Active Fault Trace Identification Using a LiDAR High-Resolution DEM: A Case Study of the Central Yangsan Fault, Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Settings

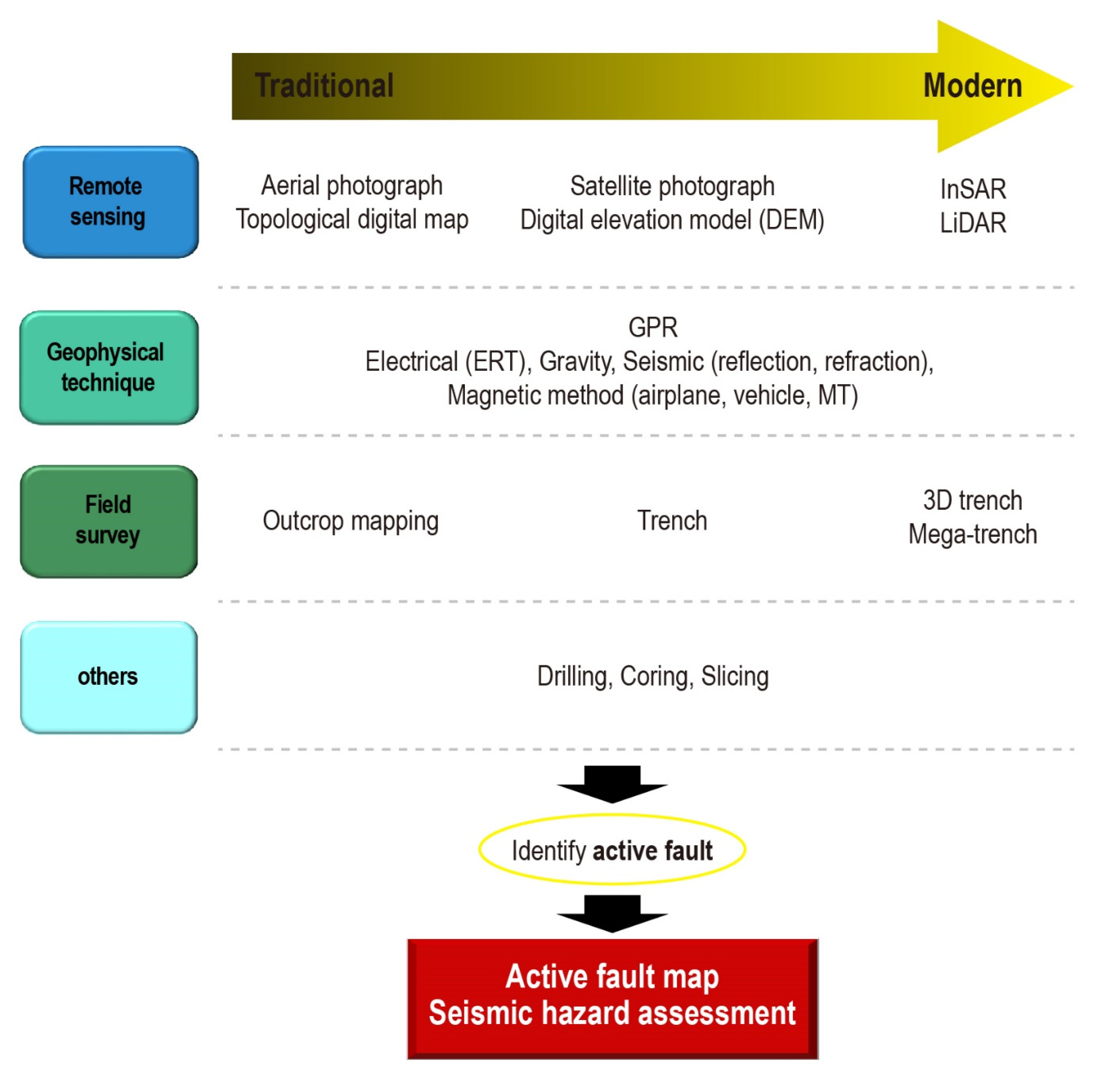
3. Methods
3.1. Acquisition of LiDAR Data
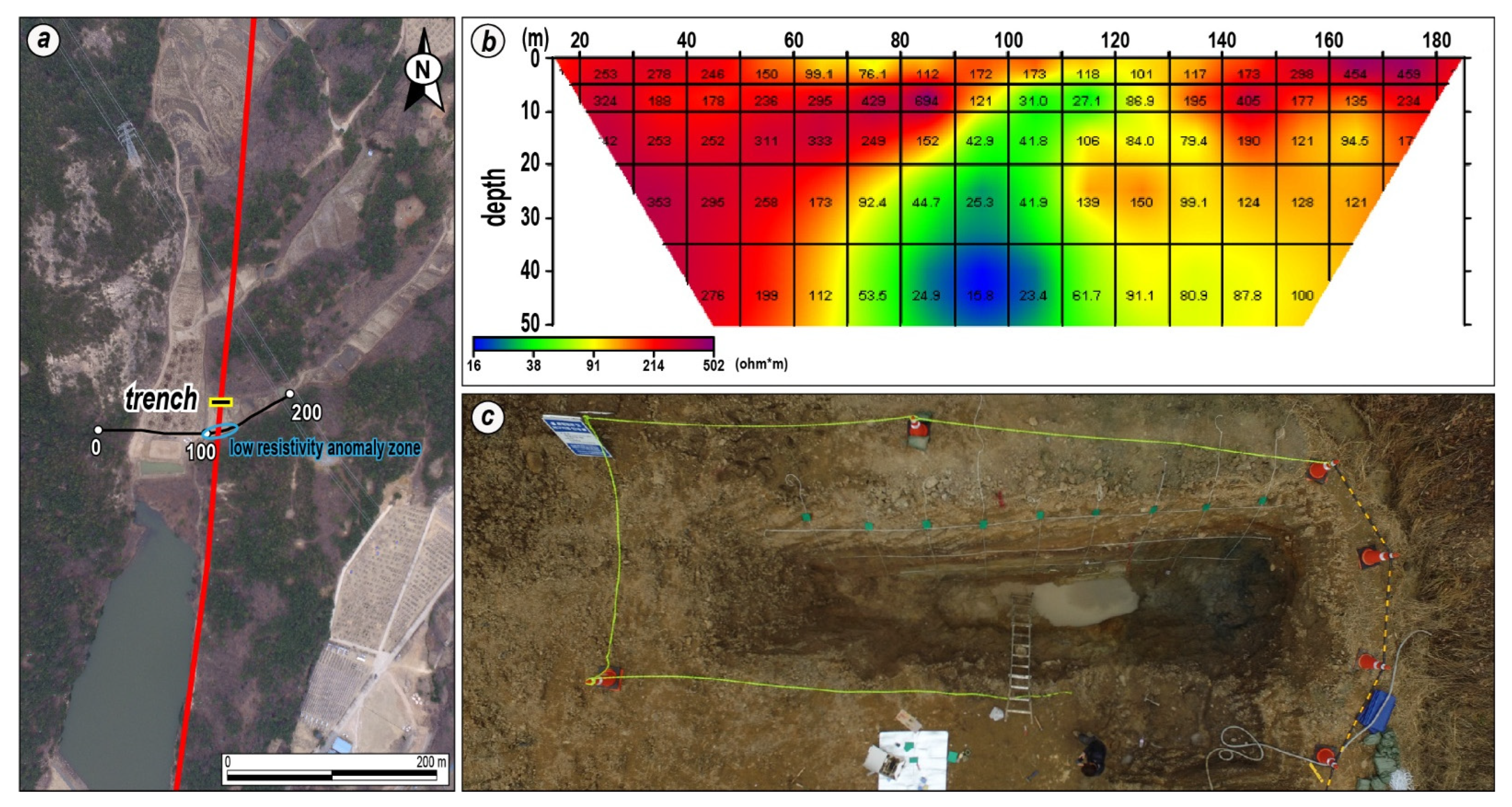
3.2. Electrical Resistivity & Trench Survey for Site Selection
4. Results
4.1. Topographic Mapping Using High-Resolution LiDAR Data DEMs
4.2. Electrical Resistivity and Trench Survey
4.2.1. Electrical Resistivity Survey
4.2.2. Quaternary Fault Characteristics in the Trench
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coburn, A.W.; Spence, R.J.S. Earthquake Protection, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Blaikie, P.; Cannon, T.; Davis, I.; Wisner, B. At Risk: Natural Hazards, People’s Vulnerability and Disasters, 2nd ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2004; p. 496. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, S.; Wysession, M. An Introduction to Seismology, Earthquakes, and Earth Structure; Blackwell Scientific: Malden, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- McCalpin, J.P. Chapter 9: Application of Paleoseismic Data to Seismic Hazard Assessment and Neotectonic Research. In Paleoseismology, 2nd ed.; International Geophysics Series; McCalpin, J.P., Ed.; Academic Press-Elsevier: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 95, pp. 1–106. [Google Scholar]
- Gurpinar, A. The importance of paleoseismology in seismic hazard studies for critical facilities. Tectonophysics 2005, 408, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, L. Earthquake Hazard Analysis: Issue and Insights; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; p. 254. [Google Scholar]
- McCalpin, J.P.; Nelson, A.R. Chapter 1: Introduction to paleoseismology. In Paleoseismology, 2nd ed.; International Geophysics Series; McCalpin, J.P., Ed.; Academic Press-Elsevier: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 95, pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Crone, A.J.; Omdahl, E.M. Directions in Paleoseismology. In U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report; USGS: Denver, CO, USA, 1987; pp. 87–673. [Google Scholar]
- Yeats, R.S.; Prentice, C.S. Introduction to special section: Paleoseismology. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 5847–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCalpin, J.P. Chapter 2A: Field Techniques in Paleoseismology-Terrestrial Environments. In Paleoseismology, 2nd ed.; International Geophysics Series; McCalpin, J.P., Ed.; Academic Press-Elsevier: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 95, pp. 29–118. [Google Scholar]
- Goldfinger, C. Chapter 2B: Sub-Aqueous Paleoseismology. In Paleoseismology, 2nd ed.; McCalpin, J.P., Ed.; International Geophysics Series; Academic Press-Elsevier: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 95, pp. 119–170. [Google Scholar]
