Machine Learning Classifier Evaluation for Different Input Combinations: A Case Study with Landsat 9 and Sentinel-2 Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Data Used
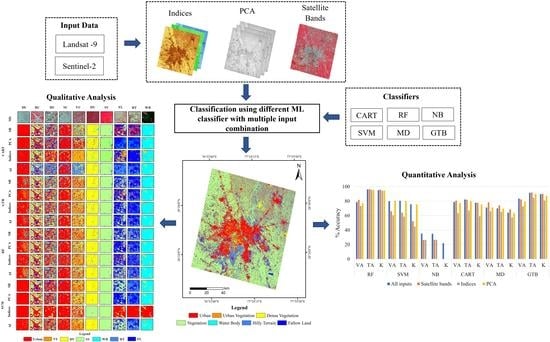
4. Methodology
4.1. Input Selection
4.1.1. Band Optimization
4.1.2. Spectral Indices Calculation
4.1.3. Principal Component Analysis
4.2. LULC Classification Using Machine Learning
4.3. Class and Site Selection for Targeted Feature Analysis
5. Results
5.1. Quantitative Performance Evaluation of Machine Learning Classifiers at Comprehensive Class
5.2. Qualitative Performance Evaluation of Classifiers at Targeted Feature
5.2.1. Analysis with Landsat Image
5.2.2. Analysis with Sentinel Image
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Twisa, S.; Buchroithner, M.F. Land-use and land-cover (LULC) change detection in Wami river basin, Tanzania. Land 2019, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Souza, J.M.; Morgado, P.; da Costa, E.M.; de Vianna, N.L.F. Modeling of Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) Change Based on Artificial Neural Networks for the Chapecó River Ecological Corridor, Santa Catarina/Brazil. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathiba, A.P.; Rastogi, K.; Jain, G.V.; Kumar, V.V.G. Building Footprint Extraction from Very-High-Resolution Satellite Image Using Object-Based Image Analysis (OBIA) Technique. Lect. Notes Civ. Eng. 2020, 33, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Maithani, S.; Kumar, P. Feature Extraction in Urban Areas Using UAV Data; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merugu, S.; Tiwari, A.; Sharma, S.K. Spatial–Spectral Image Classification with Edge Preserving Method. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2021, 49, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Avtar, R.; Prathiba, A.; Mishra, P.K.; Tiwari, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Singh, C.H.; Chandra Yadav, B.; Jain, K. Uncrewed Aerial Systems in Water Resource Management and Monitoring: A Review of Sensors, Applications, Software, and Issues. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2023, 2023, 3544724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Jain, K. Automatic extraction of urban land information from unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) data. Earth Sci. Inform. 2020, 13, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibs, H.; Hasab, H.A.; Mahmoud, A.S.; Al-Ansari, N. Fusion Methods and Multi-classifiers to Improve Land Cover Estimation Using Remote Sensing Analysis. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2021, 39, 5825–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Sharma, L.K.; Nathawat, M.S. Improved Land-use/Land-cover classification of semi-arid deciduous forest landscape using thermal remote sensing. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Ni, S. Use of normalized difference built-up index in automatically mapping urban areas from TM imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathiba, A.P.; Jain, K. Geospatial Landscape Analysis of an Urban Agglomeration: A Case Study of National Capital Region of India. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 6371–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hais, M.; Jonášová, M.; Langhammer, J.; Kučera, T. Comparison of two types of forest disturbance using multitemporal Landsat TM/ETM+ imagery and field vegetation data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.E.; Yang, Z.; Cohen, W.B. Detecting trends in forest disturbance and recovery using yearly Landsat time series: 1. LandTrendr—Temporal segmentation algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2897–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lo, C.P. Using a time series of satellite imagery to detect land use and land cover changes in the Atlanta, Georgia metropolitan area. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 1775–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.-C. NDWI—A Normalized Difference Water Index for Remote Sensing of Vegetation Liquid Water from Space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0034425796000673 (accessed on 24 December 2020). [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Geng, X.; Sun, K.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, P. Target Detection Method for Water Mapping Using Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS Imagery. Water 2015, 7, 794–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, P.; Huang, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Huang, W.; Huang, X.; Yuan, Y. The spatiotemporal evolution of urbanization of the countries along the Belt and Road Initiative using the compounded night light index. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Sachdeva, K.; Joshi, P.K. Mapping long-term land use and land cover change in the central Himalayan region using a tree-based ensemble classification approach. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 74, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, H.; Calvo, A.C.; Rauchecker, M.; Rojas-Zamora, O.; Brokamp, G.; Schütt, B. Article assessment of land cover changes in the hinterland of Barranquilla (Colombia) using landsat imagery and logistic regression. Land 2018, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talukdar, S.; Singha, P.; Mahato, S.; Shahfahad; Pal, S.; Liou, Y.-A.; Rahman, A. Land-use land-cover classification by machine learning classifiers for satellite observations—A review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeferino, L.B.; de Souza, L.F.T.; Amaral, C.H.; Filho, E.I.F.; de Oliveira, T.S. Does environmental data increase the accuracy of land use and land cover classification? Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 91, 102128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, T. Unsupervised change detection in satellite images using principal component analysis and κ-means clustering. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, A.H.; El-Samie, F.E.A.; Metwalli, M.R.; Allah, O.S.F.; El-Rabaie, S. Satellite image fusion based on principal component analysis and high-pass filtering. JOSA A 2010, 27, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldhshan, S.R.S.; Shafri, H.Z.M. Change detection on land use/land cover and land surface temperature using spatiotemporal data of Landsat: A case study of Gaza Strip. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, P.; Chen, Y. Remote sensing imagery classification using adaboost with a weight vector (WV adaboost). Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 8, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Rahman, A.; Paul, S.K.; Kundu, A. Changing pattern of urban landscape and its effect on land surface temperature in and around Delhi. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.N.; Prasad, R.; Rai, P.K.; Vishwakarma, A.K.; Arora, A. Performance evaluation of textural features in improving land use/land cover classification accuracy of heterogeneous landscape using multi-sensor remote sensing data. Earth Sci. Inform. 2019, 12, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alifu, H.; Vuillaume, J.F.; Johnson, B.A.; Hirabayashi, Y. Machine-learning classification of debris-covered glaciers using a combination of Sentinel-1/-2 (SAR/optical), Landsat 8 (thermal) and digital elevation data. Geomorphology 2020, 369, 107365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avudaiammal, R.; Elaveni, P.; Selvan, S.; Rajangam, V. Extraction of Buildings in Urban Area for Surface Area Assessment from Satellite Imagery based on Morphological Building Index using SVM Classifier. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2020, 48, 1325–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, A.E.; Warner, T.A.; Fang, F. Implementation of machine-learning classification in remote sensing: An applied review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2784–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szuster, B.W.; Chen, Q.; Borger, M. A comparison of classification techniques to support land cover and land use analysis in tropical coastal zones. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Hen, A.; Gey, S.; Poggi, J.-M. Influence Measures for CART Classification Trees. J. Classif. 2015, 32, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.Y.; Hu, Y.Y. Land cover changes and their driving mechanisms in Central Asia from 2001 to 2017 supported by Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sang, X.; Guo, Q.Z.; Wu, X.X.; Fu, Y.; Xie, T.Y.; Wei, H.C.; Zang, J.L. Intensity and stationarity analysis of land use change based on cart algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Ma, Q.; Ding, H.; Liang, H. Detection of urban expansion and land surface temperature change using multi-temporal landsat images. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 128, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Liu, F.; Guo, H.; Kong, W.; Zhang, C.; He, Y. Fast detection of sclerotinia sclerotiorum on oilseed rape leaves using low-altitude remote sensing technology. Sensors 2018, 18, 4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elmahdy, S.I.; Ali, T.A.; Mohamed, M.M.; Howari, F.M.; Abouleish, M.; Simonet, D. Spatiotemporal Mapping and Monitoring of Mangrove Forests Changes From 1990 to 2019 in the Northern Emirates, UAE Using Random Forest, Kernel Logistic Regression and Naive Bayes Tree Models. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.Y.; He, H.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Huang, H. A generalized image scene decomposition-based system for supervised classification of very high resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.F.; Yin, J.Y. Variational Bayesian independent component analysis-support vector machine for remote sensing classification. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2013, 39, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M. Detection of urban sprawl using a genetic algorithm-evolved artificial neural network classification in remote sensing: A case study in Jiading and Putuo districts of Shanghai, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 1485–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Cao, C.; Xing, Y.; Li, X. Automatic Classification of Remote Sensing Images Using Multiple Classifier Systems. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 954086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gong, J.; Li, P. A supervised artificial immune classifier for remote-sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3957–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Huang, B.; Xu, B. Multi-source remotely sensed data fusion for improving land cover classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 124, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranza-García, M.; García-Gutiérrez, J.; Riquelme, J.C. A framework for evaluating land use and land cover classification using convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karimi, F.; Sultana, S.; Babakan, A.S.; Suthaharan, S. An enhanced support vector machine model for urban expansion prediction. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 75, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, G.; Jenkerson, C.; Masek, J.; Vermote, E.; Gao, F. Landsat Ecosystem Disturbance Adaptive Processing System (LEDAPS) Algorithm Description; USGS: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2013. Available online: http://www.usgs.gov/pubprod (accessed on 18 August 2022).
