Developing a Pixel-Scale Corrected Nighttime Light Dataset (PCNL, 1992–2021) Combining DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data
3. Methods
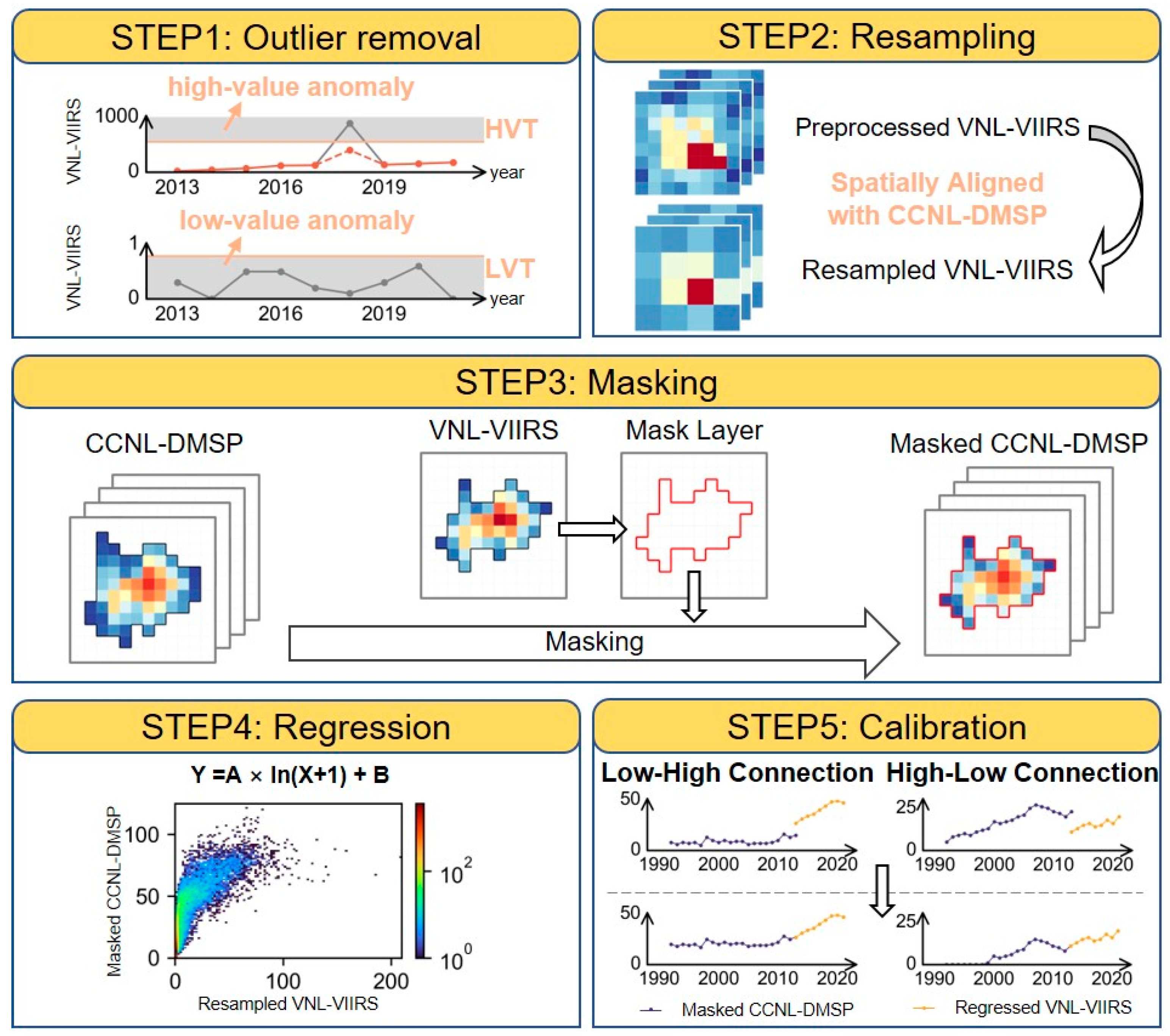
3.1. Production Process of PCNL
- STEP 1: Outlier removal
- STEP 2: Resampling
- STEP 3: Masking
- STEP 4: Regression
- STEP 5: Calibration at the pixel-scale
3.2. Evaluation Methods of Global NTL Products
4. Results
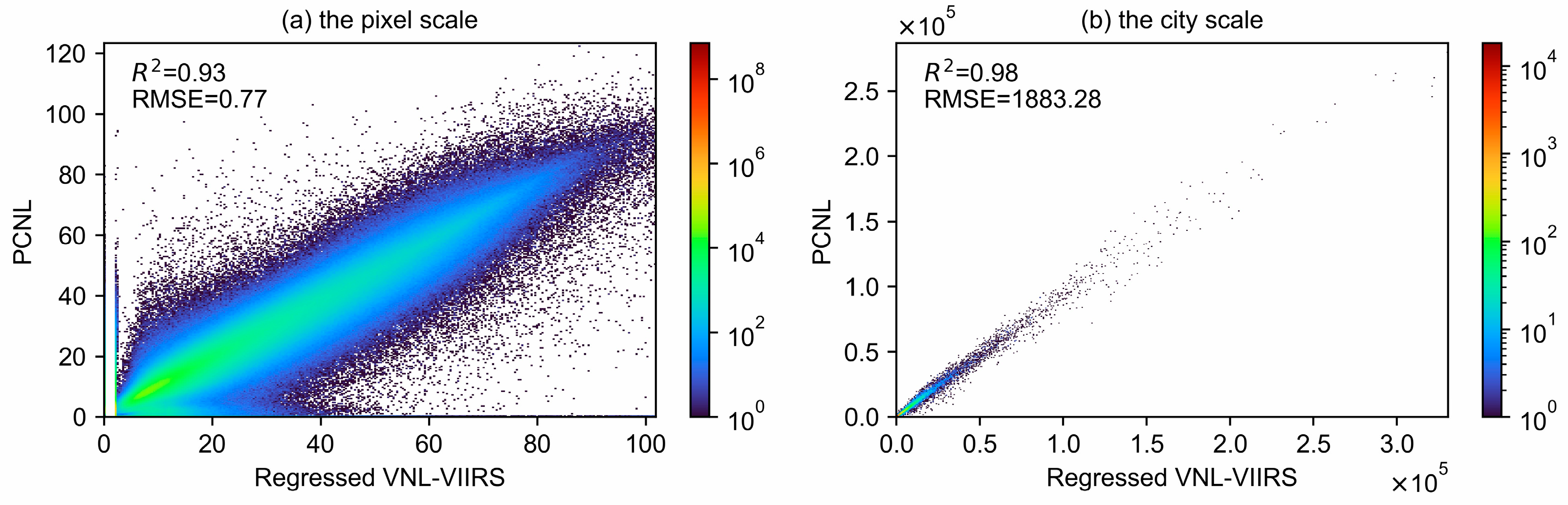
4.1. Overall Accuracy
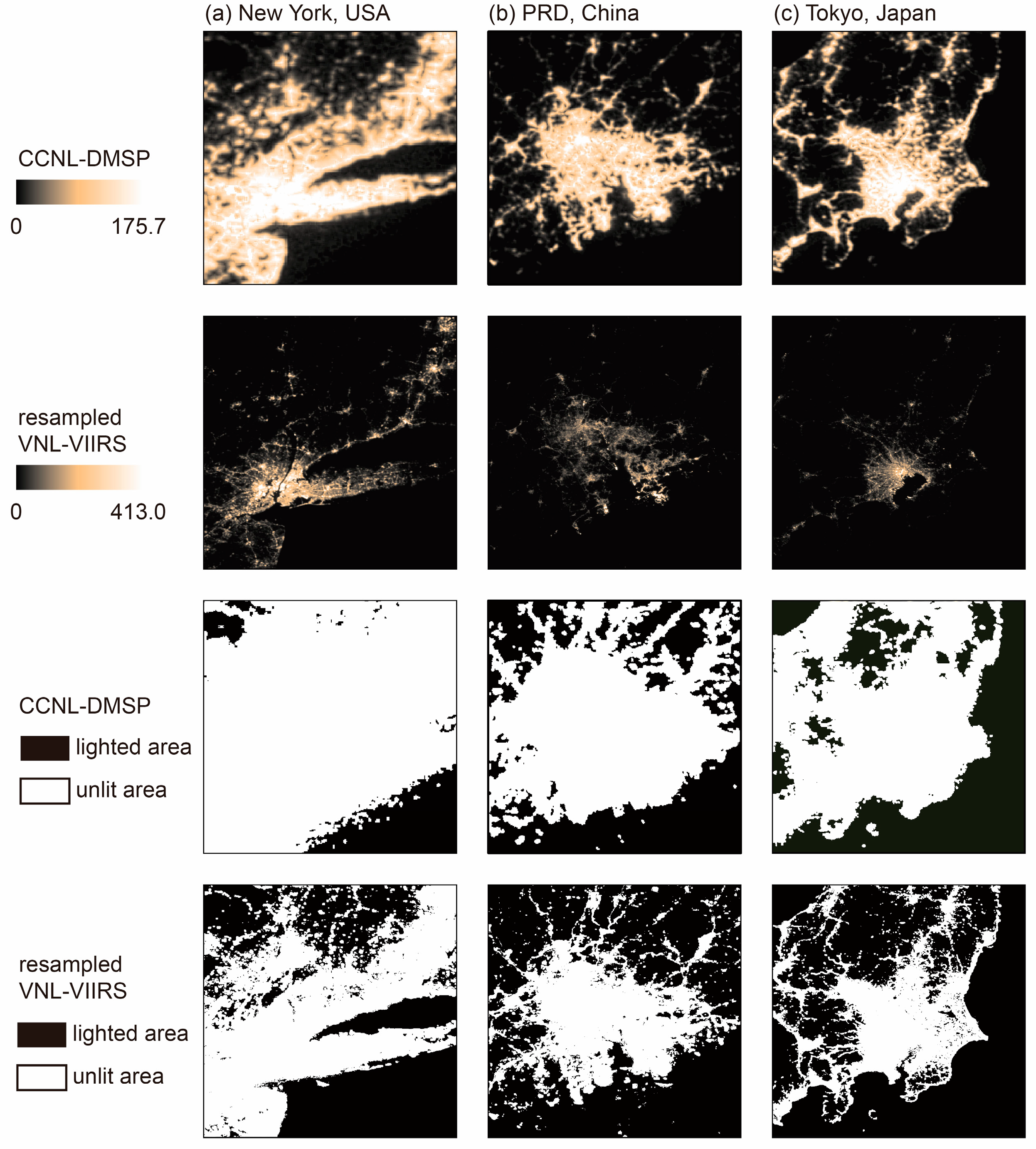
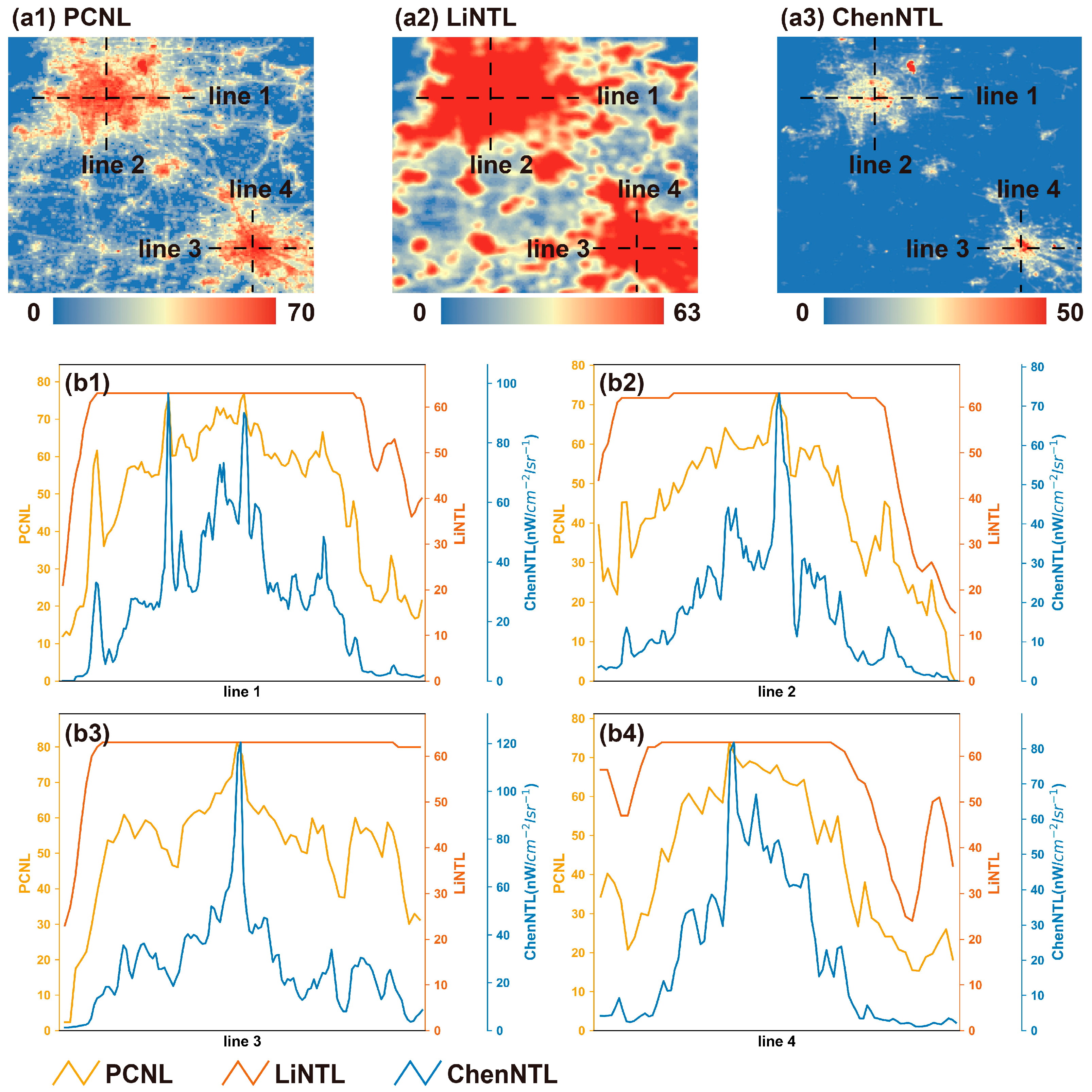
4.2. Evaluation of Spatial Consistency
4.3. Evaluation of Temporal Consistency at Regional Scales
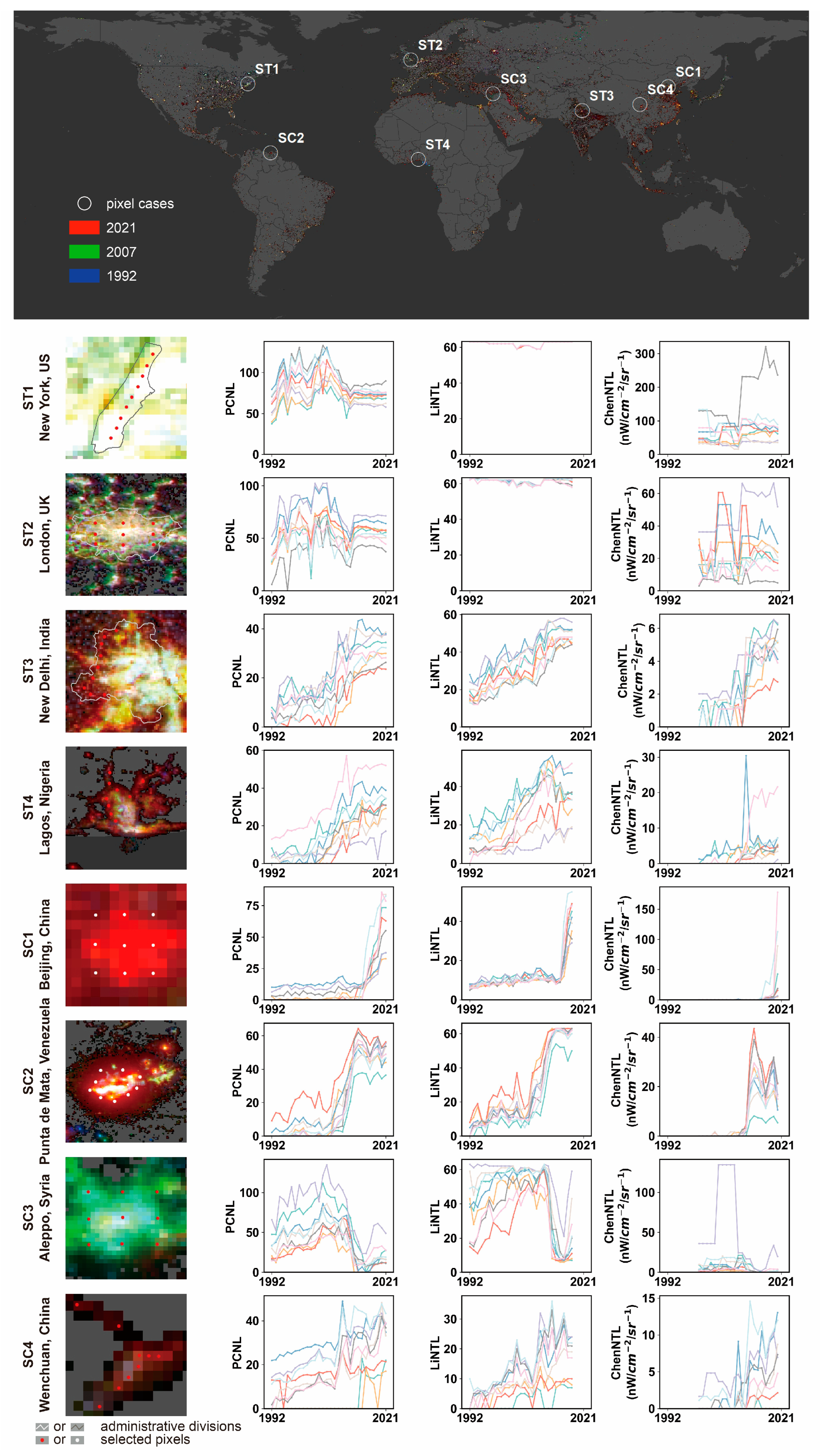
4.4. Evaluation of Temporal Consistency at the Pixel-Scale
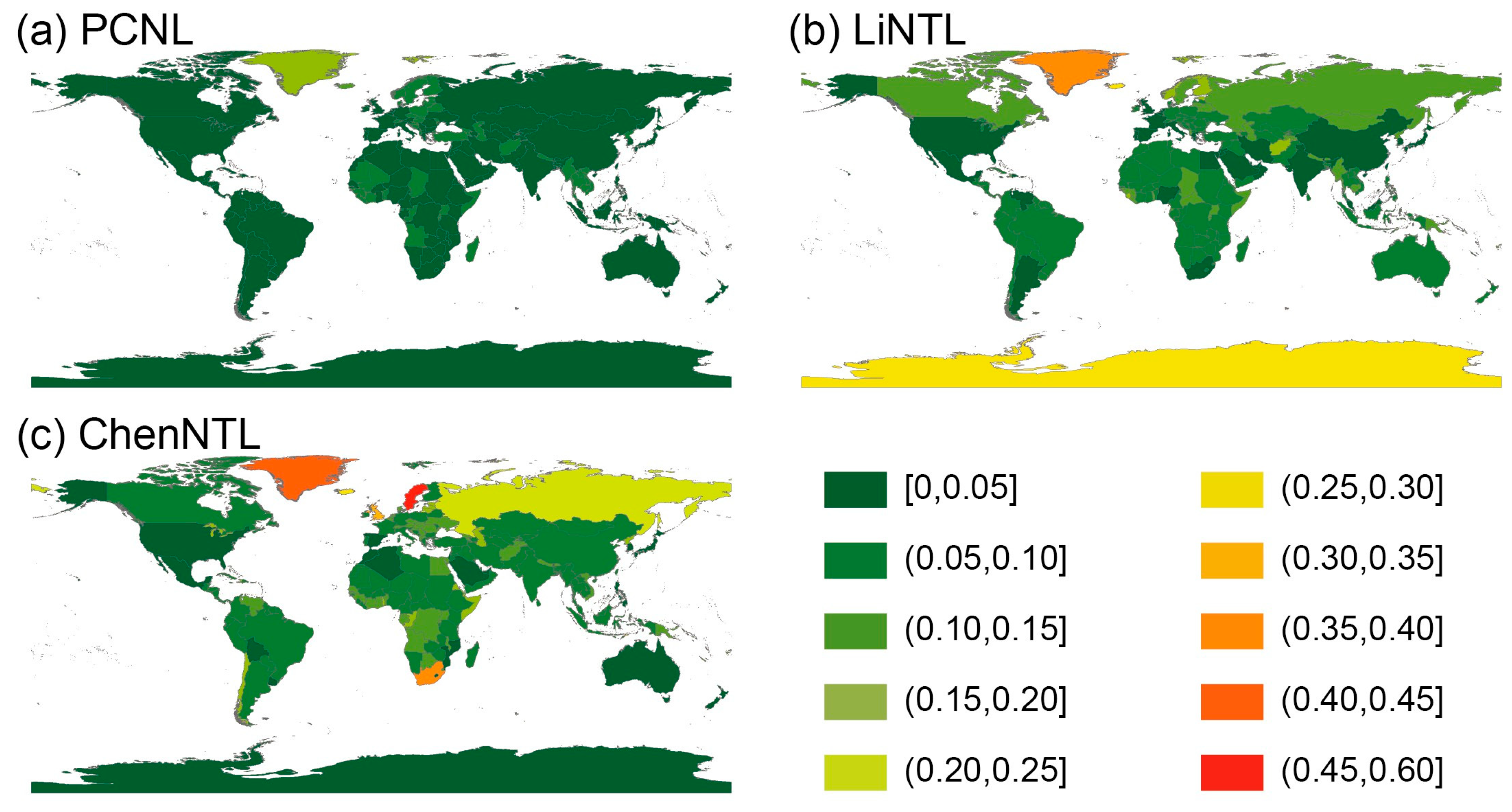
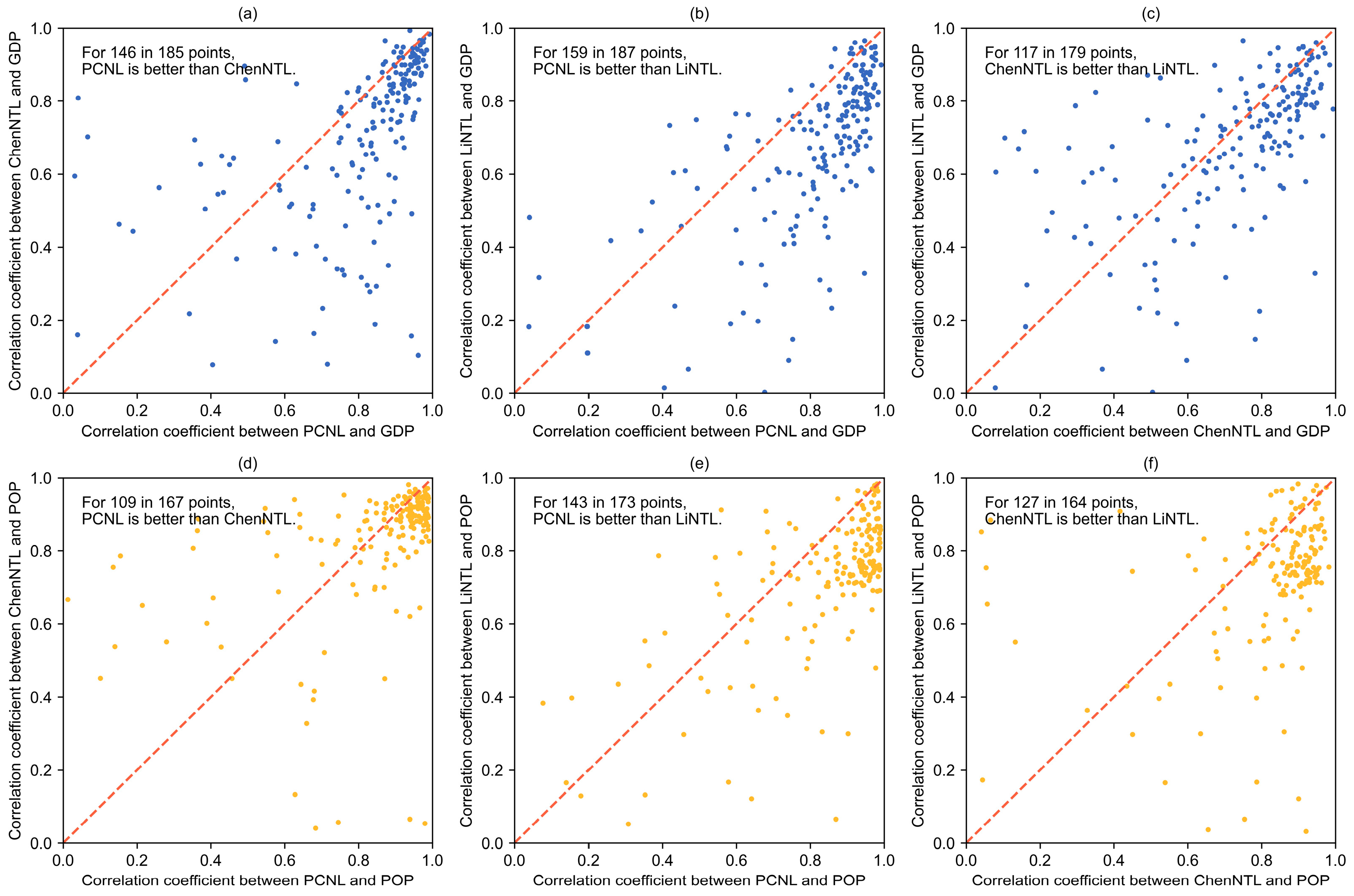
4.5. Applicability in the Socio-Economic Field
5. Discussion
5.1. Comprehensive Comparison of the Three NTL Products
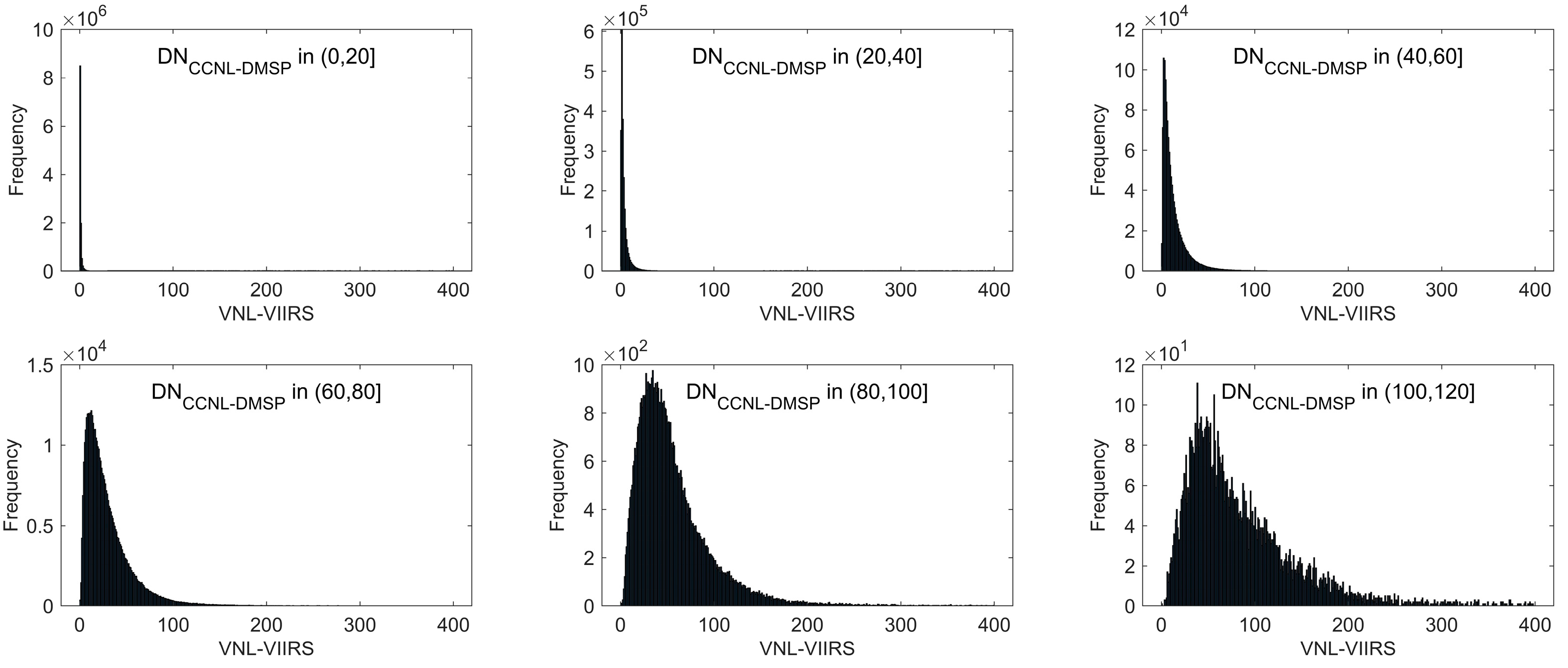
5.2. Understanding of the Role of PCNL Production Steps
5.3. Limitations of PCNL
