An Analytical Method for Dynamic Wave-Related Errors of Interferometric SAR Ocean Altimetry under Multiple Sea States
Abstract
1. Introduction
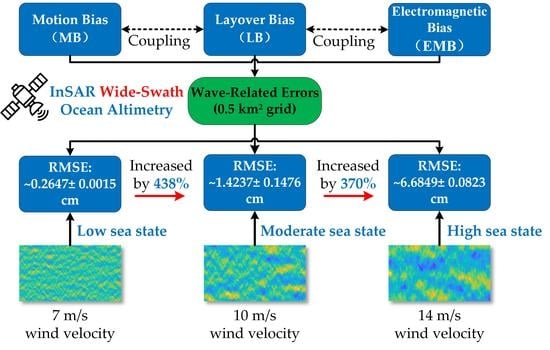
- The mechanisms of the dynamic wave-related errors for InSAR ocean altimetry are analyzed, and a detailed numerical model is derived. Three key error sources are considered, MB, EMB, and LB, which means that the analysis is comprehensive. This is conducive to characterizing the impact of ocean waves on the SSH retrieved by InSAR.
- Based on the wind-generated wave spectrum and three-scale second-order EM backscattering model, the dynamic wave-related errors of InSAR altimetry can be characterized for different radar parameters under various sea states, and this can be used for the error budget of InSAR altimetry under multiple scenarios.
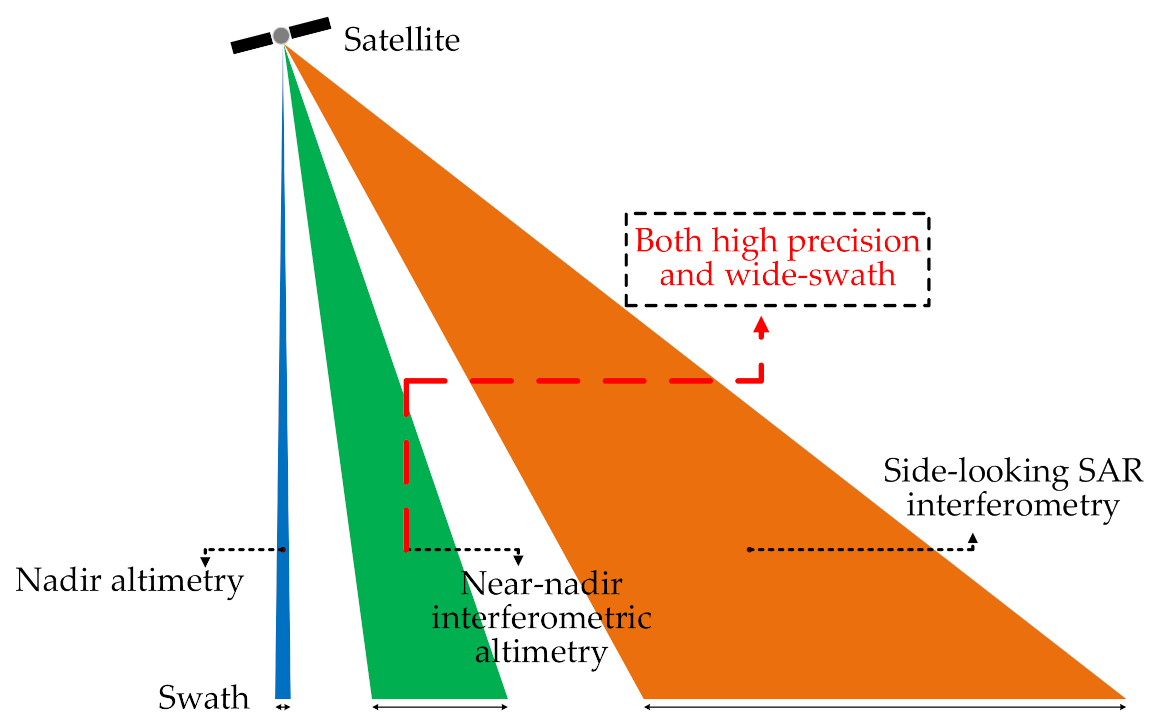
- The RMSEs of three radar frequencies, X-band, Ku-band, and Ka-band, under three kinds of sea states are given; the results show that the frequencies have little impact on the dynamic wave-related errors, and the error compensation is needed for moderate and higher sea states for centimetric accuracy requirement. This can provide relevant suggestions for application scenarios and error compensation methods for future InSAR ocean altimetry.
