Abstract
The replenishment of aquifers depends mainly on precipitation rates, which is of vital importance for determining water budgets in arid and semi-arid regions. El-Qaa Plain in the Sinai Peninsula is a region that experiences constant population growth. This study compares the performance of two sets of satellite-based data of precipitation and in situ rainfall measurements. The dates selected refer to rainfall events between 2015 and 2018. For this purpose, 0.1° and 0.25° spatial resolution TMPA (Tropical Rainfall Measurement Mission Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis) and IMERG (Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement) data were retrieved and analyzed, employing appropriate statistical metrics. The best-performing data set was determined as the data source capable to most accurately bridge gaps in the limited rain gauge records, embracing both frequent light-intensity rain events and more rare heavy-intensity events. With light-intensity events, the corresponding satellite-based data sets differ the least and correlate more, while the greatest differences and weakest correlations are noted for the heavy-intensity events. The satellite-based records best match those of the rain gauges during light-intensity events, when compared to the heaviest ones. IMERG data exhibit a superior performance than TMPA in all rainfall intensities.
1. Introduction
Sufficiently accurate measurements of precipitation are indispensable for a large spectrum of socio-economic human activities [1]. Such precipitation measurements are essential over a wide range of spatiotemporal scales. However, over several regions around the world, precipitation measurements from rain gauges or other in situ rainfall measuring instruments are limited by the scarcity of observations from a locally coarse network [2,3,4]. Data from other ground-based platforms (e.g., ground-based weather radars) cannot fill in the gap. The Sinai Peninsula in Egypt is an example of a region with insufficient ground-based measurements from rain gauges. Nevertheless, satellites can provide estimations of precipitation at broader geographical scales [5,6,7] and, thus, satellite-derived rainfall estimations offer a potential source for obtaining higher-quality spatiotemporal precipitation distributions over the Sinai Peninsula. This is particularly important in cases where socio-economic activities greatly rely on aquifers for water resources, as in the geographical area referred to in this case study. However, monitoring precipitation by the spaceborne sensors in arid areas is a challenging task because such areas are characterized by low precipitation intensities and large spatial heterogeneities [8].
In arid and semi-arid areas, replenishment of aquifers by precipitation is influenced by the recharge rate and general water cycle equilibrium [9]. Increased precipitation, especially during monsoons, reduces stress on aquifers, either by a direct recharge or indirectly by the reduction of abstraction [10]. Consequently, precipitation is the most prominently analyzed factor in most hydrological studies, particularly those on flash flood risk assessment, groundwater location, climate change, and forecasting [11]. Precipitation intensity is determined by the storm extent, strength, and movement, which varies over small-scale areas in arid and semi-arid regions [12,13]. Low precipitation rates negatively affect the continuity of land reclamation [14]. However, the significance of light-intensity events lies in their frequency. These are the most frequent event types in most arid regions of the world, when compared to more rare heavy-intensity rain events [15,16]. The contribution of the most frequent light rainfall events to infiltration and aquifer recharge rates is, therefore, greater than that of the heavy-intensity events.
Event intensity was previously determined primarily by a combination of rain gauge and radar data [17,18]. However, rain gauge data on its own produces the most accurate measurement of precipitation rates both in terms of spatial resolution and rainfall accumulation depth [11,19]. Several types of rain gauges exist, including accumulation gauges, tipping bucket gauges, weighing gauges, and optical gauges. Each carries its own advantages and disadvantages [11,19,20]. Although rain gauges have been ranked as the most accurate tool for rainfall detection, they are sparsely distributed or even non-existent in most developing countries, particularly those in mountainous regions [17,21,22]. However, there exist numerous, freely available sets of satellite-based rainfall estimates and reanalysis products, which enable users to bridge gaps in data derived from rain gauge networks.
The El-Qaa Plain in the Sinai Peninsula was selected as a test site. This region was chosen for its standing as one of the most promising areas in the Sinai Peninsula for further development and, in particular, tourism. These prospects have already led to a gradual increase in the number of inhabitants and expansion of land exploitation. As a result, local water consumption is gradually increasing in an area where the main source of groundwater is the regional quaternary aquifer [23,24]. This aquifer extends from Wadi Feiran to the head of Ras-Mohamed and is mainly recharged by rainfall [25].
For a more effective management of the limited water resources in the area, it is clear that it is critical to acquire sufficient data on the spatiotemporal distribution of the rainfall events with special emphasis on light events [26]. The existing coarse rain gauge network is not sufficient to shed light on this aspect and it seemed that the knowledge gap can be filled by exploiting rainfall estimates from satellite missions that are capable of providing data on spatiotemporal distributions of rainfall. In order to demonstrate that satellite-derived data can meet this need, two sets of satellite-based rainfall data are tested and compared in this study. The first dataset refers to the most commonly used dataset related to the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM). This dataset is the Multi-Satellite Precipitation Analysis, Version7 (3B42V7), hereafter, denoted as TMPA (Tropical Rainfall Measurement Mission Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis) [27,28,29,30,31]. The second dataset refers to another more recent satellite rainfall measuring effort, the Global Precipitation Mission (GPM [7]). This dataset is the Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for GPM, hereafter, denoted as IMERG (Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement) [32].
The performance of TMPA and IMERG has been investigated in several studies over different parts of the world and it is still an ongoing topic of study [33,34,35,36]. Bearing in mind that the availability of the GPM-related dataset started after the launch and operational functioning of the core observatory in 2015. Studies that make use of IMERG products have only been published recently. Manz et al. [37] compared IMERG and TMPA in the tropical Andes and Tan and Duan [38] assessed them over Singapore. Xu et al. [39] evaluated the two datasets against rain gauge records in the Tibetan Plateau. The study was followed by another study over the same area by Zhang et al. [40]. A similar study was carried out by Anjum et al. [41] over another mountainous region in Pakistan. Tan and Santo [42] have used the two datasets in their study over Malaysia. The performance of the satellite-based analyses was also tested over the mountainous region of Northwest China [43]. Palomino-Ángel et al. [44] compared reference and satellite-based mean daily precipitations over Northwestern South America. In addition, Zhang et al. [45] have assessed the two datasets over a humid basin in China.
From the above brief listing of the recently published research on the comparative assessment of TMPA and IMERG, it is evident that the respective investigators have been focusing mainly on areas where rainfall is not scarce, and a sufficient network for ground measurements is in place. However, it is challenging to investigate the performance of these two datasets in an arid environment with the employment of a rather inadequate rain gauge network where rainfall estimations are highly desirable.
Bearing in mind the above, the objective of the present study is to compare TMPA and IMERG analyses against ground measurements of precipitation over an arid area covered with a coarse rain-gauge network. The targeted area is the El-Qaa Plain in the Sinai Peninsula. The present study will form the basis for making recommendations on improving and expanding the current rain gauge network. The utilization and contrasting of the two precipitation data sets against the existing in situ data set was performed in support of a double-sided study aiming to optimize the design of a new rain gauge network over the test site. In addition to other decisive factors and the adoption of suitable statistical metrics, the better performance of the two satellite-based data sets may be used as providing an objective criterion for site selection of a future denser rain-gauge network.
Several authors have investigated the groundwater localization in the area under study [24,46,47,48,49]. Nevertheless, the local precipitation rate and spatiotemporal distribution of rainfall have been insufficiently investigated due to the limited number of rain gauges in the region. Consequently, the present study offers a foundation for addressing the climatological and hydrological concerns at the test site. Moreover, these results can promote continual development in the area, as they serve as a basis for the preservation of the region’s water table. Moreover, this study comprises the first part of the double-sided study mentioned before. Therefore, the methodology and results of one side of the study will be launched in the current manuscript and contribute in complementing the other side, which is targeting the optimization of the existing rain gauge network in the test site, and will be discussed in a companion paper.
Following this introduction, a brief account of the study area is given in Section 2. In Section 3, the data used in this study are presented with emphasis on the TMPA and IMERG data features and the in-situ rainfall measurements. Section 4 presents the methodology adopted. Results and discussions are presented in Section 5 with concluding remarks and plans for future work given in Section 6.
