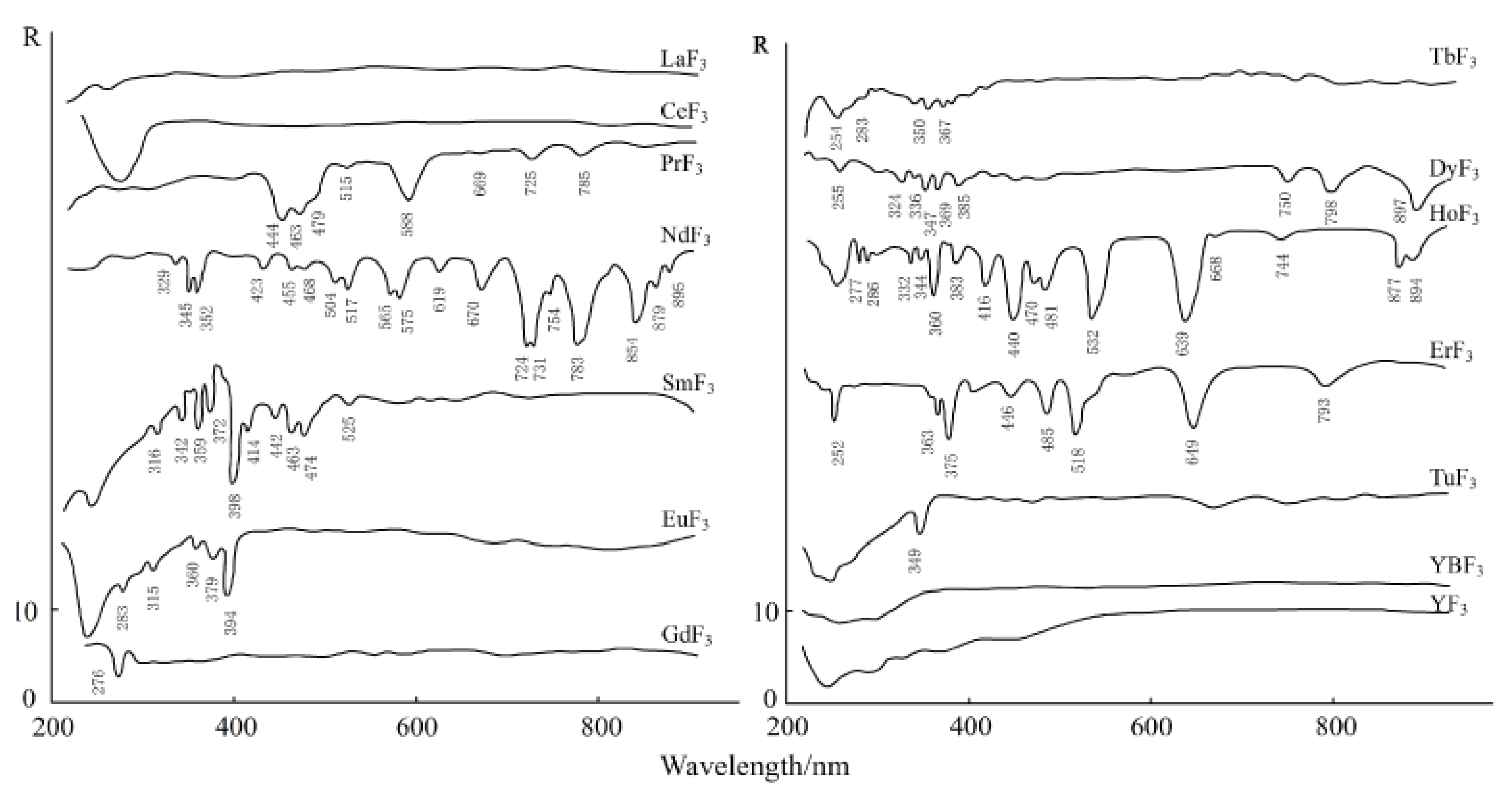
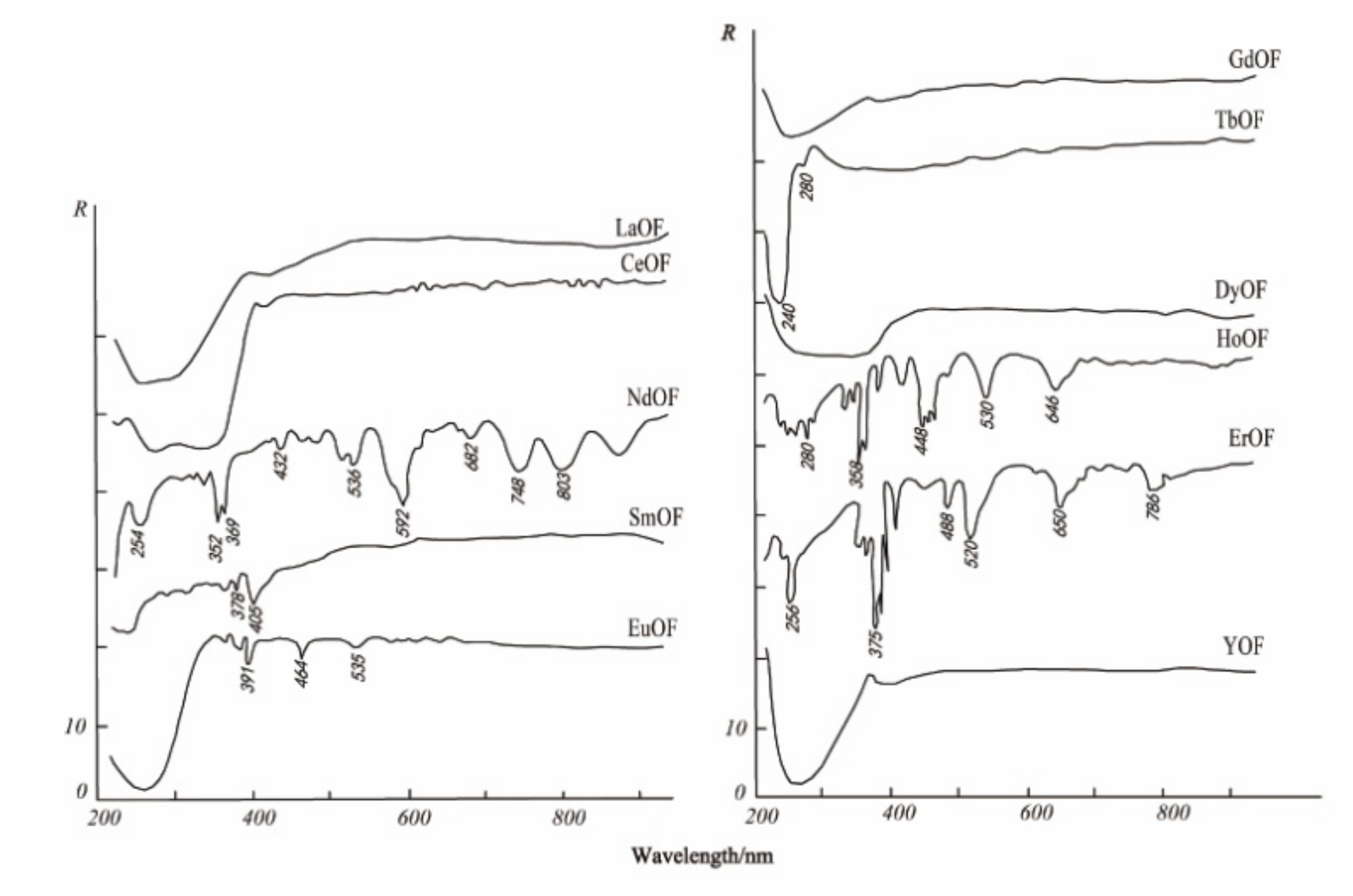
3.3. Spectral Response for the Contents of REEs
3.4. Modeling Prediction
3.5. Distribution Characteristics of REEs
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- FD, MSC, CR, SD, and SNV are used for spectral transformation to eliminate the baseline effect and enhance absorption characteristics. PLS, RF, and BPNN are used to carry out iterative modeling. By comparing the accuracy of various models, it is shown that BPNN has the highest accuracy after FD transformation, and R2 between the predicted values and measured contents is 0.986.
- (2)
- The contents of REEs are 157.3–358.7 mg/kg for soil samples collected at Anxin County, and the reported contents of REEs are in the range of 30–700 mg/kg. The C.V. of REEs is less than 1, which indicates that the spatial distribution of REEs is random and uniform, and it is little affected by human activities.
