Focus Improvement of Spaceborne-Missile Bistatic SAR Data Using the Modified NLCS Algorithm Based on the Method of Series Reversion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Spaceborne Missile Bistatic SAR Geometry and Signal Model
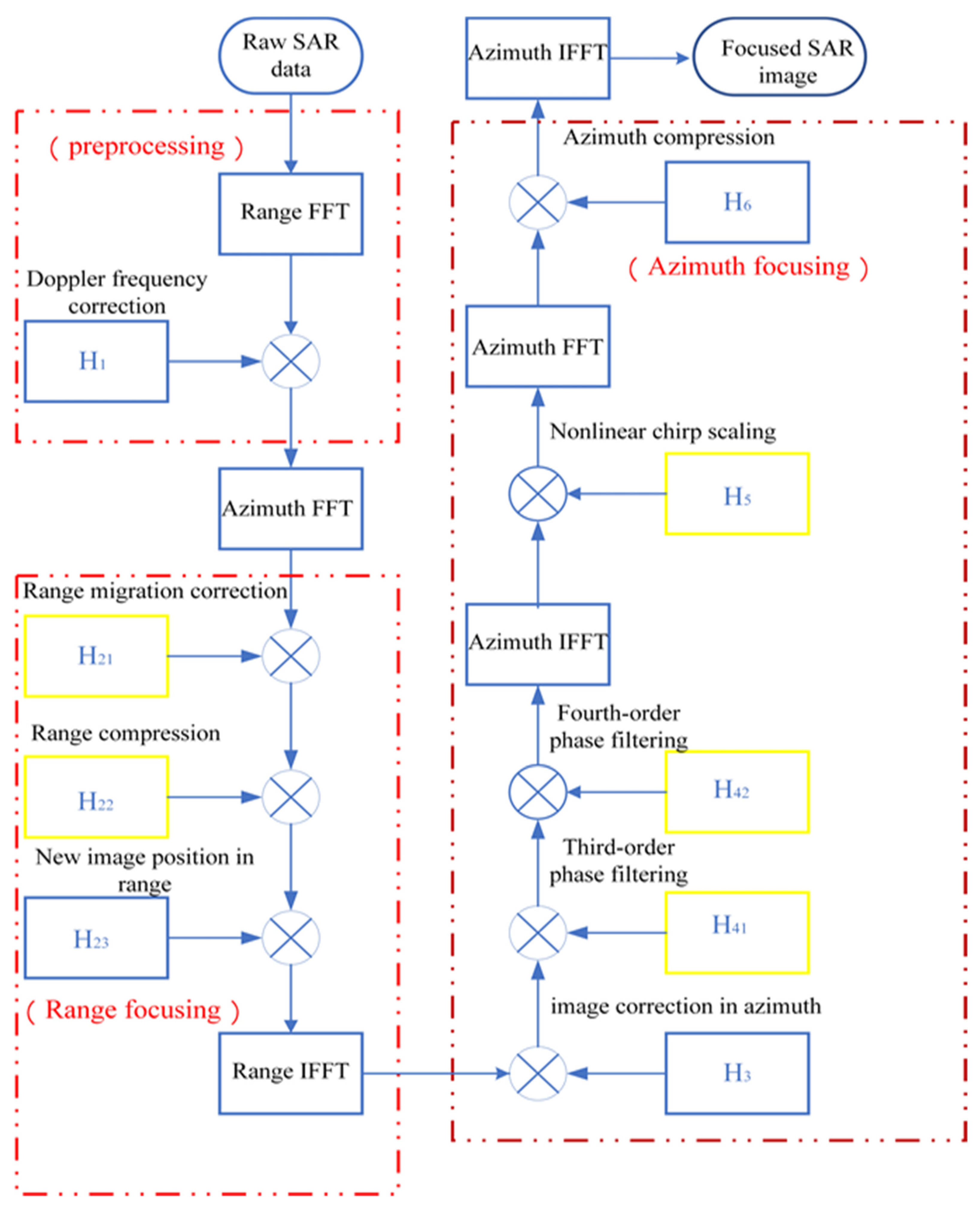
3. The Specific Steps of the Algorithm
3.1. Doppler Frequency Correction
3.2. Derivation of the Signal 2-D Spectrum
3.3. The Operations in Range
3.4. Azimuth Compression by a Modified Bistatic Azimuth NLCS Algorithm
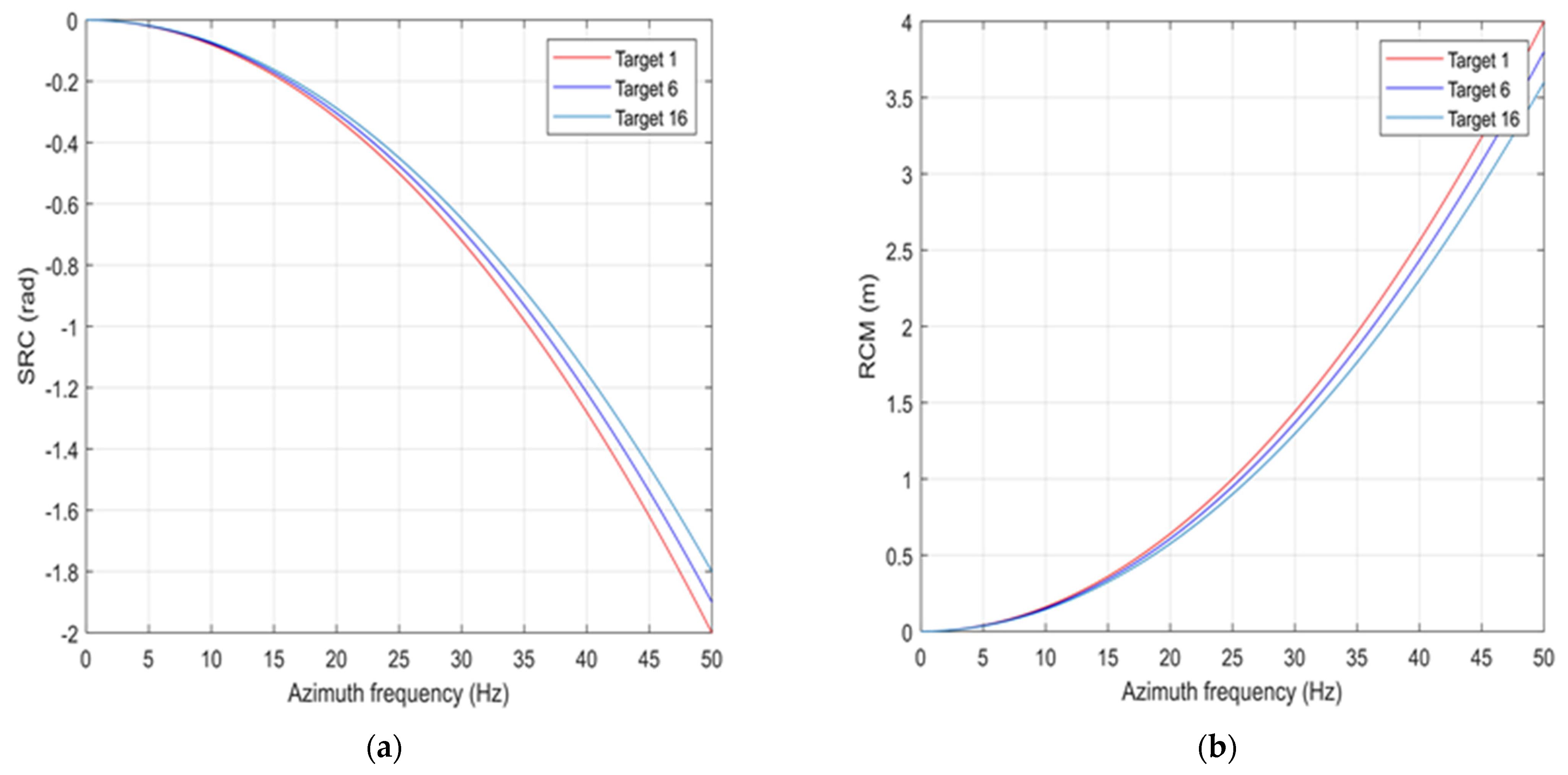
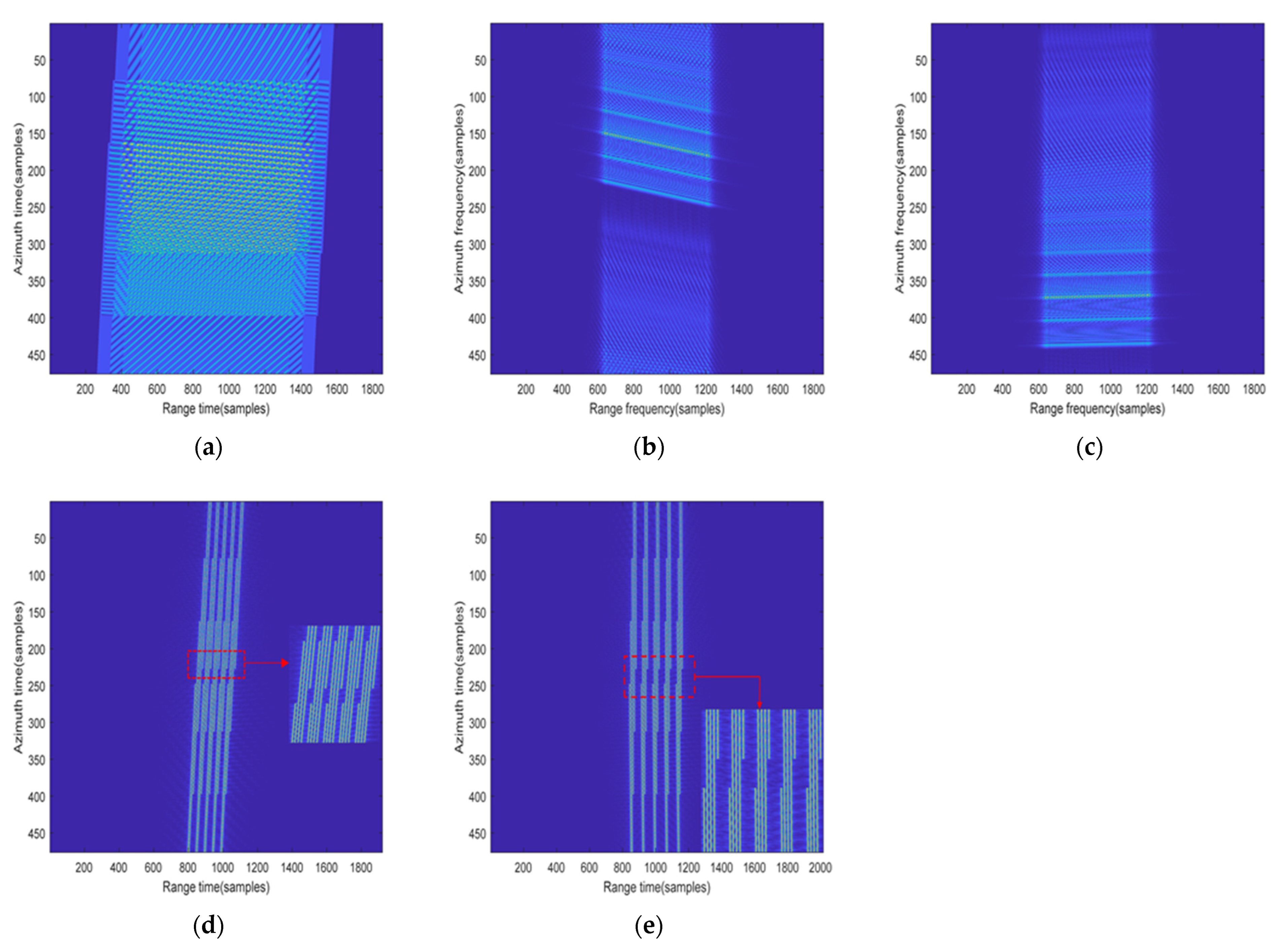
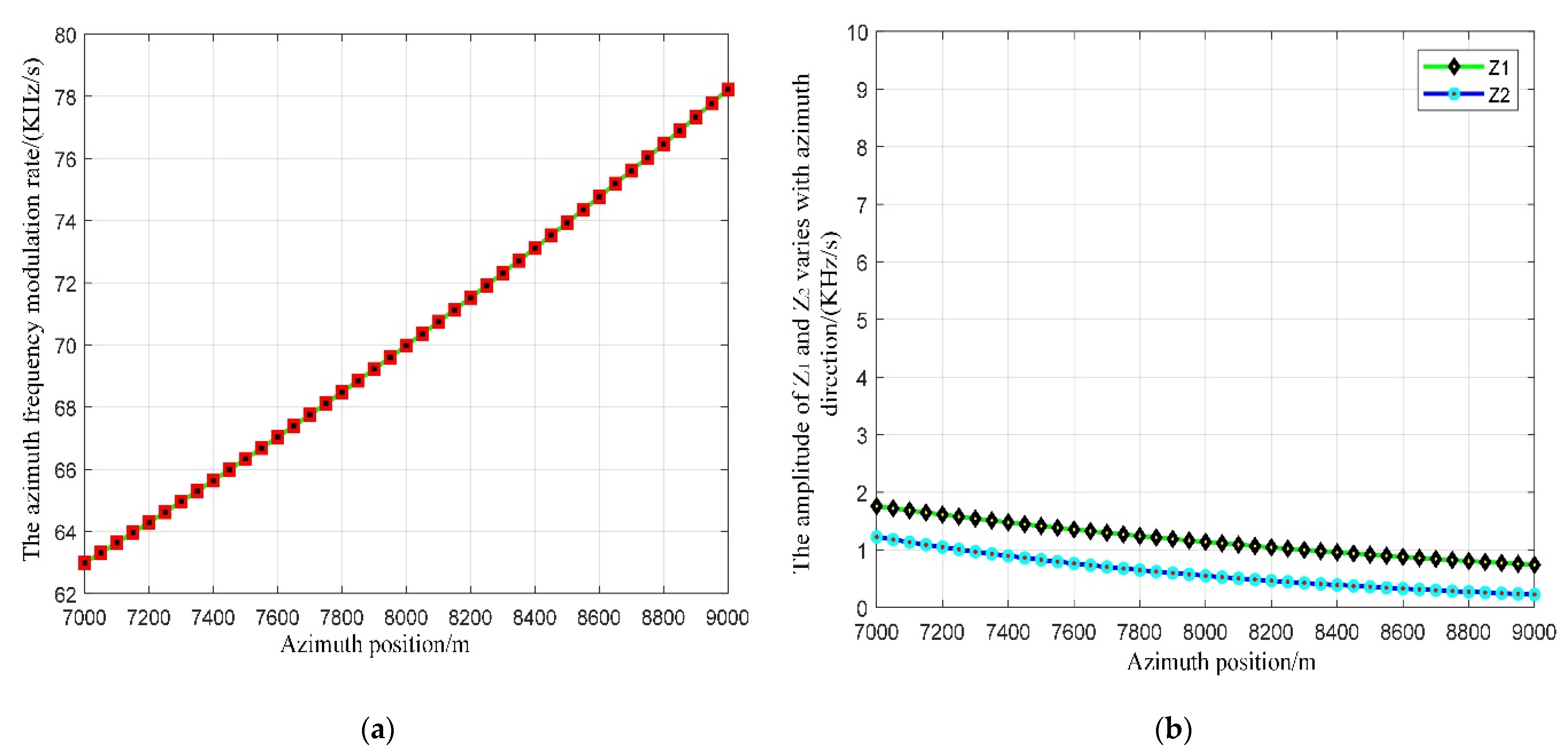
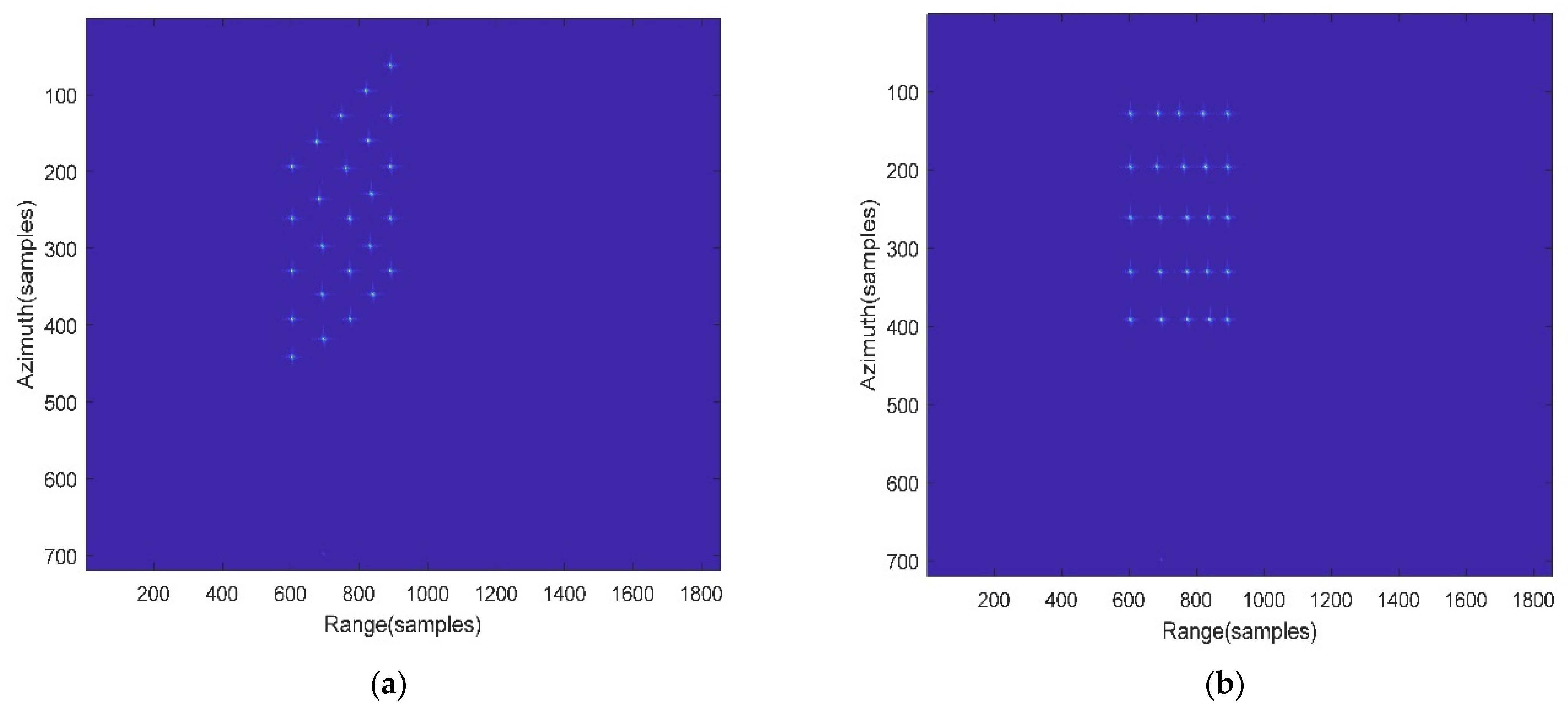
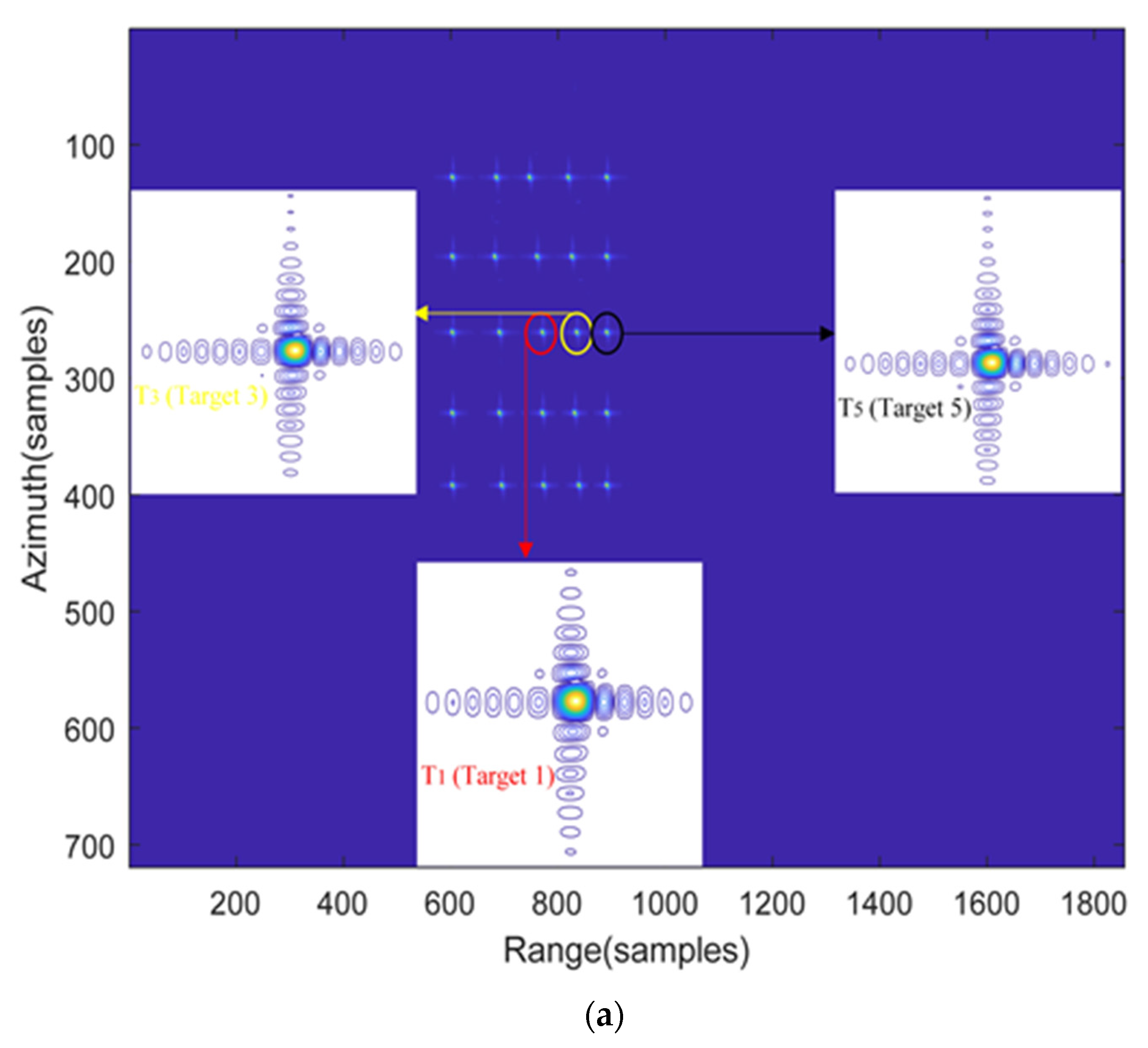
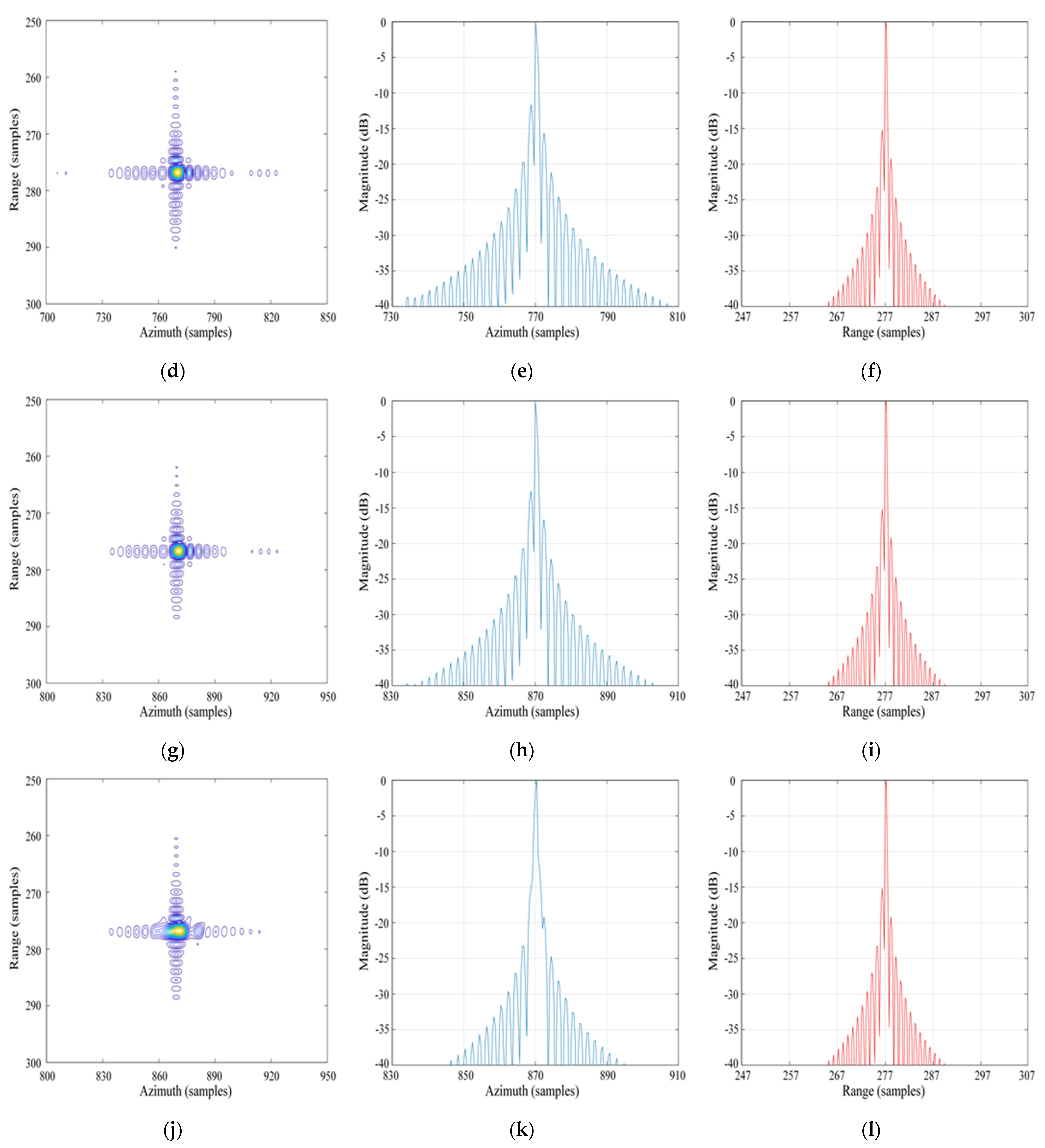
4. Experimental Simulations and Discussion
4.1. Simulation Results by the Proposed Algorithm
4.2. Comparison of Algorithm Efficiency
4.3. Comparison of Imaging Effects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cruz, H.; Véstias, M.; Monteiro, J.; Neto, H.; Duarte, R.P. A Review of Synthetic-Aperture Radar Image Formation Algorithms and Implementations: A Computational Perspective. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Dong, X.; Chen, Z.; Hu, C.; Tian, W. A Long-Time Coherent Integration STAP for GEO Spaceborne-Airborne Bistatic SAR. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Numerical Simulation of SAR Image for Sea Surface. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Sun, Z.; An, H.; Wu, J.; Yang, J. BeiDou-based passive multistatic radar maritime moving target detection technique via space–time hybrid integration processing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5802313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; An, H.; He, X. Geosynchronous spaceborne–airborne bistatic SAR data focusing using a novel range model based on one-stationary equivalence. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 1214–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Deng, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, K.; Liu, D.; Jin, G.; Zhang, Y. Focusing the L-band spaceborne bistatic SAR mission data using a modified RD algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tang, S.; Ren, Y.; Guo, P.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wan, J.; Zhang, L. Curvilinear Flight Synthetic Aperture Radar (CF-SAR): Principles, Methods, Applications, Challenges, and Trends. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zuo, L.; Wang, W. Adaptive Beamforming for Passive Synthetic Aperture with Uncertain Curvilinear Trajectory. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Xia, X.-G.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Liu, X.; Liao, G.; Jiang, X. Imaging and relocation for extended ground moving targets in multichannel SAR-GMTI systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5214024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Tang, S.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, L. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Extraction Based on Radargrammetry for Single-Channel Curvilinear SAR System. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffeld, O.; Nies, H.; Peters, V.; Knedlik, S. Models and useful relations for bistatic SAR processing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Fu, Z.; Chang, J.; Wu, L.; Li, N. A Novel High-Squint Spotlight SAR Raw Data Simulation Scheme in 2-D Frequency Domain. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Loffeld, O.; Ul-Ann, Q.; Nies, H.; Ortiz, A.M.; Samarah, A. A bistatic point target reference spectrum for general bistatic SAR processing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.T.; Sjögren, T.K.; Pettersson, M.I. Two-dimensional spectrum for BiSAR derivation based on Lagrange inversion theorem. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 11, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Natroshvili, K.; Loffeld, O.; Nies, H.; Ortiz, A.M.; Knedlik, S. Focusing of general bistatic SAR configuration data with 2-D inverse scaled FFT. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2718–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Loffeld, O.; Nies, H.; Knedlik, S.; Ender, J.H. Chirp-scaling algorithm for bistatic SAR data in the constant-offset configuration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 47, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, P.; Dai, X. Focusing multireceiver SAS data based on the fourth-order legendre expansion. Circ Syst Signal Pr. 2019, 38, 2607–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, B.; Quan, Y.; Sun, G.-C.; Liu, W.; Xing, M. A modified range model and Doppler resampling based imaging algorithm for high squint SAR on maneuvering platforms. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 1923–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y. Focus Improvement of Airborne High-Squint Bistatic SAR Data Using Modified Azimuth NLCS Algorithm Based on Lagrange Inversion Theorem. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1916. [Google Scholar]
- Neo, Y.L.; Wong, F.; Cumming, I.G. A two-dimensional spectrum for bistatic SAR processing using series reversion. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, H. An improved RD algorithm for maneuvering bistatic forward-looking SAR imaging with a fixed transmitter. Sensors 2017, 17, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Qiu, X.; Hu, D.; Ding, C. Focusing of medium-earth-orbit SAR with advanced nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 49, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W.; Li, W.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Z. An extended omega-K algorithm with integrated motion compensation for bistatic forward-looking SAR. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon), Arlington, VA, USA, 10–15 May 2015; pp. 1291–1295. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Xu, Z.; Wang, F.; Yang, D.; Guo, G. An improved back-projection algorithm for GNSS-R BSAR imaging based on CPU and GPU platform. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, R.; Deng, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, N. An accelerated backprojection algorithm for monostatic and bistatic SAR processing. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z. Acceleration of fast factorized back projection algorithm for bistatic SAR. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium-IGARSS, Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 2493–2496. [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura, T.; Kageme, S.; Suwa, K. Study on Three-Dimensional Fast Factorized Back Projection Using One-Dimensional Bistatic Antenna Array for Security Radar. In Proceedings of the 2021 7th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Bali Island, Indonesia, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, X.; Hu, D.; Ding, C. An improved NLCS algorithm with capability analysis for one-stationary BiSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3179–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.; Yeo, T.S. New