Optical and SAR Image Registration Based on Pseudo-SAR Image Generation Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
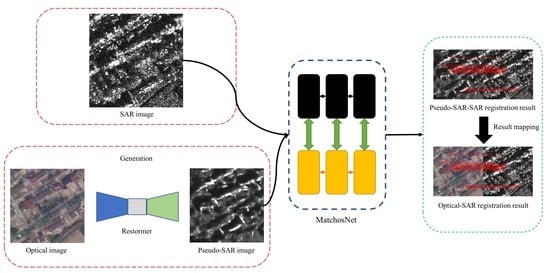
- In the pseudo-SAR generation strategy, this paper use the improved Restormer network to eliminate the feature differences between optical and SAR images.
- For the registration part, a refined keypoint extraction method using the ROEWA operator is designed to construct the Harris scale space and used to extract the extreme points in each scale.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pseudo-SAR Image Generation Strategy
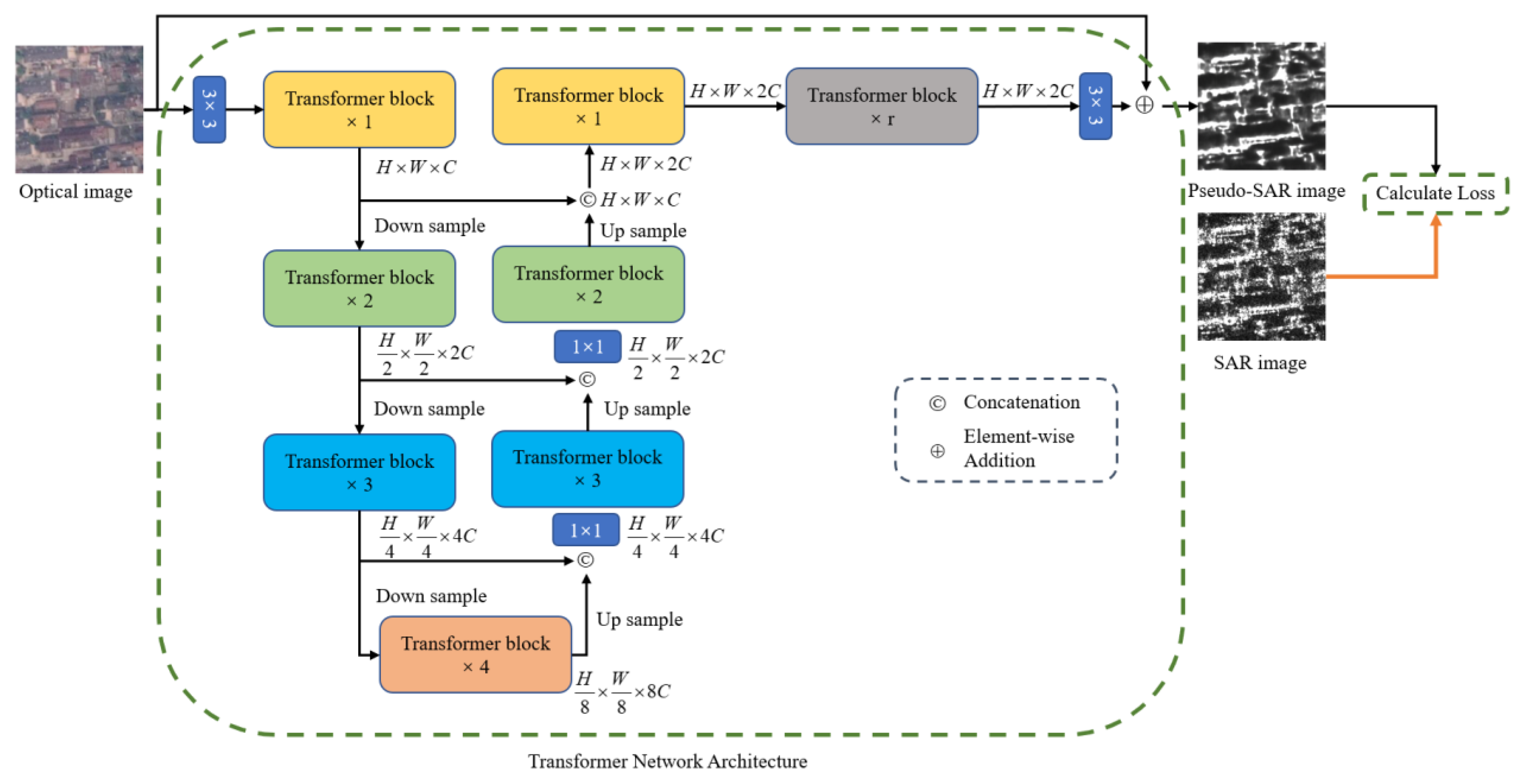
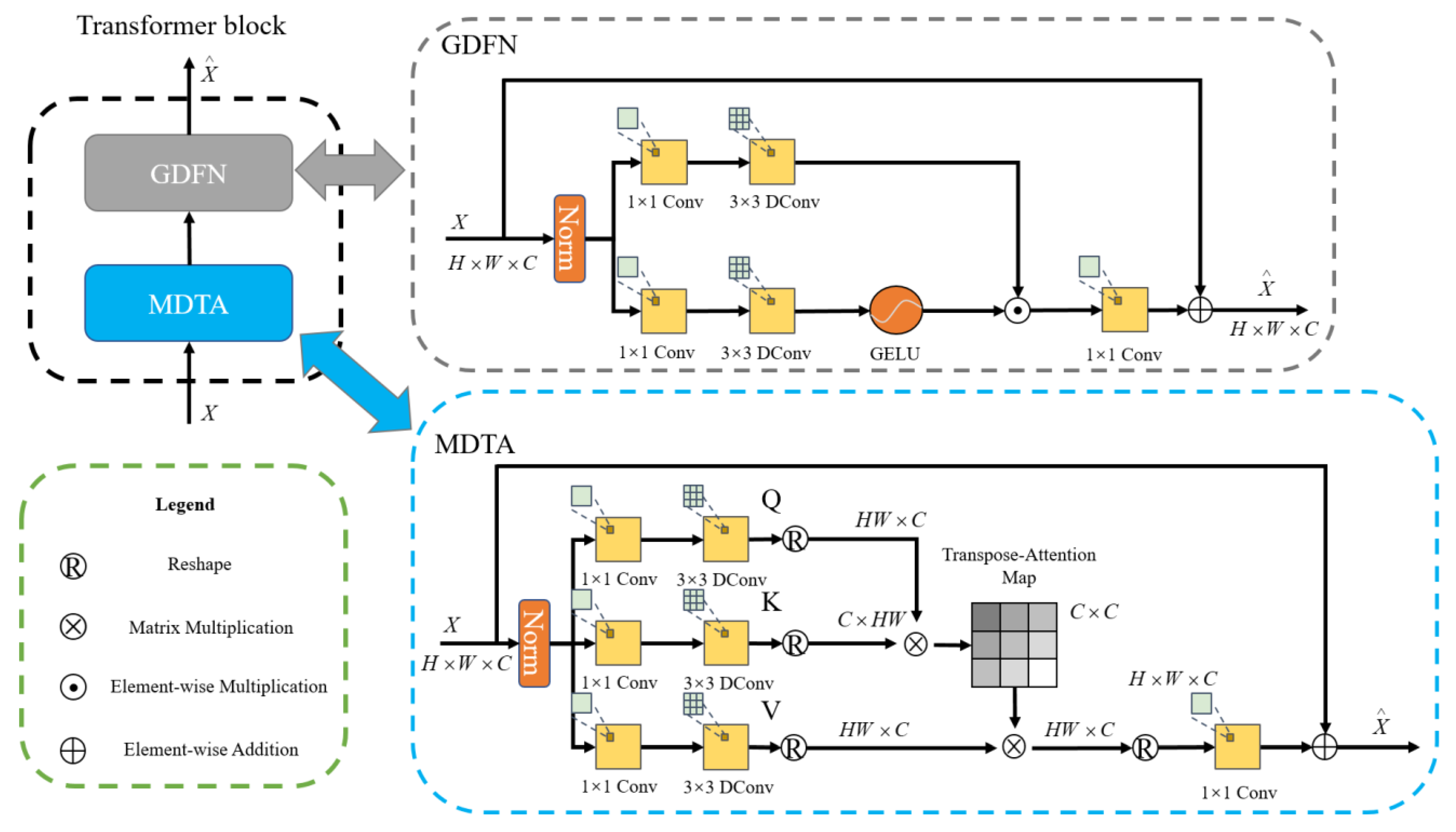
2.1.1. Network Architecture
2.1.2. Pseudo-SAR Generation Network Loss Function
