Sea Surface Wind Retrieval under Rainy Conditions from Active and Passive Microwave Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. HY-2B Data
2.2. GPM IMERG_F Rain Data
2.3. ECMWF ERA5 Data
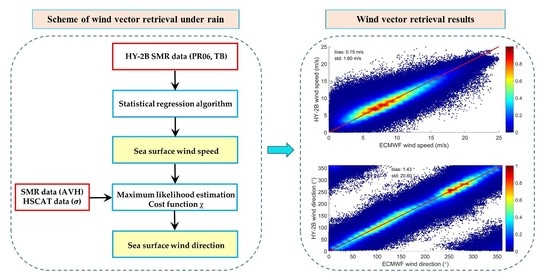
3. Results
3.1. Geophysical Model Functions (GMFs)
3.1.1. Backscatter GMF under Rainy Conditions
3.1.2. AVH Model Function under Rainy Conditions
3.2. Wind Vector Retrieval Model
3.2.1. Statistical Linear Regression for Wind Speed
3.2.2. Wind Direction Retrieval Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vogelzang, J.; Stoffelen, A. Scatterometer wind vector products for application in meteorology and oceanography. J. Sea Res. 2012, 74, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yueh, S.H.; Wilson, W.J.; Li, F.K.; Nghiem, S.V.; Ricketts, W.B. Polarimetric measurements of sea surface brightness temperatures using an aircraft K-band radiometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, W.L.; Schroefer, L.C.; Boggs, D.H.; Bracalente, E.M.; Brown, R.A.; Dome, G.J.; Pierson, W.J.; Wentz, F.J. The SEASAT-A satellite scatterometer: The geophysical evaluation of remotely sensed wind vectors over the ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 1982, 87, 3297–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wei, E.; Jin, X.; Lv, A.; Dang, H. The performance of dual-frequency polarimetric scatterometer in sea surface wind retrieval. J. Ocean Univ. China 2019, 18, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentz, F.J.; Smith, D.K. A model function for the ocean-normalized radar cross section at 14 GHz derived from NSCAT observations: NSCAT validation and science. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 11499–11514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.T.; Ruf, C.S.; Lyzenga, D.R. An emissivity-based wind vector retrieval algorithm for the WindSat polarimetric radiometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.B.; Cui, X.D.; Li, Y.N.; Jin, X.; Zhou, W.; Dang, H.X.; Li, H. Retrieval of sea surface temperature from the scanning microwave radiometer aboard HY-2B. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 4621–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettenhausen, M.H.; Smith, C.K.; Bevilacqua, R.M.; Wang, N.-Y.; Gaiser, P.W.; Cox, S. A nonlinear optimization algorithm for WindSat wind vector retrievals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Stoffelen, A.; Zou, J.; Lin, W.; Verhoef, A.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Lin, M. Validation of new sea surface wind products from scatterometers Onboard the HY-2B and MetOp-C satellites. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 4387–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive. Volume II: Radar Remote Sensing and Surface Scattering and Emission Theory; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, C.; Long, D.G. A C-band wind/rain backscatter model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, B.S.; Sikhakolli, R.; Gangwar, R.K.; Kiran Kumar, A.S. Oceanic rain flagging using radar backscatter and noise measurements from Oceansat-2 scatterometer. IEEE Trans. Geosc. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Perrie, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L. Rain effects on the hurricane observations over the ocean by C-band Synthetic Aperture Radar. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amarin, R.A.; Jones, W.L.; El-Nimri, S.F.; Johnson, J.W.; Ruf, C.S.; Miller, T.L.; Uhlhorn, E. Hurricane wind speed measurements in rainy conditions using the airborne hurricane imaging radiometer (HIRAD). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.J. Wind-vector retrievals under rain with passive satellite microwave radiometers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 3065–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Yang, J.S.; Zheng, G.; Wang, J. A Ku-band wind and rain backscatter model at low-incidence angles using Tropical Rainfall Mapping Mission precipitation radar data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 1388–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, D.W.; Long, D.G. Simultaneous wind and rain retrieval using SeaWinds data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laupattarakasem, P.; Jones, W.L.; Hennon, C.C.; Allard, J.R.; Harless, A.R.; Black, P.G. Improved