- Deng, C.; Zhu, Z. Continuous subpixel monitoring of urban impervious surface using Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 238, 110929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzekri, S.; Lasbet, A.A.; Lachehab, A. A New Spectral Index for Extraction of Built-Up Area Using Landsat-8 Data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2015, 43, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, H.; Latif, Z.A.; Adnan, N.A. Urban vegetation classification with NDVI threshold value method with very high resolution (VHR) Pleiades imagery. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. ISPRS Arch. 2019, 42, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, G.R.F. Urban land use land cover changes and their effect on land surface temperature: Case study using Dohuk City in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. Climate 2017, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phan, T.N.; Kuch, V.; Lehnert, L.W. Land cover classification using google earth engine and random forest classifier-the role of image composition. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.E. Compressive-projection principal component analysis. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2009, 18, 2230–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Gao, X.; Shen, Z.; Li, R. Expansion of Urban Impervious Surfaces in Xining City Based on GEE and Landsat Time Series Data. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 147097–147111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adepoju, K.A.; Adelabu, S.A. Improving accuracy evaluation of Landsat-8 OLI using image composite and multisource data with Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 11, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phalke, A.R.; Özdoğan, M.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Erickson, T.; Gorelick, N.; Yadav, K.; Congalton, R.G. Mapping croplands of Europe, Middle East, Russia, and Central Asia using Landsat, Random Forest, and Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 167, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.N. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfowitz, J. Estimation by the Minimum Distance Method in Nonparametric Stochastic Difference Equations. Ann. Math. Stat. 1954, 25, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees. Biometrics 1984, 40, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, D.; Chen, S.; Qiao, K.; Cao, S. Integrating CART algorithm and multi-source remote sensing data to estimate sub-pixel impervious surface coverage: A case study from Beijing Municipality, China. Chinese Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Wu, C.; Cao, Z.; Fan, W.; Tarolli, P. Improving impervious surface estimation: An integrated method of classification and regression trees (CART) and linear spectral mixture analysis (LSMA) based on error analysis. GIScience Remote Sens. 2018, 55, 583–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, C.; Valero, S.; Inglada, J.; Champion, N.; Dedieu, G. Assessing the robustness of Random Forests to map land cover with high resolution satellite image time series over large areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Galiano, V.F.; Ghimire, B.; Rogan, J.; Chica-Olmo, M.; Rigol-Sanchez, J.P. An assessment of the effectiveness of a random forest classifier for land-cover classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 67, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Brandt, M.; Hiernaux, P.; Herrmann, S.; Rasmussen, L.V.; Rasmussen, K.; Tian, F.; Tagesson, T.; Zhang, W.; Fensholt, R. The forgotten land use class: Mapping of fallow fields across the Sahel using Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurqani, H.A.; Post, C.J.; Mikhailova, E.A.; Schlautman, M.A.; Sharp, J.L. Geospatial analysis of land use change in the Savannah River Basin using Google Earth Engine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 69, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Chen, C.; Zhou, H.; Liu, B.; Ma, Q. Prediction of Protein-Protein Interactions Based on L1-Regularized Logistic Regression and Gradient Tree Boosting. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sachdeva, S.; Bhatia, T.; Verma, A.K. A novel voting ensemble model for spatial prediction of landslides using GIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 929–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orieschnig, C.A.; Belaud, G.; Venot, J.-P.; Massuel, S.; Ogilvie, A. Input imagery, classifiers, and cloud computing: Insights from multi-temporal LULC mapping in the Cambodian Mekong Delta. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 54, 398–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddin, S.; Jozdani, B.; Johnson, A.; Chen, D. Comparing Deep Neural Networks, Ensemble Classifiers, and Support Vector Machine Algorithms for Object-Based Urban Land Use/Land Cover Classification. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1713. [Google Scholar]