2. Study Area
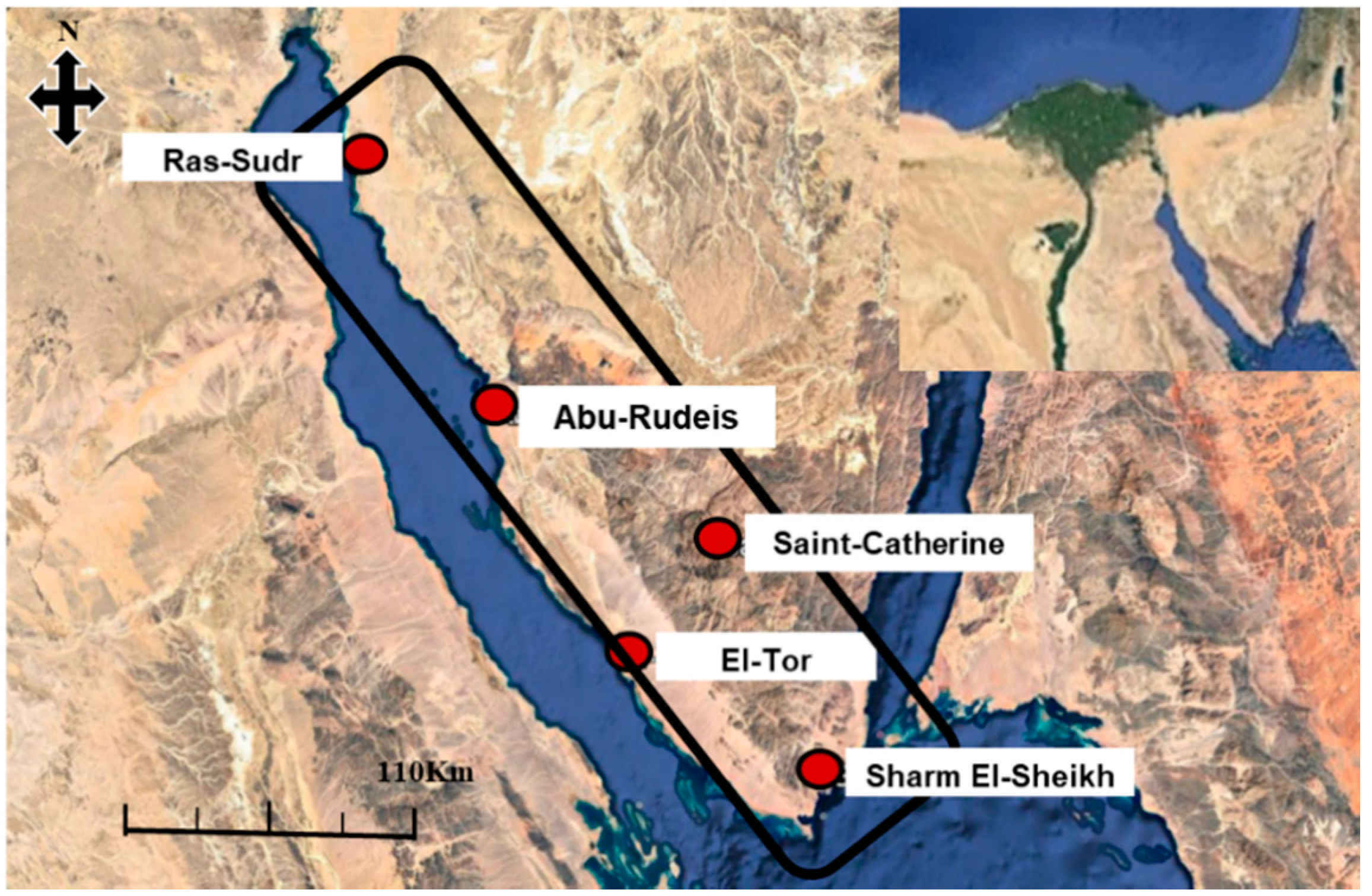
The Southwestern corner of the Sinai Peninsula contains the El-Qaa Plain, located between latitudes 28°30′ and 28°40′ North and longitudes 33°17′ and 33°37′ East and neighboring the Gulf of Suez [47] (Figure 1). Its area is roughly 6070 km2 with a maximum length of 150 km and a maximum width of 20 km [50]. The El-Qaa Plain was defined by the Precambrian eastern mountain region that borders the study area to the East and North and features a maximum elevation of 2624 m and a minimum elevation of 300 m [47]. This section of the Sinai Peninsula comprises several varieties of igneous rock, such as diorite, granite, meta-gabbro, and volcanic rocks [26,51]. Its sedimentary section comprises Gabal Qabaliat in the northwestern region of the study site and features an elevation of 250 m and a moderate slope toward the El-Qaa Plain, separating the Gulf of Suez from the plain. The central plain is composed mainly of Quaternary deposits, which are not perfectly flat and are dissected by several wadies, alluvial fans, palaya, and terraces [52]. Sherief [26] distinguished between old alluvial deposits and wadi deposits.
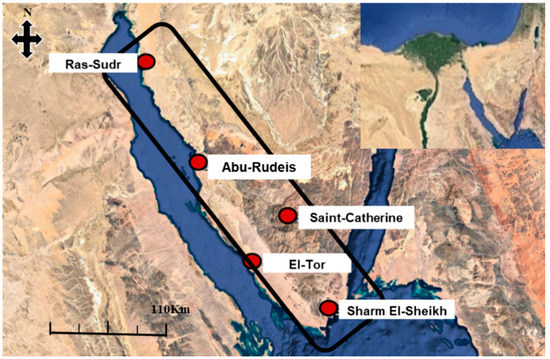
Figure 1.
Satellite map showing the study area. El-Qaa Plain is contained within the black outline with its five ground-based stations identified (source: Google Earth, 2017).
The study area was separated into two sub-areas on the basis of the topographical elevation above mean sea level: (a) the Lowland sub-area, ranging in elevation from 0 to 300 m, includes the Ras-Sudr (29.59°N, 32.71°E, 12 m) and Abu-Rudeis (28.89°N, 33.18°E, 13 m) stations in the northern part of the area, the El-Tor (28.24°N, 33.62°E, 13 m) station in the middle, and the Sharm El-Sheikh (27.93°N, 34.32°E, 38 m) station in the South. (b) The highland sub-area, ranging in elevation from 300 to 2000 m, is represented by the Saint-Catherine (28.55°N, 33.98°E, 1562 m) station in the middle of the area. Generally, highland receives more of rainfall than lowland.
3. Materials
3.1. TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA)
Precipitation-based remotely sensed data can provide a broad solution to the extensive problems that arise due to the low number and sparse distribution of rain gauges in certain areas. Moreover, it provides both a high spatial (4 to 25 km) and temporal resolution (every 30 min to 6 h). Furthermore, it offers annual, seasonal, and daily coverage at local and regional scales [53].
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) provided the first widely used remote sensing data for estimating rainfall in tropical and subtropical areas [17,54]. TRMM was a joint space mission between the US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) [55,56]. The TRMM carried onboard five instruments: a Precipitation Radar (PR, operating at 13.8 GHz), a TRMM Microwave Imager (TMI, a nine-channel passive microwave radiometer), a Visible Infrared Scanner (VIRS, a five-channel visible/infrared radiometer), a Clouds & Earths Radiant Energy System (CERES), and a Lightning Imaging Sensor (LSI). It operated at one transmitting/receiving frequency and one polarization, providing information about rain type, strength, and distribution [55]. The TRMM Microwave Imager (TMI) provided quantitative information about rainfall, water vapor, cloud water content, and sea surface temperature (SST) [55]. The PR complemented the results of the TMI and passive microwave sensors to provide measurements of radiance through precipitating clouds along the sensor view path. Radiance frequency reflects the properties of clouds and precipitation particles [57]. The active microwave sensors provided information about cloud height by measuring a backscatter delay [57]. The Visible and Infrared Scanner (VIRS) provided indirect measurements of rainfall intensity, distribution, and type [55,56]. The VIRS provided less reliable data on its own [57]. However, it provided more frequent data when compared to the infrequent data captured by the TMI and PR. The LIS was a lightning sensor, which played an important role in connecting lightning occurrence to precipitation events, while the CERES allowed for the determination of the total radiant energy balance. Analyzed together with the latent heating derived from precipitation, it was then possible to construct a significantly improved picture of our atmospheric energy system [57].
For each of the rainfall events studied here, the temporal resolution is eight TMPA scenes in a day (i.e., one per 3 h) retrieved from the official NASA webpage (mirador.gsfc.nasa.gov (accessed on 4 February 2021)) in the netcdf format. The ArcGIS 10.5 software was subsequently used to process these data. Processing was performed in four steps, complementing the first stage of the statistical metrics. The data were first opened as a raster layer and clipped to match the study area. The data pixel size was subsequently resampled, adopting the nearest-neighbor interpolation, in order to match the IMERG data spatial resolution. Finally, the value of each pixel was calculated and recorded, including the starting point of the events (0 h), after three hours (3 h), six hours (6 h), nine hours (9 h), 12 hours (12 h), and one day (24 h). This time series was sufficient to cover all rainfall events, as the precipitation ceases after 12 hours. Next, the satellite-based rainfall data was divided into lowland and highland groups, according to the respective pixel’s elevation. Data recorded at points with elevations ranging from 0 to 300 m belong to the lowland group, while those from 300 to 2000 m belong to the highland group. The values of pixels coinciding with rain gauges were collected at both 0.25° and 0.1° resolutions on a daily basis.
After seventeen years with the TRMM satellite in orbit, its mission came to an end in 2015, and was succeeded by the Global Precipitation Mission (GPM, see Section 3.2). Nevertheless, the plan is that TMPA will continue to be computed with climatological coefficients for several months after the IMERG is retrospectively processed to the start of TRMM in order to allow a transition for users, like in the present study.
3.2. Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG)
The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission is the most recent joint space venture between NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) with contributions from several other countries and organizations (e.g., France’s CNES, the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), the USA’s NOAA, EUMETSAT, and others). The GPM expands upon the TRMM mission with higher spatial and temporal coverage and higher accuracy. It provides the next generation of global rain and snow observations. The scientific community responded immediately to the availability of the new source of spatiotemporal distributions of rainfall data [58].
The GPM core observatory satellite was launched on 27 February 2014, carrying an advanced set of instruments onboard. It houses a Ku/Ka-band Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) and a multi-channel GPM Microwave Imager (GMI) capable of sensing light rain and snow fall [7,54,59,60]. The GPM mission is characterized by its distinct orbit, inclined 65°, allowing continuous sampling over all hours of the day [59]. The core observatory is complemented by a constellation of other spacecrafts. The core observatory provides a new calibration standard for the rest of the satellite constellation. The data from all satellites comprising GPM form the basis for the products of this mission.
The Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) is the GPM’s Level 3 multi-satellite precipitation algorithm. It combines intermittent precipitation estimates from all constellation microwave sensors, IR-based observations from geosynchronous satellites, and monthly gauge precipitation data [47,50]. Three different daily IMERG products exist: IMERG Day 1 Early Run (near real-time with a latency of 6 h), IMERG Day 1 Late Run (reprocessed near real-time with a latency of 18 h), and IMERG Day 1 Final Run (gauged-adjusted with a latency of four months) [57]. The IMERG Final Run product provides more accurate precipitation information than the near-real-time products across GPCC-gauged (Global Precipitation Climatology Centre) regions [50] (see Table 1).

Table 1.
Summary of the differences between TMPA and IMERG [17].