2. Materials and Methods
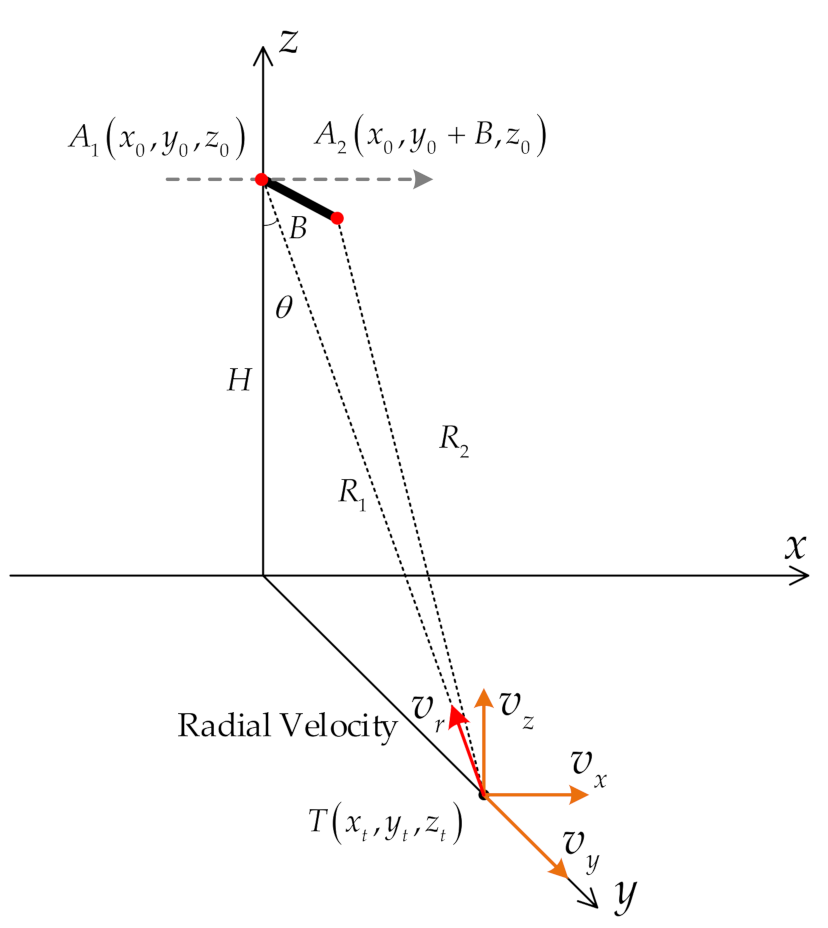
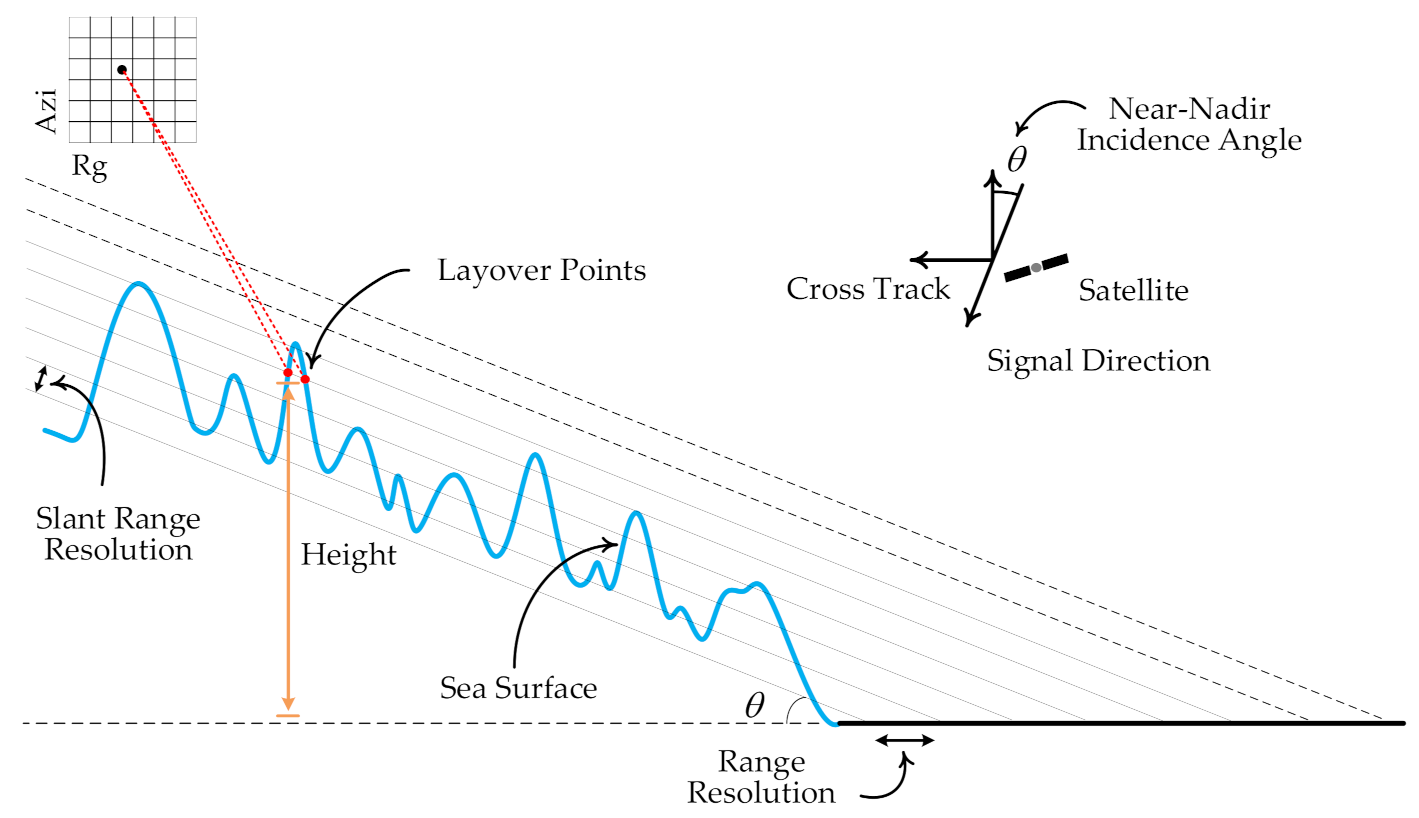
2.1. Principle of InSAR Altimetry
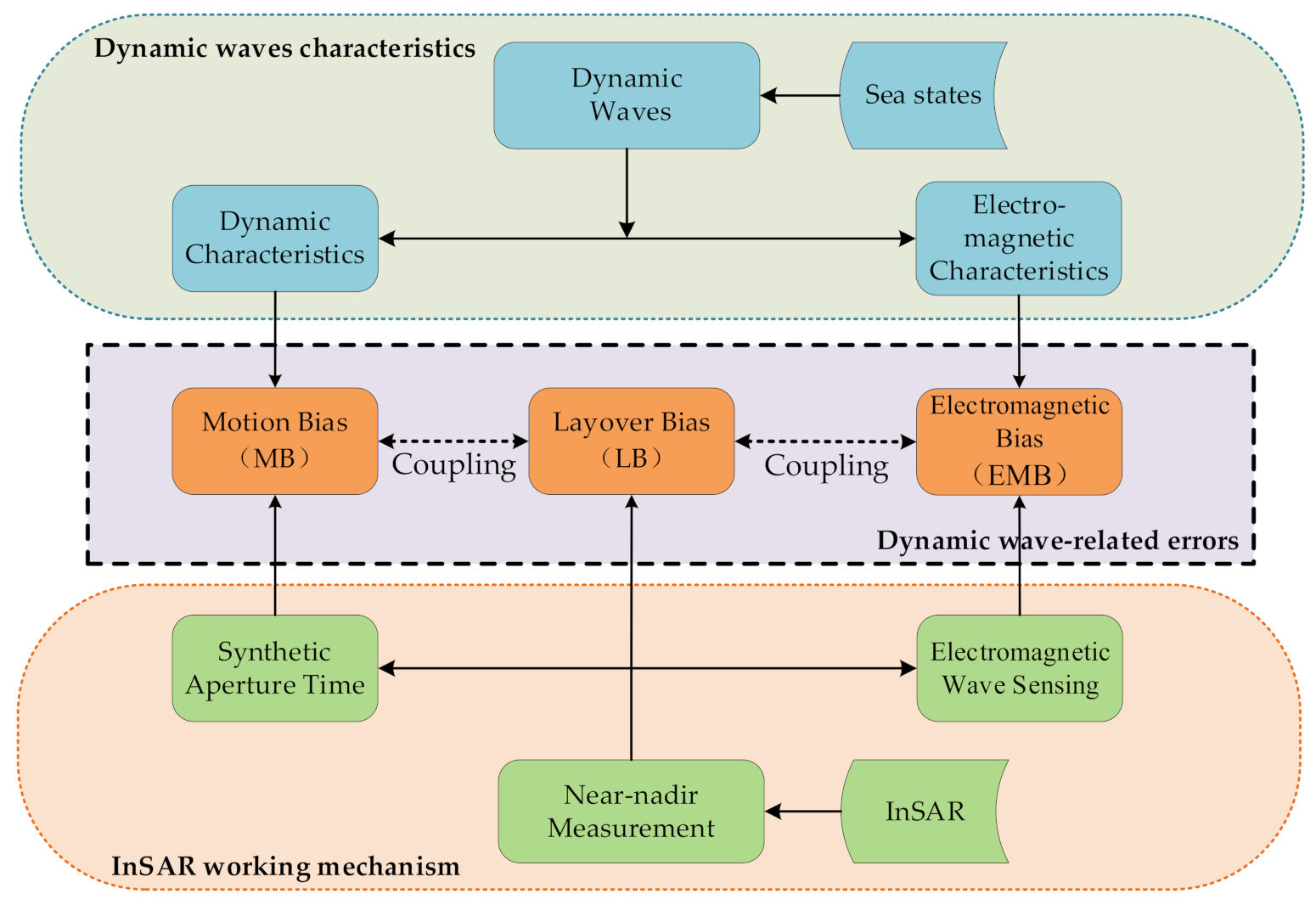
2.2. Mechanisms of the Dynamic Wave-Related Errors
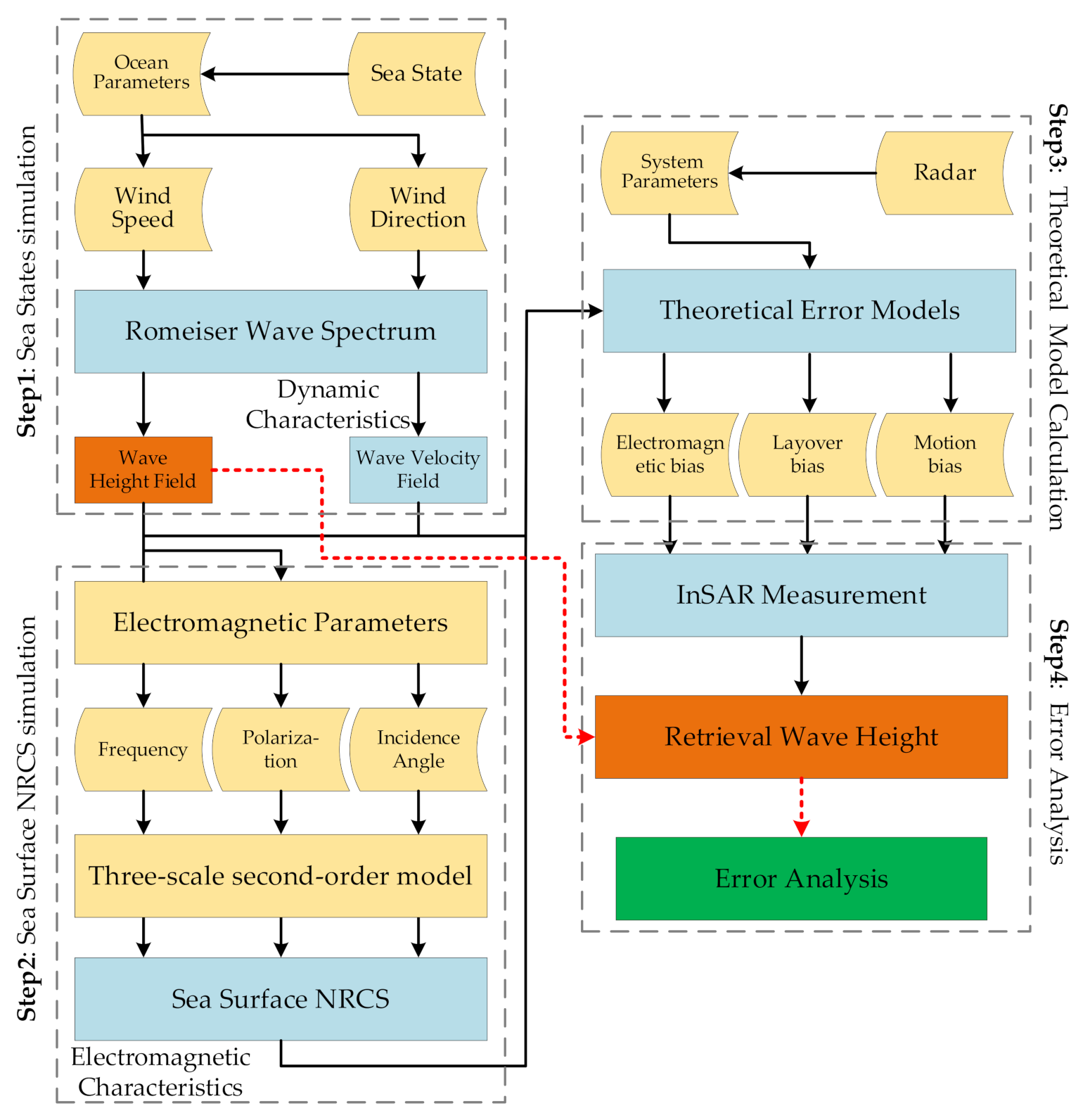
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. Romeiser Wave Spectrum
2.3.2. Three-Scale Second-Order Sea Surface Scattering Model
2.3.3. Analytical Flowchart
3. Results
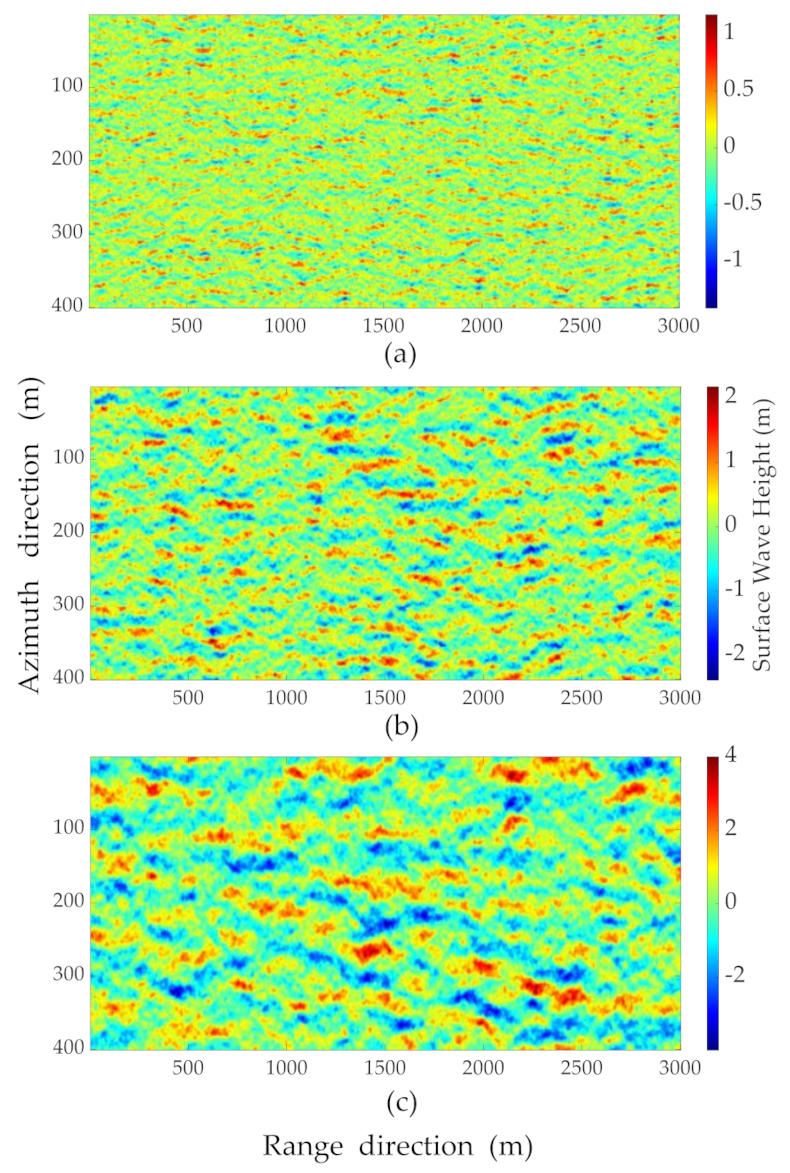
3.1. Stochastic Sea Scenes Simulation
3.2. Experimental Verification with SWOT Error Budget
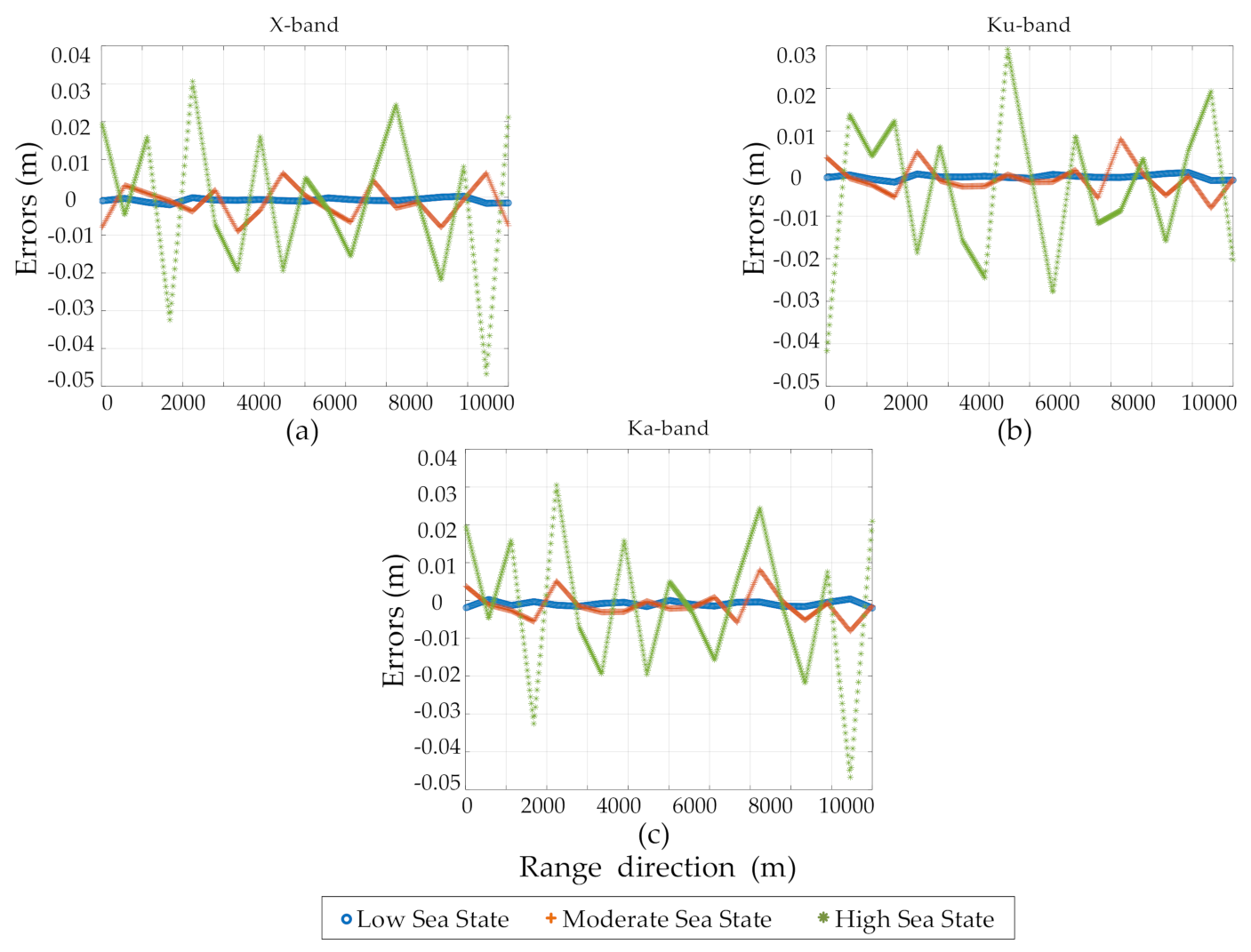
3.3. Experiments under Multiple Scenarios
4. Discussion
4.1. Suggestions for the System Design of InSAR Altimetry
4.2. Possible Method to Reduce Dynamic Wave-Related Errors
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | The full name |
| SSH | Sea Surface Height |
| InSAR | Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| NRCS | Normalized Radar Cross Section |
| RMSE | Root-Mean-Square Error |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| SWOT | Surface Water and Ocean Topography |
| TOPEX | Topography Experiment |
| CryoSat-2 | Cryosphere Satellite 2 |
| Jason-CS | Jason Continuity of Services Satellite |
| HY-2A/B/C | Haiyang 2A, 2B, and 3C Satellites |
| OST | Ocean Surface Topography |
| IRA | Interferometric Radar Altimeter |
| SRTM | Shuttle Radar Topography Mission |
| EMB | Electromagnetic Bias |
| KaRIn | Ka-band Radar Interferometer |
| InIRA | Interferometric Imaging Radar Altimeter |
| NSSCCAS | National Space Science Center of Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| SSB | Sea State Bias |
| NLMSTC | National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology of China |
| SWH | Significant Wave Height |
| POD | Precision Orbit Determination |
| LB | Layover Bias |
| MB | Motion Bias |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| JONSWAP | Joint North Sea Wave Project |
| OBP | Onboard Processor |
| AIRAS | Airborne Interferometric Radar Altimeter System |
Appendix A. Detailed Derivation of the Motion Bias
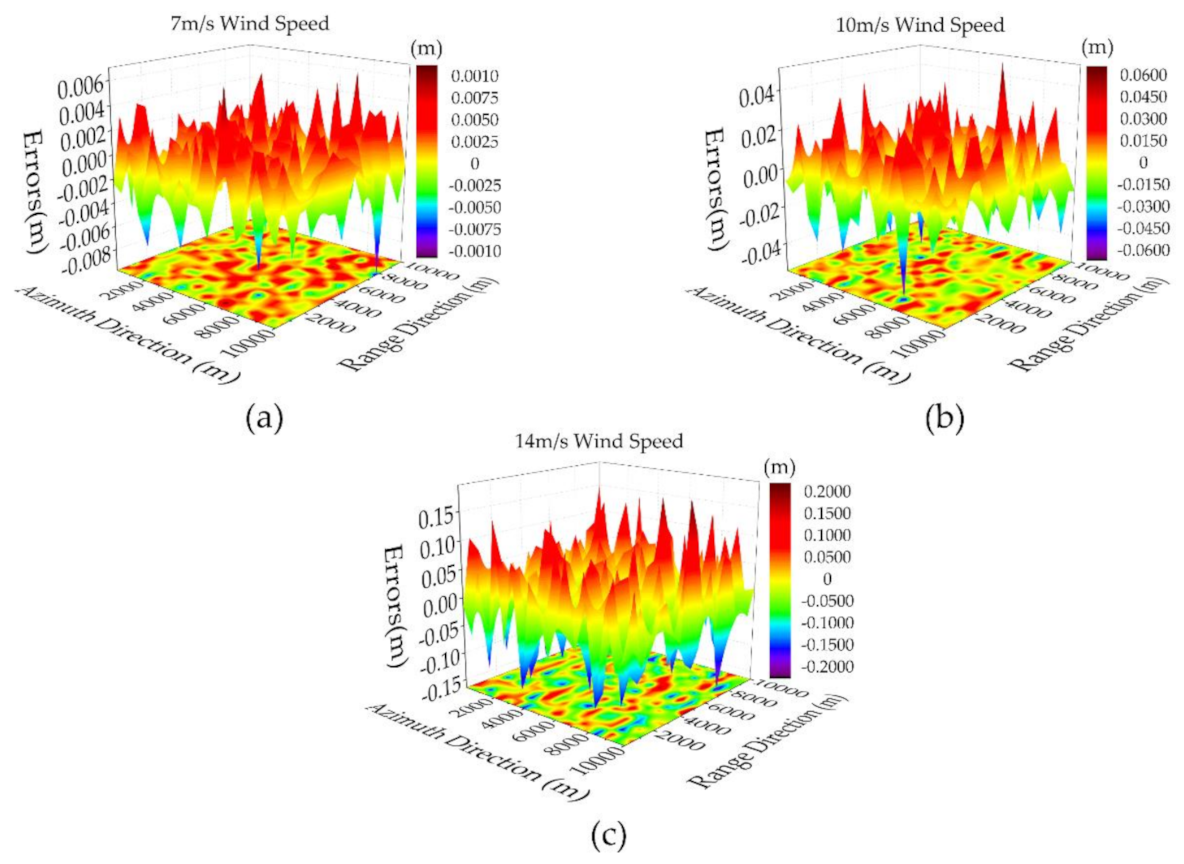
Appendix B. Three-Dimensional Distribution of the Simulated Dynamic Wave-Related Errors