- Abdi, A.M. Land cover and land use classification performance of machine learning algorithms in a boreal landscape using Sentinel-2 data. GIScience Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Luo, T.; Du, M.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; He, C.; Wang, S.; Yang, K. Machine Learning Comparison and Parameter Setting Methods for the Detection of Dump Sites for Construction and Demolition Waste Using the Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, T.M.; Jiang, P. Comparison of common classification strategies for large-scale vegetation mapping over the Google Earth Engine platform. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 115, 103092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackdavong, M.; Akitoshi, H. Comparison of Machine Learning Classifiers for Land Cover Changes using Google Earth Engine. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Aerospace Electronics and Remote Sensing Technology (ICARES), Bali, Indonesia, 3–4 November 2021; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=9665186&tag=1 (accessed on 3 May 2023).
- Sultana, S.; Satyanarayana, A.N.V. Assessment of urbanisation and urban heat island intensities using landsat imageries during 2000–2018 over a sub-tropical Indian City. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 52, 101846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Tyagi, D.; Sharma, S.K.; Suresh, M.; Jain, K. Multi-criteria decision analysis for identifying potential sites for future urban development in Haridwar, India. Lect. Notes Electr. Eng. 2019, 500, 761–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qi, Z.; Ye, X.; Cai, Y.; Ma, W.; Chen, M. Analysis of land use/land cover change, population shift, and their effects on spatiotemporal patterns of urban heat islands in metropolitan Shanghai, China. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 44, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Sensor | Date | Path, Row/Tile No. | Spatial Resolution | % Cloud Cover |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 9 | 11 March 2022 | 146,040 | 30 m | 0.09 |
| 11 March 2022 | 146,041 | 30 m | 0.03 | |
| 02 March 2022 | 147,040 | 30 m | 0.60 | |
| Sentinel-2 | 05 March 2022 | 43 RFM | 10 m, 20 m | 0.00 |
| 05 March 2022 | 43 RFN | 10 m, 20 m | 0.20 | |
| 05 March 2022 | 43 RGM | 10 m, 20 m | 0.00 | |
| 05 March 2022 | 43 RGN | 10 m, 20 m | 0.00 |
| Method | No. of Input Bands Used | Names of the Input (Predictors) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | Blue, Green, Red, NIR, SWIR-1, and SWIR-2 |
| 2 | 3 | NDBI, NDVI, and NDWI |
| 3 | 3 | PC-1, PC-2, and PC-3 |
| 4 | 12 | Blue, Green, Red, NIR, SWIR-1, SWIR-2, NDBI, NDVI, NDWI, PC-1, PC-2, and PC-3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palanisamy, P.A.; Jain, K.; Bonafoni, S. Machine Learning Classifier Evaluation for Different Input Combinations: A Case Study with Landsat 9 and Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133241
Palanisamy PA, Jain K, Bonafoni S. Machine Learning Classifier Evaluation for Different Input Combinations: A Case Study with Landsat 9 and Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(13):3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133241
Chicago/Turabian StylePalanisamy, Prathiba A., Kamal Jain, and Stefania Bonafoni. 2023. "Machine Learning Classifier Evaluation for Different Input Combinations: A Case Study with Landsat 9 and Sentinel-2 Data" Remote Sensing 15, no. 13: 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133241
APA StylePalanisamy, P. A., Jain, K., & Bonafoni, S. (2023). Machine Learning Classifier Evaluation for Different Input Combinations: A Case Study with Landsat 9 and Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sensing, 15(13), 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133241