Reconstructing High-Spatiotemporal-Resolution (30 m and 8-Days) NDVI Time-Series Data for the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau from 2000–2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
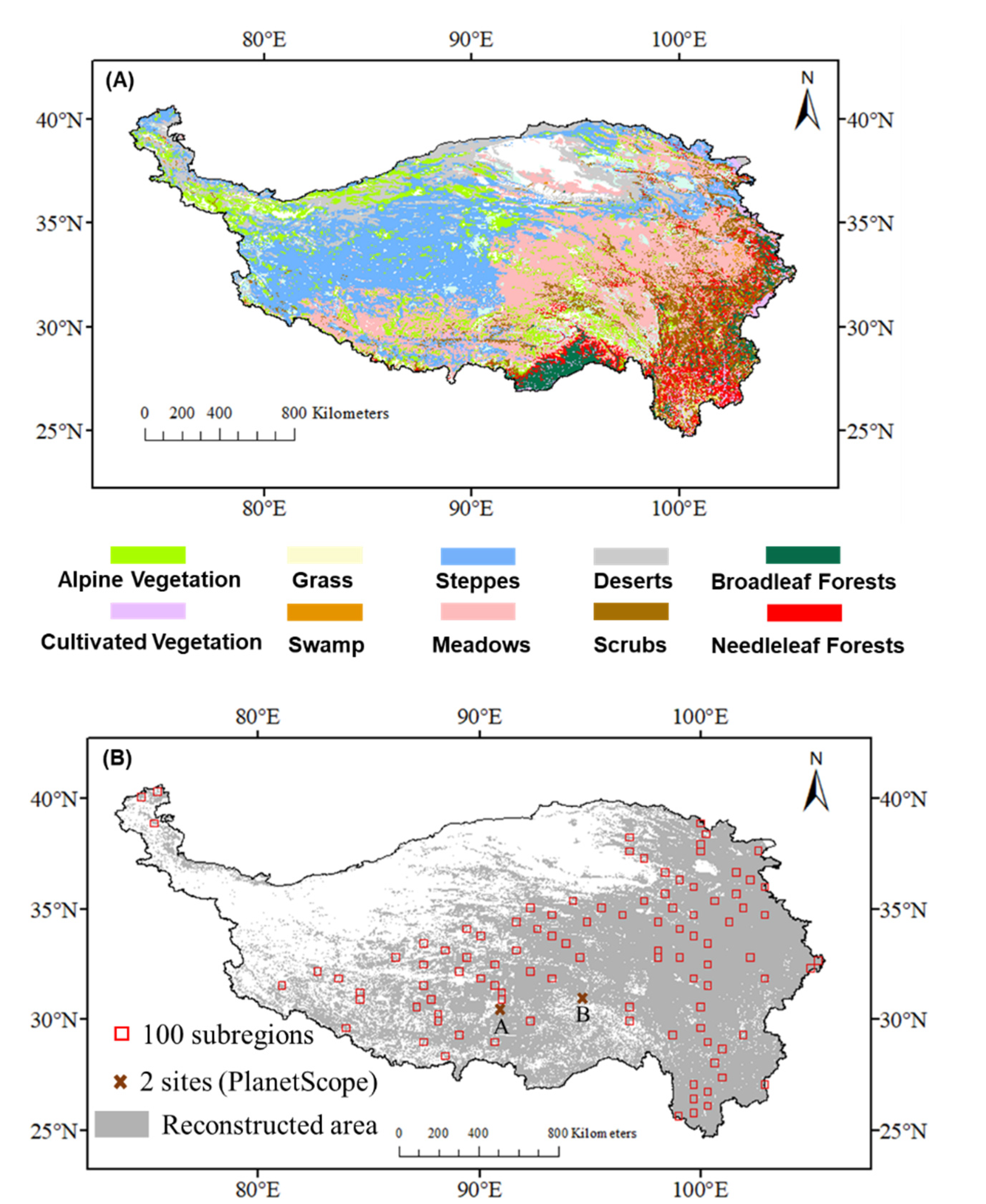
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Satellite Data
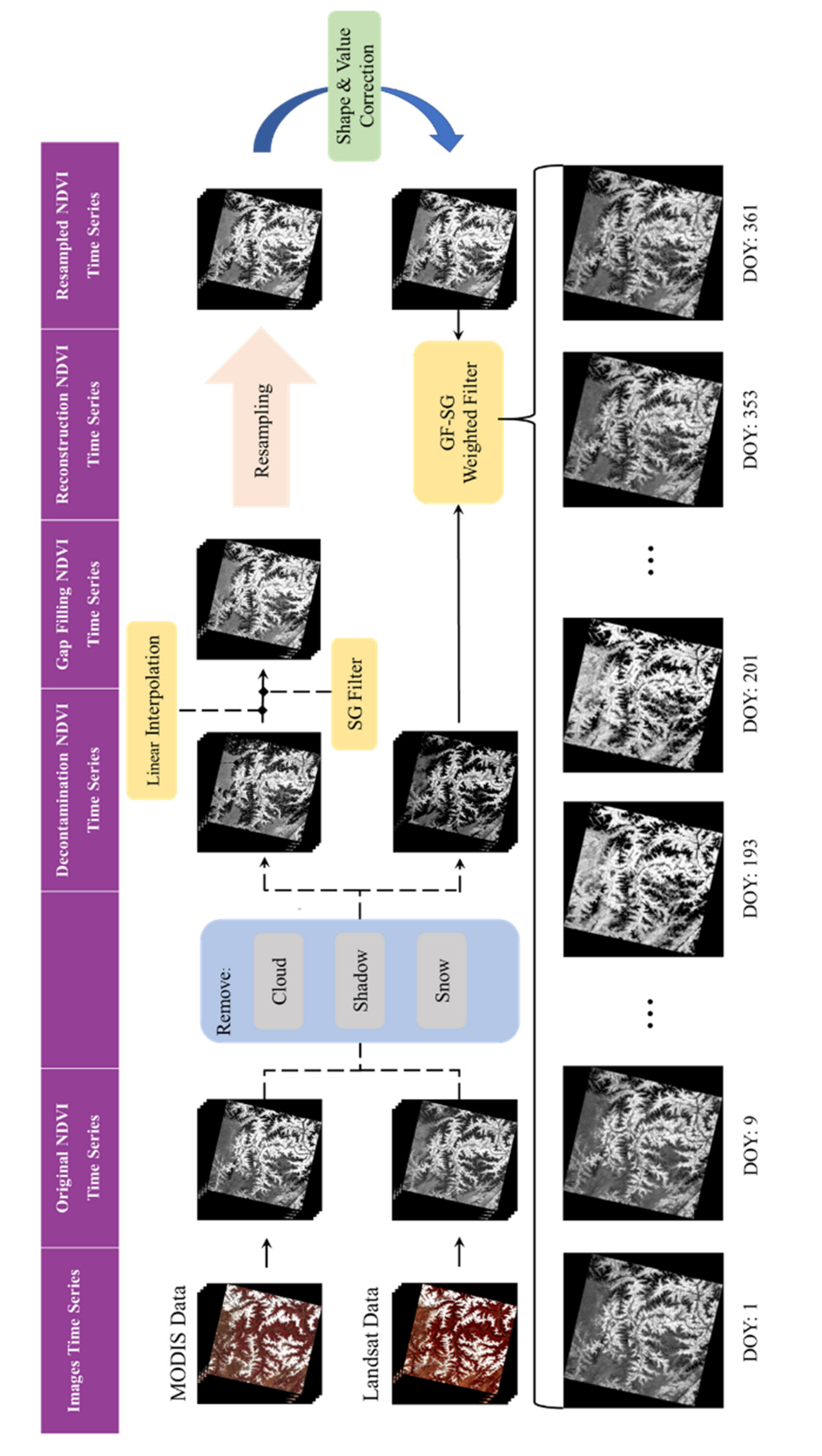
2.3. The Landsat NDVI Time-Series Data Reconstruction Method
2.4. Experiments and Accuracy Assessments
3. Results
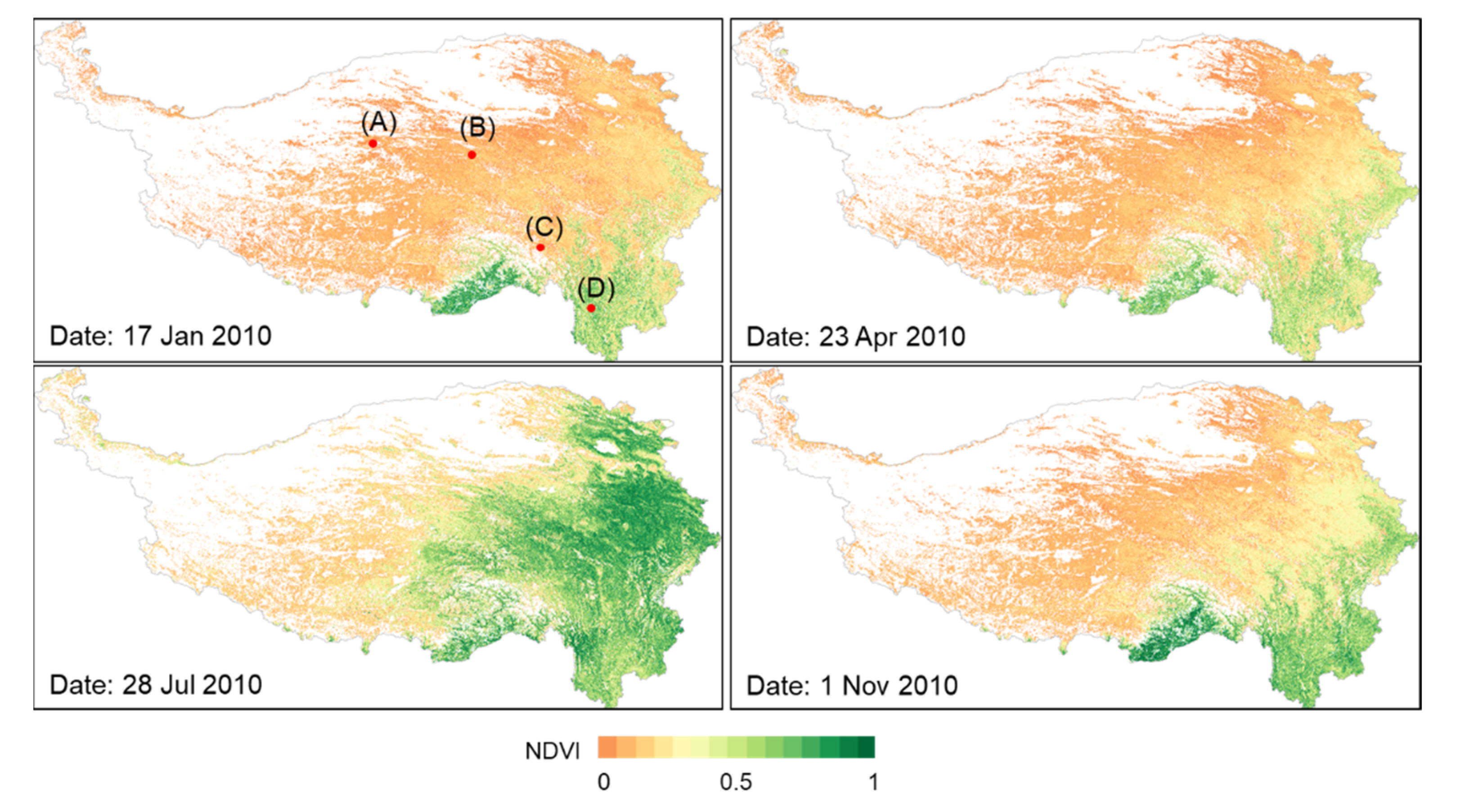
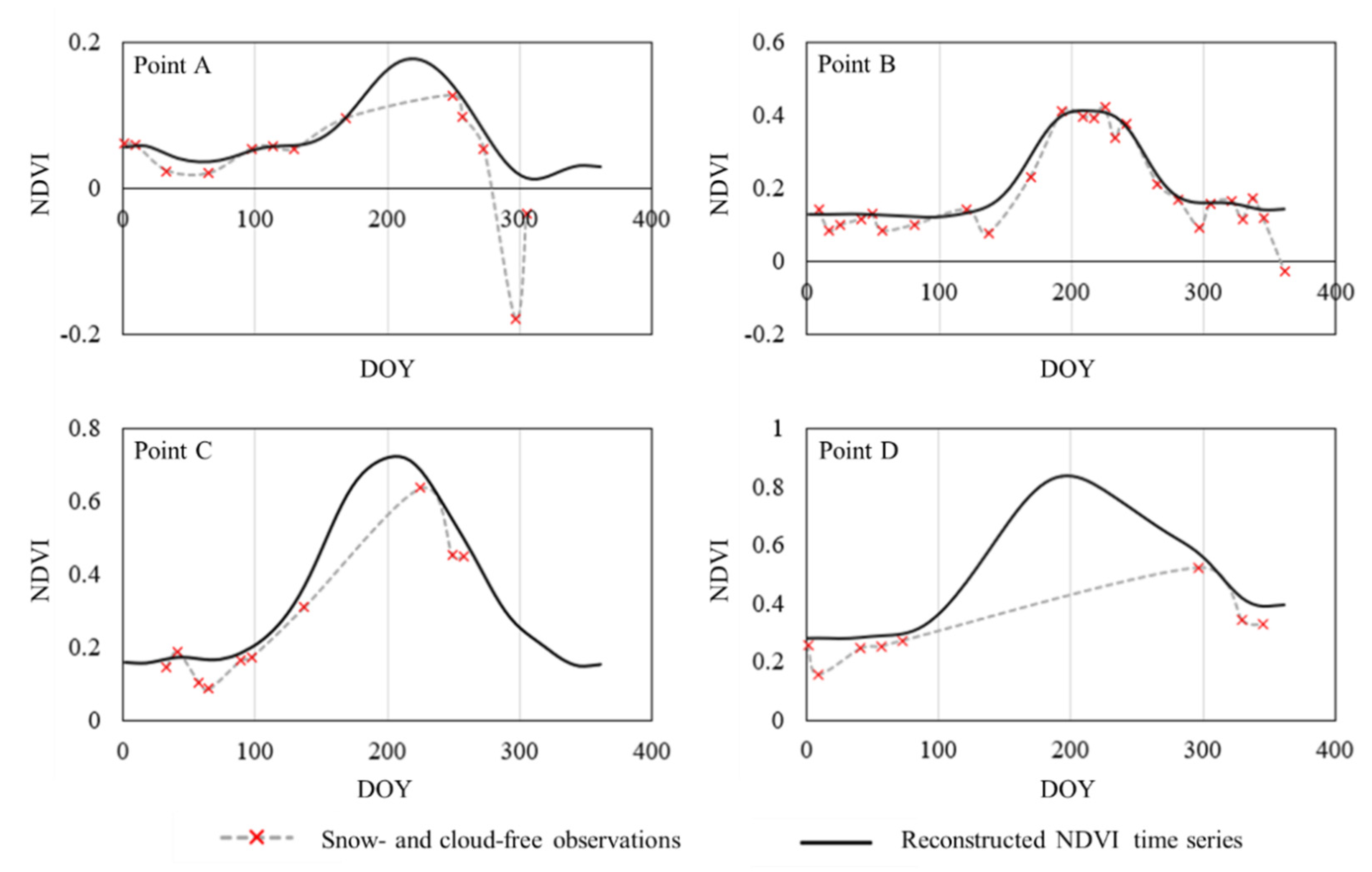
3.1. Spatiotemporal Patterns of QTP-NDVI30
3.2. Quantitative Assessments with the Reference Landsat NDVI Images
3.3. Quantitative Assessments Using the PlanetScope NDVI Images
3.4. An Application of QTP-NDVI30 to Detect Vegetation Phenology
4. Discussion
4.1. The Value and Robustness of the QTP-NDVI30 Data
4.2. Limitations of QTP-NDVI30
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- You, Q.; Min, J.; Kang, S. Rapid warming in the Tibetan Plateau from observations and CMIP5 models in recent decades. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2660–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D. Elevation dependence of drought legacy effects on vegetation greenness over the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 295, 108190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, H.; Wang, C.; Ji, L.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; Dai, L. The long-term trends (1982–2006) in vegetation greenness of the alpine ecosystem in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 