Fifty daily IMERG scenes collected at half-hour intervals were retrieved from the official NASA Mirador webpage to cover precipitation events from 2015 to 2018 (in a netcdf format). The data were opened and clipped in ArcGIS10.5 software. The mean of the half-hourly scenes was calculated every three hours. This step facilitated the statistical comparison between the half-hourly GPM(IMERG) data and the three-hourly TRMM(3B42V7) data with eight scenes for each type. The value of each pixel in the previously mentioned scenes was calculated and stored in a spreadsheet. Next, the pixel values that coincided with rain gauges were collected in a separate spreadsheet to further calculate statistical metrics.
3.3. In Situ Rain Gauge Data
The in-situ rainfall measurements from a network of tipping bucket rain gauges for the period from 2015 to 2018 have been provided by the Egyptian Meteorological Authority (EMA). The rain gauge data are daily totals. A preliminary analysis of the rain records was carried out in order to select the rainfall events to be included in this study. Bearing in mind the small number of rain gauges installed in the region of El-Qaa Plain in Sinai Peninsula, the precipitation events selected for investigation in the present study are comprised of rainy days for which all the rain gauges have recorded precipitation. On the basis of these in-situ data, the rainiest days in this period were deduced. The large majority of records from this arid region exhibit either no precipitation at all (i.e., 0 mm) or very small precipitation amounts (i.e., 1 mm) at some stations. The preliminary analysis of the data has revealed that, in this four-year period, there was just a single significant event in each year that is worth studying. In general, one major day-long event in each year was recorded by all existing rain gauges. These four significant events were subsequently used to evaluate the performance of the satellite-based datasets discussed above in Section 3.1 and Section 3.2.
The selected events occurred on 25 October 2015, 27 October 2016, 12 April 2017, and 28 April 2018. Based on Sherief’s [26] rainfall intensity classifications, these four events were classified as moderate, heavy, light, and light events, respectively.
In all the events studied herein, light precipitation started at around 7:00 a.m., which was followed by a gradual increase in intensity reaching the peak at 1:00 pm or 2:00 p.m. and then started to decrease gradually until 7:00 p.m. or 8:00 p.m. It is also worth noting that the 2015 and 2016 events characterized as moderate and heavy intensity caused destructive flash floods that damaged properties and caused loss of lives.
4. Methods
Classification of Rainfall Events
Rainfall events are very rare over the study area. Regional rainfall intensity was analyzed by Sherief [26], using data collected by the Egyptian Meteorological Authority over a period of 55 years (1934–1989). He categorized precipitation into light (0.1 to 1 mm), moderate (1 to 10 mm), and heavy (>10 mm) intensity events. The rainfall intensity distribution revealed that 61% of the yearly events are light, 34% are moderate, and 5% are heavy. In addition, mean annual precipitation received at the site was 77 mm, 43 mm, and 6 mm for light, moderate, and heavy events, respectively. From the above, it is indicated that light events are extremely important. This fact stresses the importance of the capability of any alternative or complimentary system to the rain gauge measurements in estimating such light events. This desired feature of the satellite-based estimations will further be investigated in this study.
Sherief [26] performed an analysis of the underlying rainfall mechanisms in the study area. He concluded that rainfall can be broadly categorized into three groups. The first group is associated with a convectional mechanism producing rainfall that usually results from excessive heating of the near-surface air during the hot seasons. This type is forming large, thundery clouds that release considerable amounts of water in heavy rainy events. This type is well known in the Saint-Catherine mountain area in the Eastern side of the Gulf of Suez. The second group embraces frontal rainfall and mostly affects the coastal areas, causing intense rainy events with a shorter duration. This type is typical for the area from El-Tor to Sharm El-Sheikh. The third mechanism is orographic, generating significant thundery events, especially in the Eastern part of the Gulf of Suez, whereas the effect of rain shadow renders the lee side mostly dry.
The reader may refer to the Supplementary Material accompanying this paper and which includes a short discussion on the synoptic evolution for each case study, together with animations of sequences of the respective surface synoptic analyses, analyses at 500 hPa, and satellite images.
In the following information, a statistical analysis is performed between different satellite-based data (IMERG and TMPA) on one hand, and between the in-situ rain gauge measurements and the satellite-based data, on the other hand. The statistical metrics used are given in the Appendix A.
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. TMPA and IMERG
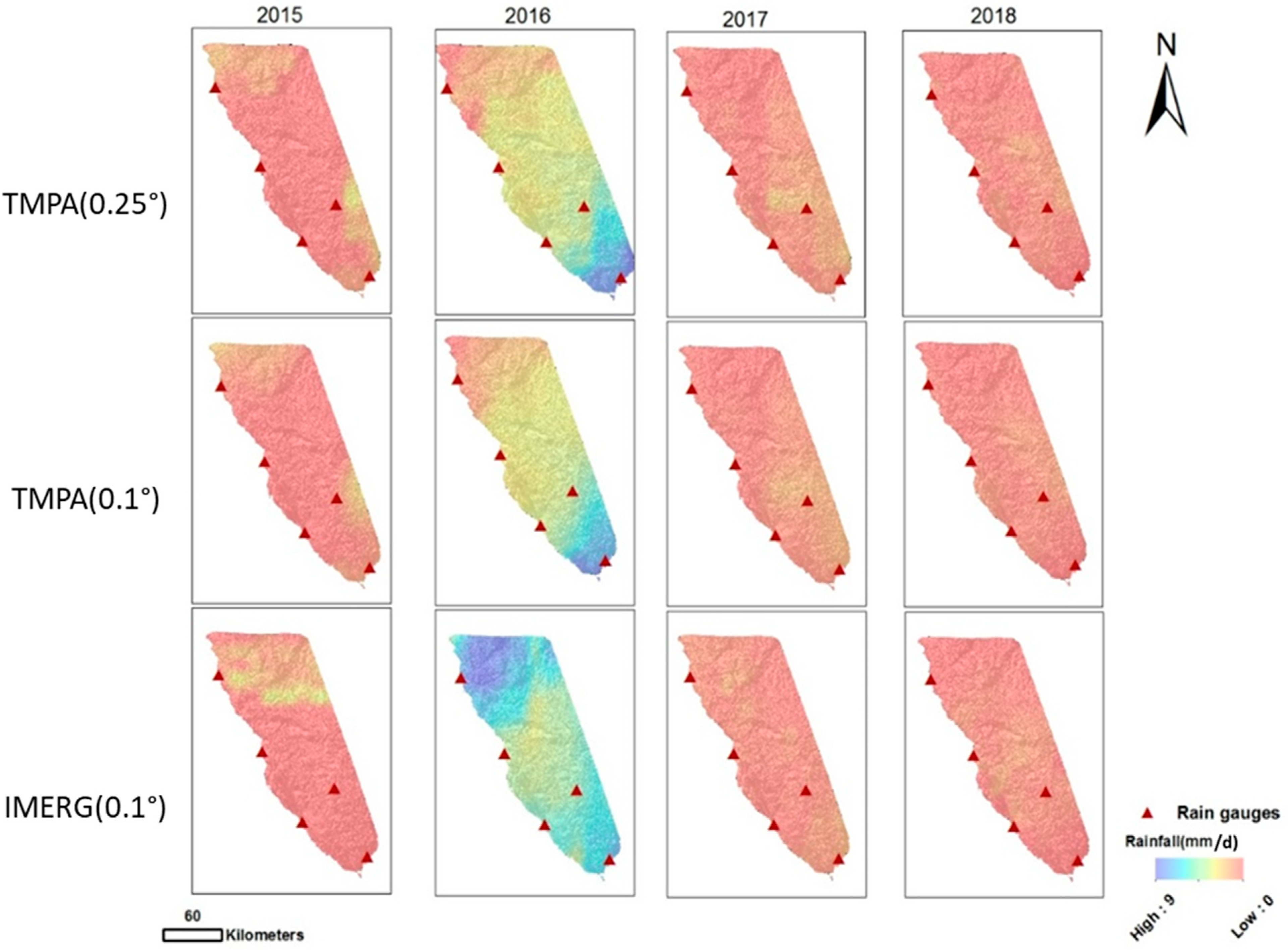
The separate accumulation of the TMPA (180-min temporal resolution and both 0.25° and 0.1° spatial resolutions) and IMERG (30-min temporal resolution and 0.1° spatial resolution) were used to generate the daily precipitation maps for each of the selected rainfall events shown in Figure 2. These spatial distributions illustrate the similarities and differences between the three resolution-based datasets. TRMM (0.25° and 0.1°) display very similar distributions. However, noticeable changes are noted between TMPA and IMERG, especially in the heavy-intensity 2016 event. In the following information, a comparison between the 0.1° resolution TMPA and IMERG data is performed and the results are shown in Table 2.
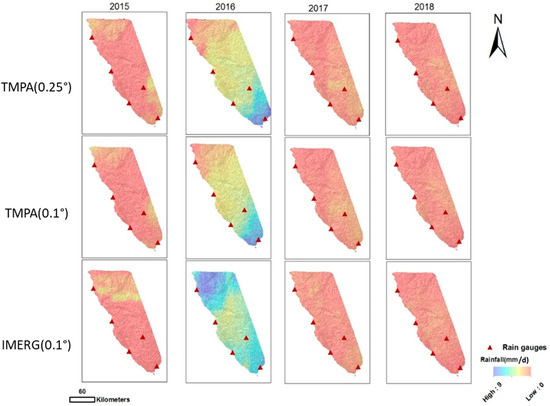
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of rainfall over the area for each of the four events studied using TMPA and IMERG accumulated scenes (mm/d).

Table 2.
Results of the statistical metrics for comparing TMPA and IMERG data over the highland and lowland regions at successive times of 0 h, 3 h, 6 h, 9 h, 12 h, and 24 h from the start of the rainfall event: (a) the Wilcoxon signed-rank tests (pw, values pw < 0.05 are denoted as D, indicating a significant difference between the two sets, otherwise they are denoted as ND (No Difference), (b) the Spearman correlation coefficient (Rs; negative values indicate a negative correlation), (c) the Spearman p-value range (ps, where VS (Very Strong) denotes very strong evidence for rejecting the null hypothesis [ps < 0.01], S strong evidence [0.01 ≤ ps < 0.05], W weak evidence [0.05 ≤ ps < 0.1], and VW (Very Weak) very weak evidence [ps ≥ 0.1].
