Assessing the Performance of Irrigation Systems in Large Scale Urban Parks: Application to the Case of Valdebebas, Madrid (Spain)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Approach for Assessing Irrigation Performance in Large Scale Urban Parks
2.2. Estimation of NDVI Index
3. Case of Study
3.1. Description of Urban Parks and Irrigation Systems
3.2. Application of the Procedure to the VBB Urban Parks
4. Results
4.1. Maps of Hydrozones and Their Irrigation Performance in the VBB Urban Parks
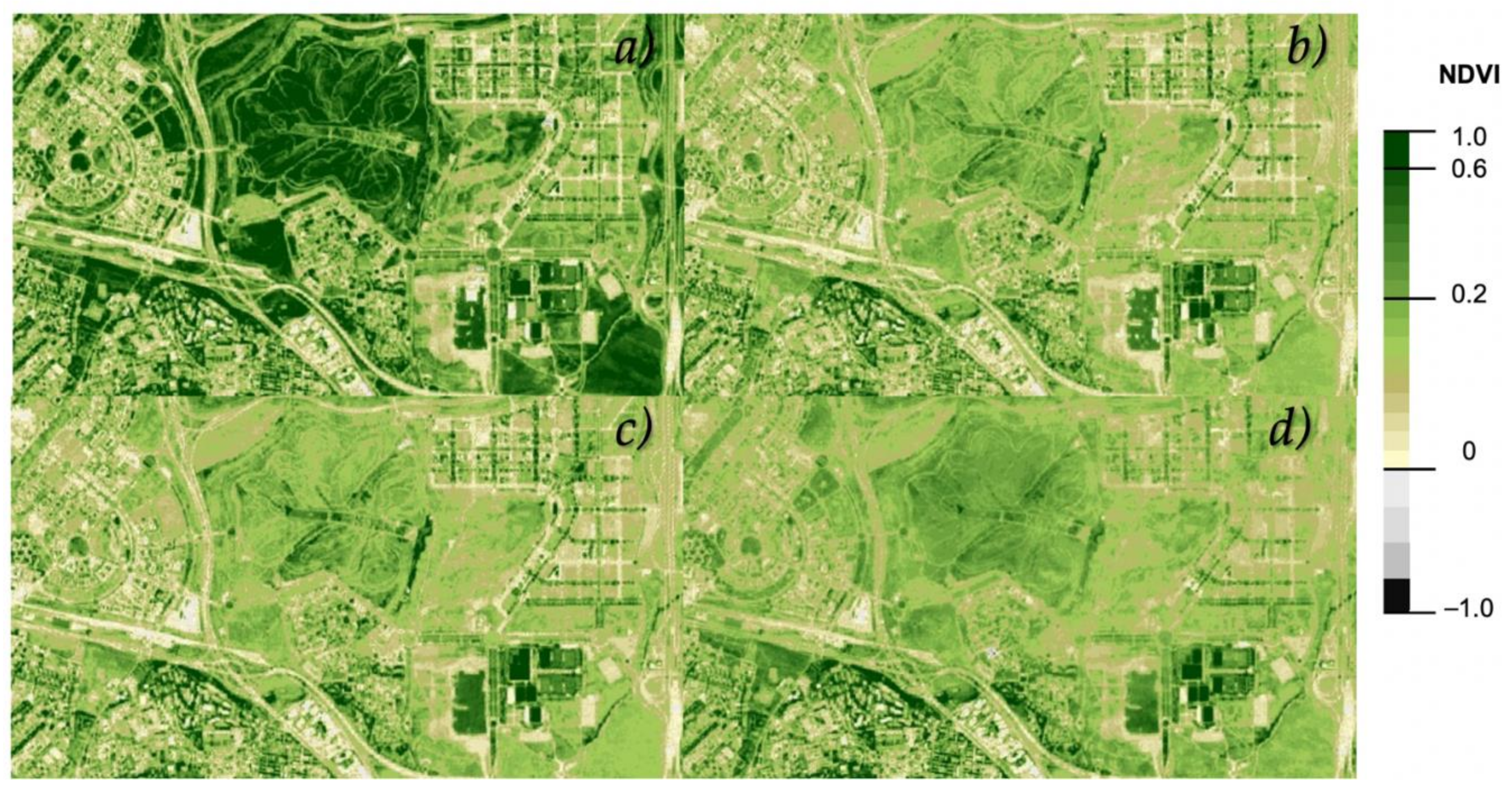
4.2. NDVI Index for the VBB Urban Parks
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cabrera, R.; Wagner, K.L.; Wherley, B. An Evaluation of Urban Landscape Water Use in Texas. Tex. Water J. 2013, 4, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, P.; Gheysari, M.; Nouri, H.; Myers, B.; Esmaeili, H. Water Requirements of Urban Landscape Plants in an Arid Environment: The Example of a Botanic Garden and a Forest Park. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 123, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halper, E.B.; Dall’erba, S.; Bark, R.H.; Scott, C.A.; Yool, S.R. Effects of Irrigated Parks on Outdoor Residential Water Use in a Semi-Arid City. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 134, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. In Proceedings of the 14th Session of Working Group I and 54th Session of the IPCC, online, 26 July–6 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mini, C.; Hogue, T.S.; Pincetl, S. Estimation of Residential Outdoor Water Use in Los Angeles, California. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 127, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Paecke, S.; Gironás, J.; Melo, O.; Vicuña, S.; Herrera, J. Irrigation of Green Spaces and Residential Gardens in a Mediterranean Metropolis: Gaps and Opportunities for Climate Change Adaptation. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 182, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abioye, E.A.; Abidin, M.S.Z.; Mahmud, M.S.A.; Buyamin, S.; Ishak, M.H.I.; Rahman, M.K.I.A.; Otuoze, A.O.; Onotu, P.; Ramli, M.S.A. A Review on Monitoring and Advanced Control Strategies for Precision Irrigation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 173, 105441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Kopecká, M.; Guo, S.; Guan, Y.; Cai, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Yao, W. Responses of Urban Land Surface Temperature on Land Cover: A Comparative Study of Vienna and Madrid. Sustainability 2018, 10, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Water Management Committee of The Irrigation Association. Turf and Landscape Irrigation Best Management Practices; Irrigation Association: Fairfax, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, L.R.; Jones, K.S. WUCOLS IV, Water Use Classification of Landscape Species; California Center for Urban Horticulture, University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nouri, H.; Beecham, S.; Hassanli, A.M.; Kazemi, F. Water Requirements of Urban Landscape Plants: A Comparison of Three Factor-Based Approaches. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 57, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukes, M.D. Water Conservation Potential of Landscape Irrigation Smart Controllers. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.; Desai, B.L. Intelligent Irrigation Control System by Employing Wireless Sensor Networks. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2013, 79, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahmani, P.; Hogue, T.S. Incorporating an Urban Irrigation Module into the Noah Land Surface Model Coupled with an Urban Canopy Model. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1440–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurtz, K.M.; Dicataldo, E.; Sowby, R.B.; Williams, G.P. Insights into Efficient Irrigation of Urban Landscapes: Analysis Using Remote Sensing, Parcel Data, Water Use, and Tiered Rates. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segovia-Cardozo, D.A.; Rodríguez-Sinobas, L.; Zubelzu, S. Living Green Walls: Estimation of Water Requirements and Assessment of Irrigation Management. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 46, 126458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalacáin, D.; Bienes, R.; Sastre-Merlín, A.; Martínez-Pérez, S.; García-Díaz, A. Influence of Reclaimed Water Irrigation in Soil Physical Properties of Urban Parks: A Case Study in Madrid (Spain). Catena 2019, 180, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Urrestarazu, L.; Egea, G.; Ruiz-Alcalá, C.; Roldán-Olmo, F.; Fernández-Cañero, R. Water Management Assessment in a Historic Garden: The Case Study of the Real Alcazar (Seville, Spain). Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 29, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, R.; Bautista-Capetillo, C.; Playán, E. Irrigation Performance in Private Urban Landscapes: A Study Case in Zaragoza (Spain). Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 100, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Droogers, P.; Kite, G.; Murray-Rust, H. Use of Simulation Models to Evaluate Irrigation Performance Including Water Productivity, Risk and System Analyses. Irrig. Sci. 2000, 19, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemmens, A.J.; Molden, D.J. Water Uses and Productivity of Irrigation Systems. Irrig. Sci. 2007, 25, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorite, I.J.; Mateos, L.; Fereres, E. Evaluating Irrigation Performance in a Mediterranean Environment. Irrig. Sci. 2004, 23, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malano, H.; Burton, M. Guidelines for Benchmarking Performance in the Irrigation and Drainage Sector. Knowledge Syntesis Report; Food & Agriculture Org.: Rome, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, G. Relative Water Supply, an Explanatory Variable for Irrigations Systems; Technical Report no 6; The determinations of Irrigation Projects in Developing Countries; Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Lei, Y.; Li, C.; Manevski, K.; Shen, Y. Using NDVI Percentiles to Monitor Real-Time Crop Growth. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 162, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segovia-Cardozo, D.A.; Rodríguez-Sinobas, L.; Zubelzu, S. Water Use Efficiency of Corn among the Irrigation Districts across the Duero River Basin (Spain): Estimation of Local Crop Coefficients by Satellite Images. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez López, J.J.; Puertas, J.; Anta, J.; Jácome, A.; Álvarez-Campana, J.M. Integrated Management of Water Resources in Urban Water System: Water Sensitive Urban Development as a Strategic Approach. Ing. Del Agua 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bousbih, S.; Zribi, M.; el Hajj, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Lili-Chabaane, Z.; Gao, Q.; Fanise, P. Soil Moisture and Irrigation Mapping in a Semi-Arid Region, Based on the Synergetic Use of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Recanatesi, F.; Giuliani, C.; Ripa, M.N. Monitoring Mediterranean Oak Decline in a Peri-Urban Protected Area Using the NDVI and Sentinel-2 Images: The Case Study of Castelporziano State Natural Reserve. Sustain. Switz. 2018, 10, 3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wei, W.; Zhao, B. Effects of Urban Parks on Residents’ Expressed Happiness before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 212, 104118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváthová, E.; Badura, T.; Duchková, H. The Value of the Shading Function of Urban Trees: A Replacement Cost Approach. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 62, 127166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Wang, J.; Qian, Y. From Quantity to Quality: Enhanced Understanding of the Changes in Urban Greenspace. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Gao, M.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, B. Quantifying Emotional Differences in Urban Green Spaces Extracted from Photos on Social Networking Sites: A Study of 34 Parks in Three Cities in Northern China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 62, 127133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales-Ide, F.; Zubelzu, S.; Rodríguez-Sinobas, L. Irrigation Systems in Smart Cities Coping with Water Scarcity: The Case of Valdebebas, Madrid (Spain). J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, L.R.; Jones, K.S. WUCOLS. A Guide to the Water Needs of Landscape Plants; University of California, Cooperative Extension: Oakland, CA, USA, 1994; Available online: http://ucanr.edu/sites/oc/files/132534.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2018).
