Underwater Image Restoration via Contrastive Learning and a Real-World Dataset †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- SQUID (http://csms.haifa.ac.il/profiles/tTreibitz/datasets/ambient_forwardlooking/index.html, accessed on 25 July 2022) [15]: The Stereo Quantitative Underwater Image Dataset includes 57 stereo pairs from four different sites, two in the Red Sea and the other two in the Mediterranean Sea. Every image contains multiple color charts and its range map without providing the reference images.
- TURBID (http://amandaduarte.com.br/turbid/, accessed on 25 July 2022) [26]: TURBID consists of five different subsets of degraded images with its respective ground-truth reference image. Three subsets are publicly available: they are degraded by milk, deepblue, and chlorophyll. Each subset contains 20, 20, and 42 images, respectively.
- UWCNN Synthetic Dataset (https://li-chongyi.github.io/proj_underwater_image_synthesis.html, accessed on 25 July 2022) [23]: UWCNN synthetic dataset contains ten subsets, each subset representing one water type with 5000 training images and 2495 validation images. The dataset is synthesized from the NYU-v2 RGB-D dataset [31]. The first 1000 clean images are used to generate the training set and the remaining 449 clean images are used to generate the validation set. Each clean image is used to generate five images based on different levels of atmospheric light and water depth.
- Sea-thru dataset (http://csms.haifa.ac.il/profiles/tTreibitz/datasets/sea_thru/index.html, accessed on 25 July 2022) [32]: This dataset contains five subsets, representing five diving locations. It contains 1157 images in total; every image is with its range map. Color charts are available within the partial dataset. No reference images are provided.
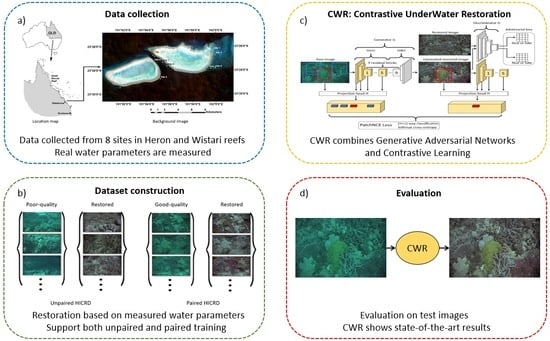
- We constructed a large-scale, high-resolution underwater image dataset with real underwater images and restored images. The Heron Island Coral Reef Dataset (HICRD) provides a platform to evaluate the performance of various underwater image restoration models on real underwater images with various water types. It also enables the training of both supervised and unsupervised underwater image restoration models.
- We proposed an unsupervised learning-based model, i.e., CWR, which leverages contrastive learning to maximize the mutual information between the corresponding patches of the raw image and the restored image to capture the content and color feature correspondences between the two image domains.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. A Real-World Dataset
2.1.1. Data Collection
2.1.2. Water Parameter Estimation
2.1.3. Detailed Information of HICRD
2.1.4. Underwater Imaging Model and Reference Image Generation
2.2. Proposed Method
2.2.1. Adversarial Loss
2.2.2. PatchNCE Loss
2.2.3. Identity Loss
2.2.4. Full Objective
2.3. Implementation Details
2.3.1. Architecture of Generator and Layers Used for PatchNCE Loss
2.3.2. Architecture of Discriminator
3. Results
3.1. Baselines
3.2. Training Details
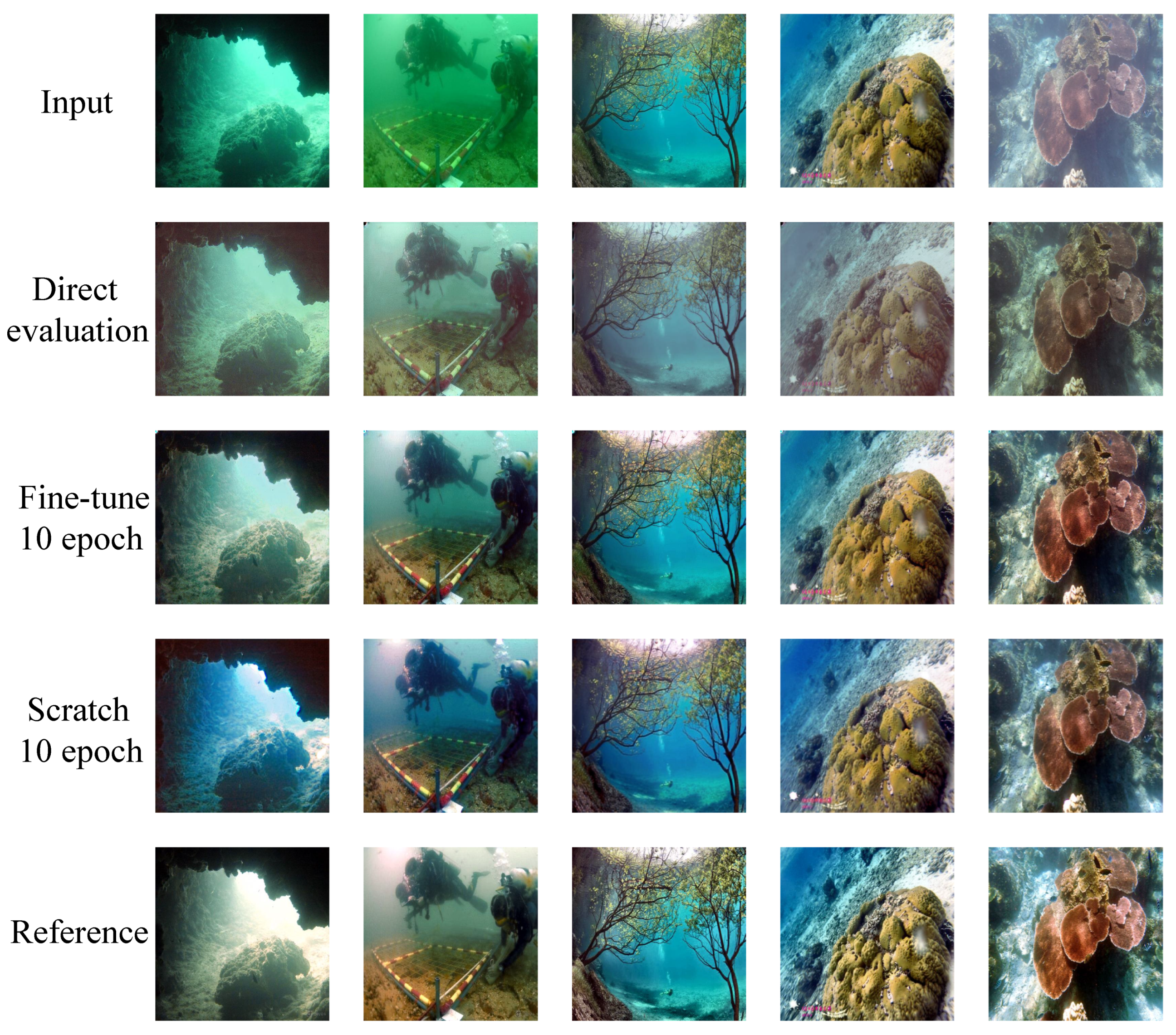
3.3. Evaluation Protocol
3.4. Evaluation Results
3.5. Generalization Performance on UIEB
3.6. Ablation Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reggiannini, M.; Moroni, D. The Use of Saliency in Underwater Computer Vision: A Review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.P.; Fakiris, E. Exploiting environmental information for improved underwater target classification in sonar imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6284–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludeno, G.; Capozzoli, L.; Rizzo, E.; Soldovieri, F.; Catapano, I. A microwave tomography strategy for underwater imaging via ground penetrating radar. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, T.; Kraus, D.; Zoubir, A.M. Contributions to automatic target recognition systems for underwater mine classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlevaris-Bianco, N.; Mohan, A.; Eustice, R.M. Initial results in underwater single image dehazing. In Proceedings of the Oceans 2010 Mts/IEEE Seattle, Seattle, WA, USA, 20–23 September 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Akkaynak, D.; Treibitz, T. A Revised Underwater Image Formation Model. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6723–6732. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Cao, W.; Cai, Z.; Su, B. An Underwater Image Vision Enhancement Algorithm Based on Contour Bougie Morphology. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 8117–8128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 33, 2341–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Drews, P.; Nascimento, E.; Moraes, F.; Botelho, S.; Campos, M. Transmission estimation in underwater single images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2–8 December 2013; pp. 825–830. [Google Scholar]