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Imura, H.; Higashi, O. A SVM-Based Method to Extract Urban Areas from DMSP-OLS and SPOT VGT Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2205–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, K.C. Mapping Urbanization Dynamics at Regional and Global Scales Using Multi-Temporal DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.; He, C. Quantifying Spatiotemporal Patterns of Shrinking Cities in Urbanizing China: A Novel Approach Based on Time-Series Nighttime Light Data. Cities 2021, 118, 103346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Xia, P.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H. Quantifying Urbanization Levels on the Tibetan Plateau with High-Resolution Nighttime Light Data. Geogr. Sustain. 2020, 1, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, W. Dasymetric Mapping of Urban Population in China Based on Radiance Corrected DMSP-OLS Nighttime Light and Land Cover Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Xin, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Xiang, W. Modeling Population Density Based on Nighttime Light Images and Land Use Data in China. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 90, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y. Improving Population Mapping Using Luojia 1-01 Nighttime Light Image and Location-Based Social Media Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, V.; Storeygard, A.; Weil, D.N. A Bright Idea for Measuring Economic Growth. Am. Econ. Rev. 2011, 101, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, B.; Shi, K.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Poverty Evaluation Using NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Composite Data at the County Level in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.; Gaba, K.M.; Sarr, O.F.; Agalassou, A. Detection of Rural Electrification in Africa Using DMSP-OLS Night Lights Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 8118–8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Shi, F. Spatialization of Electricity Consumption of China Using Saturation-Corrected DMSP-OLS Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 28, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Huang, B.; Li, S.; Lin, Y. Estimation and Analysis of the Nighttime PM2.5 Concentration Based on LJ1-01 Images: A Case Study in the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration of China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ghosh, T.; Hsu, F.