hurricane ocean vector winds using SeaWinds active/passive retrievals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2909–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilburn, K.A.; Wentz, F.J.; Smith, D.K.; Ashcroft, P.D. Correcting active scatterometer data for the effects of rain using passive radiometer data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2006, 45, 382–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meissner, T.; Ricciardulli, L.; Manaster, A. Tropical cyclone wind speeds from WindSat, AMSR and SMAP: Algorithm development and testing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaster, A.; Ricciardulli, L.; Meissner, T. Tropical cyclone winds from WindSat, AMSR2, and SMAP: Comparison with the HWRF model. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentz, F.J. Measurement of oceanic wind vector using satellite microwave radiometers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 960–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.J. An updated analysis of the ocean surface wind direction signal in passive microwave brightness temperatures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soisuvarn, S.; Jelenak, Z.; Jones, W.L. An ocean surface wind vector model function for a spaceborne microwave radiometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3119–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsweiss, S.O.; Laupattarakasem, P.; Jones, W.L. A novel Ku-band radiometer/scatterometer approach for improved oceanic wind vector measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3189–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossan, A.; Jacob, M.M.; Jones, W.L. Ocean vector wind retrievals from TRMM using a novel combined active/passive algorithm. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5569–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mu, B.; Lin, M.; Song, Q. An evaluation of the Chinese HY-2B satellite’s microwave scatterometer instrument. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 4513–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, H.; Wang, Z.; Yin, X.; Yang, L.; Du, H.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W. Evaluation of the initial sea surface temperature from the HY-2B scanning microwave radiometer. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Lin, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, Y. Evaluating Chinese HY-2B HSCAT ocean wind products using buoys and other scatterometers. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Kidd, C.; Nelkin, E.J.; Sorooshian, S.; Tan, J.; Xie, P. NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG), Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD) Version 06; NASA GSFC: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2020. Available online: https://gpm.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/2020-05/IMERG_ATBD_V06.3.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2021).
- OSI SAF. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document for the OSI SAF Wind Products and NSCAT-4 Geophysical Model Function. Available online: http://projects.knmi.nl/scatterometer/nscat_gmf/ (accessed on 28 July 2020).
- Nielsen, S.N.; Long, D.G. A wind and rain backscatter model derived from AMSR and SeaWinds data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, I.; Strachan, P. Practical application of uncertainty analysis. Energy Build. 2001, 33, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodlie, K.; Allendes, O.R.; Lopes, A. A Review of Uncertainty in Data Visualization. In Expanding the Frontiers of Visual Analytics and Visualization; Dill, J., Earnshaw, R., Kasik, D., Vince, J., Wong, P.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 81–109. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, K.V.; Kuok, S.C. Bayesian methods for updating dynamic models. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2011, 64, 080102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, S.J.; Dunbar, R.S.; Hsiao, S.V.; Long, D.G. A median-filter-based ambiguity removal algorithm for NSCAT. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1991, 29, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]













| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Orbital altitude | 971 km |
| Inclination angle | 99.34° |