The results of the Shapiro-Wilk normality test [61] have revealed that both datasets are non-normally distributed with psw < 0.05, at all times and for both the lowland and highland regions. This test was essential for determining the subsequent statistical analysis to be applied, as elaborated below.
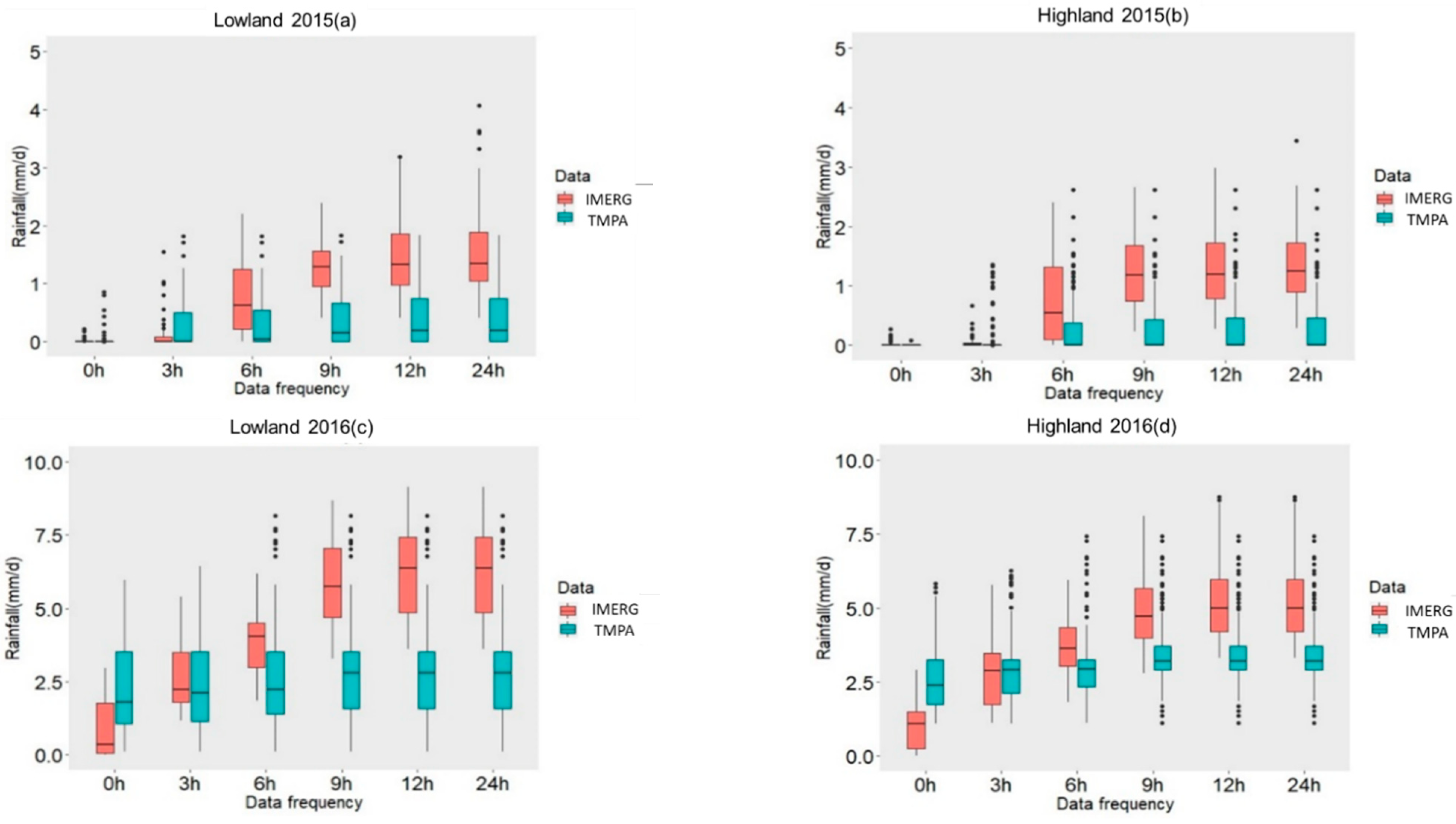
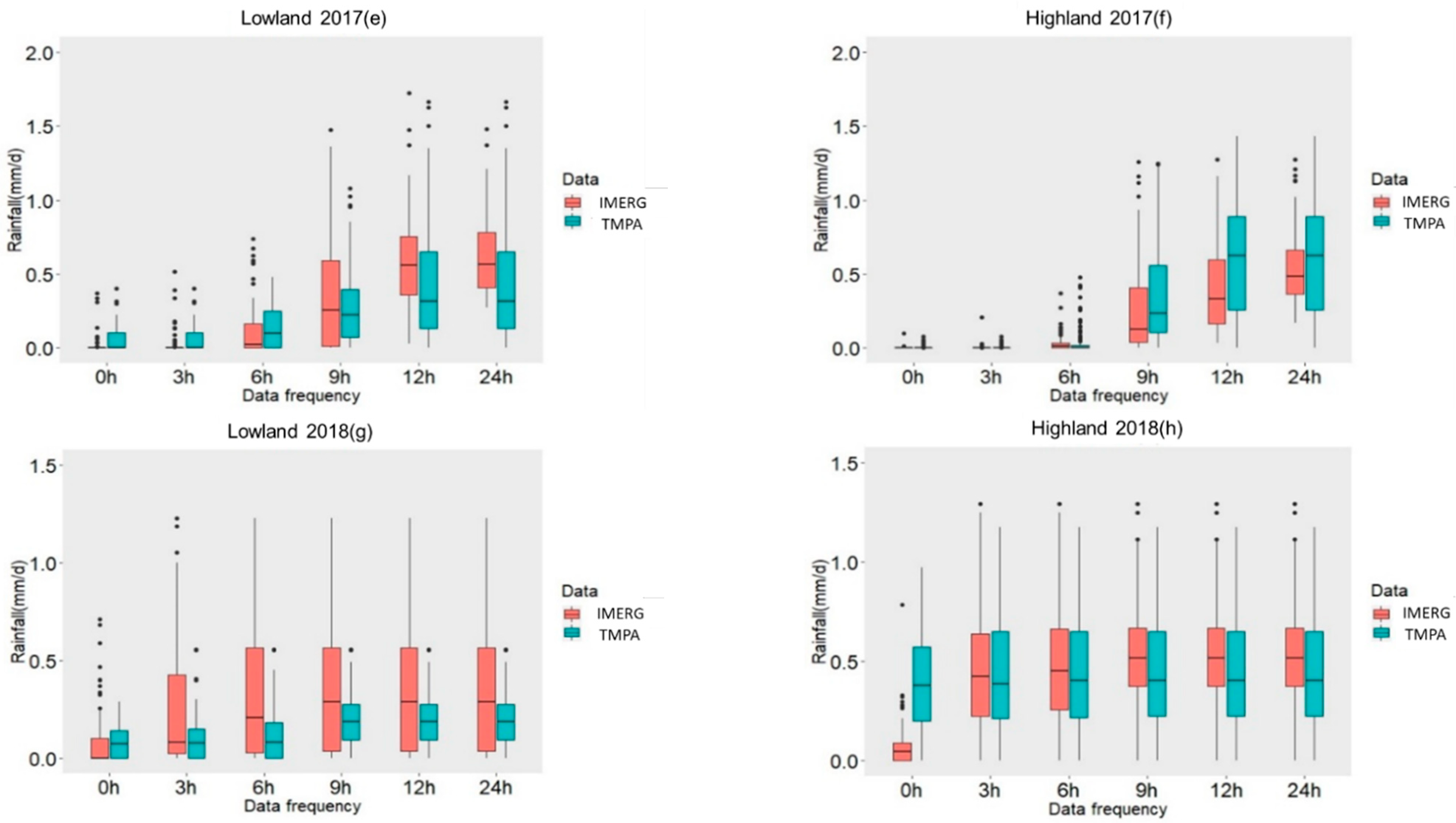
First, given that the data was determined to be non-normally distributed, the Wilcoxon signed-rank test [62] was applied in order to elucidate the similarities and differences between the two sets. For the 2015 lowland event, no significant differences between the two datasets were noted at the start of the event, but significant differences were noted later. Moreover, the two data sets pertaining to the highland region featured significant differences at all time thresholds of the precipitation event. For the 2016 event, a large difference was observed between the two datasets, in both the lowland and highland regions nearly every time. For the 2017 event, no significant differences were noted between the lowland datasets at time thresholds 0 h, 6 h, and 9 h. Significant differences were, however, apparent at the 3 h, 12 h, and 24 h time marks. Regarding the highland region, there were significant differences at 0 h, 6 h, 9 h, and 12 h, and no significant differences at 3 h and 24 h. The 2018 event featured highly significant differences between the two sets collected over the lowland region at 0 h, 6 h, and 9 h. However, no differences were recorded at 3 h, 12 h, and 24 h. The highland region is marked with no significant differences between the two datasets at 3 h and 6 h, but with highly significant differences at 0 h, 9 h, 12 h, and 24 h. Comparing the dataset differences during light-intensity events with those of the moderate-intensity to heavy-intensity events, it is clear that the data associated with light-intensity events generally features reduced variability and higher coherence. Comparing data from the lowland and highland regions, there was also a greater uniformity over the lowland region (Figure 3 and Table 2).