-C.; Zhizhin, M.; Bazilian, M. The Dimming of Lights in China during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D. Can Night-Time Light Images Play a Role in Evaluating the Syrian Crisis? Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6648–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.M.; Smith, L.C. Advances in Using Multitemporal Night-Time Lights Satellite Imagery to Detect, Estimate, and Monitor Socioeconomic Dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 176–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Pandey, B.; Seto, K.C. A Robust Method to Generate a Consistent Time Series From DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5821–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y. A Stepwise Calibration of Global DMSP/OLS Stable Nighttime Light Data (1992–2013). Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Z.; Zhu, X.; Cao, X.; Chen, J. Measurement of Blooming Effect of DMSP-OLS Nighttime Light Data Based on NPP-VIIRS Data. Ann. GIS 2019, 25, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Shi, F.; Zhuo, L.; Chen, J. A Simple Self-Adjusting Model for Correcting the Blooming Effects in DMSP-OLS Nighttime Light Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Román, M.; Kalb, V.; Shrestha, R.; Stokes, E.; Paynter, I. Uncertainties in VIIRS Nighttime Light Time Series Analysis. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020–2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Online, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 156–159. [Google Scholar]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C.; Ghosh, T. VIIRS Night-Time Lights. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5860–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Xu, T. Nighttime Light Derived Assessment of Regional Inequality of Socioeconomic Development in China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1242–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, H.; Yang, J.; Xue, B.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.; Jin, C.; Li, X. Spatial Evolution of Population Change in Northeast China during 1992–2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 146023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Seto, K.C.; Zhou, Y.; You, S.; Weng, Q. Nighttime Light Remote Sensing for Urban Applications: Progress, Challenges, and Prospects. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 202, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, S.; Qian, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Wu, J. An Extended Time Series (2000–2018) of Global NPP-VIIRS-like Nighttime Light Data from a Cross-Sensor Calibration. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Wu, C. Intercalibration between DMSP/OLS and VIIRS Night-Time Light Images to Evaluate City Light Dynamics of Syria’s Major Human Settlement during Syrian Civil War. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5934–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ma, M.; Yang, H.; Ge, W. Modeling the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Gross Domestic Product in China Using Extended Temporal Coverage Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Global Nighttime Light Change from 1992 to 2017: Brighter and More Uniform. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ji, G.; Yue, Y.; Lai, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, D.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Urban Residential CO2 Emissions and Their Driving Forces in China Using the Integrated Two Nighttime Light Datasets. Appl. Energy 2019, 235, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-H.K.; Prishchepov, A.V.; Fensholt, R.; Sabel, C.E. Detecting and Monitoring Long-Term Landslides in Urbanized Areas with Nighttime Light Data and Multi-Seasonal Landsat Imagery across Taiwan from 1998 to 2017. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, W.; Li, M.; Huang, K. Building a Series of Consistent Night-Time Light Data (1992–2018) in Southeast Asia by Integrating DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 1843–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Weng, Q.; Wang, K. Developing a New Cross-Sensor Calibration Model for DMSP-OLS and Suomi-NPP VIIRS Night-Light Imageries. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 153, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, X. A Harmonized Global Nighttime Light Dataset 1992–2018. Sci Data 2020, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Cao, X.; Chen, X.; Cui, X. A Consistent and Corrected Nighttime Light Dataset (CCNL 1992–2013) from DMSP-OLS Data. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Cao, X. A Pixel-Scale Corrected Nighttime Light Dataset (PCNL, 1992–2021) Combining DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. Zenodo. 2023. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7612389 (accessed on 7 July 2023).