- (3)
- The average contents of REEs are 261.3 mg/kg for hyperspectral images, which is slightly higher than the average of 207 mg/kg in the crust. It is demonstrated that the control measures are effective, and the contents of REEs satisfy the demands of daily life for most regions of the study area.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Voncken, J.H.L. The Rare Earth Elements: An Introduction; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.M.; Bakar, N.K.A.; Bakar, A.F.A.; Ashraf, M.A. Chemical speciation and bioavailability of rare earth elements (REEs) in the ecosystem: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 22764–22789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikołajczak, P.; Borowiak, K.; Niedzielski, P. Phytoextraction of rare earth elements in herbaceous plant species growing close to roads. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 14091–14103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, L.; Ding, Q.; Wang, S.; Tang, Y.T.; Zhang, T.; Qiu, R.L. Structure, variation, and co-occurrence of soil microbial communities in abandoned sites of a rare earth elements mine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11481–11490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, E.; Sherman, A.M.; Wallington, T.J.; Everson, M.P.; Field, F.R.; Roth, R.; Kirchain, R.E. Evaluating rare earth element availability: A case with revolutionary demand from clean technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3406–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redling, K. Rare Earth Elements in Agriculture with Emphasis on Animal Husbandry. Ph.D. Thesis, LMU, Munich, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z. The biological hormesis-effects of rare earths and potential effects of application of rare earths on agricultural eco-environment. Rural. Eco-Environ. 2004, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Liu, W.; Huot, H.; Yang, Y.; Guo, M.; Morel, J.L.; Tang, Y.; Qiu, R. Responses of ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.) to increasing rare earth element (REE) concentrations in a hydroponic system. J. Rare Earths 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, G.; Guida, M.; Tommasi, F.; Oral, R. Health effects and toxicity mechanisms of rare earth elements—Knowledge gaps and research prospects. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 115, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, M.; Zhong, M.; Shahid, M.Z.; Liu, Y. Effects of topography and soil properties on the distribution and fractionation of REEs in topsoil: A case study in Sichuan Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Ou, X.; Chen, J. Calculation of toxicity coefficient of potential ecological risk assessment of rare earth elements. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 104, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turra, C.; Bacchi, M.A. Evaluation on rare earth elements of Brazilian agricultural supplies. J. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2011, 3, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bünzli, J.C.G.; Eliseeva, S.V. Basics of Lanthanide Photophysics, Lanthanide Luminescence: Photophysical, Analytical and Biological Aspects; Series on Fluorescence; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, R.N.; Rencz, A.N. Spectroscopy of rocks and minerals, and principles of spectroscopy. Man. Remote Sens. 1999, 3, 3–58. [Google Scholar]
- Rowan, L.C.; Kingston, M.J.; Crowley, J.K. Spectral reflectance of carbonatites and related alkalic igneous rocks; selected samples from four North American localities. Econ. Geol. 1986, 81, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, R.; Brandmeier, M.; Andreani, L.; Mhopjeni, K.; Gloaguen, R. Remote sensing exploration of Nb-Ta-LREE-enriched carbonatite (Epembe/Namibia). Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boesche, N.K.; Rogass, C.; Lubitz, C.; Brell, M.; Herrmann, S.; Mielke, C.; Tonn, S.; Appelt, O.; Altenberger, U.; Kaufmann, H. Hyperspectral REE (rare earth element) mapping of outcrops—Applications for neodymium detection. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5160–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Song, L.; Han, Z.; Liao, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhai, J.; Zhu, R. Climate-related risks in the construction of Xiongan New Area, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 141, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, M.E.; Schwieters, J.B. The development of multiple collector mass spectrometry for isotope ratio measurements. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 242, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooistra, L.; Wehrens, R.; Leuven, R.S.E.W.; Buydens, L.M.C. Possibilities of visible–near-infrared spectroscopy for the assessment of soil contamination in river floodplains. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 446, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, H.; Naes, T. Multivariate Calibration; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Moros, J.; Vallejuelo, S.F.O.D.; Gredilla, A.; Diego, A.D.; Madariaga, J.M.; Garrigues, S.; Guardia, M.D.L. Use of reflectance infrared spectroscopy for monitoring the metal content of the estuarine sediments of the Nerbioi-Ibaizabal River (Metropolitan Bilbao, Bay of Biscay, Basque Country). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9314–9320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.N.; Roush, T.L. Reflectance spectroscopy: Quantitative analysis techniques for remote sensing applications. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1984, 89, 6329–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, E.; Banin, A. Near-infrared analysis as a rapid method to simultaneously evaluate several soil properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1995, 59, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.W.; Laird, D.; Mausbach, M.J.; Hurburgh, C.R., Jr. Near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy–principal components regression analyses of soil properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wold, S.; Sjöström, M.; Eriksson, L. PLS-regression: A basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 58, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayanand, M.; Varahamoorthi, R.; Kumaradhas, P.; Sivamani, S.; Kulkarni, M.V. Regression-BPNN modelling of surfactant concentration effects in electroless NiB coating and optimization using genetic algorithm. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 409, 126878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Morgan CL, S.; Wijewardane, N.K. Visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy analysis of soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, J.; Wu, Y.; Ling, T. Reflectance Spectroscopy and Hyperspectral Detection of Rare Earth Element. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2018, 38, 3801–3808. [Google Scholar]
- Balsam, W.L. Sediment dispersal in the Atlantic Ocean: Evaluation by visible light spectra. Rev. Aquat. Sci. 1991, 4, 411–447. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.Q.; Mao, Y.Q.; Ji, J.F.; Ma, H.R.; Chen, J.; Liao, Q.L. Reflectance spectroscopy study of Cd contamination in the sediments of the Changjiang River, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3449–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsanov, S.S.; Derbeneva, S.S.; Batsanova, L.R. Electronic spectra of fluorides, oxyfluorides, and oxides of rare-earth metals. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 1969, 10, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, F.K.; Roger, N.C.; Gregg, A.S. USGS Spectral Library. 2017. Available online: https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/ds1035 (accessed on 3 November 2021).