1827–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Lv, C.; Wang, G.; Feng, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wan, L.; Tong, Y. Vegetation phenology and its variations in the Tibetan Plateau, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 3323–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, G.; Cong, N.; Wang, S.; Kong, W.; Piao, S. Increasing altitudinal gradient of spring vegetation phenology during the last decade on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Kong, D.; Shi, P.; Singh, V.P.; Sun, P. Vegetation phenology on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and its response to climate change (1982–2013). Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 248, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Shang, Z.; Gao, J.; Boone, R.B. Enhancing sustainability of grassland ecosystems through ecological restoration and grazing management in an era of climate change on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 287, 106684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, C.; Jetz, W.; Paulsen, J.; Payne, D.; Rudmann-Maurer, K.; Spehn, E.M. A global inventory of mountains for bio-geographical applications. Alp. Bot. 2017, 127, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atzberger, C.; Eilers, P.H. A time series for monitoring vegetation activity and phenology at 10-daily time steps covering large parts of South America. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2011, 4, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Chen, Y.; Shen, M.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, W. A simple method to improve the quality of NDVI time-series data by integrating spatiotemporal information with the Savitzky-Golay filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jönsson, P.; Tamura, M.; Gu, Z.; Matsushita, B.; Eklundh, L. A simple method for reconstructing a high-quality NDVI time-series data set based on the Savitzky–Golay filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Pan, Y.; He, H.; Wang, L.; Mou, M.; Liu, J. A changing-weight filter method for reconstructing a high-quality NDVI time series to preserve the integrity of vegetation phenology. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 50, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, X.; Shen, M. Thick cloud removal in Landsat images based on autoregression of Landsat time-series data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 249, 112001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Roy, D.P. The availability of cloud-free Landsat ETM+ data over the conterminous United States and globally. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1196–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, X.; Cheng, Q.; Zeng, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Zhang, L. Missing information reconstruction of remote sensing data: A technical review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2015, 3, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Yan, D.; Henebry, G.M. An exploration of terrain effects on land surface phenology across the Qinghai–Tibet plateau using Landsat ETM+ and OLI data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, H.; Wang, S. Exploring the Applicability and Scaling Effects of Satellite-Observed Spring and Autumn Phenology in Complex Terrain Regions Using Four Different Spatial Resolution Products. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Zhu, X.; Shen, M.; Wang, Y.; Cao, R.; Chen, X.; Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Tang, Y. Mismatch in elevational shifts between satellite observed vegetation greenness and temperature isolines during 2000–2016 on the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 5411–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Shen, X.; Cao, R. Elevational Movement of Vegetation Greenness on the Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from the Landsat Satellite Observations during the Last Three Decades. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Huete, A.R.; Shen, M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; He, G.; Yu, L.; Xu, X. Characteristics of Greening along Altitudinal Gradients on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Based on Time-Series Landsat Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Bai, Z.; Rong, L.; Li, Y.; Ding, J.; Tao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Wang, W. Investigation method for regional soil erosion based on the Chinese Soil Loss Equation and high-resolution spatial data: Case study on the mountainous Yunnan Province, China. Catena 2020, 184, 104237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.T.; Knight, J.F.; McRoberts, R.E. Harmonic regression of Landsat time series for modeling attributes from national forest inventory data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 137, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Roy, D.P. Spatially and temporally complete Landsat reflectance time series modelling: The fill-and-fit approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, R.; Chen, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G.; Shen, M.; Chen, X.; Yang, W. A new cross-fusion method to automatically determine the optimal input image pairs for NDVI spatiotemporal data fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 5179–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, J. An improved method for producing high spatial-resolution NDVI time series datasets with multi-temporal MODIS NDVI data and Landsat TM/ETM+ images. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7865–7891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Helmer, E.H.; Gao, F.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Lefsky, M.A. A flexible spatiotemporal method for fusing satellite images with different resolutions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 172, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Feng, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J. A Supplementary Module to Improve Accuracy of the Quality Assessment Band in Landsat Cloud Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. Thick cloud and cloud shadow removal in multitemporal imagery using progressively spatio-temporal patch group deep learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 162, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, R.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Matsushita, B. A practical approach to reconstruct high-quality Landsat NDVI time-series data by gap filling and the Savitzky–Golay filter. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 180, 174–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, S.; Yong, S.