IMU-Aided Precise Point Positioning Performance Assessment with Smartphones in GNSS-Degraded Urban Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
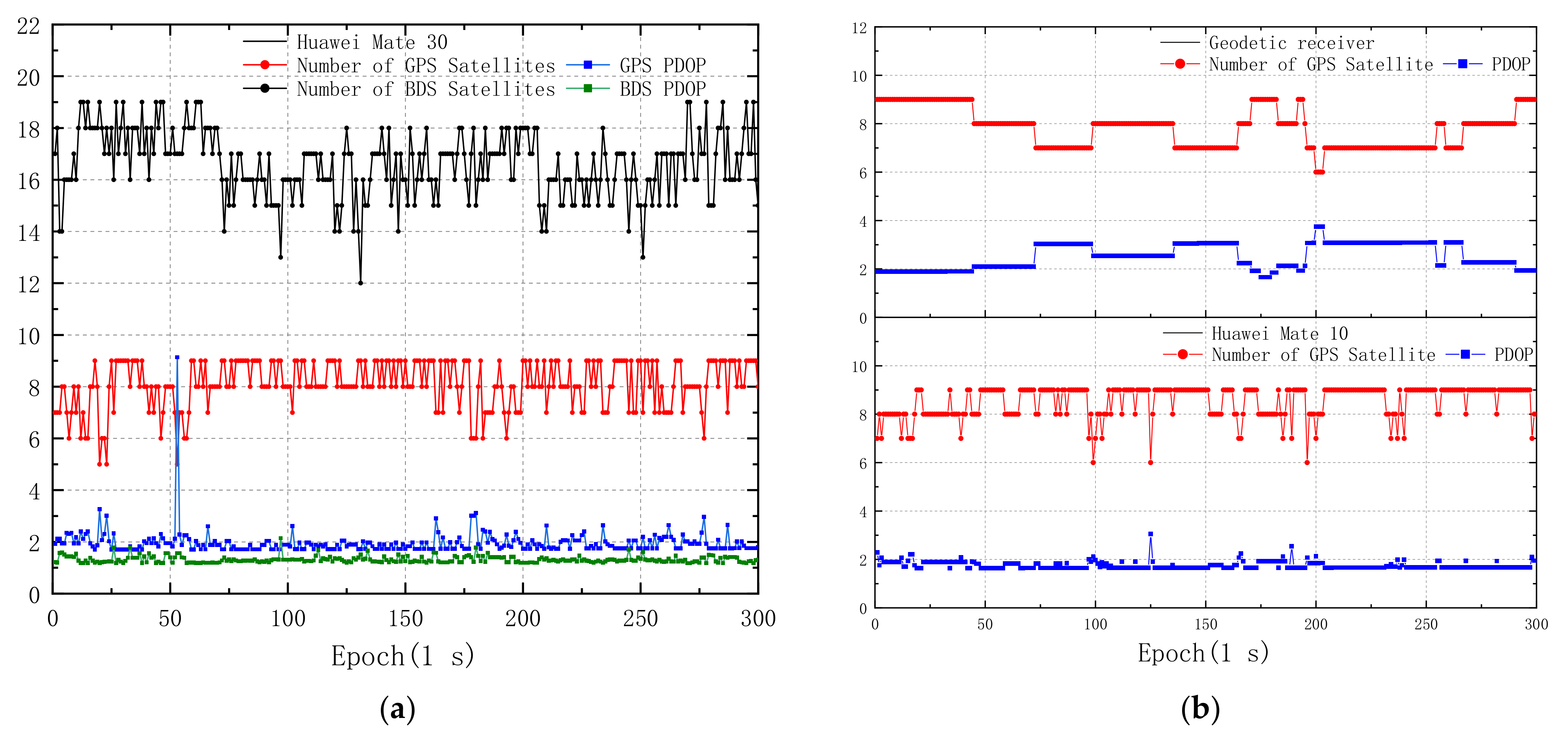
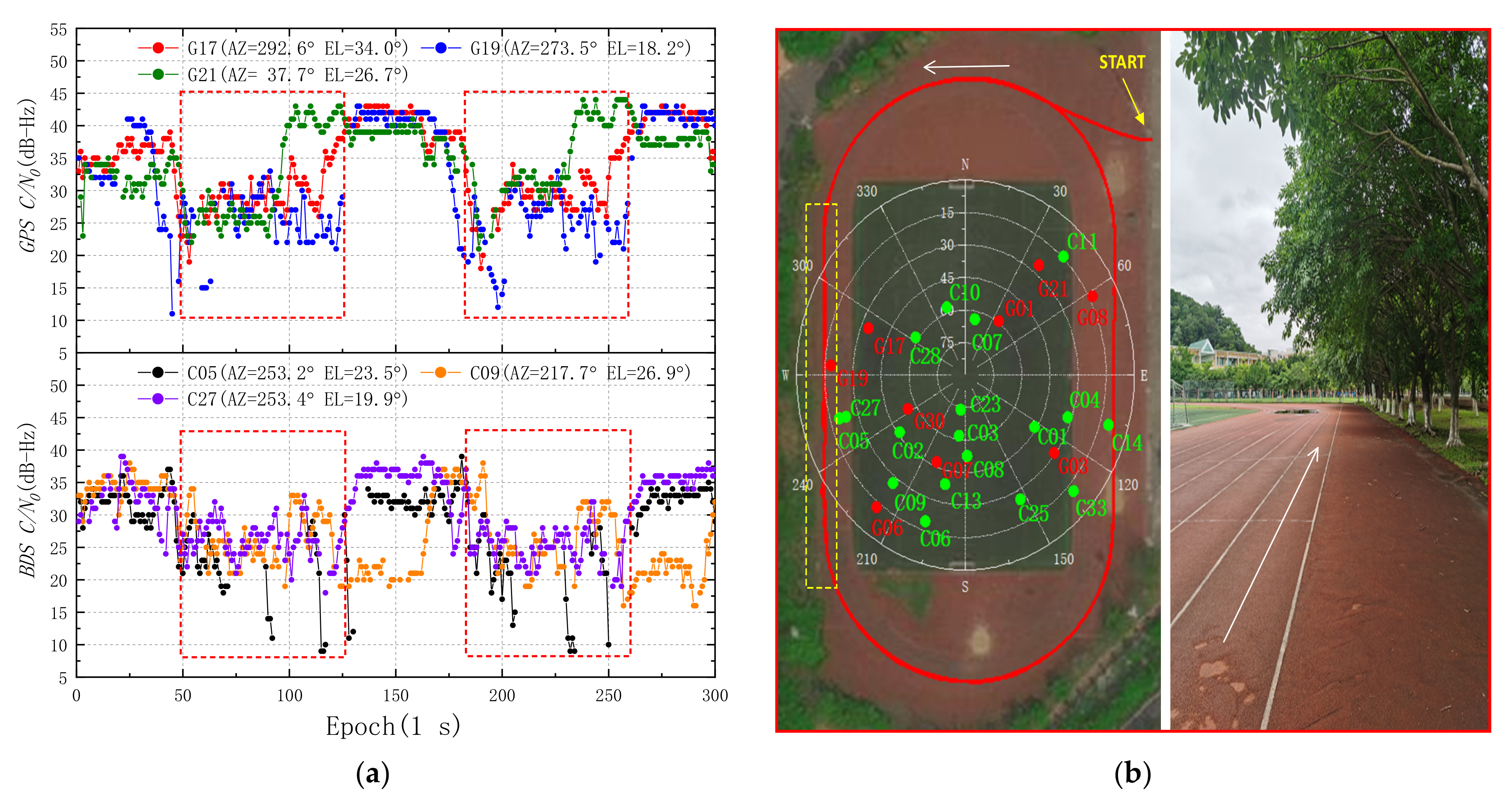
2. GNSS/IMU Sensors Data Characteristics Analysis
