Past, Present and Future Marine Microwave Satellite Missions in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Development of Marine Satellites in China
2.1. Progress History of China’s Marine Dynamic Environmental Satellites
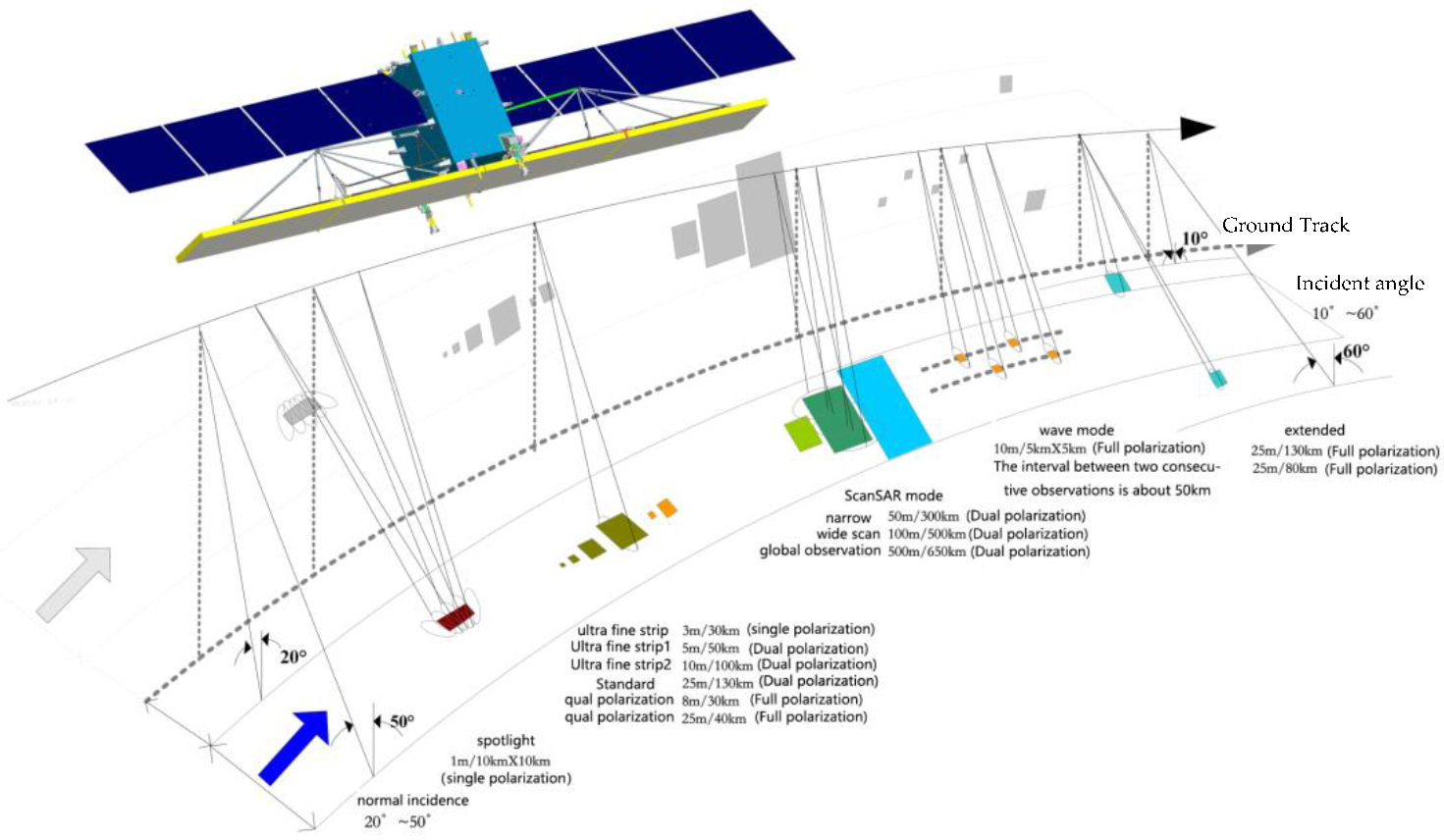
2.2. Progress History of China’s Marine Surveillance Satellites
3. Progress History of China’s Marine Microwave Satellite Remote Sensing Technology
3.1. Retrieval Technology for Marine Dynamic Environmental Elements
3.2. Calibration Technology for Marine Dynamic Environmental Satellites
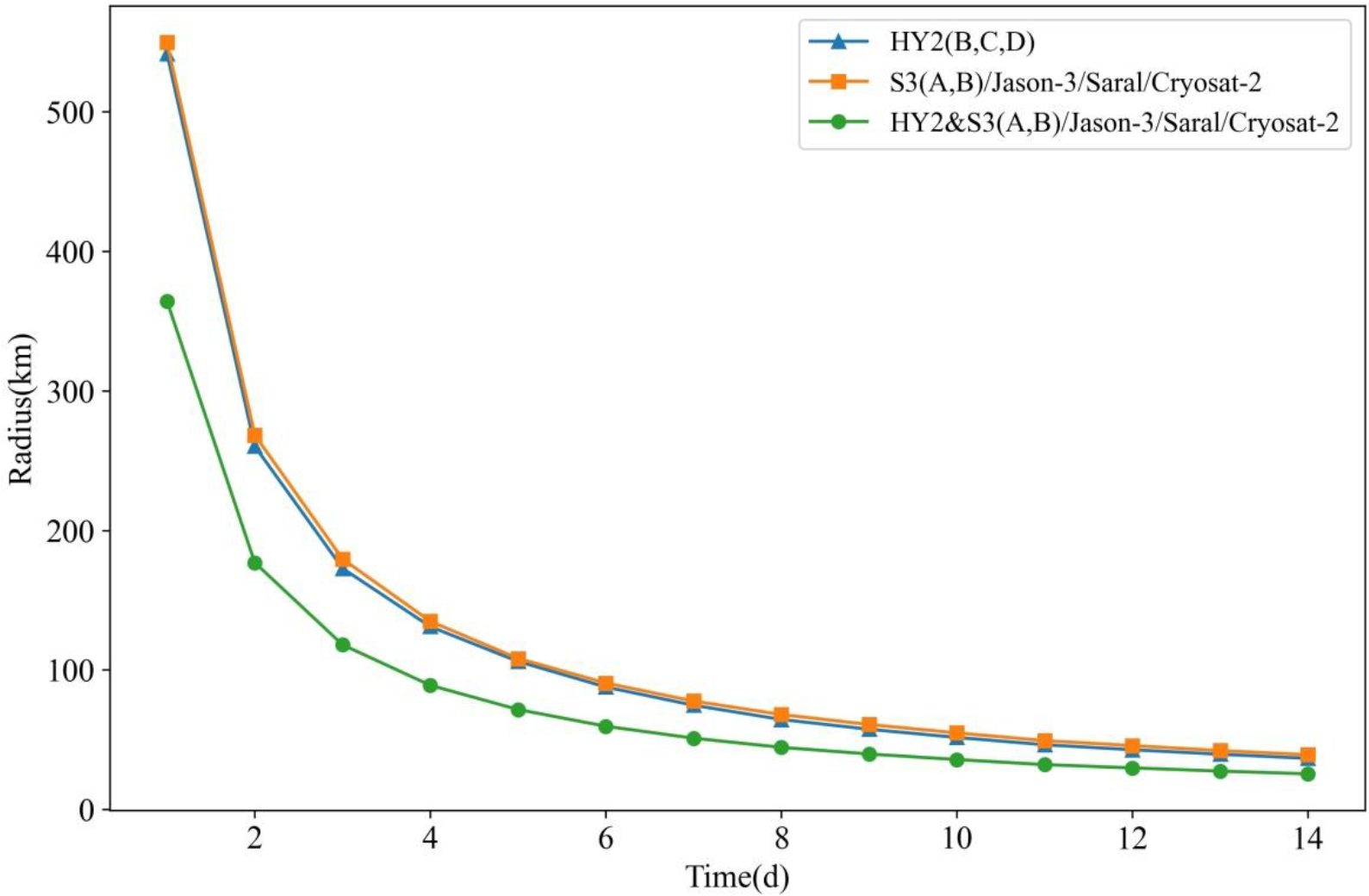
3.3. Precise Orbital Determination Technology
4. History of Progress in China’s Marine Surveillance Satellite Remote Sensing Technology
4.1. Oceanographic Information Retrieval Technology
4.2. Marine Target Recognition Technology
5. Development Trends of Marine Microwave Remote Sensing Satellites in China
5.1. Development Trends of Marine Dynamic Environment Satellites in China
5.2. Development Trends of Surveillance Satellites in China
6. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sternberg, S. Performance and Evaluation of Satellites Tiros I and Tiros II. ARS J. 1961, 31, 1495–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, M.H., Jr. Optical Instrumentation for TIROS. Appl. Opt. 1962, 1, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyt, D.V.; Kyle, H.L.; Hickey, J.R.; Maschhoff, R.H. The Nimbus 7 solar total irradiance: A new algorithm for its derivation. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloersen, P.; Cavalieri, D.J.; Wilheit, T.T.; Chang, A.; Campbell, W.J.; Johannessen, O.M.; Katsaros, K.B.; Künzi, K.F.; Ross, D.B.; Staelin, D.; et al. Summary of results from the first nimbus 7 smmr observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1984, 89, 5335–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huh, O.K. Limitations and capabilities of the noaa satellite advanced very high resolution radiometer (AVHRR) for remote sensing of the earth’s surface. Prev. Vet. Med. 1991, 11, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Li, Y. The Development of Marine Optical Remote Sensing and the Frontiers. Eng. Sci. 2003, 5, 39–43, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y. Monitoring regional sea ice of the Bohai Sea by SSM/I scattering indices. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 1998, 20, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.; Wu, H. Sea ice in the Bohai sea in China. Mar. Forecast. 1999, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y. Measurement analyses and evaluations of sea-level heights using the HY-2A satellite’s radar altimeter. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 38, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, G.; Yu, L.; Zhao, R.; Deng, M.; Xu, K. Multi-mode GF-3 satellite image geometric accuracy verification using the RPC model. Sensors 2017, 17, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, R.; Sun, Z. GF-3 SAR image despeckling based on the improved non-local means using non-subsampled shearlet transform. In The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Proceedings of the ISPRS TC III Mid-Term Symposium “Developments, Technologies and Applications in Remote Sensing”, Beijing, China, 7–10 May 2018; ISPRS: Hannover, Germany, 2018; Volume XLII-3. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Jiang, X. Ocean observation from Haiyang satellites. Chin. J. Space Sci. 2020, 40, 898–907. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Lin, M. Ocean observation from Haiyang satellites: 2012–2014. Chin. Space Sci. Act. 2014, 34, 191–201. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Lin, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, X.; Peng, H.; Zhou, W. The HY-2 satellite and its preliminary assessment. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2012, 5, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Jiang, X. HY-2 Ocean Dynamic Environment Mission and Payloads. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Quebec, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Lin, M.; Song, Q. On the construction of China’s Ocean satellite radar altimetry calibration site. Ocean Dev. Manag. 2016, 33, 8–15, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Q.; Xie, X.; Zou, J. Application study of the HY-2 scatterometer on monitoring typhoon events in the northwest Pacific Ocean. Strateg. Study CAE 2014, 16, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Lin, M.; Zou, B.; Guo, M.; Cui, S. Automated cyclone detection using HY-2 satellite data. Haiyang Xuebao 2015, 37, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Lin, M.; Zou, B.; Guo, M.; Cui, S. Fusion of sea surface wind vector data acquired by multi-source active and passive sensors in China sea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 6477–6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Yang, J.; Lin, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, C. Global assessments of the HY-2B measurements and cross-calibrations with jason-3. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Jiang, T.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W. Evaluation of sea surface winds and waves retrieved from the chinese HY-2B data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote 2021, 14, 9624–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Lin, M.; Zhang, Y. Evaluations of the significant wave height products of HY-2B satellite radar altimeters. Mar. Geod. 2020, 43, 396–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, Q.; Chen, G. Validation of HY-2A remotely sensed wave heights against buoy data and Jason-2 altimeter measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 1270–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, G. Validation and intercomparison of HY-2A/MetOp-A/Oceansat-2 scatterometer wind products. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 33, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Lin, M.; Zhang, Y. Current status of the HY-2A satellite radar altimeter and its prospect. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Shi, H.; Dong, X.; Zhu, D. In-orbit calibration and performance evaluaiotn of HY-2 scatterometer. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 4614–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Lin, M.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, H. First sixmonths quality assessment of HY-2A SCAT wind products using in situmeasurements. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2013, 32, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Yu, R.; Jiang, M.; Xia, C.; Chen, W. In-orbit verifacation of HY-2 radiometer. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium—IGARSS, Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 1940–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guan, L.; Zhao, W.; Chen, G. Evaluation of Sea Surface Temperature From the HY-2 Scanning Microwave Radiometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Hu, X.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, A.; Lin, M.; Sun, L.; Chen, L.; Xu, N. FY-3E: The first operational meteorological satellite mission in an early morning orbit. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Q. Assessment of GF-3 Polarimetric SAR Data for Physical Scattering Mechanism Analysis and Terrain Classification. Sensors 2017, 17, 2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q. System design and key technologies of the GF-3 satellite. Acta Geo. Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- An, Q.; Pan, Z.; You, H. Ship Detection in Gaofen-3 SAR Images Based on Sea Clutter Distribution Analysis and Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2018, 18, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, Q.; Yao, S.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, S.; Ma, J. Soil moisture retrieval from the chinese gf-3 satellite and optical data over agricultural fields. Sensors 2018, 18, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Feng, Q.; Ren, Y.; Shi, Y. Retrieval of sea surface wind speeds from gaofen-3 full polarimetric data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Sun, B.; Zhang, S.; Xu, K. SZ-4 main payload—Multi-mode microwave remote sensor. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2005, 20, 74–80, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Yuan, J.; Niu, Y.; Ji, B. A new method of satellite radar altimeter waveform retracking based on waveform derivative. Rev. Int. Métodos Numér. Cálc. Diseñoing 2020, 36, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Xu, K.; Liu, Y. Calibration and Validation of Reprocessed HY-2A Altimeter Wave Height Measurements Using Data from Buoys, Jason-2, Cryosat-2 and SARAL/Altika. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2018, 36, 1331–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Jing, Y.; Jia, Y.; Lin, M.; Zhang, G.; Wang, G. Nonparametric estimations of the sea state bias for a radar altimeter. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 36, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, H.F.; Yao, S.; Li, L. Spline-based nonparametric estimation of the altimeter sea-state bias correction. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 577–581. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Miao, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Study on parametric model of sea state bias in altimeter based on fusion dataset of collinear and crossover. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2014, 29, 176–180. [Google Scholar]
- Gommenginger, C.; Srokosz, M.; Bellingham, C.; Snaith, H.; Pires, N.; Fernandes, M.J.; Tran, N.; Vandemark, D.; Moreau, T.; Labroue, S.; et al. Sea state bias: 25 years on, Presentation at and Abstract. In Proceedings of the 25 Years of Progress in Radar Altimetry, Ponta Delgada, São Miguel Island Azores Archipelago, Portugal, 24–29 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gommenginger, C.P.; Srokosz, M.A.; Wolf, J.; Janssen, P.A.E.M. An investigation of altimeter sea state bias theories. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xu, Q.; Gao, L.; Li, X.; Liu, T. Sea state bias variability in satellite altimetry data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Miao, H.; Zhang, G.; Jing, Y.; Wang, G. Study on neural network model of estimating the sea state bias for radar altimeters. Haiyang Xuebao 2017, 39, 126–132, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Liu, J.; Lin, M.; Zhang, Y. Comparison of wind speed from 3 main payloads of HY-2 satellite. Eng. Sci. 2014, 16, 27–32, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Lin, M.; Zou, B.; Guo, M.; Zhang, Y. A routine operational backscattering coefficient regrouping algorithm for a HY-2A scatterometer. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, M.; Song, Q. Evaluation of Geolocation Errors of the Chinese HY-2A Satellite Microwave Scatterometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 6124–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mu, B.; Lin, M.; Song, Q. An evaluation of the chinese hy-2b satellite’s microwave scatterometer instrument. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 99, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. The Improvement of HY-2 SCAT Wind Rerrieval Algorithm Based on MSS and 2DVAR Method. Ph.D. Dissertation, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2014. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Meng, J.; Fan, C. An inversion algorithm research of altimeter wind speed based on automatic gain control. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 34, 55–60, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bao, J.; Li, Y.; Shen, H. Study on retrieval algorithm of ocean parameters for the HY-2 scanning microwave radiometer. Eng. Sci. 2014, 16, 70–82, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Guan, D.; Zhao, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Research on observing sea surface temperature (SST) based on microwave remote sensing by satellite. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2013, 28, 721–730, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Wang, Q.; Bin, B.Z.; Shi, Y.; Jiao, M. Arctic sea ice concentration retrieval using HY-2 radiometer data. Chin. J. Polar Res. 2014, 26, 410–417, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Henan University of Technology. An Improved ASI Sea Ice Density Inversion Algorithm Manufacturing Technology. Algorithm Patent (ZL201711101312.1), 9 November 2018. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Spreen, G.; Kaleschke, L.; Heygster, G. Sea ice remote sensing using AMSR-E 89-GHz channels. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, C02S03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swift, C.; Cavalieri, D. Passive microwave remote sensing for sea ice research. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1985, 66, 1210–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, M. Research progress of calibration site and calibration method of satellite altimeter. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2007, 26, 87–92; discussion 116, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Chen, C.; Zhai, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X. Influencing factors research of GPS buoy measurement precision. Eng. Sci. 2014, 16, 102–108, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, X.; Xu, Q.; Ke, B.; Mu, B.; Zhu, L. Research status of satellite altimeter calibration. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 23, 392–407, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Kong, Q.; Qin, J.; Sun, Y. On precise orbit determination of HY-2 with space geodetic techniques. Acta Geophys. 2013, 61, 752–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Jiang, K.; Li, W.; Zhao, Q.; Peng, H.; Lin, M. Precise orbit determination of the Haiyang 2C altimetry satellite using attitude modeling. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhou, X.; Wu, B. Precise orbit determination of Haiyang-2 using satellite laser ranging. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Peng, H.; Zhao, Q.; Li, M. Precise orbit determination technology based on dual-frequency GPS solution for HY-2 satellite. Eng. Sci. 2014, 16, 97–101, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, J. Centimeter precise orbit determination for HY-2 Via DORIS. J. Astronaut. 