References
- Fu, L.-L.; Chelton, D.B.; Le Traon, P.-Y.; Morrow, R. Eddy dynamics from satellite altimetry. Oceanography 2010, 23, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelton, D.; Ries, J.; Haines, B.; Fu, L.; Callahan, P. Satellite Altimetry and Earth Sciences: A Handbook of Techniques and Applications; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Legeais, J.; Ablain, M.; Zawadzki, L. An improved and homogeneous altimeter sea level record from the ESA Climate Change Initiative. Earth Syst. Sci. Data. 2018, 10, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablain, M.; Meyssignac, B.; Zawadzki, L. Uncertainty in satellite estimates of global mean sea-level changes, trend and acceleration. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharroo, R.; Bonekamp, H.; Ponsard, C.; Parisot, F.; von Engeln, A.; Tahtadjiev, M.; de Vriendt, K.; Montagner, F. Jason continuity of services: Continuing the Jason altimeter data records as Copernicus Sentinel-6. Ocean Sci. 2016, 12, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Yang, J.; Lin, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Fan, C. Global assessments of the HY-2B measurements and cross-calibrations with Jason-3. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Tang, J.; Zhao, C.; Wu, S.; Yu, F.; Ma, C.; Xu, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Concept design of the “Guanlan” science mission: China’s novel contribution to space oceanography. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, M.; Li, Z.; Fu, L. Increasing the space-time resolution of mapped sea surface height from altimetry. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 124, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharffenberg, M.; Stammer, D. Time-space sampling-related uncertainties of altimetric Global Mean Sea Level estimates. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 7743–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Liu, B.; Sui, X.; Zhang, R.; Sun, J. Ocean surface topography altimetry by large baseline cross-interferometry from satellite formation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Fernandez, D. SWOT Project Mission Performance and Error Budget Document. JPL D-79084; 2017; pp. 19–73. Available online: https://pdms.jpl.