Significant Wave Height Retrieval Using XGBoost from Polarimetric Gaofen-3 SAR and Feature Importance Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
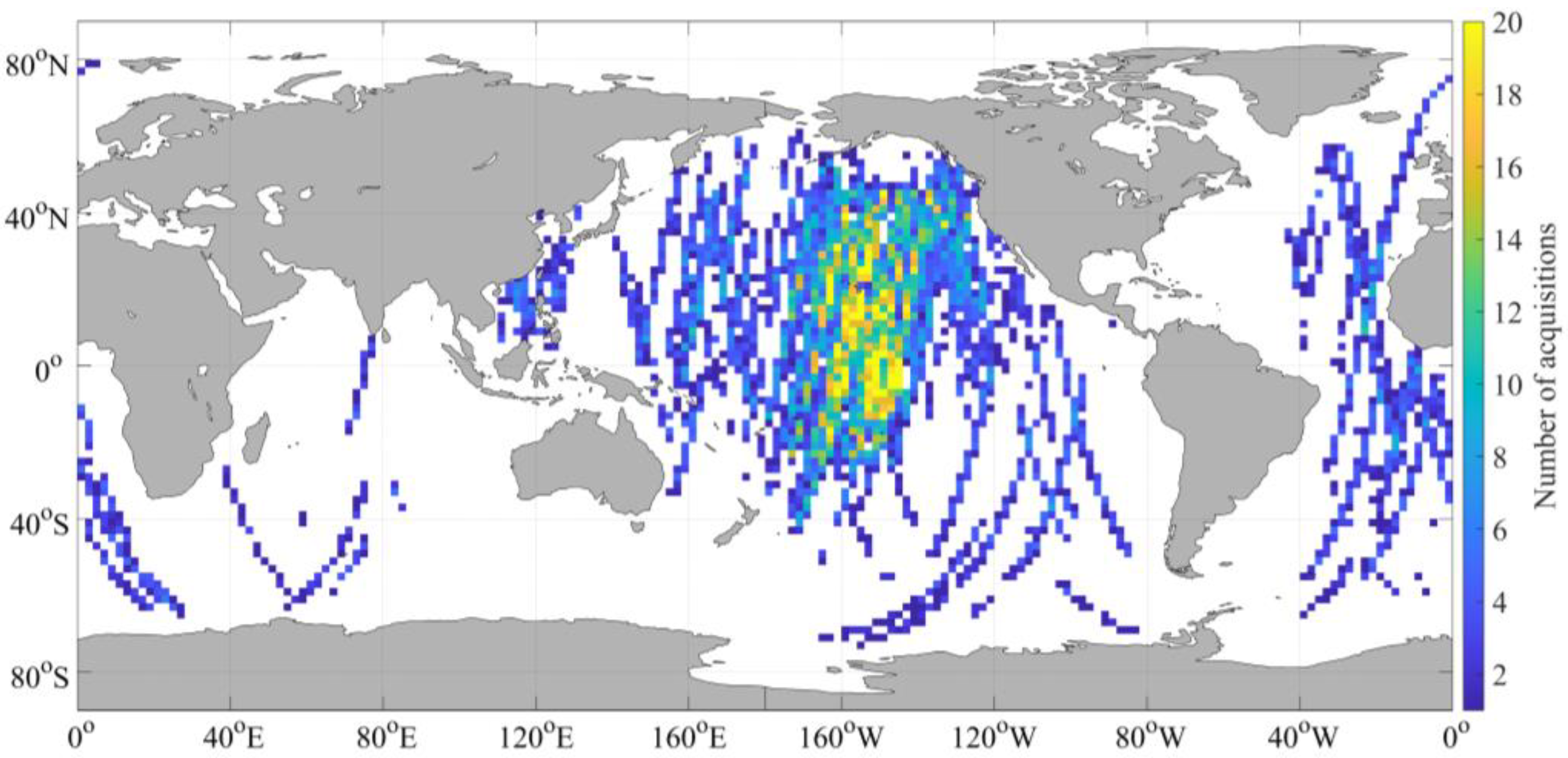
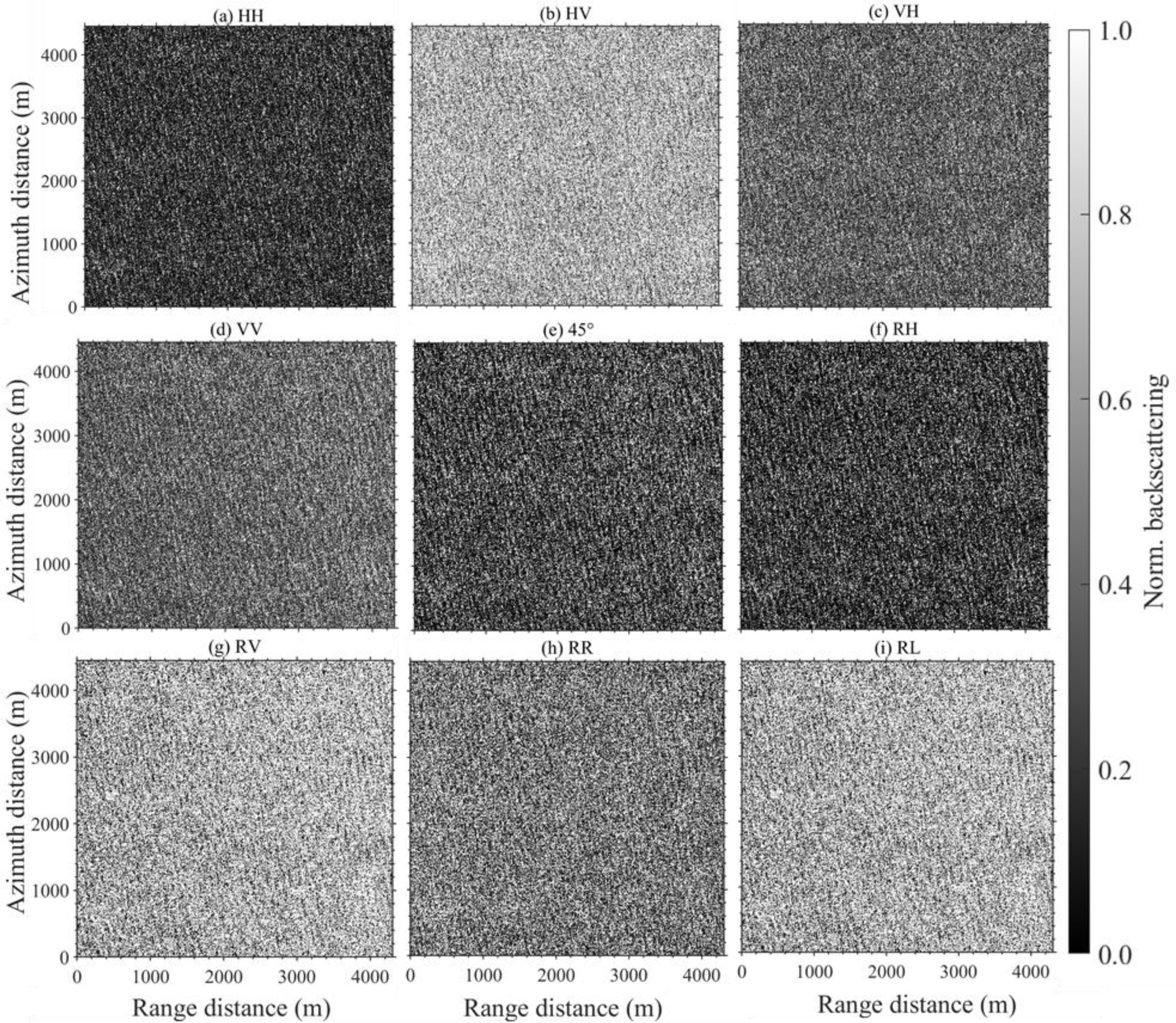
2.1. Gaofen-3 SAR Data
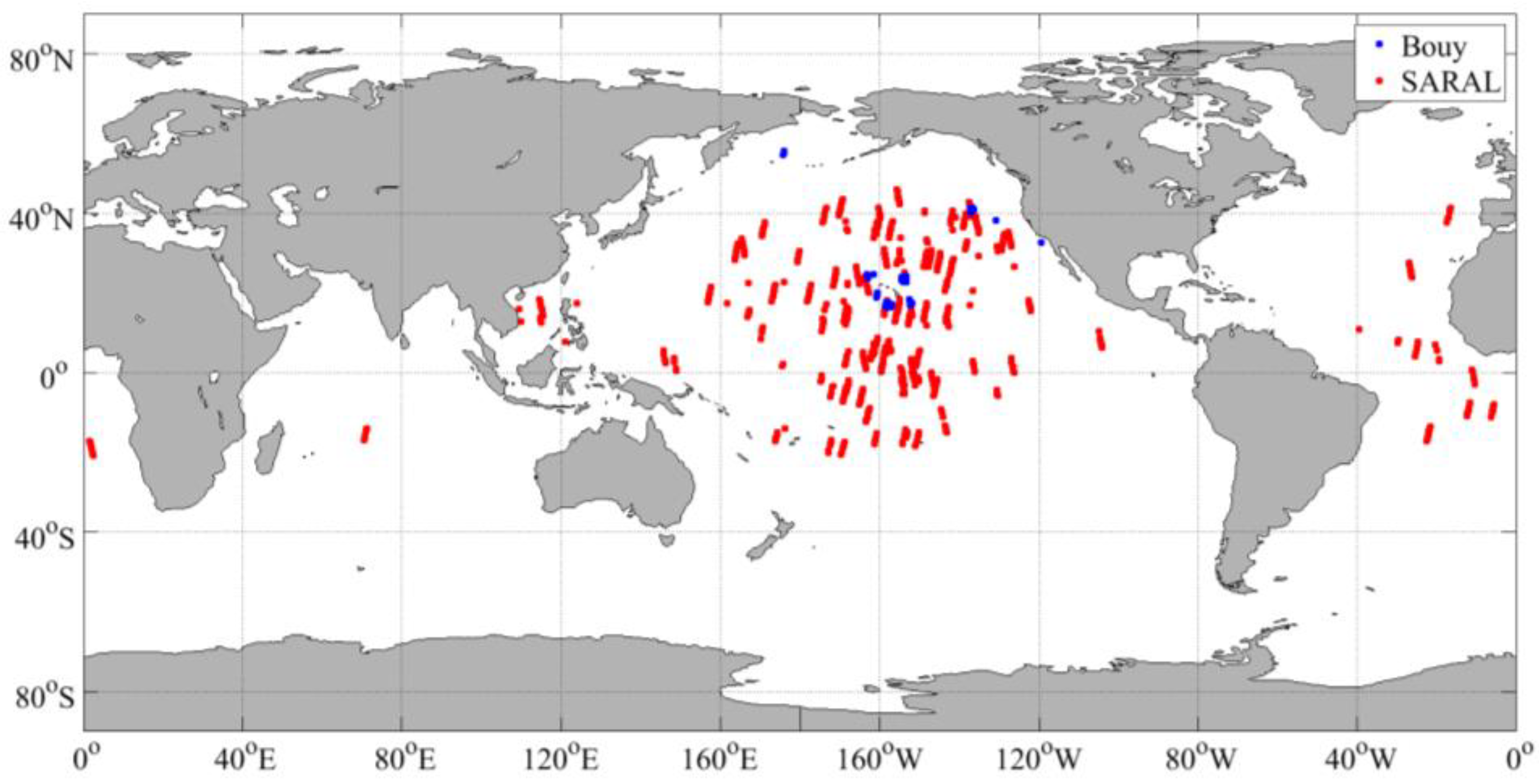
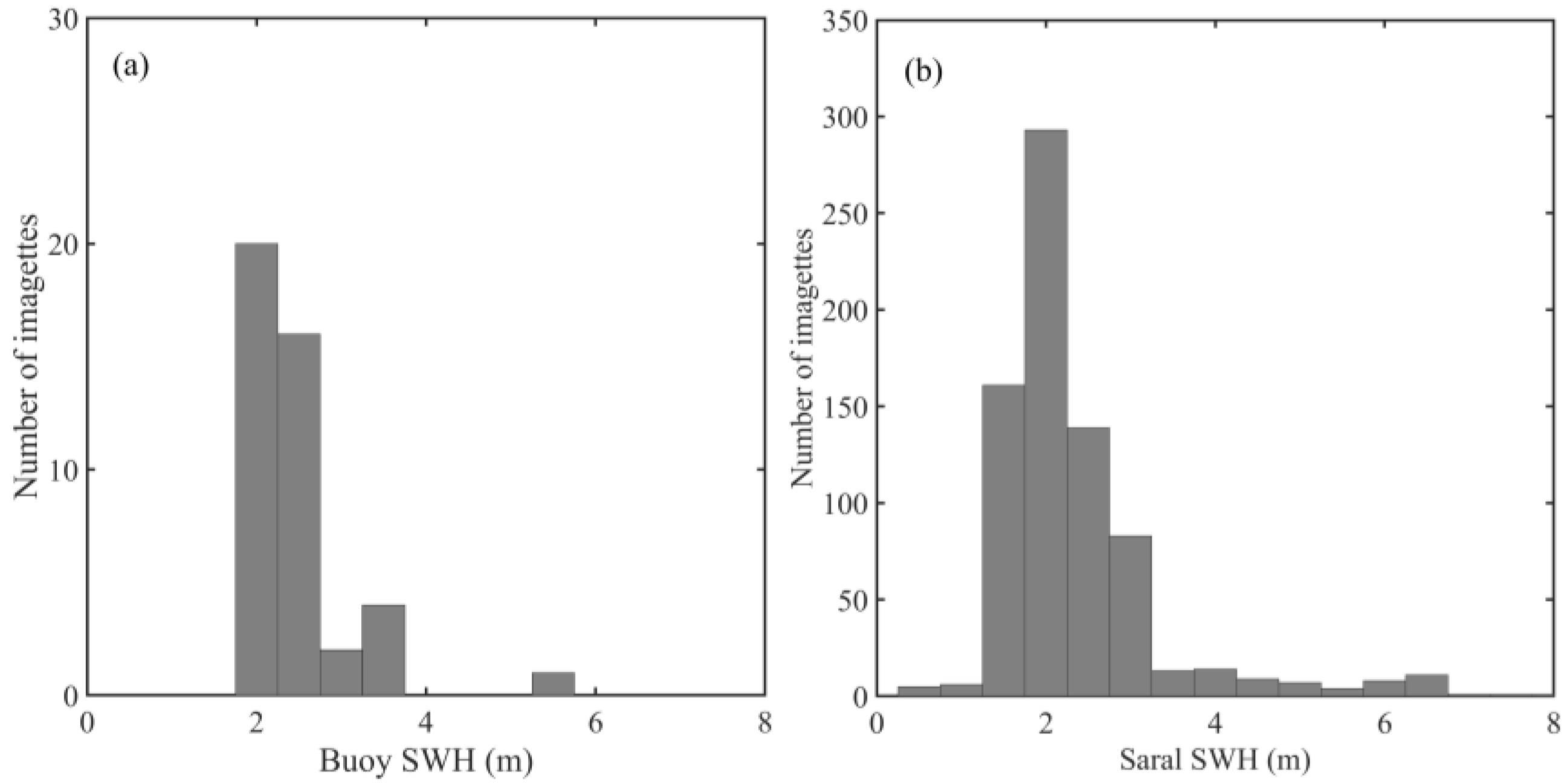
2.2. Reference SWH
2.3. Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) Model
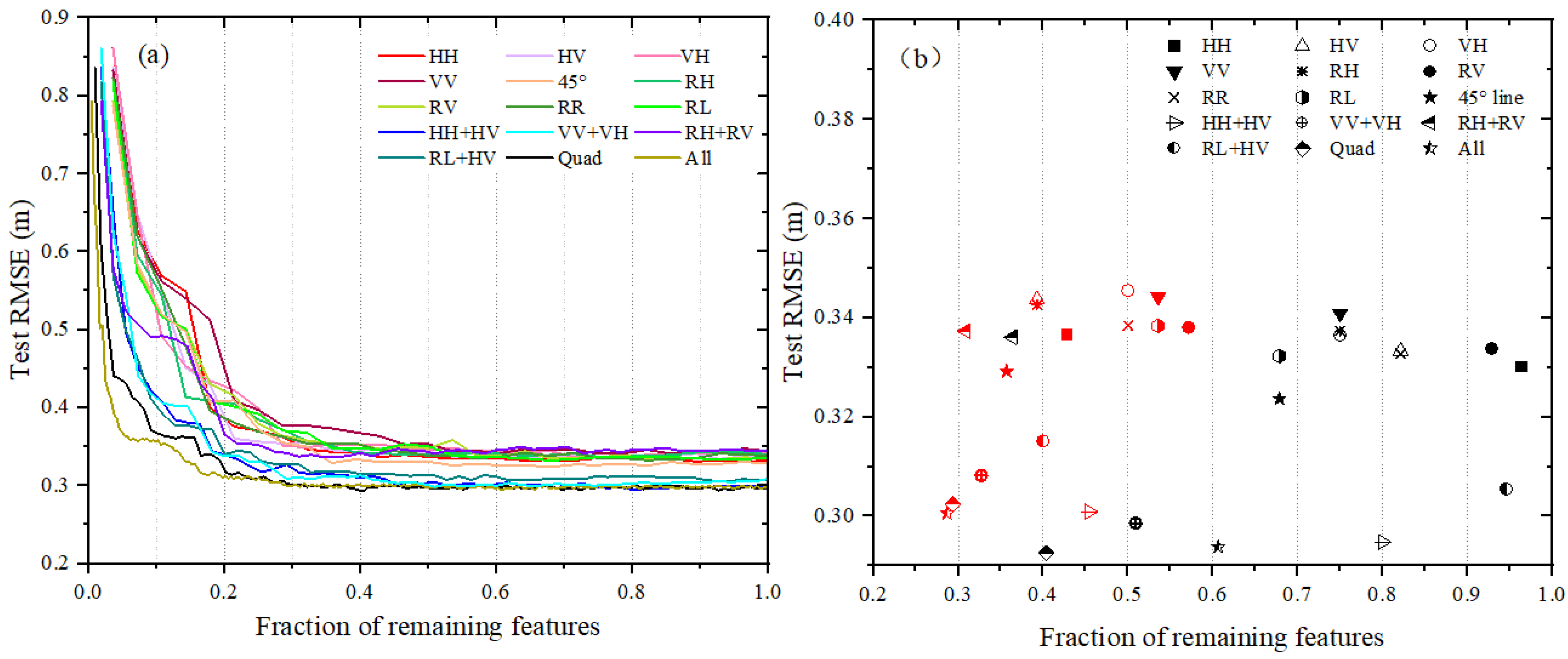
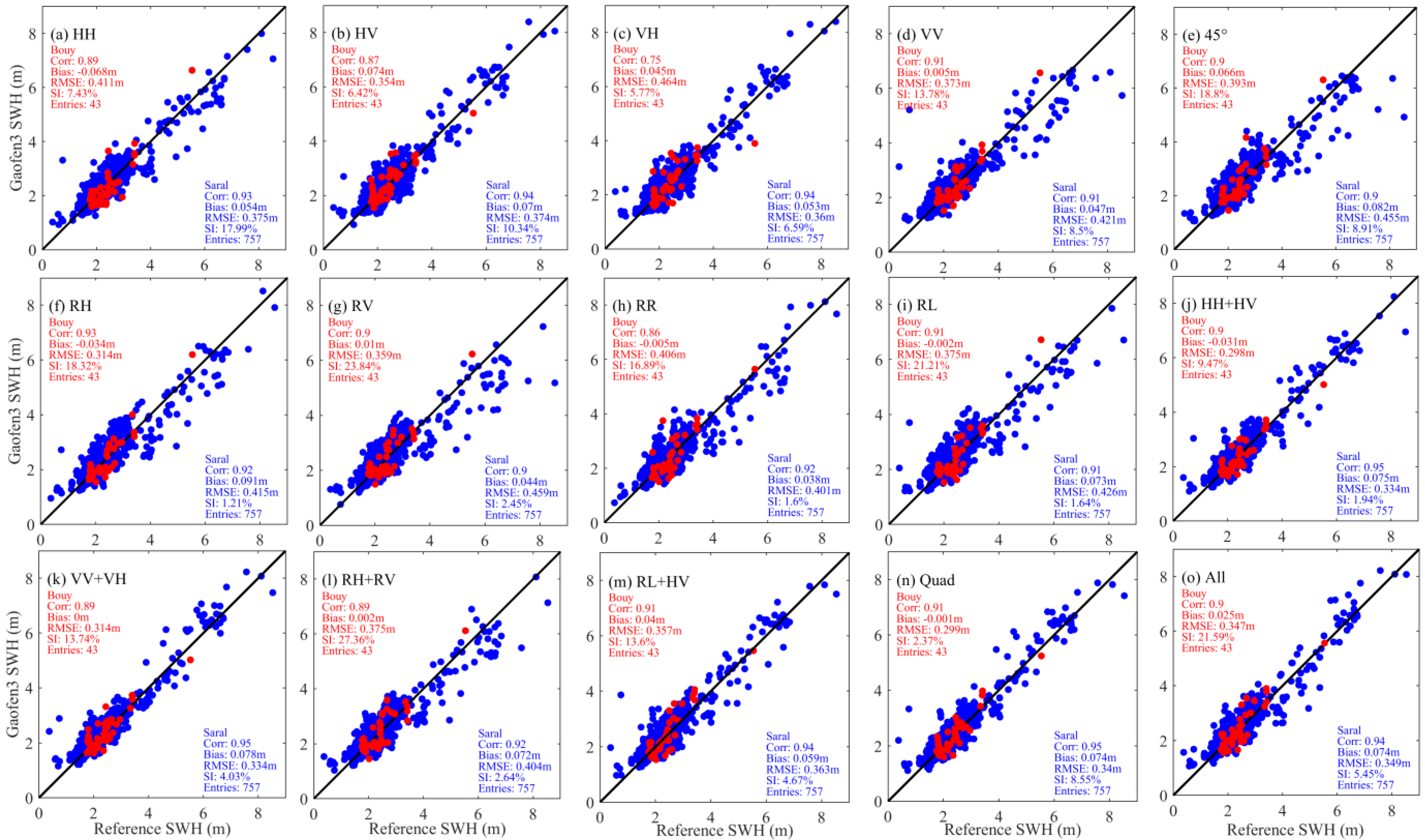
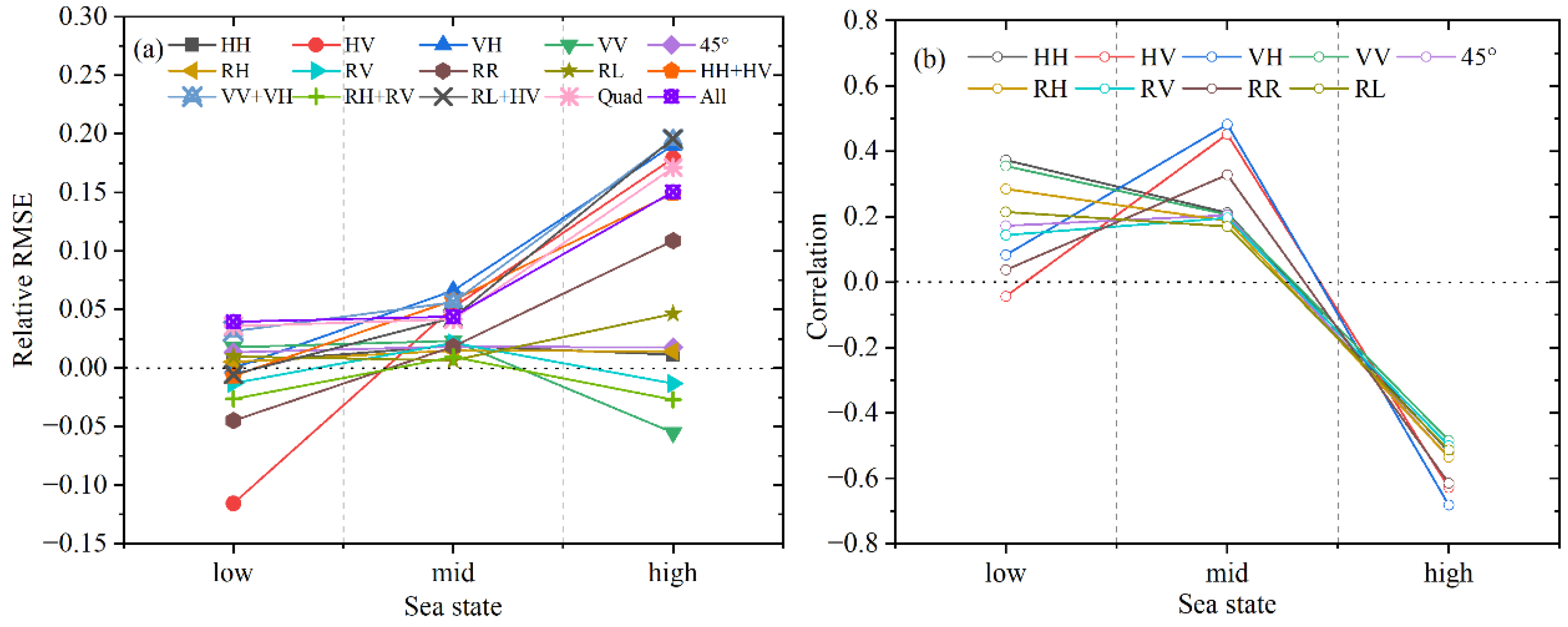
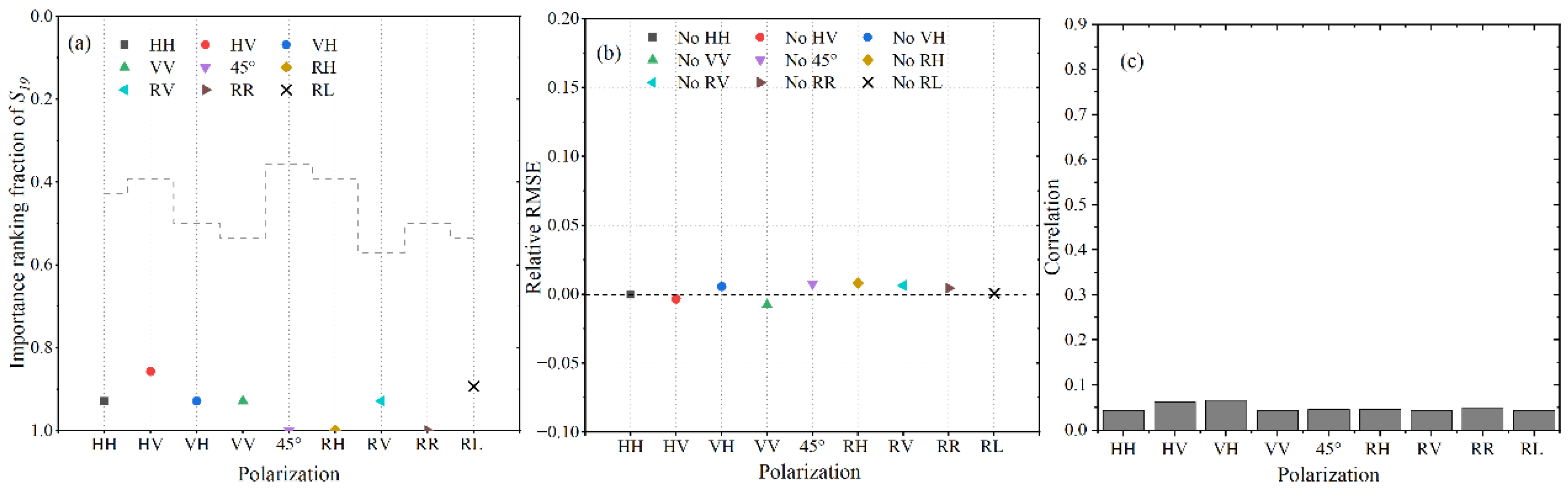
3. Results
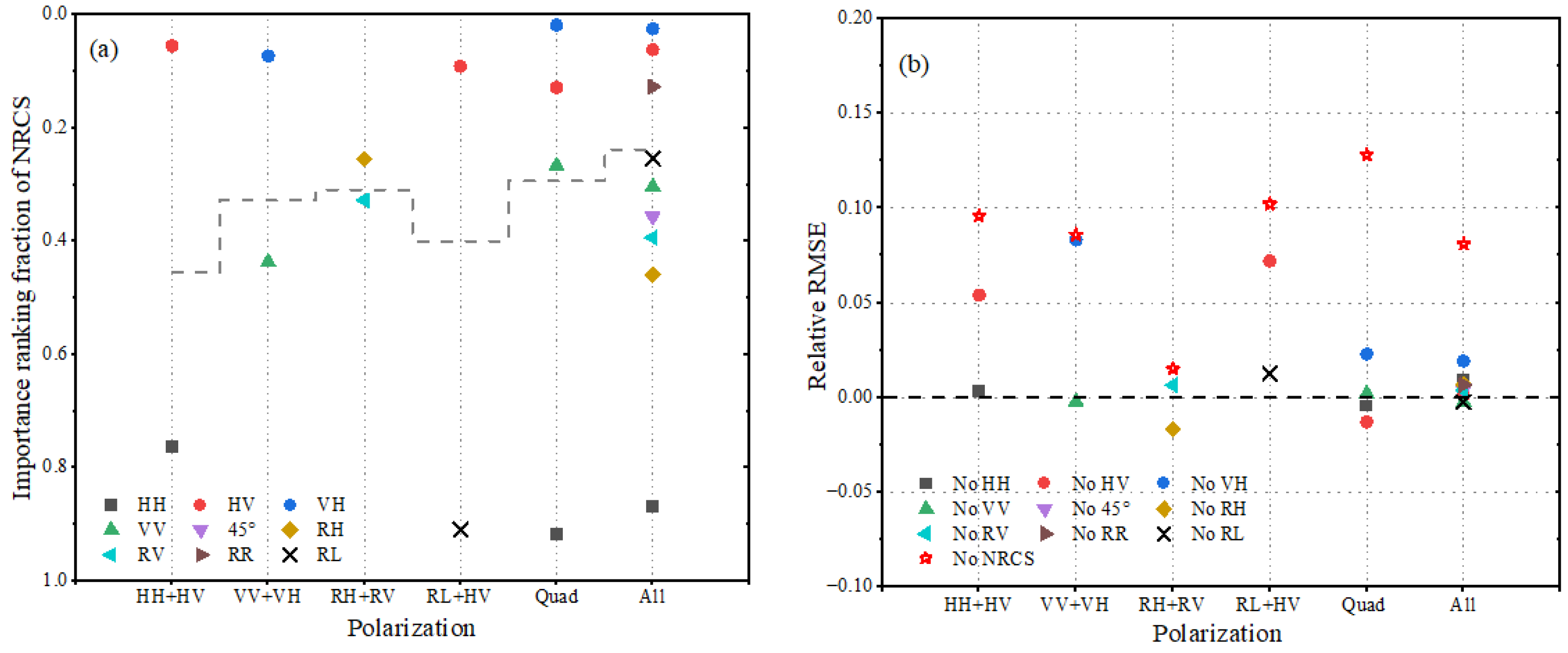
4. Discussion
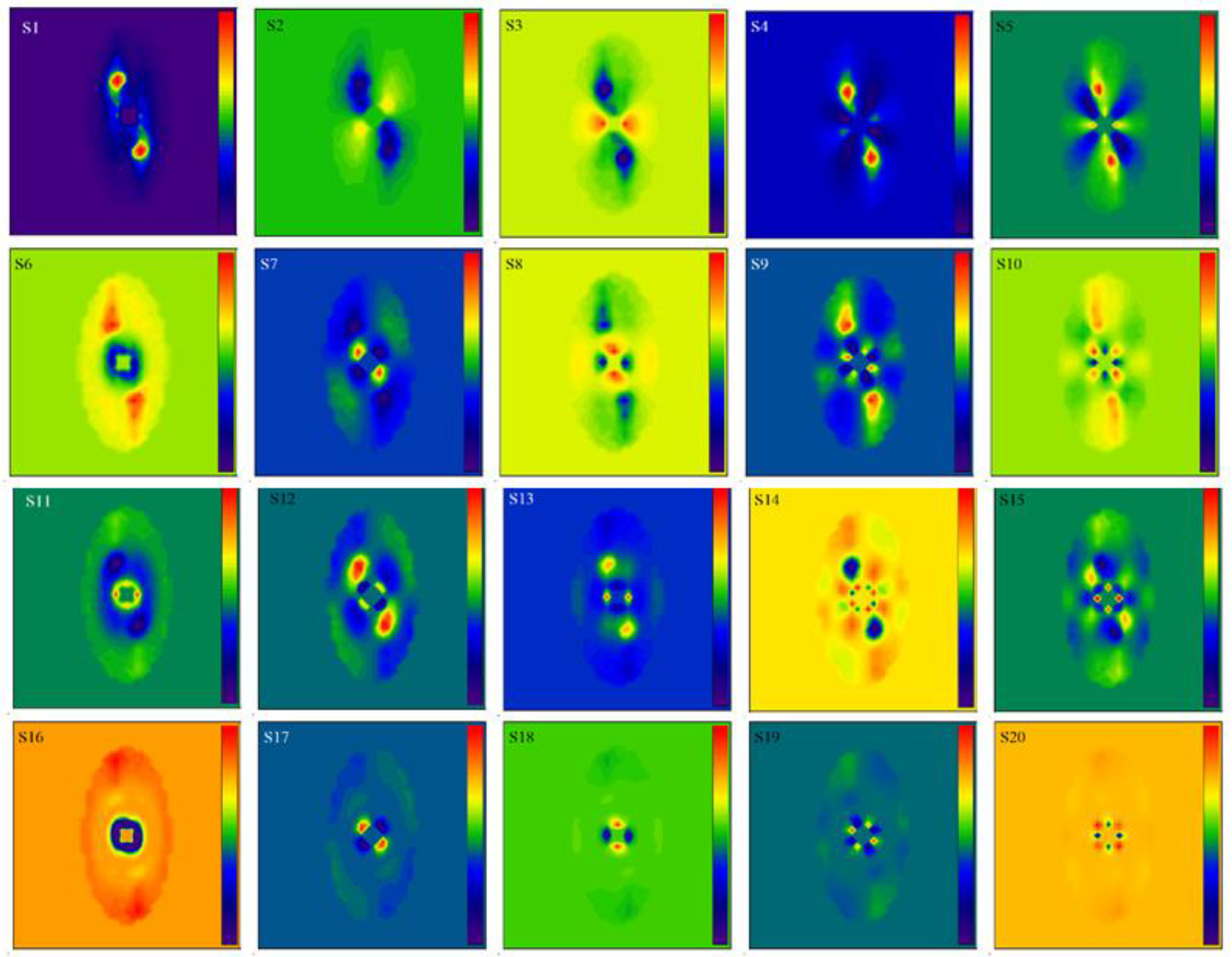
4.1. The Importance of NRCS
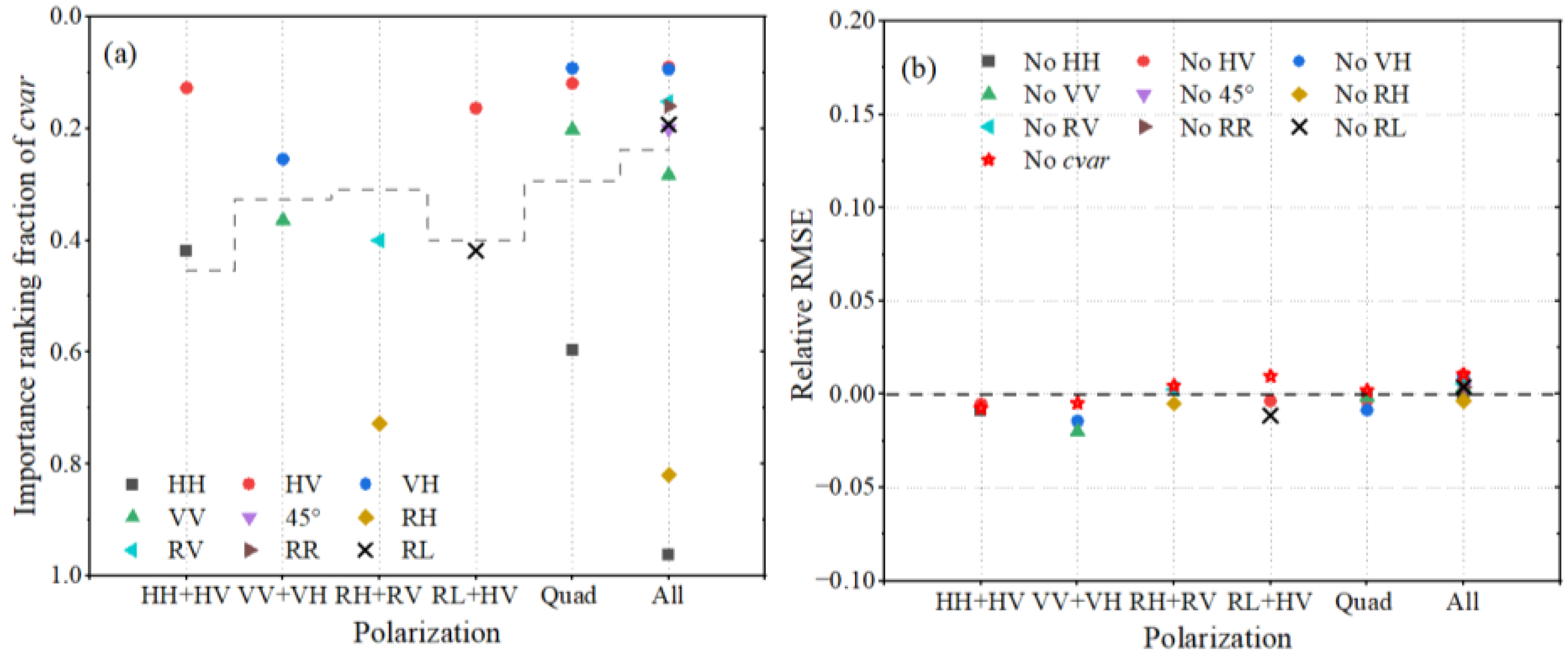
4.2. The Importance of Cvar
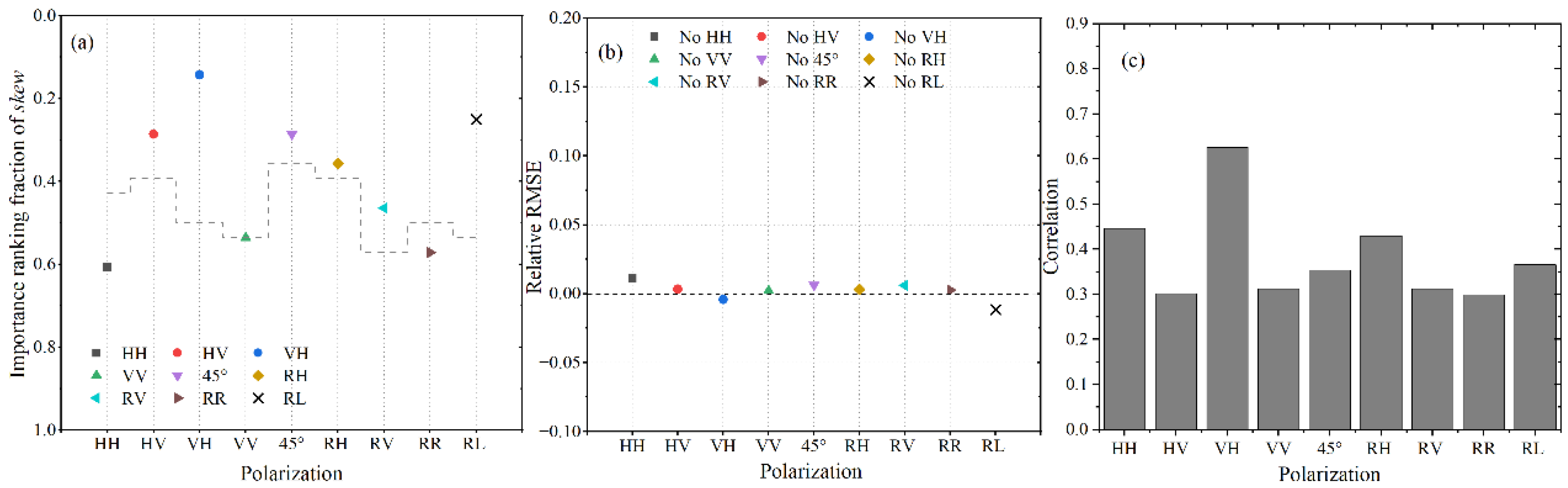
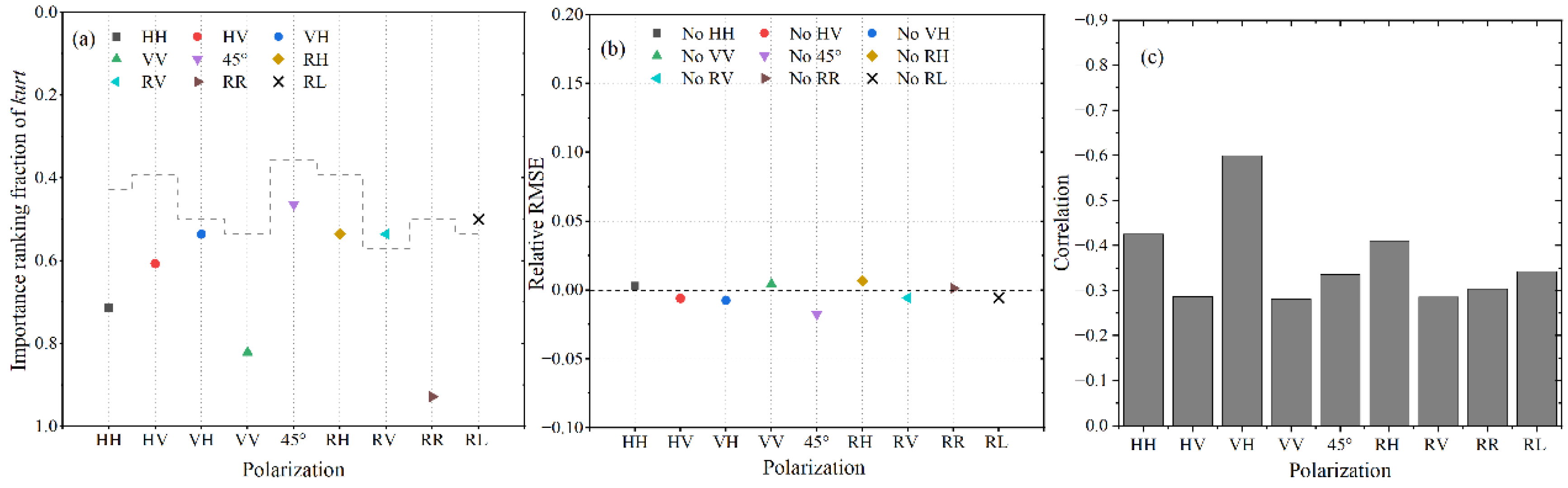
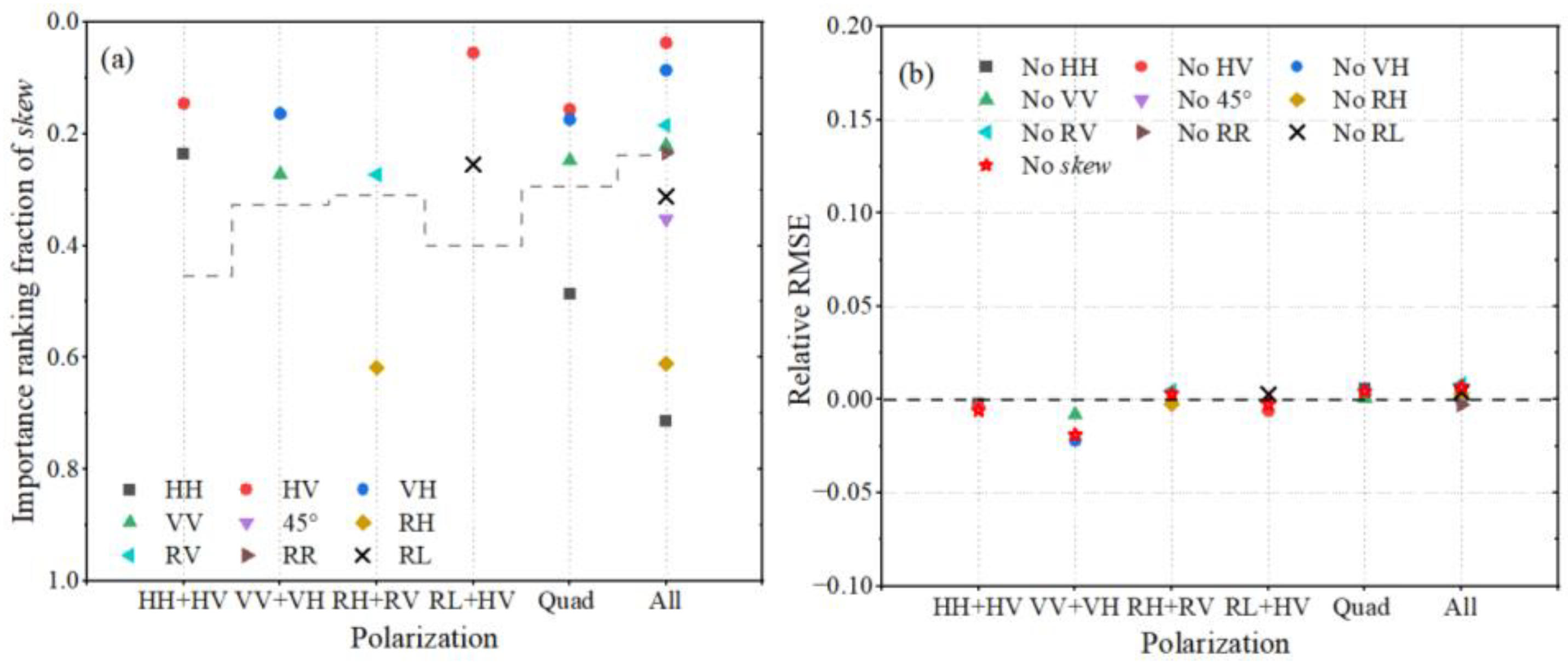
4.3. The Importance of Skew and Kurt
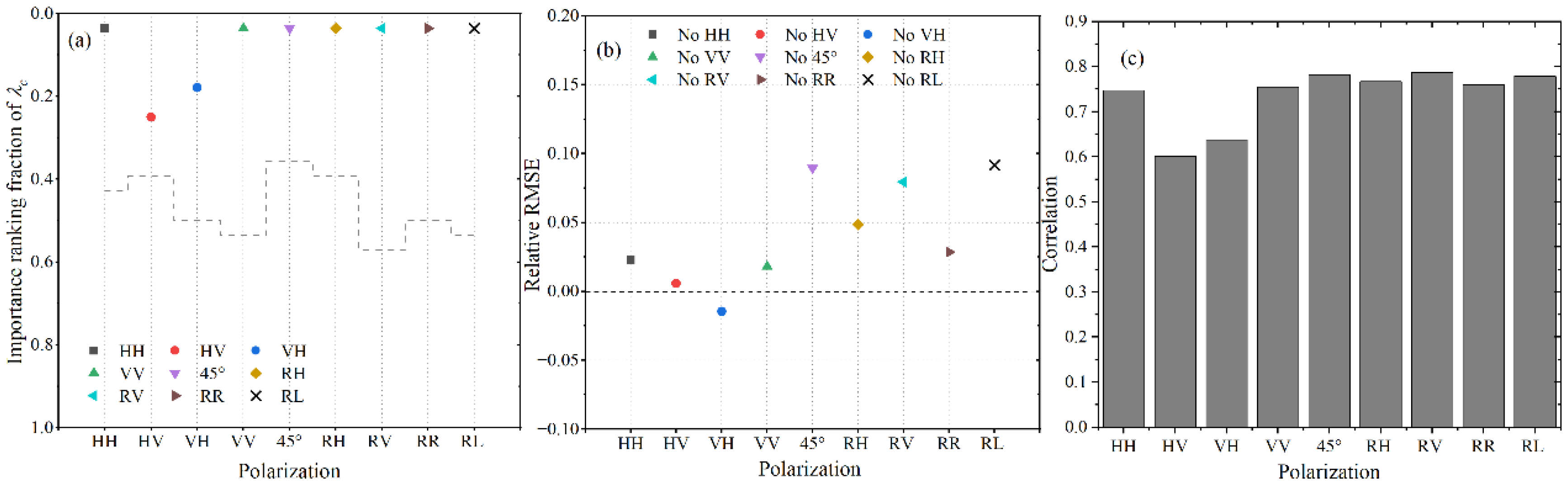
4.4. The Importance of λc/β
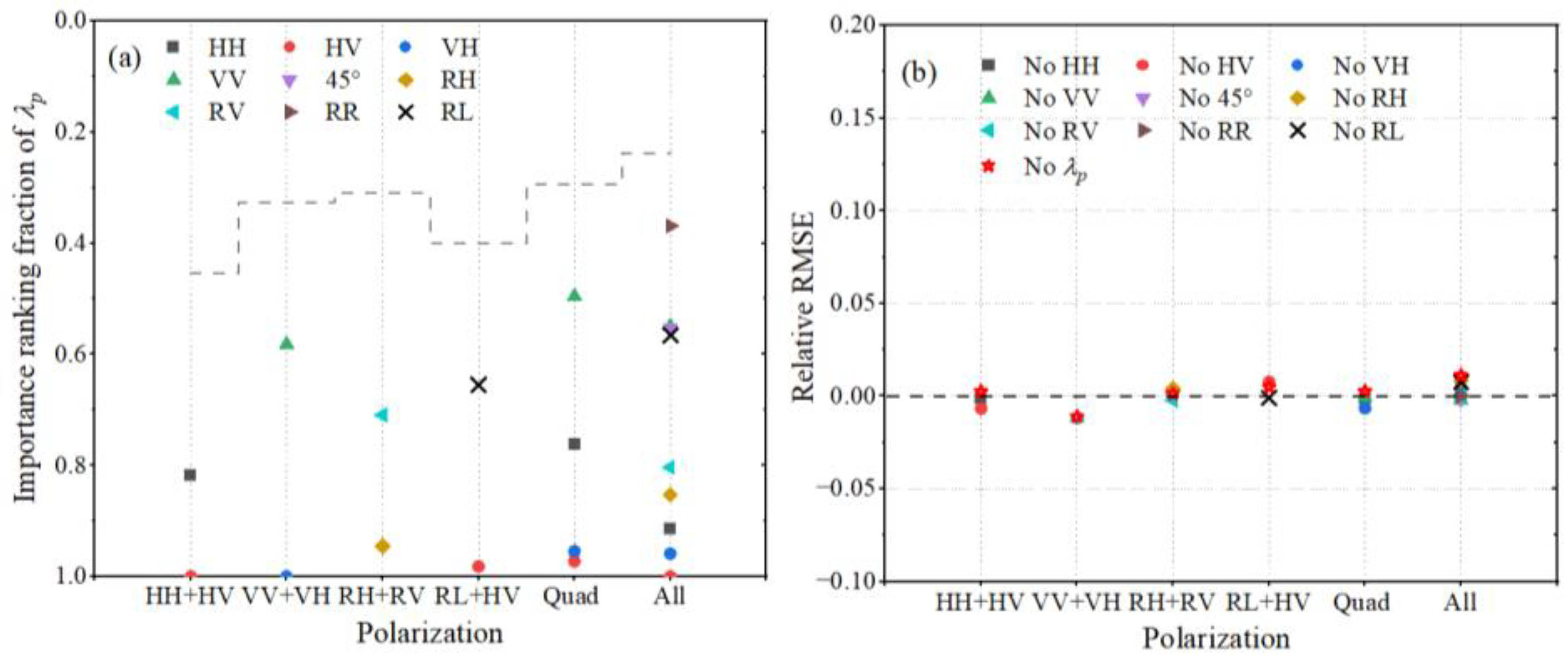
4.5. The Importance of λp and φ
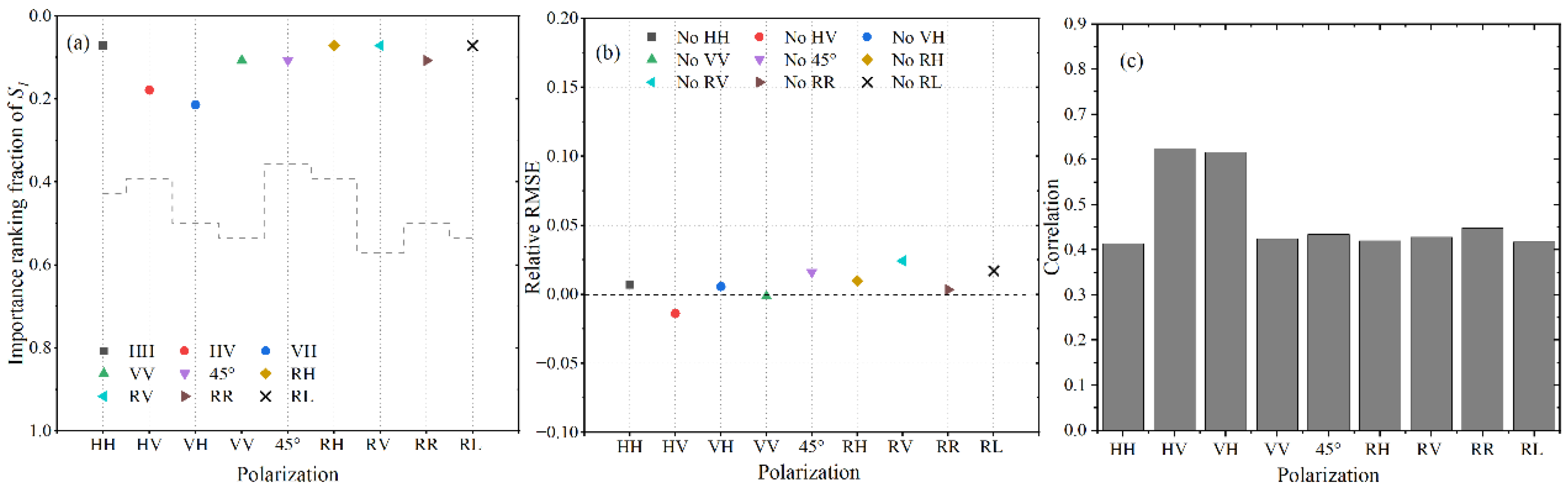
4.6. The Importance of CWAVE Spectral Parameters
4.7. The Importance of θ
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Polarization | Features Selected in Optimal Model (Ranked from Highest to Lowest Importance) |
|---|---|
| HH | λc_HH, S1_HH, S6_HH, S16_HH, θ, σ0_HH, S10_HH, S8_HH, S11_HH, S13_HH, S18_HH, S2_HH |
| HV | S3_HV, S6_HV, S10_HV, σ0_HV, S1_HV, θ, λc_HV, skew_HV, cvar_HV, S8_HV, S11_HV |
| VH | S3_VH, S6_VH, σ0_VH, skew_VH, λc_VH, S1_VH, S10_VH, θ, cvar_VH, S16_VH, S11_VH, S5_VH, S13_VH, S8_VH |
| VV | λc_VV, S6_VV, S1_VV, S16_VV, S13_VV, θ, S11_VV, S18_VV, S2_VV, S8_VV, S9_VV, S10_VV, σ0_VV, S12_VV, skew_VV |