2013, 34, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Shi, C.; Li, M. Beidou satellite real-time precise orbit determination using ultra-rapid ephemeris’ constraint. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2018, 38, 937–942, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, P.A.; Fois, F. Surface roughness and breaking wave properties retrieved from polarimetric microwave radar backscattering. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 3640–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, T.; Jie, C.; Yu, Z. Simulation study on sar signatures of ocean thermal fronts. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 237, 032008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Zhang, X.; Dang, H.; Tan, X. Analysis of microwave backscattering from nonlinear sea surface with currents: Doppler spectrum and SAR images. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2020, 12, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. A Wave Parameter Inversion Method Based on Same Polarization SAR Data. CN201810278250.X, 12 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. The Research of Retrieving Sea Surface Wind and Ocean Wave Parameters from Synthetic Aperture Radar. Ph.D. Dissertation, Zhejiang Ocean University, Hangzhou, China, 2017. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Ye, X.; Yuan, X. The first quantitative joint observation of typhoon by Chinese GF-3 SAR and HY-2A microwave scatterometer. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 36, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, J.; Chu, X. Estimation of sea surface velocities from SAR images using the Doppler shift. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2019, 34, 293–302, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Liang, C.; Chen, J.; Cui, S.; Lang, S. An optimal parametric analysis of monitoring oil spill based on SAR. Haiyang Xuebao 2011, 33, 36–44, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Zou, B.; Liang, C.; Cui, S.; Lang, S. Multiple index information extraction of marine oil spills. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2012, 14, 265–269, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Su, C. Summary of Research Progress on the Recognition of Ship Target from SAR Image. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer Engineering, Information Science & Application Technology (ICCIA 2019), Chongqing, China, 30–31 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lei, Z.; Zhuang, L.; Yu, H. A CNN Based Method to Solve Class Imbalance Problem in SAR Image Ship Target Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 5th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 12–14 March 2021; pp. 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, X.; Ji, K.; Yang, K.; Zou, H. A Bilateral CFAR Algorithm for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Lang, F. A New Automatic Ship Detection Method Using L-Band Polarimetric SAR Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 7, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Wu, F.; Jiang, S. A novel hierarchical ship classifier for COSMO—SkyMed SAR data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Research on Detection Method of the Small Targets at Sea. Ph.D. Dissertation, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, C. Research on Marine Target Recognitlon Algorithm from SAR Image. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia University, Huhhot, China, 2016. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chao, W.; Hong, Z. Ship classification in high-resolution sar images using deep learning of small datasets. Sensors 2018, 18, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Yang, J.; Zhang, B.; Ma, C. Thoughts and prospects on the new generation of marine science satellite. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2019, 49, 110–117, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Zhou, W.; Lin, M.; Liu, T.; Zhu, Y.; He, Y.; Liao, T. End to end study of the Chinese salinity mission. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 3544–3547. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, X.; Ding, C.; Lei, B.; Han, B.; Li, F. A novel proposal of gaofen-3 satellite constellation for multi-applications. In Proceedings of the ISPRS—International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, XLII-2/W7, Wuhan, China, 18–22 September 2017; pp. 635–639. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Lin, M.; Zhang, Y. Progress and prospect of Chinese ocean satellites. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 20, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; He, X.; Lin, M.; Gong, F.; Ye, X.; Pan, D. Progresses on ocean satellite remote sensing application in China. Haiyang Xuebao 2019, 41, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y. Microwave Remote Sensing and Its Development in China. J. Microwaes 2020, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; He, X.; Jia, Y.; Bai, Y.; Ye, X.; Gong, F. Advances in Marine Satellite Remote Sensing Technology in China. Haiyang Xuebao 2019, 41, 99–112. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Frequency | 13.58 & 5.25 GHz |
| Pulse-limited footprint | <2 km |
| Frequency bandwidth | 320 MHz |
| PRF | 2 KHz |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Frequency | 13.256 GHz |
| Transmit power | 120 W |
| Pulse width | 1.5 ms |
| Swath | 1350/1750 km |
| Polarization | HH/VV |
| Look angle | 34.8°/40.8° |
| Incidence angle | 41°/48° |
| Scanning mode | conically scanning |
| σ0 measurement accuracy | 0.5 dB |
| σ0 measurement range | −40~+20 dB |
| Wind cell resolution | 25 km |
| Wind speed accuracy | <2 m/s |
| Wind direction accuracy | <20° |
| Mission lifetime | 3 years |
| Parameter | Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency (GHz) | 6.6 | 10.7 | 18.7 | 23.8 | 37.0 |
| Polarization | V H | V H | V H | V | V H |
| Scan width | 1600 km | ||||
| Footprint size(km) | 100 | 70 | 40 | 35 | 25 |
| Sensitivity (K) | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.8 |
| Dynamic range | 3–350 K | ||||
| CAL precision | 1 K (180~320 K) | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, M.; Jia, Y. Past, Present and Future Marine Microwave Satellite Missions in China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061330
Lin M, Jia Y. Past, Present and Future Marine Microwave Satellite Missions in China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(6):1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061330
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Mingsen, and Yongjun Jia. 2022. "Past, Present and Future Marine Microwave Satellite Missions in China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 6: 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061330
APA StyleLin, M., & Jia, Y. (2022). Past, Present and Future Marine Microwave Satellite Missions in China. Remote Sensing, 14(6), 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061330






