The Spatiotemporal Change of Glacier Runoff Is Comparably Attributed to Climatic Factors and Physical Properties in Northwestern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
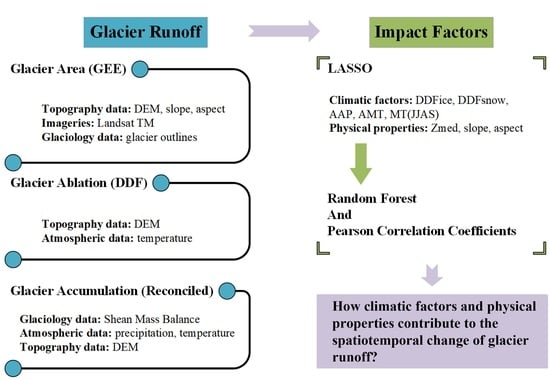
2. Materials and Methods
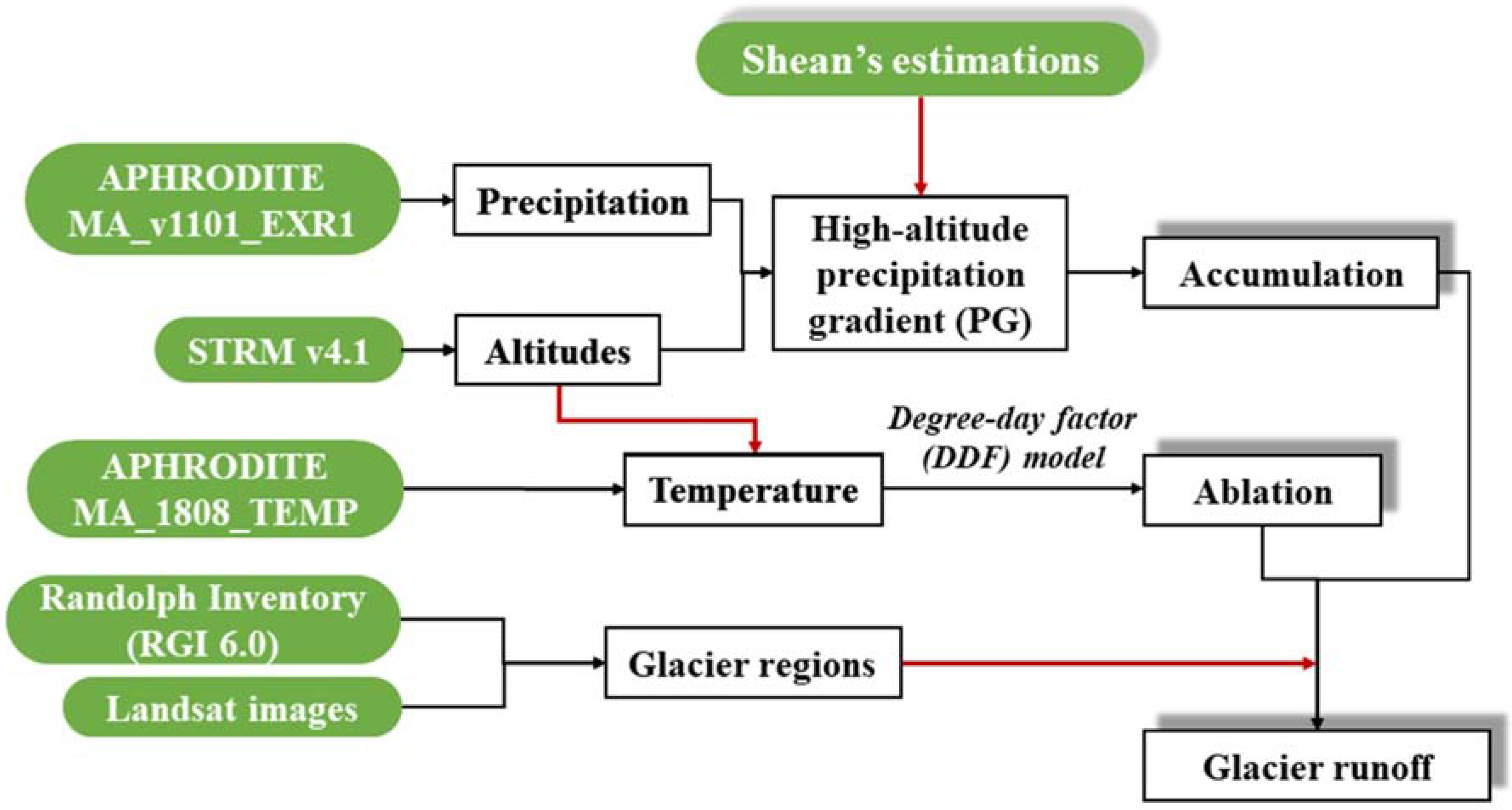
2.1. Observations
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Glacial Accumulation
2.3.2. Glacial Ablation
2.3.3. Mass Balance
2.3.4. Precipitation Gradient
2.3.5. Glacial Runoff
2.3.6. Glacial Area
2.3.7. Total Uncertainty Analysis
2.3.8. Trend Analysis
3. Results
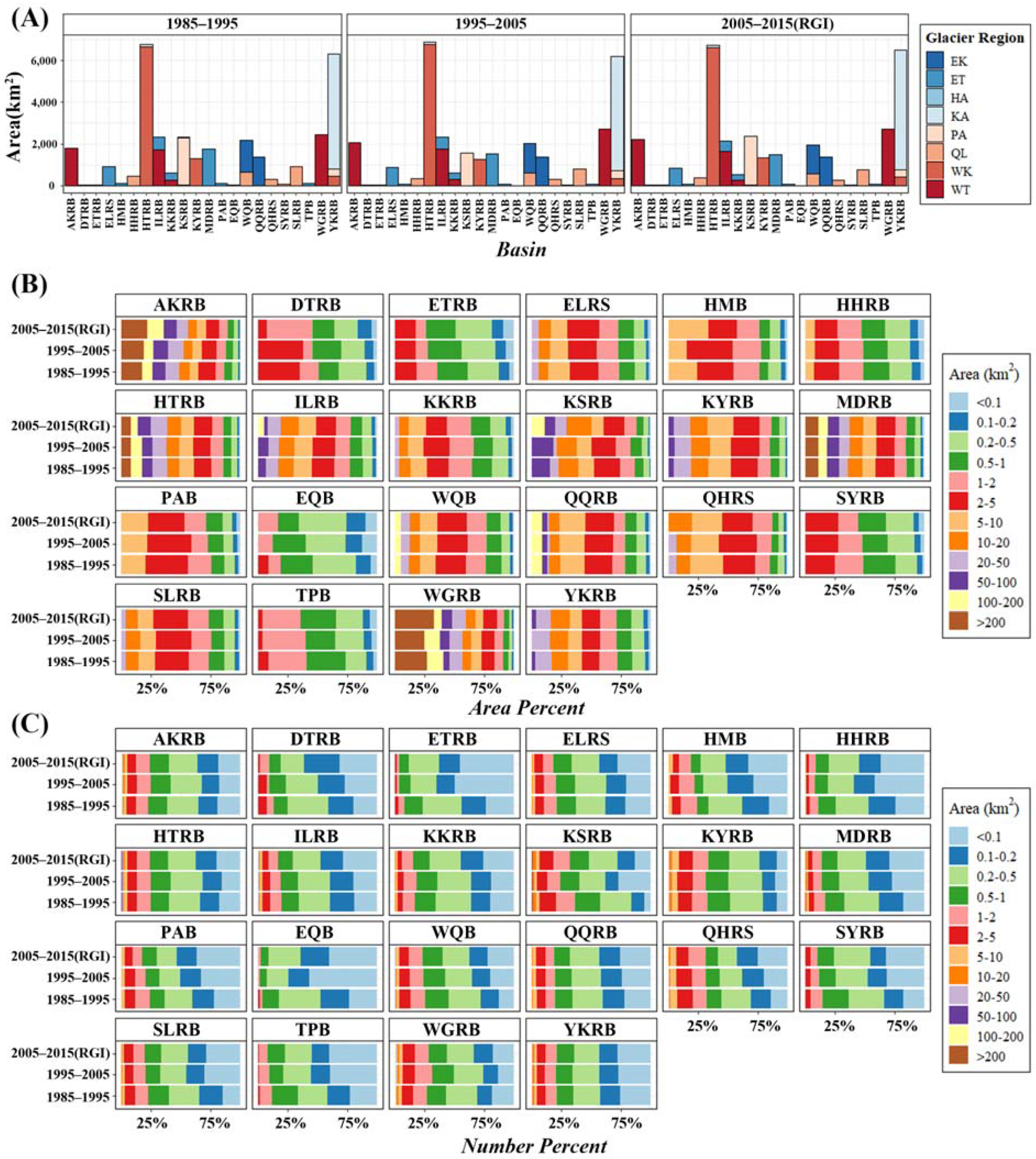
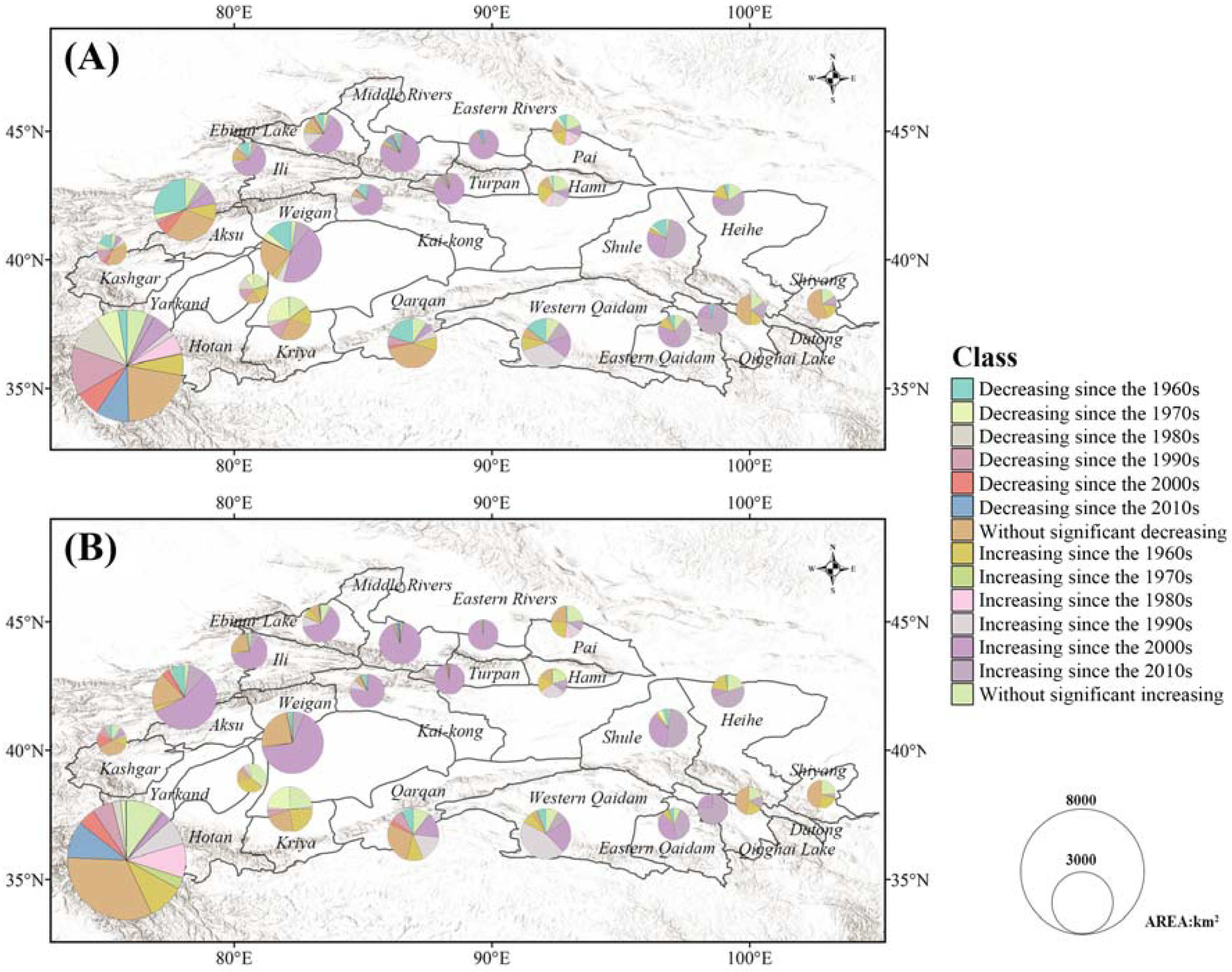
3.1. Glacial Area Change
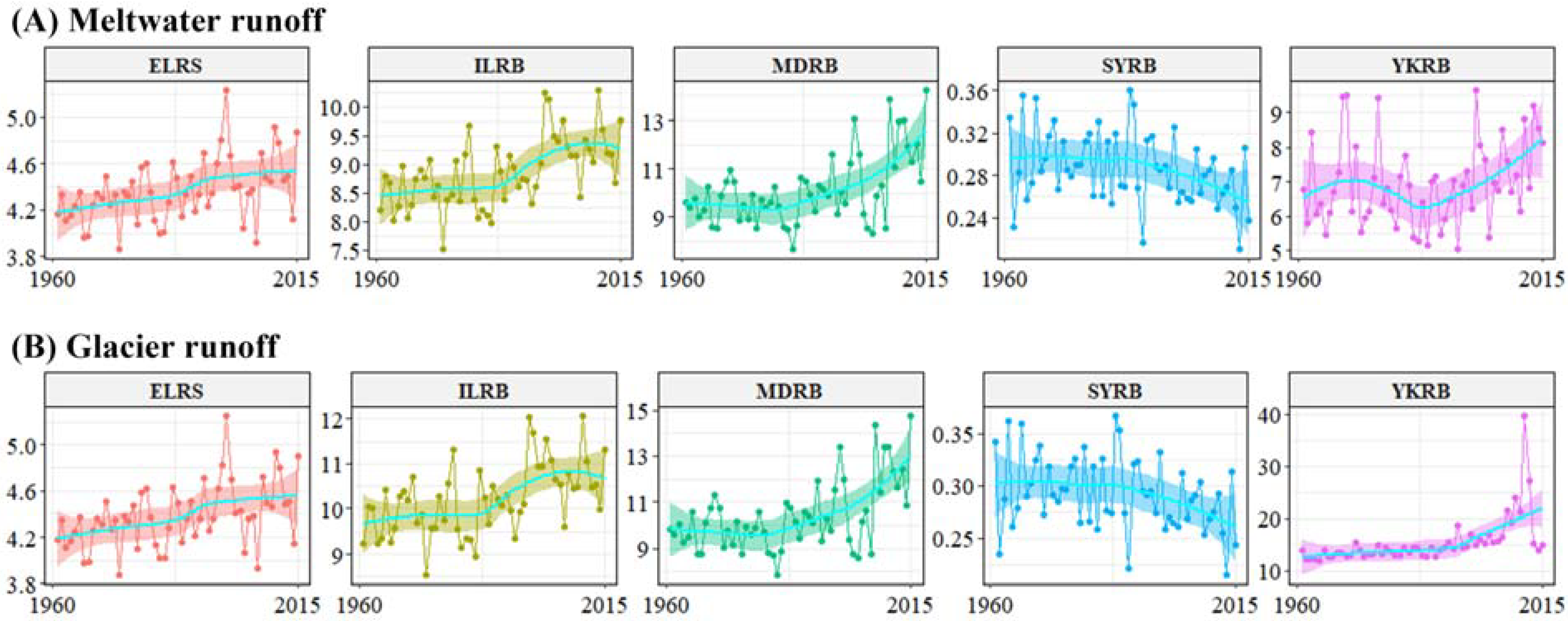
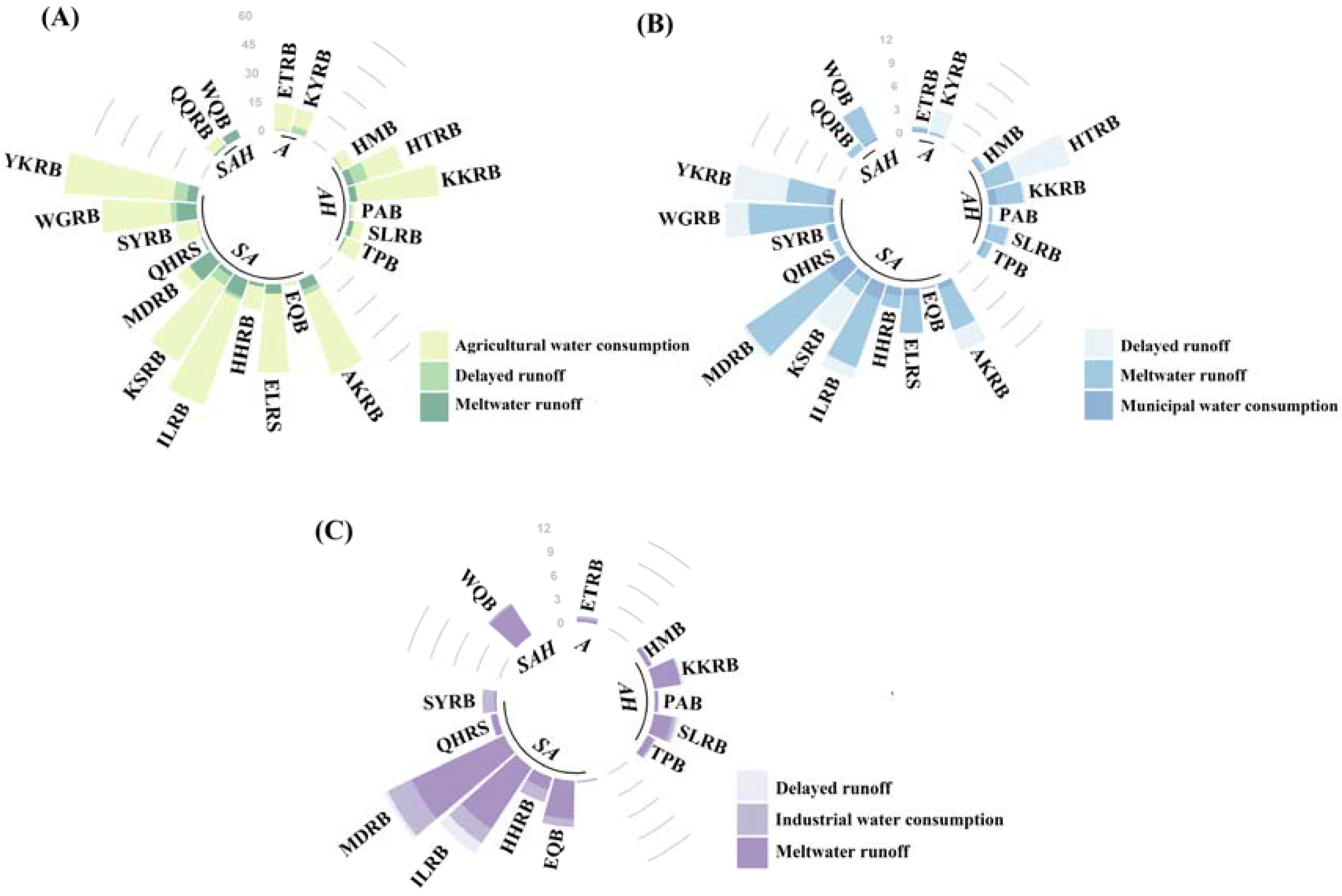
3.2. Glacial Runoff from 1961 to 2015
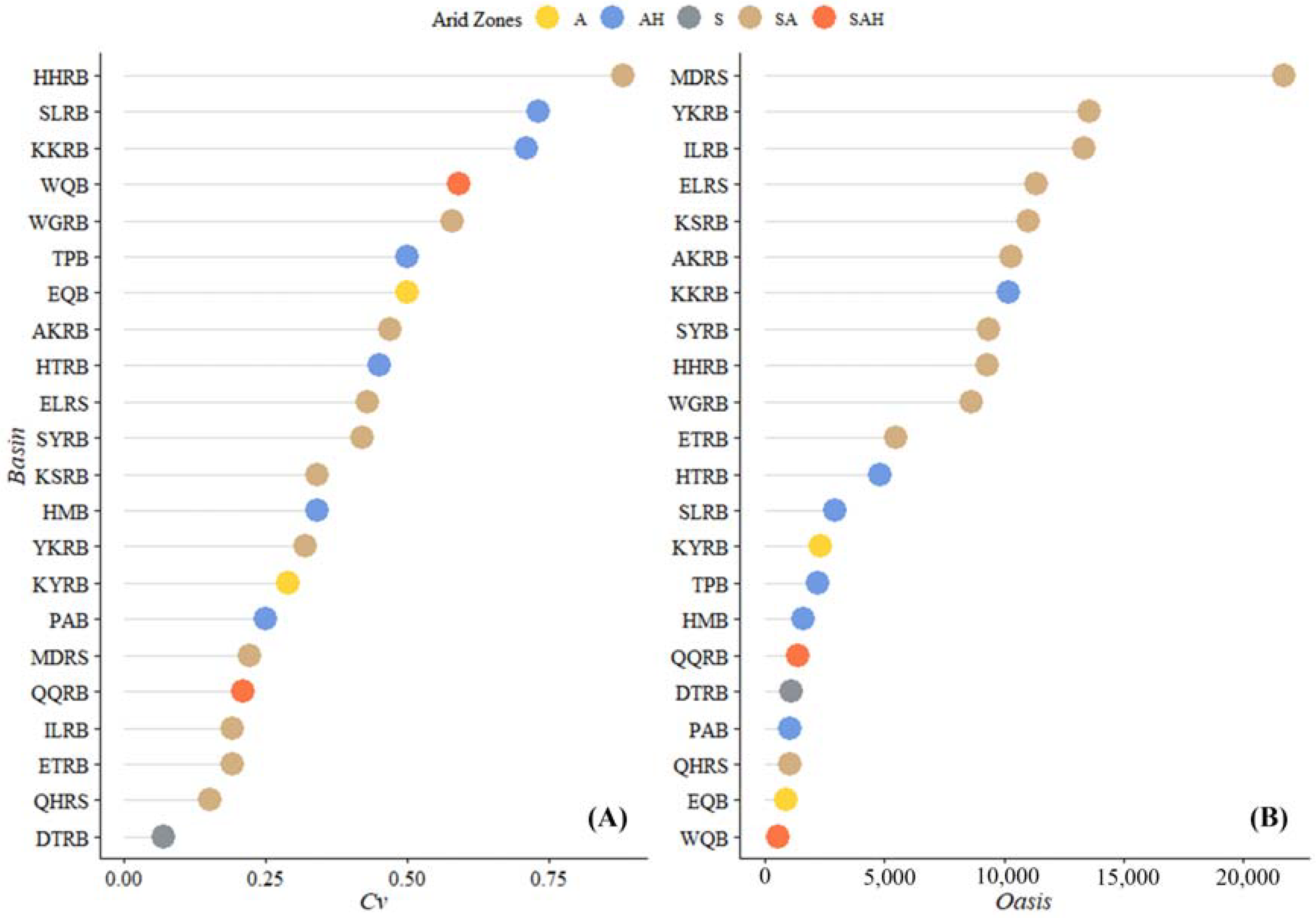
3.3. Sustainability of Glaciers in the DAC
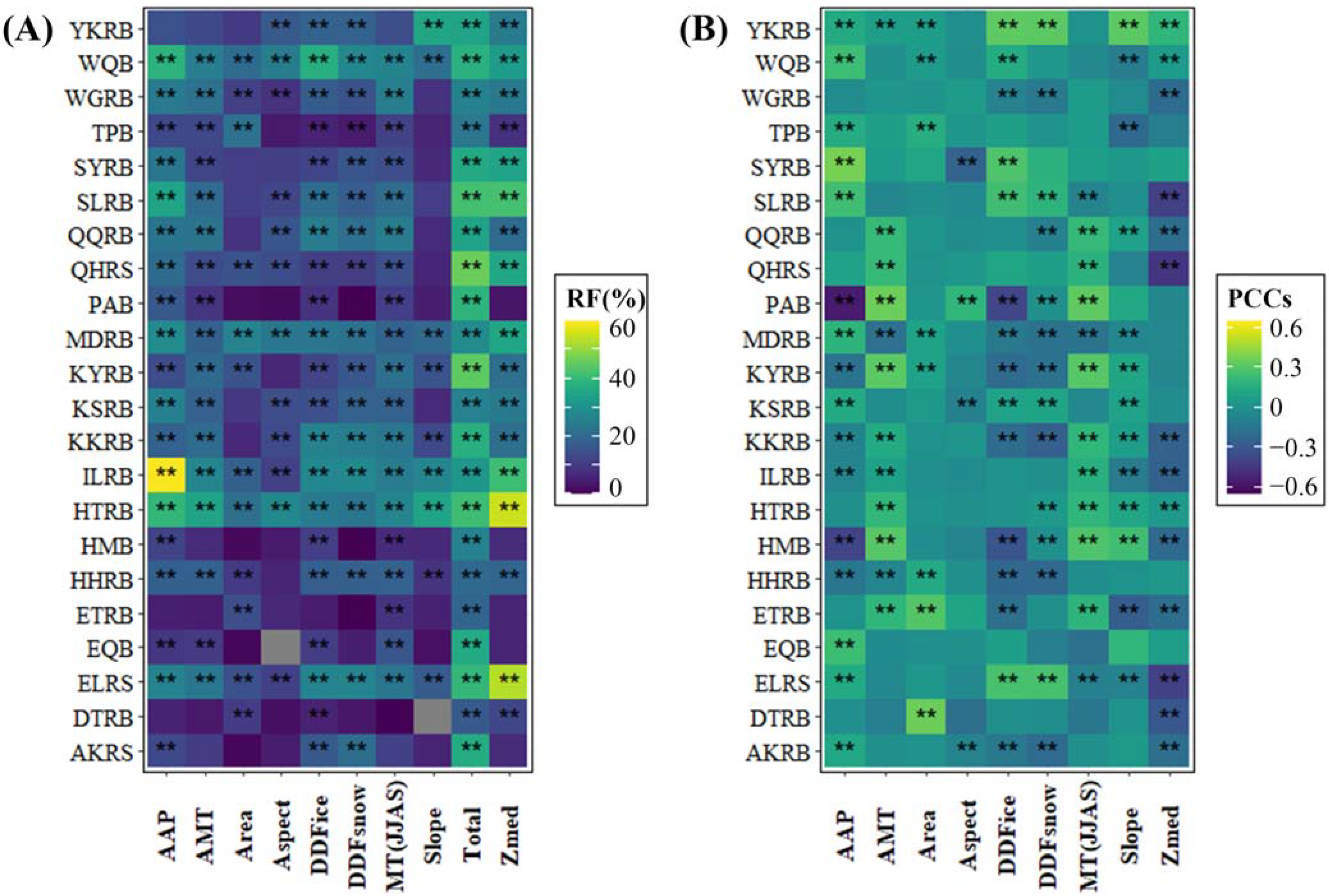
3.4. Climatic Factors and Physical Properties Explain the Spatiotemporal Patterns of GR
4. Discussion
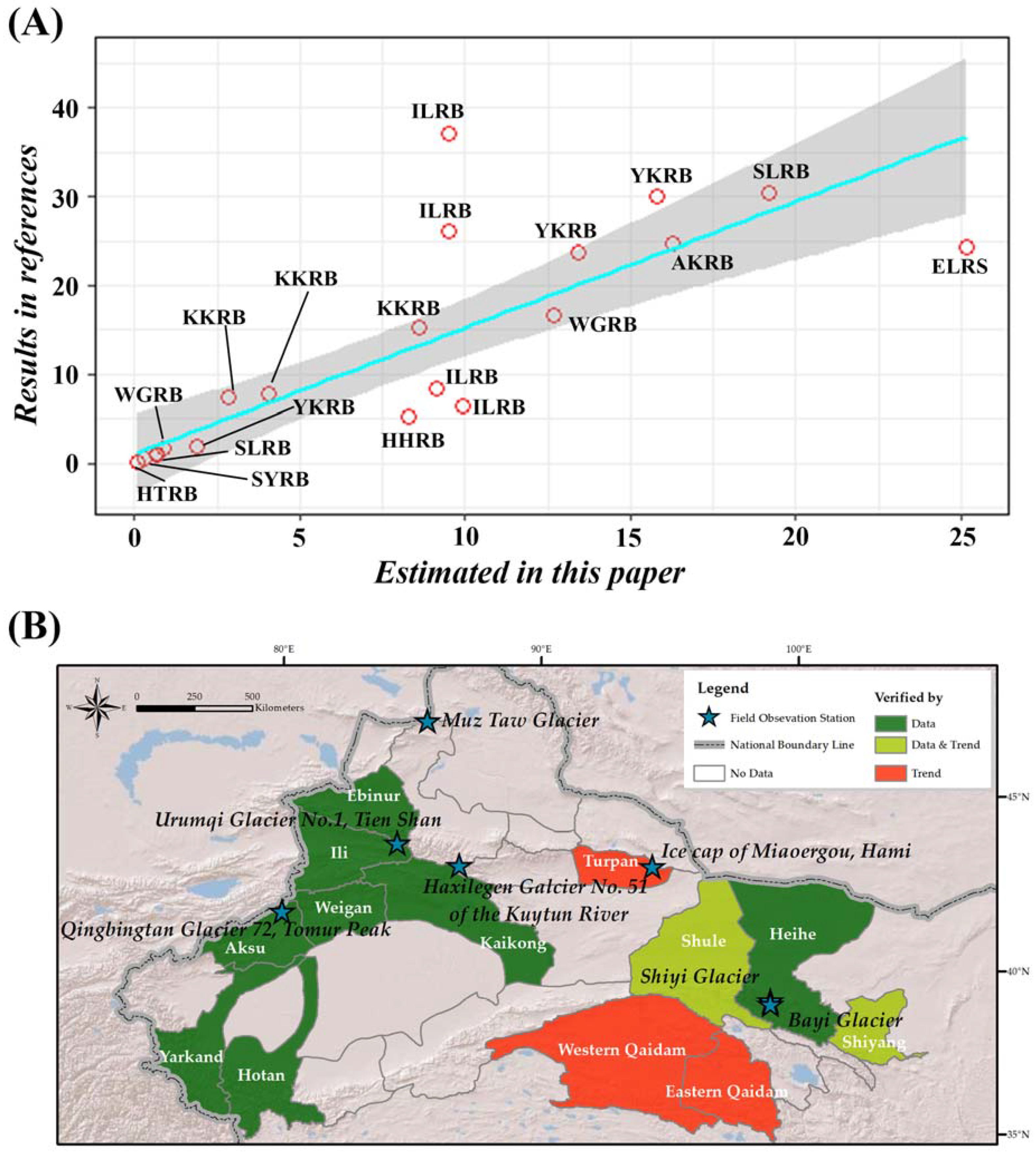
4.1. Precipitation Correction at High Altitudes
4.2. Comparison of GR Estimations
4.3. Implications for the Evaluation and Prediction of GR
4.4. Socioeconomic Consequences
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Beniston, M.; Stoffel, M. Assessing the impacts of climatic change on mountain water resources. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraaijenbrink, P.D.A.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Lutz, A.F.; Immerzeel, W.W. Impact of a global temperature rise of 1.5 degrees Celsius on Asia’s glaciers. Nature 2017, 549, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaser, G.; Großhauser, M.; Marzeion, B. Contribution potential of glaciers to water availability in different climate regimes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, C.; Ciais, P.; Liu, D.; Yang, H.; Piao, S.; Yao, T. Atmospheric dynamic constraints on Tibetan Plateau freshwater under Paris climate targets. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Xiao, C.; Chen, D.; Huang, Y.; Che, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zou, M.; Guo, R.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; et al. Glacier change in China over past decades: Spatiotemporal patterns and influencing factors. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 226, 103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarfl, C.; Lumsdon, A.E.; Berlekamp, J.; Tydecks, L.; Tockner, K. A global boom in hydropower dam construction. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 77, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, L.; Dou, W.; Jie, J.; Ma, X. Evaluation of Glacier Tourism Service Potential in Different Periods based on GIS-Taking Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region as an Example. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2020, 16, 1283–1291. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Asia’s water balance. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghari, A.N.; Vanham, D.; Rauch, W. The Indus basin in the framework of current and future water resources management. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 1063–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Zhou, B.; Xiao, C. Progress in studies of cryospheric changes and their impacts on climate of China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2014, 28, 732–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ding, Y.; Fang, Y. Adaptation research of cryosphere change in China: Advances and prospections. Clim. Chang. Res. 2019, 15, 178–186. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, K.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B.; et al. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, T.; Kang, S.; Shangguan, D.; Luo, X. Albedo reduction as an important driver for glacier melting in Tibetan Plateau and its surrounding areas. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 220, 103735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yao, T.; Yang, W.E.I.; Xu, B.; Wu, G.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y. Reconstruction of the mass balance of Muztag Ata No. 15 glacier, eastern Pamir, and its climatic drivers. J. Glaciol. 2018, 64, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, D.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Hameed, A.; Tseng, K.-H.; Jan, B.; Abbas, N.; Kao, H.-C.; Lan, W.-H.; Imani, M. Spaceborne Satellite for Snow Cover and Hydrological Characteristic of the Gilgit River Basin, Hindukush–Karakoram Mountains, Pakistan. Sensors 2019, 19, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, S.; Keshari, A.K. Investigating mass balance of Parvati glacier in Himalaya using satellite imagery based model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Ma, W.; Yao, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Qin, D. Evaluation and spatiotemporal characteristics of glacier service value in the Qilian Mountains. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 1233–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; He, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, P. Evaluation on glaciers ecological services value in the Tianshan Mountains, Northwest China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huss, M.; Hock, R. Global-scale hydrological response to future glacier mass loss. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avtar, R.; Aggarwal, R.; Kharrazi, A.; Kumar, P.; Kurniawan, T.A. Utilizing geospatial information to implement SDGs and monitor their Progress. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 192, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolch, T.; Shea, J.M.; Liu, S.; Azam, F.M.; Gao, Y.; Gruber, S.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Kulkarni, A.; Li, H.; Tahir, A.A.; et al. Status and Change of the Cryosphere in the Extended Hindu Kush Himalaya Region. In The Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment: Mountains, Climate Change, Sustainability and People; Wester, P., Mishra, A., Mukherji, A., Shrestha, A.B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 209–255. [Google Scholar]