applications of nonlinear chirp scaling in SAR data processing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y. Improved nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for dechirped missile-borne synthetic aperture radar. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Deng, Y.; Wang, R. Imaging for high-resolution wide-swath spaceborne SAR using cubic filtering and NUFFT based on circular orbit approximation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 55, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Sui, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Hu, C. Modeling and Analysis of RFI Impacts on Imaging between Geosynchronous SAR and Low Earth Orbit SAR. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wu, J.; Pei, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J. Inclined geosynchronous spaceborne–airborne bistatic SAR: Performance analysis and mission design. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 54, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, Y.L.; Wong, F.H.; Cumming, I.G. Processing of azimuth-invariant bistatic SAR data using the range Doppler algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 46, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lin, H.; Liu, H.; Liao, G.; Tan, X. Focus improvement for high-resolution highly squinted SAR imaging based on 2-D spatial-variant linear and quadratic RCMs correction and azimuth-dependent Doppler equalization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.H.; Cumming, I.G.; Neo, Y.L. Focusing bistatic SAR data using the nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 2493–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Simulation Experimental Parameters | Transmitter | Receiver | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Velocity in x-direction | 5200 m/s | ||
| Velocity in y-direction | −5200 m/s | 100 m/s | |
| Velocity in z-direction | −50 m/s | ||
| Acceleration in y-direction | 10 m/s2 | ||
| Acceleration in z-direction | −10 m/s2 | ||
| Initial coordinate | (280, 280, 755) km | (0, 10, 5) km | |
| Signal bandwidth | 80 MHz | ||
| Pulse width | 10 μs | ||
| Carrier frequency | 5.4 GHz | ||
| Azimuth sampling interval | 0.001 s | ||
| Synthetic aperture time | 5 s | ||
| Range sampling frequency | 160 MHz |
| Method | Azimuth | Range | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target | Resolution(m) | PSLR(dB) | ISLR(dB) | Resolution(m) | PSLR(dB) | ISLR(dB) | |
| Modified NLCS algorithm | T1 | 1.09 | −13.55 | −9.61 | 1.83 | −13.21 | −10.34 |
| T3 | 1.12 | −13.26 | −9.52 | 1.86 | −13.12 | −10.21 | |
| T5 | 1.21 | −12.96 | −9.48 | 1.88 | −13.18 | −10.03 | |
| Traditional NLCS algorithm | T1 | 1.13 | −12.98 | −9.50 | 1.84 | −12.96 | −10.10 |