| SMR frequency: spatial resolution | 6.925 GHz: 150 km × 90 km 10.7 GHz: 110 km × 70 km 18.7 GHz: 60 km × 36 km 23.8 GHz: 52 km × 30 km 37 GHz: 35 km × 20 km |
| SMR polarization | Vertical and horizontal polarization, except 23.8 GHz (vertical polarization only) |
| SMR incidence | 53° |
| SMR swath width | 1600 km |
| HSCAT frequency: spatial resolution | 13.25 GHz: 25 km × 3.2 km |
| HSCAT peak power | 120 W |
| HSCAT polarization/incidence angle | HH/41.5° (inner beam) and VV/48.6° (outer beam) |
| HSCAT swath width | 1350 km (inner beam) and 1750 km (outer beam) |
| Source | Dataset | Download URL |
|---|---|---|
| HY-2B data (swath data) | SMR L2A brightness temperature data | https://osdds.nsoas.org.cn/ (accessed on 5 December 2020) |
| SCA L2A backscatter data | ||
| GPM IMERG_F Data (0.5 h and 0.1° global gridded data) | Rain rate data | https://gpm.nasa.gov/data/directory (accessed on 8 May 2021) |
| ECMWF ERA5 Data (3 h and 0.25° global gridded data) | Sea surface wind vector data | https://www.ecmwf.int/en/forecasts/datasets/reanalysis-datasets/era5 (accessed on 8 May 2021) |
| Sea surface temperature data |
| Polarization | Wind Speed and PR06 Intervals | 4 m/s | 8 m/s | 13 m/s | 15 m/s | 22 m/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VV polarization: Model RMS difference (dB) and peak-to-peak value (dB) | 0.280~0.286 | 2.45 and 0.65 | 1.62 and 2.24 | 1.04 and 3.35 | 0.83 and 3.51 | 0.43 and 2.62 |
| 0.292~0.298 | 2.90 and 0.72 | 1.79 and 2.96 | 0.95 and 4.42 | 0.70 and 4.23 | 0.40 and 3.38 | |
| 0.304~0.310 | 3.10 and 1.22 | 1.80 and 4.44 | 0.75 and 4.95 | 0.71 and 4.49 | \ | |
| 0.316~0.322 | 3.20 and 2.35 | 1.46 and 5.92 | 1.56 and 4.89 | 1.92 and 4.92 | \ | |
| HH polarization: Model RMS difference (dB) and peak-to-peak value (dB) | 0.280~0.286 | 2.98 and 0.62 | 1.95 and 1.58 | 1.31 and 3.36 | 1.07 and 3.84 | 0.52 and 3.22 |
| 0.292~0.298 | 3.42 and 0.93 | 1.97 and 2.27 | 1.11 and 4.49 | 0.82 and 4.64 | 0.32 and 2.69 | |
| 0.304~0.310 | 3.54 and 1.15 | 1.74 and 3.66 | 0.85 and 5.00 | 0.84 and 4.78 | \ | |
| 0.316~0.322 | 3.38 and 2.41 | 1.32 and 4.72 | 1.33 and 3.76 | 1.74 and 3.83 | \ |
| PR06 Interval | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.200~0.280 | 63.4998 | 0.7273 | −0.5065 | −0.3073 | 1.2236 | −0.0099 | −0.0135 | −0.0138 | 0.0146 |
| 0.280~0.286 | 30.2937 | −0.1421 | −2.1581 | 0.2069 | 1.3784 | 0.0004 | −0.0325 | −0.0172 | 0.0185 |
| 0.286~0.292 | 26.7480 | −0.5484 | −2.6971 | 0.5210 | 1.8160 | 0.0094 | −0.0379 | −0.0227 | 0.0233 |
| 0.292~0.298 | −5.3135 | −0.8931 | −4.2596 | 0.7864 | 2.3520 | 0.0188 | −0.0512 | −0.0283 | 0.0283 |
| 0.298~0.304 | −72.3653 | −1.3605 | −7.4698 | 1.1681 | 3.4433 | 0.0317 | −0.0781 | −0.0367 | 0.0387 |
| 0.304~0.310 | −202.8874 | −2.0352 | −13.2763 | 1.7080 | 5.2163 | 0.0548 | −0.1246 | −0.0513 | 0.0539 |
| 0.310~0.316 | −250.7017 | −2.1427 | −16.1397 | 1.6320 | 6.5187 | 0.0672 | −0.1452 | −0.0588 | 0.0621 |
| 0.316~0.322 | −247.5439 | −1.9890 | −16.7695 | 1.2410 | 7.0538 | 0.0720 | −0.1474 | −0.0600 | 0.0624 |
| 0.322~0.328 | −220.3869 | −1.6669 | −15.7192 | 0.8394 | 6.9067 | 0.0661 | −0.1353 | −0.0542 | 0.0577 |
| 0.328~0.360 | −116.1451 | −0.5278 | −7.5864 | −0.0672 | 2.7349 | 0.0286 | −0.0643 | −0.0213 | 0.0211 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhou, W.; Lv, A.; Jin, X.; Dang, H. Sea Surface Wind Retrieval under Rainy Conditions from Active and Passive Microwave Measurements. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133016
Liu S, Li Y, Yang X, Zhou W, Lv A, Jin X, Dang H. Sea Surface Wind Retrieval under Rainy Conditions from Active and Passive Microwave Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(13):3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133016
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shubo, Yinan Li, Xiaojiao Yang, Wu Zhou, Ailing Lv, Xu Jin, and Hongxing Dang. 2022. "Sea Surface Wind Retrieval under Rainy Conditions from Active and Passive Microwave Measurements" Remote Sensing 14, no. 13: 3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133016
APA StyleLiu, S., Li, Y., Yang, X., Zhou, W., Lv, A., Jin, X., & Dang, H. (2022). Sea Surface Wind Retrieval under Rainy Conditions from Active and Passive Microwave Measurements. Remote Sensing, 14(13), 3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133016