- Ganas, A.; Pavlides, S.; Karastathis, V. DEM-based morphometry of range-front escarpments in Attica, central Greece, and its relation to fault slip rates. Geomorphology 2005, 65, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguchi, T.; Aoki, T.; Matsuta, N. Identification of an active fault in the Japanese Alps from DEM-based hill shading. Comput. Geosci. 2003, 29, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, X.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z. Segmentation of the active Liumugao Fault, NE Tibetan Plateau as revealed by DEM-derived geomorphic indices. Geosyst. Geoenviron. 2022, 1, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viveen, W.; Baby, P.; Hurtado-Enríquez, C. Assessing the accuracy of combined DEM-based lineament mapping and the normalised SL-index as a tool for active fault mapping. Tectonophysics 2021, 813, 228942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisely, B.A.; Schmidt, D. Deciphering vertical deformation and poroelastic parameters in a tectonically active fault-bound aquifer using InSAR and well level data, San Bernardino basin, California. Geophys. J. Int. 2010, 181, 1185–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Dutta, R.; Jónsson, S. Identifying Active Faults by Improving Earthquake Locations with InSAR Data and Bayesian Estimation: The 2004 Tabuk (Saudi Arabia) Earthquake Sequence. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2015, 105, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, X. Types and characteristics of slow-moving slope geo-hazards recognized by TS-InSAR along Xianshuihe active fault in the eastern Tibet Plateau. Nat. Hazards 2017, 88, 1727–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayournajarkar, N.; Fukushima, Y. Determination of the dipping direction of a blind reverse fault from InSAR: Case study on the 2017 Sefid Sang earthquake, northeastern Iran. Earth Planets Space 2020, 72, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lawrence, J.; Ghail, R.; Mason, P.; Carpenter, A.; Agar, S.; Morgan, T. Characterizing Micro-Displacements on Active Faults in the Gobi Desert with Time-Series InSAR. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wright, T.J.; Liu-Zeng, J.; Peng, L. Strain rate distribution in south-central Tibet from two decades of InSAR and GPS. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 5170–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Qu, C.; Shan, X.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G. InSAR and GPS derived coseismic deformation and fault model of the 2017 Ms7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake in the Northeast Bayanhar block. Tectonophysics 2018, 726, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-G.; Shih, T.-Y.; Huang, C. Characterizing the Hsincheng active fault in northern Taiwan using airborne LiDAR data: Detailed geomorphic features and their structural implications. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2007, 31, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, P.Z.; Liu, J.; Li, C.Y.; Ren, Z.K.; Hudnut, K.W. Quantitative study of tectonic geomorphology along Haiyuan fault based on airborne LiDAR. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 2396–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, L.E.; Howle, J.F.; Rose, R.S.; Bawden, G.W. LiDAR-Assisted Identification of an Active Fault near Truckee, California. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2011, 101, 1162–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D.; Grebby, S.; Tansey, K.; Gosar, A.; Kastelic, V. Application of airborne LiDAR to mapping seismogenic faults in forested mountainous terrain, southeastern Alps, Slovenia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L20308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.-F.; Lin, C.-W.; Chen, Y.-H.; He, T.-C.; Fei, L.-Y. Detecting and Characterizing Active Thrust Fault and Deep-Seated Landslides in Dense Forest Areas of Southern Taiwan Using Airborne LiDAR DEM. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15443–15466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, C.S.; Crosby, C.J.; Whitehill, C.S.; Arrowsmith, J.R.; Furlong, K.P.; Phillips, D.A. Illuminating Northern California’s Active Faults. Eos Trans. AGU 2009, 90, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Heitaro, K.; Sakae, M.; Norichika, A.; Tatsuro, C. Detection of subtle tectonic–geomorphic features in densely forested mountains by very high-resolution airborne LiDAR survey. Geomorphology 2013, 182, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, A.; Benedetti, L.; Gosar, A.; Rupnik, P.J.; Rizza, M.; Bourlès, D.; Ritz, J.F. Determining the present-day kinematics of the Idrija fault (Slovenia) from airborne LiDAR topography. Tectonophysics 2014, 628, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.P.; DeLong, S.B.; Arrowsmith, J.R. Distribution of aseismic deformation along the Central San Andreas and Calaveras faults from differencing repeat airborne lidar. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL090628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, S.; Rockwell, T.K.; Heimann, A.; Frieslander, U.; Agnon, A. Late Holocene activity of the Dead Sea Transform revealed in 3D palaeoseismic trenches on the Jordan Gorge segment. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2005, 234, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Cascales, I.; Koch, L.; Cardozo, N.; Martin-Rojas, I.; Alfaro, P.; García-Tortosa, F.J. 3D geometry and architecture of a normal fault zone in poorly lithified sediments: A trench study on a strand of the Baza Fault, central Betic Cordillera, south Spain. J. Struct. Geol. 2019, 121, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, P.A.C.; Giaccio, B.; Messina, P.; Peronace, E.; Zuppi, G.M. Palaeoseismology of the L’Aquila faults (central Italy, 2009, Mw 6.3 earthquake): Implications for active fault linkage. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 187, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrater, M.; Echeverria, A.; Masana, E.; Martínez-Díaz, J.J.; Sharp, W.D. A 3D measurement of the offset in paleoseismological studies. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 90, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.-U.; Rhie, J.; Kim, S.; Kang, T.-S.; Kim, K.-H.; Kim, Y. The 2016 Gyeongju earthquake sequence revisited: Aftershock interactions within a complex fault system. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 217, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Ree, J.