| 45°linearly | λc_45, S6_45, S1_45, S16_45, θ, S11_45, σ0_45, skew_45, S2_45, S18_45 |
| RH | λc_RH, S1_RH, S6_RH, θ, S16_RH, S11_RH, S10_RH, σ0_RH, S2_RH, skew_RH, S18_RH |
| RV | λc_RV, S1_RV, S6_RV, S16_RV, θ, S11_RV, S18_RV, S10_RV, S2_RV, S8_RV, S9_RV, S13_RV, skew_RV, S12_RV, kurt_RV, σ0_RV |
| RR | λc_RR, S6_RR, S1_RR, σ0_RR, θ, S11_RR, S13_RR, S10_RR, S2_RR, S16_RR, S8_RR, cvar_RR, S9_RR, S18_RR |
| RL | λc_RL, S1_RL, S6_RL, S16_RL, θ, S11_RL, skew_RL, S10_RL, S2_RL, S18_RL, S9_RL, S8_RL, S13_RL, kurt_RL, σ0_RL |
| HH + HV | S3_HV, S6_HV, σ0_HV, λc_HH, S1_HV, S6_HH, cvar_HV, skew_HV, S16_HH, θ, S10_HV, S1_HH, skew_HH, S10_HH, S16_HV, kurt_HH, S8_HV, S11_HH, S11_HV, S8_HH, S9_HV, S4_HH, cvar_HH, λc_HV, S2_HH |
| VV + VH | S3_VH, λc_VV, S6_VH, σ0_VH, S6_VV, S1_VH, S1_VV, S16_VV, skew_VH, θ, S11_VV, λc_VH, S4_VV, cvar_VH, skew_VH, S10_VV, kurt_VV, S10_VH |
| RH + RV | λc_RV, S1_RV, S16_RH, λc_RH, S6_RV, S6_RH, S1_RH, S16_RV, S18_RV, S10_RV, θ, S2_RV, S9_RV, σ0_RH, skew_RV, S11_RV, S8_RV |
| RL + HV | λc_RL, S6_HV, skew_HV, S3_HV, σ0_HV, S1_HV, S6_RL, S16_RL, cvar_HV, S1_RL, θ, kurt_HV, S16_HV, skew_RL, S11_HV, S11_RL, S13_HV, S10_HV, kurt_RL, S8_HV |
| Quad | S3_HV, σ0_VH, λc_VV, S6_VH, S3_VH, S6_HV, S1_VH, λc_HH, S1_VV, cvar_VH, S6_VV, S16_VV, cvar_HV, σ0_HV, S1_HV, S16_HH, skew_HV, θ, skew_VH, S6_HH, S10_HV, cvar_VV, S11_VV, S16_HV, S8_VV, S10_HH, skew_VV, kurt_VV, σ0_VV, λc_VH, S13_HV, S7_VV |
| All | λc_RV, λc_45, λc_RR, S6_HV, S6_VH, σ0_VH, S6_RH, S16_RV, skew_HV, λc_RL, S1_VH, S1_RV, λc_HH, S1_HV, σ0_HV, S16_RL, λc_RH, S1_45, S1_VV, S1_RL, skew_VH, cvar_HV, cvar_VH, S1_RH, S16_RH, S1_RR, S14_RL, S11_RV, λc_VV, S6_HH, σ0_RR, S16_HH, S2_RH, kurt_45, S13_RH, S6_VV, cvar_RV, S6_RL, cvar_RR, θ, S13_VV, S11_VV, S11_HV, S13_RV, skew_RV, S11_45, cvar_RL, S8_RR, cvar_45, S18_RR, S16_45, S6_45, S2_VV, skew_VV, S18_VV, S11_RL, skew_RR, S4_HH, S18_RV, S8_RV, S11_RR, σ0_RL, S8_RL, S4_RL, S3_RL, S4_RR, S9_RL, S10_RH, cvar_VV, S9_RV |