- Dostal, J. Rare earth element deposits of alkaline igneous rocks. Resources 2017, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.J.; Rivard, B.; Groat, L.A. Visible and short-wave infrared reflectance spectroscopy of REE fluorocarbonates. Am. Mineral. 2014, 99, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malley, D.F.; Williams, P.C. Use of near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy in prediction of heavy metals in freshwater sediment by their association with organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 3461–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossel, R.A.V.; McGlynn, R.N.; McBratney, A.B. Determining the composition of mineral-organic mixes using UV–vis–NIR diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Geoderma 2006, 137, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mleczek, P.; Borowiak, K.; Budka, A.; Niedzielski, P. Relationship between concentration of rare earth elements in soil and their distribution in plants growing near a frequented road. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 23695–23711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, S.; Liang, T.; Zhang, C.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Q. Role of ligands in accumulation and fractionation of rare earth elements in plants. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2005, 107, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Li, B.; Li, G.; Wang, W. Nutrient elements and heavy metals in the sediment of Baiyangdian and Taihu Lakes: A comparative analysis of pollution trends. Front. Agric. China 2007, 1, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
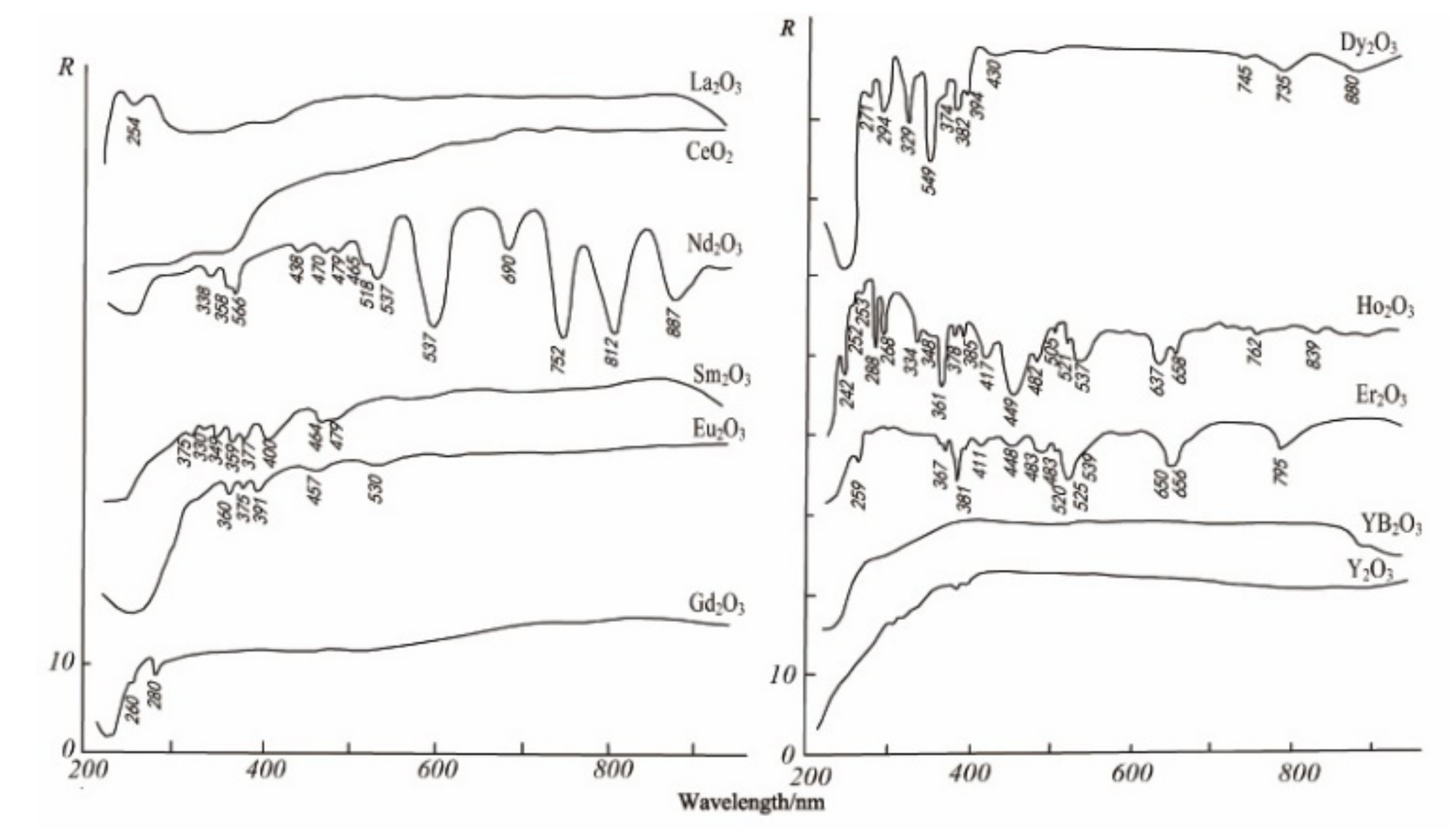
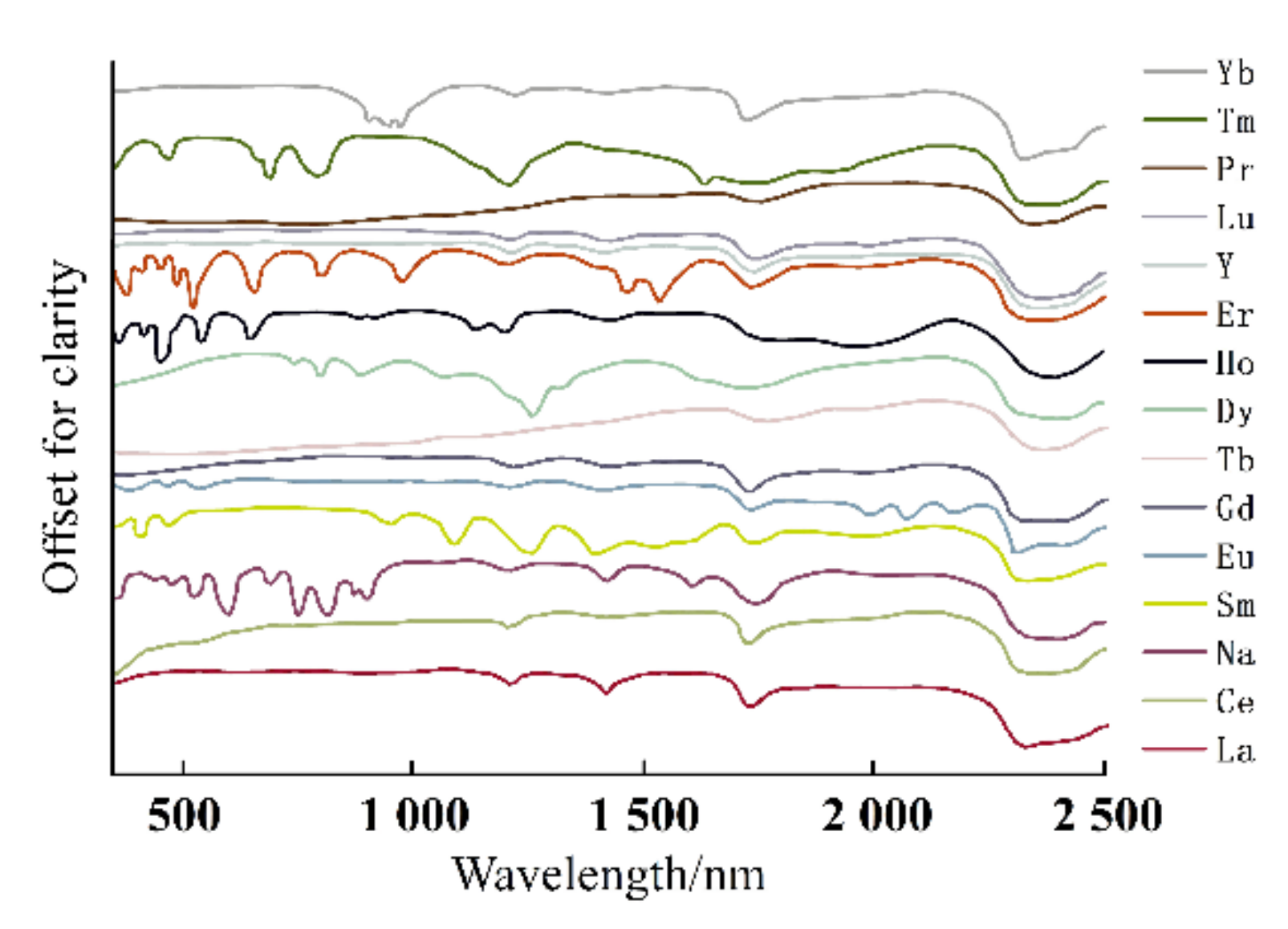
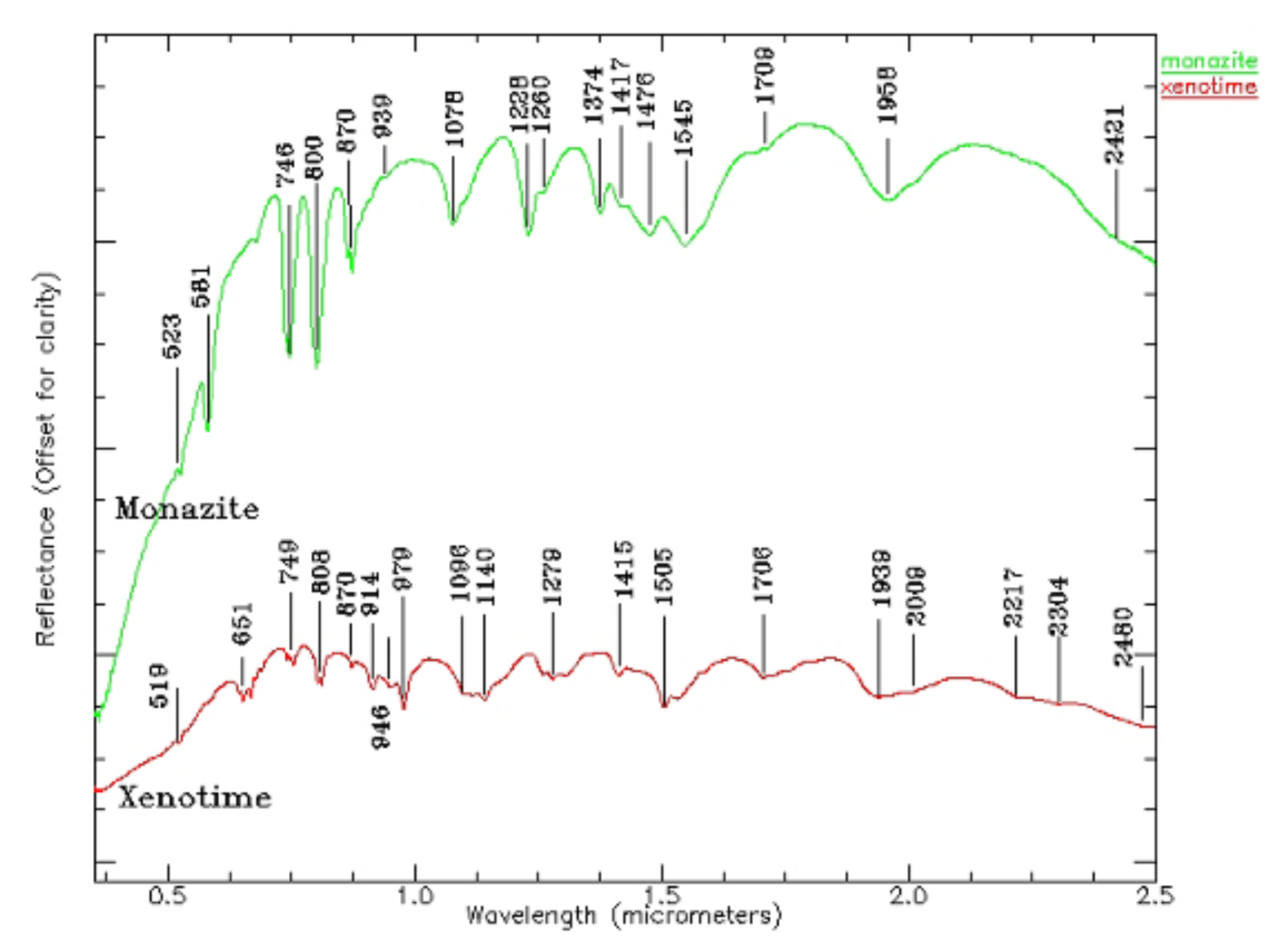
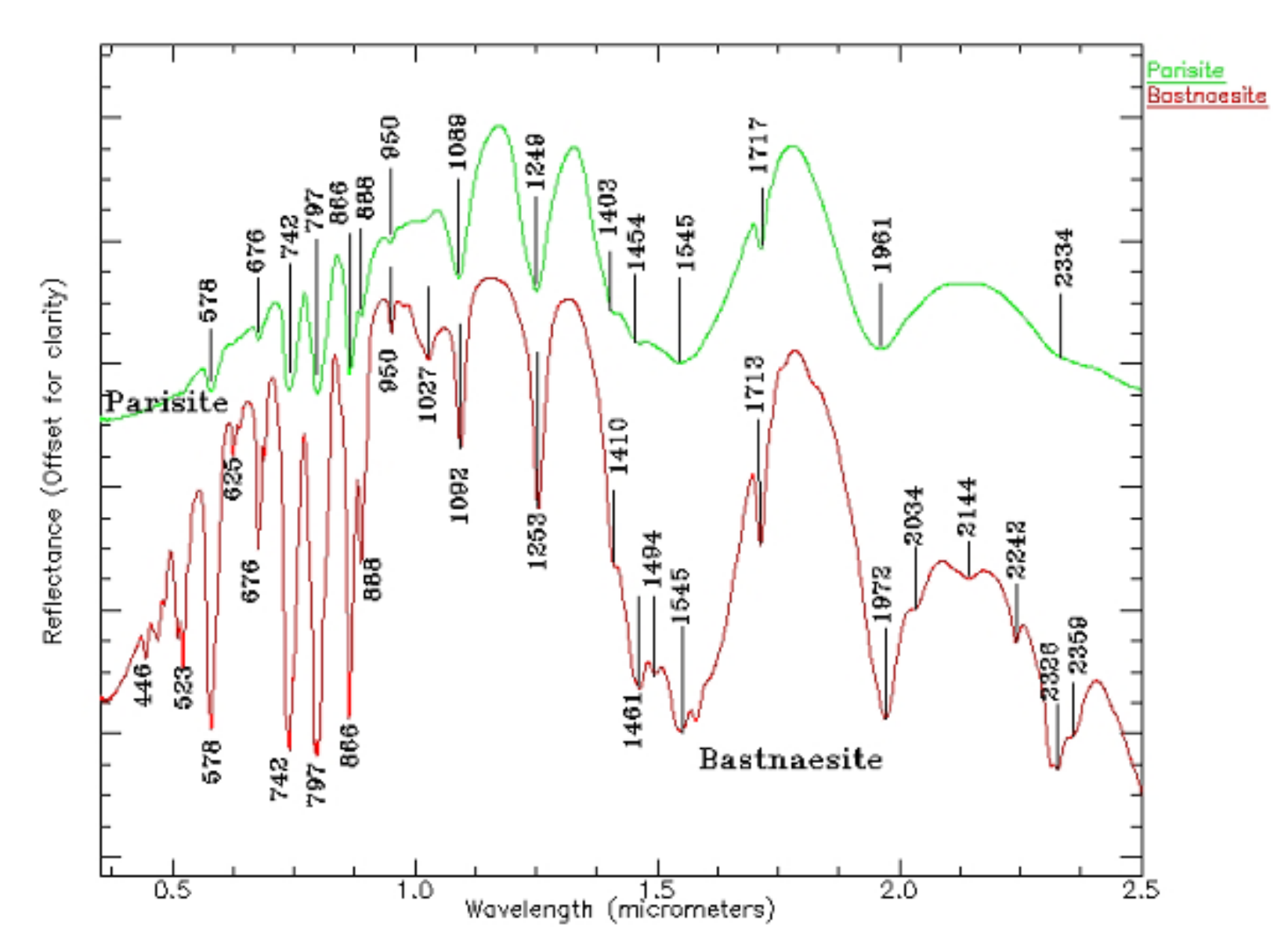
| REEs | Average | Maximum | Minimum | C.V. | UCC | Chinese Soil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La | 40.916 | 142 | 26.3 | 0.261 | 30 | 38.6 |
| Ce | 76.035 | 202 | 62.6 | 0.125 | 64 | 83.4 |
| Pr | 9.294 | 31.74 | 4.99 | 0.328 | 7.1 | 9.67 |
| Nd | 38.422 | 100.19 | 2.4 | 0.301 | 26 | 41.1 |
| Sm | 6.158 | 13.56 | 0.49 | 0.263 | 4.5 | 6.6 |
