Assessment of Socioeconomic Dynamics and Electrification Progress in Tanzania Using VIIRS Nighttime Light Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Geography and Economy of Tanzania
2.2. Nighttime Light Data
2.3. Built-Up Area Data
2.4. Other Data
3. Methods
3.1. Regional Economic Disparity
3.1.1. Examining the Correlation between Nighttime Light and Economy
3.1.2. Regional Economic Disparity Analysis Based on the TNL
3.2. Power Infrastructure in Major Cities
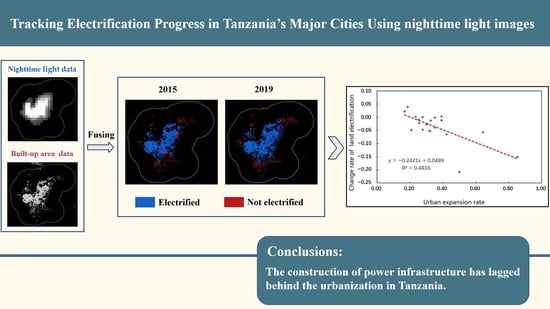
3.2.1. Land Electrification Rate
3.2.2. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Land Electrification
4. Results
4.1. Results of Regional Economic Disparity
4.1.1. Results of Correlation Analysis between TNL and GDP
4.1.2. Results of Regional Economic Disparity Analysis Based on TNL
4.2. Temporal and Spatial Dynamics of Power Infrastructure in Major Cities
4.2.1. Results of Land Electrification Rate
4.2.2. Correlation Analysis between the Change Rate of Land Electrification and Other Factors
5. Discussion
5.1. Advantages of Nighttime Light Remote Sensing
5.2. The Relationship between Nighttime Light Data and Power Infrastructure
5.3. The Outlier Moshi
5.4. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Potential of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Imagery for Modeling the Regional Economy of China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3057–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y. Urban mapping using DMSP/OLS stable night-time light: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 6030–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, A.C.; Bruce, D.A. The use of night-time lights satellite imagery as a measure of Australia’s regional electricity consumption and population distribution. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 4459–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Yue, H. Urban Land Extraction Using VIIRS Nighttime Light Data: An Evaluation of Three Popular Methods. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.M.; Smith, L.C. Advances in using multitemporal night-time lights satellite imagery to detect, estimate, and monitor socioeconomic dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 176–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabi, O.; Abubakar, A.; Werkmeister, A.; Sule, S.D. Keeping the lights on or off: Tracking the progress of access to electricity for sustainable development in Nigeria. Geojournal 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.; Gaba, K.M.; Sarr, O.F.; Agalassou, A. Detection of rural electrification in Africa using DMSP-OLS night lights imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 8118–8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, B. Identification of Poverty Areas by Remote Sensing and Machine Learning: A Case Study in Guizhou, Southwest China. Isprs Int. Geo. Inf. 2021, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Hall, O.; Archila, M.F. How Data-Poor Countries Remain Data Poor: Underestimation of Human Settlements in Burkina Faso as Observed from Nighttime Light Data. Isprs Int. Geo. Inf. 2019, 8, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzania in Figures 2020. Available online: https://www.nbs.go.tz/index.php/en/tanzania-in-figures/641-tanzania-in-figures-2020 (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Energy Access Situation Report, 2016 Tanzania Mainland. Available online: https://www.nbs.go.tz/index.php/en/other-statistics/286-energy-access-situation-report-2016-tanzania-mainland (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Choumert-Nkolo, J.; Motel, P.C.; Le Roux, L. Stacking up the ladder: A panel data analysis of Tanzanian household energy choices. World Dev. 2019, 115, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low and Lower Middle Income Countries List. Available online: https://www.mcascientificevents.eu/ecpm/wp-content/uploads/sites/8/2019/08/LowLower-Middle-Income-Countries-List.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Bhanjee, S.; Zhang, C.H. Mapping latest patterns of urban sprawl in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Pap. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 4, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sekei, V.S.; Ganiyu, S.A.; Makwetta, J.J. Research on the Sustainability of the Standard Gauge Railway Construction Project in Tanzania. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchouamou Njoya, E. Assessing the poverty impact of the COVID-19-induced tourism crisis in Tanzania: A social accounting matrix microsimulation analysis. J. Sustain. Tour. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estmann, C.; Sorensen, B.B.; Ndulu, B.; Rand, J. Merchandise export diversification strategy for Tanzania: Promoting inclusive growth, economic complexity and structural change. World Econ. 2022, 45, 2649–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocco, M.V.; Tonini, F.; Fumagalli, E.M.; Colombo, E. Electrification pathways for Tanzania: Implications for the economy and the environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J.; Sovacool, B.K. The financial risks and barriers to electricity infrastructure in Kenya, Tanzania, and Mozambique: A critical and systematic review of the academic literature. Energy Policy 2019, 125, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.