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, R. Vegetation Map of the People’s Republic of China (1:1,000,000); Geology Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Cao, R.; Chen, J.; Shen, M.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J.; He, B. Detecting crop phenology from vegetation index time-series data by improved shape model fitting in each phenological stage. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 277, 113060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Wardlow, B.D.; Gitelson, A.A.; Verma, S.B.; Suyker, A.E.; Arkebauer, T.J. A two-step filtering approach for detecting maize and soybean phenology with time-series MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2146–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, M.D.; Malthus, T.J.; Baret, F.; Xu, H.; Chopping, M.J. Intercalibration of vegetation indices from different sensor systems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Friedl, M.A.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H.; Hodges, J.C.; Gao, F.; Reed, B.C.; Huete, A. Monitoring vegetation phenology using MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, R.; Shen, M.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J. Modeling vegetation green-up dates across the Tibetan Plateau by including both seasonal and daily temperature and precipitation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 249, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, W.; Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Helmer, E.H. An Improved Flexible Spatiotemporal DAta Fusion (IFSDAF) method for producing high spatiotemporal resolution normalized difference vegetation index time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 227, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Guan, K.; Peng, J. STAIR: A generic and fully-automated method to fuse multiple sources of optical satellite data to generate a high-resolution, daily and cloud-/gap-free surface reflectance product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Song, C.; Clark, J.S.; Seyednasrollah, B.; Rathnayaka, N.; Li, J. Understanding the continuous phenological development at daily time step with a bayesian hierarchical space-time model: Impacts of climate change and extreme weather events. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyednasrollah, B.; Swenson, J.J.; Domec, J.-C.; Clark, J.S. Leaf phenology paradox: Why warming matters most where it is already warm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
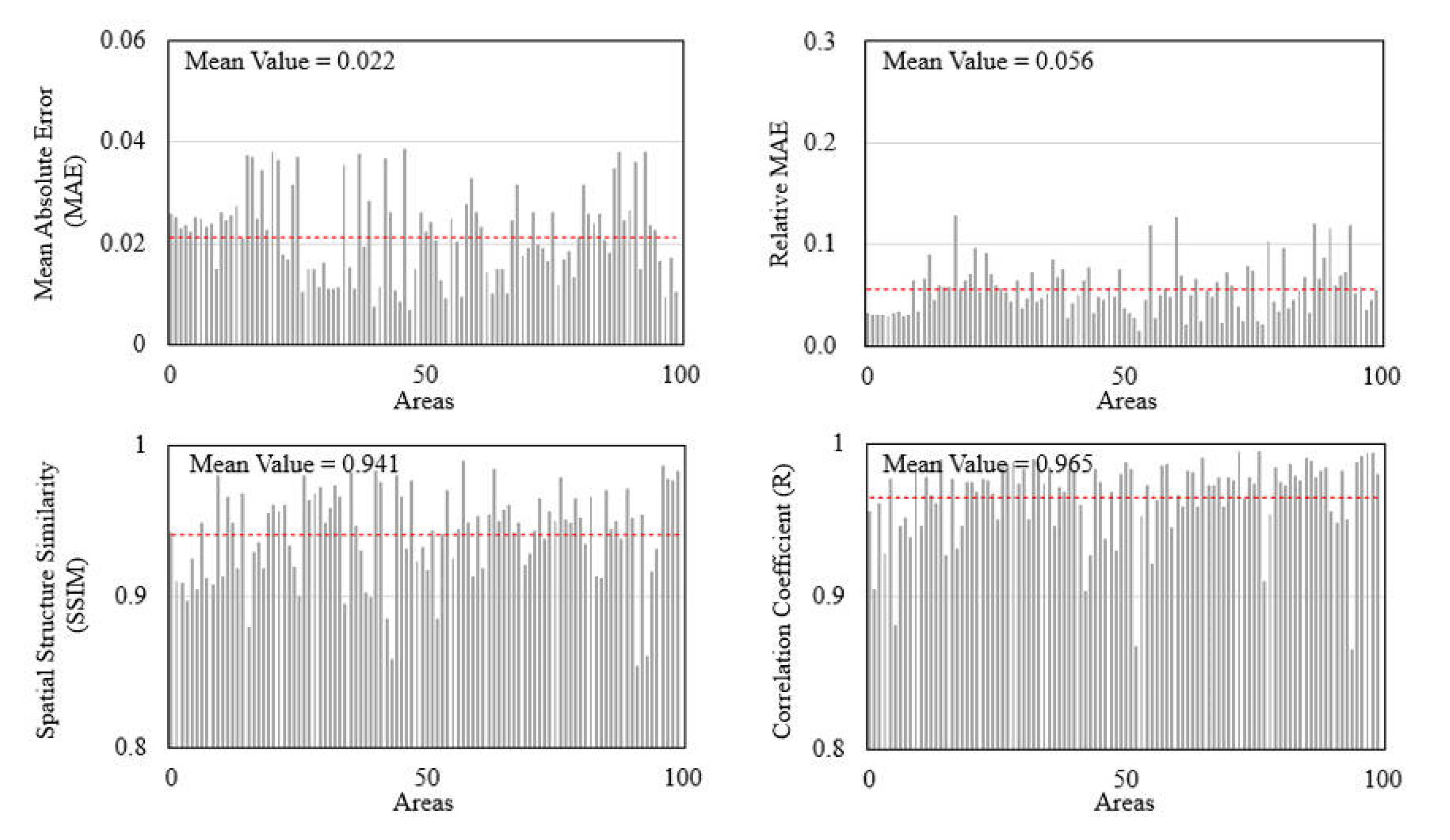
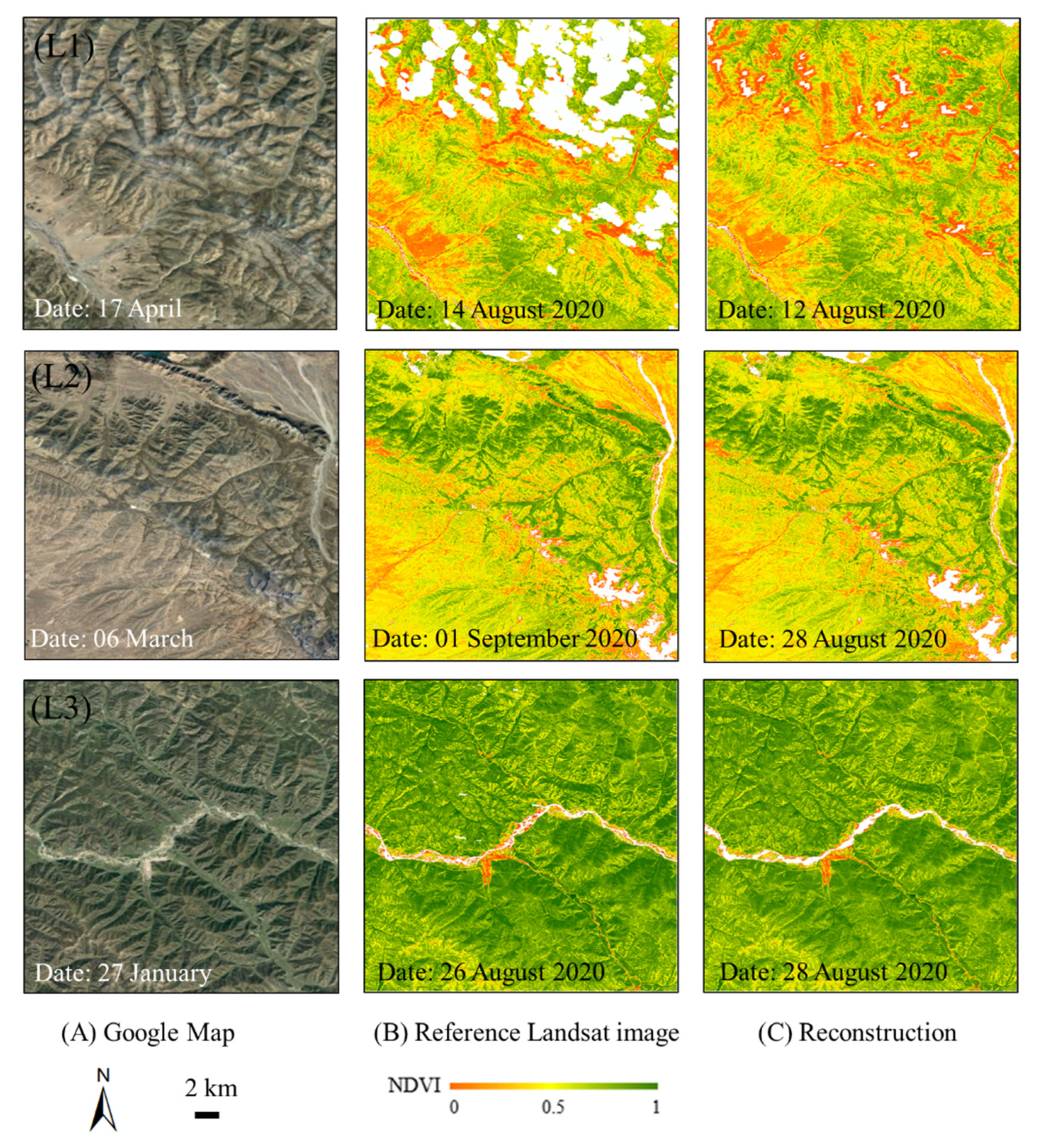



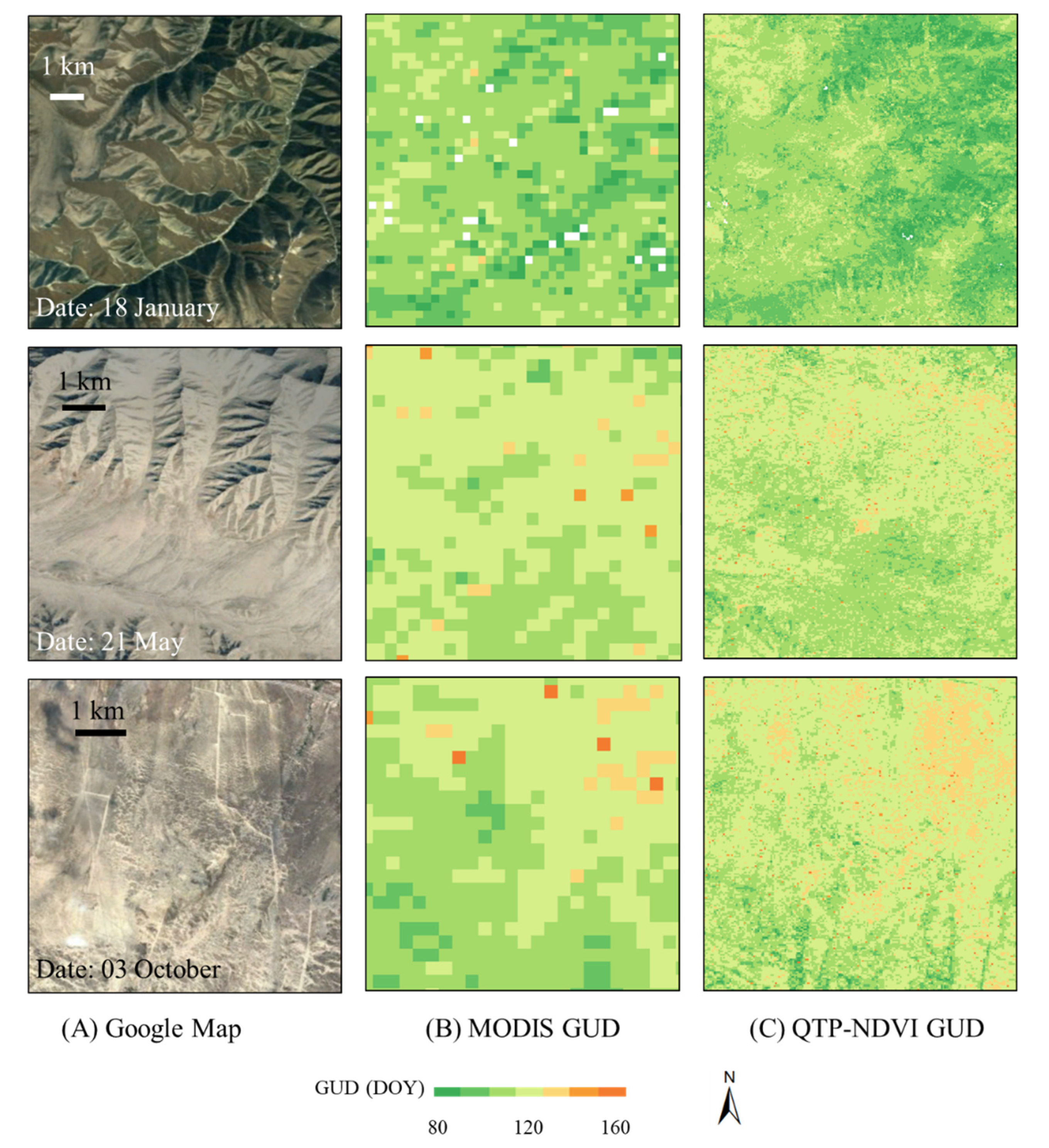
| Area ID | Date | Correlation Coefficient (R) | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-1 | 21 June 2019 | 0.8568 | 0.9037 |
| A-2 | 21 June 2019 | 0.8384 | 0.9299 |
| A-3 | 21 June 2019 | 0.8692 | 0.8994 |
| A-4 | 21 June 2019 | 0.8322 | 0.9028 |
| A-5 | 21 June 2019 | 0.8304 | 0.8422 |
| A-6 | 21 June 2019 | 0.7896 | 0.9501 |
| A-7 | 21 June 2019 | 0.8612 | 0.9245 |
| B-1 | 5 August 2010 | 0.8021 | 0.9046 |
| B-2 | 5 August 2010 | 0.7879 | 0.8347 |
| B-3 | 5 August 2010 | 0.8099 | 0.9069 |
| B-4 | 5 August 2010 | 0.8114 | 0.7879 |
| B-5 | 5 August 2010 | 0.8043 | 0.7758 |