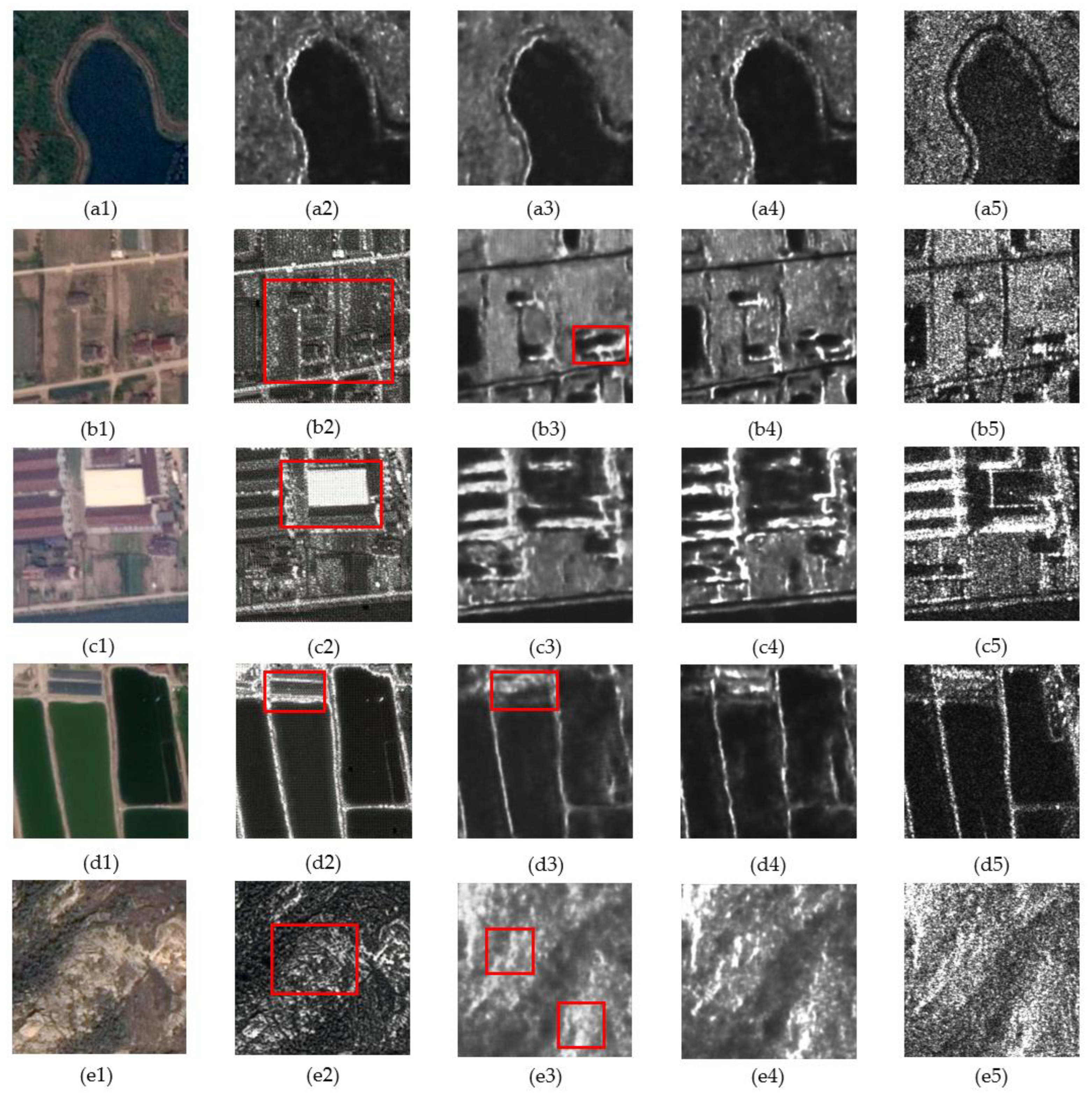
2.1.3. Pseudo-SAR Generation Performance Evaluation
- (1)
- AG
- (2)
- SSIM
- (3)
- PSNR
- (4)
- LPIPS
- (5)
- MAE
2.1.4. Parameter Analysis
2.2. Image Registration
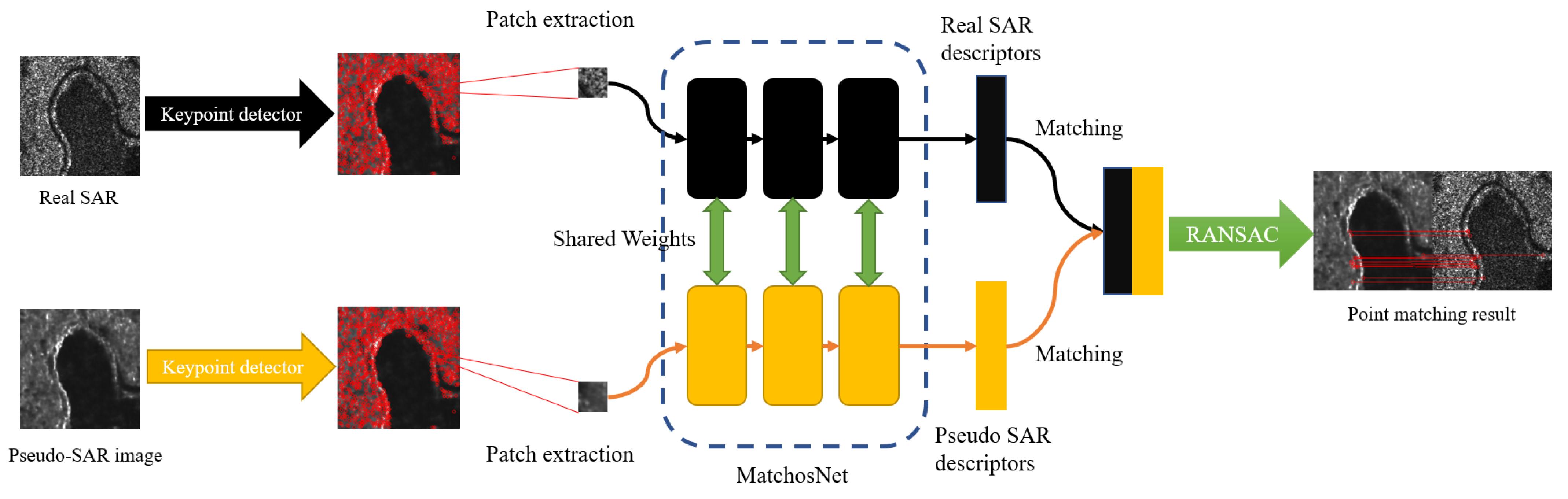
2.2.1. Keypoint Detection
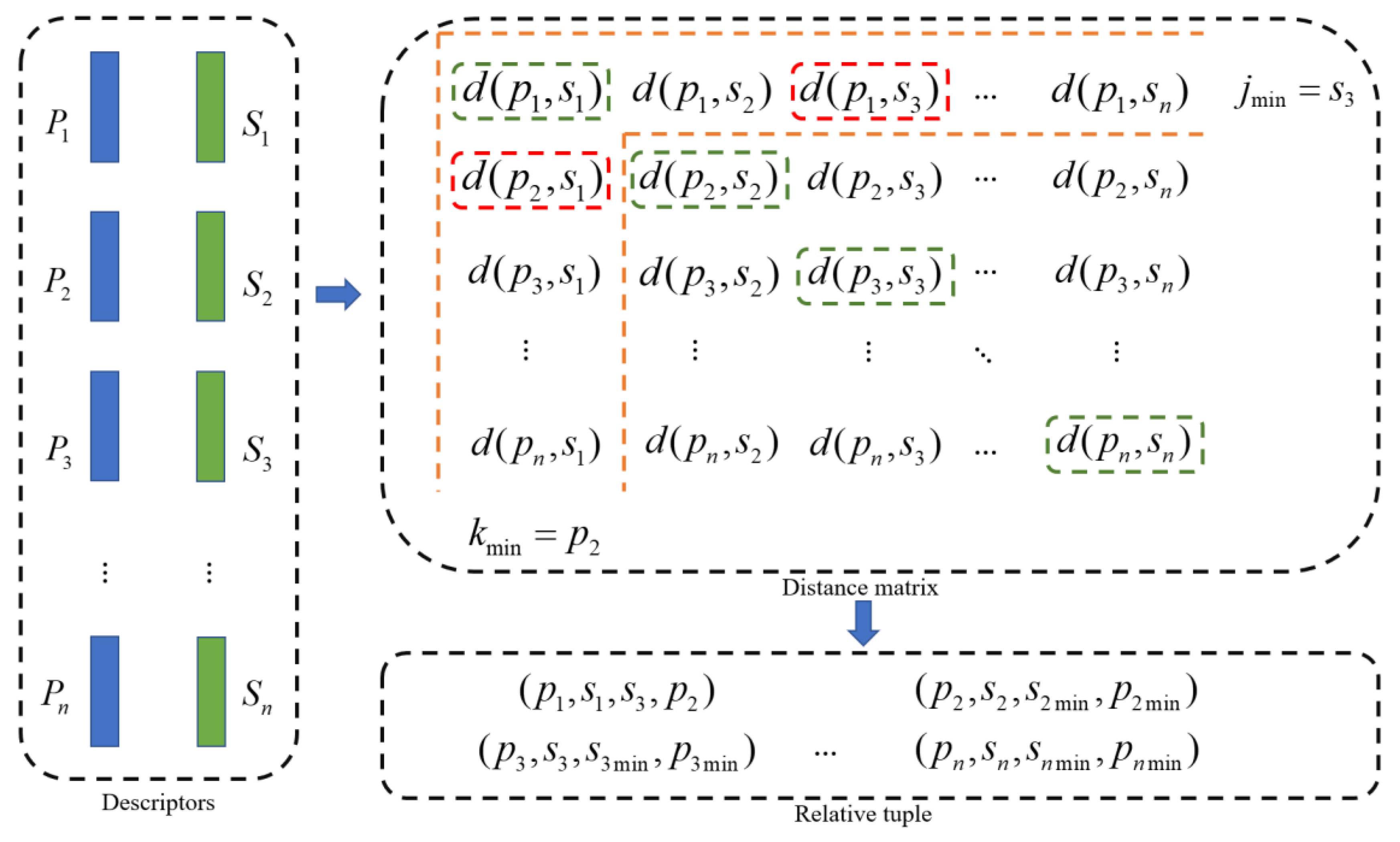
2.2.2. Feature Descriptor Construction
2.2.3. Descriptor Matching Loss Function
2.2.4. Parameter Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Experiment Preparation
3.1.1. Dataset Preparation
3.1.2. Parameter Setting
3.1.3. Registration Comparison Method
- (1)
- PSO-SIFT [49]: According to the existing SIFT method, PSO-SIFT adopts a new gradient definition to eliminate the nonlinear radiation differences between optical and SAR images.