References
- Collins, M.J.; Ma, M.; Dabboor, M. On the effect of polarization and incidence angle on the estimation of significant wave height from SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4529–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chapron, B.; Mouche, A.; Stopa, J.E. A New Ocean SAR Cross-Spectral Parameter: Definition and Directional Property Using the Global Sentinel-1 Measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 1566–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alpers, W.R.; Bruening, C. On the relative importance of motion-related contributions to the SAR imaging mechanism of ocean surface waves. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1986, GE-24, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz-Stellenfleth, J.; Koenig, T.; Lehner, S. An empirical approach for the retrieval of integral ocean wave parameters from synthetic aperture radar data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2007, 112, 3019–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lehner, S.; Bruns, T. Ocean wave integral parameter measurements using Envisat ASAR wave mode data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stopa, J.E.; Mouche, A. Significant wave heights from Sentinel-1 SAR: Validation and applications. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 1827–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grieco, G.; Lin, W.; Migliaccio, M.; Nirchio, F.; Portabella, M. Dependency of the Sentinel-1 azimuth wavelength cut-off on significant wave height and wind speed. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 5086–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Fan, C.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, J. Dependence of the Azimuth Cutoff from Quad-Polarization Gaofen-3 SAR Image on Significant Wave Height and Wind Speed, IGARSS 2022–2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. IEEE 2022, 2299–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Yang, J.; Zheng, G.; Wang, J. Significant wave height estimation using azimuth cutoff of C-band RADARSAT-2 single-polarization SAR images. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2015, 34, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.F.; Li, H. Ocean wave parameters retrieval from Sentinel-1 SAR imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Zhang, X.; Cao, C.; Wang, X.; Jia, Y.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, J. Impact of Polarization Basis on Wind and Wave Parameters Estimation Using the Azimuth Cutoff From GF-3 SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5234716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Yang, J.S. A semi-empirical algorithm for SAR wave height retrieval and its validation using Envisat ASAR wave mode data. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 31, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, Y.; Shao, W.; Zhu, S.; Sun, J.; Yuan, X. Validation of significant wave height retrieval from co-polarization Chinese Gaofen-3 SAR imagery using an improved algorithm. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Ding, Y.; Li, J.; Gou, S.; Nunziata, F.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, L. Wave retrieval under typhoon conditions using a machine learning method applied to Gaofen-3 SAR imagery. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 45, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach, B.; Glaser, Y.; Stopa, J.E.; Mouche, A.A.; Sadowski, P. Deep learning for predicting significant wave height from synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Li, X.; Huang, B. Retrieval of ocean wave heights from spaceborne SAR in the Arctic Ocean with a neural network. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Liu, Y.; Meng, J.; Jia, Y.; Fan, C. Estimating significant wave height from SAR imagery based on an SVM regression model. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Ren, L.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, X. Empirical algorithm for significant wave height retrieval from wave mode data provided by the Chinese satellite Gaofen-3. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Lin, M.; Li, W.; Zhu, J.; Ren, L.; Cui, L. Quad-polarimetric SAR sea state retrieval algorithm from Chinese Gaofen-3 wave mode imagettes via deep learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 273, 112969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Song, T.; Yan, Q.; Meng, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of Multi-Incidence Angle Polarimetric Gaofen-3 SAR Wave Mode Data for Significant Wave Height Retrieval. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Storch, H.; Zwiers, F. Statistical Analysis in Climate Research; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 2005, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd Acm Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Wong, Y.D.; Li, M.Z.-F.; Palanisamy, C.; Chai, C. A feature learning approach based on XGBoost for driving assessment and risk prediction. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 129, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz-Stellenfleth, J.; Lehner, S. Measurement of 2-D sea surface elevation fields using complex synthetic aperture radar data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, D.L.; Lee, J.S. A microwave technique to improve the measurement of directional ocean wave spectra. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Perrie, W.; Xie, T.; Zou, Q. Ocean wave spectra from a linear polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2623–2631. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Perrie, W.; He, Y. Validation of RADARSAT-2 fully polarimetric SAR measurements of ocean surface waves. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, B. Ocean wave parameters retrieved directly from compact polarimetric SAR data. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2022, 41, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, P.; Tao, H.; Zeng, J. A preliminary evaluation of the GaoFen-3 SAR radiation characteristics in land surface and compared with Radarsat-2 and Sentinel-1A. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, H.; Lin, M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Cui, L. Calibration of the copolarized backscattering measurements from Gaofen-3 synthetic aperture radar wave mode imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1748–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbaol, V.; Chapron, B.; Vachon, P.W. Analysis of ERS-1/2 synthetic aperture radar wave mode imagettes. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 7833–7846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Thépaut, J. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Data Buoy Center. Handbook of Automated Data Quality Control Checks and Procedures; NOAA National Data Buoy Center Tech, Stennis Space Center: Hancock County, MS, USA, 2009.