-H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Kang, S.Y.; Seo, W. Assessing whether the 2017 Mw 5.4 Pohang earthquake in South Korea was an induced event. Science 2018, 360, 1007–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Jin, K.; Choi, W.-H.; Kee, W.-S. Understanding of active faults: A review for recent researches. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2011, 47, 723–752, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Na, S.H. A study of microearthquake activity of the Yangsan fault. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 1983, 19, 127–135, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Okada, A.; Watanabe, M.; Sato, H.; Jun, M.S.; Jo, W.R.; Kim, S.K.; Jeon, J.S.; Chi, H.C.; Oike, K. Active fault topography and trench survey in the central part of the Yangsan fault, southeast Korea. J. Geogr. 1994, 103, 111–126, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power Co. Ltd. Preliminary Safety Analysis Report of Shin KORI Units 3; Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power Co. Ltd.: Gyeongju-si, Korea, 2002; 133p. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power Co. Ltd. Preliminary Safety Analysis Report of Shin WOLSUNG Units 1; Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power Co. Ltd.: Gyeongju-si, Korea, 2003; 574p. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Lee, J.; Kyung, J.B. A Statistical analysis of the seismicity of the Yangsan Fault System. J. Eng. Geol. 1998, 8, 99–114, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chwae, U.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, B.J.; Ryoo, C.-R.; Choi, P.-Y.; Choi, S.-J.; Cho, D.-L.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, C.B.; Kee, W.S.; et al. An Investigation and Evaluation of Capable Fault: Southeastern Part of the Korean Peninsula; KIGAM: Daejeon, Korea, 1998; p. 324. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Kyung, J.B. Paleoseismological study on the mid-northern part of Ulsan fault by trench method. J. Eng. Geol. 1997, 7, 81–90, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kyung, J.B.; Lee, K.; Okada, A. A paleoseismological study of the Yangsan fault-Anaysis of deformed topography and trench survey. J. Korean Geophys. Soc. 1999, 2, 155–168, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kyung, J.B.; Lee, K.; Okada, A.; Watanabe, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Takemura, K. Study of fault characteristics by trench survey in the Sangchon-ri area in the southern part of Yangsan fault, southeastern Korea. J. Korean Earth Sci. Soc. 1999, 20, 101–110, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kee, W.-S.; Kim, B.C.; Hwang, J.H.; Song, K.-Y.; Kihm, Y.-H. Structural Characteristics of Quaternary reverse faulting on the Eupcheon Fault, SE Korea. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2007, 43, 311–333, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Kihm, J.