- Pittenger, D.R.; Shaw, D.A. Estimating Water Needs of Urban Landscapes. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the American Society for Horticultural Science, Palm Desert, CA, USA, 2–5 August 2010; Supplement to HortScience; American Society for Horticultural Science: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2010; Volume 45. [Google Scholar]
- Kjelgren, R.; Beeson, R.C.; Pittenger, D.R.; Montague, D.T. Simplified Landscape Irrigation Demand Estimation: Slide Rules. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2016, 32, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connellan, G.J. Evaluating and Benchmarking the Performance of Urban Irrigation. In Proceedings of the New Zealand Water and Wastewater Association Conference, Christchurch, NZ, USA, 6 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Knox, J.W.; Weatherhead, E.K.; Bradley, R.I. Mapping the Total Volumetric Irrigation Water Requirements in England and Wales. Agric. Water Manag. 1997, 33, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zribi, M.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Baghdadi, N.; Segui, P.Q. Irrigation Mapping Using Sentinel-1 Time Series at Field Scale. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fontanet, M.; Scudiero, E.; Skaggs, T.H.; Fernández-Garcia, D.; Ferrer, F.; Rodrigo, G.; Bellvert, J. Dynamic Management Zones for Irrigation Scheduling. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 238, 106207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirogiannis, I.L. Optimizing Water Use Efficiency in Urban Landscapes Using GIS. Acta Hortic. 2010, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Sinobas, L.; Zubelzu, S.; Perales-Momparler, S.; Canogar, S. Techniques and Criteria for Sustainable Urban Stormwater Management. The Case Study of Valdebebas (Madrid, Spain). J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Landry, S. A Comparative Analysis of High Spatial Resolution IKONOS and WorldView-2 Imagery for Mapping Urban Tree Species. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 516–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesnel, K.J.; Ajami, N.K. Large Landscape Urban Irrigation: A Data-Driven Approach to Evaluate Conservation Behavior. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arunadevi, K.; Singh, M.; Franco, D.; Prajapati, V.K.; Ramachandran, J.; Maruthi Sankar, G.R. Real Time Soil Moisture (RTSM) Based Irrigation Scheduling to Improve Yield and Water-Use Efficiency of Green Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Grown in North India. Agronomy 2022, 12, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.; Riad, K.; Alqahtani, N. Efficient IoT-Based Control for a Smart Subsurface Irrigation System to Enhance Irrigation Management of Date Palm. Sensors 2021, 21, 3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Celaya-Echarri, M.; Azpilicueta, L.; Lopez-Iturri, P.; Falcone, F.; Fernández-Caramés, T.M. Design and Empirical Validation of a LoRaWAN IoT Smart Irrigation System. Proceedings 2020, 42, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nouri, H.; Beecham, S.; Anderson, S.; Nagler, P. High Spatial Resolution WorldView-2 Imagery for Mapping NDVI and Its Relationship to Temporal Urban Landscape Evapotranspiration Factors. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 580–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haghverdi, A.; Singh, A.; Sapkota, A.; Reiter, M.; Ghodsi, S. Developing Irrigation Water Conservation Strategies for Hybrid Bermudagrass Using an Evapotranspiration-Based Smart Irrigation Controller in Inland Southern California. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.D.; Belitz, K. A Remote Sensing Approach for Estimating the Location and Rate of Urban Irrigation in Semi-Arid Climates. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414–415, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Plant Typology | Cover Area | Irrigation Rate | Weekly Irrigation Schedule |
