Moving Multitarget Detection Using a Multisite Radar System with Widely Separated Stations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- 1.
- A scheme of space mapping is presented to integrate the observation data of a moving target from different views. The observation data are gathered in the corresponding SRC, so the multitarget detection problem is split into several statistical decision problems in each SRC. The relationships between physical targets and “ghost targets” are analyzed.
- 2.
- The interference discrimination (ID)-based detector is developed to overcome the “ghost target” problem. The detection problem is formulated based on ternary hypothesis testing and can be solved in two steps. The background interference is discriminated between “ghost target” and pure noise, and then the presence of target is decided based on GLRT.
- 3.
- Experiments performed on simulation database verify the advantages of the proposed ID-based detector compared with the traditional GLRT detector.
2. Signal Model
2.1. Received Signal
2.2. Spatial Mapping
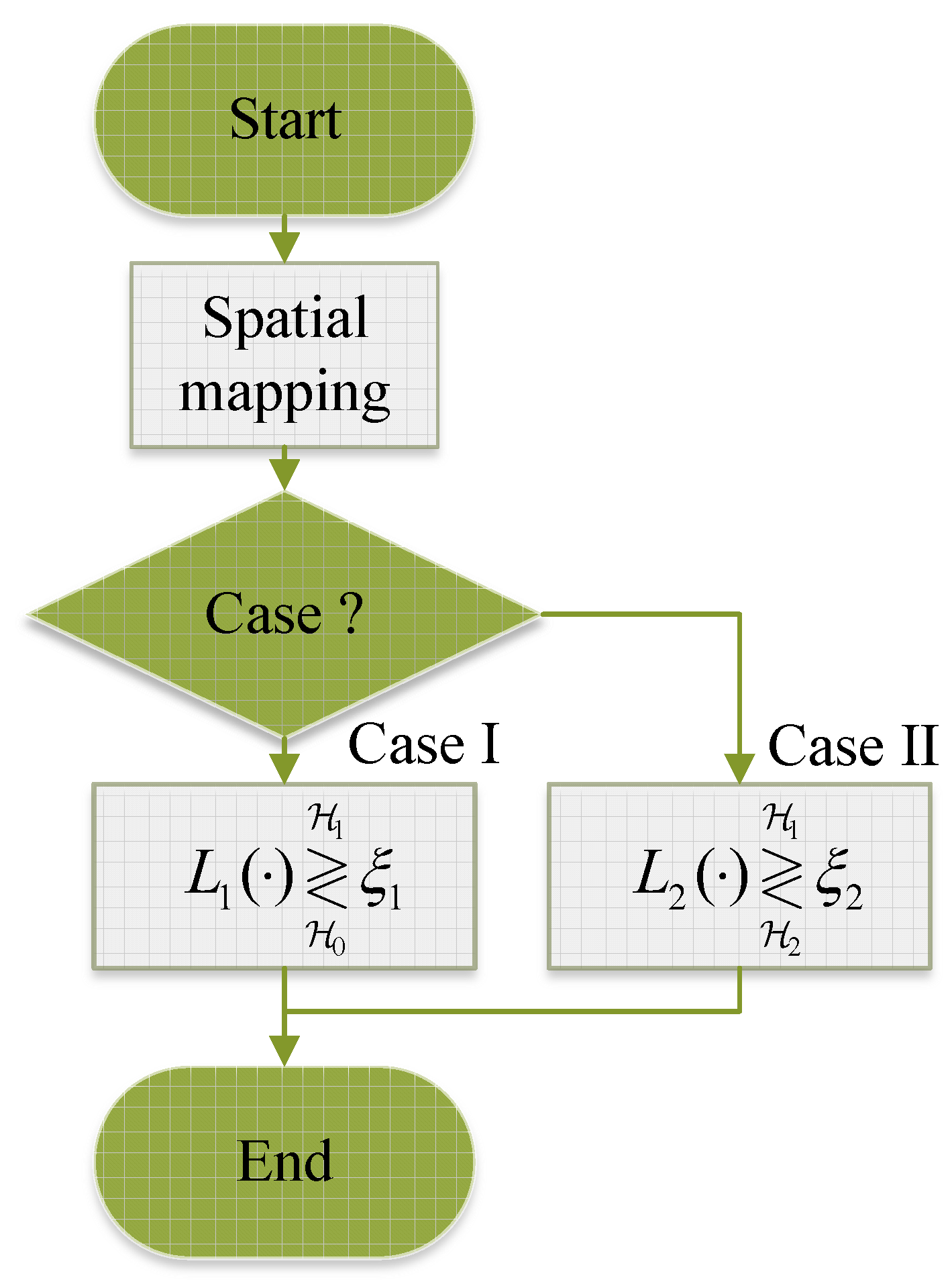
3. Detection of Multiple Moving Targets
3.1. Interference Discrimination-Based Detection Method
3.1.1. Interference Discrimination
3.1.2. Target Detection Method
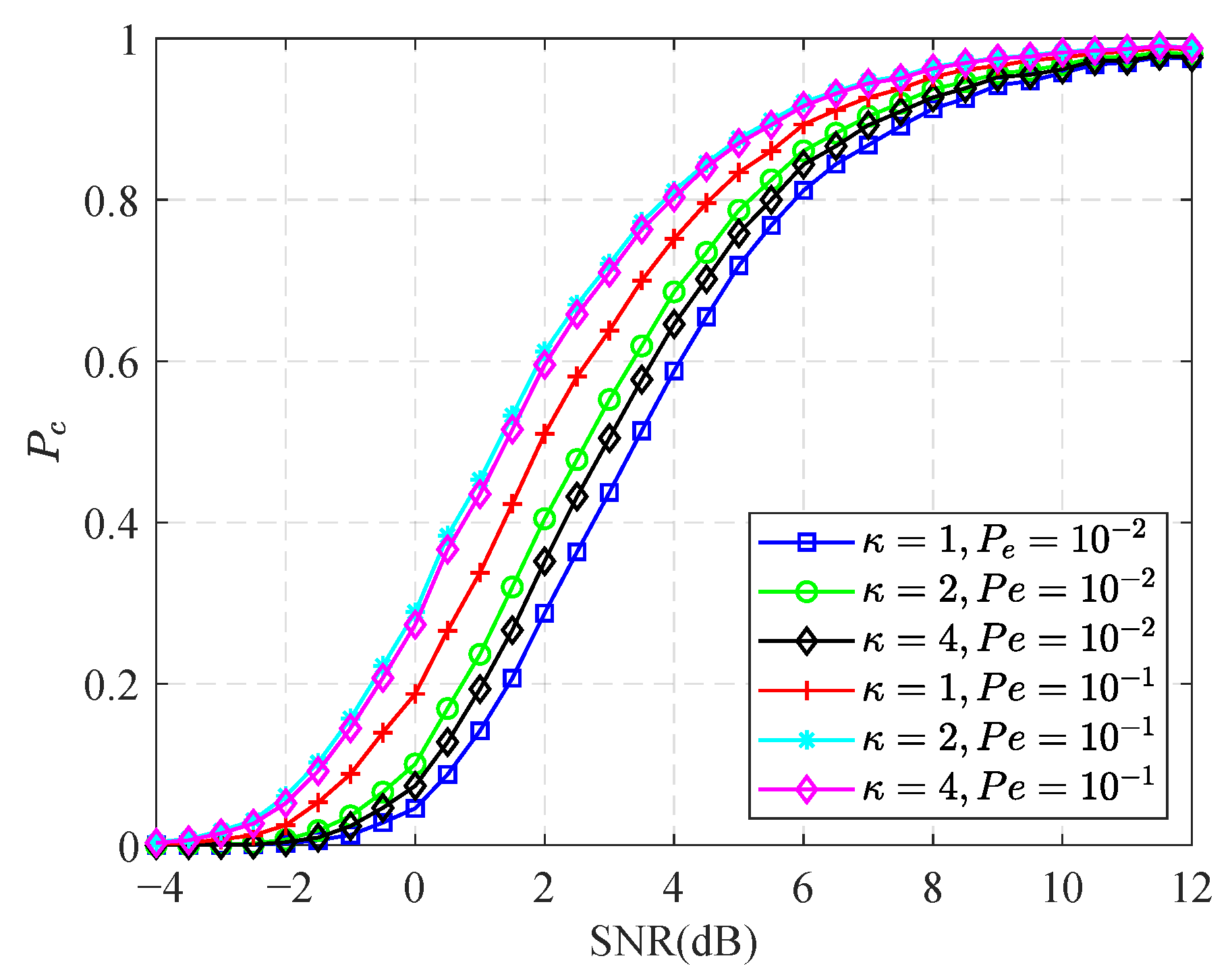
3.2. Performance Analysis
3.2.1. Performance of Original Detector
3.2.2. Performance of ID-Based Detector
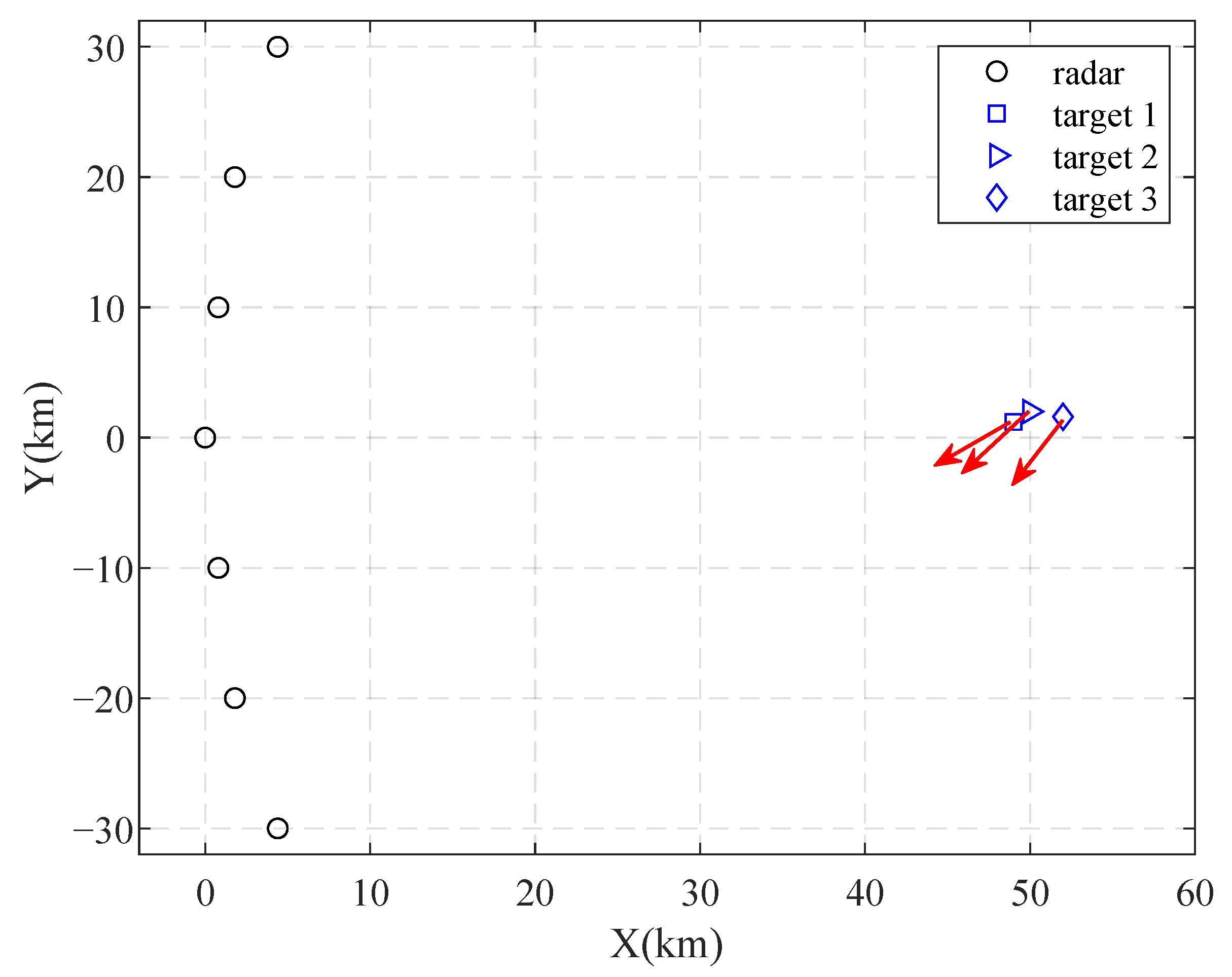
4. Numerical Experiment
