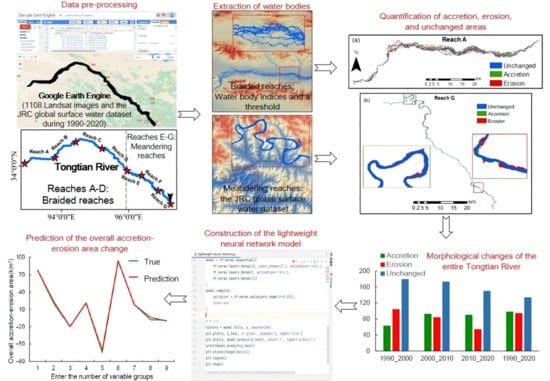
Monitoring and Predicting Channel Morphology of the Tongtian River, Headwater of the Yangtze River Using Landsat Images and Lightweight Neural Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Landsat Images
2.3. Extracting Water Bodies from Satellite-Based Databases
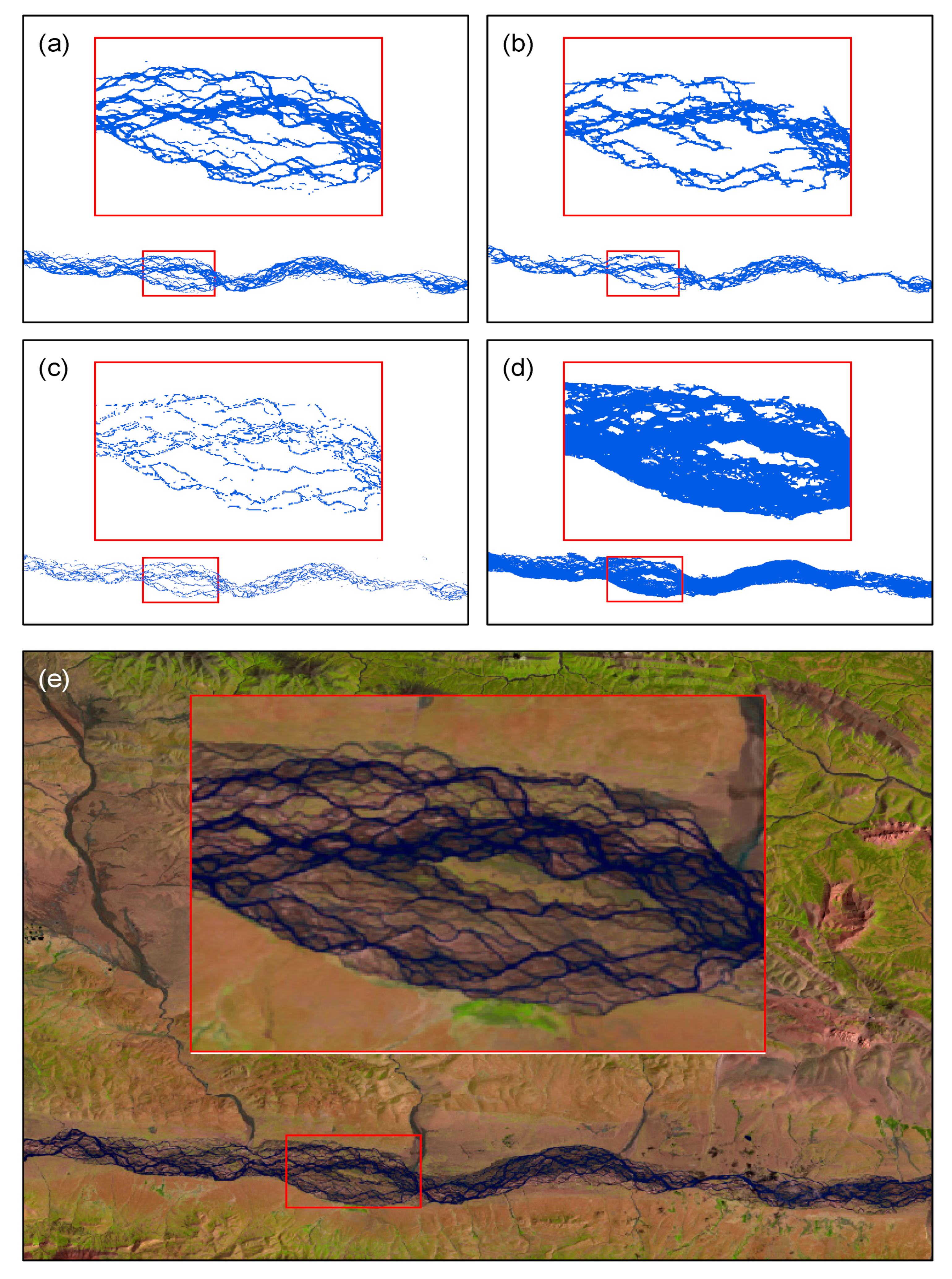
2.4. Comparing Different Water-Body Extraction Methods for Different River Reaches
2.5. Quantification of Accretion, Erosion, and Unchanged Areas during Different Periods
2.6. Statistical Analysis
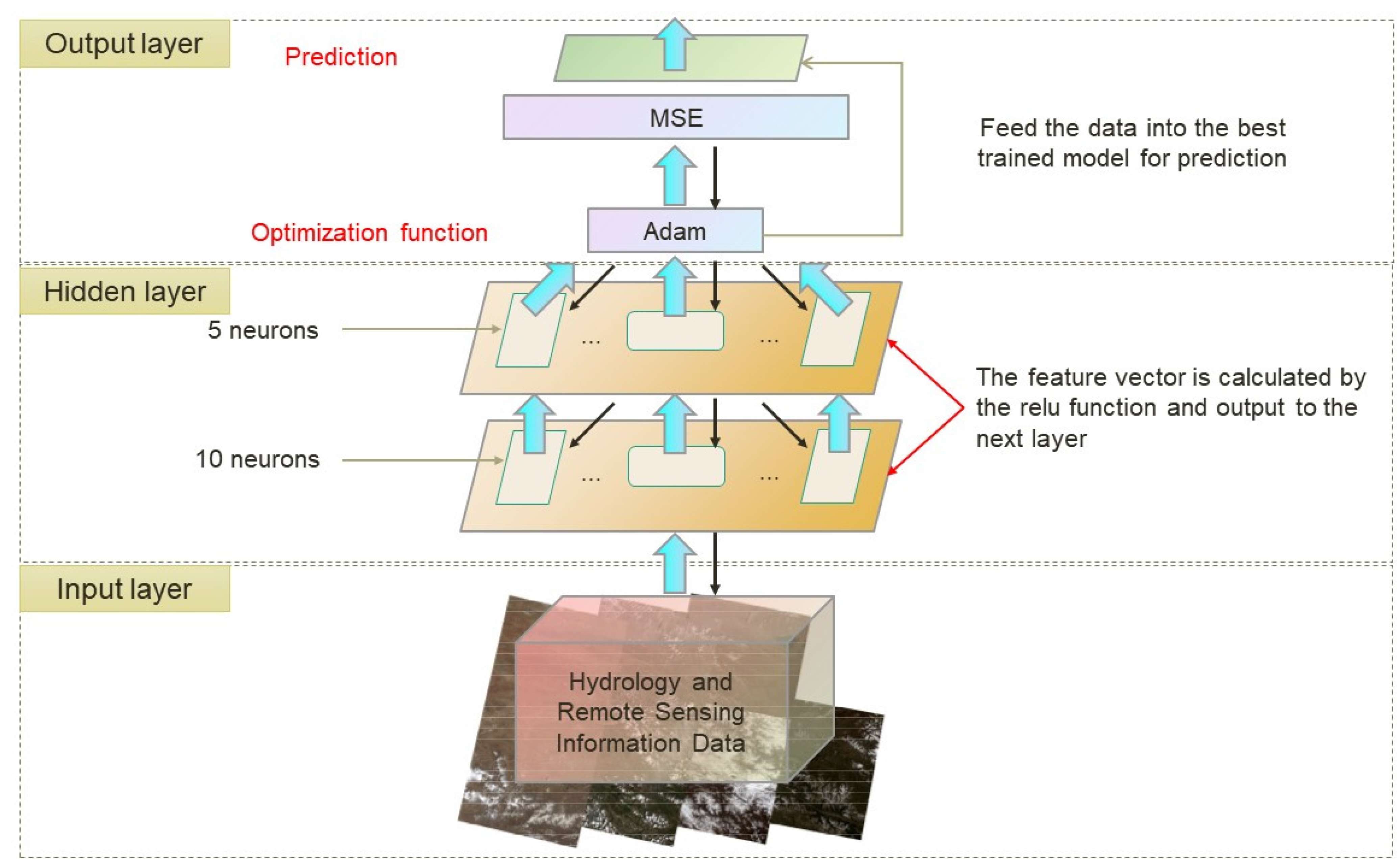
2.7. The Lightweight Intelligent Predictive Model
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy Assessment of Different Water-Body-Extraction Methods for the Braided Reaches
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variability of River-Channel Morphology at Different Reaches
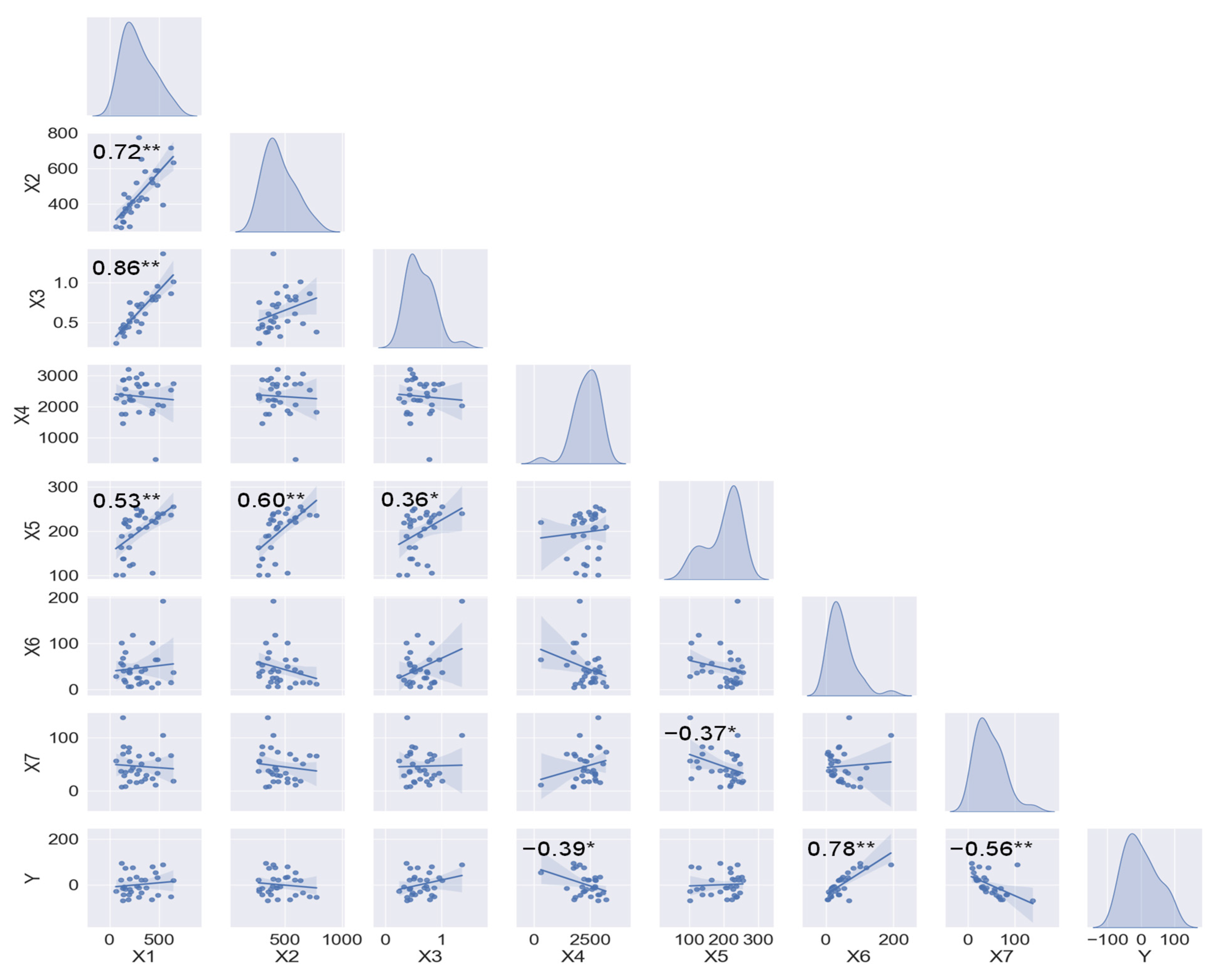
3.3. Data Distribution and Correlation Analysis
3.4. Predictive Performance of the Lightweight Neural-Network Model
4. Discussion
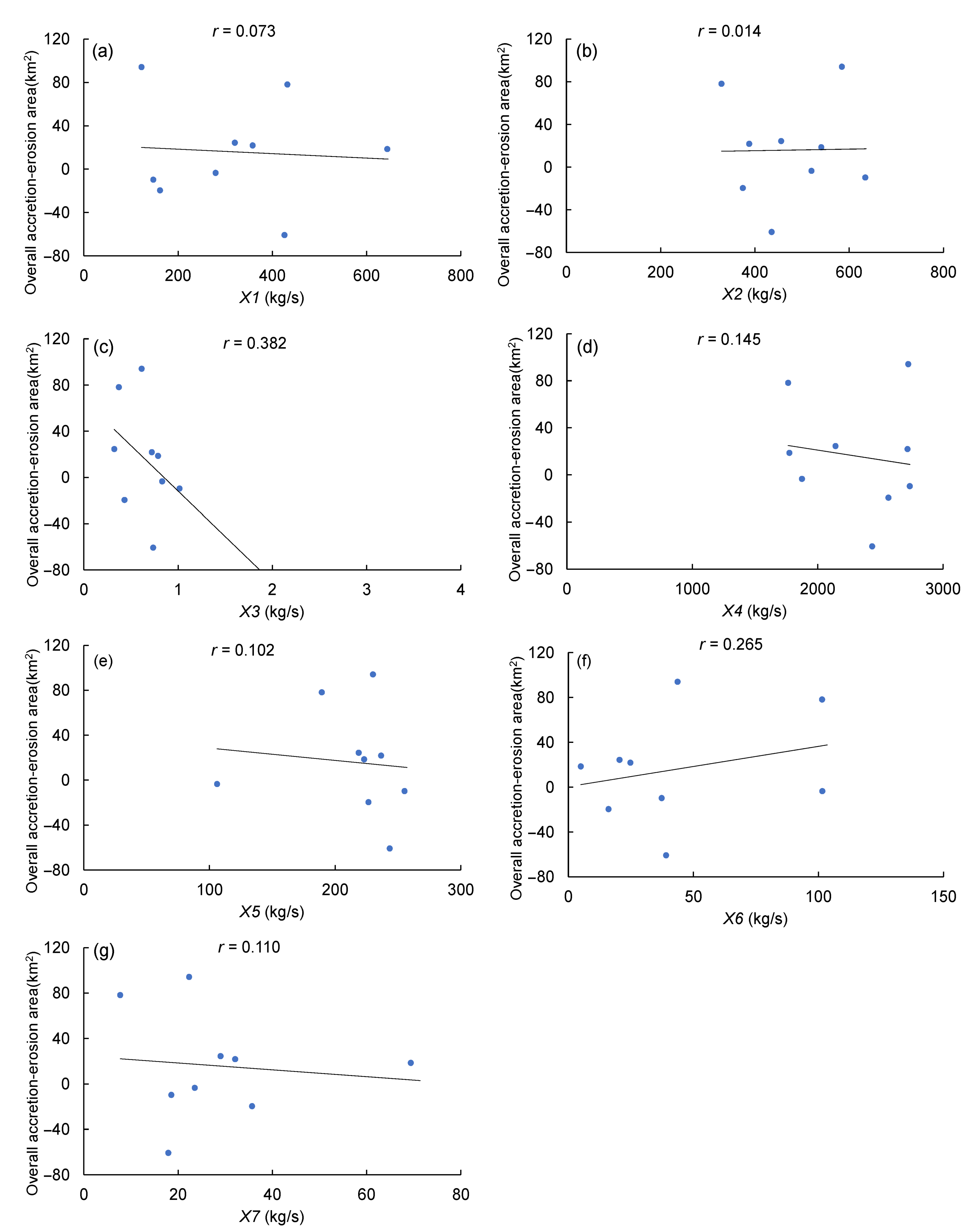
4.1. Factors Influencing River-Channel Morphology
4.2. Characteristics and Formation of Braided River Courses of the Tongtian River
4.3. Problems Associated with the JRC Dataset
4.4. Evaluation of the Lightweight Neural-Network Prediction Model
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piégay, H.; Grant, G.; Nakamura, F.; Trustrum, N. Braided river management: From assessment of river behaviour to improved sustainable development. Braided Rivers Process Depos. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 36, 257–275. [Google Scholar]
- Brierley, G.; Fryirs, K.; Outhet, D.; Massey, C. Application of the River Styles framework as a basis for river management in New South Wales, Australia. Appl. Geogr. 2002, 22, 91–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, X.; Wu, M.; Liu, Z. Spatiotemporal evolution trajectory of channel morphology and controlling factors of Yongding River, Beijing, China. Water 2021, 13, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, X. Morphological Features and Spatial-temporal Change of Braided Reach of Tongtian River in the Yangtze River Source Region. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2018, 35, 6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Lu, H.; Gao, P.; You, Y.; Hu, X. Characterizing braided rivers in two nested watersheds in the Source Region of the Yangtze River on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geomorphology 2020, 351, 106945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ran, S.; Jiang, C. Characteristics and Mechanism of Water Flow Eroding Group Bars in Braided Channel of the Yangtze River Source. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 2020, 28, 11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Ran, S.; Li, Z. Spatiotemporal variations in side bars related to runoff in two typical braided reaches in the Yangtze River source region. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2019, 38, 1–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Meng, L. Long-term spatiotemporal changes of surface water and its influencing factors in the mainstream of Han River, China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 40, 101009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Song, C.; Liu, K.; Ke, L.; Zhang, W.; Ma, R.; Zhu, J.; Wu, Q. Remote sensing estimation of catchment-scale reservoir water impoundment in the upper Yellow River and implications for river discharge alteration. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Li, Z.; You, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Piégay, H. Assessing functional characteristics of a braided river in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Geomorphology 2022, 403, 108180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Pal, S. Effects of damming on the hydrological regime of Punarbhaba river basin wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 135, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worden, J.; Beurs, K.M.D. Surface water detection in the Caucasus. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 91, 102159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Ke, X. Analysis on urban lake change during rapid urbanization using a synergistic approach: A case study of Wuhan, China. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2015, 89, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Duan, W.; Nover, D.; Sahu, N.; Chen, Y. An integrated assessment of surface water dynamics in the Irtysh River Basin during 1990–2019 and exploratory factor analyses. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessica, J.; Walker, J.J.; Soulard, C.E.; Petrakis, R.E. Integrating stream gage data and Landsat imagery to complete time-series of surface water extents in Central Valley, California-ScienceDirect. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 84, 101973. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhao, G.; Tseng, K.-H. A high-resolution bathymetry dataset for global reservoirs using multi-source satellite imagery and altimetry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 244, 111831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, N.; Shahzad, M.; Malik, M.I.; Schwanecke, U.; Ulges, A.; Kovács, G.; Shafait, F. UCL: Unsupervised Curriculum Learning for water body classification from remote sensing imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 105, 102568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseiny, H. A deep learning model for predicting river flood depth and extent. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 145, 105186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Essam, Y.; Ahmed, A.N.; Huang, Y.F.; El-Shafie, A. An assessment of sedimentation in Terengganu River, Malaysia using satellite imagery. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 3429–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Mahmud, S.; Elahi, M.L.; Ahmed, S.; Sujauddin, M. Forecasting river sediment deposition through satellite image driven unsupervised machine learning techniques. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 13, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ding, F.; Jiao, L.; Chen, J.W.; Wang, M. Lightweight convolutional neural network for bitemporal SAR image change detection. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 036501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Lightweight Deep Neural Network Method for Water Body Extraction from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images with Multisensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 7397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, P.; He, G.; Guo, H. A New Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network for Multi-Scale Land Surface Water Extraction from GaoFen-1D Satellite Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Zhang, M.; Tian, B.; Zhen, L. Extraction of Glacial Lake Outlines in Tibet Plateau Using Landsat 8 Imagery and Google Earth Engine. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 4002–4009. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhang, G.; Qin, Y.; Thau, D.; Biradar, C.; Iii, B.M. Mapping paddy rice planting area in northeastern Asia with Landsat 8 images, phenology-based algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Cao, W.; Shao, Q. Change of ecological condition in the headwater of the Yangtze River before and after the implementation of the ecological conservation and construction project. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2016, 18, 1069–1076. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Du, C.; Ren, H.; Qin, Q.; Meng, J.; Li, J. Split-window algorithm for estimating land surface temperature from Landsat 8 TIRS data. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 3–18 July 2014; pp. 3578–3581. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, H.; Venevsky, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, M. NDVI-based vegetation dynamics and its response to climate changes at Amur-Heilongjiang River Basin from 1982 to 2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2051–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham Van, C.; Nguyen-Van, G. Assessment of the Water Area in the Lowland Region of the Mekong River Using MODIS EVI Time Series. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Science, Applied Mathematics and Applications, Hanoi, Vietnam, 19–20 December 2019; pp. 197–207. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Liu, R.; Zou, Z.; Zhao, G.; Ge, Q. Continuous monitoring of lake dynamics on the Mongolian Plateau using all available Landsat imagery and Google Earth Engine. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, K.; Grabowski, R.C. Human impact on river planform within the context of multi-timescale river channel dynamics in a Himalayan river system. Geomorphology 2021, 381, 107659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wang, G.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Huang, K.; Chen, X.; Li, Y. Net ecosystem carbon budget of a grassland ecosystem in central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Integrating terrestrial and aquatic carbon fluxes at catchment scale. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 290, 108021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Hu, H.; Li, T. The influence of freeze–thaw cycles of active soil layer on surface runoff in a permafrost watershed. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tian, B.; Schwarz, C.; Zhang, C.; Guo, L.; Xu, F.; Zhou, Y.; He, Q. Quantifying delta channel network changes with Landsat time-series data. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraga, Y.; Kazama, S.; Ekkawatpanit, C.; Touge, Y. Impact of reclamation on the environment of the lower mekong river basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 18, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, K.; Khozani, Z.S.; Cooper, J.R. Predicting stable gravel-bed river hydraulic geometry: A test of novel, advanced, hybrid data mining algorithms. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 144, 105165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, M.; de Castro Neto, M.; Sarmento, P. A mixed approach for urban flood prediction using Machine Learning and GIS. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 56, 102154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, A.; Ozturk, P.; Chau, K.-W. Flood prediction using machine learning models: Literature review. Water 2018, 10, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beyaztas, U.; Shang, H.L.; Yaseen, Z.M. A functional autoregressive model based on exogenous hydrometeorological variables for river flow prediction. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.A.; Cabral, N.R.; Bezerra, S.Y.J.A.; Araújo, N.C.W.; de Sousa, M.W.; Germano, V.; Tales, T.; Bezerra, Y.J.A. Near-infrared spectroscopy for prediction of potentially toxic elements in soil and sediments from a semiarid and coastal humid tropical transitional river basin. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Tian, Z.; Ye, Q.; Ke, Q.; Fan, D.; Mao, G.; Chen, A.; Liu, J. Evaluation of short-term streamflow prediction methods in Urban river basins. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2021, 123, 103027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaghaghi, S.; Bonakdari, H.; Gholami, A.; Ebtehaj, I.; Zeinolabedini, M. Comparative analysis of GMDH neural network based on genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization in stable channel design. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 313, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Chen, G.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, W. Prediction of river damming susceptibility by landslides based on a logistic regression model and InSAR techniques: A case study of the Bailong River Basin, China. Eng. Geol. 2022, 299, 106562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Warrens, M.J.; Jurman, G. The coefficient of determination R-squared is more informative than SMAPE, MAE, MAPE, MSE and RMSE in regression analysis evaluation. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surian, N.; Ziliani, L.; Comiti, F.; Lenzi, M.A.; Mao, L. Channel adjustments and alteration of sediment fluxes in gravel-bed rivers of North-Eastern Italy: Potentials and limitations for channel recovery. River Res. Appl. 2010, 25, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ca Mpana, D.; Marchese, E.; Theule, J.I.; Comiti, F. Channel degradation and restoration of an Alpine river and related morphological changes. Geomorphology 2014, 221, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langat, P.K.; Kumar, L.; Koech, R.; Ghosh, M.K. Characterisation of channel morphological pattern changes and flood corridor dynamics of the tropical Tana River fluvial systems, Kenya. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2020, 163, 103748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P.; Zhang, L. At-a-station hydraulic geometry relations, 1: Theoretical development. Hydrol. Processes: Int. J. 2008, 22, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Xu, X.; Zhao, T.; Yao, T.; Zhang, D.; Wang, N.; Ma, Y.; Ma, W.; Chen, B.; Zhang, S. Distinct impacts of vapor transport from the tropical oceans on the regional glacier retreat over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, C.; Zhou, X.; Lei, K.; Guo, B.; Cao, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, X.; He, M. Concentrations, fluxes, and potential sources of nitrogen and phosphorus species in atmospheric wet deposition of the Lake Qinghai Watershed, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 682, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, C.; Chongyi, E.; Liu, X. Atmospheric dry deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus in Lake Qinghai, Tibet Plateau. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.K.; Hossain, F.; Eldardiry, H.; Pavelsky, T.M. A fusion approach for water area classification using visible, near infrared and synthetic aperture radar for South Asian conditions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 2471–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulard, C.E.; Walker, J.J.; Petrakis, R.E. Implementation of a surface water extent model in Cambodia using cloud-based remote sensing. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.; Rahaman, M.M. Impacts of Farakka barrage on hydrological flow of Ganges river and environment in Bangladesh. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 4, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Sun, X.; Zhang, B. Water clarity changes in Lake Taihu over 36 years based on Landsat TM and OLI observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Shi, K.; Yang, X. Water clarity mapping of global lakes using a novel hybrid deep-learning-based recurrent model with Landsat OLI images. Water Res. 2022, 215, 118241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, K.; Khozani, Z.S.; Mao, L. A comparison between advanced hybrid machine learning algorithms and empirical equations applied to abutment scour depth prediction. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