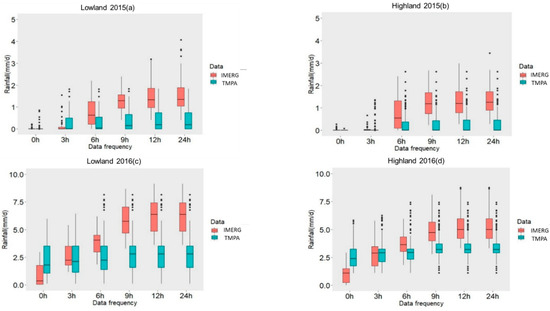
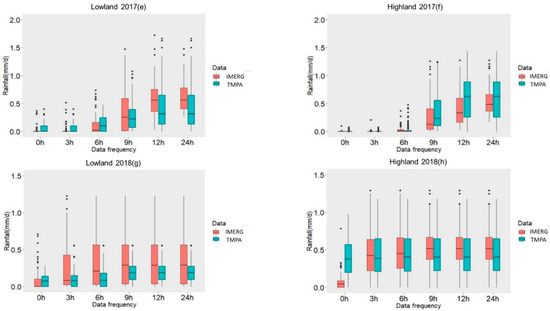
Figure 3.
Boxplots illustrating the differences between the TMPA and the IMERG at 0.1° spatial resolution, for successive time thresholds (0 h, 3 h, 6 h, 9 h, 12 h, and 24 h) and for each event: (a) Lowland 2015, (b) Highland 2015, (c) Lowland 2016, (d) Highland 2016, (e) Lowland 2017, (f) Highland 2017, (g) Lowland 2018, and (h) Highland 2018.
Secondly, the calculations for the Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient (Rs) and its associated p-value (ps) revealed a very strong evidence for a positive correlation between the two 2018 satellite-based datasets at all times and for both the lowland and highland regions. However, for the other events, the situation is not straightforward. At the onset of the 2015 event, very weak evidence that the data are correlated was observed over the lowland region. However, strong or very strong evidence of correlation was found for the subsequent time thresholds. Over the highland region, the 2015 satellite-based datasets exhibit a negative Rs at all times, with a very weak evidence for correlation at onset and at 3 h, but with very strong evidence afterward. For the 2016 event, there is very strong evidence that the two data sets are correlated except for limited times after the onset of the events. Additionally, the correlation was found to be negative for all time thresholds from 9 h onwards, for both the lowland and highland regions. For the 2017 event, the lowland region exhibits evidence for a very strong correlation during the first 6 h of the event, which subsequently changes into a weak or very weak event. The correlation is positive at almost all time points. Regarding the highland region, the situation is generally reversed with very weak evidence during the first 6 h, subsequently changing into very strong events. The correlation coefficient is positive initially, but it turns negative in the later stages of the event.
5.2. Satellite-Based Versus In-Situ Data
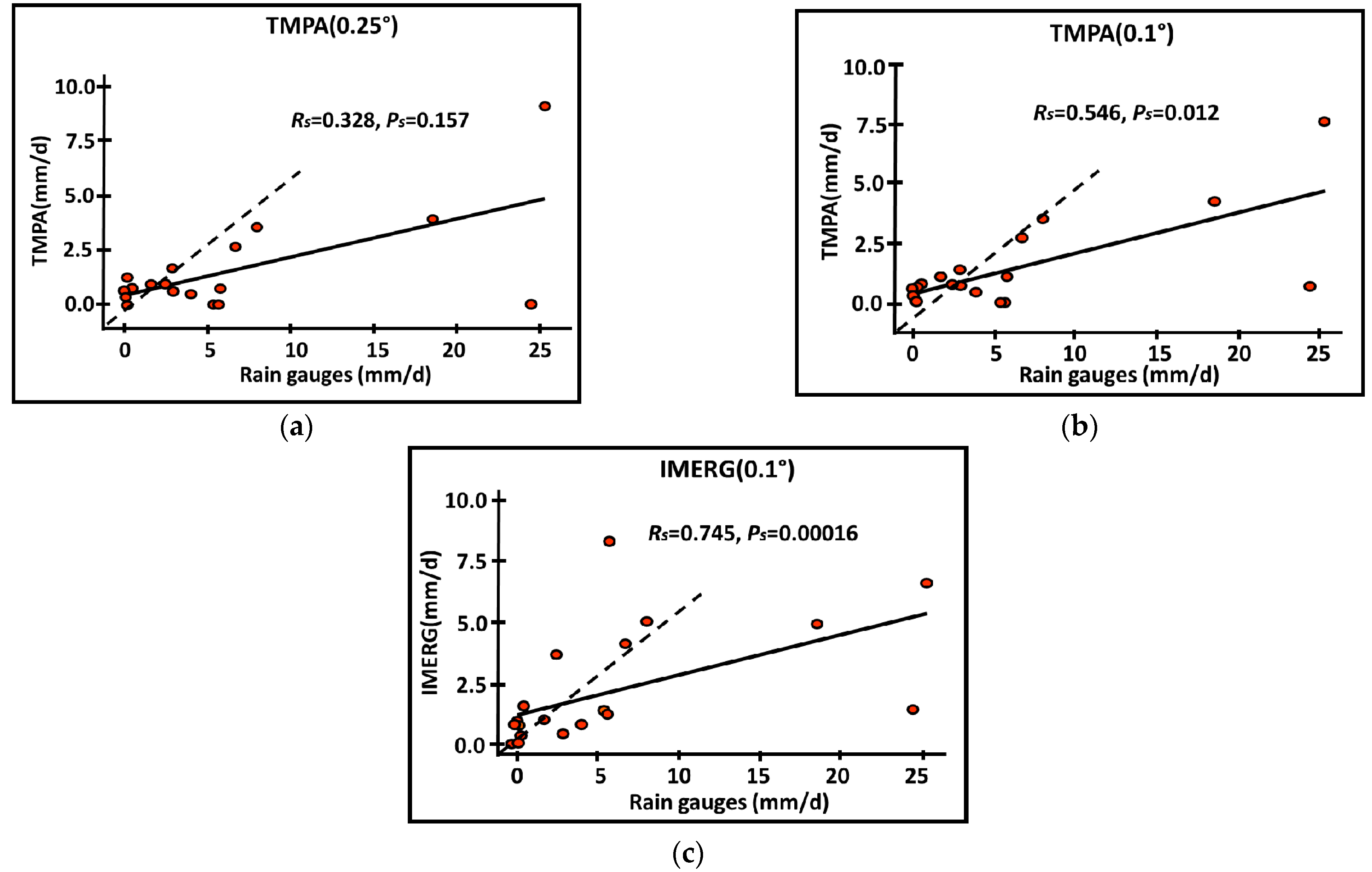
The Spearman correlation coefficient and the respective p-value were also calculated in an attempt to establish the relationship between the in-situ rain gauge records, on the one hand, and the 0.25° resolution TMPA data, on the other hand. In this respect, it was found that Rs = 0.328 and ps = 0.157 (see Figure 4). A similar approach was followed in establishing the relationship between the in-situ rain gauge records and the 0.1° resolution TMPA, where Rs = 0.546 and ps = 0.012. For the relationship between the in-situ rain gauge records and the 0.1° resolution IMERG, Rs = 0.745 and ps = 0.00016. Bearing in mind these results, it can be inferred that IMERG exhibited the strongest evidence for correlation with the rain gauges, whereas the 0.25° resolution TRMM data showed evidence for correlation with the rain gauges was very weak. Moreover, the 0.25° and 0.1° spatial resolution TMPA records revealed an underestimation of precipitation during the moderate and heavy-intensity events, while the light event records were highly coherent with the rain gauge records. IMERG displayed this same coherence with the light events, but both underestimated and overestimated values were recorded during the heavy-intensity events.
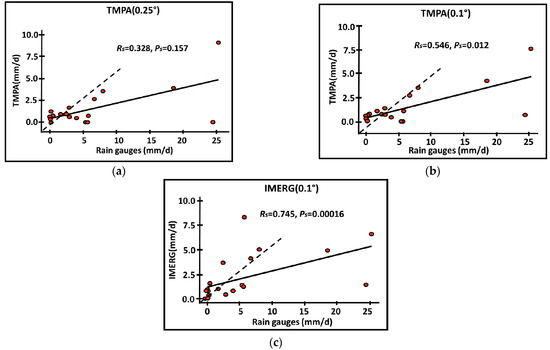
Figure 4.
Spearman correlation (Rs) and p-value (ps) between remote sensing data, at spatial resolutions of (a) TMPA 0.25°, (b) TMPA 0.1°, and (c) IMERG 0.1° and rain gauge records. The solid line represents the fitted linear regression.
The Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and Bias (BIAS) metrics were calculated for each event and are summarized in Table 3. The IMERG dataset displayed the lowest RMSE values for the 2015, 2016, and 2018 precipitation events (10.677, 10.562, and 1.883 mm, respectively). In addition, IMERG exhibited the lowest MAE values for the 2015, 2016, and 2018 events (6.726, 8.076, and 1.367 mm, respectively). The values from the TMPA 0.1° dataset were close to those of the TMPA 0.25° dataset, but with better performance. As expected, the lowest bias is related to the coarsest resolution data set, namely IMERG. Furthermore, in the BIAS test for the 2015 and 2016 events, IMERG exhibited values closest to 0.

Table 3.
Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and Bias (BIAS) for each recorded event with spatial resolutions specified.