- (2)
- MatchosNet [23]: MatchosNet proposes a deep convolution Siamese network based on CSPDenseNet to obtain powerful matching descriptors to improve the matching effect.
- (3)
- CycleGAN + MatchosNet [26]: This method uses CycleGAN [50] to generate pseudo-optical images from SAR images, and it uses SIFT to match the pseudo-optical and optical images to obtain the final registration results. In the ablation experiment, the CycleGAN network and the improved Restormer network are compared in the pseudo-SAR generation strategy. In the registration experiment, we make improvements to this method by converting the optical image into a pseudo-SAR image and replacing the SIFT with MatchosNet to better evaluate the registration method proposed in this paper.
3.1.4. Experimental Platform
3.2. Experiment Result
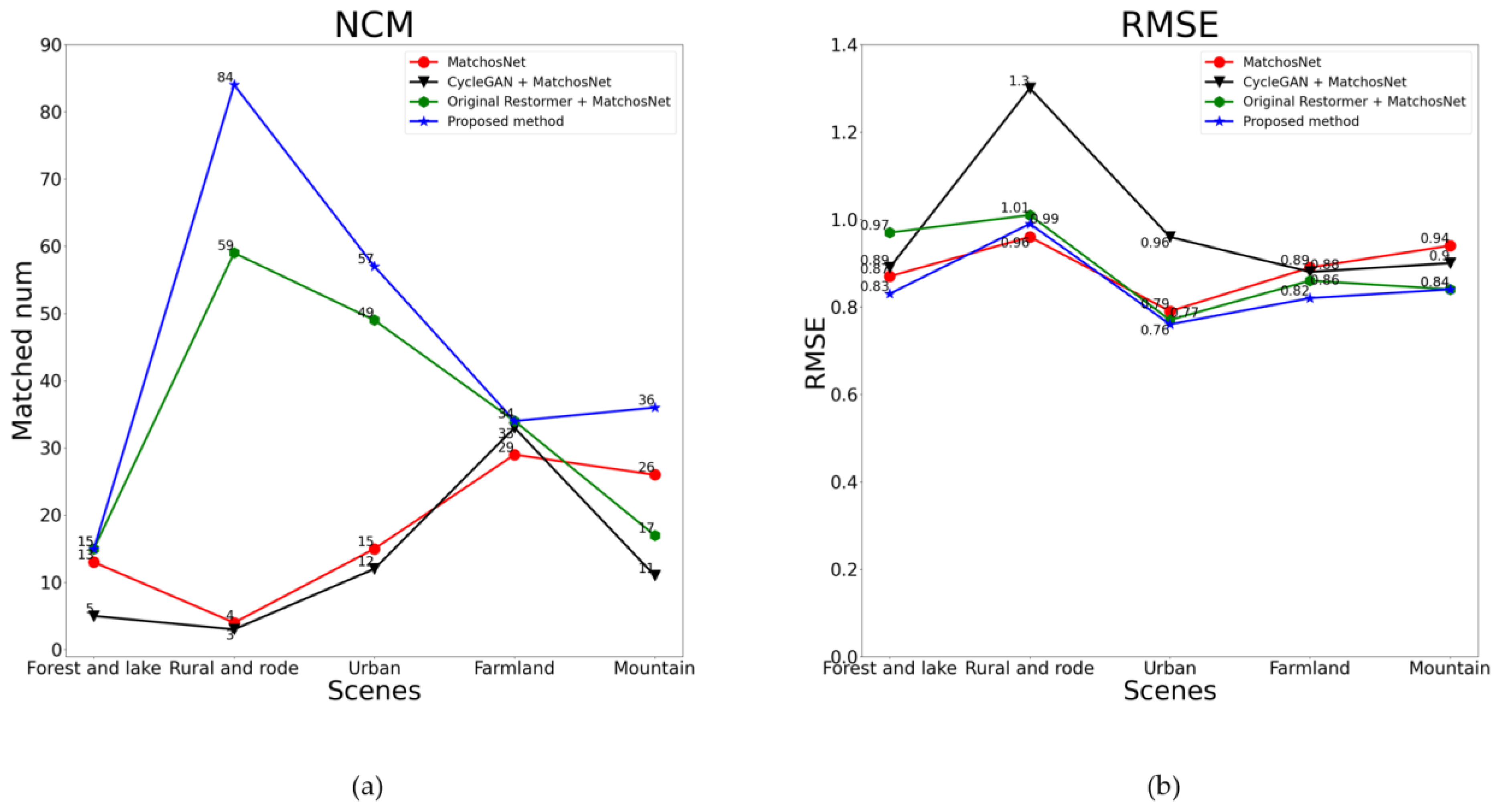
3.2.1. Comparison of Registration Results
- (1)
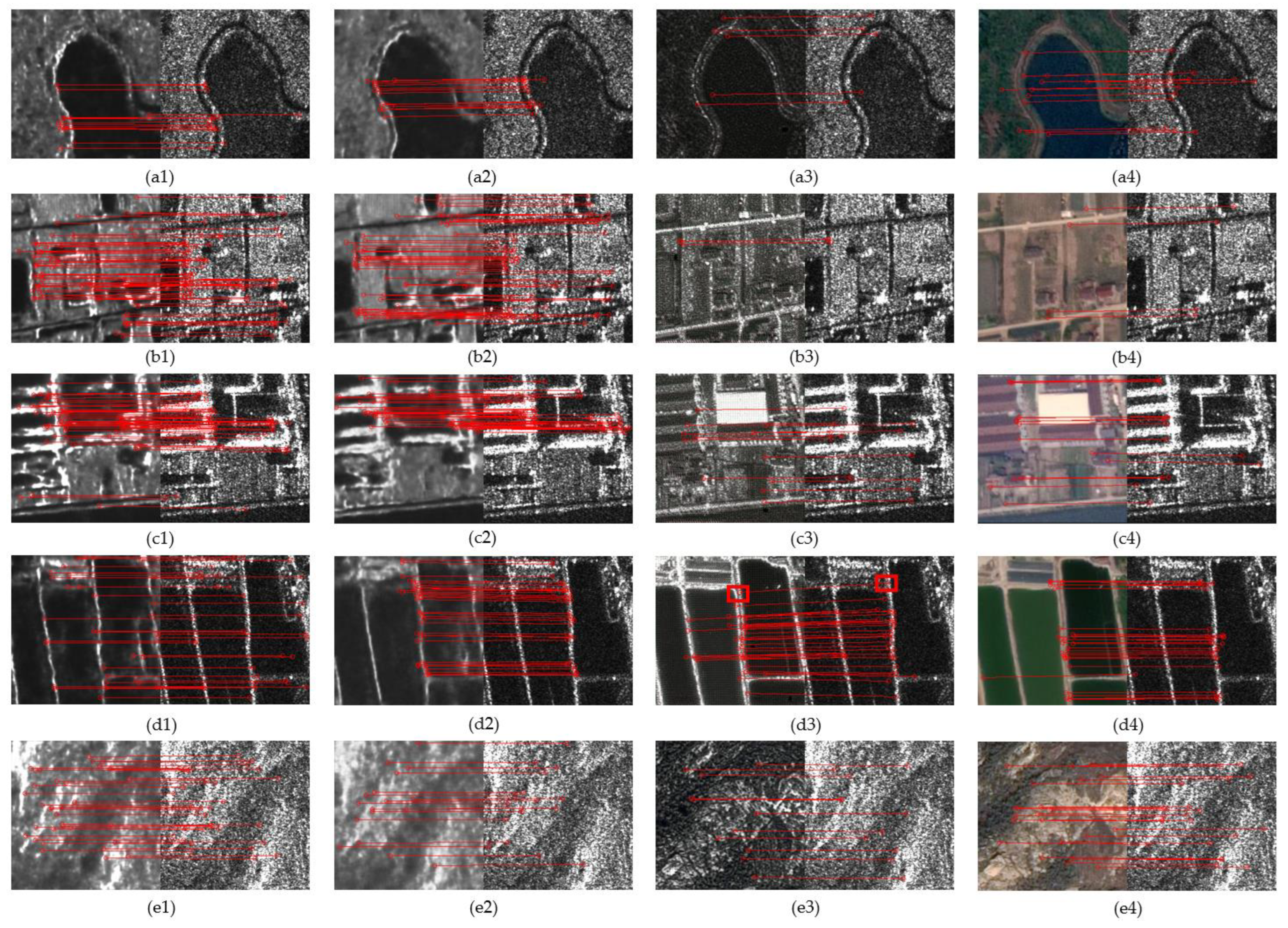
- Keypoint matching analysis
- (2)
- Checkerboard image experiment analysis
3.2.2. Ablation Experiment
- (1)
- Pseudo-SAR generation strategy validity analysis
- (2)
- The validity analysis of pseudo-SAR generation strategy for registration
- (3)
- Keypoint extraction strategy validity analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le Moigne, J.; Netanyahu, N.S.; Eastman, R.D. Image Registration for Remote Sensing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Leng, C.; Hong, Y.; Pei, Z.; Cheng, I.; Basu, A. Multimodal remote sensing image registration methods and advancements: A survey. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiras, A.; Davatzikos, C.; Paragios, N. Deformable medical image registration: A survey. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2013, 32, 1153–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, D.; Holden, E.-J. A fast and fully automatic registration approach based on point features for multi-source remote-sensing images. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Su, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, X.; Min, W. Remote sensing image registration using convolutional neural network features. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehureau, G.; Tupin, F.; Tison, C.; Oller, G.; Petit, D. Registration of metric resolution SAR and optical images in urban areas. In Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2–5 June 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Han, C.; Sun, H.; Cao, Y. Registration of high resolution SAR and optical images based on multiple features. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2005, IGARSS’05, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 29 July 2005; pp. 3542–3544. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-M.; Varshney, P.K.; Arora, M.K. Performance of mutual information similarity measure for registration of multitemporal remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2445–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Konofagou, E.E. A fast normalized cross-correlation calculation method for motion estimation. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 2010, 57, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Huang, Q.; Gao, W. Image matching by normalized cross-correlation. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing Proceedings, Toulouse, France, 14–19 May 2006; p. II. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Vemuri, B.C. Non-rigid multi-modal image registration using cross-cumulative residual entropy. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2007, 74, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinrich, M.P.; Jenkinson, M.; Bhushan, M.; Matin, T.; Gleeson, F.V.; Brady, M.; Schnabel, J.A. MIND: Modality independent neighbourhood descriptor for multi-modal deformable registration. Med. Image Anal. 2012, 16, 1423–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Wang, F.; You, H. OS-SIFT: A Robust SIFT-Like Algorithm for High-Resolution Optical-to-SAR Image Registration in Suburban Areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3078–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczyk, K.; Schmid, C. A performance evaluation of local descriptors. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 1615–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fjortoft, R.; Lopes, A.; Marthon, P. An optimal multiedge detector for SAR image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sedaghat, A.; Mokhtarzade, M.; Ebadi, H. Uniform Robust Scale-Invariant Feature Matching for Optical Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4516–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Ma, J.; Yu, K.; Zhang, J.; Fu, W. Multispectral Remote Sensing Image Matching via Image Transfer by Regularized Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks and Local Feature. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Leung, T.; Jia, Y.; Sukthankar, R.; Berg, A.C. MatchNet: Unifying Feature and Metric Learning for Patch-Based Matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3279–3286. [Google Scholar]
- Balntas, V.; Riba, E.; Ponsa, D.; Mikolajczyk, K. Learning local feature descriptors with triplets and shallow convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 27th British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), York, UK, 19–22 September 2016; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Fan, B.; Wu, F. L2-Net: Deep Learning of Discriminative Patch Descriptor in Euclidean Space. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6128–6136. [Google Scholar]
- Mishchuk, A.; Mishkin, D.; Radenovic, F.; Matas, J. Working hard to know your neighbor’s margins: Local descriptor learning loss. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.; Di, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, A.; Liu, J.; Lu, M.; Duan, Q. Feature Matching and Position Matching Between Optical and SAR With Local Deep Feature Descriptor. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 448–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Xie, Y.; Cheng, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y. Optical and SAR Image Registration Based on Feature Decoupling Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5235913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiolo, L.; Solarna, D.; Moser, G.; Serpico, S.B. Registration of Multisensor Images through a Conditional Generative Adversarial Network and a Correlation-Type Similarity Measure. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wen, L.; Ding, J. SAR and optical image registration method based on improved CycleGAN. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Xiamen, China, 26–29 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, H. A Transformer-Based Coarse-to-Fine Wide-Swath SAR Image Registration Method under Weak Texture Conditions. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Goodfellow, I.; Metaxas, D.; Odena, A. Self-attention generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach Convention & Entertainment Center, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 7354–7363. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Li, M.; Tang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Jiao, L. Homo–heterogenous transformer learning framework for RS scene classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2223–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Wu, B.; Zhao, K.; Ye, Y.; Wang, W. Two-stream swin transformer with differentiable sobel operator for remote sensing image classification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazi, Y.; Bashmal, L.; Rahhal, M.; Dayil, R.; Ajlan, N. Vision Transformers for Remote Sensing Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Y.; Yin, G.; Johnson, B.A. Deep learning in remote sensing applications: A meta-analysis and review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwind, P.; Suri, S.; Reinartz, P.; Siebert, A. Applicability of the SIFT operator to geometric SAR image registration. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 1959–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellinger, F.; Delon, J.; Gousseau, Y.; Michel, J.; Tupin, F. SAR-SIFT: A SIFT-Like Algorithm for SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bovik, A.C. On detecting edges in speckle imagery. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1988, 36, 1618–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Lopes, A.; Bousquet, P. A statistical and geometrical edge detector for SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1988, 26, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.-L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Tian, X.; Yang, Z.; Bian, F. Exploring the potential of unsupervised image synthesis for SAR-optical image matching. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 71022–71033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.-H. Restormer: Efficient transformer for high-resolution image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5728–5739. [Google Scholar]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Zhang, X.; Huo, C.; Xue, B.; Wang, L.; Pan, C. TR-MISR: Multiimage super-resolution based on feature fusion with transformers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 1373–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhan, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, J. A Super-resolution Method of Remote Sensing Image Using Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2021 11th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications (IDAACS), Cracow, Poland, 22–25 September 2021; pp. 905–910. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M.; Wu, Y.-H.; Chen, P.-Y.; Hsieh, J.-W.; Yeh, I.H.; Ieee Comp, S.O.C. CSPNet: A New Backbone that can Enhance Learning Capability of CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Electr Network, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1571–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Xu, Y.; Qian, L.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, W.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Xiang, X. The QXS-SAROPT Dataset for Deep Learning in SAR-Optical Data Fusion. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.08259. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.; Tao, R.; Wang, F.; You, H.; Han, B. Automatic registration of optical and SAR images via improved phase congruency model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5847–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Jiao, L.; Gong, M.