- Galdran, A.; Pardo, D.; Picón, A.; Alvarez-Gila, A. Automatic red-channel underwater image restoration. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2015, 26, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Underwater image enhancement by wavelength compensation and dehazing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 21, 1756–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Serikawa, S. Contrast enhancement for images in turbid water. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2015, 32, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.T.; Cosman, P.C. Underwater image restoration based on image blurriness and light absorption. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 1579–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerlov, N.G. Marine Optics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, D.; Levy, D.; Avidan, S.; Treibitz, T. Underwater single image color restoration using haze-lines and a new quantitative dataset. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 2822–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schechner, Y.Y.; Karpel, N. Recovery of underwater visibility and structure by polarization analysis. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2005, 30, 570–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, T. Polarimetric image recovery method combining histogram stretching for underwater imaging. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, T. Polarimetric underwater image recovery via deep learning. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 133, 106152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Peng, Y.T.; Cosman, P.C. Underwater image restoration using deep networks to estimate background light and scene depth. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Southwest Symposium on Image Analysis and Interpretation (SSIAI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 8–10 April 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, W.V.; Amaral, H.G.; Rocha, T.L.; Nascimento, E.R. Visual-quality-driven learning for underwater vision enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Athens, Greece, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 3933–3937. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, B.; Xu, X.; Jia, K.; Qing, C.; Tao, D. Dehazenet: An end-to-end system for single image haze removal. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 5187–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Liu, R.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z. Joint residual learning for underwater image enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Athens, Greece, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 4043–4047. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Anwar, S.; Porikli, F. Underwater scene prior inspired deep underwater image and video enhancement. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 98, 107038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Guo, C.; Ren, W.; Cong, R.; Hou, J.; Kwong, S.; Tao, D. An underwater image enhancement benchmark dataset and beyond. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 4376–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.; Codevilla, F.; Gaya, J.D.O.; Botelho, S.S. A dataset to evaluate underwater image restoration methods. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2016-Shanghai, Shanghai, China, 10–13 April 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fabbri, C.; Islam, M.J.; Sattar, J. Enhancing underwater imagery using generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 7159–7165. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.J.; Xia, Y.; Sattar, J. Fast underwater image enhancement for improved visual perception. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y. Underwater image restoration based on a parallel convolutional neural network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, J.; Guo, C. Emerging from water: Underwater image color correction based on weakly supervised color transfer. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberman, N.; Derek Hoiem, P.K.; Fergus, R. Indoor Segmentation and Support Inference from RGBD Images. In Proceedings of the ECCV, Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Akkaynak, D.; Treibitz, T. Sea-Thru: A Method for Removing Water From Underwater Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 1682–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, S.; Li, C. Diving deeper into underwater image enhancement: A survey. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2020, 89, 115978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Girshick, R. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9729–9738. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Kornblith, S.; Norouzi, M.; Hinton, G. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Virtual Event, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 1597–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Shoeiby, M.; Malthus, T.; Botha, E.; Anstee, J.; Anwar, S.; Wei, R.; Petersson, L.; Armin, M.A. Single Underwater Image Restoration by contrastive learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Salmond, J.; Passenger, J.; Kovacs, E.; Roelfsema, C.; Stetner, D. Reef Check Australia 2018 Heron Island Reef Health Report; Reef Check Foundation Ltd.: Marina Del Rey, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schönberg, C.H.; Suwa, R. Why bioeroding sponges may be better hosts for symbiotic dinoflagellates than many corals. In Porifera Research: Biodiversity, Innovation and Sustainability; Museu Nacional: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2007; pp. 569–580. [Google Scholar]
- Boss, E.; Twardowski, M.; McKee, D.; Cetinić, I.; Slade, W. Beam Transmission and Attenuation Coefficients: Instruments, Characterization, Field Measurements and Data Analysis Protocols, 2nd ed.; IOCCG Ocean Optics and Biogeochemistry Protocols for Satellite Ocean Colour Sensor Validation; IOCCG: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Oubelkheir, K.; Ford, P.W.; Clementson, L.A.; Cherukuru, N.; Fry, G.; Steven, A.D.L. Impact of an extreme flood event on optical and biogeochemical properties in a subtropical coastal periurban embayment (Eastern Australia). J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 6024–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, A.; Novak, M.G.; Nelson, N.B.; Belz, M.; Berthon, J.F.; Blough, N.V.; Boss, E.; Brichaud, A.; Chaves, J.; Del Castillo, C.; et al. Measurement Protocol of Absorption by Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) and Other Dissolved Materials, 1st ed.; IOCCG Ocean Optics and Biogeochemistry Protocols for Satellite Ocean Colour Sensor Validation; IOCCG: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, R.W.; Petzold, T.J. The Determination of the Diffuse Attenuation Coefficient of Sea Water Using the Coastal Zone Color Scanner. In Oceanography from Space; Gower, J.F.R., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1981; pp. 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Shanmugam, P. A new model for the vertical spectral diffuse attenuation coefficient of downwelling irradiance in turbid coastal waters: Validation with in situ measurements. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 30082–30106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panetta, K.; Gao, C.; Agaian, S. Human-visual-system-inspired underwater image quality measures. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2015, 41, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Soundararajan, R.; Bovik, A.C. Making a “completely blind” image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2012, 20, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Moorthy, A.K.; Bovik, A.C. No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 4695–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serikawa, S.; Lu, H. Underwater image dehazing using joint trilateral filter. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2014, 40, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Efros, A.A.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, J.Y. Contrastive learning for unpaired image-to-image translation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September; pp. 319–345.