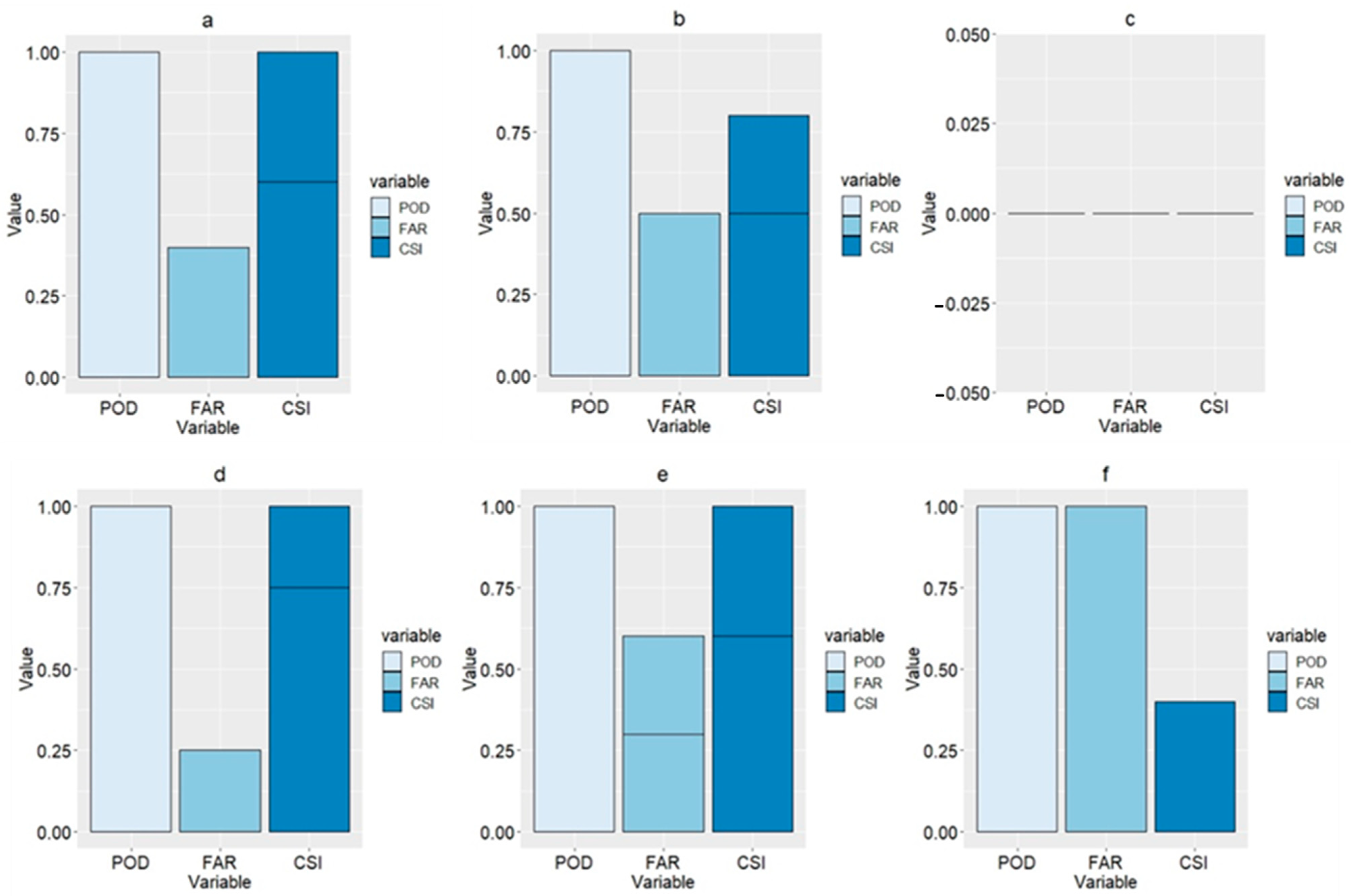
The third group of categorical statistics was applied to the three different precipitation thresholds: 0.1 mm, 1 mm, and 10 mm. The results illustrated the high capability of the TMPA and IMERG analyses in detecting light-intensity events, as the 0.1-mm threshold performed best with both types of remote sensing data, calculating a 1 in the Probability of Detection (POD) and Critical Success Index (CSI) tests (Figure 5a,d), and 0.4 and 0.2 in the False Alarm Test (FAR) test. The second threshold also results in a 1 in the POD test for both data sets, but the CSI calculates at 0.8 and 1, and the FAR test results in 0.4 and 0.5 (Figure 5b,e). The last threshold, 10 mm, produces the worst results. TMPA amounts to a 0 on all the previously mentioned tests. IMERG records a 1, 1, and 0.3 for the POD, FAR, and CSI, respectively (Figure 5c,f). In general, the IMERG data shows better results than that of the TMPA. Both datasets featured higher certainty for light-intensity events.
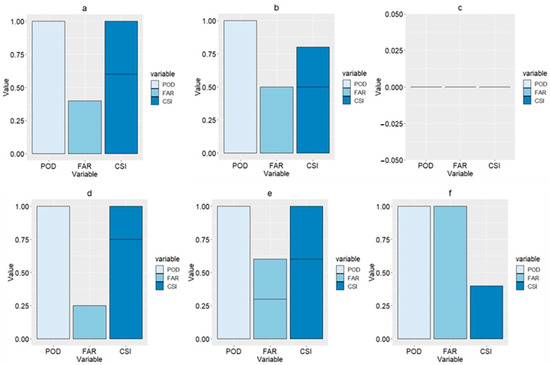
Figure 5.
Bar plots of Probability of Detection (POD), False Alarm Rate (FAR), and Critical Success Index (CSI) results of the TMPA and IMERG at three different thresholds (0.1, 1, and 10) using data from all mentioned events. (a), (b), and (c) represent the thresholds of 0.1, 1, and 10 for the TMPA data, respectively, (d), (e), and (f) represent the thresholds of 0.1, 1, and 10 for the IMERG data.
6. Concluding Remarks
With an increasing spatiotemporal resolution of the satellite-based rainfall datasets, more emphasis is given worldwide in using these sources of rainfall analyses for a wide range of applications. Two such datasets have been utilized in the present study, namely, TMPA and IMERG. These datasets were compared between them and again a local rain gauge network in El-Qaa Plain, Sinai Peninsula. The IMERG dataset now includes TRMM-era data extending back to 2000, rendering this dataset a valuable tool in many hydrological applications. Research in the application of the IMERG database in several sectors that need rainfall records will certainly continue in the years to come and this study is a contribution toward better assessing this valuable data source.
The statistical metrics used demonstrate the low correlation and significant differences between the pixel values of the TMPA and IMERG datasets in the moderate and heavy-intensity 2015 and 2016 events. Datasets from the light-intensity events, namely, 2017 and 2018, were more highly correlated. Additionally, the values recorded over the lowland region were more uniform than those of the highland region, where a greater variation was observed.
When the two satellite-based rainfall datasets were compared to the rain gauge data, it was noted that their performance was best during the light-intensity events, particularly around the event onset (3 h and 6 h). In contrast, poorer performance was noted during intense events and at the later precipitation stages in such events (12 h and 24 h). These findings are in good agreement with the findings by Wu et al. [63] who performed a similar comparative analysis over China. However, the two geographical areas have different climatic characteristics. The same authors found that both satellite-based products overestimate light rain, whereas both underestimate moderate to heavy rainfall. Furthermore, data coherence and uniformity were lower in the highland region (referenced to the Saint-Catherine station) when compared to the lowland region data (derived from the Ras-Sudr, Abu-Rudies, El-Tor, and Sharm El-Sheikh rain gauge stations). TMPA and IMERG were compared to the limited rain gauge records, using various statistical metrics to evaluate their effectiveness in replicating in-situ observations. Performance varied, with the IMERG data demonstrating the best performance, producing the lowest RMSE, BIAS, and MAE values. This was followed by the 0.1° resolution TMPA, and, lastly, the 0.25° resolution TMPA data, with the latter exhibiting the weakest performance.
In the present study, categorical statistics have indicated high performance by both the TMPA and IMERG, during the light-intensity events. However, a low certainty was observed for the high-intensity events. Overall, the IMERG datasets performed better than the TMPA in all thresholds. The findings of this study could be used to support the postulation on the superior performance of IMERG over TMPA in arid and semi-arid areas, but this cannot be generalized. Several comparative studies confirm the superiority of the IMERG product over the TRMM-era one. For example, Kim et al. [17] compared the performance of TRMM (3B42v7) and GPM (IMERG) over Far-East Asia during the pre-monsoon and monsoon seasons. Their results showed that GPM-3IMERGHH performed better than TRMM3B42V7. However, both satellite-based products had several drawbacks with regard to topographical factors, especially for orographic regions. Moreover, they found that GPM-3IMERGHH is a useful next-generation rainfall product not only for acquiring ancillary datasets at ungauged locations (especially in a complex terrain), but also for enhancing observations of both light precipitation and convective rainfall, which has been a limitation of TRMM 3B42 V7. In addition, Chen et al. [64] compared the performance of the TRMM 3B42V7 and IMERG over the Huaihe River basin in China and they confirmed that the IMERG product had better performance for detecting precipitation and provided more accurate precipitation estimates than TRMM 3B42 v7 data due to finer spatial and temporal resolutions. They underscored the need to assess the potential of the IMERG product in hydrological applications in a range of different environments. However, in contrast to the above two examples, the comparative study by Yuan et al. [65] in the Chindwin River basin, Myanmar, did not find any superiority of one of the satellite-derived precipitation products over the other. The authors underscore the importance of IMERG algorithm refinement in order to improve the accuracy of IMERG products over the country, where plenty of rainfall data are urgently needed for hydrological utilities, as indicated in the present study. For a more comprehensive survey of the literature on IMERG and TMPA comparisons, the reader is referred to Retalis et al. [66].
Despite the superior performance of the IMERG dataset in the present study, gaps in data persisted over mountainous regions as well as heavy-intensity precipitation events, indicating that it would not be used as a substitute for rain gauge data. However, it can be used as a promising alternative for rain gauge records during the relatively frequent light-intensity events until a new rain gauge network is in place, optimized, and implemented. Even when such an upgrade network is put into operation, IMERG can continue to supplement the in-situ data, either for monitoring purposes or for filling-in gaps in the network.
The results of this study show that any alternative or complementary rainfall estimating system (i.e., satellite-based) adopted in arid and semi-arid environments receive most of their precipitation during cases with small amounts of rainfall. The skill of such a system to estimate precipitation adequately during such events is very important.