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, L. Remote Sensing Image Registration with Modified SIFT and Enhanced Feature Matching. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.-M.; Yang, H.-S.; Seong, W.-J. Compressive underwater sonar imaging with synthetic aperture processing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, H.; Sun, H.; Ying, W. Multireceiver SAS imagery based on monostatic conversion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 10835–10853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Environment | Version |
|---|---|
| Platform | Windows 11, Linux |
| Torch | V 1.9.0 |
| Matlab | 2021a |
| CPU | Inter Core i7-10700 |
| Memory | 16 G |
| Video memory | 6 G |
| Method | Scene | NCM | RMSE (pix) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSO-SIFT | Forest and lake | 4 | 1.15 |
| Rural and road | 12 | 1.57 | |
| Urban | 6 | 0.98 | |
| Farmland | 7 | 0.90 | |
| Mountain | 15 | 0.99 | |
| CycleGAN + MatchosNet | Forest and lake | 5 | 0.89 |
| Rural and road | 3 | 1.30 | |
| Urban | 12 | 0.96 | |
| Farmland | 33 | 0.88 | |
| Mountain | 11 | 0.90 | |
| MatchosNet | Forest and lake | 13 | 0.87 |
| Rural and road | 4 | 0.96 | |
| Urban | 15 | 0.79 | |
| Farmland | 29 | 0.89 | |
| Mountain | 26 | 0.94 | |
| Proposed Method | Forest and lake | 15 | 0.83 |
| Rural and road | 84 | 0.99 | |
| Urban | 57 | 0.76 | |
| Farmland | 34 | 0.82 | |
| Mountain | 36 | 0.84 |
| Method | Evaluation Metrics | Scenes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest and Lake | Rural and Road | Urban | Farmland | Mountain | ||
| CycleGAN | AG↑ | 11.39 | 16.19 | 17.56 | 12.00 | 17.05 |
| SSIM↑ | 0.64 | 0.80 | 0.78 | 0.79 | 0.72 | |
| PSNR↑ | 12.70 | 10.02 | 8.64 | 12.14 | 10.02 | |
| LPIPS↓ | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.62 | 0.57 | 0.56 | |
| MAE↓ | 173.28 | 127.16 | 121.04 | 89.15 | 136.67 | |
| Original Restormer | AG↑ | 15.86 | 25.04 | 23.05 | 19.96 | 24.86 |
| SSIM↑ | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.81 | 0.97 | |
| PSNR↑ | 15.30 | 12.33 | 11.78 | 15.76 | 14.30 | |
| LPIPS↓ | 0.56 | 0.60 | 0.58 | 0.54 | 0.50 | |
| MAE↓ | 143.58 | 113.39 | 115.57 | 95.24 | 123.57 | |
| Improved Restormer | AG↑ | 16.91 | 27.03 | 26.73 | 21.19 | 25.34 |
| SSIM↑ | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.88 | 0.99 | |
| PSNR↑ | 16.17 | 12.80 | 12.69 | 16.00 | 14.54 | |
| LPIPS↓ | 0.50 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.51 | 0.54 | |
| MAE↓ | 141.02 | 123.16 | 114.45 | 92.89 | 123.12 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, C.; Zhu, R.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; Xiang, D. Optical and SAR Image Registration Based on Pseudo-SAR Image Generation Strategy. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143528
Hu C, Zhu R, Sun X, Li X, Xiang D. Optical and SAR Image Registration Based on Pseudo-SAR Image Generation Strategy. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(14):3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143528
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Canbin, Runze Zhu, Xiaokun Sun, Xinwei Li, and Deliang Xiang. 2023. "Optical and SAR Image Registration Based on Pseudo-SAR Image Generation Strategy" Remote Sensing 15, no. 14: 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143528
APA StyleHu, C., Zhu, R., Sun, X., Li, X., & Xiang, D. (2023). Optical and SAR Image Registration Based on Pseudo-SAR Image Generation Strategy. Remote Sensing, 15(14), 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143528