-H.; Jin, K. Interpretation of the rupture history of a low slip-rate active fault by analysis of progressive displacement accumulation: An example from the Quaternary Eupcheon Fault, SE Korea. J. Geol. Soc. 2011, 168, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonenshain, L.P.; Savostin, L.A. Geodynamics of the Baikal rift zone and plate tectonics of Asia. Tectonophysics 1981, 76, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minster, J.B.; Jordan, T.H. Present-day plate motions. J. Geophys. Res. 1978, 83, 5331–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMets, C.; Gordon, R.G.; Argus, D.F.; Stein, S. Current plate motions. Geophys. J. Int. 1990, 101, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMets, C.; Gordon, R.G.; Argus, D.F.; Stein, S. Effect of recent revisions to the geomagnetic reversal time scale on estimates of current plate motions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, P. An updated digital model of plate boundaries. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2003, 4, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Meteorological Administration. Available online: https://www.weather.go.kr/w/eqk-vol/archive/stat/trend.do (accessed on 16 March 2022). (In Korean).
- Lee, K. Historical earthquake data of Korean. J. Korea Geophys. Soc. 1998, 1, 3–22, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Yang, W.-S. Historical Seismicity of Korea. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2006, 96, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kang, T.-S.; Rhie, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, Y.; Kang, S.Y.; Han, M.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Kim, M.; et al. The 12 September 2016 Gyeongju earthquakes: 2. Temporary seismic network for monitoring aftershocks. Geosci. J. 2016, 20, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Seo, W.; Hang, J.; Kwon, J.; Kang, S.Y.; Ree, J.-H.; Kim, S.; Liu, K. The 2017 ML 5.4 Pohang earthquake sequence, Korea, recorded by a dense seismic network. Tectonophysics 2020, 774, 228306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Kim, K.-H.; Son, M.; Kang, S.Y.; Park, J.-H. Location of recent micro earthquakes in the Gyeongju area. Geophys. Geophys. Explor. 2016, 19, 97–104, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ryoo, Y.; Park, S.C.; Ham, Y.M.; Park, J.S.; Kim, M.S.; Park, S.M.; Cho, H.G.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, I.S.; et al. Seismicity of the 2016 ML 5.8 Gyeongju earthquake and aftershocks in South Korea. Geosci. J. 2018, 22, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Ree, J.-H.; Yoo, S.-H. Fault slip analysis of Quaternary faults in southeastern Korea. Gondwana Res. 2006, 9, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-C.; Jung, S.; Yoon, S.; Jeong, R.-Y.; Song, C.W.; Son, M. Neotectonic crustal deformation and current stress field in the Korean Peninsula and Their Tectonic Implications: A review. J. Petrol. Soc. Korea 2016, 25, 169–193, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahm, W.-H.; Lee, H.; Jun, C.-P. Holocene uplift rates in Korea. Korean J. Quat. Res. 2018, 32, 41–50. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.Y.; Seong, Y.B.; Choi, K.H.; Yu, B.Y. Cosmogenic 10Be and OSL dating of marine terraces along the central -east coast of Korea: Spatio-temporal variations in uplift rates. Open Geogr. J. 2015, 7, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Meteorological Administration. In 2021 Year Book. Available online: https://www.kma.go.kr (accessed on 6 March 2022). (In Korean).