Due to the limited amount of in-situ data, the effect of elevation on the estimation of rainfall from satellite-derived products cannot be done in a satisfactory way in the present study. This is a very challenging viewpoint that has been pursued in other studies with more ground-based data [58,66]. This challenging viewpoint will be part of future work to investigate this aspect as well but following a substantial upgrade of the rain gauge network over the area.
The value of the current study stems, on the one hand, from the impact it will have on the test site. The installation of the upgraded rain gauge network proposed by the authors (which will be presented in a companion paper) is a direct outcome of the present study. The upgraded network will drastically change the future of this arid area in many respects. On the other hand, it is clear from the present study that the available ad hoc data sources are limited and that there are also limitations in the resources of acquiring information about the rainy events in the test site, associated with the inadequate use of the corresponding remote sensing data (e.g., an extensive verification of the satellite-based precipitation estimations was not feasible). However, many of these limitations will be removed when the proposed network is put in operation. In addition, developers of IMERG algorithms will then have access to more on-the-ground information after the installation step is completed.
The inconsistencies between the satellite-derived products and the in-situ measurements underline the necessity for improving future versions of IMERG algorithms, by taking into account variations in meteorology and geography, especially in semi-arid areas of the globe. The need is for more efficient physically-based algorithms, based on a comparison with surface observations across all major precipitating synoptic conditions.
Most of the arid regions feature a very limited number of rain gauges, thus, reducing the reliability of the results produced. The study for the upgrade of the existing network, which is under preparation will put forward a series of steps for overcoming the issue of data scarcity. Once resolved, this could then promote the greatly needed hydrological studies on topics, such as the spatiotemporal distribution of rainfall, the mitigation of flash floods hazards, and the minimization of soil erosion.
The study site contains only five rain gauges. This small number of in-situ instrumentation is an obstacle to the optimum understanding of the rainfall frequency and rain rates as well as the possible recharge options. Therefore, the second part of the study will suggest the most suitable sites for 31 new rain gauges. These new stations will provide the most efficient and appropriate coverage.
In the upcoming study for a proposed, upgraded network of stations, a Digital Elevation Model and IMERG data will be used to identify the most suitable locations. These two datasets will be clustered using a k-means clustering to produce an elbow graph whose elbow-shaped region offers several possible options for the number of optimum clusters at the test site. Three different cluster sizes (namely, 3, 6, and 9) will be used to calculate the possible centroids for each size. These centroids will be tested using the Empirical Cumulative Distribution Function (ECDF), once the sum of the IMERG scenes, the scene limits, and the elevation map limits are determined. At this stage, the optimal size established is nine. Nine centroids are, therefore, taken, along with the existing five gauges, as a basis for standard error kriging. This allows a gradual minimization of the error via looping. The proposed rain gauge sites will be tested with an ECDF. The complete spectrum of rainfall and elevation is efficiently covered by 31 new rain gauge locations, and the five existing gauges.
Lastly, the present study lays the foundations for further meteorological and hydrological studies at the test site. The results statistically affirm the superior performance of the IMERG dataset compared to the TMPA data typically used at the test site. Therefore, IMERG data is recommended for the optimization of a new, expanded rain gauge network with additional gauges steered by the local topography of the site. Taken together, this can promote the transformation of the study site from a dormant to a commercially active state.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/13/4/588/s1. Document S1: Synoptic Discussions of case studies.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the paper, as follows. Conceptualization: M.M. and P.D. Methodology, investigation and analysis: M.M. Resources: M.M. and Y.S. Writing, review, and editing: M.M. and S.M. Visualization: M.M., P.D., T.S., E.B., Y.S., and S.M. Supervision: P.D. and T.S. Project administration: P.D. and T.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Helmholtz Center for Environmental Research in Leipzig, Germany, the Tübingen University, Germany, and the Suez Canal University, Egypt. The authors wish to acknowledge that the provision of the TMPA and IMERG data by the NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center’s Mesoscale Atmospheric Processes Laboratory and Precipitation Processing Center, which developed and computed them as a contribution to TRMM and GPM, respectively. Silas Michaelides was supported by the EXCELSIOR project (www.excelsior2020.eu (accessed on 4 February 2021)) that has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme, under grant agreement no. 857510, as well as matching co-funding by the Government of the Republic of Cyprus through the Directorate General for the European Programmes, Coordination, and Development. The authors wish to express their gratitude to the anonymous reviewers whose insightful and constructive comments and suggestions have led to improvements of the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Statistical Metrics
The first set of statistical tests was performed with the purpose of evaluating the differences, coherence, and correlation between the TMPA data and the IMERG data, both with 0.1° spatial resolution. These tests include the Shapiro-Wilk normality test [61]. This test rejects the hypothesis of normality when the respective p-value (denoted by psw) is less or equal to 0.05 (i.e., psw ≤ 0.05). The Wilcoxon signed-ranked test [62] compares two dependent samples to determine if their populations have the same distribution by comparing their medians. The two samples show no differences and considerable dependency when the respective p-value (denoted by pw) is greater than 0.05 (i.e., pw > 0.05). The Spearman correlation coefficient (denoted by Rs) determines the correspondence between two variables. If the two samples exhibit a perfect positive correlation, then Rs = 1. For a perfect negative correlation, Rs = −1 and, for no correlation, Rs = 0. The null hypothesis (H0) that any correlation between the two variables due to chance is tested by calculating the Spearman test p-value (denoted by ps). This test examines whether the rankings of each data set are similar (the relationship does not have to be linear). In this study, for ps < 0.01, H0 is very strongly rejected, for 0.01 ≤ ps < 0.05, H0 is strongly rejected, for 0.05 ≤ ps < 0.1, the evidence for rejecting H0 is weak and, for ps ≥ 0.1, the evidence for rejecting H0 is very weak.
The second group of verification statistics was selected with the purpose of identifying the remote sensing product with higher compatibility to the in-situ gauges. A Spearman correlation coefficient test was applied between the rain gauge data and the TMPA (0.25°), TMPA (0.1°), and IMERG (0.1°) data, which were all collected between 2015 and 2018. This was done to determine the correlational strength between the remote sensing data and the benchmark. The verification statistics used here are the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE, Equation (A1)) and the Mean Absolute Error (MAE, Equation (A2)). A BIAS test (Equation(A3)) was also used [17,54].
In the above relationships, Psat refers to satellite precipitation records, Pgau represents the records derived from the in-situ rain gauges, and n is the number of samples.
A third group of categorical statistics was used to verify the potential of the satellite products in detecting rainfall at various rainfall thresholds (i.e., 0.1, 1, and 10 mm). These are the Probability of Detection (POD, Equation (A4)), the False Alarm Ratio (FAR, Equation (A5)), and the Critical Success Index (CSI, Equation (A6)), calculated for each single event [17,54].
Hits are defined as rain detected by both gauges and satellites and misses as rain observed by gauges but not detected by a satellite. False alarms were described as rain detected by satellites but not observed by ground rain gauges [54].
References
- Ebert, E.E.; Janowiak, J.E.; Kidd, C. Comparison of near-real-time precipitation estimates from satellite observations and numerical models. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Hong, Y.; Ren, L.-L.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Khan, S.I. Assessment of evolving TRMM-based multisatellite real-time precipitation estimation methods and their impacts on hydrologic prediction in a high latitude basin. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2012, 117, D09108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, A.; Behrangi, A.; Hong, Y.; Ndayisaba, F.; Hu, J.; Stepanian, P.M. Early assessment of integrated multi-satellite retrievals for global precipitation measurement over China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 176–177, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.Q.; Ma, Y.Z.; Long, D.; Zhong, L.; Hong, Y. Evaluation of GPM Day-1 IMERG and TMPA version-7 legacy products over mainland China at multiple spatiotemporal scales. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C.; Levizzani, V. Status of satellite precipitation retrievals. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C.; Bauer, P.; Turk, J.; Huffman, G.J.; Joyce, R.; Hsu, K.-L.; Braithwaite, D. Intercomparison of high resolution precipitation products over northwest Europe. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The Global Precipitation Measurement Mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, Z.; Song, Y.; Duan, Z.; Mo, K.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q. Performance of multiple satellite precipitation estimates over a typical arid mountainous area of China: Spatiotemporal patterns and extremes. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkadir, A.; Wuddivira, M.N.; Abdu, N.; Mudiare, O.J. Use of Horton infiltration model in estimating infiltration characteristics of an alfisol in the Northern Guinea Savanna of Nigeria. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2011, A1, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asoka, A.; Gleeson, T.; Wada, Y.; Mishra, V. Relative contribution of monsoon precipitation and pumping to changes in groundwater storage in India. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiador, F.J.; Turk, F.J.; Petersen, W.; Hou, A.Y.; García-Ortega, E.; Machado, L.A.; Angelis, C.F.; Salio, P.; Kidd, C.; Huffman, G.J.; et al. Global precipitation measurement: Methods, datasets and applications. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104, 70–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.Y.; Yang, Z.-L. Assessing a land surface model’s improvement with GRACE estimates. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.Y.; Yang, Z.-L. Effects of frozen soil on snowmelt runoff and soil water storage at a continental scale. J. Hydrometeorol. 2006, 7, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiros, G.; Shetty, A.; Nandagiri, L. Analysis of variability and trends in rainfall over northern Ethiopia. Arabian J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.J.; Bienes, R.; Jiménez, L.; Pérez-Rodríguez, R. Effect of vegetal cover on runoff and soil erosion under light intensity events. Rainfall simulation over USLE plots. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 378, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stomph, T.J.; De Ridder, N.; Van de Giesen, N.C. A flume design for the study of slope length effects on runoff. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms. J. Br. Geomorphol. Res. Group 2001, 26, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Park, J.; Baik, J.; Choi, M. Evaluation of topographical and seasonal feature using GPM IMERG and TRMM 3B42 over Far-East Asia. Atmos. Res. 2017, 187, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneis, D.; Chatterjee, C.; Singh, R. Evaluation of TRMM rainfall estimates over a large Indian river basin (Mahanadi). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 11, 1169–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Miao, C.; Duan, Q.; Ashouri, H.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.L. A review of global precipitation data sets: Data sources, estimation, and intercomparisons. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 79–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.K.; Prakash, N.R. Design of an improvised tipping bucket rain gauge for measurement of rain and snow precipitation. Int. J. Instrum. Technol. 2011, 1, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poméon, T.; Diekkrüger, B.; Kumar, R. Computationally efficient multivariate calibration and validation of a grid-based hydrologic model in sparsely gauged west African river basins. Water 2018, 10, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Bisai, D.; Barman, N.K. Analysis of change point in surface temperature time series using cumulative sum chart and bootstrapping for Asansol weather observation station, West Bengal, India. Am. J. Clim. Chang. 2014, 3, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Refai, A.A. Water Resources of Southern Sinai, Egypt. (Geomorphological and Hydrogeological Studies). Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Science, University of Cairo, Giza, Egypt, 1992; p. 357. [Google Scholar]
