Low Contrast Infrared Target Detection Method Based on Residual Thermal Backbone Network and Weighting Loss Function
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose a novel residual thermal infrared network (ResTNet) based on an attention mechanism to alleviate the inherent feature loss problem of infrared image targets. A novel multi-spatial attention network (MSAN) is designed in ResTNet, which uses a Transformer structure for attention operation. The network can establish the information path between local regions of different scales in each position of the image in the feature extraction process, so as to enhance the extraction of target feature in the image by integrating the context information;
- A contrast enhancement loss function (CTEL) is proposed related to target contrast to suppressing the imbalance between low contrast targets and other targets. Specifically, the weight of low contrast targets loss values is optimized by CTEL, which effectively improved the detection effect of low-contrast difficult targets and compensate for the gradient of the low-contrast targets in training back propagation;
- We produce a new infrared dataset about remote sensing and verify our method on it. The experimental results on the FLIR dataset and our dataset show that our method is far superior to the current most advanced algorithm.
2. Method
2.1. Overall Network Architecture
2.2. ResTNet
2.3. Contrast Enhancement Loss Function
| Algorithm 1. Contrast Calculation Method. |
| Require: ImgData: the matrix of the image; TargetRegion: location of the target; α: visual field coefficient; β: visual field coefficient; Ensure: contrast x get the matrix of the target region with scale (h,w) as t; get the matrix of surrounding the target region with scale ((1+α)h,(1+β)w); split four background regions as [b1,b2,b3,b4] for k = 1; k < 4; k++ do mk =0 for i = 1; i <= 255; i++ do compute the number of pixel value i compute the frequency of pixel value i in the target area and background area as pt and pd mk += ||(i + 1)ptlog(pt) − (i + 1)pdlog(pd)|| end for end for x = max(m1,m2,m3,m4) |
| Algorithm 2. CTEL Calculation Method. |
| Require: PreResult: a prediction result; GT: a annotation box; Fciou: calculation function of CIoU; δ: hyper-parameter of mapping function; k: hyper-parameter of mapping function; b: hyper-parameter of mapping function; Ensure: regression loss l compute CIoU loss Lciou = Fciou(GT, PreResult) compute the contrast of the target as x Index = c = b = b + 1 w = ce−Index + b compute value of regression loss l = wLciou |
3. Experiment and Analysis
3.1. Dataset Introduction
3.2. Implementation Details
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
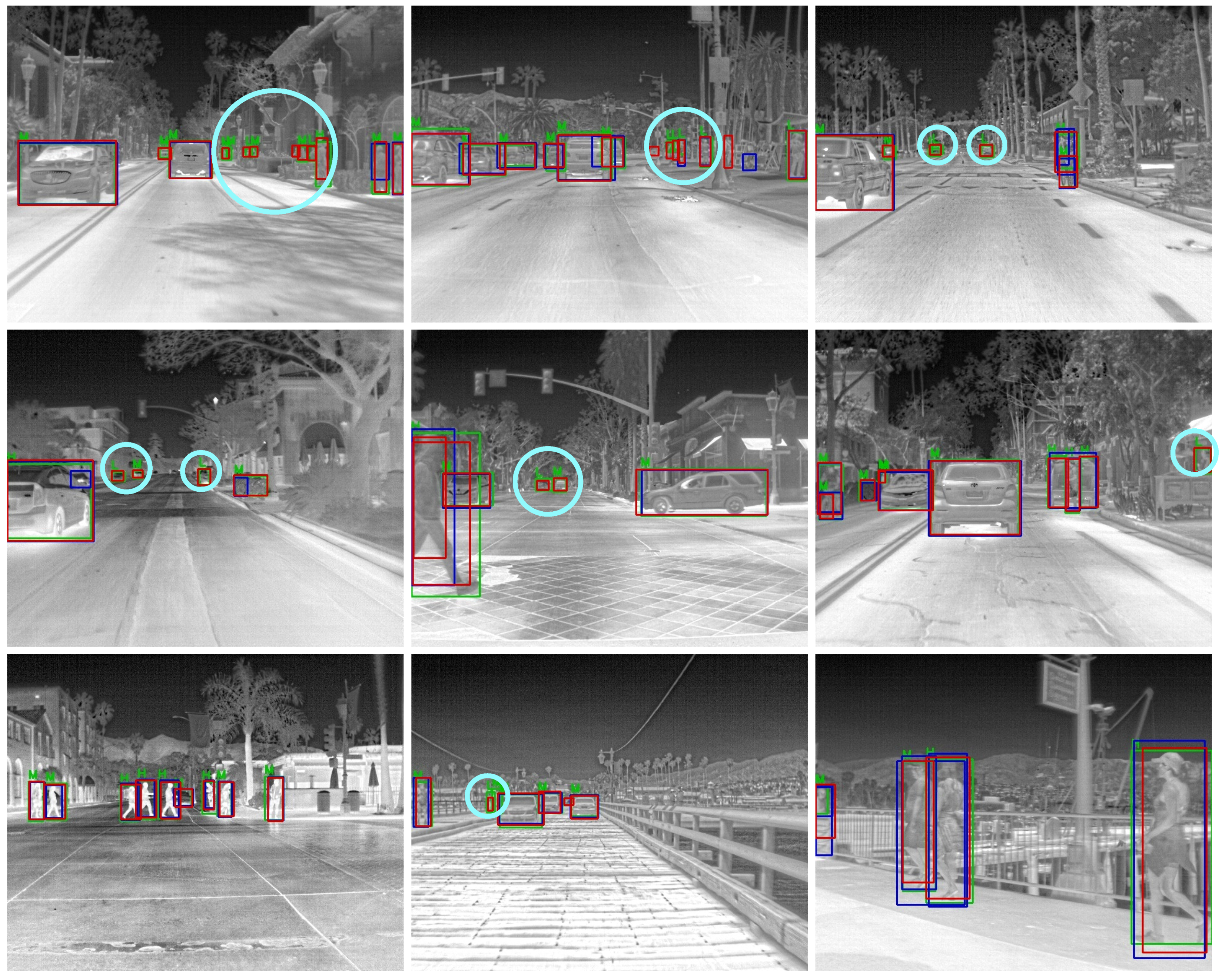
3.4. Analysis of Results
3.4.1. Experiments on the FLIR-ADAS Dataset
| Method | Person | Car | Bicycle | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSD [24] | 40.9 | 61.6 | 43.6 | 48.7 |
| Faster R-CNN [17] | 39.6 | 67.5 | 54.6 | 53.9 |
| Retinanet [25] | 52.3 | 71.5 | 61.3 | 61.7 |
| FCOS [26] | 69.7 | 79.7 | 67.4 | 72.3 |
| MMTOD-UNIT [11] | 49.4 | 70.7 | 64.4 | 61.5 |
| MMTOD-CG [11] | 50.2 | 70.6 | 63.3 | 61.4 |
| RefineDet [27] | 77.1 | 84.5 | 57.2 | 72.9 |