-C. Why VIIRS data are superior to DMSP for mapping nighttime lights. Proc. Asia Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 35, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Report for the United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/980tanzania.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Shao, Z.F.; Sumari, N.S.; Portnov, A.; Ujoh, F.; Musakwa, W.; Mandela, P.J. Urban sprawl and its impact on sustainable urban development: A combination of remote sensing and social media data. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 24, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.; Olivia, S.; Boe-Gibson, G.; Li, C. Which night lights data should we use in economics, and where? J. Dev. Econ. 2021, 149, 102602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, E.C.; Seto, K.C. Characterizing urban infrastructural transitions for the Sustainable Development Goals using multi-temporal land, population, and nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 234, 111430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Five Year Development Plan 2021/22–2025/26. Available online: http://faolex.fao.org/docs/pdf/tan205461.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Levin, N.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Zhang, Q.L.; de Miguel, A.S.; Roman, M.O.; Li, X.; Portnov, B.A.; Molthan, A.L.; Jechow, A.; Miller, S.D.; et al. Remote sensing of night lights: A review and an outlook for the future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, M.O.; Wang, Z.S.; Sun, Q.S.; Kalb, V.; Miller, S.D.; Molthan, A.; Schultz, L.; Bell, J.; Stokes, E.C.; Pandey, B.; et al. NASA’s Black Marble nighttime lights product suite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconcini, M.; Metz-Marconcini, A.; Ureyen, S.; Palacios-Lopez, D.; Hanke, W.; Bachofer, F.; Zeidler, J.; Esch, T.; Gorelick, N.; Kakarla, A.; et al. Outlining where humans live, the World Settlement Footprint 2015. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadm. Available online: https://gadm.org/data.html (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Geofabric. Available online: http://download.geofabrik.de/ (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Africapolis. Available online: https://africapolis.org/en (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations-a new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabus, B.; Eineder, M.; Roth, A.; Bamler, R. The shuttle radar topography mission—A new class of digital elevation models acquired by spaceborne radar. Isprs J. Photogramm. 2003, 57, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Accounts Statistics. Available online: https://www.nbs.go.tz/index.php/en/census-surveys/national-accounts-statistics/na-statistics-by-subject (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, K.C. Mapping urbanization dynamics at regional and global scales using multi-temporal DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Impact of Floods on Tanzania’s Commercial Capital. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/opinion/2019/10/01/draining-dars-economy---the-impact-of-floods-on-tanzanias-commercial-capital (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Mtwara Port Set for Major Upgrade. Available online: https://www.theeastafrican.co.ke/business/-/2560/2459712/-/6oekjt/-/index.html (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Mahenge Graphite Total Mineral Resource Increase by 25%. Available online: https://tanzania883.rssing.com/chan-61021254/all_p3.html (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- TAZARA to Allow Private Investments. Available online: https://www.tanzaniainvest.com/transport/tazara-private-investments (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Tanzania Roads. Available online: https://www.tanzaniainvest.com/roads (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Tanzania Standard Gauge Railway. Available online: https://www.tanzaniainvest.com/sgr (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Bulengela, G.S.; Onyango, P.O.; Brehm, J.M. Exploring the agentic power in fishery: Reflections from fishing communities of Lake Tanganyika, Kigoma, Tanzania. Marit. Stud. 2020, 19, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2016 Tanzania Earthquake. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2016_Tanzania_earthquake (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Tanzania Mainland Poverty Assessment. Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/33031 (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Wwf Tanzania Annual Report 2019. Available online: https://www.wwfadria.org/?1169441/Tanzania-Country-Office-2019-Annual-Report (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Hojas-Gascon, L.; Eva, H.D.; Ehrlich, D.; Pesaresi, M.; Achard, F.; Garcia, J. Urbanization and Forest Degradation in East Africa—A Case Study Around Dar Es Salaam, Tanzania. In Proceedings of the 36th IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 7293–7295.