- Kee, W.-S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Choi, D.-L.; Kim, B.-C.; Song, K.-Y.; Koh, H.-J.; Lee, S.R.; Gwang, Y.Y.; Hwang, S.-H.; et al. South Eastern Fault Variable Research and DB Construction; KIGAM: Daejeon, Korea, 2009; 327p. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.-J.; Jeon, J.S.; Song, G.Y.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, B.Y.; Chwae, W.C.; Han, J.G.; Ryoo, C.R.; Seon, C.G.; et al. Active Fault Map and Seismic Hazard Map; NEMA: Seuol, Korea, 2012; 939p. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Cheon, Y.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, N.; Lee, H.; Choi, I.; Bae, H.; Rockwell, T.K.; Lee, S.R.; Ryoo, C.-R.; Choi, H. Late Quaternary transpressional earthquakes on a long-lived intraplate fault: A case study of the Southern Yangsan Fault, SE Korea. Quat. Int. 2020, 553, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, Y.; Ha, S.; Lee, S.; Cho, H.; Son, M. Deformation features and history of the Yangsan Fault Zone in the Eonyang-Gyeongju area, SE Korea. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2017, 53, 95–114, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, Y.; Cho, H.; Ha, S.; Kang, H.-C.; Kim, J.-S.; Son, M. Tectonically controlled multiple stages of deformation along the Yangsan Fault Zone, SE Korea, since Late Cretaceous. J. Asian Sci. 2019, 170, 188–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, Y.; Choi, J.-H.; Choi, Y.; Bae, H.; Han, K.-H.; Son, M.; Choi, S.-J.; Ryoo, C.-R. Understanding the distribution and internal structure of the main core of the Yangsan Fault Zone: Current trends and future work. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2020, 56, 619–640, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Klinger, Y. Recent progress in studies on the characteristics of surface rupture associated with large earthquakes. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2017, 53, 129–157, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H.; Woo, B.G.; Lee, J.H.; Park, S.O.; Yao, A. Cretaceous and early Cenozoic stratigraphy and history of eastern Kyongsang Basin, S. Korea. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 1990, 26, 471–487. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, B.H.; Lee, J.D.; Yang, K. Petrological study of the granitic rocks around the Yangsan fault: Lateral displacement of the Yangsan fault. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2004, 40, 161–178, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, B.H.; Lee, J.D.; Yang, K.; McWilliams, M. Cenozoic strike-slip displacement along the Yangsan fault, southeast Korean Peninsula. Int. Geol. Rev. 2007, 49, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.H.; McWilliams, M.; Son, M.; Yang, K. Tectonic implication of A-type granites across the Yangsan fault, Gigye and Gyeongju areas, southeast Korean Peninsula. Int. Geol. Rev. 2007, 49, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, C.-R.; Lee, B.-J.; Cho, D.-L.; Chwae, U.-C.; Choi, S.-J.; Kim, J.-Y. Quaternary fault of Dangu-ri in Gyeongju Gangdong-myeon: Byeokgye fault. In Proceedings of the Korean Society of Economic and Environmental Geology/The Korean Society of Mineral and Energy Resources Engineers/Korean Society of Earth and Exploration Geophysicists, Spring Joint Conference, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea, 14 April 1999; p. 334. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Rezaei, S.; Hong, Y.; Choi, J.-H.; Choi, J.-H.; Choi, W.-H.; Rhee, K.-W.; Kim, Y.-S. Quaternary fault analysis through a trench investigation on the northern extension of the Yangsan fault at Dangu-ri, Gyungju-si, Gyeongsangbuk-do. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2015, 51, 471–485, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Cho, D.R.; Song, K.Y. Explanatory Note of The Andong Sheet, 1:1:250,000; Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources: Daejeon, Korea, 1996; 67p. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.H.; Hwang, J.H.; Park, K.H.; Song, K.Y. Explanatory Note of The Pusan Sheet, 1:1:250,000; Korea Institute of Energy and Resources: Daejeon, Korea, 1998; 62p. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Son, M.; Song, C.W.; Kim, M.