Deciphering China’s Socio-Economic Disparities: A Comprehensive Study Using Nighttime Light Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- What does nighttime light data reveal about the spatial and temporal patterns of socio-economic development disparities across the Hu Line?
- How have these socio-economic development disparities evolved over time, considering factors like urbanization, ecological changes, and resource endowment?
- Can the use of nighttime light data offer a detailed understanding of socio-economic development dynamics in China’s coastal regions as compared to the western areas along the Hu Line?
2. Materials and Methods
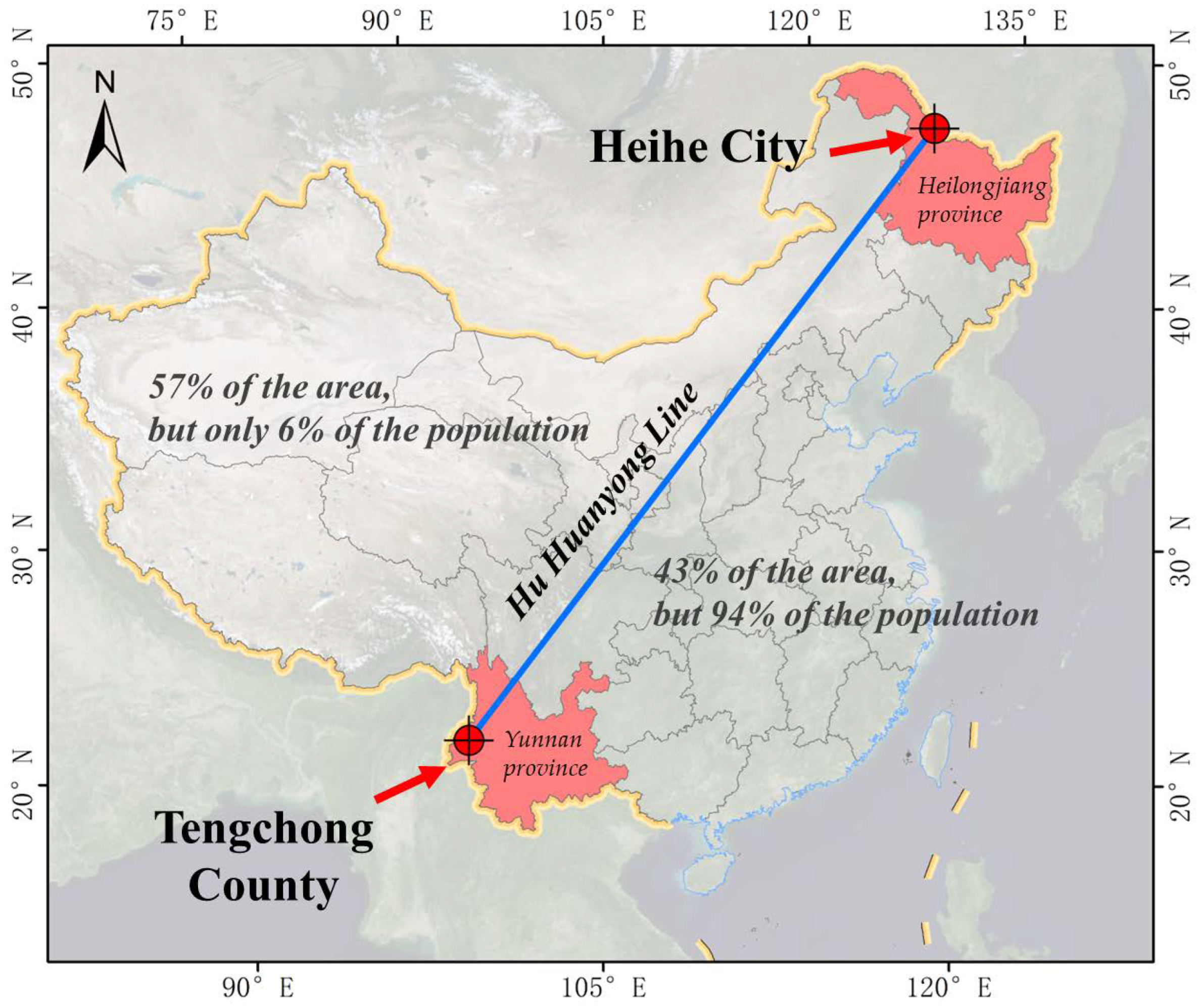
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.2.1. Nighttime Light Data
2.2.2. Vegetation Index Data
2.3. Exploratory Data Analysis
2.3.1. Analyzing Developmental Trends
2.3.2. Spatial-Temporal Economic Center
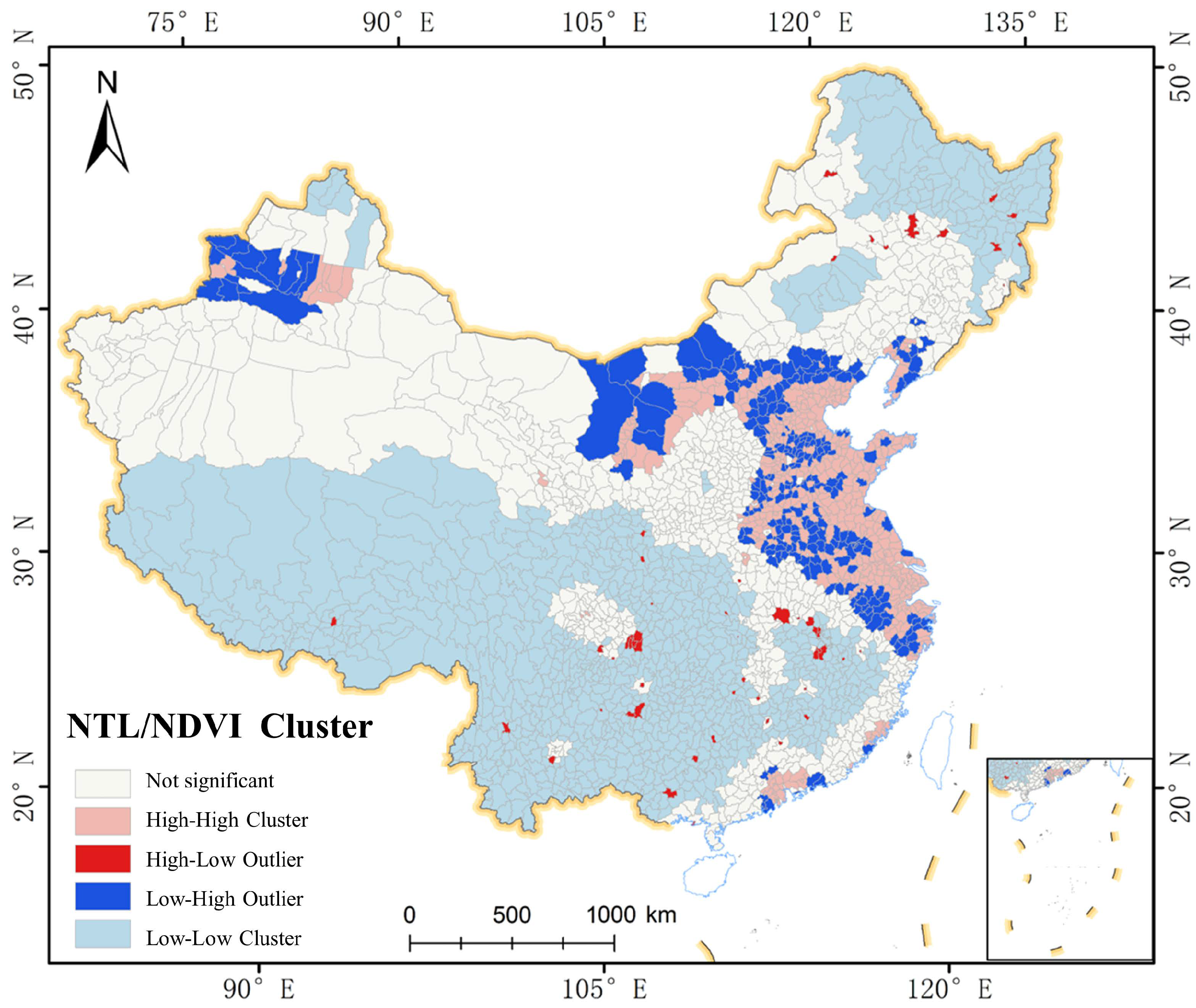
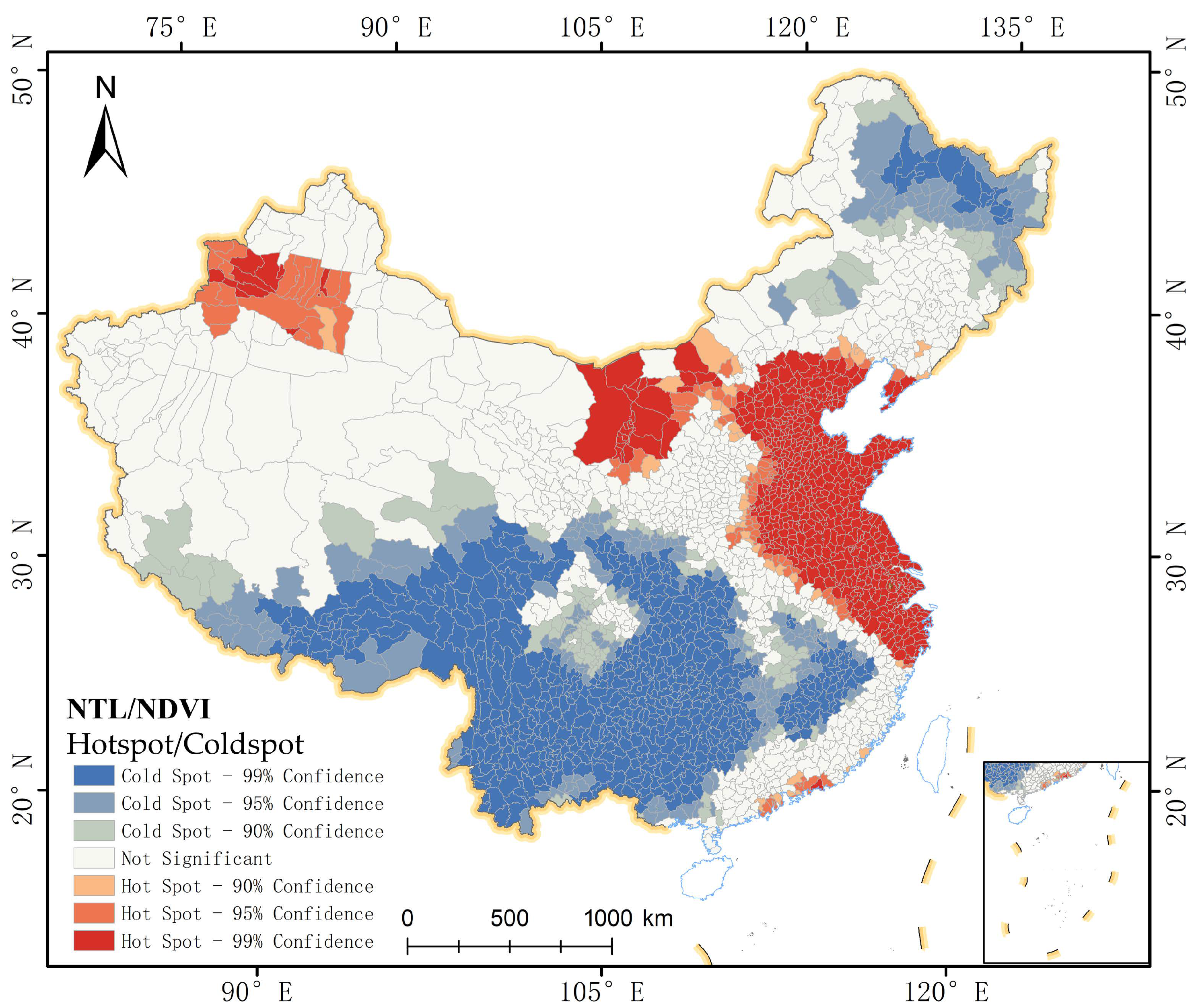
2.3.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
2.3.4. Nightlight-Vegetation Ratio Index
2.3.5. Gini Coefficient
3. Results
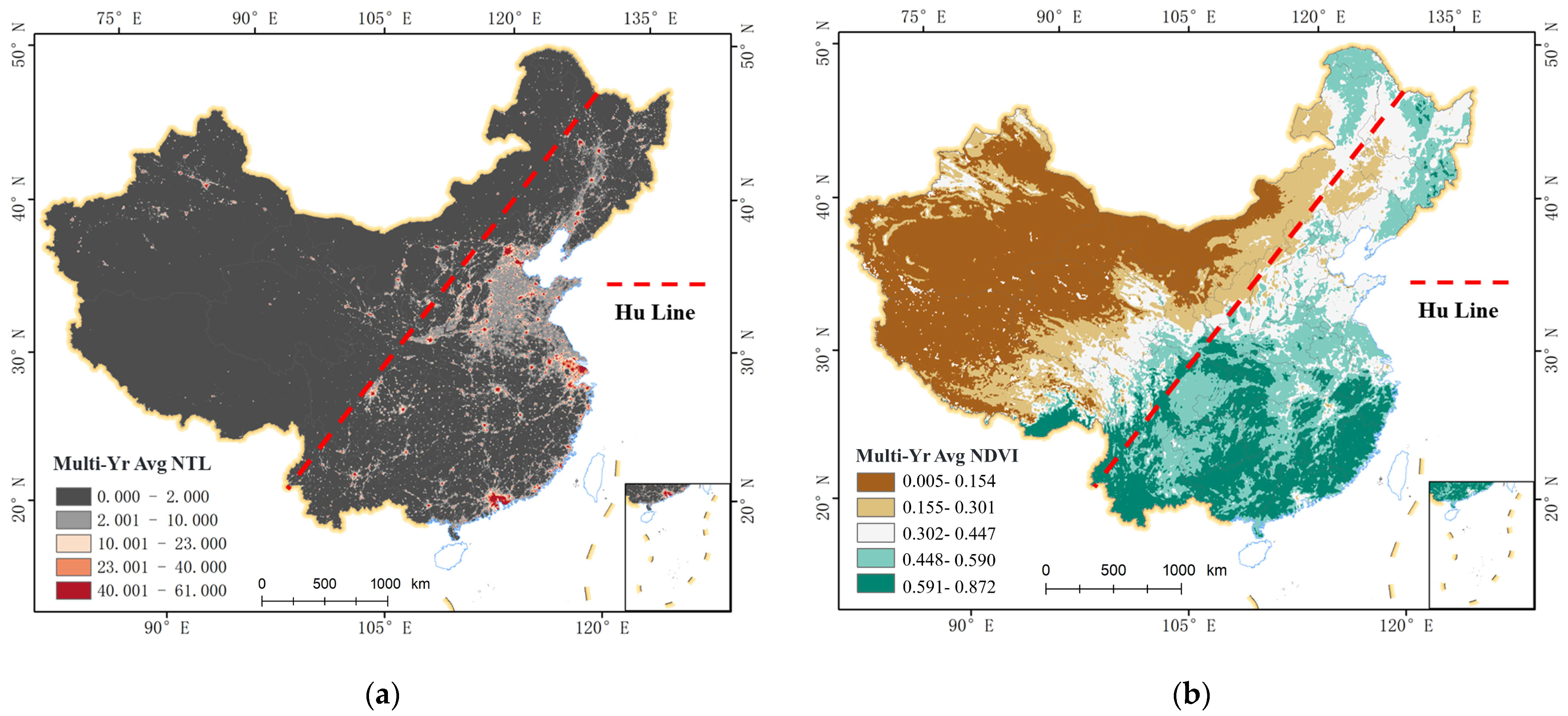
3.1. Spatial-Temporal Patterns of Nighttime Lights and Green Spaces
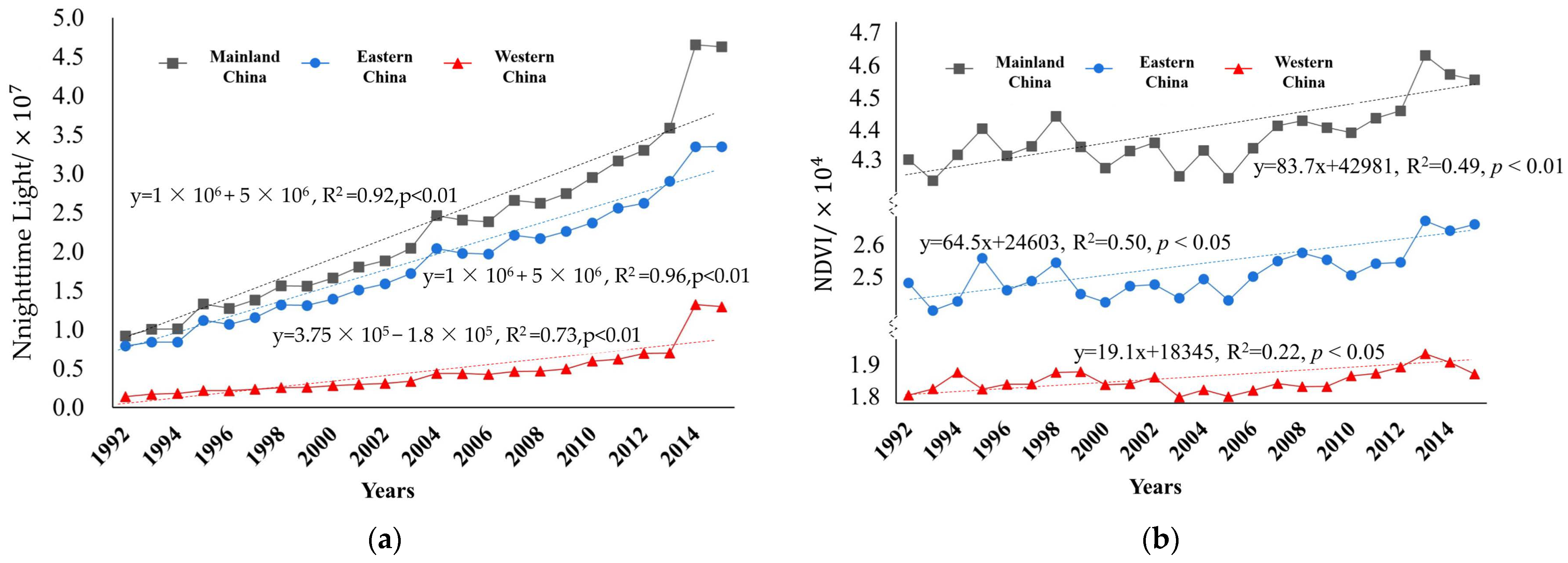
3.2. Long-Term Trends in Nighttime Lights and Green Spaces
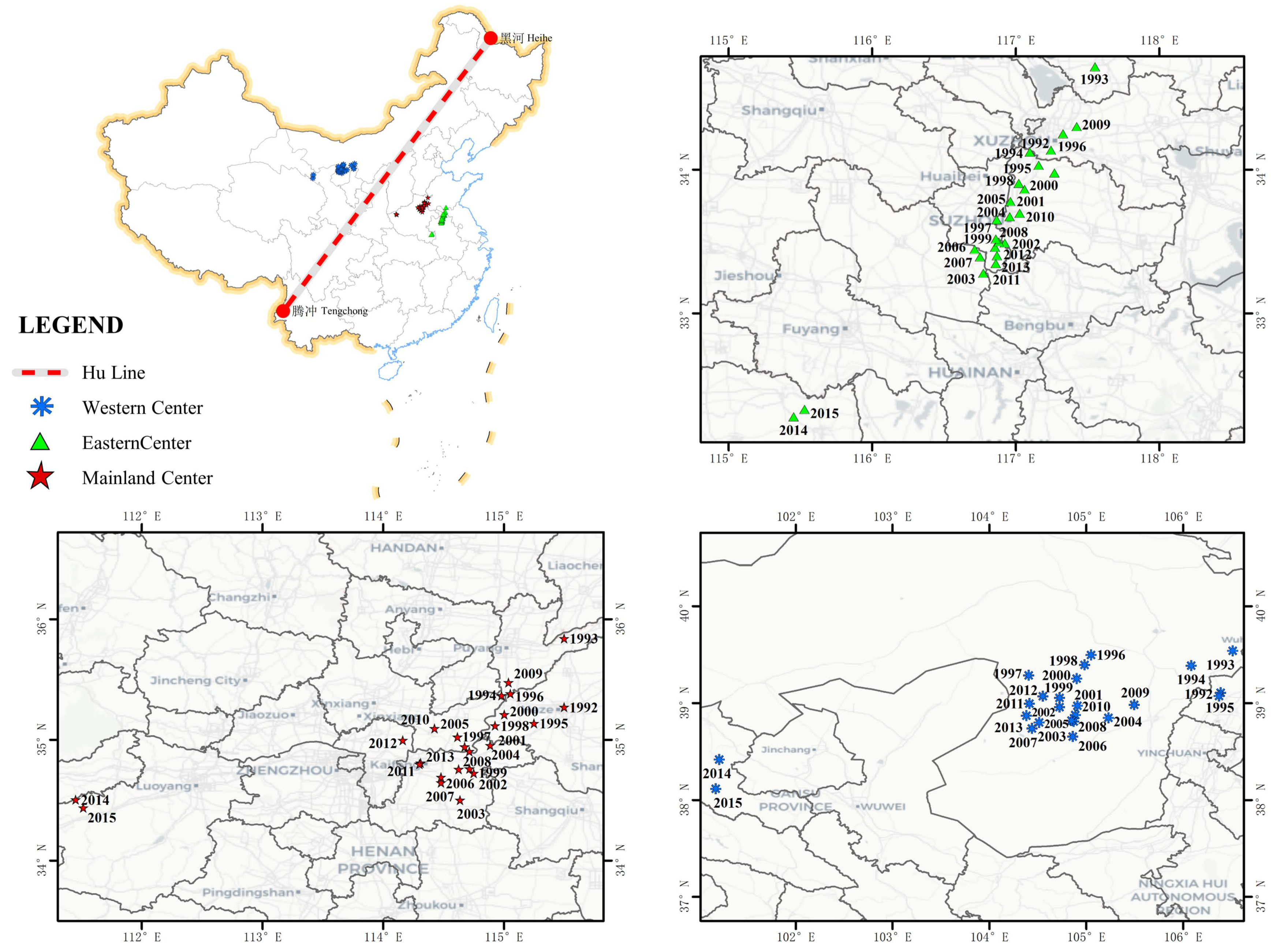
3.3. Spatial-Temporal Economic Center of Gravity
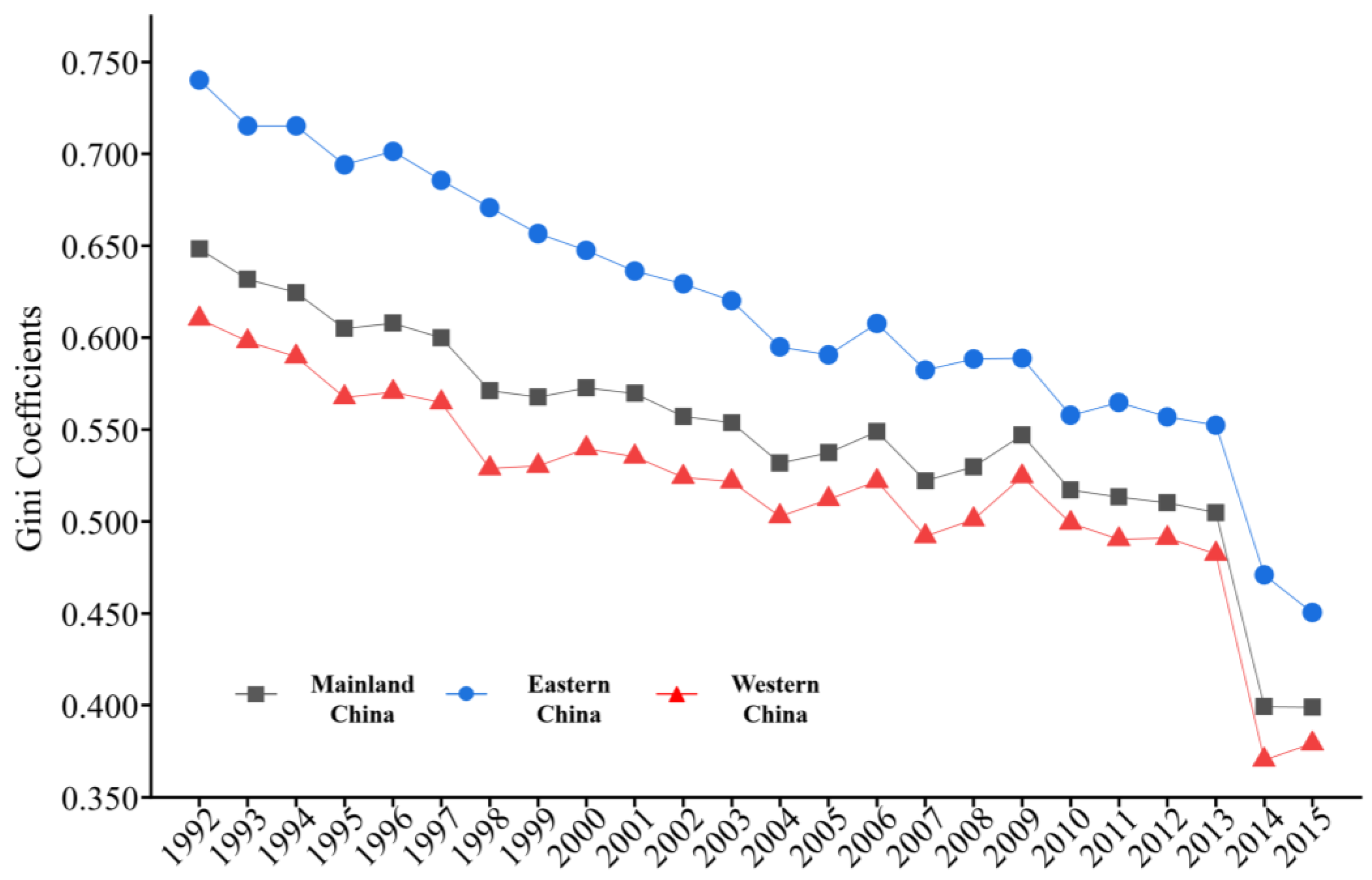
3.4. Gini Coefficient Tracking Inequalities
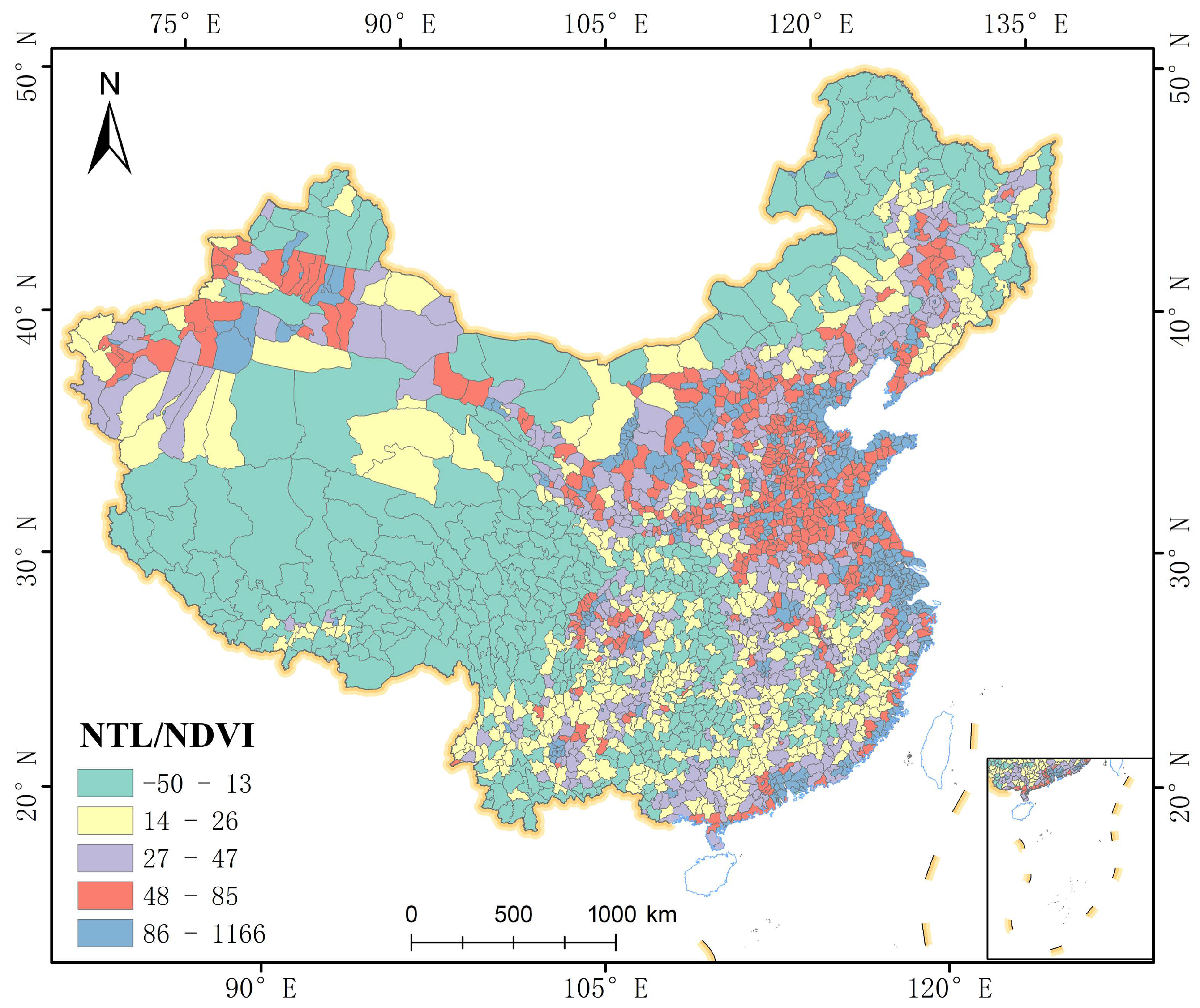
3.5. Interactions between Development and Green Spaces the NTL/NDVI Index
4. Discussion
4.1. Disparities in Development: A Closer Look at Coastal and Western Nighttime Lights
4.2. Comparison with Established Baselines
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Province | Nighttime Light | NDVI Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Jiangsu | 101,533 | 0.95 |
| Shandong | 92,666 | 3.22 |
| Xinjiang | 87,761 | −1.60 |
| Inner Mongolia | 79,558 | 1.32 |
| Guangdong | 78,660 | 5.15 |
| Zhejiang | 73,123 | 2.22 |
| Hebei | 72,063 | 2.82 |