| Eu | 1.350 | 3.027 | 0.14 | 0.259 | 0.88 | 1.18 |
| Gd | 6.304 | 15.6 | 0.51 | 0.282 | 3.8 | 5.39 |
| Tb | 0.856 | 1.911 | 0.057 | 0.321 | 0.64 | 0.67 |
| Dy | 4.941 | 11.847 | 0.274 | 0.401 | 3.5 | 3.92 |
| Ho | 0.962 | 2.365 | 0.046 | 0.487 | 0.8 | 0.73 |
| Er | 2.871 | 7.633 | 0.175 | 0.453 | 2.3 | 2.09 |
| Tm | 0.457 | 1.743 | 0.021 | 0.580 | 0.33 | 0.3 |
| Yb | 2.651 | 2.98 | 1.98 | 0.071 | 2.2 | 1.97 |
| Lu | 0.424 | 1.666 | 0.307 | 0.186 | 0.32 | 0.28 |
| Y | 27.497 | 124 | 0.3 | 0.260 | 22 | 20.1 |
| Total | 219.136 | 358.701 | 157.327 | 0.122 | 168.37 | 216 |
| Model | Trans. | R2 | Calibration RMSE | RPD | RER | R2 | Validation RMSE | RPD | RER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLS | SNV | 0.812 | 11.608 | 2.308 | 12.608 | 0.847 | 12.002 | 2.187 | 19.227 |
| FD | 0.726 | 14.409 | 1.909 | 8.671 | 0.847 | 12.959 | 1.862 | 9.966 | |
| SD | 0.715 | 14.780 | 1.872 | 8.778 | 0.553 | 16.924 | 1.436 | 6.615 | |
| MSC | 0.778 | 12.604 | 2.122 | 10.412 | 0.824 | 13.106 | 2.029 | 15.677 | |
| CR | 0.864 | 9.988 | 2.208 | 14.815 | 0.803 | 12.294 | 2.103 | 14.405 | |
