Investigation of the Vertical Distribution Characteristics and Microphysical Properties of Summer Mineral Dust Masses over the Taklimakan Desert Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Campaign
2.2. UAV
2.3. Dust Monitor Spectrometer
2.4. Radiosonde
2.5. Meteorology Elements
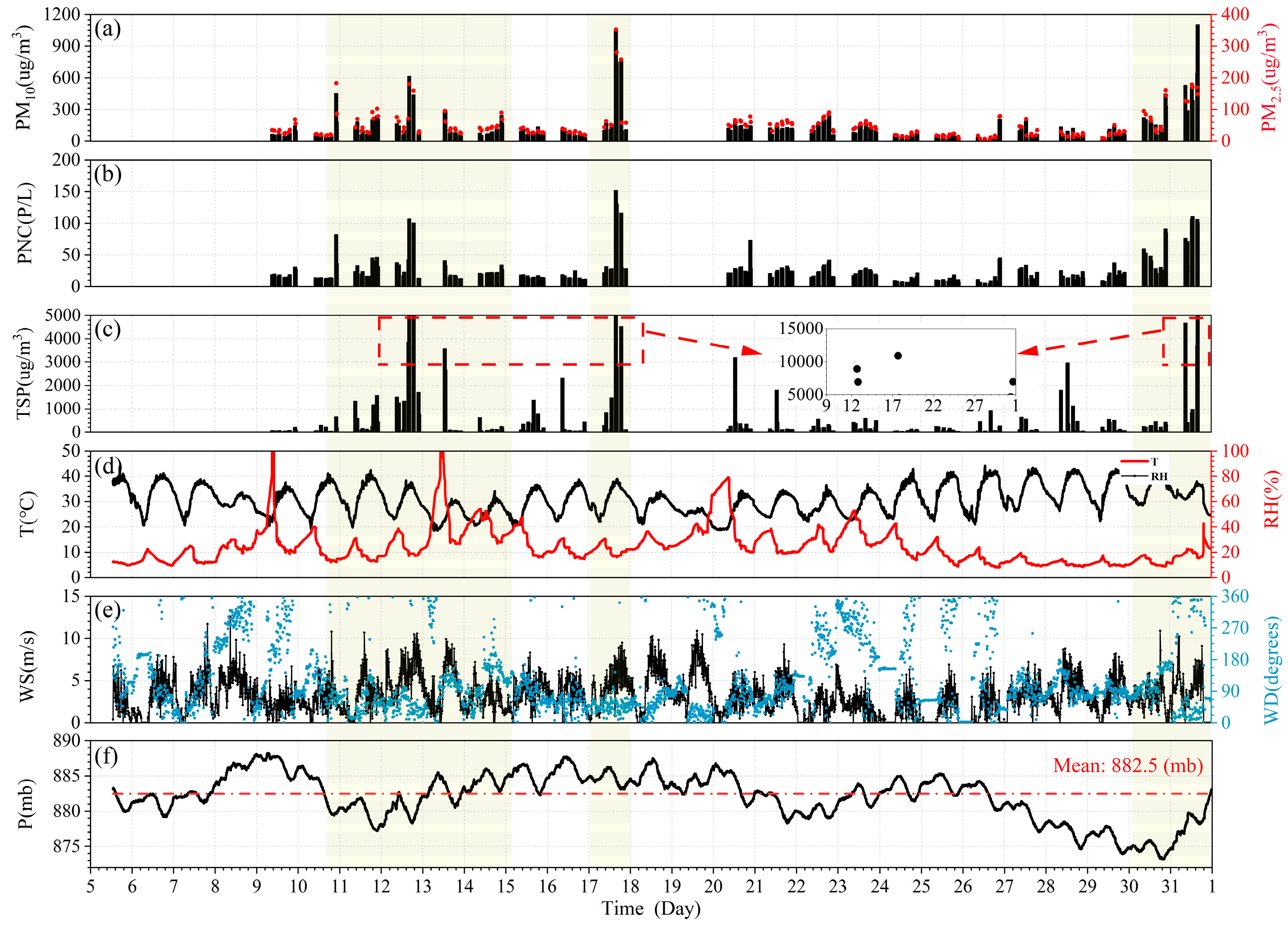
3. Results
3.1. Measurement Overview
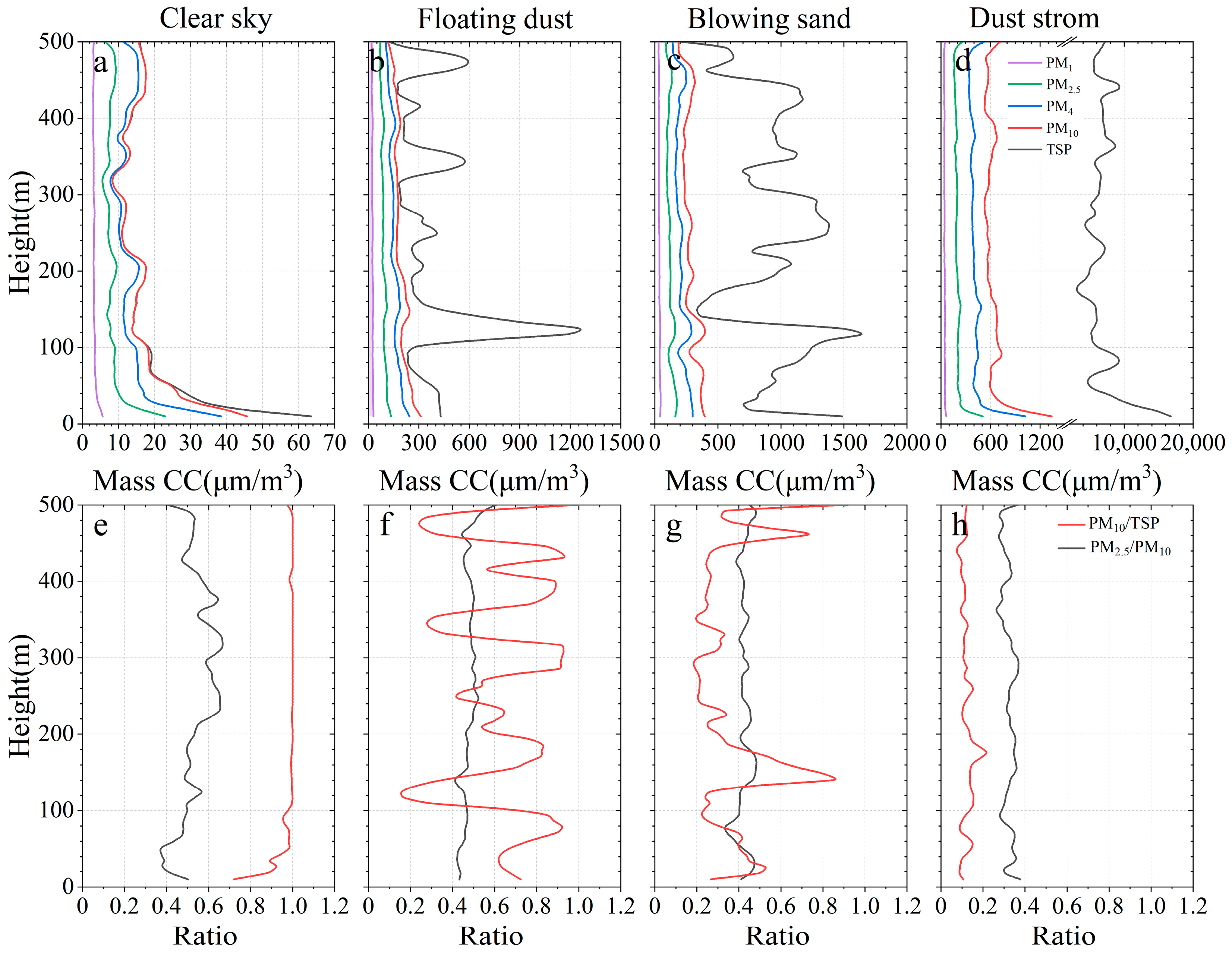
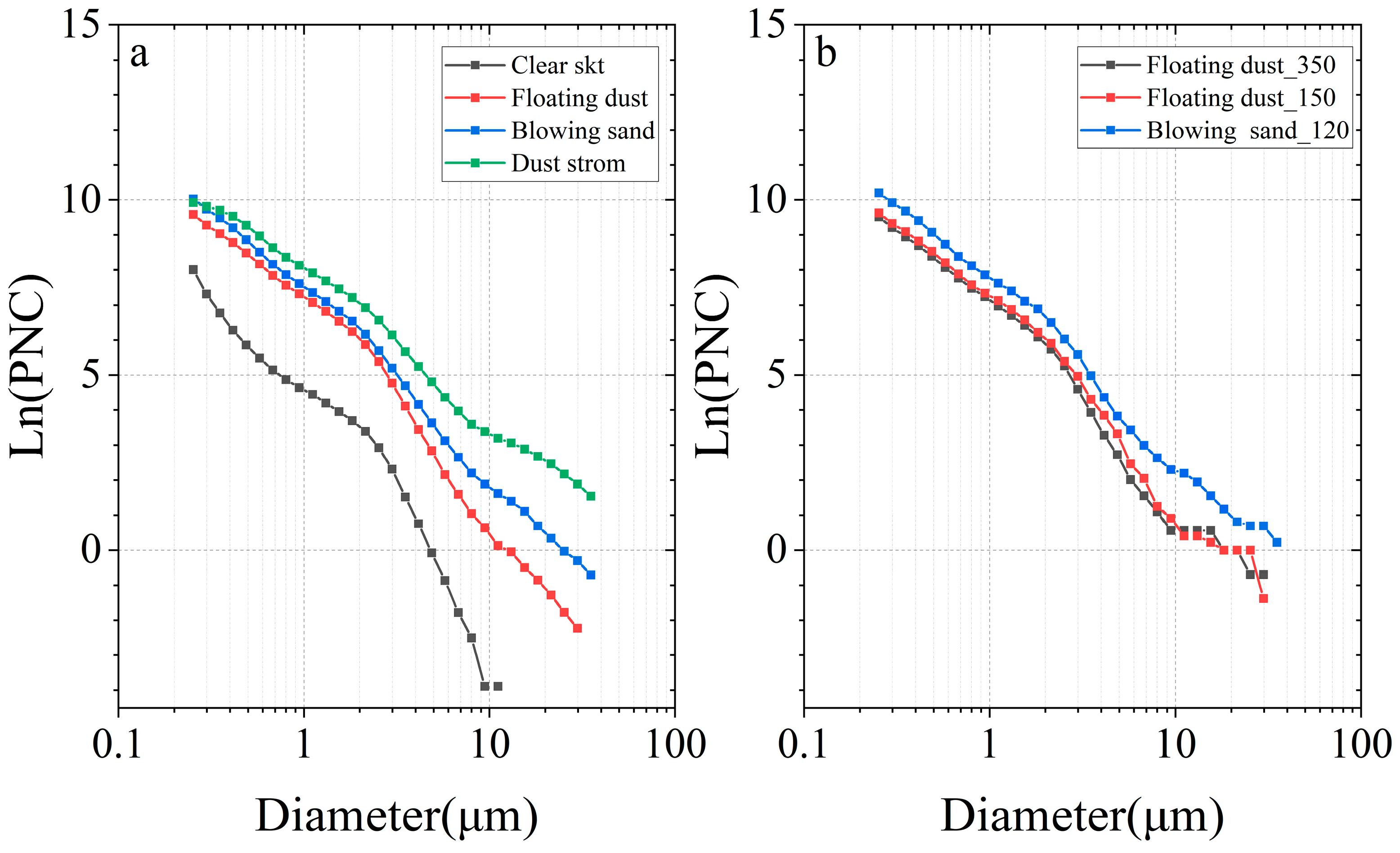
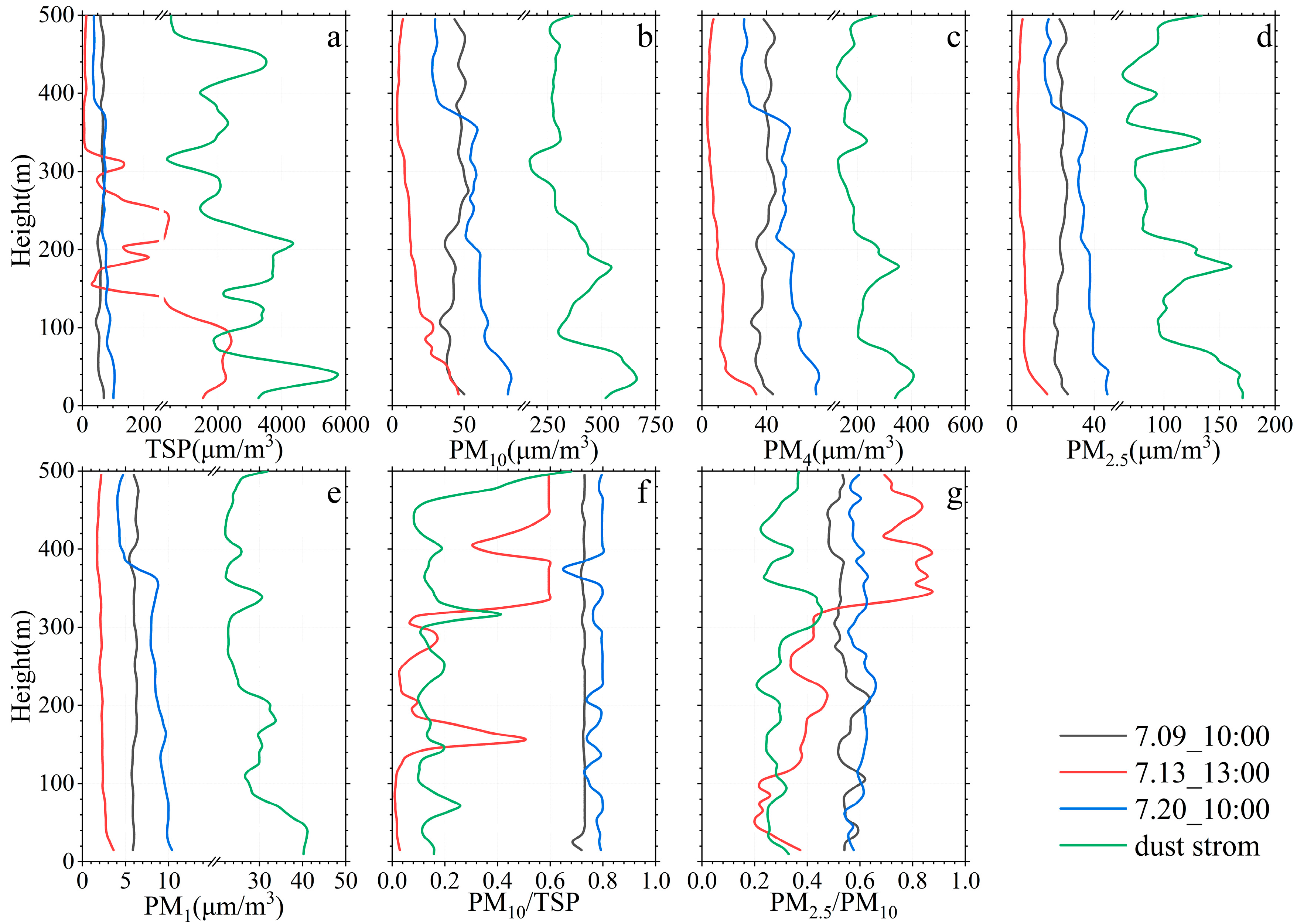
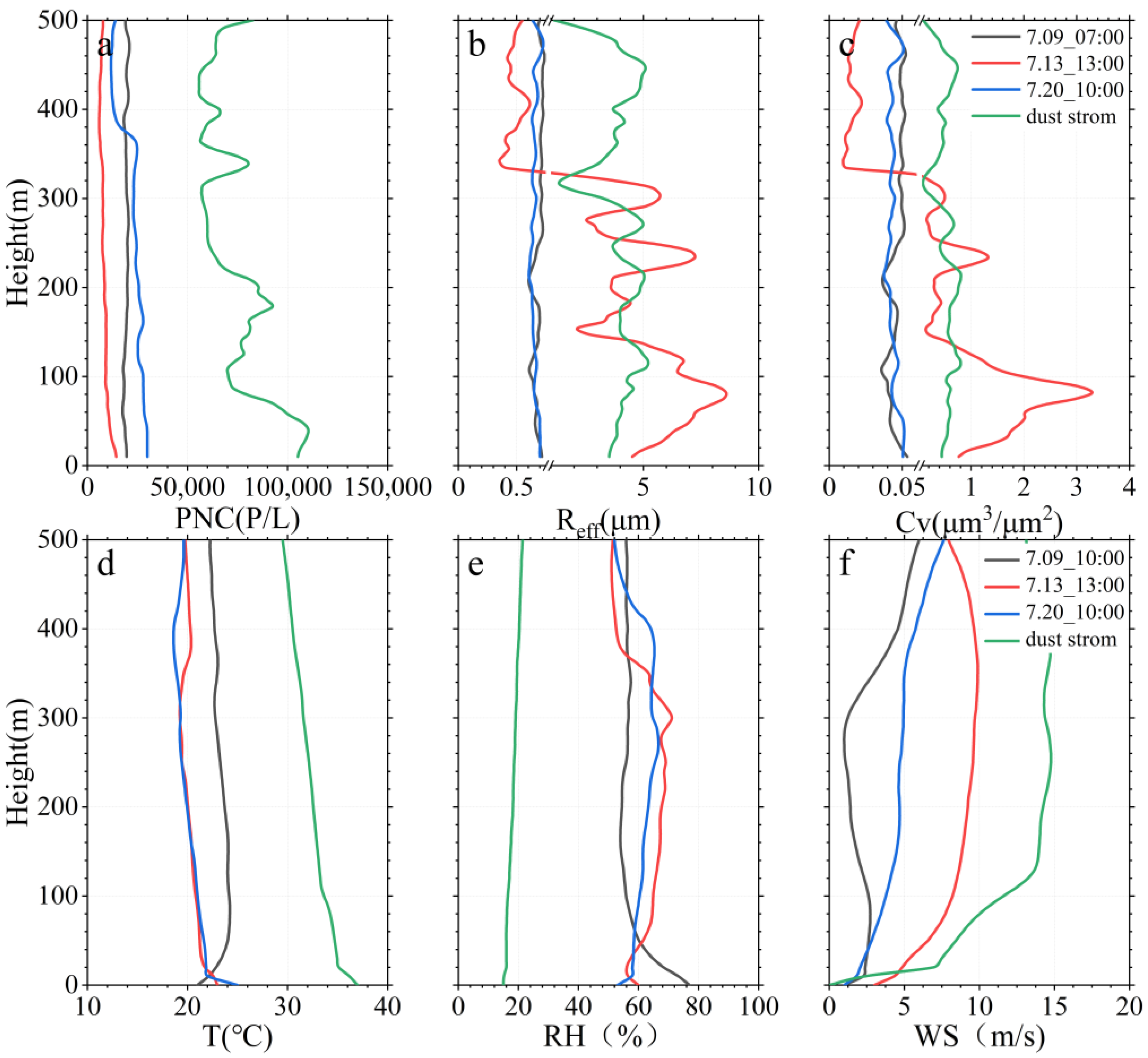
3.2. Vertical Characteristics under Clear and Dust Scenarios
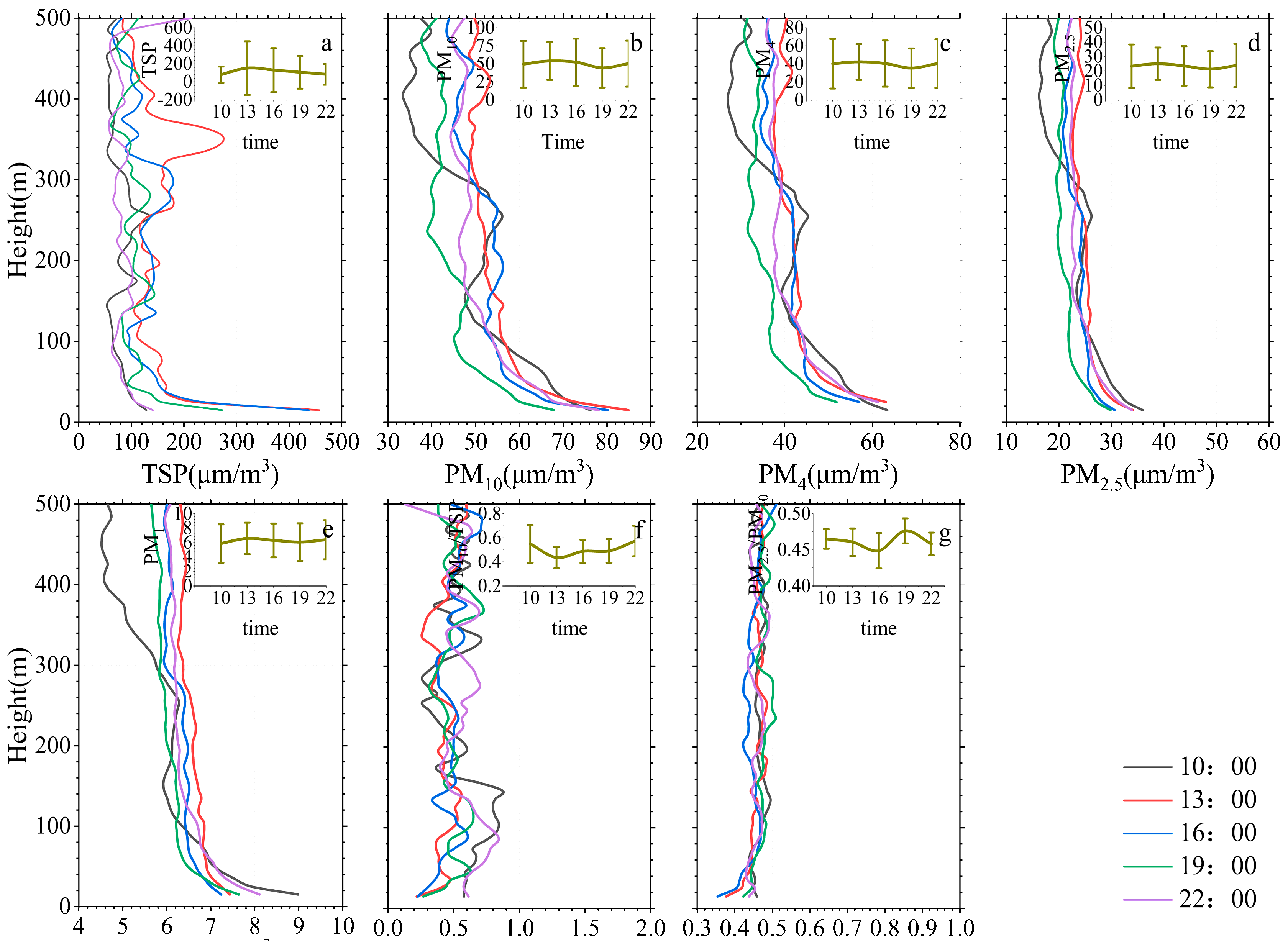
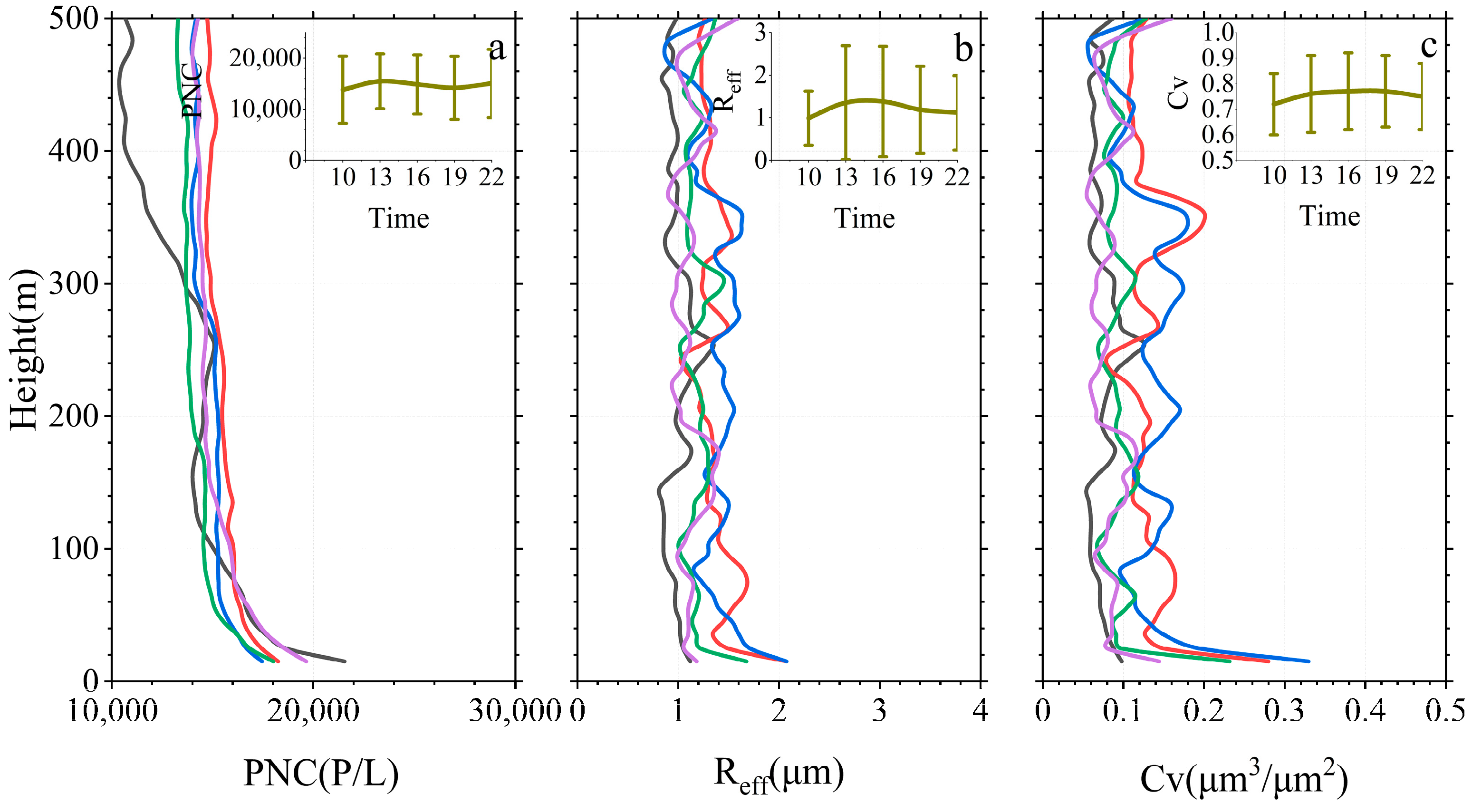
3.3. Diurnal Evolution
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Previous Studies
4.2. Vertical Characteristics of Postprecipitation Scenarios
4.3. The Importance of UAV Observations for Lidar Inversion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palacios-Pena, L.; Baro, R.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Brunner, D.; Jimenez-Guerrero, P. Evaluating the representation of aerosol optical properties using an online coupled model over the Iberian Peninsula. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kala, N.K.; Anand, N.S.; Manoj, M.R.; Pathak, H.S.; Moorthy, K.K.; Satheesh, S.K. Zonal variations in the vertical distribution of atmospheric aerosols over the Indian region and the consequent radiative effects. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 6067–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano, C.; Wiegner, M.; Gross, S.; Freudenthaler, V.; Gasteiger, J.; Mueller, D.; Mueller, T.; Schladitz, A.; Weinzierl, B.; Torres, B.; et al. Optical properties of aerosol mixtures derived from sun-sky radiometry during SAMUM-2. Tellus Ser. B-Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2011, 63, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Fu, C.; Chen, F.; Fu, Q.; Dai, A.; Shinoda, M.; Ma, Z.; Guo, W.; Li, Z.; et al. Dryland climate change: Recent progress and challenges. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 719–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, Z.; Li, M.; Shen, X.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Bi, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; et al. Vertical Structure of Dust Aerosols Observed by a Ground-Based Raman Lidar with Polarization Capabilities in the Center of the Taklimakan Desert. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, R.; Mao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ji, Z.; Gong, Y.; Guan, Y. Sources characteristics and climate impact of light-absorbing aerosols over the Tibetan Plateau. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 232, 104111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Cong, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B. The transboundary transport of air pollutants and their environmental impacts on Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull.-Chin. 2019, 64, 2876–2884. [Google Scholar]
- Gogoi, M.M.; Babu, S.S.; Pandey, S.K.; Nair, V.S.; Vaishya, A.; Girach, I.A.; Koushik, N. Scavenging ratio of black carbon in the Arctic and the Antarctic. Polar Sci. 2018, 16, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, K. Health Impact Assessment of Asian Dust/Cross-border Air Pollutant and Necessary Preventive Measure. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi Jpn. J. Hyg. 2017, 72, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhou, T.; Fang, S.; Zhou, X.; Han, B.; Bai, Y. The short-term effects of air pollutants on pneumonia hospital admissions in Lanzhou, China, 2014–2019: Evidence of ecological time-series study. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2022, 15, 2199–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, J. The Three-Dimensional Structure of Transatlantic African Dust Transport: A New Perspective from CALIPSO LIDAR Measurements. Adv. Meteorol. 2012, 2012, 850704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wang, Z.; Luo, T.; Yang, K.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, T.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Fu, Q. Seasonal Variation of Dust Aerosol Vertical Distribution in Arctic Based on Polarized Micropulse Lidar Measurement. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemba, L.D.; Thornhill, K.L.; Ferrare, R.; Barrick, J.; Beyersdorf, A.J.; Chen, G.; Crumeyrolle, S.N.; Hair, J.; Hostetler, C.; Hudgins, C.; et al. Airborne observations of aerosol extinction by in situ and remote-sensing techniques: Evaluation of particle hygroscopicity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wu, L.; Guo, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; et al. Measurement report: Vertical distribution of atmospheric particulate matter within the urban boundary layer in southern China—size-segregated chemical composition and secondary formation through cloud processing and heterogeneous reactions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 6435–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbussche, S.; Kochenova, S.; Vandaele, A.C.; Kumps, N.; De Maziere, M. Retrieval of desert dust aerosol vertical profiles from IASI measurements in the TIR atmospheric window. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2577–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangert, M.; Nenes, A.; Vogel, B.; Vogel, H.; Barahona, D.; Karydis, V.A.; Kumar, P.; Kottmeier, C.; Blahak, U. Saharan dust event impacts on cloud formation and radiation over Western Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 4045–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D. Atmosphere. Aerosols, clouds, and climate. Science 2006, 312, 1323–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creamean, J.M.; Primm, K.M.; Tolbert, M.A.; Hall, E.G.; Wendell, J.; Jordan, A.; Sheridan, P.J.; Smith, J.; Schnell, R.C. HOVERCAT: A novel aerial system for evaluation of aerosol-cloud interactions. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 3969–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.L.; Tegen, I. Radiative forcing of a tropical direct circulation by soil dust aerosols. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 2403–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, B.; Dubovik, O.; Toledano, C.; Berjon, A.; Cachorro, V.E.; Lapyonok, T.; Litvinov, P.; Goloub, P. Sensitivity of aerosol retrieval to geometrical configuration of ground-based sun/sky radiometer observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 847–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowottnick, E.; Colarco, P.; Ferrare, R.; Chen, G.; Ismail, S.; Anderson, B.; Browell, E. Online simulations of mineral dust aerosol distributions: Comparisons to NAMMA observations and sensitivity to dust emission parameterization. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D03202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, M.; Zhao, X.; Ke, Z.; Brown, H. Relative importance of high-latitude local and long-range-transported dust for Arctic ice-nucleating particles and impacts on Arctic mixed-phase clouds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 2909–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.; Nickovic, S.; Baldasano, J.M.; Sicard, M.; Rocadenbosch, F.; Cachorro, V.E. A long Saharan dust event over the western Mediterranean: Lidar, Sun photometer observations, and regional dust modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D15214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegen, I.; Lacis, A.A. Modeling of particle size distribution and its influence on the radiative properties of mineral dust aerosol. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 19237–19244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Deng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Bai, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhuoga, D.; Bian, J. Measurement report: Vertical profiling of particle size distributions over Lhasa, Tibet—tethered balloon-based in situ measurements and source apportionment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 6217–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, T.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Xie, M.; Zhuang, B. Lidar- and UAV-Based Vertical Observation of Spring Ozone and Particulate Matter in Nanjing, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3051. [Google Scholar]
- Song, R.-f.; Wang, D.-S.; Li, X.-B.; Li, B.; Peng, Z.-R.; He, H.-d. Characterizing vertical distribution patterns of PM2.5 in low troposphere of Shanghai city, China: Implications from the perspective of unmanned aerial vehicle observations. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 265, 118724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, W.; Song, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhi, X.; Yang, F.; Ma, M.; Zhou, C.; Yang, X.; Mamtimin, A.; He, Q. Relationships between Near-Surface Horizontal Dust Fluxes and Dust Depositions at the Centre and Edge of the Taklamakan Desert. Land 2022, 11, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, L.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Q.; Ding, X.; Hu, W.; Fu, P.; Zhang, D. Overview of primary biological aerosol particles from a Chinese boreal forest: Insight into morphology, size, and mixing state at microscopic scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Xie, H.; Bi, J.; Huang, Z.; Huang, J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, W. Lidar Measurements of Dust Aerosols during Three Field Campaigns in 2010, 2011 and 2012 over Northwestern China. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, B.; Wu, D.; Yang, H.; Mao, X.; Tan, J.; Liang, Y.; Sun, J.Y.; Xia, R.; Sun, J.; et al. Vertical profiling of black carbon and ozone using a multicopter unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) in urban Shenzhen of South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhou, T.; Fu, Q.; Huang, J.; Huang, Z.; Bi, J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, B.; Ge, J. Automated detection of cloud and aerosol features with SACOL micro-pulse lidar in northwest China. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 30732–30753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallet, M.; Dulac, F.; Formenti, P.; Nabat, P.; Sciare, J.; Roberts, G.; Pelon, J.; Ancellet, G.; Tanré, D.; Parol, F.; et al. Overview of the Chemistry-Aerosol Mediterranean Experiment/Aerosol Direct Radiative Forcing on the Mediterranean Climate (ChArMEx/ADRIMED) summer 2013 campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 455–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinzierl, B.; Petzold, A.; Esselborn, M.; Wirth, M.; Rasp, K.; Kandler, K.; Schuetz, L.; Koepke, P.; Fiebig, M. Airborne measurements of dust layer properties, particle size distribution and mixing state of Saharan dust during SAMUM 2006. Tellus Ser. B-Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2009, 61, 96–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesche, M.; Ansmann, A.; Mueller, D.; Althausen, D.; Mattis, I.; Heese, B.; Freudenthaler, V.; Wiegner, M.; Esselborn, M.; Pisani, G.; et al. Vertical profiling of Saharan dust with Raman lidars and airborne HSRL in southern Morocco during SAMUM. Tellus Ser. B-Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2009, 61, 144–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kezoudi, M.; Keleshis, C.; Antoniou, P.; Biskos, G.; Bronz, M.; Constantinides, C.; Desservettaz, M.; Gao, R.-S.; Girdwood, J.; Harnetiaux, J.; et al. The Unmanned Systems Research Laboratory (USRL): A New Facility for UAV-Based Atmospheric Observations. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kezoudi, M.; Tesche, M.; Smith, H.; Tsekeri, A.; Baars, H.; Dollner, M.; Estelles, V.; Buehl, J.; Weinzierl, B.; Ulanowski, Z.; et al. Measurement report: Balloon-borne in situ profiling of Saharan dust over Cyprus with the UCASS optical particle counter. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 6781–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knippertz, P.; Ansmann, A.; Althausen, D.; Mueller, D.; Tesche, M.; Bierwirth, E.; Dinter, T.; Mueller, T.; Von Hoyningen-Huene, W.; Schepanski, K.; et al. Dust mobilization and transport in the northern Sahara during SAMUM 2006—A meteorological overview. Tellus Ser. B-Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2009, 61, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Fang, Z.; Yang, H.; Cheng, L.; Chen, J.; Xie, C. UAVC: A New Method for Correcting Lidar Overlap Factors Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Vertical Detection. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wei, W.; Ruan, Z.; He, Q.; Ge, R. Application of wind-profiling radar data to the analysis of dust weather in the Taklimakan Desert. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 4819–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Liu, Y.; He, Q.; Zhong, X.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, F.; Huo, W.; Mamtimin, A.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Dust Characteristics Observed by Unmanned Aerial Vehicle over the Taklimakan Desert. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.P.; Minnis, P.; Yi, Y.H.; Tang, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.X.; Liu, Z.Y.; Ayers, K.; Trepte, C.; Winker, D. Summer dust aerosols detected from CALIPSO over the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L18805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X. Observation of Ground Temperature at Shallow Layer of Different Dune Types in the Tazhong Area. Arid. Zone Res. 2011, 28, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Merino, C.; Mateos, D.; Toledano, C.; Prospero, J.M.; Molinie, J.; Euphrasie-Clotilde, L.; Gonzalez, R.; Cachorro, V.E.; Calle, A.; de Frutos, A.M. Impact of long-range transport over the Atlantic Ocean on Saharan dust optical and microphysical properties based on AERONET data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 9411–9424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, D.; Lee, K.H.; Gasteiger, J.; Tesche, M.; Weinzierl, B.; Kandler, K.; Mueller, T.; Toledano, C.; Otto, S.; Althausen, D.; et al. Comparison of optical and microphysical properties of pure Saharan mineral dust observed with AERONET Sun photometer, Raman lidar, and in situ instruments during SAMUM 2006. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D07211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET). Publications—Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET). Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Tong, X.; Ho, J.M.W.; Li, Z.; Lui, K.H.; Kwok, T.C.Y.; Tsoi, K.K.F.; Ho, K.F. Prediction model for air particulate matter levels in the households of elderly individuals in Hong Kong. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 135323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Chen, Q.; Qi, D.; Xu, L.; Wang, J. A Case Analysis of Dust Weather and Prediction of PM10 Concentration Based on Machine Learning at the Tibetan Plateau. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y. Research on the characteristics of dusty weather and floating dust observation standards in Dalian. J. Desert Res. 2010, 30, 1229–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, W.; He, Q.; Yang, F.; Yang, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Mamtimin, A.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Observed particle sizes and fluxes of Aeolian sediment in the near surface layer during sand-dust storms in the Taklamakan Desert. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 130, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, X.; Fang, S.; Huang, J.; He, Q.; Huang, Z.; Wang, M. A New Algorithm of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height Determined from Polarization Lidar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, L.; Xue, Y.; Guang, J.; Che, Y.; Fan, C.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y. Towards a comprehensive view of dust events from multiple satellite and ground measurements: Exemplified by the May 2017 East Asian dust storm. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 3187–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crumeyrolle, S.; Schwarzenboeck, A.; Roger, J.C.; Sellegri, K.; Burkhart, J.F.; Stohl, A.; Gomes, L.; Quennehen, B.; Roberts, G.; Weigel, R.; et al. Overview of aerosol properties associated with air masses sampled by the ATR-42 during the EUCAARI campaign (2008). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4877–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinzierl, B.; Sauer, D.; Esselborn, M.; Petzold, A.; Veira, A.; Rose, M.; Mund, S.; Wirth, M.; Ansmann, A.; Tesche, M.; et al. Microphysical and optical properties of dust and tropical biomass burning aerosol layers in the Cape Verde region-an overview of the airborne in situ and lidar measurements during SAMUM-2. Tellus Ser. B-Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2011, 63, 589–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, I.N.; Munkelwitz, H.R. Composition and temperature dependence of the deliquescence properties of hygroscopic aerosols. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1993, 27, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionisi, D.; Barnaba, F.; Diemoz, H.; Di Liberto, L.; Gobbi, G.P. A multiwavelength numerical model in support of quantitative retrievals of aerosol properties from automated lidar ceilometers and test applications for AOT and PM10 estimation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 6013–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Clear Sky | Floating Dust | Blowing Sand | Dust Storm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM10 (μg/m3) | 0–150 | 150–350 | 350–500 | >500 |
