A Semi-Empirical Anisotropy Correction Model for UAS-Based Multispectral Images of Bare Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Multispectral Imaging System
2.2. Data Collection and Pre-Processing
2.3. ANIF Correction Model
2.4. Correction Evaluation
3. Results
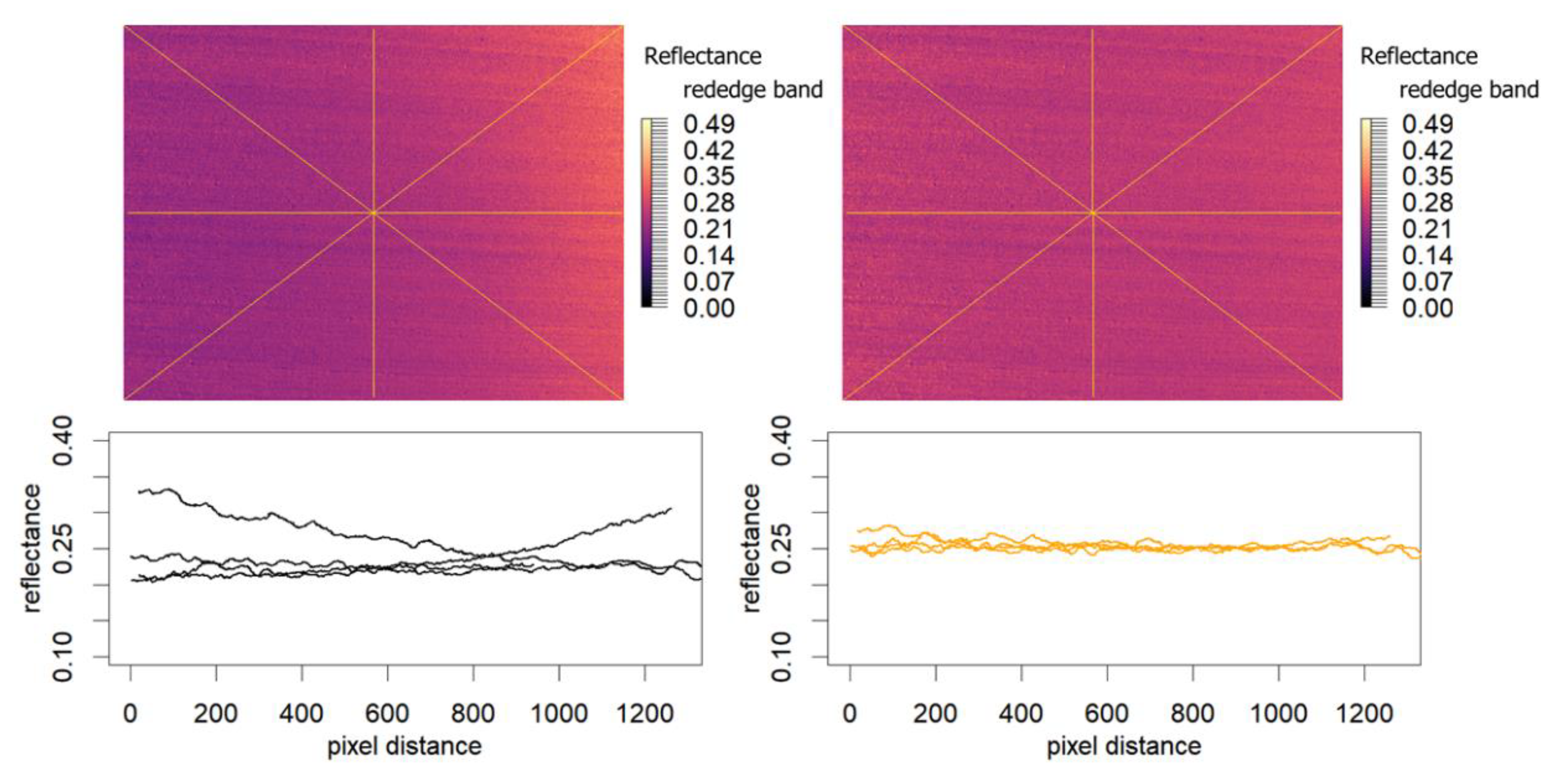
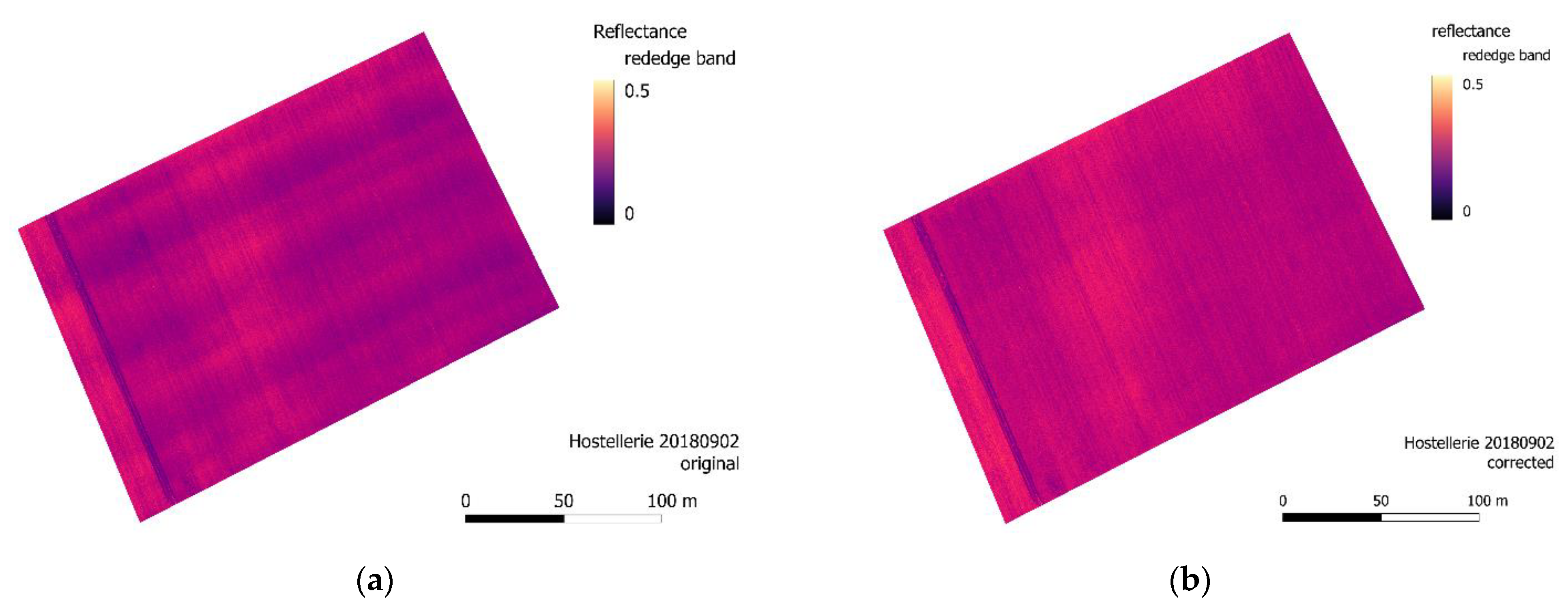
3.1. Striping Issue
3.2. Model Fit
3.3. Correction Evaluation Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Walvoort, D.J.J.; McBratney, A.B.; Janik, L.J.; Skjemstad, J.O. Visible, near infrared, mid infrared or combined diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for simultaneous assessment of various soil properties. Geoderma 2006, 131, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, E. Soil spectral imaging: Moving from proximal sensing to spatial quantitative domain. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, 1, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Colomina, I.; Molina, P. Unmanned aerial systems for photogrammetry and remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 92, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soriano-Disla, J.M.; Janik, L.J.; Allen, D.J.; McLaughlin, M.J. Evaluation of the performance of portable visible-infrared instruments for the prediction of soil properties. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 161, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldana-Jague, E.; Heckrath, G.; Macdonald, A.; van Wesemael, B.; Van Oost, K. UAS-based soil carbon mapping using VIS-NIR (480–1000 nm) multi-spectral imaging: Potential and limitations. Geoderma 2016, 275, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies Pluer, E.G.; Robinson, D.T.; Meinen, B.U.; Macrae, M.L. Pairing soil sampling with very-high resolution UAV imagery: An examination of drivers of soil and nutrient movement and agricultural productivity in southern Ontario. Geoderma 2020, 379, 114630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrhan, M.; Rauneker, P.; Sommer, M. UAV-based estimation of carbon exports from heterogeneous soil landscapes—A case study from the carboZALF experimental area. Sensors 2016, 16, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aasen, H.; Honkavaara, E.; Lucieer, A.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J. Quantitative remote sensing at ultra-high resolution with UAV spectroscopy: A review of sensor technology, measurement procedures, and data correctionworkflows. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicodemus, F. Book Reviews. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1977, 67, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Beisl, U. Correction of Bidirectional Effects in Imaging Spectrometer Data; Remote Sensing Series 37; Zurich: Hong Kong, China, 2001; ISBN 3037030011. [Google Scholar]