| Henan | 71,239 | 4.18 |
| Sichuan | 65,411 | 6.29 |
| Shaanxi | 58,846 | 7.10 |
| Yunnan | 58,186 | 4.59 |
| Anhui | 54,903 | 3.89 |
| Heilongjiang | 53,611 | −4.06 |
| Liaoning | 51,854 | 0.67 |
| Guangxi | 42,920 | 9.01 |
| Fujian | 42,816 | 3.29 |
| Gansu | 42,371 | 5.79 |
| Shanxi | 42,131 | 5.98 |
| Hubei | 41,008 | 4.50 |
| Jilin | 40,549 | −2.32 |
| Hunan | 39,434 | 4.89 |
| Guizhou | 33,446 | 5.48 |
| Jiangxi | 31,134 | 4.35 |
| Chongqing | 22,243 | 3.23 |
| Qinghai | 15,880 | 2.52 |
| Ningxia | 15,767 | 1.10 |
| Tianjin | 14,001 | 0.15 |
| Shanghai | 12,841 | 0.07 |
| Beijing | 11,941 | 0.30 |
| Tibet | 10,715 | −1.32 |
| Year/Buffer (km) | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | 604 | 643 | 647 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 1993 | 582 | 633 | 647 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 1994 | 581 | 631 | 646 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 1995 | 586 | 638 | 647 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 1996 | 585 | 636 | 647 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 1997 | 584 | 637 | 647 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 1998 | 573 | 632 | 647 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 1999 | 571 | 634 | 647 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 2000 | 564 | 630 | 647 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 2001 | 567 | 635 | 647 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 2002 | 566 | 634 | 647 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 2003 | 566 | 636 | 647 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 2004 | 527 | 606 | 640 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 2005 | 526 | 606 | 639 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 2006 | 543 | 620 | 644 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 2007 | 533 | 614 | 643 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 2008 | 536 | 615 | 642 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 2009 | 524 | 604 | 636 | 647 | 647 | 647 |
| 2010 | 492 | 580 | 620 | 640 | 647 | 647 |