2.1. GNSS Measurements
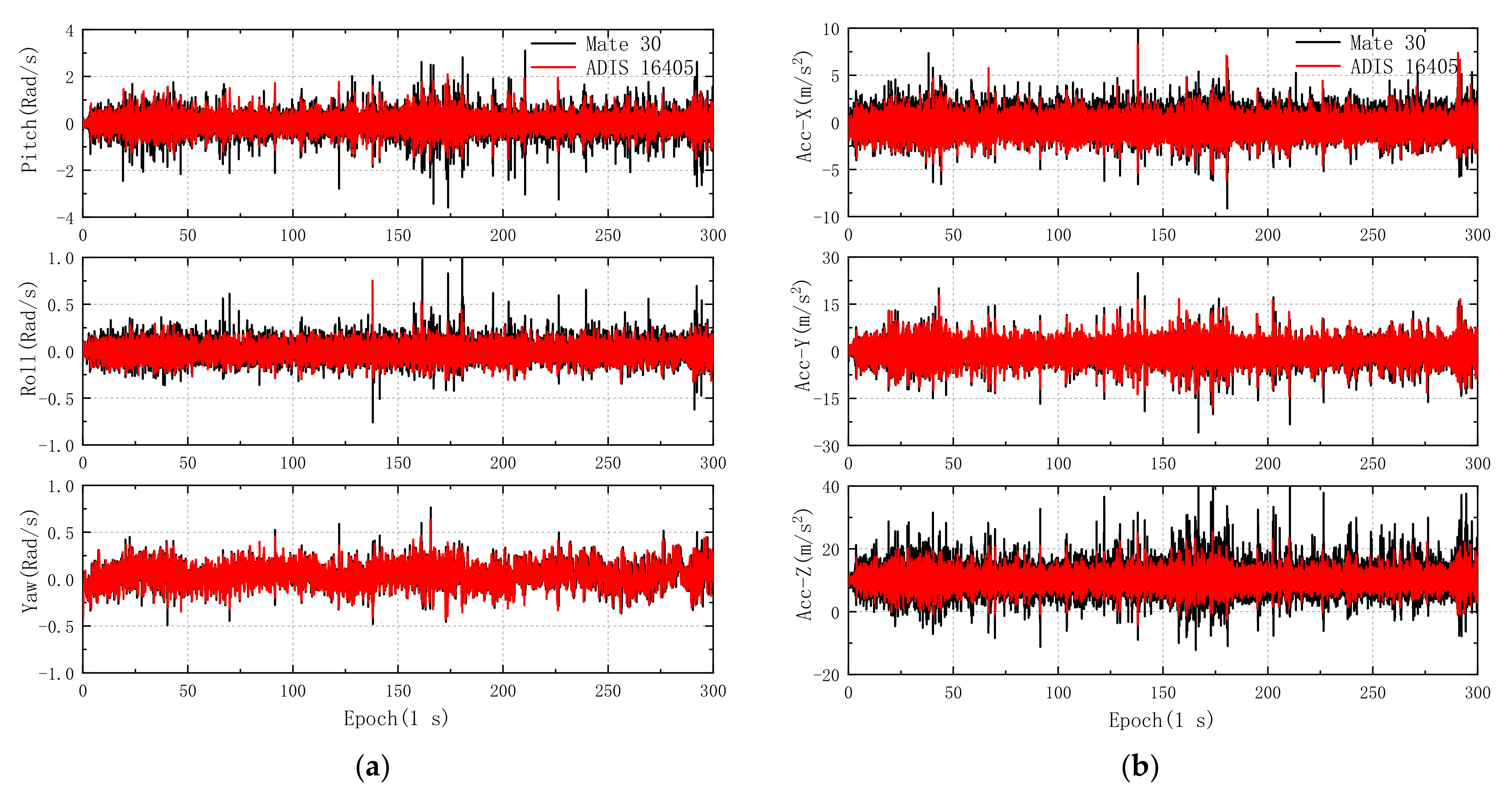
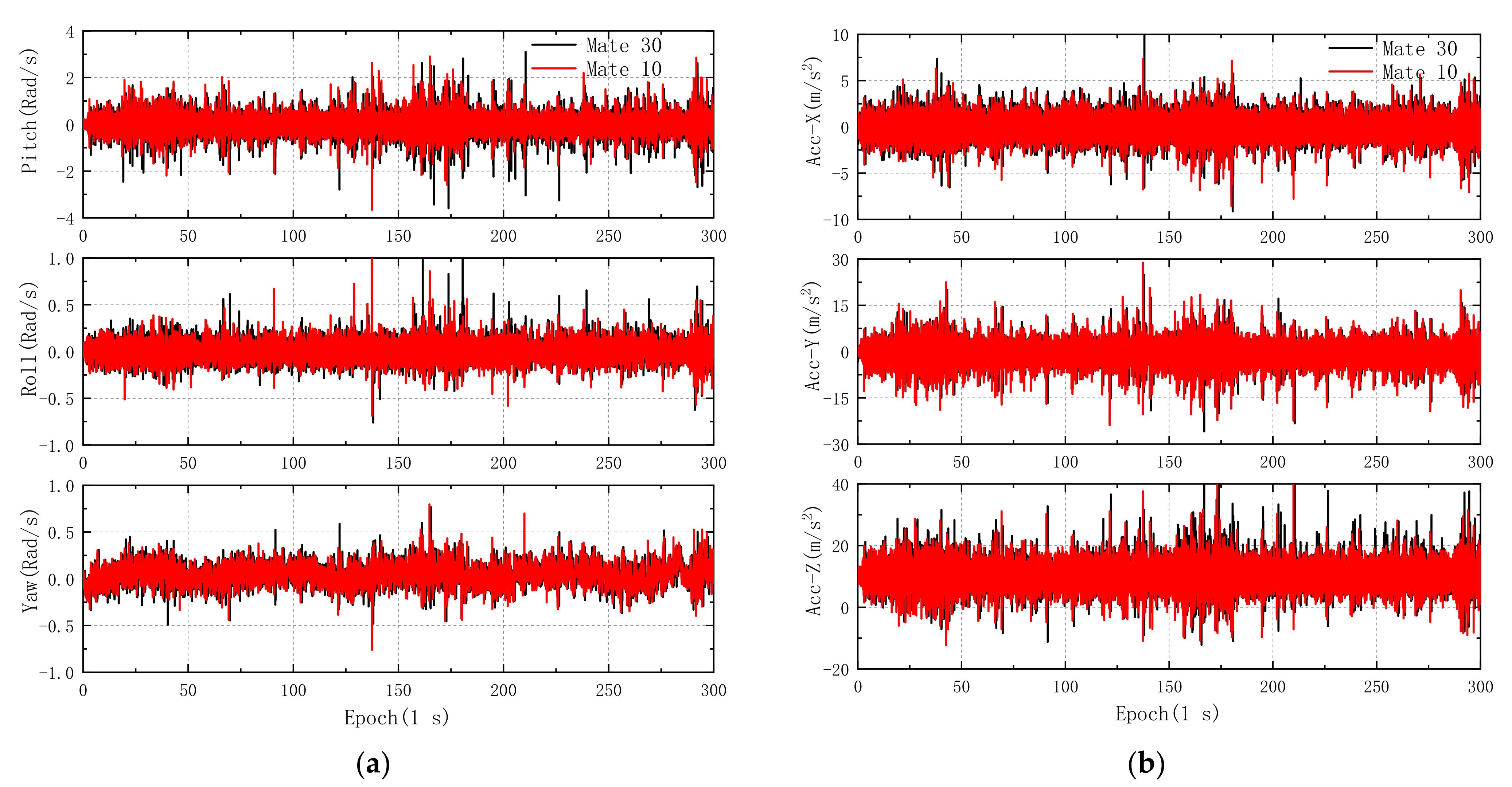
2.2. IMU Data
3. Multi-GNSS PPP/INS Mathematical Model
3.1. Uncombined PPP Model
3.2. MEMS–INS Model
3.3. Uncombined PPP/INS Coupled Model