- Roosjen, P.P.J.; Suomalainen, J.M.; Bartholomeus, H.M.; Kooistra, L.; Clevers, J.G.P.W. Mapping reflectance anisotropy of a potato canopy using aerial images acquired with an unmanned aerial vehicle. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aasen, H.; Bolten, A. Multi-temporal high-resolution imaging spectroscopy with hyperspectral 2D imagers–From theory to application. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 374–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlapfer, D.; Richter, R.; Feingersh, T. Operational BRDF effects correction for wide-field-of-view optical scanners (BREFCOR). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandmeier, S.; Müller, C.; Hosgood, B.; Andreoli, G. Sensitivity analysis and quality assessment of laboratory BRDF data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 64, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SZ DJI Technology Co., Ltd. Shenzhen, China. Version 2.0.15; 2018. Available online: https://www.dji.com/it/downloads/products/ground-station-pro (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Pix4Dmapper SA. Prilly, Switzerland. Version 4.4.12; 2021. Available online: https://pix4d.com/product/pix4dmapper-photogrammetry-software (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- RedEdge Camera Radiometric Calibration Model. Available online: https://support.micasense.com/hc/en-us/articles/115000351194-Rededge-Camera-Radiometric-Calibration-Model (accessed on 8 February 2020).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; Version 3.6.3; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Schaepman-Strub, G.; Painter, T.; Huber, S.; Dangel, S.; Schaepman, M.E.; Martonchik, J.; Berendse, F. About the importance of the definition of reflectance quantities—Results of case studies. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.—ISPRS Arch. 2004, 35, 361–366. [Google Scholar]
- Benoit Thieurmel and Achraf Elmarhraoui. Suncalc: Compute Sun Position, Sunlight Phases, Moon Position and Lunar Phase; R Package Version 0.5.0; 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/suncalc (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Brennan, B.; Bandeen, W.R. Anisotropic reflectance characteristics of natural earth surfaces. Appl. Opt. 1970, 9, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, E.J.; Webb, J.P. Ground radiometry and airborne multispectral survey of bare soils. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1987, 8, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, H.; Anderson, K.; Kuhn, N.J. Reflectance anisotropy for measuring soil surface roughness of multiple soil types. Catena 2012, 93, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.; Croft, H. Remote sensing of soil surface properties. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2009, 33, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, R.; Kellenberger, T.; Kaufmann, H. Comparison of topographic correction methods. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakob, S.; Zimmermann, R.; Gloaguen, R. The Need for accurate geometric and radiometric corrections of drone-borne hyperspectral data for mineral exploration: MEPHySTo-A toolbox for pre-processing drone-borne hyperspectral data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crucil, G.; Van Oost, K. Towards mapping of soil crust using multispectral imaging. Sensors 2021, 21, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Movia, A.; Beinat, A.; Crosilla, F. Shadow detection and removal in RGB VHR images for land use unsupervised classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 119, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, H.; Anderson, K.; Kuhn, N.J. Evaluating the influence of surface soil moisture and soil surface roughness on optical directional reflectance factors. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Field Name | Date | Lateral Overlap (%) | Flight Line Azimuth (deg) | Sun Azimuth (deg) | Sun Zenith (deg) | Model Calibration/ Validation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seumoy | 7 May 2018 | 80 | 60/240 | 220 | 38 | Cal |
| Thorembais * | 7 May 2018 | 75 | 40/220 | 150 | 37 | Cal |
| Beuzet Sud | 8 May 2018 | 75 | 127/307 | 240 | 46 | Cal |
| Hostellerie * | 2 September 2018 | 75 | 65/245 | 140 | 49 | Cal |
| Geeste 1 | 2 September 2018 | 75 | 67/247–147/327 | 160 | 44 | Cal |
| Geeste 3 | 2 September 2018 | 75 | 65/245 | 190 | 43 | Cal |
| Ernage * | 20 April 2019 | 75 | 35/215 | 140 | 44 | Cal |
| Villeroux a1 * | 27 August 2019 | 80 | 45/225 | 200 | 42 | Cal |
| Villeroux a2 * | 14 September 2019 | 80 | 45/225 | 190 | 47 | Cal |
| Gembloux F2 * | 23 April 2021 | 60 | 115/295 | 130 | 47 | Cal |
| Gembloux F3 * | 23 April 2021 | 60 | 115/295 | 190 | 38 | Cal |
| Gembloux F4 * | 23 April 2021 | 60 | 115/295 | 230 | 49 | Cal |
| Marbaix West | 6 May 2018 | 75 | 35/215 | 150 | 37 | Val |
| Beuzet Nord | 8 May 2018 | 75 | 140/320 | 230 | 42 | Val |
| Sicy * | 2 September 2018 | 75 | 150/330 | 130 | 52 | Val |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crucil, G.; Zhang, H.; Pauly, K.; Van Oost, K. A Semi-Empirical Anisotropy Correction Model for UAS-Based Multispectral Images of Bare Soil. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030537
Crucil G, Zhang H, Pauly K, Van Oost K. A Semi-Empirical Anisotropy Correction Model for UAS-Based Multispectral Images of Bare Soil. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(3):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030537
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrucil, Giacomo, He Zhang, Klaas Pauly, and Kristof Van Oost. 2022. "A Semi-Empirical Anisotropy Correction Model for UAS-Based Multispectral Images of Bare Soil" Remote Sensing 14, no. 3: 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030537
APA StyleCrucil, G., Zhang, H., Pauly, K., & Van Oost, K. (2022). A Semi-Empirical Anisotropy Correction Model for UAS-Based Multispectral Images of Bare Soil. Remote Sensing, 14(3), 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030537