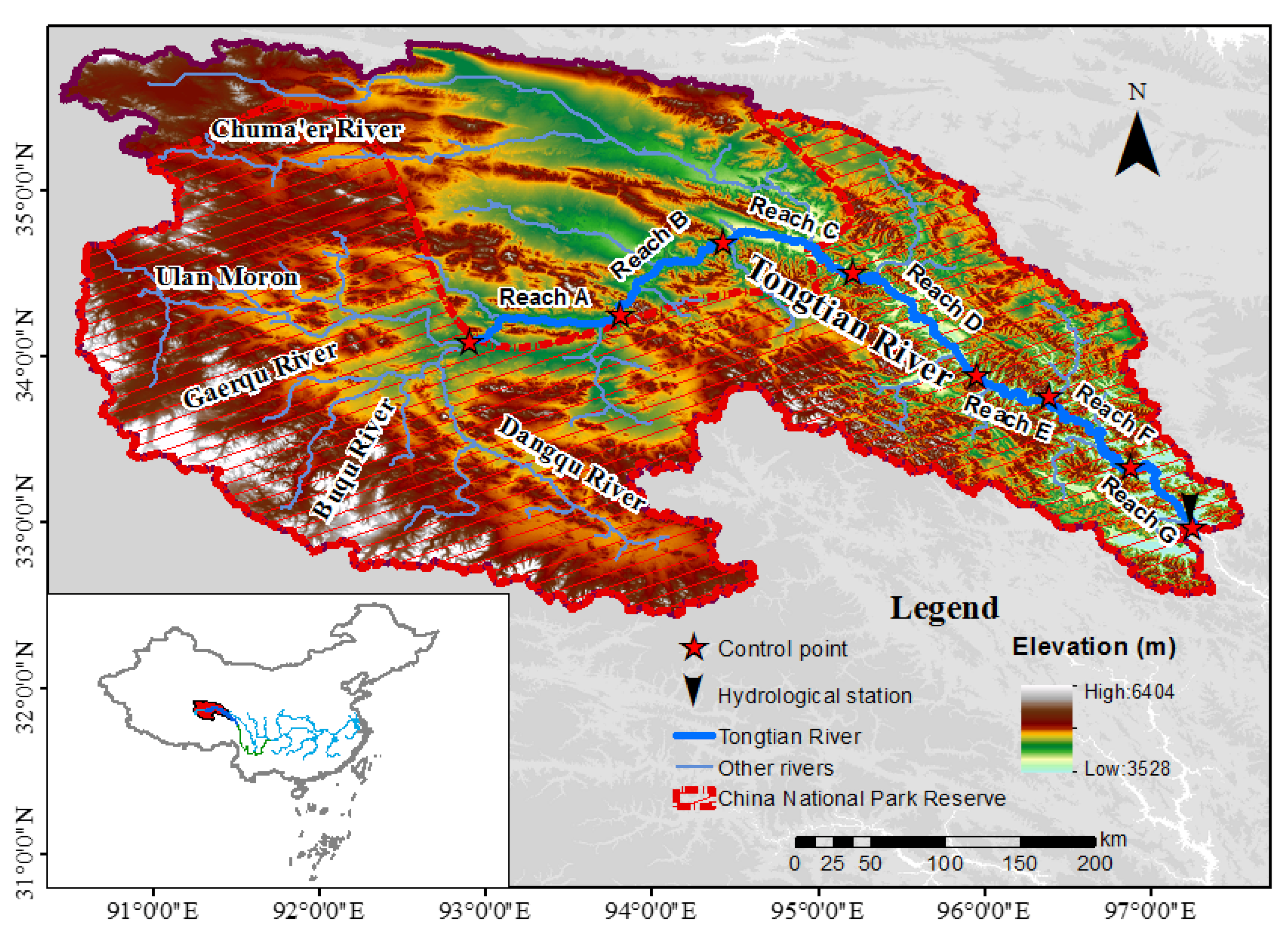



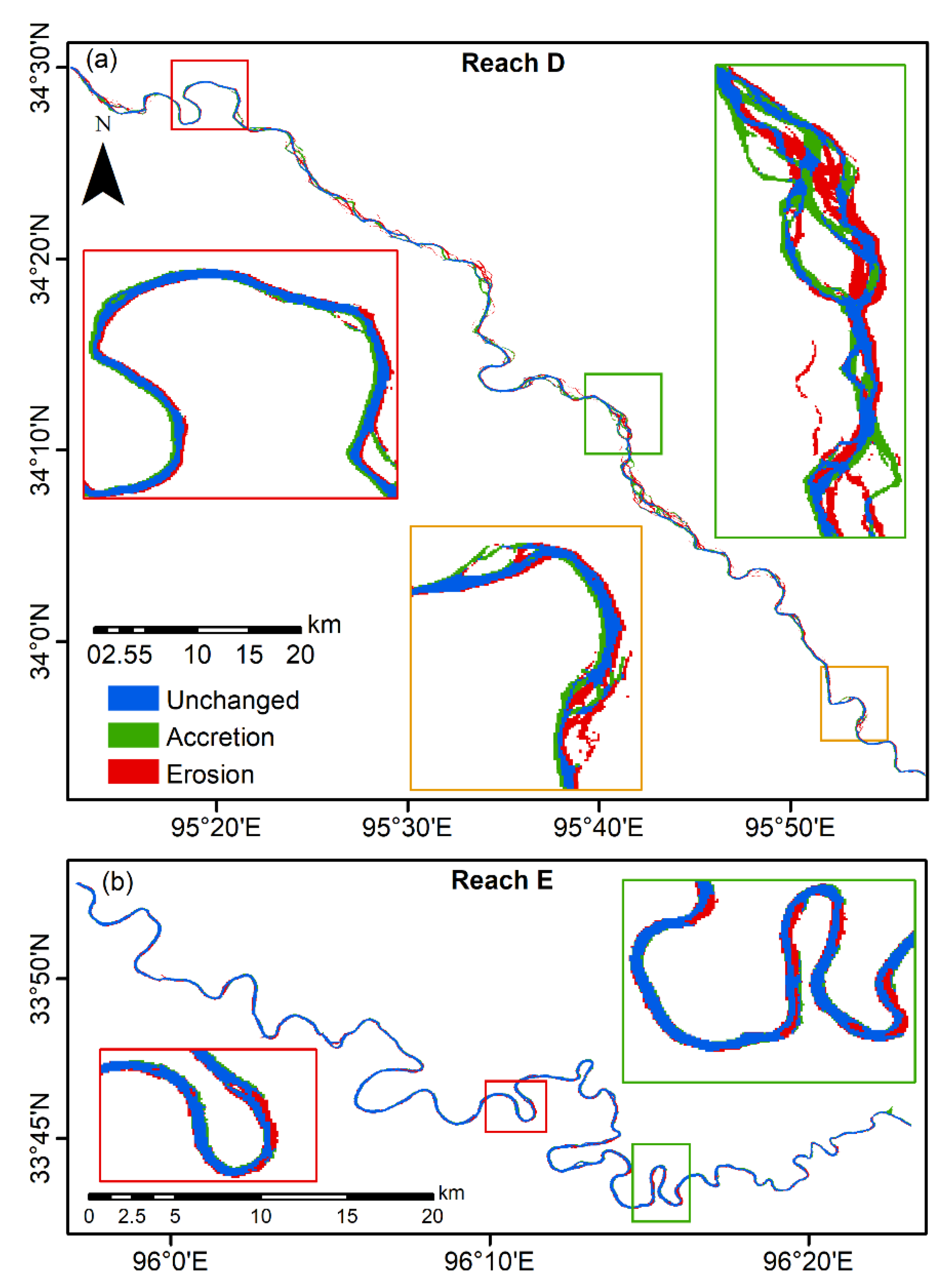
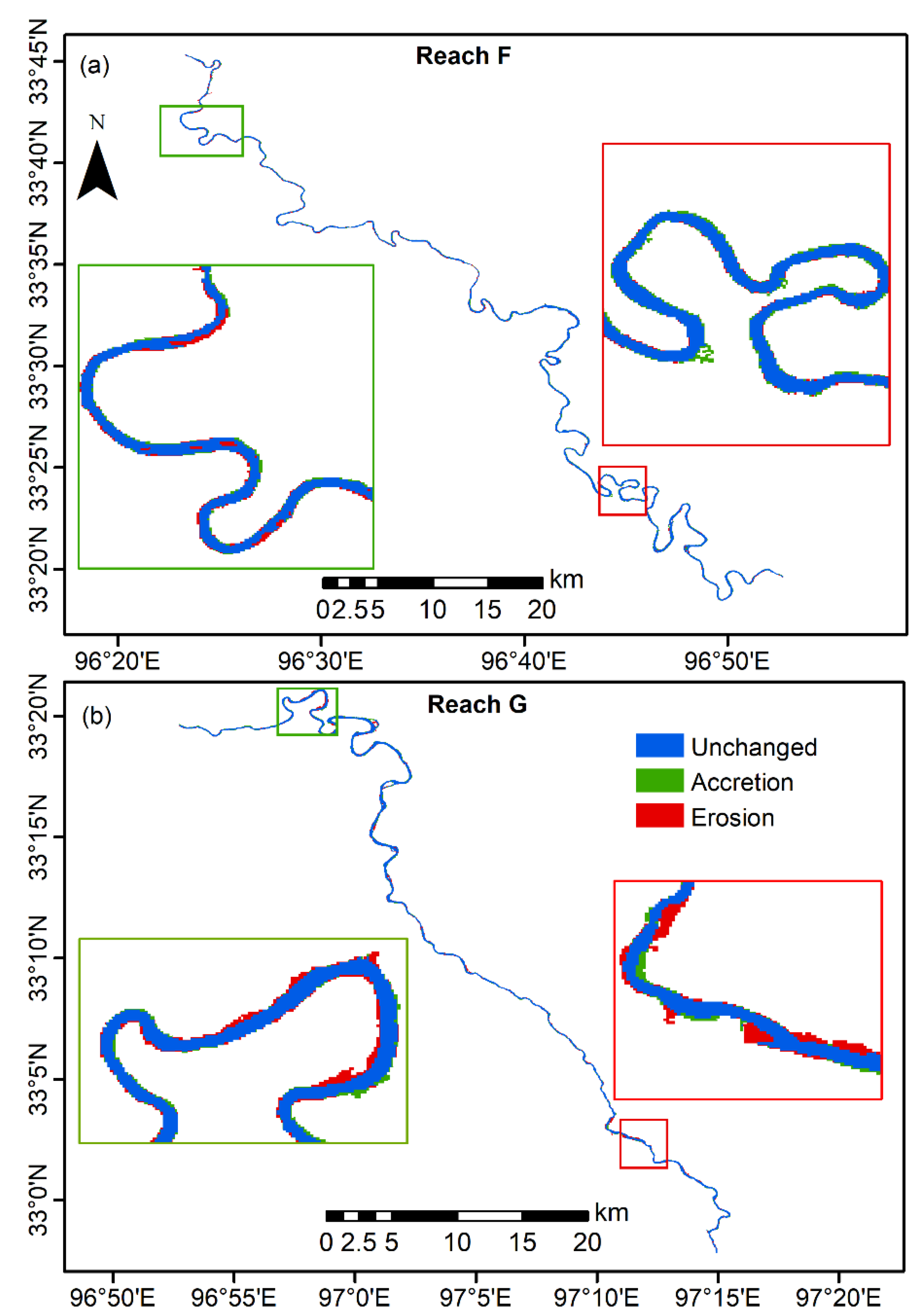


| Control Point | Longitude | Latitude | Channel Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Starting point | 92.907 | 34.086 | main braided reach (reach A) | |
| 1 | 93.807 | 34.246 | main braided reach (reach B) | |
| 2 | 94.426 | 34.682 | main braided reach (reach C) | |
| 3 | 95.206 | 34.500 | minor braided reach (reach D) | |
| 4 | 95.950 | 33.883 | main meandering reach (reach E) | |
| 5 | 96.387 | 33.755 | main meandering reach (reach F) | |
| 6 | 96.879 | 33.328 | minor meandering reach (reach G) | |
| End point | 97.248 | 32.963 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, B.; Xiong, K.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Liu, J.; Luo, W.; Xiang, Y. Monitoring and Predicting Channel Morphology of the Tongtian River, Headwater of the Yangtze River Using Landsat Images and Lightweight Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3107. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133107
Deng B, Xiong K, Huang Z, Jiang C, Liu J, Luo W, Xiang Y. Monitoring and Predicting Channel Morphology of the Tongtian River, Headwater of the Yangtze River Using Landsat Images and Lightweight Neural Network. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(13):3107. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133107
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Bin, Kai Xiong, Zhiyong Huang, Changbo Jiang, Jiang Liu, Wei Luo, and Yifei Xiang. 2022. "Monitoring and Predicting Channel Morphology of the Tongtian River, Headwater of the Yangtze River Using Landsat Images and Lightweight Neural Network" Remote Sensing 14, no. 13: 3107. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133107
APA StyleDeng, B., Xiong, K., Huang, Z., Jiang, C., Liu, J., Luo, W., & Xiang, Y. (2022). Monitoring and Predicting Channel Morphology of the Tongtian River, Headwater of the Yangtze River Using Landsat Images and Lightweight Neural Network. Remote Sensing, 14(13), 3107. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133107