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Shoeiby, M.; Petersson, L.; Armin, M.A. Dual Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognitio (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Y.; Guo, J.C.; Cong, R.M.; Pang, Y.W.; Wang, B. Underwater image enhancement by dehazing with minimum information loss and histogram distribution prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 5664–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zhuang, P.; Huang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Ding, X. A retinex-based enhancing approach for single underwater image. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 4572–4576. [Google Scholar]
- Ancuti, C.O.; Ancuti, C.; De Vleeschouwer, C.; Bekaert, P. Color balance and fusion for underwater image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 27, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyato, T.; Kataoka, T.; Koyama, M.; Yoshida, Y. Spectral normalization for generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.05957. [Google Scholar]
- Ulyanov, D.; Vedaldi, A.; Lempitsky, V. Instance normalization: The missing ingredient for fast stylization. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.08022. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Banff, AB, Canada, 14–16 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Hochreiter, S. Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mangeruga, M.; Bruno, F.; Cozza, M.; Agrafiotis, P.; Skarlatos, D. Guidelines for underwater image enhancement based on benchmarking of different methods. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, D.; Treibitz, T.; Avidan, S. Diving into haze-lines: Color restoration of underwater images. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), London, UK, 4–7 September 2017; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Akkaynak, D.; Treibitz, T.; Shlesinger, T.; Loya, Y.; Tamir, R.; Iluz, D. What Is the Space of Attenuation Coefficients in Underwater Computer Vision? In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4931–4940. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Fan, X.; Zhu, M.; Hou, M.; Luo, Z. Real-world underwater enhancement: Challenges, benchmarks, and solutions under natural light. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 30, 4861–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.H.; Gong, Z.; Jech, J.M.; Ratilal, P.; Makris, N.C. Instantaneous 3D continental-shelf scale imaging of oceanic fish by multi-spectral resonance sensing reveals group behavior during spawning migration. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Shang, X.; Sun, X.; Yu, H.; Song, M.; Chang, C.I. Underwater hyperspectral target detection with band selection. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogstad, A.A.; Johnsen, G.; Ludvigsen, M. Shallow-water habitat mapping using underwater hyperspectral imaging from an unmanned surface vehicle: A pilot study. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumke, I.; Ludvigsen, M.; Ellefmo, S.L.; Søreide, F.; Johnsen, G.; Murton, B.J. Underwater hyperspectral imaging using a stationary platform in the Trans-Atlantic Geotraverse hydrothermal field. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 2947–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Song, H.; Liu, H.; Wei, H.; Yang, P.; Zhan, S.; Wang, H.; Huang, H.; Liao, N.; Mu, Q.; et al. Model-based restoration of underwater spectral images captured with narrowband filters. Optics Express 2016, 24, 13101–13120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Site 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | Site 4 | Site 5 | Site 6 | Site 7 | Site 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-quality images | 47 | 53 | 458 | 1923 | 1726 | 117 | 961 | 718 |