- Georg, G.; William, S.K. Mountain Forests and Sustainable Development: The Potential for Achieving the United Nations’ 2030 Agenda. Mt. Res. Dev. 2017, 37, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, R.; Sulser, T.B.; Huefner, R.; Mason-D’Croz, D.; Dunston, S.; Nautiyal, S.; Ringler, C.; Schuengel, J.; Tikhile, P.; Wimmer, F.; et al. Agricultural Development and Land Use Change in India: A Scenario Analysis of Trade-Offs between UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Earths Future 2020, 8, e2019EF001287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, G.; Molden, D. The Global Social and Economic Consequences of Mountain Cryospheric Change. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Guo, S.; Huang, H.; Liu, W.; Xiang, Y. Information and Communications Technologies for Sustainable Development Goals: State-of-the-Art, Needs and Perspectives. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 2389–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.K.; Mishra, I. United Nations Sustainable Development Goals 2030 and environmental sustainability: Race against time. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 2, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagno, L.; Eggs, S.; Huss, M.; Zekollari, H.; Farinotti, D. Brief communication: Do 1.0, 1.5, or 2.0 °C matter for the future evolution of Alpine glaciers? Cryosphere 2021, 15, 2593–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausner, V.H.; Engen, S.; Brattland, C.; Fauchald, P. Sámi knowledge and ecosystem-based adaptation strategies for managing pastures under threat from multiple land uses. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 57, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, R.; Clivaz, M.; Reynard, E.; Backhaus, N. Increasing Landscape Appreciation through the Landscape Services Approach. A Case Study from Switzerland. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-López, B.; Leister, I.; Lorenzo Cruz, P.; Palomo, I.; Grêt-Regamey, A.; Harrison, P.A.; Lavorel, S.; Locatelli, B.; Luque, S.; Walz, A. Nature’s contributions to people in mountains: A review. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, H.; Fang, G.; Li, Z. Changes in Central Asia’s Water Tower: Past, Present and Future. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Sillanpää, M.; Gjessing, E.T.; Vogt, R.D. Water quality in the Tibetan Plateau: Major ions and trace elements in the headwaters of four major Asian rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 6242–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, J. Spatial and temporal trends of climate change in Xinjiang, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Liu, W.; Yin, Z.; Fu, G.; Zheng, C. How Will Climate Change Affect the Water Availability in the Heihe River Basin, Northwest China? J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1517–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, B.; Gui, D.; Liu, Y.; Feng, L.; Dai, H. Assessing water distribution and agricultural expansion in the Cele Oasis, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Guo, H.; Qin, D.; Pan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, W.; Ma, X. Contribution of recycled moisture to precipitation in the monsoon marginal zone: Estimate based on stable isotope data. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Ge, Y.; Li, H.; Han, F.; Hu, X.; Tian, W.; Tian, Y.; Pan, X.; Nian, Y.; et al. Hydrological Cycle in the Heihe River Basin and Its Implication for Water Resource Management in Endorheic Basins. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 890–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.P.; Adam, J.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions. Nature 2005, 438, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W. Variation of baseflows in the headstreams of the Tarim River Basin during 1960–2007. J. Hydrol. 2013, 487, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, H.D. Asia’s shrinking glaciers protect large populations from drought stress. Nature 2019, 569, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Wu, L.; Shangguan, D.; Yao, X.; Wei, J.; Bao, W.; Yu, P.; Liu, Q.; et al. The second Chinese glacier inventory: Data, methods and results. J. Glaciol. 2015, 61, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemp, M.; Huss, M.; Thibert, E.; Eckert, N.; McNabb, R.; Huber, J.; Barandun, M.; Machguth, H.; Nussbaumer, S.U.; Gärtner-Roer, I.; et al. Global glacier mass changes and their contributions to sea-level rise from 1961 to 2016. Nature 2019, 568, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, F.; Berthier, E.; Wagnon, P.; Kääb, A.; Treichler, D. A spatially resolved estimate of High Mountain Asia glacier mass balances from 2000 to 2016. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shean, D.E.; Bhushan, S.; Montesano, P.; Rounce, D.R.; Arendt, A.; Osmanoglu, B. A Systematic, Regional Assessment of High Mountain Asia Glacier Mass Balance. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 7, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Nie, L.; Xu, J.; Lu, X.; Li, S. Exploration of the Snow Ablation Process in the Semiarid Region in China by Combining Site-Based Measurements and the Utah Energy Balance Model—A Case Study of the Manas River Basin. Water 2019, 11, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shi, X.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Pan, X.; Déry, S.J.; Zhou, P. Partitioning the contributions of glacier melt and precipitation to the 1971–2010 runoff increases in a headwater basin of the Tarim River. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.-Z.; Yang, T.-B.; Lv, H.; Li, C.-X.; He, Y.