|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (mm h−1) | ||
| LAW | 9 | 20.7 | Daily (Mon to Fri) |
| SHR | 79 | 9.2 | Mon-Wed-Fri |
| TREE | 4 | 20.7 | Thurs |
| FLO | 8 | 9.0 | Mon-Wed-Fri |
| Park | Kd | Kmc |
|---|---|---|
| 107 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| 108 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| 202 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
| 203 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| 204 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| 301 | 1.1 | 1.0 |
| 302 | 1.1 | 1.0 |
| Plant Typology | Specie | Variety | Kc Manager | Ks | Ks Mix | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shu PLA A | Viburnum | tinus | 0.5 | 0.5 | ||
| Viburnum | tinus | ‘Eve Price’ | 0.8 | 0.5 | ||
| Viburnum | tinus | ‘Purpureum’ | 0.5 | |||
| Shu PLA B | Escallonia | ssp. | ‘Iveyi’ | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.45 |
| Lonicera | nitida | ‘Elegant’ | 0.4 | |||
| Shu PLA C | Pittosporum | tobira | ‘Nana’ | 0.8 | 0.45 | 0.45 |
| Flo PLA D1 | Festuca | glauca | 0.4 | 0.4 | ||
| Tulbaghia | violacea | 0.8 | 0.4 | |||
| Tulbaghia | violacea | ‘Blanca’ | 0.4 | |||
| Lavandula | angustifolia | ‘Hidcote Pink’ | 0.3 | |||
| Gaura | lindheimeri | 0.5 | ||||
| Gaura | lindheimeri | ‘Siskiyou Pink’ | 0.5 | |||
| Cistus | x skanbergii | 0.3 | ||||
| Cistus | florentinus | 0.3 | ||||
| Flo PLA D2 | Liriope | muscari | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.4 | |
| Iris | germanica | 0.3 | ||||
| Pennisetum | alopecuroides | 0.2 | ||||
| Tulbaghia | violacea | 0.4 | ||||
| Tulbaghia | violacea | ‘Blanca’ | 0.4 | |||
| Hedera | hibernica | ‘Sagittifolia’ | 0.5 | |||
| Flo M | Chrysanthemum | leucanthemum | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| Flo I | Iris | ssp. | Multiples | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Flo H | Hemerocallis | ssp. | Multiples | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Flo R | Rosa | ssp. | Multiples | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Law PLA S1 | Cynodon | dactylon | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | |
| Flo PLA E | Trachelospermum | jasminoides | ‘Tricolor’ | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Tre ARB 01 | Acacia | dealbata | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.2 | |
| Tre ARB 06 | Acer | platanoides | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| Tre ARB 14 | Cercis | siliquastrum | ‘Multi-stem’ | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Tre ARB 25 | Lagerstroemia | indica | ‘Rosea’ | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Tre ARB 31 | Morus | alba | ‘Fruitless’ | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Tre ARB 50 | Sophora | japonica | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.4 | |
| Tre ARB 51 | Sorbus | aria | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| Tre ARB 53 | X Chitalpa | tashkentensis | ‘Summer bells’ | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Canales-Ide, F.; Zubelzu, S.; Segovia-Cardozo, D.; Rodríguez-Sinobas, L. Assessing the Performance of Irrigation Systems in Large Scale Urban Parks: Application to the Case of Valdebebas, Madrid (Spain). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051060
Canales-Ide F, Zubelzu S, Segovia-Cardozo D, Rodríguez-Sinobas L. Assessing the Performance of Irrigation Systems in Large Scale Urban Parks: Application to the Case of Valdebebas, Madrid (Spain). Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(5):1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051060
Chicago/Turabian StyleCanales-Ide, Freddy, Sergio Zubelzu, Daniel Segovia-Cardozo, and Leonor Rodríguez-Sinobas. 2022. "Assessing the Performance of Irrigation Systems in Large Scale Urban Parks: Application to the Case of Valdebebas, Madrid (Spain)" Remote Sensing 14, no. 5: 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051060
APA StyleCanales-Ide, F., Zubelzu, S., Segovia-Cardozo, D., & Rodríguez-Sinobas, L. (2022). Assessing the Performance of Irrigation Systems in Large Scale Urban Parks: Application to the Case of Valdebebas, Madrid (Spain). Remote Sensing, 14(5), 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051060