3.4. Robust Kalman Filter Parameter Estimation Model
4. Experiment and Result
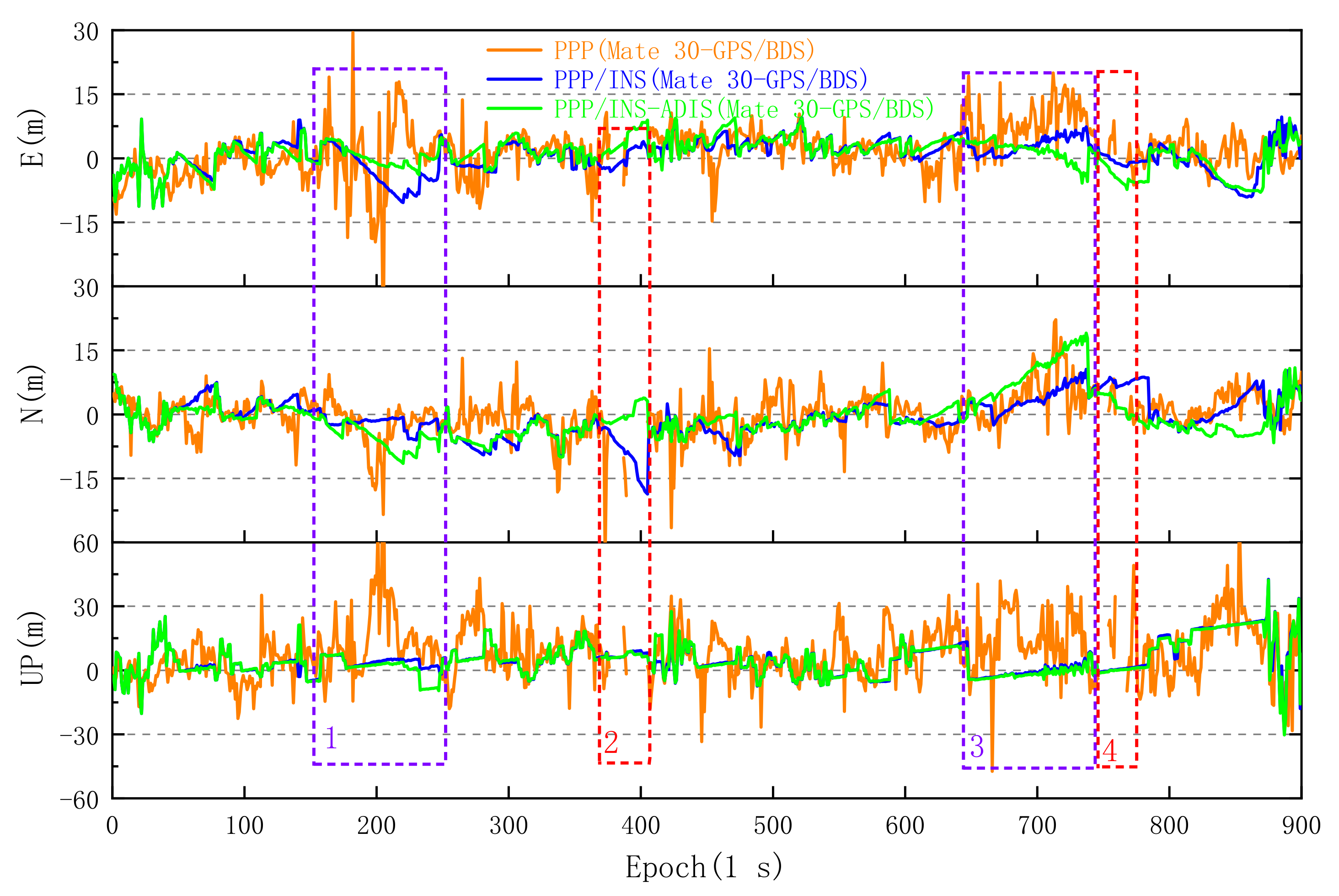
4.1. PPP/INS Solutions on the Playground and Sidewalk
4.2. PPP/INS Solutions for Tunnel and Long Trajectory
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- More than half of the carrier phase measurements cannot be observed in dynamic mode by the early single-frequency smartphones such as the Mate 10 in some areas where GNSS signal degrades slightly. Although the positioning accuracy of the Mate 10 is improved with the PPP/INS coupled model, its absolute positioning accuracy is still closely related to PPP accuracy. The weak positioning performance of single-frequency smartphones makes it difficult to meet the requirements of a precision location service, even in the open area.