| RF | SNV | 0.842 | 11.787 | 2.273 | 7.413 | 0.612 | 17.640 | 1.388 | 3.703 |
| FD | 0.898 | 10.792 | 2.549 | 8.701 | 0.764 | 13.180 | 1.531 | 5.758 | |
| SD | 0.899 | 11.096 | 2.494 | 7.990 | 0.547 | 16.725 | 1.453 | 4.057 | |
| MSC | 0.806 | 12.363 | 2.163 | 7.551 | 0.448 | 19.804 | 1.343 | 4.084 | |
| CR | 0.923 | 9.273 | 2.917 | 10.572 | 0.565 | 17.738 | 1.657 | 3.594 | |
| BPNN | SNV | 0.782 | 11.983 | 2.128 | 11.225 | 0.900 | 11.297 | 2.053 | 14.702 |
| FD | 0.891 | 9.181 | 3.021 | 17.324 | 0.986 | 3.158 | 2.607 | 45.004 | |
| SD | 0.910 | 7.833 | 2.815 | 20.672 | 0.967 | 6.168 | 2.418 | 27.625 | |
| MSC | 0.753 | 13.658 | 1.895 | 16.475 | 0.915 | 10.187 | 1.406 | 17.393 | |
| CR | 0.822 | 11.364 | 2.343 | 16.208 | 0.940 | 7.044 | 2.167 | 16.578 |
| Trans. | R2 | Calibration RMSE | RPD | RER | R2 | Validation RMSE | RPD | RER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FD | 0.929 | 6.922 | 3.648 | 21.472 | 0.994 | 2.558 | 13.184 | 51.782 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Z.; Huang, W.; Li, S.; Ni, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, M.; Zhu, F. Inversion Evaluation of Rare Earth Elements in Soil by Visible-Shortwave Infrared Spectroscopy. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4886. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234886
Huang Z, Huang W, Li S, Ni B, Zhang Y, Wang M, Chen M, Zhu F. Inversion Evaluation of Rare Earth Elements in Soil by Visible-Shortwave Infrared Spectroscopy. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(23):4886. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234886
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Zhaoqiang, Wenxuan Huang, Sheng Li, Bin Ni, Yalong Zhang, Mingwei Wang, Maolin Chen, and Fuxiao Zhu. 2021. "Inversion Evaluation of Rare Earth Elements in Soil by Visible-Shortwave Infrared Spectroscopy" Remote Sensing 13, no. 23: 4886. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234886
APA StyleHuang, Z., Huang, W., Li, S., Ni, B., Zhang, Y., Wang, M., Chen, M., & Zhu, F. (2021). Inversion Evaluation of Rare Earth Elements in Soil by Visible-Shortwave Infrared Spectroscopy. Remote Sensing, 13(23), 4886. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234886