| ThermalDet [9] | 78.2 | 85.5 | 60.0 | 74.6 |
| Cascade R-CNN [13] | 77.3 | 79.8 | 84.3 | 80.5 |
| YOLOv5s [14] | 68.3 | 80.0 | 67.1 | 71.8 |
| YOLOF [15] | 67.8 | 79.4 | 68.1 | 71.8 |
| YOLOX [16] | 78.2 | 80.2 | 85.4 | 81.2 |
| baseline | 69.7 | 79.9 | 61.5 | 70.4 |
| baseline + CTEL | 74.9 | 84.0 | 75.7 | 79.2 |
| baseline +ResTNet | 77.8 | 87.5 | 83.6 | 82.9 |
| ResTNet+ CTEL | 78.0 | 87.4 | 87.4 | 84.3 |
3.4.2. Experiments on the Remote Sensing Infrared Dataset
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, J.; Chen, J.; Cho, Y.K.; Kang, D.Y.; Son, B.J. CNN-Based Person Detection Using Infrared Images for Night-Time Intrusion Warning Systems. Sensors 2019, 20, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Shin, H. Pedestrian Detection at Night in Infrared Images Using an Attention-Guided Encoder-Decoder Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, H.; Xia, M.; Zhou, G.; Chang, Y.; Yan, L. Infrared Small UAV Target Detection Based on Residual Image Prediction via Global and Local Dilated Residual Networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.D.; Er, M.; Ronda, V.; Chan, P. Max-mean and max-median filters for detection of small-targets. Proc. SPIE 1999, 3809, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Zhang, C.; Mu, T.; Yan, T.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Multiscale Local Gray Dynamic Range Method for Infrared Small-Target Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 1846–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liu, S.; Qin, G.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, N. A Local Contrast Method Combined with Adaptive Background Estimation for Infrared Small Target Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1442–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, Z. Infrared small target detection based on partial sum of the tensor nuclear norm. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, Q.; Wang, Z.; Tan, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, W. RISTDnet: Robust Infrared Small Target Detection Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhu, X.; Su, Y. Every Feature Counts: An Improved One-Stage Detector in Thermal Imagery. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 5th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 6–9 December 2019; pp. 1965–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, M.; Shi, Y.; Fan, J.; Mu, C.; Xu, L. Infrared Target Detection Using Intensity Saliency and Self-Attention. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 25–28 October 2020; pp. 1991–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaguptapu, C.; Akolekar, N.; Sharma, M.M.; Balasubramanian, V.N. Borrow from Anywhere: Pseudo Multi-Modal Object Detection in Thermal Imagery. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Barnard, K. Attentional Local Contrast Networks for Infrared Small Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 9813–9824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into High Quality Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Glenn, J.; Alex, S.; Jirka, B.; NanoCode012; Christopher, S.; Liu, C.; Prashant, R. Yolov5. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 (accessed on 29 August 2021).
- Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, X.I.; Cheng, J.; Sun, J. You Only Look One-level Feature. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.09460. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO Series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.-H.; Cheng, M.-M.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Yang, M.-H.; Torr, P. Res2Net: A New Multi-Scale Backbone Architecture. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU Loss: Faster and Better Learning for Bounding Box Regression. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1911.08287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cao, Z.; Huang, T. UnitBox: An Advanced Object Detection Network. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM international conference on Multimedia (MM’16), Amsterdam The Netherlands, 15–19 October 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FA Group. Flir Thermal Dataset for Algorithm Training. 2018. Available online: https://www.flir.in/oem/adas/adas-dataset-form/ (accessed on 29 August 2021).
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Graz, Austria, 8 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2999–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. FCOS: Fully Convolutional One-Stage Object Detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.01355. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wen, L.; Bian, X.; Lei, Z.; Li, S.Z. Single-shot refinement neural network for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4203–4212. [Google Scholar]









| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| ResTNet.m1–4 | 3, 4, 23, 3 |
| ResTNet.n | 3 |
| CTEL.delta | 100 |
| CTEL.k,b | 0.75, 0.1 |
| Method | Low | Mid | High |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSD [24] | 32.5 | 47.9 | 63.4 |
| Retinanet [25] | 44.8 | 64.4 | 79.5 |
| FCOS [26] | 57.4 | 75.1 | 86.6 |
| Cascade R-CNN [13] | 64.3 | 79.8 | 90.3 |
| YOLOv5s [14] | 61.2 | 77.8 | 86.1 |
| YOLOF [15] | 61.2 | 77.7 | 86.2 |
| YOLOX [16] | 68.2 | 79.0 | 86.3 |
| baseline | 61.3 | 76.7 | 87.2 |
| baseline + CTEL | 63.9 | 81.5 | 88.9 |
| baseline + ResTNet | 71.1 | 84.1 | 91.7 |
| ResTNet + CTEL | 73.3 | 84.2 | 91.6 |
| Method | mAP |
|---|---|
| SSD [24] | 13.9 |
| Retinanet [25] | 41.1 |
| FCOS [26] | 51.0 |
| Cascade R-CNN [13] | 58.4 |
| YOLOv5s [14] | 62.4 |
| YOLOF [15] | 52.5 |
| YOLOX [16] | 60.5 |
| baseline | 49.7 |
| baseline + CTEL | 59.8 |
| baseline + ResTNet | 66.6 |
| ResTNet + CTEL | 67.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Su, N.; Yan, Y.; Xing, X. Low Contrast Infrared Target Detection Method Based on Residual Thermal Backbone Network and Weighting Loss Function. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010177
Zhao C, Wang J, Su N, Yan Y, Xing X. Low Contrast Infrared Target Detection Method Based on Residual Thermal Backbone Network and Weighting Loss Function. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(1):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010177
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Chunhui, Jinpeng Wang, Nan Su, Yiming Yan, and Xiangwei Xing. 2022. "Low Contrast Infrared Target Detection Method Based on Residual Thermal Backbone Network and Weighting Loss Function" Remote Sensing 14, no. 1: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010177
APA StyleZhao, C., Wang, J., Su, N., Yan, Y., & Xing, X. (2022). Low Contrast Infrared Target Detection Method Based on Residual Thermal Backbone Network and Weighting Loss Function. Remote Sensing, 14(1), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010177