- (2)
- Unlike the geodetic receiver, the number of visible GNSS satellites observed by the Mate 30 fluctuate within a narrow range, which is caused by the weak multipath suppression ability of GNSS antenna of smartphones. In some areas where GNSS signals are significantly degraded due to the buildings and trees on both sides, the RMS of smartphone PPP horizontal positioning errors can even reach more than 10 m.
- (3)
- With the proposed PPP/INS coupled method, the RMS of PPP horizontal and vertical positioning errors on smartphone decreased significantly in various GNSS-degraded environments, and long trajectory experimental results indicated that the RMS of PPP/INS horizontal errors in the eastern and western areas decrease by 49.37% and 48.29%, respectively, compared with convention PPP solutions. Meanwhile, the results of several experiments also show that the positioning accuracy of PPP/INS is roughly equivalent to that of PPP/INS–ADIS.
- (4)
- Moreover, the position of smartphone can be outputted continuously while moving through the tunnel with a length of about 80 m; the PPP/INS trajectory deviation of smartphone in the tunnel remained stable. The horizontal deviation from the reference point is more than 8 m after 29 epochs, and the positioning points quickly approach the reference trajectory after leaving the tunnel.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Engelbrecht, J.; Booysen, M.J.; van Rooyen, G.J.; Bruwer, F.J. Survey of smartphone-based sensing in vehicles for intelligent transportation system applications. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2015, 9, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, C.; Szot, T.; Dabrowski, P.; Specht, M. Testing GNSS receiver accuracy in Samsung Galaxy series mobile phones at a sports stadium. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 064006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewski, J. Recent advances and perspectives for positioning and applications with smartphone GNSS observations. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 091001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.C.; Geng, J.H. Characteristics of raw multi-GNSS measurement error from Google Android smart devices. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.H.; Shi, C. Using Inertial Sensors of iPhone 4 for Car Navigation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ION Position Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Myrtle Beach, SC, USA, 23–26 April 2012; pp. 555–561. [Google Scholar]
- Elarabi, T.; Suprem, A. Orientation and Displacement Detection for Smartphone Device Based Inertial Measurement Units. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 7–10 December 2015; pp. 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.K.; Shi, X.; Zhu, F.; Tao, X.L.; Wang, F.H. Quality analysis of multi-GNSS raw observations and a velocity-aided positioning approach based on smartphones. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 2358–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.Y.; Xia, L.Y.; Wu, D.J.; Xia, J.C.; Li, Q.X. Study on Multi-GNSS Precise Point Positioning Performance with Adverse Effects of Satellite Signals on Android Smartphone. Sensors 2020, 20, 6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmezayen, A.; El-Rabbany, A. Precise Point Positioning Using World’s First Dual-Frequency GPS/GALILEO Smartphone. Sensors 2019, 19, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Sun, M.F.; Zhou, C.J.; Zhang, P. Precise Point Positioning Using Dual-Frequency GNSS Observations on Smartphone. Sensors 2019, 19, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Gao, C.F.; Liu, Y.S.; Sun, P.Y. Real-time Precise Point Positioning with a Xiaomi MI 8 Android Smartphone. Sensors 2019, 19, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M.; Webb, F.H. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heroux, P.; Kouba, J. GPS precise point positioning using IGS orbit products. Phys. Chem. Earth Part A-Solid Earth Geod. 2001, 26, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linty, N.; Lo Presti, L.; Dovis, F.; Crosta, P. Performance analysis of duty-cycle power saving techniques in GNSS mass-market receivers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Monterey, CA, USA, 5–8 May 2014; pp. 1096–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Paziewski, J.; Sieradzki, R.; Baryla, R. Signal characterization and assessment of code GNSS positioning with low-power consumption smartphones. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, N.; Minetto, A.; Linty, N.; Dovis, F. A Controlled-Environment Quality Assessment of Android GNSS Raw Measurements. Electronics 2019, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakansson, M. Characterization of GNSS observations from a Nexus 9 Android tablet. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, T.E.; Murrian, M.; van Diggelen, F.; Podshivalov, S.; Pesyna, K.M. On the Feasibility of cm-Accurate Positioning via a Smartphone’s Antenna and GNSS Chip. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Savannah, GA, USA, 11–14 April 2016; pp. 232–242. [Google Scholar]