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Quartly, G.D.; Chen, G.; Nencioli, F.; Morrow, R.; Picot, N. An overview of requirements, procedures and current advances in the calibration/validation of radar altimeters. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.; Martin, J.M. Theory and design of interferometric synthetic aperture radars. Radar Signal Process. IEE Proc. 1992, 39, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, H.; Zan, F.; Parizzi, A. Study of systematic bias in measuring surface deformation with SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 1285–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Fu, H.; Zhu, J.; Zuo, T. A framework for correcting ionospheric artifacts and atmospheric effects to generate high accuracy InSAR DEM. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.; Morris, C.S.; Belz, E.J. A global assessment of SRTM performance. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinel, S.; Bonnet, M.; Silva, J.; Moreira, D.; Calmant, S.; Satgé, F.; Seyler, F. Correction of interferometric and vegetation biases in the SRTMGL1 spaceborne DEM with hydrological conditioning towards improved hydrodynamics modeling in the Amazon Basin. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16108–16130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peral, E.; Rodríguez, E.; Esteban-Fernández, D. Impact of surface waves on SWOT’s projected ocean accuracy. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14509–14529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, M.; Wang, X.; Huang, H. Error analysis of dynamic sea surface height measurement by near-nadir interferometric SAR. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2020, 42, 547–554. [Google Scholar]