- Sepulveda, H.; Queffeulou, P.; Ardhuin, F. Assessment of SARAL/AltiKa wave height measurements relative to buoy, Jason-2, and Cryosat-2 data. Mar. Geod. 2015, 38, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Yuan, J.; Chen, L. Short-term load forecasting using EMD-LSTM neural networks with a Xgboost algorithm for feature importance evaluation. Energies 2017, 10, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees. In Wadsworth International Group; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Belmont, CA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Ustebay, S.; Turgut, Z.; Aydin, M.A. Intrusion detection system with recursive feature elimination by using random forest and deep learning classifier. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Congress on Big Data, Deep Learning and Fighting Cyber Terrorism (IBIGDELFT), Ankara, Turkey, 3–4 December 2018; pp. 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Du, X.; Zhao, T.; Hou, Q.; Jin, X. Estimating the grade of storm surge disaster loss in coastal areas of China via machine learning algorithms. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of estimators | 200 |
| max_depth | 50 |
| learning_rate | 0.05 |
| reg_lambda | 1 |
| reg_alpha | 0 |
| min_child_weight | 1 |
| gamma | 0 |
| subsample | 1 |
| Polarization | All Features | Best Feature Sets | Optimal Feature Sets | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | RMSE (m) | Number | RMSE (m) | Number | RMSE (m) | |
| HH | 28 | 0.332 | 27 | 0.330 | 12 | 0.337 |
| HV | 28 | 0.339 | 23 | 0.333 | 11 | 0.343 |
| VH | 28 | 0.342 | 21 | 0.336 | 14 | 0.345 |