-B. Climate change and glacier area variations in China during the past half century. J. Mt. Sci. 2016, 13, 1345–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, L.; Yue, X. Glaciers in Xinjiang, China: Past Changes and Current Status. Water 2020, 12, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ding, Y.; Shangguan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Han, H.; Wang, J.; Xie, C. Glacier retreat as a result of climate warming and increased precipitation in the Tarim river basin, northwest China. Ann. Glaciol. 2006, 43, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Du, M.; Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, P. Quantitative evaluation of glacier change and its response to climate change in the Chinese Tien Shan. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 153, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Zhou, P.; Wang, W.; Jin, S.; Li, H.; Wang, F.; Yao, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L. Recent changes of two selected glaciers in Hami Prefecture of eastern Xinjiang and their impact on water resources. Quat. Int. 2015, 358, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Shu, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S. Analysis of water level variation of lakes and reservoirs in Xinjiang, China using ICESat laser altimetry data (2003–2009). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Jin, H. Evolutions of water stable isotopes and the contributions of cryosphere to the alpine river on the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 75, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Han, C.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Kang, E. Maximum precipitation altitude on the northern flank of the Qilian Mountains, northwest China. Hydrol. Res. 2018, 49, 1696–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, K. Tributary glacier surges: An exceptional concentration at Panmah Glacier, Karakoram Himalaya. J. Glaciol. 2007, 53, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; van Beek, L.P.H.; Konz, M.; Shrestha, A.B.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Hydrological response to climate change in a glacierized catchment in the Himalayas. Clim. Chang. 2012, 110, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tuerxunbai, G.; Su, L.; Li, Q. Spatial and temporal characteristics of climate change at different altitudes in Xinjiang in the past 60 years. Arid Land Geogr. 2019, 42, 822–829. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Nuimura, T. Spatially heterogeneous wastage of Himalayan glaciers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, A.; Nuimura, T.; Fujita, K.; Takenaka, S.; Nagai, H.; Lamsal, D. Climate regime of Asian glaciers revealed by GAMDAM glacier inventory. Cryosphere 2015, 9, 865–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Ding, Y. Observed degree-day factors and their spatial variation on glaciers in western China. Ann. Glaciol. 2006, 43, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Wanders, N.; Lutz, A.F.; Shea, J.M.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Reconciling high-altitude precipitation in the upper Indus basin with glacier mass balances and runoff. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4673–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kääb, A.; Berthier, E.; Nuth, C.; Gardelle, J.; Arnaud, Y. Contrasting patterns of early twenty-first-century glacier mass change in the Himalayas. Nature 2012, 488, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, P.; Bhambri, R.; Kawishwar, P.; Dobhal, D.P. Water level changes of high altitude lakes in Himalaya–Karakoram from ICESat altimetry. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 122, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Granados, F.; Jurado-Expósito, M.; Peña-Barragán, J.M.; García-Torres, L. Using geostatistical and remote sensing approaches for mapping soil properties. Eur. J. Agron. 2005, 23, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, F.; Barry, R.G.; Cogley, J.G.; Frey, H.; Haeberli, W.; Ohmura, A.; Ommanney, C.S.L.; Raup, B.; Rivera, A.; Zemp, M. Recommendations for the compilation of glacier inventory data from digital sources. Ann. Glaciol. 2009, 50, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racoviteanu, A.E.; Paul, F.; Raup, B.; Khalsa, S.J.S.; Armstrong, R. Challenges and recommendations in mapping of glacier parameters from space: Results of the 2008 Global Land Ice Measurements from Space (GLIMS) workshop, Boulder, Colorado, USA. Ann. Glaciol. 2009, 50, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Non-Parametric Test against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M. Rank Correlation Mehods, 4th ed.; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Bliss, A.; Hock, R.; Radić, V. Global response of glacier runoff to twenty-first century climate change. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagg, W.; Mayer, C.; Lambrecht, A.; Kriegel, D.; Azizov, E. Glacier changes in the Big Naryn basin, Central Tian Shan. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 110, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, F.; Frey, H.; Le Bris, R. A new glacier inventory for the European Alps from Landsat TM scenes of 2003: Challenges and results. Ann. Glaciol. 2011, 52, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clouse, C.; Anderson, N.; Shippling, T. Ladakh’s artificial glaciers: Climate-adaptive design for water scarcity. Clim. Dev. 2017, 9, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S. Robust Locally Weighted Regression and Smoothing Scatterplots. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S.; Devlin, S.J. Locally weighted regression: An approach to regression analysis by local fitting. J. Am Stat. Assoc. 1988, 83, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Liu, S.; Yao, X.; Guo, W.; Xu, J. Glacier changes in the Qilian Mountains in the past half-century: Based on the revised First and Second Chinese Glacier Inventory. Acta Geograpica Sin. 2015, 70, 1402–1414. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Zhao, Q.D.; Wu, J.H.; Ding, Y.J.; Qin, J.; Wei, H.; Zeng, D. Quantitative simulation of the runoff components and its variation characteristics in the upstream of the Shule River. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2019, 41, 907–917. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-Q.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X.-W. Glacial runoff likely reached peak in the mountainous areas of the Shiyang River Basin, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2015, 12, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.F.; Srivastava, S. Mass balance and runoff modelling of partially debris-covered Dokriani Glacier in monsoon-dominated Himalaya using ERA5 data since 1979. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, C.; Xu, Z.; Zuo, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, J. Vertical influence of temperature and precipitation on snow cover variability in the Yarlung Zangbo River basin, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 1148–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baojuan, H.; Weijun, S.; Junyao, W.; Yetang, W.; Zhongqin, L.; Hui, Z. A long glacier mass balance record analysis in Chinese Urumqi Glacier No. 1 and the relationships with changes in large-scale circulations. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, B.; Jakobs, C.L.; van Pelt, W.J.J.; Lhermitte, S.; Wouters, B.; Kohler, J.; Hagen, J.O.; Luks, B.; Reijmer, C.H.; van de Berg, W.J.; et al. Low elevation of Svalbard glaciers drives high mass loss variability. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Shi, F.; Sheng, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z.; Han, M.; Yilihamu, Y. Regional Differentiation Characteristics of Precipitation Changing with Altitude in Xinjiang Region in Recent 50 Years. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2011, 33, 1203–1213. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Li, L.; Shi, C.; Liu, T.; Meng, X.; Yang, Y. An Overview of Precipitation Characteristics and Its Research Progress in Tianshan Mountains Area, China. J. North China Univ. Water Resour. Electr. Power (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2011, 38, 38–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A. The Climate of the Gongga Shan Range, Sichuan Province, PR China. Arct. Alp. Res 1997, 29, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G. The Study of Glacier Changes in the Gongga Mountains. Doctoral Dissertation, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2012. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CDFD1214&filename=1013122660.nh (accessed on 18 June 2021).
- Zhang, H. Precipitation Gradient in Tianshan Mountain Area Based on Multi-Source Precipitation Data. Master’s Thesis, Northwest Normal University, Lanzhou, China, 2020. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD202101&filename=1020977265.nh (accessed on 18 June 2021).
- Wang, X. Hydrological Response to Atmospheric Temperature Changes in the Qaidam Basin and Its Surroundings over Past 60 Years. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2019. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD202001&filename=1019674546.nh (accessed on 18 June 2021).