- Reale, F.; Dentale, F.; Carratelli, E.P.; Fenoglio-Marc, L. Influence of sea state on sea surface height oscillation from doppler altimeter measurements in the North Sea. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpers, W.; Rufenach, C.L. The effect of orbital motions on synthetic aperture radar imagery of ocean waves. IEEE Trans. Antenn. Propag. 1979, 27, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T. Numerical research on clear imaging of azimuth-traveling ocean waves in SAR images. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, M.; Feng, J.; Huang, H.; Chen, G.; Chen, Z. Analysis of the sea state bias in interferometric radar altimeter. In Proceedings of the China International SAR Symposium, Shanghai, China, 11 October 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Guo, X.; Zhang, H.; Di, J.; Chen, G. An investigation of the influences of SWOT sampling and errors on ocean eddy observation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Chong, J.; Tan, H. Performance analysis of ocean surface topography altimetry by Ku-Band near-nadir interferometric SAR. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Yang, J.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y. Preliminary evaluation and correction of sea surface height from Chinese Tiangong-2 interferometric imaging radar altimeter. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, H.; Chen, G.; Wang, P.; Mertikas, S.; Fu, Y.; et al. Calibration of an airborne interferometric radar altimeter over the Qingdao Coast Sea, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Chen, G. Impact of ocean waves on Guanlan’s IRA measurement error. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, P.; Ogor, F.; Le Traon, P.Y.; Zanife, O.Z. Estimating the sea state bias of the TOPEX and Poseidon altimeters from crossover differences. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1994, 99, 24981–24994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, M.; Nadzir, Z.A.; Quartly, G.D. Improving the precision of sea level data from satellite altimetry with high-frequency and regional sea state bias corrections. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 218, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.; Pollard, B.; Martin, J. Wide-swath ocean altimetry using radar interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 624–626. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2014/17962 (accessed on 28 October 2020).