- Shinghal, G.; Bisnath, S. Conditioning and PPP processing of smartphone GNSS measurements in realistic environments. Satell. Navig. 2021, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, V.; Perakis, H. Rigorous Performance Evaluation of Smartphone GNSS/IMU Sensors for ITS Applications. Sensors 2016, 16, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.S.; Zhao, J.J.; Zhou, K.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yuan, H. Smart Device-Supported BDS/GNSS Real-Time Kinematic Positioning for Sub-Meter-Level Accuracy in Urban Location-Based Services. Sensors 2016, 16, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jukic, O.; Iliev, T.B.; Sikirica, N.; Lenac, K.; Spoljar, D.; Filjar, R. A method for GNSS positioning performance assessment for location-based services. In Proceedings of the 28th Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR), Belgrade, Serbia, 24–25 November 2020; pp. 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.K.; Zhu, D.F.; Chi, C.; Tang, J.H.; Liao, C.Y.; Yang, X. Visual-Inertial State Estimation with Pre-integration Correction for Robust Mobile Augmented Reality. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM), Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 1410–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Bahillo, A.; Aguilera, T.; Alvarez, F.J.; Perallos, A. WAY: Seamless Positioning Using a Smart Device. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 94, 2949–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, F.H.; Sang, J.Z.; Lin, X.H.; Gong, X.W.; Zhang, W.W. Characteristics Analysis of Raw Multi-GNSS Measurement from Xiaomi Mi 8 and Positioning Performance Improvement with L5/E5 Frequency in an Urban Environment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.S.; Wang, N.B.; Wang, Z.Y. Real-time GNSS precise point positioning for low-cost smart devices. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, S.; Wei, Y.Z.; Renaudin, V. Analysis of IMU and GNSS Data Provided by Xiaomi 8 Smartphone. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Univ Oberta Catalunya, Lloret de Mar, Spain, 29 November–2 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.; Kim, W.; Seo, J. Effects of Initial Attitude Estimation Errors on Loosely Coupled Smartphone GPS/IMU Integration System. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), Busan, Korea, 13–16 October 2020; pp. 800–803. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.L.; Bastos, L.; Magalhaes, A. Performance Assessment of the Android Smartphone’s IMU in a GNSS/INS Coupled Navigation Model. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 171073–171083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.L.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Wang, L.J.; Mao, Y.; Wang, A.S.; Zhao, C.S. A Modified Kalman Filter for Integrating the Different Rate Data of Gyros and Accelerometers Retrieved from Android Smartphones in the GNSS/IMU Coupled Navigation. Sensors 2020, 20, 5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, K.W.; Le, D.T.; Duong, T.T.; Sun, R. The Performance Analysis of INS/GNSS/V-SLAM Integration Scheme Using Smartphone Sensors for Land Vehicle Navigation Applications in GNSS-Challenging Environments. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K.; Qiao, L.; Dempster, A.G. Effect of PDOP on performance of Kalman Filters for GNSS-based space vehicle position estimation. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doong, S.H. A closed-form formula for GPS GDOP computation. GPS Solut. 2009, 13, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J.; Springer, T. New IGS Station and Satellite Clock Combination. GPS Solut. 2001, 4, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, F.K.; Hartinger, H.; Troyer, L. GPS signal diffraction modelling: The stochastic SIGMA-Delta model. J. Geod. 1999, 73, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartinger, H.; Brunner, F.N. Variances of GPS Phase Observations: The SIGMA-e Model. GPS Solut. 