Comparing the Ability of Burned Area Products to Detect Crop Residue Burning in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
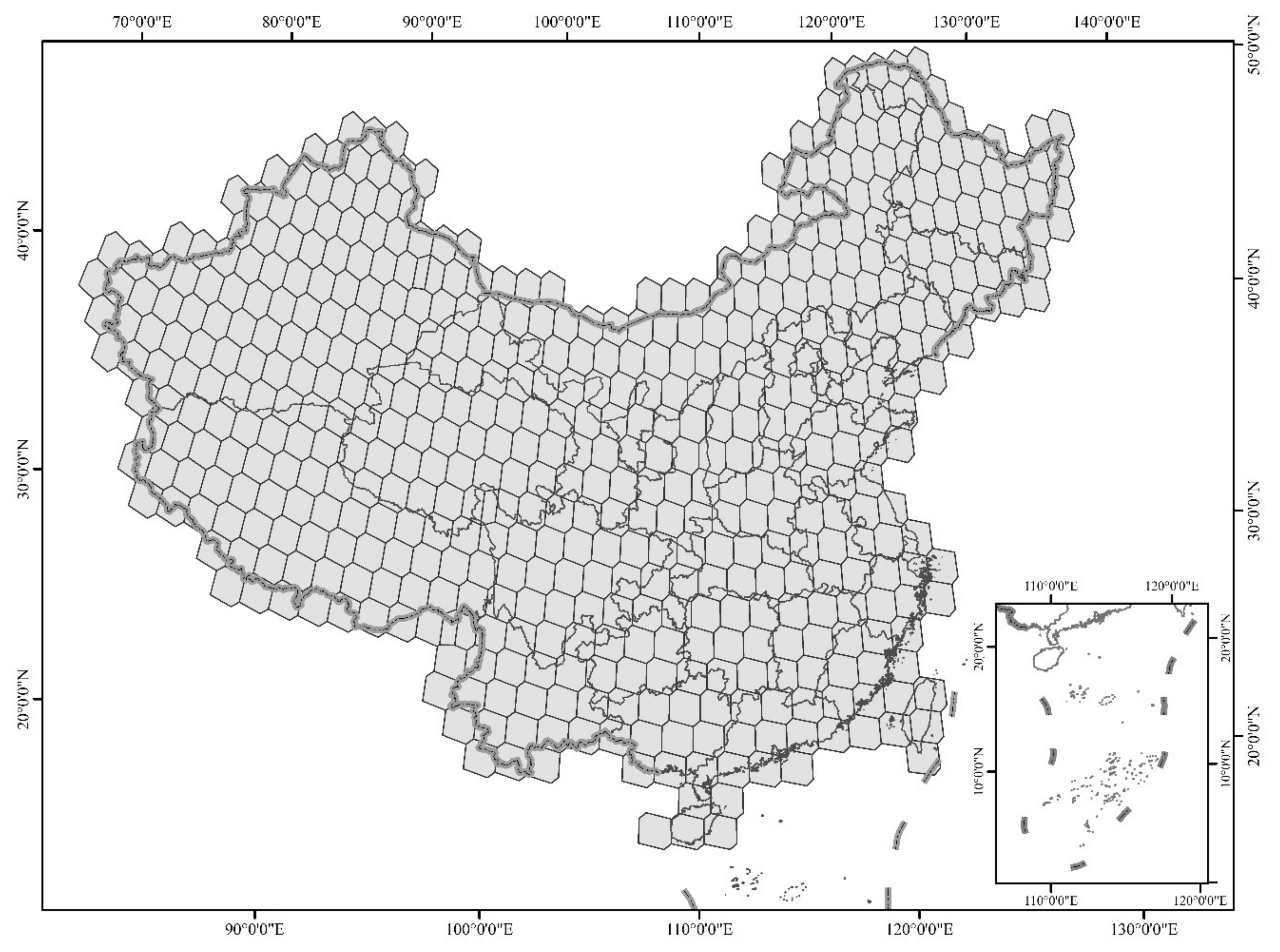
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Global Burned Area Products
| Name of Product | Satellite Sensor | Time Span | Temporal Resolution | Spatial Resolution | Algorithm Source | Download Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCD64A1 Collection 6 | MODIS Aqua and Terra | 2001 to present | monthly | 500 m | [24] | https://modis-fire.umd.edu/ba.html (accessed on 26 September 2021) |
| FireCCI 5.1 | MODIS Aqua and Terra | 2001–2019 | monthly | 250 m | [25] | https://data.ceda.ac.uk/neodc/esacci/fire/data/burned_area/MODIS/pixel/v5.1/compressed (accessed on 26 September 2021) |
| Copernicus Burnt Area | PROBA-V | 2014 to present | 10 days | 300 m | [23] | https://land.copernicus.eu/global/products/BA (accessed on 26 September 2021) |
| Land cover | PROBA-V | 2015–2019 | annual | 100 m | [26] | https://land.copernicus.eu/global/products/lc (accessed on 26 September 2021) |
2.2.2. Land Cover Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Pre-Processing of Burned Area Products
2.3.2. Comparison of Burned Area Products
3. Results
3.1. Total Burned Area
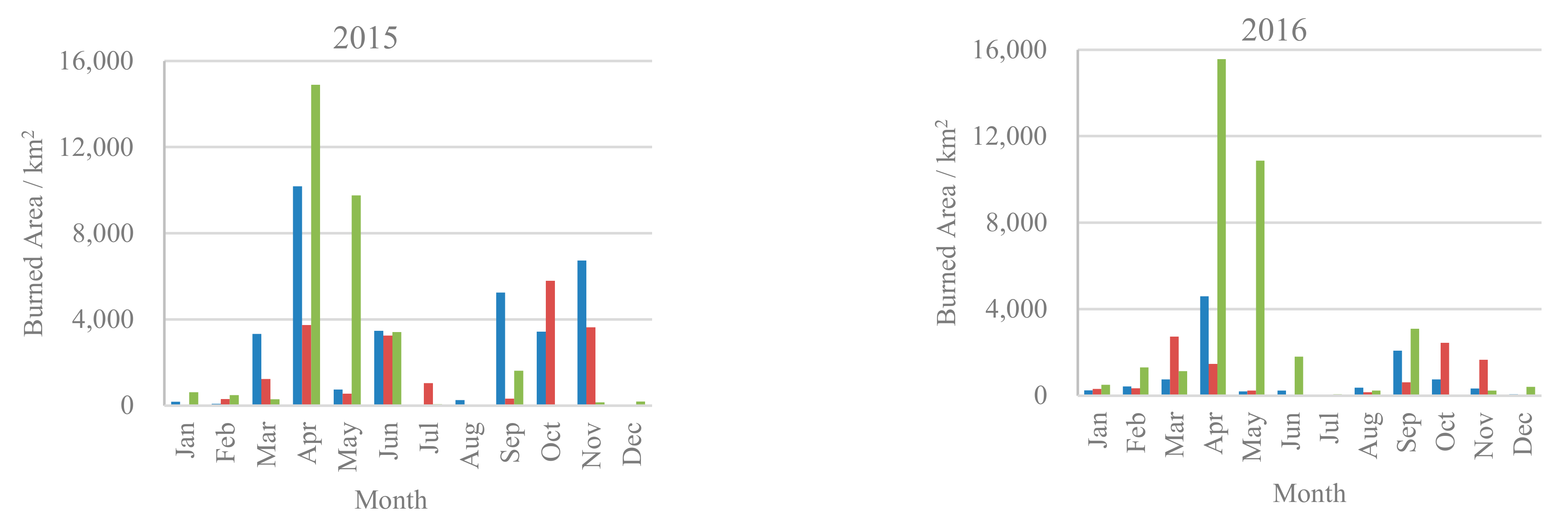
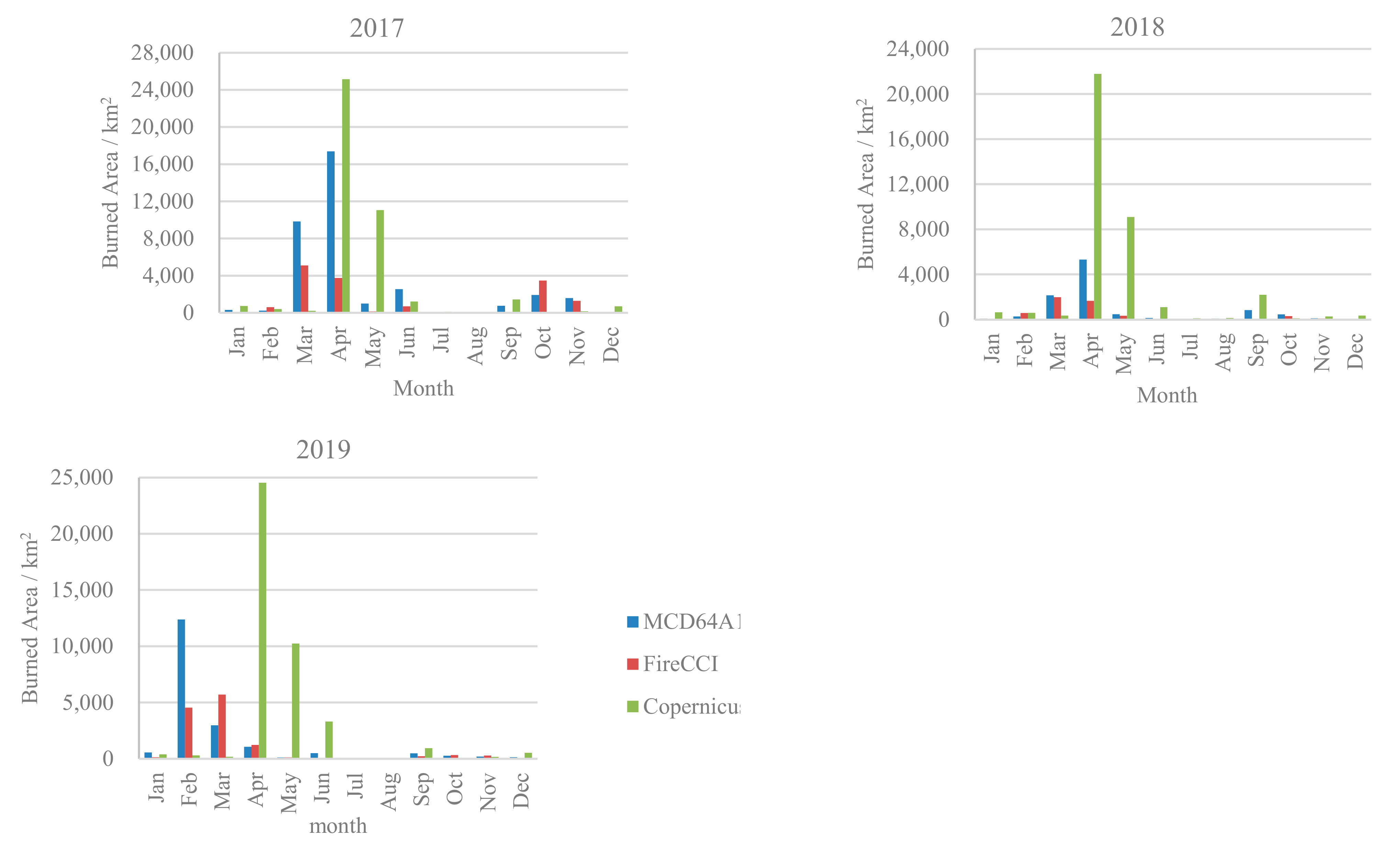
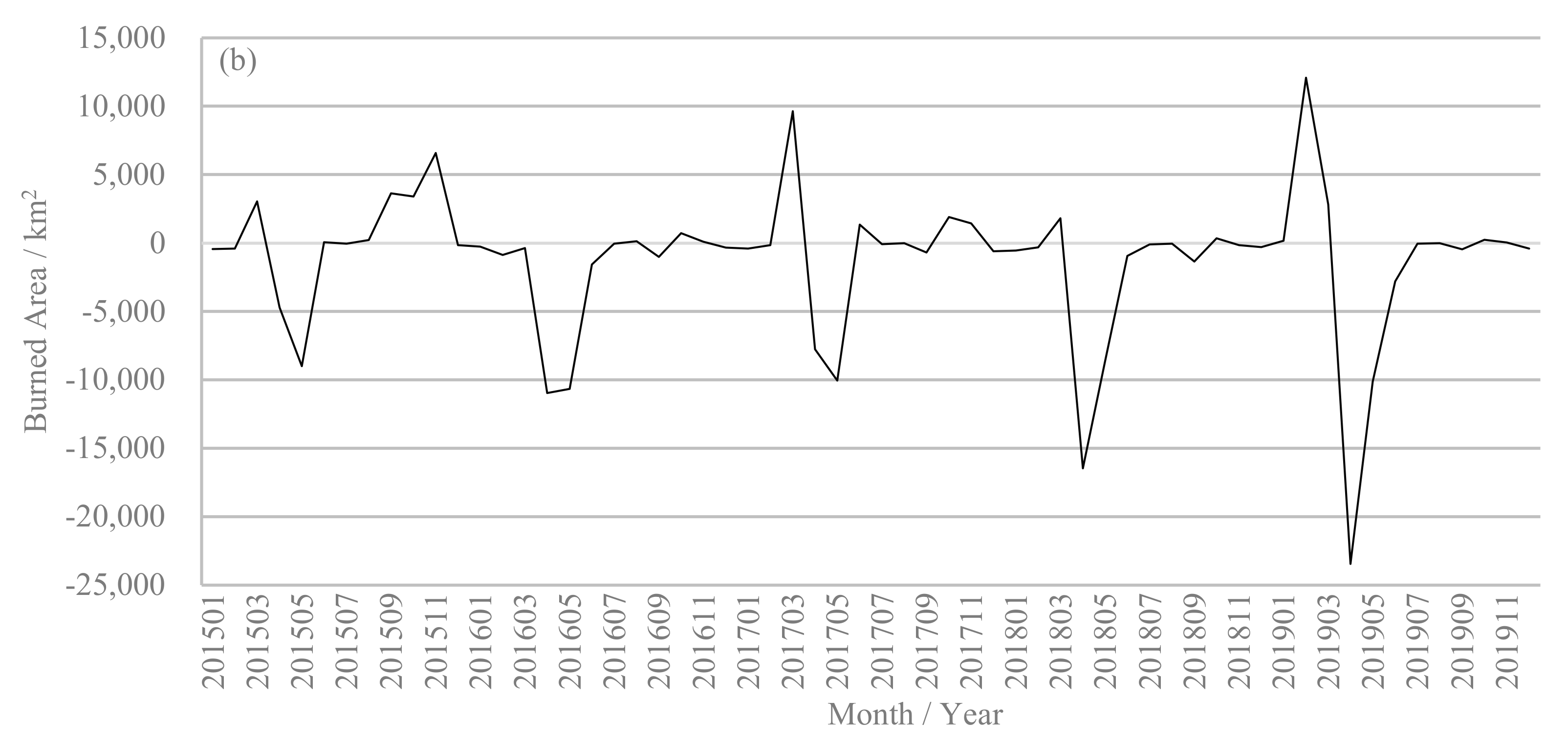
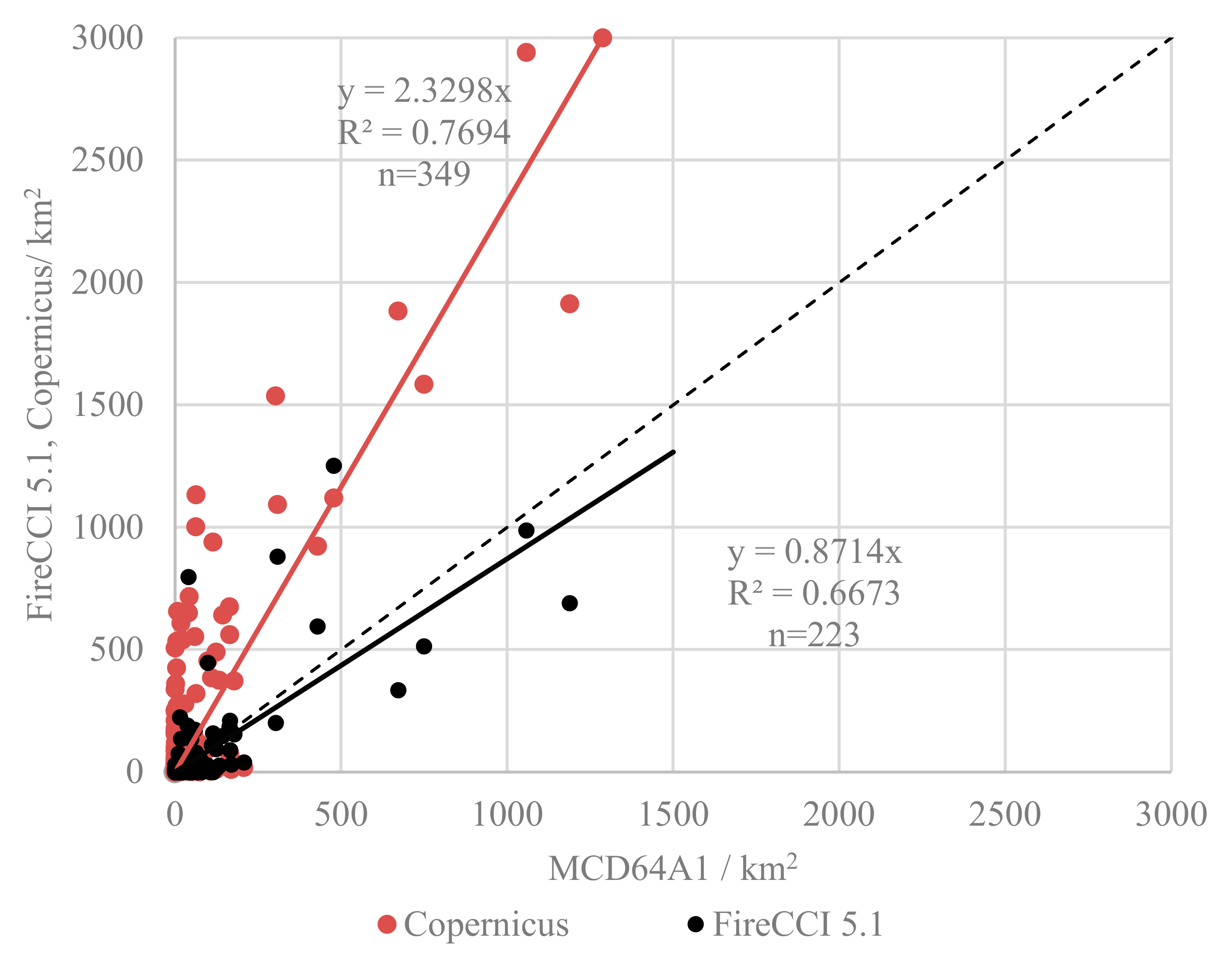
