Analysis of Long-Term Aerosol Optical Properties Combining AERONET Sunphotometer and Satellite-Based Observations in Hong Kong
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
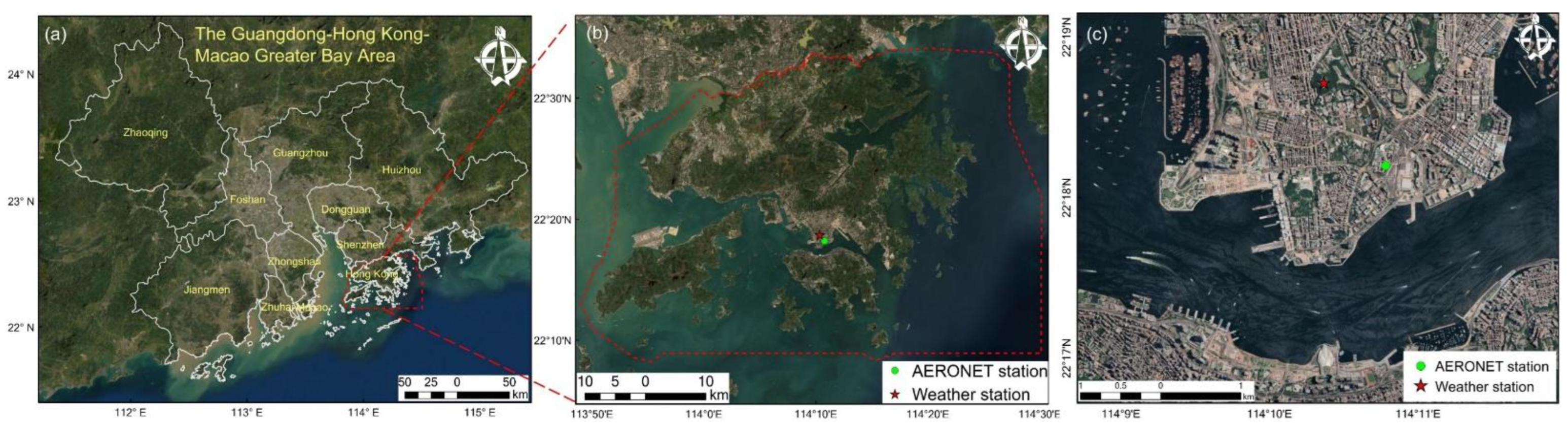
2.1. AERONET Data and Sampling Site
2.2. Satellite-Based Observations
2.3. Meteorological Data
2.4. Extreme-Point Symmetric Mode Decomposition (ESMD)
2.5. Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost)
3. Results
3.1. Aerosol Optical Characteristics and Aerosol Type Classification
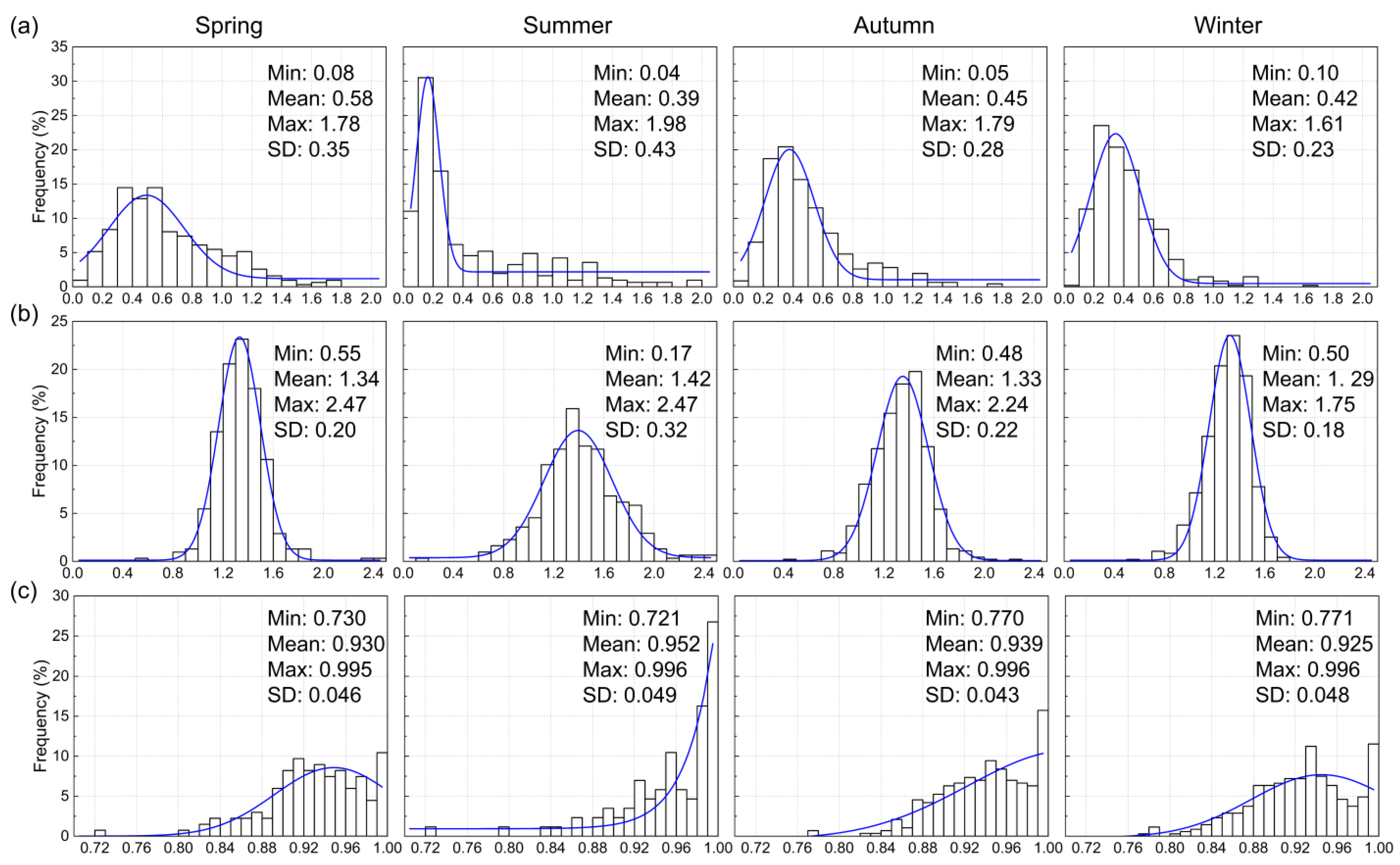
3.1.1. Statistical Description of Aerosol Optical Parameters
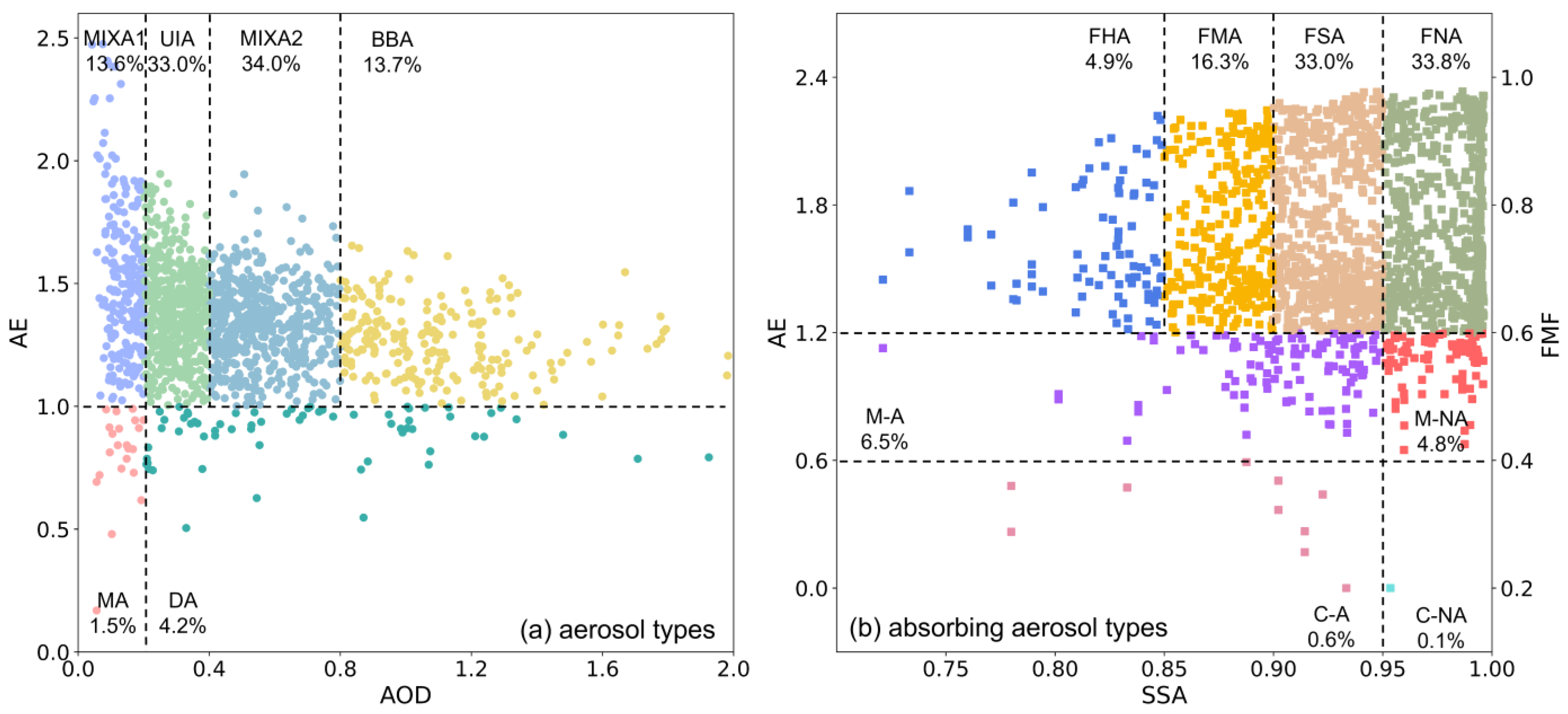
3.1.2. Aerosol Types and Absorbing Aerosol Types
3.2. Trend Analysis of Aerosol Optical Characteristics
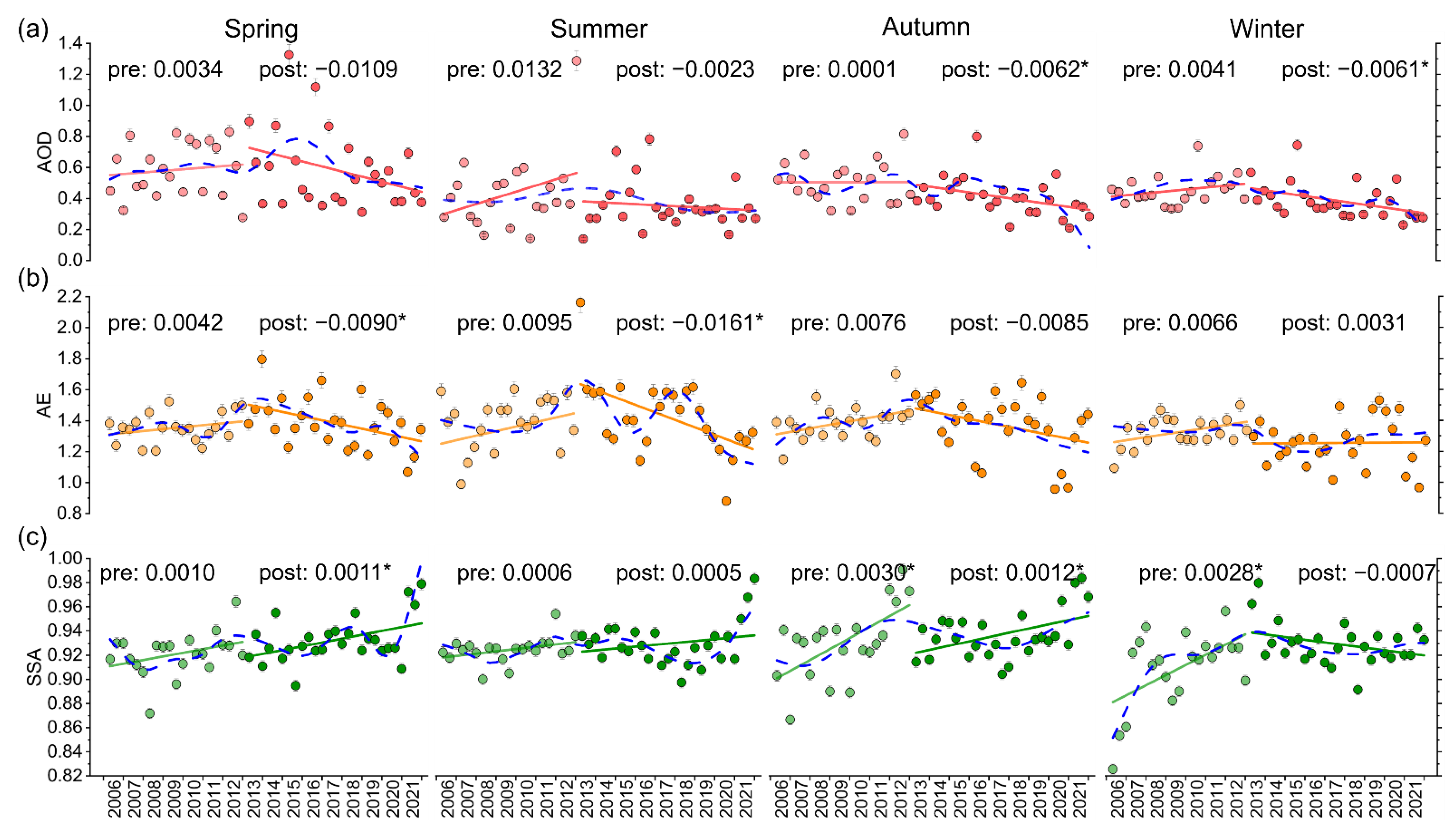
3.2.1. Long-Term Variations of Aerosol Optical Parameters
3.2.2. Seasonal Variations of Aerosol Optical Parameters
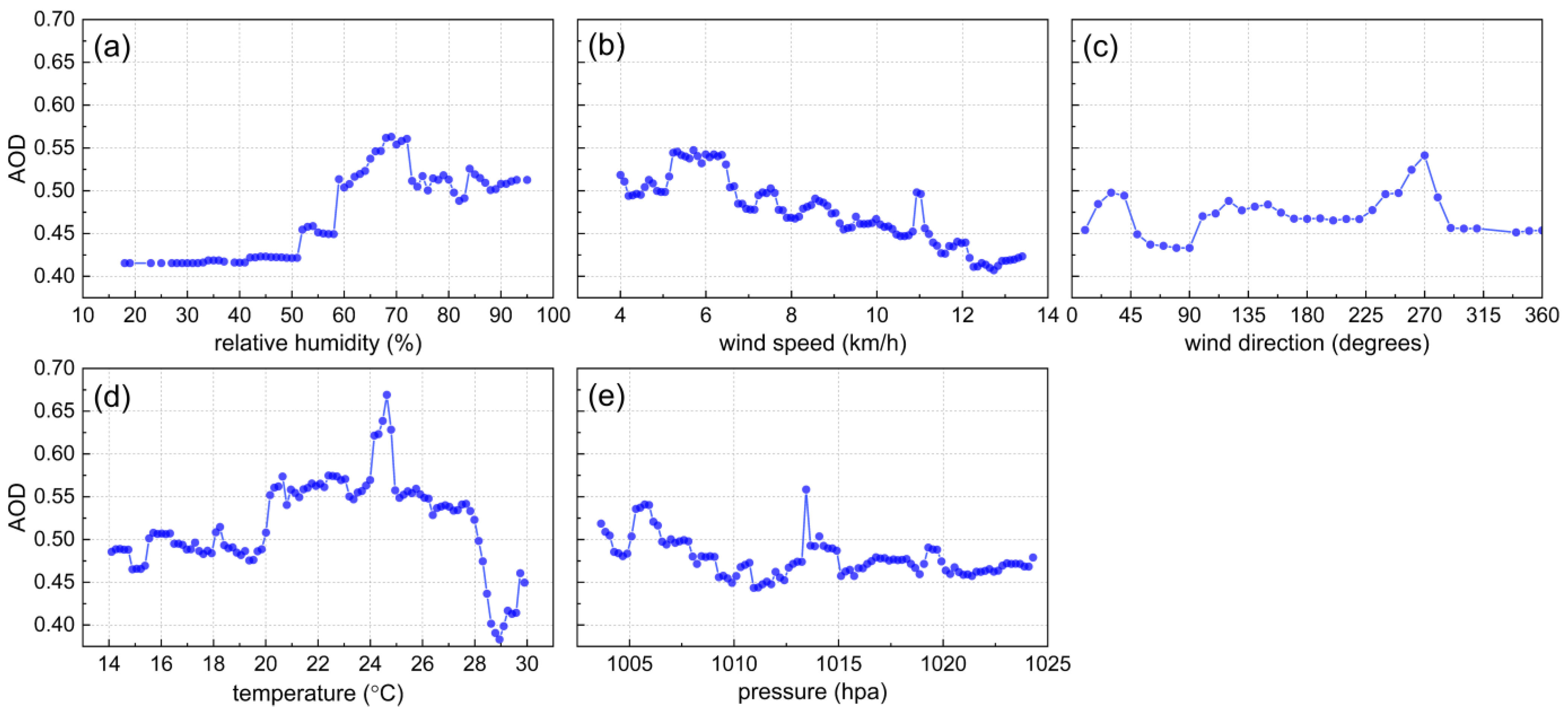
3.3. Quantitative Impacts of Meteorological Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, M.; Kim, J.; Wong, M.S.; Yoon, J.; Lee, J.; Wu, D.; Chan, P.; Nichol, J.E.; Chung, C.-Y.; Ou, M.L. Improvement of aerosol optical depth retrieval over Hong Kong from a geostationary meteorological satellite using critical reflectance with background optical depth correction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 142, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, M.S.; Lee, K.H.; Nichol, J.E.; Li, Z. Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Thickness Using MODIS 500 × 500 m2, a Study in Hong Kong and the Pearl River Delta Region. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3318–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.S.; Nichol, J.E.; Lee, K.H. An operational MODIS aerosol retrieval algorithm at high spatial resolution, and its application over a complex urban region. Atmos. Res. 2011, 99, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebert, B.J.; Bates, T.; Russell, P.B.; Shi, G.; Kim, Y.J.; Kawamura, K.; Carmichael, G.; Nakajima, T. An overview of ACE-Asia: Strategies for quantifying the relationships between Asian aerosols and their climatic impacts. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheesley, R.J.; Schauer, J.J.; Chowdhury, Z.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R. Characterization of organic aerosols emitted from the combustion of biomass indigenous to South Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pye, H.O.; Ward-Caviness, C.K.; Murphy, B.N.; Appel, K.W.; Seltzer, K.M. Secondary organic aerosol association with cardiorespiratory disease mortality in the United States. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Khatri, P.; Zhou, J.; Takamura, T.; Shi, G. Seasonal characteristics of aerosol optical properties at the SKYNET Hefei site (31.90 N, 117.17 E) from 2007 to 2013. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 6128–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate change 2013: The physical science basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.K., Tignor, M.M.H.L., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 1535. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Shi, C.; Wu, B.; Chen, Z.; Nie, S.; He, D.; Zhang, H. Analysis of aerosol characteristics and their relationships with meteorological parameters over Anhui province in China. Atmos. Res. 2012, 109, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J. Remote sensing of direct and indirect aerosol forcing. In Aerosol Forcing of Climate; Charlson, R.J., Heintzenberg, J., Eds.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 297–332. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, T.; Campanelli, M.; Che, H.; Estellés, V.; Irie, H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, J.; Liu, D.; Nishizawa, T.; Pandithurai, G.; et al. An overview of and issues with sky radiometer technology and SKYNET. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 4195–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Xu, H.; Li, K.T.; Li, D.H.; Xie, Y.S.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.F.; Zhao, W.; Tian, Q.J.; et al. Comprehensive study of optical, physical, chemical, and radiative properties of total columnar atmospheric aerosols over China: An overview of Sun–Sky Radiometer Observation Network (SONET) measurements. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 739–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.A.; Tanre, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinne, S.; Lohmann, U.; Feichter, J.; Schulz, M.; Timmreck, C.; Ghan, S.; Easter, R.; Chin, M.; Ginoux, P.; Takemura, T.; et al. Monthly averages of aerosol properties: A global comparison among models, satellite data, and AERONET ground data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, L.; Lacis, A.A.; Carlson, B.E. An optimal fitting approach to improve the GISS ModelE aerosol optical property parameterization using AERONET data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D16211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, X. Variability of aerosol optical depth and Angstrom wavelength exponent derived from AERONET observations in recent decades. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 044011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Leeuw, G.; Sogacheva, L.; Rodriguez, E.; Kourtidis, K.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Alexandri, G.; Amiridis, V.; Proestakis, E.; Marinou, E.; Xue, Y.; et al. Two decades of satellite observations of AOD over mainland China using ATSR-2, AATSR and MODIS/Terra: Data set evaluation and large-scale patterns. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1573–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Che, H.; Gui, K.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Holben, B.N.; Goloub, P.; Cuevas-Agulló, E.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Large contribution of meteorological factors to inter-decadal changes in regional aerosol optical depth. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 10497–10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramachandran, S.; Rupakheti, M. Trends in the types and absorption characteristics of ambient aerosols over the Indo-Gangetic Plain and North China Plain in last two decades. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Wong, M.S.; Nichol, J. Global trends of aerosol optical thickness using the ensemble empirical mode decomposition method. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 4358–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, G. Multi-spatiotemporal patterns of aerosol optical depth and influencing factors during 2000–2020 from two spatial perspectives: The entire Yellow River Basin region and its urban agglomerations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 106, 102643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, L.; Huang, B.; Wei, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhong, Y. Anthropogenic and meteorological drivers of 1980–2016 trend in aerosol optical and radiative properties over the Yangtze River Basin. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, B.; Xu, W.; Wang, F.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Feng, Y.; Shi, G. Machine learning combined with the PMF model reveal the synergistic effects of sources and meteorological factors on PM2.5 pollution. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Shi, H.; Tang, H.; Yang, X. Geographical and temporal encoding for improving the estimation of PM2.5 concentrations in China using end-to-end gradient boosting. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; King, M.D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I. Accuracy assessments of aerosol optical properties retrieved from Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 9791–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyapustin, A.; Martonchik, J.; Wang, Y.; Laszlo, I.; Korkin, S. Multiangle implementation of atmospheric correction (MAIAC): 1. Radiative transfer basis and look-up tables. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D03210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Che, H.; Chen, L. Performance of MODIS high-resolution MAIAC aerosol algorithm in China: Characterization and limitation. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, A. On the atmospheric transmission of sun radiation and on dust in the air. Geogr. Ann. 1929, 11, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.A.; Gaitley, B.J. An analysis of global aerosol type as retrieved by MISR. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 4248–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Shang, H.; Wang, L.; Letu, H. Assessment and improvement of MISR Angstrom exponent and single-scattering albedo products using AERONET data in China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahn, R.A.; Gaitley, B.J.; Garay, M.J.; Diner, D.J.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N. Multiangle Imaging SpectroRadiometer global aerosol product assessment by comparison with the Aerosol Robotic Network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D23209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Li, Z.J. Extreme-point symmetric mode decomposition method for data analysis. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2013, 5, 1350015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lian, L. Spatio-temporal variations of nonlinear trends of precipitation over an arid region of northwest China according to the extreme-point symmetric mode decomposition method. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2239–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Fang, G.; Wang, F.; Liu, H. The impact of climate change and human activities on the Aral Sea Basin over the past 50 years. Atmos. Res. 2020, 245, 105125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lü, R.; Liu, C.; Yuan, L.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, B.; Lei, L. Seasonal variation of columnar aerosol optical properties and radiative forcing over Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.R.; Kang, N.; Sivakumar, V.; Griffith, D. Temporal characteristics of columnar aerosol optical properties and radiative forcing (2011–2015) measured at AERONET’s Pretoria_CSIR_DPSS site in South Africa. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; He, J.; Lai, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Gong, S.; Che, H. Influence of atmospheric circulation on aerosol and its optical characteristics in the pearl river delta region. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, X.; Che, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, H.; Cong, Z.; Deng, X.; Fan, X.; Fu, Y.; Goloub, P.; Jiang, H.; et al. Ground-based remote sensing of aerosol climatology in China: Aerosol optical properties, direct radiative effect and its parameterization. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, S.V.; Chew, B.N.; Liew, S.C. Retrievals of aerosol optical depth and Ångström exponent from ground-based Sun-photometer data of Singapore. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, T.; Wu, F.; Qiu, Y. Analysis of influential factors for the relationship between PM2.5 and AOD in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 13473–13489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellouin, N.; Boucher, O.; Haywood, J.; Reddy, M.S. Global estimate of aerosol direct radiative forcing from satellite measurements. Nature 2005, 438, 1138–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Zang, Z.; Li, Z.; Luo, N.; Zuo, C.; Jiang, Y.; Li, D.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, W.; Shi, W.; et al. A global land aerosol fine-mode fraction dataset (2001–2020) retrieved from MODIS using hybrid physical and deep learning approaches. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 1193–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Yao, Y. Multi-time scale analysis of regional aerosol optical depth changes in national-level urban agglomerations in China using modis collection 6.1 datasets from 2001 to 2017. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Chang, X.; Hao, J. The impact of the “air pollution prevention and control action plan” on PM2.5 concentrations in Jing-Jin-Ji region during 2012–2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchholz, R.R.; Worden, H.M.; Park, M.; Francis, G.; Deeter, M.N.; Edwards, D.P.; Emmons, L.K.; Gaubert, B.; Gille, J.; Martínez-Alonso, S.; et al. Air pollution trends measured from Terra: CO and AOD over industrial, fire-prone, and background regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; He, K.; Huo, H. Cleaning China’s air. Nature 2012, 484, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong Kong Environmental Protection Department (HKEPD). Air Pollution Control Strategies. 2019. Available online: https://www.epd.gov.hk/epd/english/environmentinhk/air/prob_solutions/strategies_apc.html (accessed on 22 August 2022).
