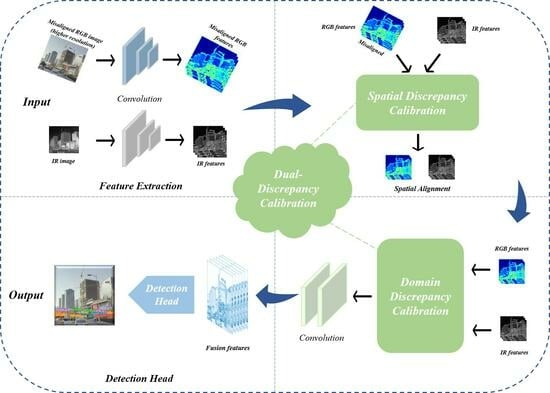
Misaligned RGB-Infrared Object Detection via Adaptive Dual-Discrepancy Calibration
Abstract
Share and Cite
He, M.; Wu, Q.; Ngan, K.N.; Jiang, F.; Meng, F.; Xu, L. Misaligned RGB-Infrared Object Detection via Adaptive Dual-Discrepancy Calibration. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4887. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194887
He M, Wu Q, Ngan KN, Jiang F, Meng F, Xu L. Misaligned RGB-Infrared Object Detection via Adaptive Dual-Discrepancy Calibration. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(19):4887. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194887
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Mingzhou, Qingbo Wu, King Ngi Ngan, Feng Jiang, Fanman Meng, and Linfeng Xu. 2023. "Misaligned RGB-Infrared Object Detection via Adaptive Dual-Discrepancy Calibration" Remote Sensing 15, no. 19: 4887. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194887
APA StyleHe, M., Wu, Q., Ngan, K. N., Jiang, F., Meng, F., & Xu, L. (2023). Misaligned RGB-Infrared Object Detection via Adaptive Dual-Discrepancy Calibration. Remote Sensing, 15(19), 4887. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194887