- El-Fakharany, M.A. Geophysical and hydrogeochemical investigations of the Quaternary aquifer at the middle part of El Qaa Plain SW Sinai, Egypt. Egypt. J. Geol. 2016, 47, 1003–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Wahid, A.; Madden, M.; Khalaf, F.; Fathy, I. Geospatial analysis for the determination of hydro-morphological characteristics and assessment of flash flood potentiality in Arid Coastal Plains: A case in Southwestern Sinai, Egypt. Earth Sci. Res. J. 2016, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherief, Y. Flash Floods and Their Effects on the Development in El-Qaá Plain Area in South Sinai, Egypt, a Study in Applied Geomorphology Using GIS and Remote Sensing. Ph.D. Thesis, Mainz University, Mainz, Germany, 2008. Available online: https://openscience.ub.uni-mainz.de/handle/20.500.12030/2211 (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- Lonfat, M. Tropical Cyclone Rainfall: An Observational and Numerical Study of the Structure and Governing Physical Processes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Miami, ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, Miami, FL, USA, 2004; p. 135. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, K.M.; Zhou, Y.P.; Wu, H.T. Have tropical cyclones been feeding more extreme rainfall? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchok, T.; Rogers, R.; Tuleya, R. Validation schemes for tropical cyclone quantitative precipitation forecasts: Evaluation of operational models for US landfalling cases. Weather Forecast. 2007, 22, 726–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuleya, R.E.; De Maria, M.; Kuligowski, R.J. Evaluation of GFDL and simple statistical model rainfall forecasts for US landfalling tropical storms. Weather Forecast. 2007, 22, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Kidd, C.; Nelkin, E.J.; Sorooshian, S.; Stocker, E.F.; Tan, J.; et al. Integrated multi-satellite retrievals for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission (IMERG). In Satellite Precipitation Measurement; Levizzani, V., Kidd, C., Kirschbaum, D., Kummerow, C., Nakamura, K., Turk, F.J., Eds.; Springer Nature: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 343–354. ISBN1 978-3-030-24567-2. ISBN2 978-3-030-24568-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.R.; Li, X. Evaluation of IMERG and TRMM 3B43 monthly precipitation products over mainland China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Yang, W.; Luan, Y.; Du, J.; Lin, A.; Zhao, L. Evaluation of the TRMM 3B42 and GPM IMERG products for extreme precipitation analysis over China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 223, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Qiao, X.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of GPM IMERG V05B and TRMM 3B42V7 Precipitation Products over High Mountainous Tributaries in Lhasa with Dense Rain Gauges. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Chen, X.; Chang, J. Evaluation of the GPM IMERG v5 and TRMM 3B42 v7 Precipitation Products in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Water 2019, 11, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, B.; Páez-Bimos, S.; Horna, N.; Buytaert, W.; Ochoa-Tocachi, B.; Lavado-Casimiro, W.; Willems, B. Comparative ground validation of IMERG and TMPA at variable spatiotemporal scales in the Tropical Andes. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 2469–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Duan, Z. Assessment of GPM and TRMM precipitation products over Singapore. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Tian, F.; Yang, L.; Hu, H.; Lu, H.; Hou, A. Ground validation of GPM IMERG and TRMM 3B42V7 rainfall products over southern Tibetan Plateau based on a high-density rain gauge network. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2017, 122, 910–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wand, D.; Qin, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, J. Assessment of the GPM and TRMM precipitation products using the rain gauge network over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Meteorol. Res. 2018, 32, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.N.; Ding, Y.; Shangguan, D.; Ahmad, I.; Ijaz, M.W.; Farid, H.U.; Yagoub, Y.E.; Zaman, M.; Adnan, M. Performance evaluation of latest integrated multi-satellite retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement (IMERG) over the northern highlands of Pakistan. Atmos. Res. 2018, 205, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Santo, H. Comparison of GPM IMERG, TMPA 3B42 and PERSIANN-CDR satellite precipitation products over Malaysia. Atmos. Res. 2018, 202, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.N.; Ahmad, I.; Ding, Y.; Shangguan, D.; Zaman, M.; Ijaz, M.W.; Sarwar, K.; Han, H.; Yang, M. Assessment of IMERG-V06 precipitation product over different hydro-climatic regimes in the Tianshan mountains, North-Western China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino-Ángel, S.; Anaya-Acevedo, J.A.; Botero, B.A. Evaluation of 3B42V7 and IMERG daily-precipitation products for a very high-precipitation region in northwestern South America. Atmos. Res. 2019, 217, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tian, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Duan, Z. Hydrologic evaluation of TRMM and GPM IMERG satellite-based precipitation in a humid basin of China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.; Sauck, W.; Soliman, F. Gravity, magnetic, and geoelectric survey on El-Qaa plain, southwest Sinai, Egypt. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference Geology of Sinai for Development, Ismailia, Egypt, 3 December 2007; pp. 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sayed, M.A.A.; El-Fakharany, M.A.; Hamed, M.F. Integrated geophysical and hydrogeological studies on the Quaternary aquifer at the middle part of El Qaa plain, SW Sinai, Egypt. Egypt. Geophys. Soc. J. 2004, 2, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Sauck, W.; Kehew, A.; Soliman, F.; Smart, L.; Mesbah, M. Basin definition with gravity and resistivity (VES) in the central El Qaa Plain, Sinai, Egypt. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2005, 7. Available online: https://www.cosis.net/abstracts/EGU05/00066/EGU05-J-00066.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- Ahmed, M.; Sauck, W.; Sultan, M.; Yan, E.; Soliman, F.; Rashed, M. Geophysical constraints on the hydrogeologic and structural settings of the Gulf of Suez rift-related basins: Case study from the El Qaa Plain, Sinai, Egypt. Surv. Geophys. 2014, 35, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodeif, K.; Gorski, J. Protection of fresh ground water in El-Qaa Quaternary aquifer, Sinai, Egypt. In New Approaches Characterizing Groundwater Flow; Seiler, K.-P., Wohnlich, S., Eds.; Swets & Zeitlinger: Lisse, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 71–76. ISBN 90-2651-848-X. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.C.; Yeo, I.Y.; Alsdorf, D.; Bates, P.; Boy, J.P.; Kim, H.; Oki, T.; Rodell, M. Movement of Amazon surface water from time-variable satellite gravity measurements and implications for water cycle parameters in land surface models. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2010, 11, Q09007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, R. The Geology of Egypt; Elsevier Publishing, Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Prat, O.P.; Nelson, B.R. Evaluation of precipitation estimates over CONUS derived from satellite, radar, and rain gauge datasets (2002–2012). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 11, 11489–11531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Sheng, S.; Mansaray, L.R.; Liu, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, X. A new downscaling-integration framework for high-resolution monthly precipitation estimates: Combining rain gauge observations, satellite-derived precipitation data and geographical ancillary data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerow, C.; Barnes, W.; Kozu, T.; Shiue, J.; Simpson, J. The tropical rainfall measuring mission (TRMM) sensor package. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 1998, 15, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensterseifer, C.; Allasia, D.G.; Paz, A.R. Assessment of the TRMM 3B42 precipitation product in southern Brazil. J. Am. Water Resourc. Assoc. 2016, 52, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Bao, A.; Ndayisaba, F.; Liu, T.; Kurban, A.; De Maeyer, P. Systematical evaluation of satellite precipitation estimates over central Asia using an improved error-component procedure. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2017, 122, 10906–10927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retalis, A.; Katsanos, D.; Tymvios, F.; Michaelides, S. Validation of the first years of GPM operation over Cyprus. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skofronick-Jackson, G.; Petersen, W.A.; Berg, W.; Kidd, C.; Stocker, E.F.; Kirschbaum, D.B.; Kakar, R.; Braun, S.A.; Huffman, G.J.; Iguchi, T.; et al. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission for science and society. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 1679–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skofronick-Jackson, G.; Kirschbaum, D.; Petersen, W.; Huffman, G.; Kidd, C.; Stocker, E.; Kakar, R. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission’s scientific achievements and societal contributions: Reviewing four years of advanced rain and snow observations. Q. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcoxon, F. Individual comparisons by ranking methods. Biom. Bull. 1945, 1, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, S. Comparison of TMPA-3B42RT legacy product and the equivalent IMERG products over mainland China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, Q.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Mo, K.; Li, Z.; Tang, G. Multiscale Comparative Evaluation of the GPM IMERG v5 and TRMM 3B42 v7 Precipitation Products from 2015 to 2017 over a Climate Transition Area of China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.; Win, K.W.W.; Ren, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Assessment of GPM and TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Products in Streamflow Simulations in a Data-Sparse Mountainous Watershed in Myanmar. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retalis, A.; Katsanos, D.; Tymvios, T.; Michaelides, S. Comparison of GPM IMERG and TRMM 3B43 Products over Cyprus. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).