| 2011 | 505 | 592 | 628 | 645 | 647 | 647 |
| 2012 | 487 | 574 | 615 | 636 | 647 | 647 |
| 2013 | 501 | 586 | 625 | 644 | 647 | 647 |
| 2014 | 333 | 424 | 479 | 519 | 549 | 515 |
| 2015 | 329 | 424 | 481 | 521 | 552 | 619 |
References
- Jiang, H.; Sun, Z.; Guo, H.; Weng, Q.; Du, W.; Xing, Q.; Cai, G. An assessment of urbanization sustainability in China between 1990 and 2015 using land use efficiency indicators. NPJ Urban Sustain. 2021, 1, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Hu, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C. How Do Economic Growth, Urbanization, and Industrialization Affect Fine Particulate Matter Concentrations? An Assessment in Liaoning Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Xiao, M.; Huang, C.; Liang, Y.; Yang, Z. Land Use Scenario Simulation and Ecosystem Service Management for Different Regional Development Models of the Beibu Gulf Area, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Sarker, M.N.; Lv, Y. Coupling Coordination of the Regional Economy, Tourism Industry, and the Ecological Environment: Evidence from Western China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Fan, Z.; Long, Z.; Wan, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. Analysis of County-Scale Eco-Efficiency and Spatiotemporal Characteristics in China. Land 2023, 12, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiago, P.; Ceia-Hasse, A.; Marques, T.A.; Capinha, C.; Pereira, H.M. Spatial distribution of citizen science casuistic observations for different taxonomic groups. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, B.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Building a Better Urban Picture: Combining Day and Night Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 11887–11913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Xu, T. Nighttime Light Derived Assessment of Regional Inequality of Socioeconomic Development in China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1242–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Qi, K.; Guan, Q.; Wu, C.; Yu, J.; Qing, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wu, H.; Li, X. A Scientometric Visualization Analysis for Night-Time Light Remote Sensing Research from 1991 to 2016. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, C.; Haynie, S.; Pei, T.; Xu, T. Night-time light derived estimation of spatio-temporal characteristics of urbanization dynamics using DMSP/OLS satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Liang, L.; Wu, F.; Wang, Z.; He, S. A review of the balance of regional development in China from the perspective of development geography. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.-L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W.-X. Regional Economic Convergence in China: A Comparative Study of Nighttime Light and GDP. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 525162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Bo, L.; Haque, M.; Liu, E. Does China’s Regional Digital Economy Promote the Development of a Green Economy? Sustainability 2023, 15, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Shao, Z.; Fu, P.; Cheng, Q. The Dynamic Analysis between Urban Nighttime Economy and Urbanization Using the DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data in China from 1992 to 2012. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, J.; Yan, X.; Lin, J.; Ye, S.; Xu, Y.; Qi, X. Identifying the Spatial–Temporal Patterns of Vulnerability to Re-Poverty and its Determinants in Rural China. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2022, 15, 483–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, C.; Xu, Y. Analyzing Population Density Disparity in China with GIS-automated Regionalization: The Hu Line Revisited. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; He, B.; Guo, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fan, Y. Study on Population Distribution Pattern at the County Level of China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Gong, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, D.; Zhang, H. Population distribution and urbanization on both sides of the Hu Huanyong Line: Answering the Premier’s question. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1593–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Wei, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Ju, S. Research on Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Correlation Degree of the Historical and Cultural Towns (Villages) in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Liu, S.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Z. China’s different spatial patterns of population growth based on the “Hu Line”. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1611–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J. Quantitative estimation of urbanization dynamics using time series of DMSP/OLS nighttime light data: A comparative case study from China’s cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Yue, H. Urban Land Extraction Using VIIRS Nighttime Light Data: An Evaluation of Three Popular Methods. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, D. Correlations between Urbanization and Vegetation Degradation across the World’s Metropolises Using DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2067–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Peng, J. Exploring factors affecting the relationship between light consumption and GDP based on DMSP/OLS nighttime satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Liu, X. A Simple Method to Improve Estimates of County-Level Economics in China Using Nighttime Light Data and GDP Growth Rate. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, G. The Suitability of Different Nighttime Light Data for GDP Estimation at Different Spatial Scales and Regional Levels. Sustainability 2017, 9, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellander, C.; Lobo, J.; Stolarick, K.; Matheson, Z. Night-Time Light Data: A Good Proxy Measure for Economic Activity? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, D.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wu, Y.; Luo, P. Estimating Socio-Economic Parameters via Machine Learning Methods Using Luojia1-01 Nighttime Light Remotely Sensed Images at Multiple Scales of China in 2018. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 34352–34365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, X. Using Wavelet Transforms to Fuse Nighttime Light Data and POI Big Data to Extract Urban Built-Up Areas. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Du, Q.; Ren, F. Urban Nighttime Leisure Space Mapping with Nighttime Light Images and POI Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J.; Yu, B. Identifying and evaluating poverty using multisource remote sensing and point of interest (POI) data: A case study of Chongqing, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, Z. Green space equity: Spatial distribution of urban green spaces and correlation with urbanization in Xiamen, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Miao, Z. Towards the analysis of urban livability in China: Spatial–temporal changes, regional types, and influencing factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 60153–60172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, S.; Jahangir, S.; Haque, M.S.; Chen, R.; Kumar, P. Spatio-temporal changes of green spaces and their impact on urban environment of Mumbai, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 6481–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Liu, S. Spatial-Temporal Coupling Coordination Relationship between Urbanization and Green Development in the Coastal Cities of China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhao, K. Dynamic interaction between foreign direct investment and the new urbanization in China. J. Hous. Built Environ. 2019, 34, 1107–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Fu, L. Evaluation of Urbanization Efficiency for Coastal Port Cities in China. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 98, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, M.; Everard, M.; Irvine, K.; McInnes, R.; Middleton, B.; van Dam, A.; Davidson, N. The Wetland Book: I: Structure and Function, Management, and Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Mulkey, D.; Hackett, W.B.; Gordon, J.R. Assessing economic activity in coastal areas: A shift-share approach. Coast. Zone Manag. J. 1982, 10, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Mohamed, R.; Wang, Z. Agent-based simulation of the spatial evolution of the historical population in China. J. Hist. Geogr. 