| Good-quality images | 43 | 71 | 151 | 1042 | 1344 | 52 | 677 | 293 |
| Reference images | 25 | 16 | N.A. | 160 | 1241 | N.A. | 457 | 101 |
| Water type | 01 | 02 | N.A. | 04 | 05 | N.A. | 07 | 08 |
| Diver 1 max depth | 6.8 | 5.7 | 7.3 | 8.7 | 7.2 | 6.6 | 10.7 | 9.4 |
| Diver 2 max depth | 6.4 | 6.3 | 7.6 | 8.8 | 7.4 | 6.5 | 10.4 | 9.3 |
| Number of Images | UIQM ↑ | NIQE ↓ | BRISQUE ↓ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low quality | 6003 | 2.80 | 4.07 | 33.56 |
| Good quality | 3673 | 3.11 | 3.93 | 32.58 |
| Category | Method | Year | MSE↓ | PSNR↑ | SSIM↑ | UIQM↑ | FID↓ | Speed↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE | Histogram [54] | 2016 | 2408.8 | 14.44 | 0.618 | 5.27 | 69.15 | 10 |
| Retinex [55] | 2014 | 1227.2 | 17.36 | 0.722 | 5.43 | 71.90 | 5 | |
| Fusion [56] | 2017 | 1238.6 | 17.53 | 0.783 | 5.33 | 58.57 | 85 | |
| CR | UDCP [9] | 2013 | 3159.9 | 13.31 | 0.489 | 4.99 | 38.03 | 67 |
| DCP [8] | 2010 | 2548.2 | 14.27 | 0.534 | 4.49 | 37.52 | 168 | |
| IBLA [13] | 2017 | 803.9 | 19.42 | 0.459 | 3.63 | 23.06 | 141 | |
| Haze-line [15] | 2020 | 2305.6 | 14.69 | 0.427 | 4.71 | 53.67 | 192 | |
| LR | CUT [49] | 2020 | 170.3 | 26.30 | 0.796 | 5.26 | 22.35 | 46 |
| CycleGAN [50] | 2017 | 448.2 | 21.81 | 0.591 | 5.27 | 16.74 | 46 | |
| DCLGAN [51] | 2021 | 443.8 | 21.92 | 0.735 | 4.93 | 24.44 | 46 | |
| UWCNN [23] | 2020 | 775.8 | 20.20 | 0.754 | 4.18 | 33.43 | 55 | |
| CWR (ours) | 2022 | 127.2 | 26.88 | 0.834 | 5.25 | 18.20 | 1.5/46 |
| Method | Year | MSE↓ | PSNR↑ | SSIM↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histogram [54] | 2016 | 1576.8 | 16.48 | 0.598 |
| Retinex [55] | 2014 | 3587.3 | 14.77 | 0.549 |
| Fusion [56] | 2017 | 967.2 | 19.97 | 0.705 |
| UDCP [9] | 2013 | 6152.1 | 10.87 | 0.444 |
| DCP [8] | 2010 | 2770.8 | 15.20 | 0.639 |
| IBLA [13] | 2017 | 3587.3 | 14.77 | 0.549 |
| CUT [49] | 2020 | 860.3 | 20.34 | 0.765 |
| CWR (ours) | 2022 | 660.5 | 21.07 | 0.791 |
| Ablation | MSE↓ | PSNR↑ | SSIM↑ | UIQM↑ | FID↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 717.1 | 19.75 | 0.451 | 3.60 | 36.77 |
| II | 810.5 | 19.30 | 0.736 | 4.06 | 44.62 |
| III | 229.3 | 24.72 | 0.739 | 5.13 | 22.12 |
| IV | 217.4 | 25.28 | 0.756 | 5.40 | 37.02 |
| V | 203.9 | 25.54 | 0.779 | 5.48 | 36.35 |
| VI | 160.1 | 26.16 | 0.817 | 5.16 | 19.46 |
| CWR | 127.2 | 26.88 | 0.834 | 5.25 | 18.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Shoeiby, M.; Malthus, T.; Botha, E.; Anstee, J.; Anwar, S.; Wei, R.; Armin, M.A.; Li, H.; Petersson, L. Underwater Image Restoration via Contrastive Learning and a Real-World Dataset. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4297. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174297
Han J, Shoeiby M, Malthus T, Botha E, Anstee J, Anwar S, Wei R, Armin MA, Li H, Petersson L. Underwater Image Restoration via Contrastive Learning and a Real-World Dataset. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(17):4297. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174297
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Junlin, Mehrdad Shoeiby, Tim Malthus, Elizabeth Botha, Janet Anstee, Saeed Anwar, Ran Wei, Mohammad Ali Armin, Hongdong Li, and Lars Petersson. 2022. "Underwater Image Restoration via Contrastive Learning and a Real-World Dataset" Remote Sensing 14, no. 17: 4297. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174297
APA StyleHan, J., Shoeiby, M., Malthus, T., Botha, E., Anstee, J., Anwar, S., Wei, R., Armin, M. A., Li, H., & Petersson, L. (2022). Underwater Image Restoration via Contrastive Learning and a Real-World Dataset. Remote Sensing, 14(17), 4297. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174297