| T3 | 1.52 | −10.87 | −8.52 | 1.88 | −12.87 | −9.97 | |
| T5 | 2.08 | −9.64 | −7.69 | 1.90 | −12.90 | −9.89 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xi, Z.; Duan, C.; Zuo, W.; Li, C.; Huo, T.; Li, D.; Wen, H. Focus Improvement of Spaceborne-Missile Bistatic SAR Data Using the Modified NLCS Algorithm Based on the Method of Series Reversion. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5770. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225770
Xi Z, Duan C, Zuo W, Li C, Huo T, Li D, Wen H. Focus Improvement of Spaceborne-Missile Bistatic SAR Data Using the Modified NLCS Algorithm Based on the Method of Series Reversion. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(22):5770. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225770
Chicago/Turabian StyleXi, Zirui, Chongdi Duan, Weihua Zuo, Caipin Li, Tonglong Huo, Dongtao Li, and He Wen. 2022. "Focus Improvement of Spaceborne-Missile Bistatic SAR Data Using the Modified NLCS Algorithm Based on the Method of Series Reversion" Remote Sensing 14, no. 22: 5770. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225770
APA StyleXi, Z., Duan, C., Zuo, W., Li, C., Huo, T., Li, D., & Wen, H. (2022). Focus Improvement of Spaceborne-Missile Bistatic SAR Data Using the Modified NLCS Algorithm Based on the Method of Series Reversion. Remote Sensing, 14(22), 5770. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225770