2011, 37, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, X. A harmonized global nighttime light dataset 1992–2018. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, C.; Li, M.; Huang, K.; Wang, N. Assessing Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Urbanization Dynamics in Southeast Asia Using Time Series of DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GIMMS 3g NDVI Set and Global NDVI Trends. Available online: https://www.geobotany.org/library/talks/PinzonJE2010_yamal_tal100308.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Anselin, L. Local Indicators of Spatial Association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Luo, L.; Xu, W.; Ledwith, V. Use of local Moran’s I and GIS to identify pollution hotspots of Pb in urban soils of Galway, Ireland. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 398, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidl, M.; Saifane, M. A green intensity index to better assess the multiple functions of urban vegetation with an application to Paris metropolitan area. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 15204–15224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susaki, J.; Kubota, S. Automatic Assessment of Green Space Ratio in Urban Areas from Mobile Scanning Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumakoshi, Y.; Chan, S.Y.; Koizumi, H.; Li, X.; Yoshimura, Y. Standardized Green View Index and Quantification of Different Metrics of Urban Green Vegetation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastwirth, J. The Estimation of the Lorenz Curve and Gini Index. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1972, 54, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, J.; Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Ma, M.; Zhu, G.; Altaf Arain, M.; Andrew Black, T.; Jassal, R.S. No trends in spring and autumn phenology during the global warming hiatus. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y. Evolution and stages of China’s economic inequality from 1978 to 2018. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Sutton, P.C.; Ghosh, T.; Tuttle, B.T.; Baugh, K.E.; Bhaduri, B.; Bright, E. A global poverty map derived from satellite data. Comput. Geosci. 2009, 35, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, T. Comparative Estimation of Urban Development in China’s Cities Using Socioeconomic and DMSP/OLS Night Light Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7840–7856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Chu, G.S.F.; Chao, R. Intercity regional disparity in China. China Econ. Rev. 2000, 11, 246–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleisher, B.; Li, H.; Zhao, M.Q. Human capital, economic growth, and regional inequality in China. J. Dev. Econ. 2010, 92, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zou, D.; Wu, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Deciphering China’s Socio-Economic Disparities: A Comprehensive Study Using Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184581
Chen T, Zhou Y, Zou D, Wu J, Chen Y, Wu J, Wang J. Deciphering China’s Socio-Economic Disparities: A Comprehensive Study Using Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(18):4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184581
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tianyu, Yuke Zhou, Dan Zou, Jingtao Wu, Yang Chen, Jiapei Wu, and Jia Wang. 2023. "Deciphering China’s Socio-Economic Disparities: A Comprehensive Study Using Nighttime Light Data" Remote Sensing 15, no. 18: 4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184581
APA StyleChen, T., Zhou, Y., Zou, D., Wu, J., Chen, Y., Wu, J., & Wang, J. (2023). Deciphering China’s Socio-Economic Disparities: A Comprehensive Study Using Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sensing, 15(18), 4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184581