-C.; Cheon, Y.; Cho, H.; Sohn, Y.K. Miocene tectonic evolution of the basins and fault systems, SE Korea: Dextral, simple shear during the East Sea (Sea of Japan) opening. J. Geol. Soc. 2015, 172, 664–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.W. Study on the Evolution of the Miocene Pohang Basin Based on Its Structural Characteristics. Ph.D. Thesis, Pusan National University, Pusan, Korea, 2015; 146p. (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.-C.; Cheon, Y.; Ha, S.; Seo, K.; Kim, J.-S.; Shin, H.C.; Son, M. Geology and U-Pb age in the eastern part of Yeongdeok-gun, Gyeongsangbuk-do, Korea. J. Petrol. Soc. Korea. 2018, 27, 153–171, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Staley, D.M.; Wasklewicz, T.A.; Blaszczynski, J.S. Surficial patterns of debris flow deposition on alluvial fans in Death Valley, CA using airborne laser swath mapping data. Geomorphology 2006, 74, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volker, H.X.; Wasklewicz, T.A.; Ellis, M.A. A topographic fingerprint to distinguish alluvial fan formative processes. Geomorphology 2007, 88, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrowsmith, J.R.; Zielke, O. Tectonic geomorphology of the San Andreas Fault zone from high resolution topography: An example from the Cholame segment. Geomorphology 2009, 113, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Toda, S.; Okumura, K.; Takada, K.; Chiba, T. A fault scarp in an urban area identified by LiDAR survey: A Case study on the Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line, central Japan. Geomorphology 2008, 101, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, W.M.; Geldart, P.L.; Sheriff, R.E. Applied Geophysics, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; 770p. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, P.G.; Rodríguez-Pascua, M.A.; Giner Robles, J.L.; Élez, J.; Pérez-López, R.; Davila, M.B.B. Catalogue of the Geological Effects of Earthquakes in Spain Based on the ESI-07 Macroseismic Scale: A New Database for Seismic Hazard Analysis. Geosciences 2019, 9, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Chivelet, J.; Palma, R.M.; López-Gómez, J.; Kietzmann, D.A. Earthquake-induced soft-sediment deformation structures in Upper Jurassic open-marine microbialites (Neuquén Basin, Argentina). Sediment. Geol. 2011, 235, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, G.; Moretti, M. Identifying triggers for liquefaction-induced soft-sediment deformation in sands. Sediment. Geol. 2011, 235, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.-C.; Paik, I.S.; Lee, H.I.; Lee, J.E.; Chun, J.H. Soft-sediment deformation structures in Cretaceous non-marine deposits of southeastern Gyeongsang Basin, Korea: Occurrences and origin. Isl. Arc 2010, 19, 628–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ha, S.; Lee, S.; Kang, H.-C.; Choi, J.-H.; Son, M. Quaternary structural characteristics and paleoseismic interpretation of the Yangsan Fault at Dangu-ri, Gyeongju-si, SE Korea, through trench survey. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2020, 56, 155–173, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. Luminescence Dating of Active (Quaternary) Faults in the Southeastern Part of Korean Peninsula. Ph.D. Thesis, Pusan National University, Pusan, Korea, 2022; 146p. (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ha, S.; Son, M.; Seong, Y.B. Active Fault Trace Identification Using a LiDAR High-Resolution DEM: A Case Study of the Central Yangsan Fault, Korea. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194838
Ha S, Son M, Seong YB. Active Fault Trace Identification Using a LiDAR High-Resolution DEM: A Case Study of the Central Yangsan Fault, Korea. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194838
Chicago/Turabian StyleHa, Sangmin, Moon Son, and Yeong Bae Seong. 2022. "Active Fault Trace Identification Using a LiDAR High-Resolution DEM: A Case Study of the Central Yangsan Fault, Korea" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194838
APA StyleHa, S., Son, M., & Seong, Y. B. (2022). Active Fault Trace Identification Using a LiDAR High-Resolution DEM: A Case Study of the Central Yangsan Fault, Korea. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194838