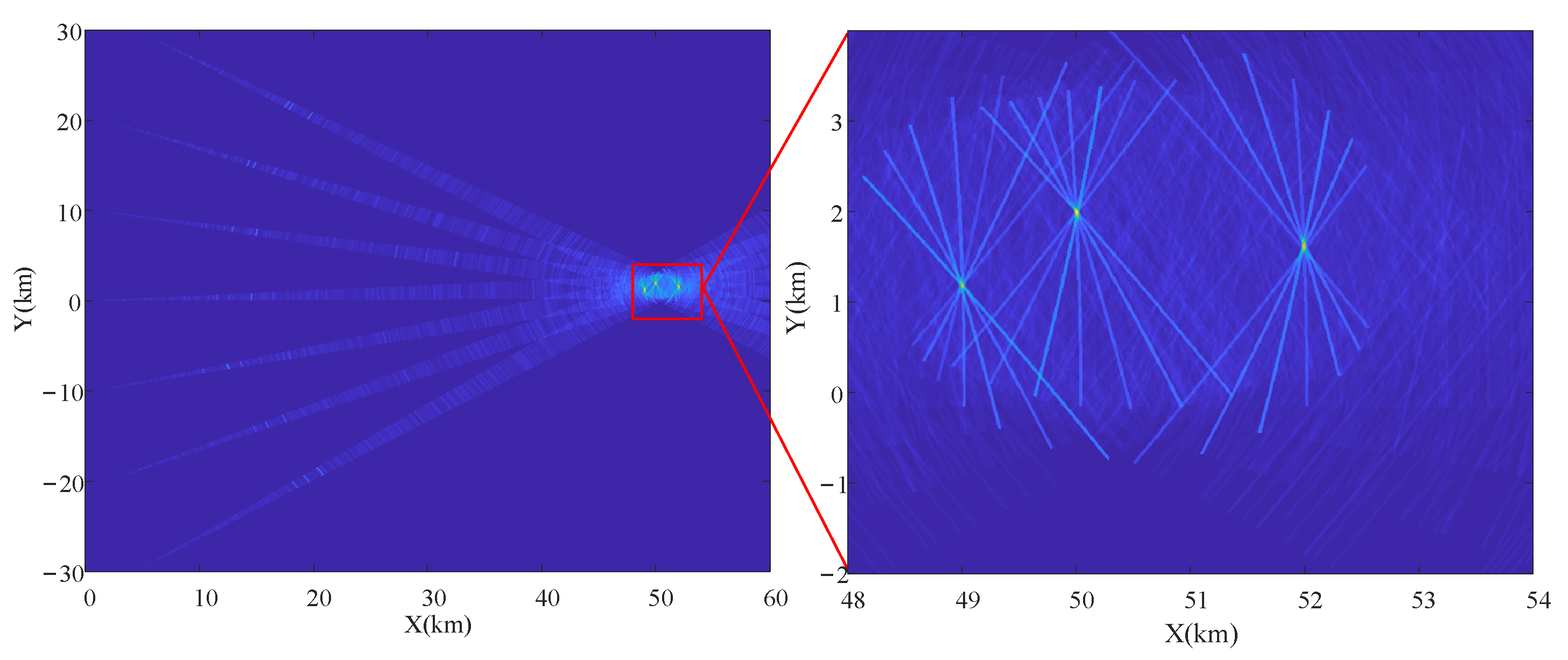
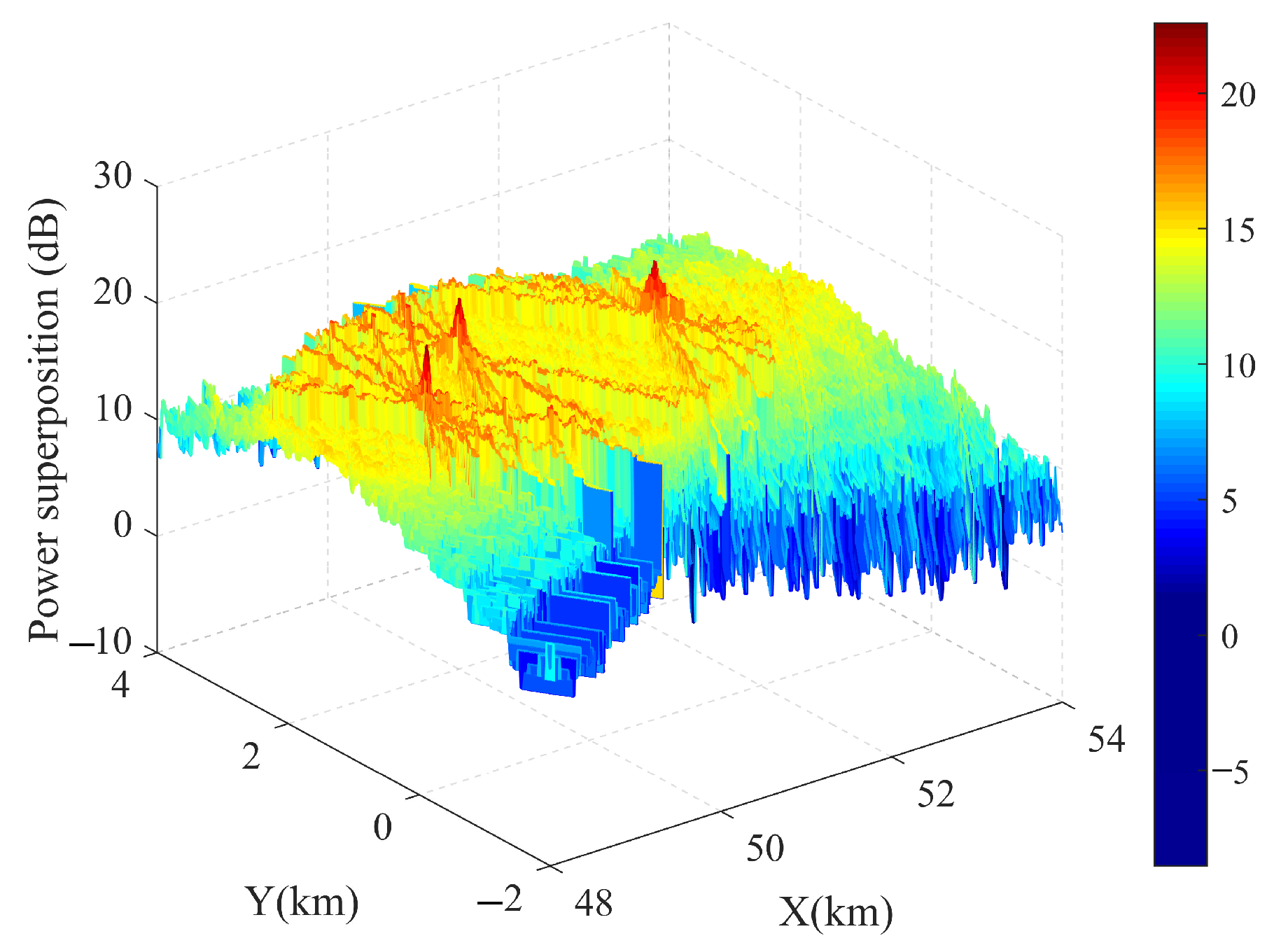
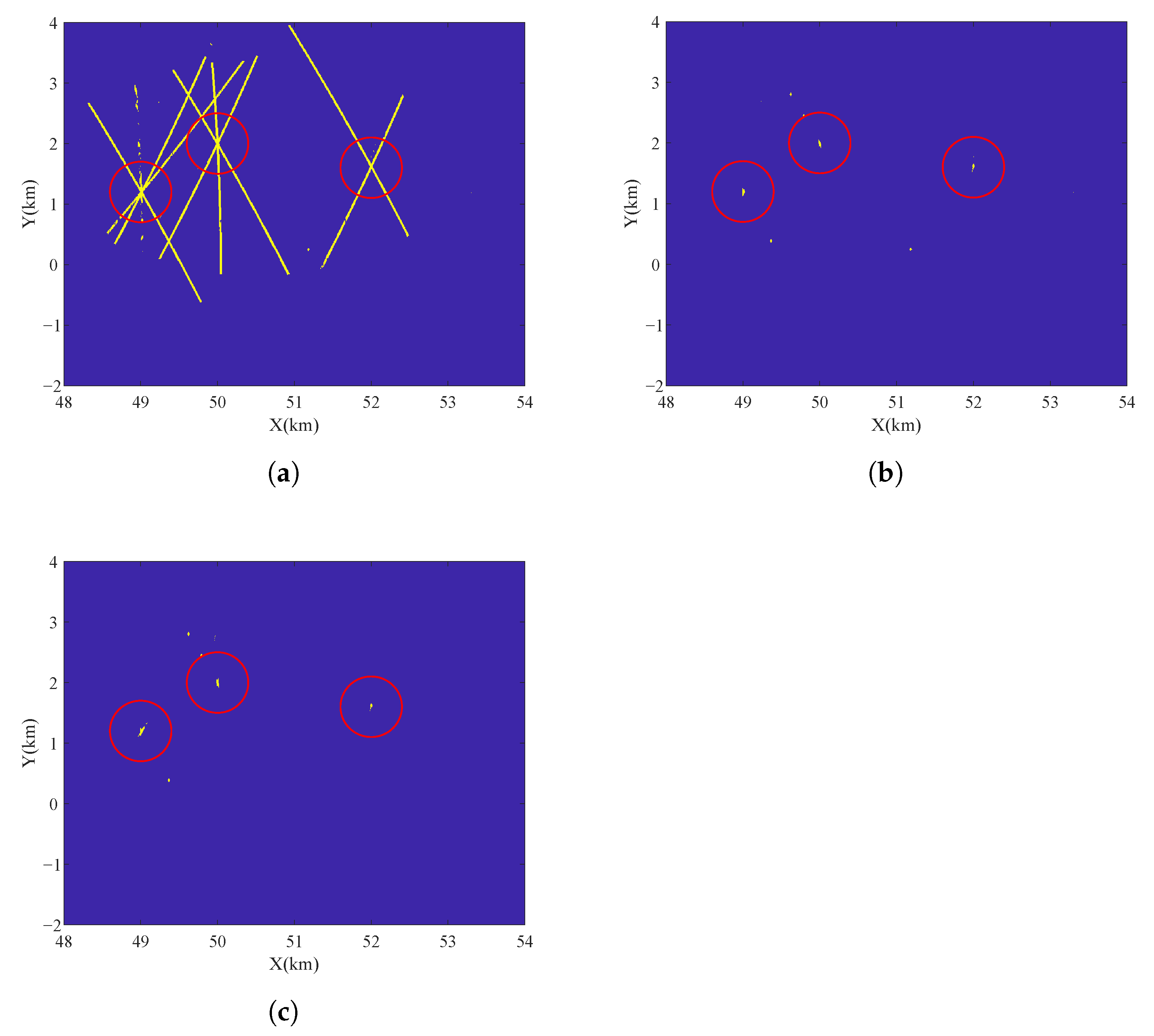
4.1. Power Superposition and “Ghost Target”
4.2. Background Interference Discrimination
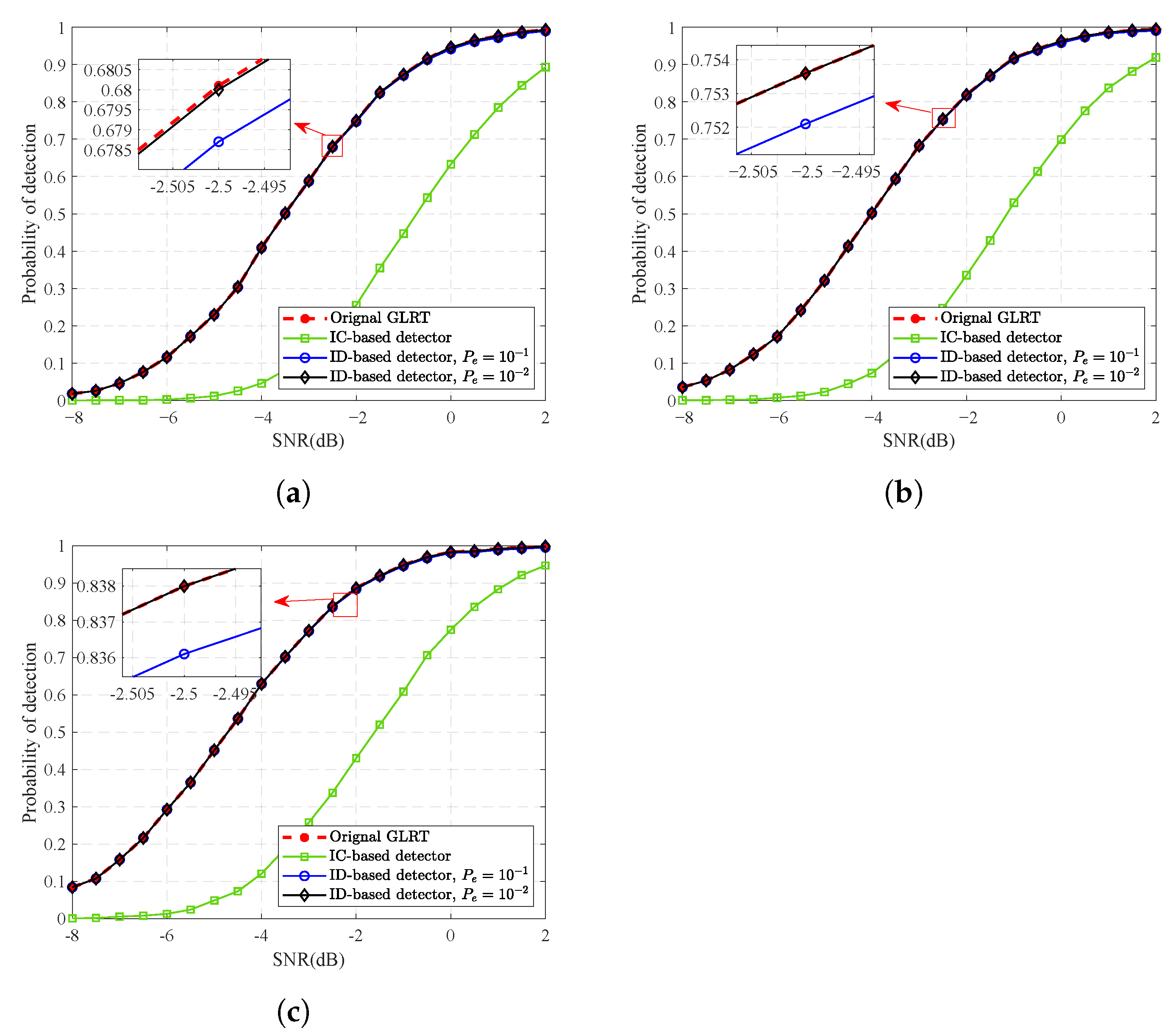
4.3. Comparison of Original GLRT and ID-Based Detector
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Chernyak, V.S. Fundamentals of Multisite Radar Systems: Multistatic Radars and Multiradar Systems; Gordon and Breach: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Zhou, X.; Yang, W. Moving Target Detection in Multi-Static GNSS-Based Passive Radar Based on Multi-Bernoulli Filter. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, S.; Su, H.; Yu, Y. Detection performance of spatial-frequency diversity MIMO radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 3137–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledergerber, A.; D’Andrea, R. A Multi-Static Radar Network with Ultra-Wideband Radio-Equipped Devices. Sensors 2020, 20, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Z.; Li, J.; Guo, Q.; Ding, J. Efficient Direct Target Localization for Distributed MIMO Radar With Expectation Propagation and Belief Propagation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 4055–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Ke, W.; Wang, T. Multi-target localization using distributed MIMO radar based on spatial sparsity. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Applications (ICAICA), Dalian, China, 28–30 June 2021; pp. 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, J. Multiple Object Localization and Vital Sign Monitoring Using IR-UWB MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2020, 56, 4437–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H. Hermitian Distance-Based Method to Discriminate Physical Targets and Active False Targets in A Distributed Multiple-Radar Architecture. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 10432–10442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, S. Polarimetric multiple-radar architectures with distributed antennas for discriminating between radar targets and deception jamming. Digit. Signal Process. 2019, 90, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Liao, G.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S. Mainlobe deceptive jammer suppression using element-pulse coding with MIMO radar. Signal Process. 2021, 182, 107955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimovich, A.M.; Blum, R.S.; Cimini, L.J. MIMO Radar with Widely Separated Antennas. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xia, X.G. Persymmetric Adaptive Detection of Subspace Signals: Algorithms and Performance Analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 6124–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghojavand, K.; Derakhtian, M.; Biguesh, M. Rao-Based Detectors for Adaptive Target Detection in the Presence of Signal-Dependent Interference. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 1662–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Ono, Y.; Peng, L.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H. Target Detection Within Nonhomogeneous Clutter Via Total Bregman Divergence-Based Matrix Information Geometry Detectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 4326–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, S.H.; Farina, A. Radar networks: A review of features and challenges. Inf. Fusion 2020, 61, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, R.; Varshney, P.K.; Cheng, Q. Distributed detection in a large wireless sensor network. Inf. Fusion 2006, 7, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, S.H.; Peiravi, A. Fusion of weighted decisions in wireless sensor networks. IET Wirel. Sens. Syst. 2015, 5, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Peng, Y.N.; He, Y.; Meng, X.W. Three types of distributed CFAR detection based on local test statistic. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2002, 38, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Lehmann, N.H.; Blum, R.S.; Haimovich, A.M. MIMO Radar Moving Target Detection in Homogeneous Clutter. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2010, 46, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishler, E.; Haimovich, A.; Blum, R.; Cimini, L.; Chizhik, D.; Valenzuela, R. Spatial Diversity in Radars—Models and Detection Performance. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 823–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, H. Space-Partition-Based Target Detection for Distributed MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2013, 49, 2717–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanipour, V.; Olfat, A. CFAR detection for multistatic radar. Signal Process. 2011, 91, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S. Signal fusion-based target detection algorithm for spatial diversity radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2011, 5, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, Z.; Derakhtian, M. Performance analysis of the matched subspace detector in the presence of signal-dependent interference for MIMO radar. Signal Process. 2020, 176, 107709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okello, N.; Challa, S. Joint sensor registration and track-to-track fusion for distributed trackers. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2004, 40, 808–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yan, J.; Peng, Y. A Distributed Detection Scheme for Multiple Monostatic Radars. In Proceedings of the 2006 CIE International Conference on Radar, Shanghai, China, 16–19 October 2006; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Su, H.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J. Target detection in distributed MIMO radar with registration errors. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2016, 52, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Su, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, S.; Huang, J. Centralized Adaptive CFAR Detection With Registration Errors in Multistatic Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 2370–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folster, F.; Rohling, H. Data association and tracking for automotive radar networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2005, 6, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsios, M.N.; Alivizatos, E.G.; Uzunoglu, N.K. Solving the association problem for a multistatic range-only radar target tracker. Signal Process. 2008, 88, 2254–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Su, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, S.; Huang, J. Spatial resolution cell based centralized target detection in multistatic radar. Signal Process. 2018, 152, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Zhou, T.; Ai, Y.; Blum, R.S. Suboptimal Low Complexity Joint Multi-Target Detection and Localization for Non-Coherent MIMO Radar With Widely Separated Antennas. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 901–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, M.A. Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Himed, B. Moving Target Detection in Distributed MIMO Radar on Moving Platforms. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2015, 9, 1524–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Wu, L. Moving Target Detection Using Colocated MIMO Radar on Multiple Distributed Moving Platforms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 4670–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, J.; Stoica, P. Waveform Design for Active Sensing Systems: A Computational Approach; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 1–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Blum, R.S.; Godrich, H.; Haimovich, A.M. Target Velocity Estimation and Antenna Placement for MIMO Radar With Widely Separated Antennas. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2010, 4, 79–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godrich, H.; Haimovich, A.M.; Blum, R.S. Target Localization Accuracy Gain in MIMO Radar-Based Systems. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2010, 56, 2783–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardillo, E.; Li, C.; Caddemi, A. Millimeter-Wave Radar Cane: A Blind People Aid With Moving Human Recognition Capabilities. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2022, 6, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Du, L. Target Detection for Multistatic Radar in the Presence of Deception Jamming. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 8130–8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, H. Target Detection With Imperfect Waveform Separation in Distributed MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro, M. Decentralized detection for censored binary observations with statistical dependence. Signal Process. 2016, 123, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S. Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing, Volume 2: Detection Theory; Prenfice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]

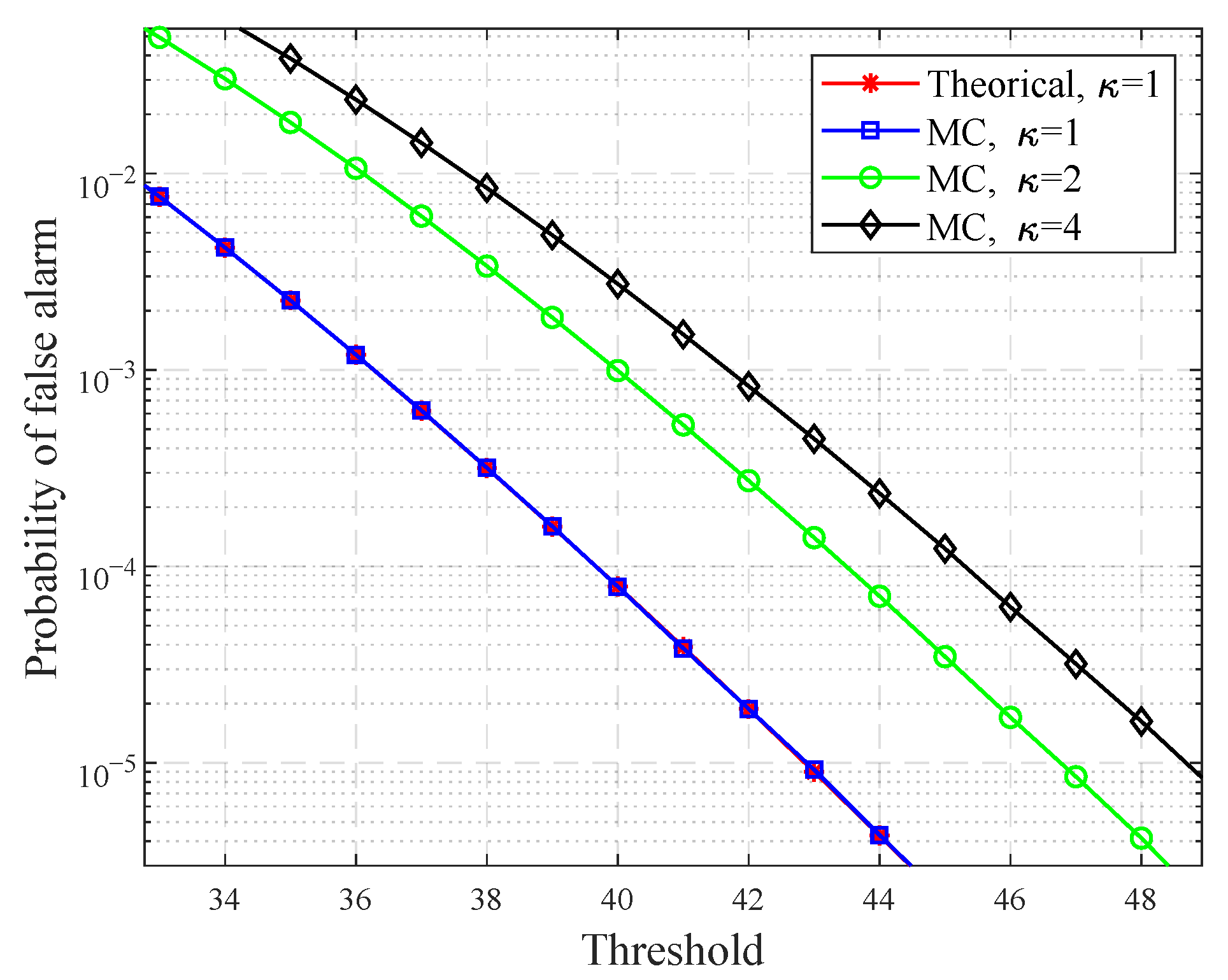
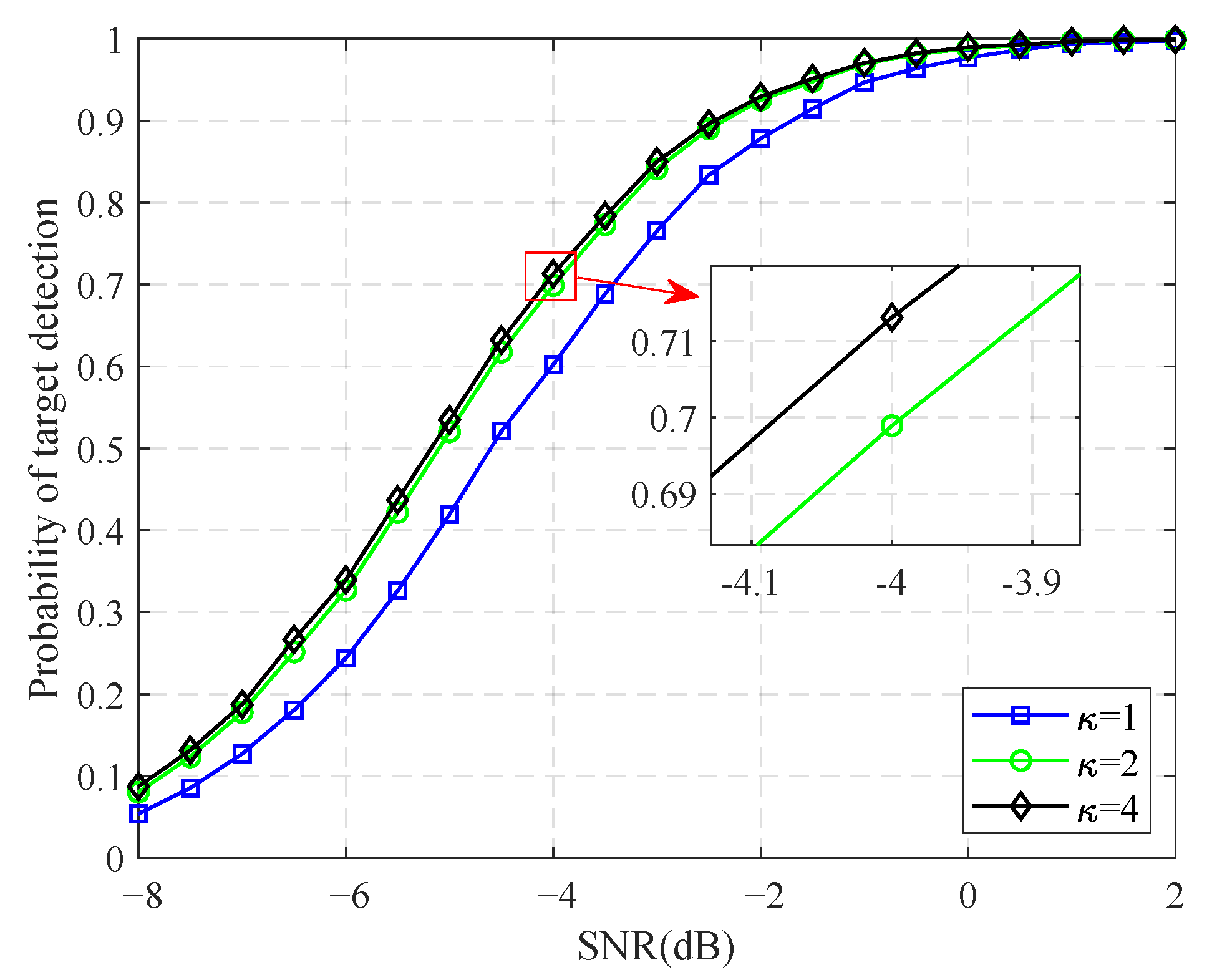
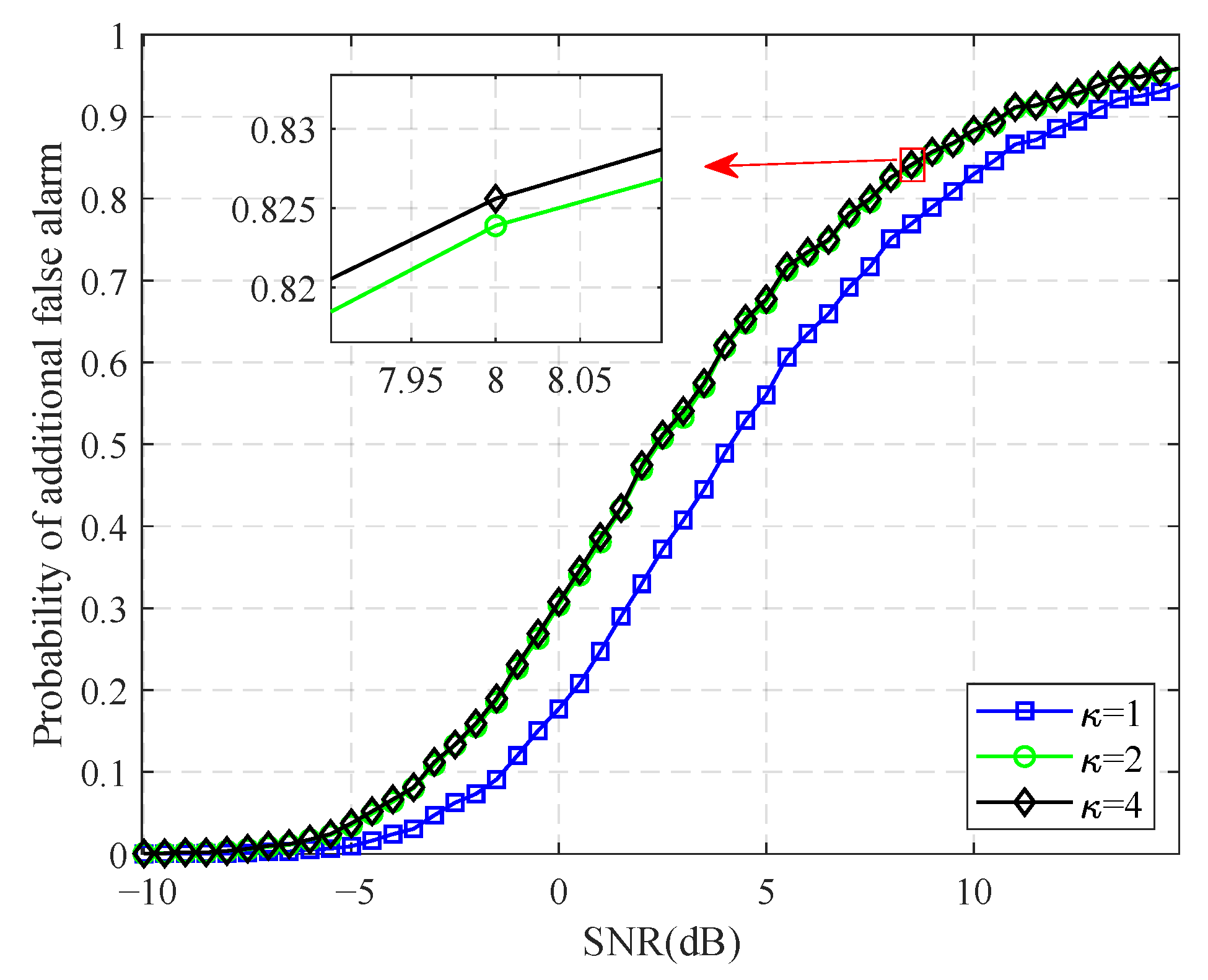
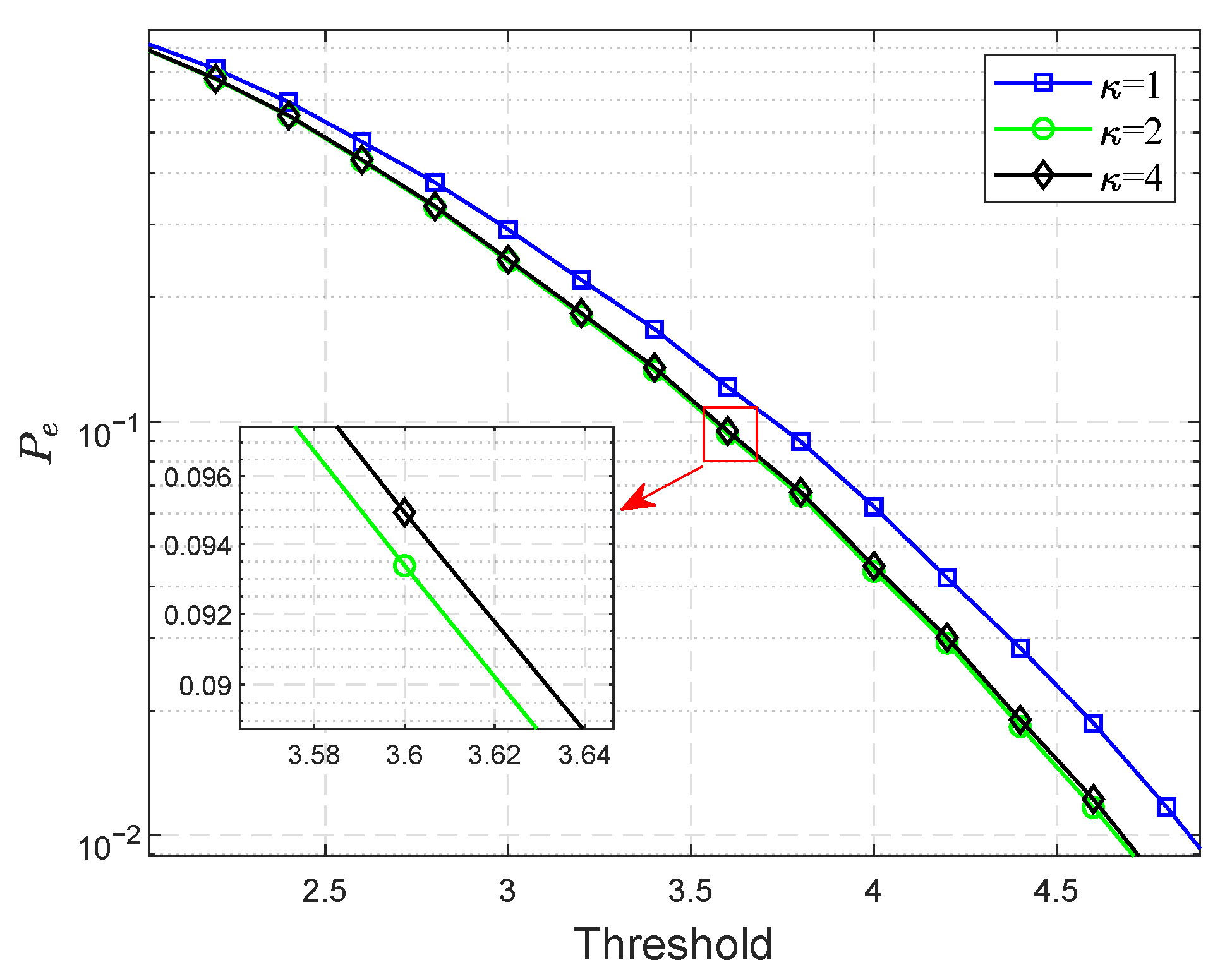


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Sha, M.; Zhang, L.; Du, L. Moving Multitarget Detection Using a Multisite Radar System with Widely Separated Stations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112660
Zhang S, Zhou Y, Sha M, Zhang L, Du L. Moving Multitarget Detection Using a Multisite Radar System with Widely Separated Stations. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(11):2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112660
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shiyu, Yu Zhou, Minghui Sha, Linrang Zhang, and Lan Du. 2022. "Moving Multitarget Detection Using a Multisite Radar System with Widely Separated Stations" Remote Sensing 14, no. 11: 2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112660
APA StyleZhang, S., Zhou, Y., Sha, M., Zhang, L., & Du, L. (2022). Moving Multitarget Detection Using a Multisite Radar System with Widely Separated Stations. Remote Sensing, 14(11), 2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112660