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhu, S.; Shen, J.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H. Responses of decline in air pollution and recovery associated with COVID-19 lockdown in the Pearl River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeren, Y.; Guo, H.; Lyu, X.; Zhou, B.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, Y. Remarkable spring increase overwhelmed hard-earned autumn decrease in ozone pollution from 2005 to 2017 at a suburban site in Hong Kong, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Guo, H.; Wang, T.J.; Cheng, H.R.; Wang, X.M.; Simpson, I.J.; Ding, A.; Saunders, S.M.; Lam, S.H.M.; Blake, D.R. An ozone episode in the Pearl River Delta: Field observation and model simulation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D22305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Fu, S.; Wang, X.; Fu, Q.; Jia, H.; Xu, H.; Qin, G.; Hu, X.; Cheng, J. Spatiotemporal variations of ambient air pollutants and meteorological influences over typical urban agglomerations in China during the COVID-19 lockdown. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 106, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Ling, Z.; Gao, M.; Sun, J.; Zhao, W.; Ma, P.; Quan, J.; Fan, S.; Liao, Z.; Ling, Z.; et al. Tropospheric ozone variability over Hong Kong based on recent 20 years (2000–2019) ozonesonde observation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Ding, A.; Cooper, O.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, D.; Wu, Z.; McClure-Begley, A.; Petropavlovskikh, I.; Andreae, M.O.; et al. ENSO and Southeast Asian biomass burning modulate subtropical trans-Pacific ozone transport. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwaa132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Evangeliou, N.; Eckhardt, S.; Huang, X.; Gao, J.; Ding, A.; Stohl, A. Black carbon emission reduction due to COVID-19 lockdown in China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xie, F.; Fan, M.Y.; Liu, X. Substantial decreases of light absorption, concentrations and relative contributions of fossil fuel to light-absorbing carbonaceous aerosols attributed to the COVID-19 lockdown in east China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casalicchio, G.; Molnar, C.; Bischl, B. Visualizing the feature importance for black box models. In Proceedings of the Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, Würzburg, Germany, 16–20 September 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; pp. 655–670.
- Malm, W.C.; Day, D.E. Estimates of aerosol species scattering characteristics as a function of relative humidity. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 2845–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Machine learning prediction of biochar yield and carbon contents in biochar based on biomass characteristics and pyrolysis conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, A.P.; Mickley, L.J.; Jacob, D.J. Correlations between fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and meteorological variables in the United States: Implications for the sensitivity of PM2.5 to climate change. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3976–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csavina, J.; Field, J.; Félix, O.; Corral-Avitia, A.Y.; Sáez, A.E.; Betterton, E.A. Effect of wind speed and relative humidity on atmospheric dust concentrations in semi-arid climates. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Yi, B. Aerosols over East and South Asia: Type identification, optical properties, and implications for radiative forcing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cúneo, L.; Ulke, A.G.; Cerne, B. Advances in the characterization of aerosol optical properties using long-term data from AERONET in Buenos Aires. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, S.; Voinea, S.; Iorga, G. Study of the aerosol optical characteristics over the Romanian Black Sea Coast using AERONET data. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1165–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, E.; Tuygun, G.T.; Elbir, T. Application of aerosol classification methods based on AERONET version 3 product over eastern Mediterranean and Black Sea. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 2226–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeisser, L.; Andrews, E.; Ogren, J.A.; Sheridan, P.; Jefferson, A.; Sharma, S.; Kim, J.E.; Sherman, J.P.; Sorribas, M.; Kalapov, I.; et al. Classifying aerosol type using in situ surface spectral aerosol optical properties. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 12097–12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, T.; Li, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, T.; Wu, H.; Guo, J. Aerosol-boundary layer interaction modulated entrainment process. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Han, W.; Shen, C.; Tan, W.; Wei, J.; Guo, J. The significant impact of aerosol vertical structure on lower atmosphere stability and its critical role in aerosol–planetary boundary layer (PBL) interactions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3713–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Types | Aerosol Optical Parameters Thresholds | |
|---|---|---|
| Criterion 1 (AOD, AE; Salinas et al. [41]) | Marine aerosol (MA) | AOD < 0.2, AE < 1.0 |
| Dust aerosol (DA) | AOD > 0.2, AE < 1.0 | |
| Mixed aerosol (MIXA1) | AOD < 0.2, AE > 1.0 | |
| Urban/industrial aerosol (UIA) | 0.2 < AOD < 0.4, AE > 1.0 | |
| Mixed aerosol (MIXA2) | 0.4 < AOD < 0.8, AE > 1.0 | |
| Biomass burning aerosol (BBA) | AOD > 0.8, AE > 1.0 | |
| Criterion 2 (AE, SSA, FMF; Zheng et al. [42]) | Coarse absorbing (C-A) | SSA < 0.95, AE < 0.6, FMF < 0.4 |
| Coarse non-absorbing (C-NA) | SSA > 0.95, AE < 0.6, FMF < 0.4 | |
| Mixed absorbing (M-A) | SSA < 0.95, 0.6 < AE < 1.2, 0.4 < FMF < 0.6 | |
| Mixed non-absorbing (M-NA) | SSA > 0.95, 0.6 < AE < 1.2, 0.4 < FMF < 0.6 | |
| Fine highly absorbing (FHA) | SSA < 0.85, AE > 1.2, FMF > 0.6 | |
| Fine medium absorbing (FMA) | 0.85 < SSA < 0.9, AE > 1.2, FMF > 0.6 | |
| Fine slightly absorbing (FSA) | 0.9 < SSA < 0.95, AE > 1.2, FMF > 0.6 | |
| Fine non-absorbing (FNA) | SSA > 0.95, AE > 1.2, FMF > 0.6 |
| Parameters | IMF1 | IMF2 | IMF3 | IMF4 | IMF5 | R | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOD | VCR (%) | 39.36 | 29.03 | 14.60 | 5.04 | 2.42 | 9.55 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.55 * | 0.54 * | 0.33 * | 0.18 * | 0.14 | 0.30 * | |
| AE | VCR (%) | 32.52 | 14.42 | 27.18 | 4.47 | 4.54 | 16.87 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.54 * | 0.37 * | 0.47 * | 0.15 * | 0.23 * | 0.39 * | |
| SSA | VCR (%) | 37.97 | 13.16 | 9.44 | 6.53 | 3.01 | 29.89 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.55 * | 0.35 * | 0.38 * | 0.41 * | 0.14 * | 0.57 * |
| R-Spring | R-Summer | R-Autumn | R-Winter | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOD | VCR (%) | 13.03 | 5.85 | 35.46 | 29.60 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.32 * | 0.26 | 0.47 * | 0.49 * | |
| AE | VCR (%) | 31.09 | 36.89 | 25.01 | 14.77 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.50 * | 0.58 * | 0.44 * | 0.29 * | |
| SSA | VCR (%) | 37.87 | 50.98 | 28.38 | 48.60 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.69 * | 0.76 * | 0.58 * | 0.71 * |
| Wind Speed | Wind Direction | Relative Humidity | Temperature | Pressure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| importance rate | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, X.; Nichol, J.; Lee, K.H.; Li, J.; Wong, M.S. Analysis of Long-Term Aerosol Optical Properties Combining AERONET Sunphotometer and Satellite-Based Observations in Hong Kong. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5220. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205220
Yu X, Nichol J, Lee KH, Li J, Wong MS. Analysis of Long-Term Aerosol Optical Properties Combining AERONET Sunphotometer and Satellite-Based Observations in Hong Kong. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(20):5220. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205220
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Xinyu, Janet Nichol, Kwon Ho Lee, Jing Li, and Man Sing Wong. 2022. "Analysis of Long-Term Aerosol Optical Properties Combining AERONET Sunphotometer and Satellite-Based Observations in Hong Kong" Remote Sensing 14, no. 20: 5220. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205220
APA StyleYu, X., Nichol, J., Lee, K. H., Li, J., & Wong, M. S. (2022). Analysis of Long-Term Aerosol Optical Properties Combining AERONET Sunphotometer and Satellite-Based Observations in Hong Kong. Remote Sensing, 14(20), 5220. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205220