1999, 2, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.F.; Dai, C.Q.; Fang, W.T.; Zheng, F.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, Q.; Lou, Y.D.; Niu, X.J. Multi-GNSS PPP/INS tightly coupled integration with atmospheric augmentation and its application in urban vehicle navigation. J. Geod. 2021, 95, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.Q.; Chai, H.Z.; Xiao, G.R.; Yin, X.; Wang, M.; Xiang, M.Z. Analyzing the contributions of multi-GNSS and INS to the PPP-AR outage re-fixing. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, H.; Xu, G. Adaptively robust filtering for kinematic geodetic positioning. J. Geod. 2001, 75, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, X.H. Adaptive robust Kalman filtering for precise point positioning. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2014, 25, 105011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Song, L.; Xu, T. Robust estimator for correlated observations based on bifactor equivalent weights. J. Geod. 2002, 76, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhao, L.D.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, J.H. An Improved Robust Adaptive Kalman Filter for GNSS Precise Point Positioning. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 4176–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J. Contributions to the theory of atmospheric refraction. II. Refraction corrections in satellite geodesy. Bull. Géodés. 1972, 105, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Parameter | Gyroscope | Parameter | Accelerometer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Bias Error (°/s) | ±3 (1 σ) | Initial Bias Error (mg) | ±50 (1 σ) |
| In-Run Bias Stability (°/s) | 0.007 (1 σ) | In-Run Bias Stability (mg) | 0.2 (1 σ) |
| Angular Random Walk (°/sqrt(h)) | 2.0 (1 σ) | Velocity Random Walk (m/s/sqrt(h)) | 0.2 (1 σ) |
| Rate Noise Density (°/s/sqrt(Hz)) | 0.05 | Noise Density (mg/sqrt(Hz)) | 0.5 |
| Smartphone Kinematic Positioning Error RMS (m) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dir | Huawei Mate 10 | Huawei Mate 30 | ||||
| G(PPP) | G(PPP/INS) | G(PPP) | G(PPP/INS) | GB(PPP) | GB(PPP/INS) | |
| E | 12.157 | 8.112 | 4.732 | 5.318 | 3.666 | 2.546 |
| N | 11.403 | 8.304 | 3.682 | 2.849 | 3.920 | 2.521 |
| H | 16.668 | 11.293 | 5.996 | 6.033 | 5.367 | 3.583 |
| V | 29.509 | 23.717 | 12.274 | 7.389 | 7.359 | 5.546 |
| 3D | 33.891 | 26.269 | 13.660 | 9.539 | 9.108 | 6.603 |
| Direction | Huawei Mate 30 Kinematic Positioning Error RMS (m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GB(PPP) | GB(PPP/INS) | GB(PPP/INS–ADIS) | |
| E | 6.589 | 4.903 | 3.470 |
| N | 6.420 | 4.241 | 4.054 |
| H | 9.200 | 6.483 | 5.336 |
| V | 13.389 | 7.768 | 7.859 |
| 3D | 16.245 | 10.118 | 9.499 |
| Direction | Huawei Mate 30 GPS/BDS Kinematic Positioning Error RMS (m) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150–250 (Epochs) | 650–750 (Epochs) | |||||
| PPP | PPP/INS | PPP/INS–ADIS | PPP | PPP/INS | PPP/INS–ADIS | |
| E | 9.837 | 5.252 | 2.267 | 9.072 | 3.532 | 3.788 |
| N | 5.799 | 2.417 | 5.998 | 7.258 | 4.860 | 6.574 |
| H | 11.419 | 5.782 | 6.412 | 11.618 | 6.008 | 7.587 |
| V | 23.190 | 4.507 | 5.083 | 19.446 | 2.784 | 7.498 |
| 3D | 25.849 | 7.331 | 8.183 | 22.652 | 6.622 | 10.667 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, H.; Xia, L.; Li, Q.; Xia, J.; Cai, Y. IMU-Aided Precise Point Positioning Performance Assessment with Smartphones in GNSS-Degraded Urban Environments. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4469. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184469
Zhu H, Xia L, Li Q, Xia J, Cai Y. IMU-Aided Precise Point Positioning Performance Assessment with Smartphones in GNSS-Degraded Urban Environments. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(18):4469. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184469
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Hongyu, Linyuan Xia, Qianxia Li, Jingchao Xia, and Yuezhen Cai. 2022. "IMU-Aided Precise Point Positioning Performance Assessment with Smartphones in GNSS-Degraded Urban Environments" Remote Sensing 14, no. 18: 4469. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184469
APA StyleZhu, H., Xia, L., Li, Q., Xia, J., & Cai, Y. (2022). IMU-Aided Precise Point Positioning Performance Assessment with Smartphones in GNSS-Degraded Urban Environments. Remote Sensing, 14(18), 4469. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184469