| Parameter | Flights | PNC P/L | Reff µm | Cv µm3/µm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 200 | 21,290 ± 3046 | 1.47 ± 1.48 | 0.16 ± 0.34 |
| Clear sky | 149 | 14,712 ± 1877 | 1.22 ± 1.12 | 0.11 ± 0.17 |
| Floating dust | 33 | 31,034 ± 4391 | 1.81 ± 1.86 | 0.28 ± 0.60 |
| Blowing sand | 4 | 64,447 ± 15,400 | 2.43 ± 2.13 | 0.35 ± 0.47 |
| Dust storm | 8 | 83,297 ± 12,881 | 3.86 ± 1.44 | 0.54 ± 0.30 |
| Postprecipitation | 6 | 16,867 ± 2885 | 1.86± 2.45 | 0.33 ± 0.70 |
| Land Type | Size Range µm | PNC P/L | Reff µm | Cv µm3/µm2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| She et al. (2018) [52] | Urban | --- | --- | 1–1.8 | --- |
| Crumeyrolle et al. (2013) [53] | Urban | --- | --- | --- | 0.005–0.47 |
| unpublished results | Urban | 229,720 | 0.87 | 0.01 | |
| Kezoudi et al. (2021) [37] | Forest | 0.5–50.0 | 1000–30,000 | 2.4 | --- |
| Weinzierl et al. (2011) [54] | Desert | 0.1–30 | 83,300 | 2.47 | --- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Zhou, T.; Fang, S.; Han, B.; He, Q. Investigation of the Vertical Distribution Characteristics and Microphysical Properties of Summer Mineral Dust Masses over the Taklimakan Desert Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143556
Zhou X, Zhou T, Fang S, Han B, He Q. Investigation of the Vertical Distribution Characteristics and Microphysical Properties of Summer Mineral Dust Masses over the Taklimakan Desert Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(14):3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143556
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xiaowen, Tian Zhou, Shuya Fang, Bisen Han, and Qing He. 2023. "Investigation of the Vertical Distribution Characteristics and Microphysical Properties of Summer Mineral Dust Masses over the Taklimakan Desert Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle" Remote Sensing 15, no. 14: 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143556
APA StyleZhou, X., Zhou, T., Fang, S., Han, B., & He, Q. (2023). Investigation of the Vertical Distribution Characteristics and Microphysical Properties of Summer Mineral Dust Masses over the Taklimakan Desert Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Remote Sensing, 15(14), 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143556