- Gommenginger, C.; Srokosz, M. An investigation of altimeter sea state bias theories. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2003, 108, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, F.; Dentale, F.; Carratelli, E.P. Numerical simulation of whitecaps and foam effects on satellite altimeter response. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3681–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J. Layover in satellite radar images of ocean waves. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1983, 88, 7719–7720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, M.; Chen, C.; Frasson, R.; Pavelsky, T.; Williams, B.; Yang, X.; Fore, A. How will radar layover impact SWOT measurements of water surface elevation and slope, and estimates of river discharge? Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.L.; Ubelmann, C. On the transition from profile altimeter to swath altimeter for observing global ocean surface topography. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjørtoft, R.; Gaudin, J.-M.; Pourthié, N.; Lalaurie, J.-C.; Mallet, A.; Nouvel, J.-F.; Martinot-Lagarde, J.; Oriot, H.; Borderies, P.; Ruiz, C. KaRIn on SWOT: Characteristics of near-nadir Ka-band interferometric SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 2172–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, J. An improved model of the ocean surface wave vector spectrum and its effects on radar backscatter. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1994, 99, 16269–16291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeiser, R.; Alpers, W.; Wismann, V. An improved composite surface model for the radar backscattering cross section of the ocean surface 1. Theory of the model and optimization/validation by scatterometer data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1997, 102, 25237–25250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeiser, R.; Alpers, W. An improved composite surface model for the radar backscattering cross section of the ocean surface 2. Model response to surface roughness variations and the radar imaging of underwater bottom topography. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1997, 102, 25251–25267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisot, O.; Nouguier, F.; Chapron, B.; Guérin, C. The GO4 model in near-nadir microwave scattering from the sea surface. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5889–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, W. A stochastic, multiscale model of microwave backscatter from the ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2002, 107, 3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M. Three-scale radar backscattering model of the ocean surface based on second-order scattering. Acta Electron. Sin. 2008, 36, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, M. Bistatic SAR raw data simulation for ocean. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 871–874. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fan, C. Sea surface imaging simulation for 3D interferometric imaging radar altimeter. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, W.J. Reconciliation of theories of synthetic aperture radar imagery of ocean waves. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 1992, 97, 7493–7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Mouche, A.; He, Y.; Perrie, W. Ku-band sea surface radar backscatter at low incidence angles under extreme wind conditions. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzki, L.; Ablain, M. Accuracy of the mean sea level continuous record with future altimetric missions: Jason-3 vs. Sentinel-3a. Ocean Sci. Discuss. 2016, 12, 1511–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, W. Design and algorithms of the Tiangong-2 interferometric imaging radar altimeter processor. In Proceedings of the Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium, St. Petersburg, Russia, 22–25 May 2017; pp. 3802–3803. [Google Scholar]
- Long, T.; Dong, X.; Hu, C.; Zeng, T. A new method of zero-doppler centroid control in GEO SAR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 8, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldarias, A.; Gómez-Enri, J.; Laiz, I.; Tejedor, B.; Vignudelli, S.; Cipollini, P. Validation of Sentinel-3A SRAL coastal sea level data at high posting rate: 80 Hz. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3809–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