- Sumari, N.S.; Cobbinah, P.B.; Ujoh, F.; Xu, G. On the absurdity of rapid urbanization: Spatio-temporal analysis of land-use changes in Morogoro, Tanzania. Cities 2020, 107, 102876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruther, H.; Martine, H.M.; Mtalo, E.G. Application of snakes and dynamic programming optimisation technique in modeling of buildings in informal settlement areas. Isprs J. Photogramm. 2002, 56, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mboga, N.; Persello, C.; Bergado, J.R.; Stein, A. Detection of Informal Settlements from VHR Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, S.S.; Gao, Q.; Shen, Q.; Kimirei, I.A.; Mapunda, D.W. Morphological Characteristics of Informal Settlements and Strategic Suggestions for Urban Sustainable Development in Tanzania: Dar es Salaam, Mwanza, and Kigoma. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.; Gaba, K.M. Tracking Electrification in Vietnam Using Nighttime Lights. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9511–9529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzania: Flood Emergency. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/united-republic-tanzania/tanzania-flood-emergency-8-june-2018 (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- Tanzania—3 Dead, 100s Displaced after Floods in Mbeya, Zanzibar and Kilimanjaro Regions. Available online: https://floodlist.com/africa/tanzania-floods-mbeya-zanzibar-kilimanjaro (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Li, Z.L.; Tang, B.H.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.Z.; Yan, G.J.; Wan, Z.M.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-derived land surface temperature: Current status and perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Shi, Q.; Liu, X.P.; Zhong, Y.F.; Zhang, L.P. Generating 2m fine-scale urban tree cover product over 34 metropolises in China based on deep context-aware sub-pixel mapping network. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2022, 106, 102667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Q.; Li, D.; Liu, S.; He, T.; Zhao, L. Anisotropic characteristic of artificial light at night—Systematic investigation with VIIRS DNB multi-temporal observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, D.; Chen, F.; Jia, M.; Wang, Y. Using radiant intensity to characterize the anisotropy of satellite-derived city light at night. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 271, 112920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Wu, C. Intercalibration between DMSP/OLS and VIIRS night-time light images to evaluate city light dynamics of Syria’s major human settlement during Syrian Civil War. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5934–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


















| Population (million) | Number of Cities | Buffer Distances 1 (km) | Buffer Distances 2 (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1~0.2 | 10 | 1 | 3 |
| 0.2~0.5 | 4 | 2 | 4 |
| 0.5~1.0 | 4 | 3 | 5 |
| >1.0 | 1 | 6 | 8 |
| Variable | Coefficient |
|---|---|
| Constant term | 1107.162 *** |
| (134.107) | |
| 0.052 *** | |
| (0.001) | |
| Time effects | No |
| Region effects | Yes |
| Observations | 184 |
| Regions | 23 |
| 0.894 |
| City | Change Rate of Land Electrification | Urban Expansion Rate | Change Rate of TNL | Steepness of the Urban Terrain (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moshi | −0.209 | 0.50 | −0.20 | 347.15 |
| Bukoba | −0.151 | 0.85 | 0.09 | 62.98 |
| Tabora | −0.065 | 0.42 | 0.17 | 20.25 |
| Kahama | −0.057 | 0.64 | 0.34 | 23.17 |
| Arusha | −0.052 | 0.32 | 0.15 | 273.75 |
| Kigoma | −0.049 | 0.21 | −0.16 | 72.39 |
| Shinyanga | −0.049 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 17.09 |
| Singida | −0.040 | 0.35 | 0.11 | 24.06 |
| Zanzibar | −0.028 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 22.53 |
| Songea | −0.026 | 0.31 | 0.32 | 56.54 |
| Mbeya | −0.023 | 0.26 | 0.38 | 227.05 |
| Sumbawanga | −0.014 | 0.33 | 0.39 | 48.53 |
| Mwanza | −0.012 | 0.39 | 0.37 | 48.93 |
| Tanga | −0.009 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 22.46 |
| Musoma | −0.002 | 0.35 | 0.25 | 43.86 |
| Dar es Salaam | −0.001 | 0.28 | 0.39 | 56.94 |
| Morogoro | 0.000 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 185.10 |
| Dodoma | 0.002 | 0.39 | 0.60 | 45.10 |
| Iringa | 0.021 | 0.17 | 0.44 | 67.34 |
| Kasulu Mjini | 0.038 | 0.19 | 0.65 | 55.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, C.; Li, X.; Ru, Y. Assessment of Socioeconomic Dynamics and Electrification Progress in Tanzania Using VIIRS Nighttime Light Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174240
Zhu C, Li X, Ru Y. Assessment of Socioeconomic Dynamics and Electrification Progress in Tanzania Using VIIRS Nighttime Light Images. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(17):4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174240
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Changjun, Xi Li, and Yuanxi Ru. 2022. "Assessment of Socioeconomic Dynamics and Electrification Progress in Tanzania Using VIIRS Nighttime Light Images" Remote Sensing 14, no. 17: 4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174240
APA StyleZhu, C., Li, X., & Ru, Y. (2022). Assessment of Socioeconomic Dynamics and Electrification Progress in Tanzania Using VIIRS Nighttime Light Images. Remote Sensing, 14(17), 4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174240