- Wu, J.; He, S.; Peng, J.; Li, W.; Zhong, X. Intercalibration of DMSP-OLS Night-Time Light Data by the Invariant Region Method. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 7356–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Cao, X.; Chen, X.; Cui, X.; Gan, L. Correcting the Saturation Effect in DMSP/OLS Stable Nighttime Light Products Based on Radiance-Calibrated Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5602011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M.; Ghosh, T.; Hsu, F.-C.; Taneja, J. Annual Time Series of Global VIIRS Nighttime Lights Derived from Monthly Averages: 2012 to 2019. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J. Responses of Suomi-NPP VIIRS-Derived Nighttime Lights to Socioeconomic Activity in China’s Cities. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Ghosh, T.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C.; Sparks, T.; Bazilian, M.; Sutton, P.C.; Houngbedji, K.; Goldblatt, R. Fifty Years of Nightly Global Low-Light Imaging Satellite Observations. Front. Remote Sens. 2022, 3, 919937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Marinello, F. The Interannual Calibration and Global Nighttime Light Fluctuation Assessment Based on Pixel-Level Linear Regression Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Kihn, E.A.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E.R.; Davis, C.W. Relation between Satellite Observed Visible-near Infrared Emissions, Population, Economic Activity and Electric Power Consumption. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Zhou, T.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, S. The Relationship between Night-Time Light and Socioeconomic Factors in China and India. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theil, H. A Rank-Invariant Method of Linear and Polynomial Regression Analysis. In Henri Theil’s Contributions to Economics and Econometrics: Econometric Theory and Methodology; Raj, B., Koerts, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 345–381. ISBN 978-94-011-2546-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, K.H.; Ramachandra Rao, A. A Modified Mann-Kendall Trend Test for Autocorrelated Data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Gupta, P.K.; Srivastav, S.K. Inter-Calibration of DMSP-OLS and SNPP-VIIRS-DNB Annual Nighttime Light Composites Using Machine Learning. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 1144–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cao, J.; Zhuo, L.; Shi, Q. A Novel Consistency Calibration Method for DMSP-OLS Nighttime Stable Light Time-Series Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2621–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Role | Datasets | Time Range | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production of PCNL | CCNL-DMSP | 1992–2013 | Zhao et al., 2022 [34] |
| VNL-VIIRS | April 2012–2021 | Earth Observation Group (https://eogdata.mines.edu/nighttime_light/annual/v21/) (accessed on 7 July 2023) | |
| Comparison with PCNL | ChenNTL | 2000–2020 | Chen et al., 2021 [25] |
| LiNTL | 1992–2018 | Li et al., 2020 [33] | |
| Examination of PCNL | GDP | 1992–2021 | World Bank (https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.CD) (accessed on 7 July 2023) |
| POP | 1992–2021 | World Bank (https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.TOTL) (accessed on 7 July 2023) | |
| Statistics and graphing | national administrative division data | Latest | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/data.aspx?DATAID=205) (accessed on 7 July 2023) |
| municipal administrative division data | Latest | Database of Global Administrative Areas (https://gadm.org/download_world.html) (accessed on 7 July 2023) |
| Evaluation Perspectives | PCNL | LiNTL | ChenNTL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time Horizon | 1992–2021 (updating) | 1992–2018 | 2000–2020 (updating) |
| Spatial Extent | Global | Global | Global |
| Spatial Resolution | 30 arc seconds (~1 km) | 30 arc seconds (~1 km) | 15 arc seconds (~500 m) |
| Overall Accuracy | Pixel-scale: R2 = 0.93, RMSE = 0.77 City scale: R2 = 0.98, RMSE = 1883.28 | Pixel-scale: R2 ≈ 0.5 in China | Pixel-scale: R2 = 0.87, RMSE = 2.96 nWcm−2sr−1 City scale: R2 = 0.95, RMSE = 3024.62 nWcm−2sr−1 |
| Spatial Consistency | Stable | Stable but saturated | Stable |
| Regional Temporal Consistency | Global: ANDI = 0.023 Developing regions: stable Developed regions: fluctuating then stable War regions: able to detect changes | Global: ANDI = 0.046 Developing regions: stable Developed region: saturated, with unreasonable abrupt changes War regions: able to detect changes | Global: ANDI = 0.042 Developing regions: stable Developed regions: fluctuating, with unreasonable abrupt changes War regions: able to detect changes |
| Pixel Temporal Consistency | Advantages: able to display stable trends and detect sudden changes Disadvantage: existence of interannual fluctuation, but acceptable | Advantages: able to display stable trends in low-value regions and detect sudden changes Disadvantage: disable to compare differences of values in high-value regions due to saturation | Advantages: able to display general trends and detect sudden changes Disadvantage: existence of many unreasonable abrupt changes and fluctuation over a larger range |
| Applicability in the socio-economic field | Global: r = 0.945 with GDP, r = 0.971 with POP Country scale: better than LiNTL and ChenNTL for both GDP and POP | Global: r = 0.776 with GDP, r = 0.815 with POP Country scale: worse than PCNL and ChenNTL for both GDP and POP | Global: r = 0.881 with GDP, r = 0.937 with POP Country scale: better than LiNTL, slightly worse than PCNL, for both GDP and POP |
| Types Identified by PCNL | Types Identified by Unmasked and Uncalibrated CCNL-DMSP and Regressed VNL-VIIRS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Significant Increase | Non-Significant Increase | Significant Decrease | Non-Significant Decrease | |
| Significant increase | 84.4% | 8.1% | 0.9% | 6.6% |
| Non-significant increase | 48.7% | 20.3% | 11.8% | 19.2% |
| Significant decrease | 12.3% | 15.7% | 54.2% | 17.8% |
| Non-significant decrease | 28.4% | 17.9% | 28.1% | 25.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Cao, X.; Zhao, C.; Jie, N.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Cui, X. Developing a Pixel-Scale Corrected Nighttime Light Dataset (PCNL, 1992–2021) Combining DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15163925
Li S, Cao X, Zhao C, Jie N, Liu L, Chen X, Cui X. Developing a Pixel-Scale Corrected Nighttime Light Dataset (PCNL, 1992–2021) Combining DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(16):3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15163925
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shijie, Xin Cao, Chenchen Zhao, Na Jie, Luling Liu, Xuehong Chen, and Xihong Cui. 2023. "Developing a Pixel-Scale Corrected Nighttime Light Dataset (PCNL, 1992–2021) Combining DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS" Remote Sensing 15, no. 16: 3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15163925
APA StyleLi, S., Cao, X., Zhao, C., Jie, N., Liu, L., Chen, X., & Cui, X. (2023). Developing a Pixel-Scale Corrected Nighttime Light Dataset (PCNL, 1992–2021) Combining DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. Remote Sensing, 15(16), 3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15163925