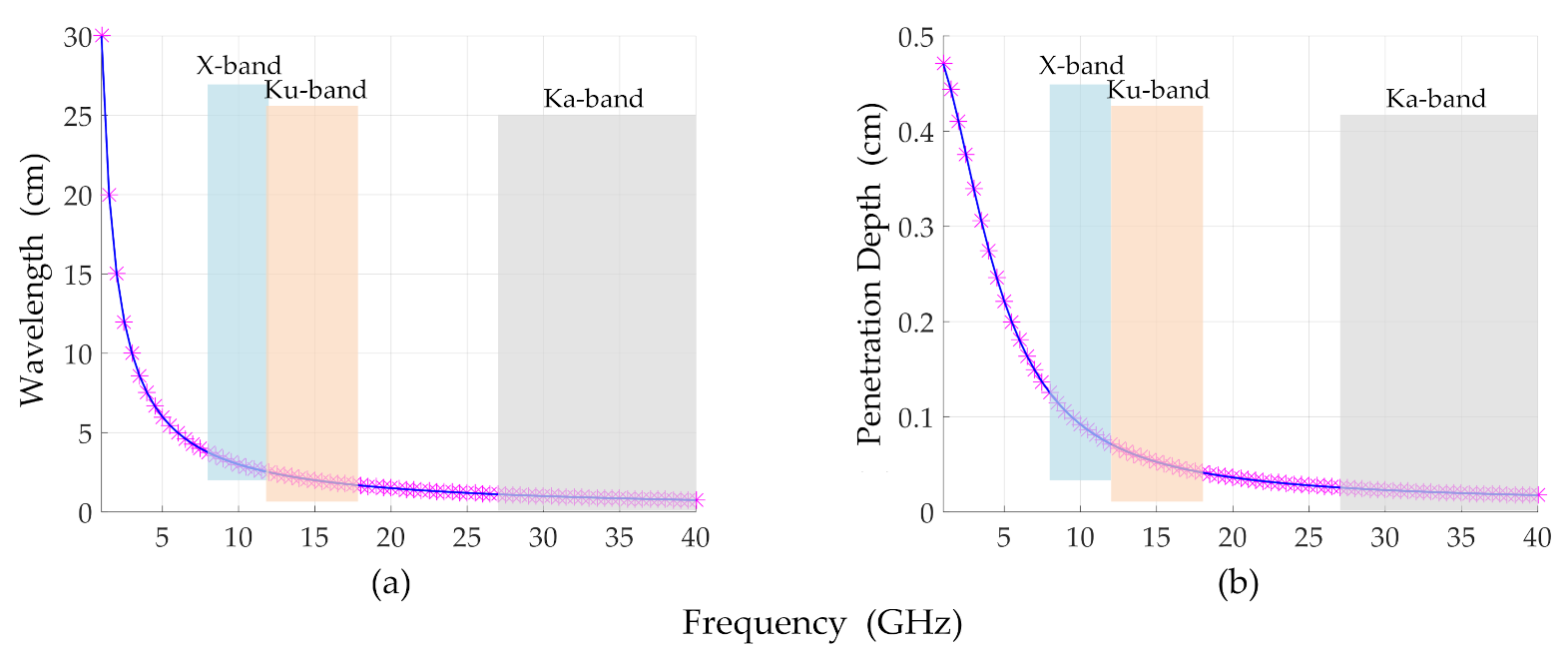
| System Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Satellite altitude (H) | 873 km |
| Physical baseline length (B) | 10 m |
| Central Frequency | 35.75 GHz |
| Incidence angle | 0.6–3.9° |
| Polarization | HH |
| Slant range resolution | 0.75 m |
| Azimuth resolution | 5 m |
| Error Sources | RMSE (cm) |
|---|---|
| Dynamic wave-related errors | 0.2486 |
| SWOT motion errors [11] | 0.2470 |
| System Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Satellite altitude (H) | 800 km |
| Physical baseline length (B) | 10 m |
| Radar wavebands | X, Ku, and Ka-bands |
| Incidence angle | 4–4.7° |
| Polarization | HH |
| Slant range posting rate | 0.75 m |
| Azimuth posting rate | 5 m |
| Range resolution | 1 m |
| Azimuth resolution | 50 m |
| Wavebands | RMSE (cm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sea States (Wind Speed) | |||
| Low (7 m/s) | Moderate (10 m/s) | High (14 m/s) | |
| X-band | 0.2635 | 1.6451 | 6.6102 |
| Ku-band | 0.2636 | 1.3105 | 6.8083 |
| Ka-band | 0.2670 | 1.3154 | 6.6361 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Duan, T. An Analytical Method for Dynamic Wave-Related Errors of Interferometric SAR Ocean Altimetry under Multiple Sea States. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050986
Chen Y, Huang M, Zhang Y, Wang C, Duan T. An Analytical Method for Dynamic Wave-Related Errors of Interferometric SAR Ocean Altimetry under Multiple Sea States. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(5):986. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050986
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yao, Mo Huang, Yuanyuan Zhang, Changyuan Wang, and Tao Duan. 2021. "An Analytical Method for Dynamic Wave-Related Errors of Interferometric SAR Ocean Altimetry under Multiple Sea States" Remote Sensing 13, no. 5: 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050986
APA StyleChen, Y., Huang, M., Zhang, Y., Wang, C., & Duan, T. (2021). An Analytical Method for Dynamic Wave-Related Errors of Interferometric SAR Ocean Altimetry under Multiple Sea States. Remote Sensing, 13(5), 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050986