| B-6 | 5 August 2010 | 0.7913 | 0.7958 |
| B-7 | 5 August 2010 | 0.8322 | 0.8358 |
| B-8 | 5 August 2010 | 0.8308 | 0.8564 |
| B-9 | 5 August 2010 | 0.8576 | 0.9350 |
| Average | 0.8253 | 0.8741 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, R.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Shen, M. Reconstructing High-Spatiotemporal-Resolution (30 m and 8-Days) NDVI Time-Series Data for the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau from 2000–2020. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3648. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153648
Cao R, Xu Z, Chen Y, Chen J, Shen M. Reconstructing High-Spatiotemporal-Resolution (30 m and 8-Days) NDVI Time-Series Data for the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau from 2000–2020. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(15):3648. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153648
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Ruyin, Zichao Xu, Yang Chen, Jin Chen, and Miaogen Shen. 2022. "Reconstructing High-Spatiotemporal-Resolution (30 m and 8-Days) NDVI Time-Series Data for the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau from 2000–2020" Remote Sensing 14, no. 15: 3648. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153648
APA StyleCao, R., Xu, Z., Chen, Y., Chen, J., & Shen, M. (2022). Reconstructing High-Spatiotemporal-Resolution (30 m and 8-Days) NDVI Time-Series Data for the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau from 2000–2020. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3648. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153648