3.2. Temporal Comparison
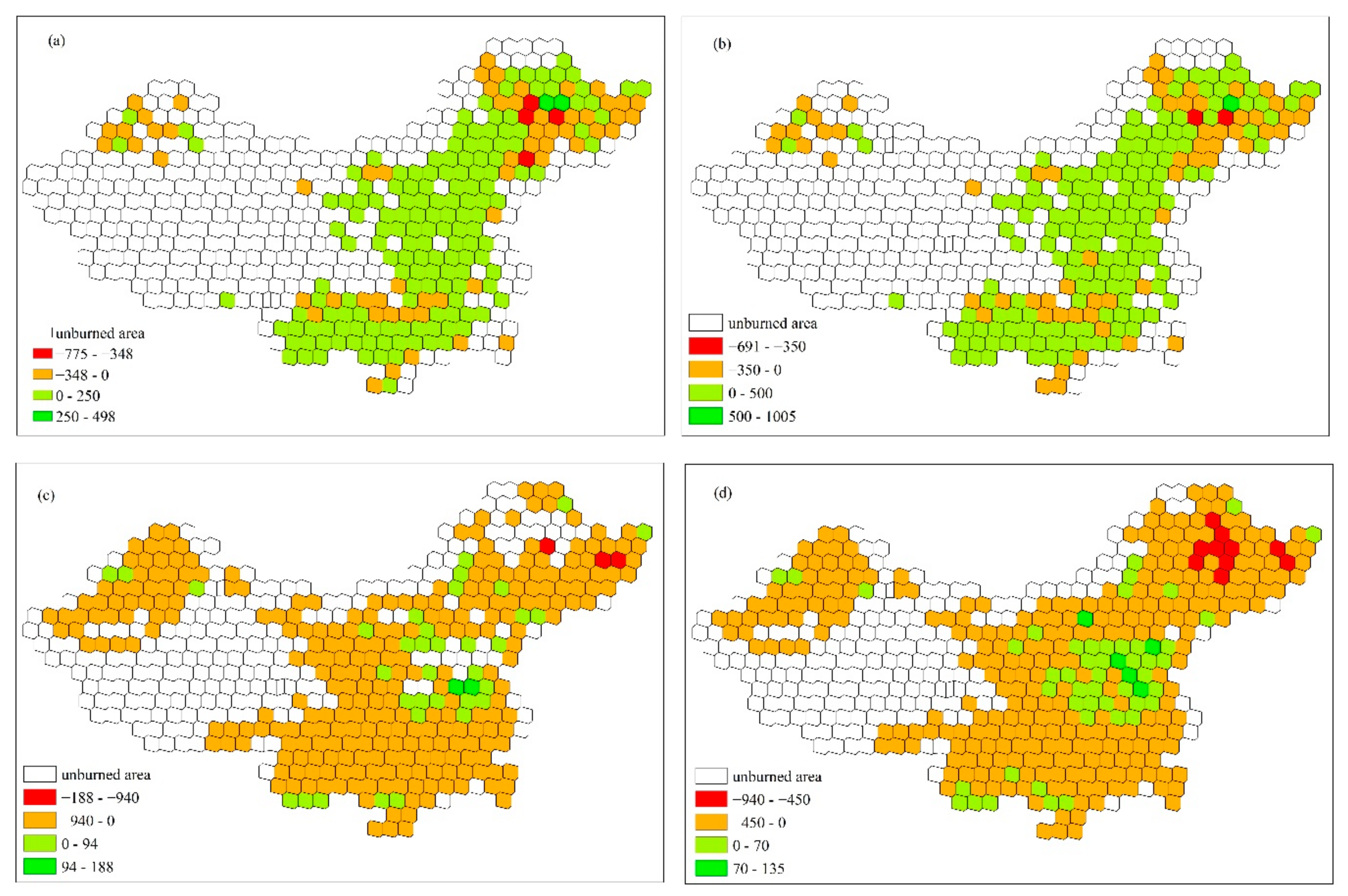
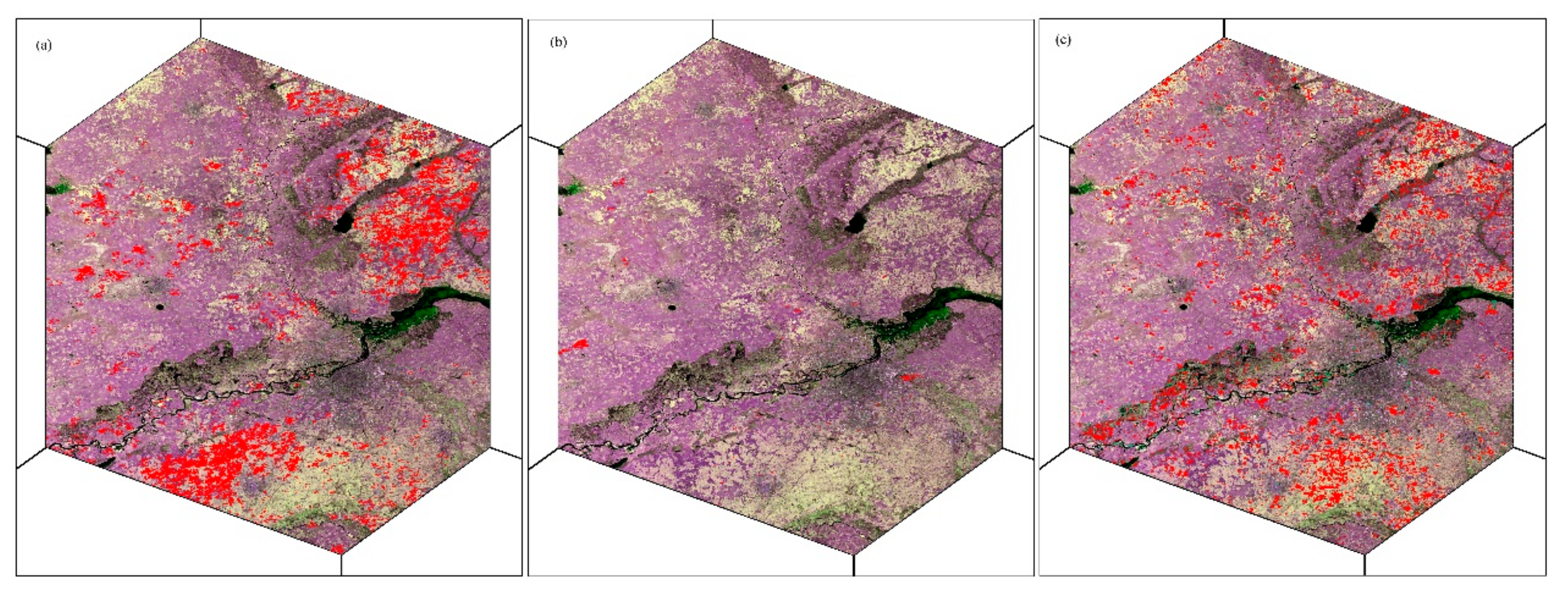
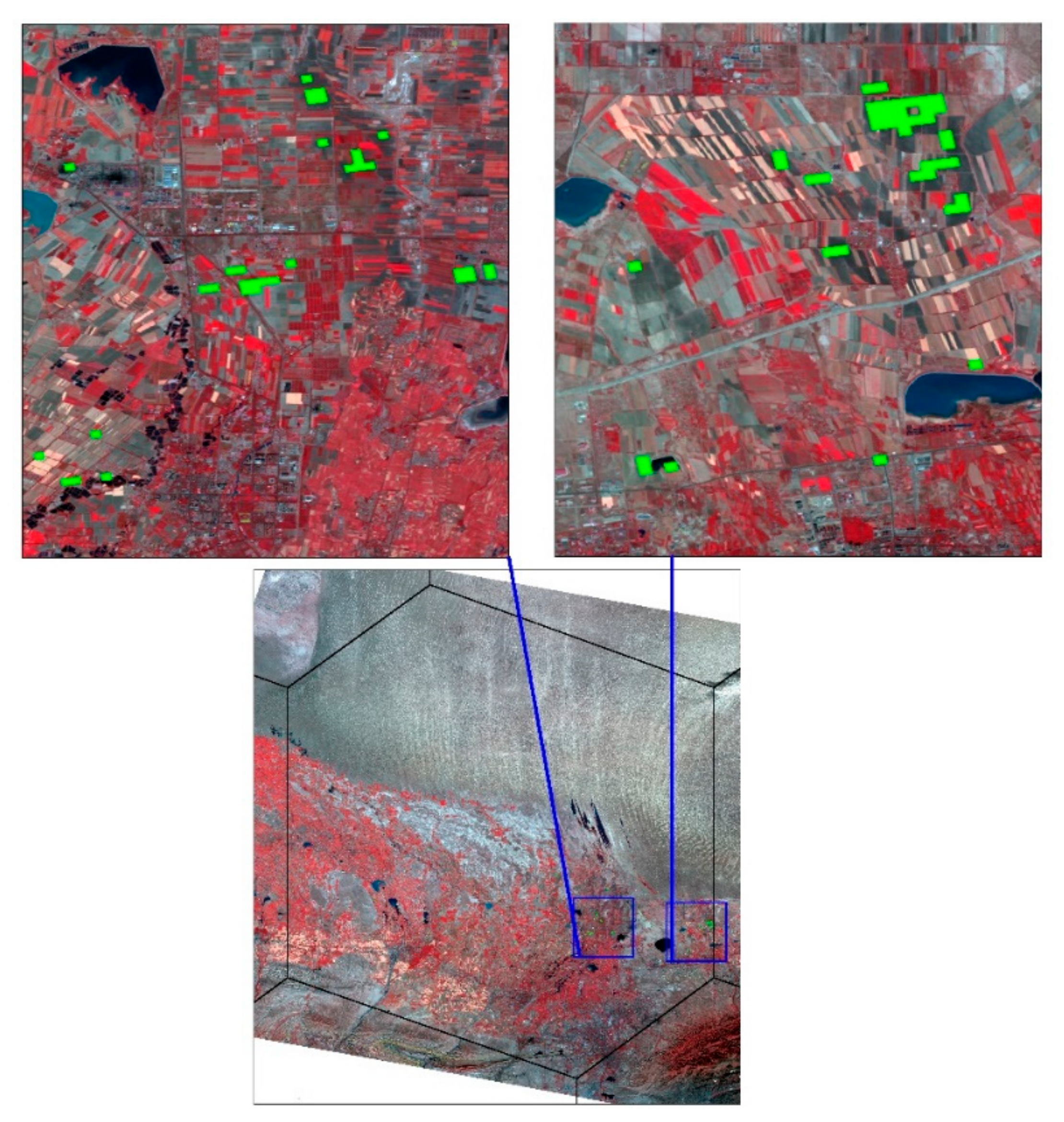
3.3. Spatial Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humber, M.L.; Boschetti, L.; Giglio, L.; Justice, C.O. Spatial and temporal intercomparison of four global burned area products. Int. J. Digit. Earth. 2019, 12, 460–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouillot, F.; Schultz, M.G.; Yue, C.; Cadule, P.; Tansey, K.; Ciais, P.; Chuvieco, E. Ten years of global burned area products from spaceborne remote sensing—A review: Analysis of user needs and recommendations for future developments. Int. J. Appl. Earth. Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boschetti, L.; Flasse, S.P.; Brivio, P.A. Analysis of the conflict between omission and commission in low spatial resolution dichotomic thematic products: The Pareto boundary. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Song, Y. Comparison of L3JRC and MODIS global burned area products from 2000 to 2007. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D16106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, L.; Camia, A.; San-Miguel-Ayanz, J. A comparison of remote sensing products and forest fire statistics for improving fire information in Mediterranean Europe. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 48, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padilla, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Chuvieco, E. Validation of the 2008 MODIS MCD45 global burned area product using stratified random sampling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 144, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Ramo, R.; Corti, D.; Hantson, S.; Oliva, P.; Alonso-Canas, I.; Bradley, A.V.; Tansey, K.; Mota, B.; et al. Comparing the accuracies of remote sensing global burned area products using stratified random sampling and estimation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santana, N.C.; Carvalho, O.; Gomes, R.; Guimares, R.F. Accuracy and spatiotemporal distribution of fire in the Brazilian biomes from the MODIS burned-area products. Int. J. Wildland Fire. 2020, 29, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramo, R.; Roteta, E.; Bistinas, I.; Wees, D.V.; Werf, G.R.V.D. African burned area and fire carbon emissions are strongly impacted by small fires undetected by coarse resolution satellite data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2011160118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.V.; Argueta, F.; Giglio, L. Validation of MCD64A1 and FireCCI 51 cropland burned area mapping in Ukraine. Int. J. Appl. Earth. Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessôa, A.; Anderson, L.O.; Carvalho, N.S.; Campanharo, W.A.; Arago, L.E.O.C. Intercomparison of Burned Area Products and Its Implication for Carbon Emission Estimations in the Amazon. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, G.M.; Anaya, J.A.; Velásquez, V.A.; Ramo, R.; Caro-Lopera, F.J. About Validation-Comparison of Burned Area Product. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenguer-Plomer, M.A.; Chuvieco, E.; Tanase, M.A. Temporal decorrelation of C-Band backscatter coefficient in Mediterranean burned areas. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ke, H.; Gong, S.; He, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y. Spatial and temporal distribution of open bio-mass burning in China from 2013 to 2017. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 210, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Gao, C.Y. Straw resource quantity and its regional distribution in China. J. Agric. Mechanizat. Res. 2010, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Ristovski, Z.; Milic, A.; Gu, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Wang, S.X.; Hao, J.M.; Zhang, H.F.; He, C.J.; et al. A review of biomass burning: Emissions and impacts on air quality, health and climate in china. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1000–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, X.; Zhao, F.; Shu, L.; Wang, M. Distribution characteristics and the influence factors of forest fires in China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 310, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Yang, X.H.; Tu, X.M.; Ning, K.X.; Luan, X.C. Spatio-temporal change of straw burning fire points in field of China from 2014 to 2018. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Justice, C.O.; Giglio, L.; Korontzi, S.; Owens, J.; Morisette, J.T.; Roy, D.; Descloitres, J.; Alleaume, S.; Petitcolin, F.; Kaufman, Y. The MODIS fire products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.A.M.; Lázaro, J.R.G.; Cano, I.D.Á.; Leal, P.H. Burned area mapping in the North American boreal forest using terra-MODIS LTDR (2001–2011): A comparison with the MCD45A1, MCD64A1 and BA GEOLAND-2 products. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 815–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fornacca, D.; Ren, G.; Xiao, W. Performance of Three MODIS Fire Products (MCD45A1, MCD64A1, MCD14ML), and ESA Fire_CCI in a Mountainous Area of Northwest Yunnan, China, Characterized by Frequent Small Fires. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vetrita, Y.; Cochrane, M.A.; Priyatna, M.; Sukowati, K.A.D.; Khomarudin, M.R. Evaluating accuracy of four MODIS-derived burned area products for tropical peatland and non-peatland fires. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 035015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansey, K.; Wolfs, D. Copernicus Global Land Service: Burnt Area and Seasonality Collection 300 m; Version 1; Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document; Zenodo: Geneve, Switzerland, 2017; p. I1.20. [Google Scholar]
- Giglio, L.; Boschetti, L.; Roy, D.P.; Humber, M.L.; Justice, C.O. The Collection 6 MODIS burned area mapping algorithm and product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizundia-Loiola, J.; Otón, G.; Ramo, R.; Chuvieco, E. A spatio-temporal active-fire clustering approach for global burned area mapping at 250m from MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchhorn, M.; Bertels, L.; Smets, B.; De Roo, B.; Lesiv, M.; Tsendbazar, N.E.; Masiliunas, D.; Linlin, L. Copernicus Global Land Service: Land Cover 100 m: Version 3 Globe 2015–2019: Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document; Zenodo: Geneve, Switzerland, 2020; p. I3.4. [Google Scholar]
- Boschetti, L.; Stehman, S.V.; Roy, D.P. A stratified random sampling design in space and time for regional to global scale burned area product validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansey, K.; Rasul, A.; Ibrahim, S. Scientific Quality Evaluation Report 2019 Burned Areas 300 m V1; Zenodo: Geneve, Switzerland, 2020; p. I1.00. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Wooster, M.J.; De Jong, M.C.; Xu, W. How well does the ‘small fire boost’methodology used within the GFED4. 1s fire emissions database represent the timing, location and magnitude of agricultural burning? Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Libonati, R.; DaCamara, C.C.; Setzer, A.W.; Morelli, F.; Melchiori, A.E. An algorithm for burned area detection in the Brazilian Cerrado using 4 μm MODIS imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15782–15803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alonso-Canas, I.; Chuvieco, E. Global burned area mapping from ENVISAT-MERIS and MODIS active fire data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 163, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korontzi, S.; Roy, D.P.; Justi Ce, C.O.; Ward, D.E. Modeling and sensitivity analysis of fire emissions in southern Africa during SAFARI 2000. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 376–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Kobayashi, H.; Kanaya, Y.; Saito, M. Size-dependent validation of MODIS MCD64A1 burned area over six vegetation types in boreal Eurasia: Large underestimation in croplands. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnolo, M.L.; Libonati, R.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Pereira, J. A comprehensive characterization of MODIS daily burned area mapping accuracy across fire sizes in tropical savannas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, P.; Schroeder, W. Assessment of VIIRS 375 m active fire detection product for direct burned area mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, J.L.; Korontzi, S.; Justice, C.O.; Loboda, T. The spatial and temporal distribution of crop residue burning in the contiguous United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5701–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Marlier, M.E.; Karambelas, A.; Jain, M.; Singh, S.; Singh, M.K.; Gautam, R.; DeFries, R.S. Missing emissions from post-monsoon agricultural fires in northwestern India: Regional limitations of MODIS burned area and active fire products. Environ. Res. Commun. 2019, 1, 011007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Z.; Tan, L. Comparing the Ability of Burned Area Products to Detect Crop Residue Burning in China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030693
Zhang S, Zhao H, Wu Z, Tan L. Comparing the Ability of Burned Area Products to Detect Crop Residue Burning in China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(3):693. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030693
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Sumei, Hongmei Zhao, Zehao Wu, and Longda Tan. 2022. "Comparing the Ability of Burned Area Products to Detect Crop Residue Burning in China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 3: 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030693
APA StyleZhang, S., Zhao, H., Wu, Z., & Tan, L. (2022). Comparing the Ability of Burned Area Products to Detect Crop Residue Burning in China. Remote Sensing, 14(3), 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030693