- Jin, X.; Zhang, L.; Gu, J.; Zhao, C.; Tian, J.; He, C. Modelling the impacts of spatial heterogeneity in soil hydraulic properties on hydrological process in the upper reach of the Heihe River in the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China. Hydrol. Processes 2015, 29, 3318–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Zhang, L.; Ou, T.; Chen, D.; Yao, T.; Tong, K.; Qi, Y. Hydrological response to future climate changes for the major upstream river basins in the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 136, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Lu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Xie, J.; Long, A.; Yin, Z.; Zou, S. Glacier changes and their impacts on the discharge in the past half-century in Tekes watershed, Central Asia. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2015, 89–90, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Cao, X.; Shen, Y.; Gao, Q.; Wang, S. Surface Water Resources and Its Trends in Weigan River Basin on the South Slope of Tianshan, China during 1956–2007. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2010, 32, 1211–1219. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Wang, R.; Giese, E. Impact of Climate Change on Surface Runoff of Tarim River Originating from the South Slopes of the Tianshan Mountains. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2008, 30, 1–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abla, M.; Eziz, M.; Yimit, H.; Anwar, G.; Mamatimin, Y. Runoff Variation Characteristics in Ebinur Lake Basin During 1964–2012. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2016, 32, 67–73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lan, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y. Mountainous runoff changes and climate factors analysis of the Shule River Basin in 1958–2015. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2017, 37, 1894. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Xu, Z. Evaluation of Gridded Precipitation Data for Driving SWAT Model in Area Upstream of Three Gorges Reservoir. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, H.; Yao, T.; Li, H.; Duan, S. Quantitative water resources assessment of Qinghai Lake basin using Snowmelt Runoff Model (SRM). J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, S.; Shangguan, D.; Radić, V.; Zhang, Y. Spatial Heterogeneity in Glacier Mass-Balance Sensitivity across High Mountain Asia. Water 2019, 11, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, K.; Wang, L. Study on recent glacier changes and their impact on water resources in Xinjiang, north western China. Quat. Sci. 2010, 30, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, S.; Ye, B.; Qiao, C. Glacier Runoff Change in the Upper Stream of Yarkand River and Its Impact on River Runoff during 1961–2006. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2010, 32, 445–453. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakko, K.P. Continuous Snow and Rain Data at 500 to 4400 m Altitude near Annapurna, Nepal, 1999–2001. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2004, 36, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Hu, Q. Changes of Precipitation-Runoff Relationship Induced by Climate Variation in a Large Glaciated Basin of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadlo, I.; Paris, C.; Callegari, M.; Marin, C.; Günther, D.; Strasser, U.; Notarnicola, C.; Bruzzone, L. Integrating Models and Remote Sensing Data for Distributed Glacier Mass Balance Estimation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 6177–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bury, J.; Mark, B.G.; Carey, M.; Young, K.R.; McKenzie, J.M.; Baraer, M.; French, A.; Polk, M.H. New Geographies of Water and Climate Change in Peru: Coupled Natural and Social Transformations in the Santa River Watershed. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2013, 103, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, E.; McCarthy, M.; Dehecq, A.; Kneib, M.; Fugger, S.; Pellicciotti, F. Health and sustainability of glaciers in High Mountain Asia. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data | Period | Resolution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation (Prmd,d) (m) | 1961–2015 | 0.25° × 0.25° and daily | Asian Precipitation—Highly Resolved Observational Data Integration towards Evaluation of Water Resources MA_v1101 and MA_v1101_EXR1, http://aphrodite.st.hirosaki-u.ac.jp/product (accessed on 16 March 2021) |
| Temperature (T) (°C) | 1961–2015 | 0.25° × 0.25° and daily | Asian Precipitation—Highly Resolved Observational Data Integration towards Evaluation of Water Resources MA_1808 TEMP, http://aphrodite.st.hirosaki-u.ac.jp/product (accessed on 16 March 2021) |
| Degree-day factor on ice (DDFice) (mm °C−1 d−1) | 0.5° × 0.5° | The Science Data Bank, http://www.sciencedb.cn/dataSet/handle/747 (accessed on 15 May 2021) | |
| Degree-day factor on snow (DDFsnow) (mm °C−1 d−1) | 0.5° × 0.5° | The Science Data Bank, http://www.sciencedb.cn/dataSet/handle/747 (accessed on 15 May 2021) | |
| DEMs (H) (m) | STRM, http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org (accessed on 14 February 2021) | ||
| Land use | 2015–2019 | 100 × 100 m | Copernicus Global Land Service (CGLS) LC100 collection 3, http://land.copernicus.eu/global/products/lc (accessed on 28 August 2021) |
| Watershed outlines | The Resource and Environment Science and Data Center of the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, http://www.resdc.cn/data.aspx?DATAID=278 (accessed on 13 Mar 2021) | ||
| Glacier outlines | Randolph Glacier Inventory, https://www.glims.org/RGI/rgi60_dl.html (accessed on 18 February 2021) |
| Name | Abbreviation | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Qilian Shan | QL | Glacier regions |
| Eastern Kunlun | EK | |
| Western Kunlun | WK | |
| Eastern Tien Shan | ET | |
| Western Tien Shan | WT | |
| Karakoram | KA | |
| Pamir | PA | |
| Hissar Alay | HA | |
| Aksu River Basin | AKRB | Watersheds |
| Datong River Above Hall | DTRB | |
| Eastern Rivers Basin | ETRB | |
| Ebinur Lake River System | ELRS | |
| Hami Basin | HMB | |
| Heihe River Basin | HHRB | |
| Hotan River Basin | HTRB | |
| Ili River Basin | ILRB | |
| Kai-kong River Basin | KKRB | |
| Kashgar River Basin | KSRB | |
| Kriya Rivers Basin | KYRB | |
| Middle Rivers Basin | MDRB | |
| Pai Basin | PAB | |
| Eastern Qaidam Basin | EQB | |
| Western Qaidam Basin | WQB | |
| Qarqan Rivers Basin | QQRB | |
| Qinghai Lake River System | QHRS | |
| Shiyang River Basin | SYRB | |
| Shule River Basin | SLRB | |
| Turpan Basin | TPB | |
| Weigan River Basin | WGRB | |
| Yarkand River Basin | YKRB | |
| Glacier runoff | GR | Glacier runoff |
| Meltwater runoff | MR | |
| Delayed water runoff | DR | |
| Hyperarid regions | HA | Dryland areas |
| Semiarid and arid regions | SA | |
| Semiarid, arid, and hyperarid regions | SAH | |
| Semiarid regions | S | |
| Arid regions | A |
| Region | Hpre_m |
|---|---|
| Qilian Shan | 4200 [54,87] |
| Eastern Tien Shan | 3000 [57] |
| Western Tien Shan | 3000 [57] |
| Eastern Kunlun | 4500 |
| Western Kunlun | 4000 |
| Karakoram | 2500 [56] |
| Pamir | 3000 [55] |
| Hissar Alay | 3000 [55] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leng, X.; Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Zhang, Y. The Spatiotemporal Change of Glacier Runoff Is Comparably Attributed to Climatic Factors and Physical Properties in Northwestern China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102393
Leng X, Feng X, Fu B, Zhang Y. The Spatiotemporal Change of Glacier Runoff Is Comparably Attributed to Climatic Factors and Physical Properties in Northwestern China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(10):2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102393
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeng, Xuejing, Xiaoming Feng, Bojie Fu, and Yu Zhang. 2022. "The Spatiotemporal Change of Glacier Runoff Is Comparably Attributed to Climatic Factors and Physical Properties in Northwestern China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 10: 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102393
APA StyleLeng, X., Feng, X., Fu, B., & Zhang, Y. (2022). The Spatiotemporal Change of Glacier Runoff Is Comparably Attributed to Climatic Factors and Physical Properties in Northwestern China. Remote Sensing, 14(10), 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102393