| VV | 28 | 0.344 | 21 | 0.340 | 15 | 0.344 |
| 45° | 28 | 0.328 | 19 | 0.323 | 10 | 0.329 |
| RH | 28 | 0.340 | 21 | 0.337 | 11 | 0.342 |
| RV | 28 | 0.335 | 26 | 0.334 | 16 | 0.338 |
| RR | 28 | 0.338 | 23 | 0.332 | 14 | 0.338 |
| RL | 28 | 0.336 | 19 | 0.332 | 15 | 0.338 |
| HH + HV | 55 | 0.301 | 44 | 0.295 | 25 | 0.300 |
| VV + VH | 55 | 0.309 | 28 | 0.299 | 18 | 0.308 |
| RH + RV | 55 | 0.344 | 20 | 0.336 | 17 | 0.337 |
| RL + HV | 55 | 0.307 | 52 | 0.306 | 22 | 0.315 |
| Quad | 109 | 0.297 | 44 | 0.293 | 32 | 0.302 |
| All | 244 | 0.297 | 148 | 0.294 | 58 | 0.301 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, T.; Yan, Q.; Fan, C.; Meng, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Significant Wave Height Retrieval Using XGBoost from Polarimetric Gaofen-3 SAR and Feature Importance Analysis. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010149
Song T, Yan Q, Fan C, Meng J, Wu Y, Zhang J. Significant Wave Height Retrieval Using XGBoost from Polarimetric Gaofen-3 SAR and Feature Importance Analysis. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(1):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010149
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Tianran, Qiushuang Yan, Chenqing Fan, Junmin Meng, Yuqi Wu, and Jie Zhang. 2023. "Significant Wave Height Retrieval Using XGBoost from Polarimetric Gaofen-3 SAR and Feature Importance Analysis" Remote Sensing 15, no. 1: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010149
APA StyleSong, T., Yan, Q., Fan, C., Meng, J., Wu, Y., & Zhang, J. (2023). Significant Wave Height Retrieval Using XGBoost from Polarimetric Gaofen-3 SAR and Feature Importance Analysis. Remote Sensing, 15(1), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010149




