Infrared Moving Small Target Detection Based on Space–Time Combination in Complex Scenes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Proposing an image-preprocessing method that leverages the local saliency of images for object enhancement.
- Proposing a multi-scale layered contrast feature extraction method that effectively suppresses false positives caused by local grayscale fluctuations in pixels.
- Utilizing a spatiotemporal context to globally “track” the image, obtaining motion information for each pixel, and using statistical characteristics to separate information related to moving targets, thereby generating an abnormal motion feature map of the image.
- Employing motion features to perform non-target suppression and target enhancement on suspicious target detection results obtained from the multi-scale layered contrast feature extraction method, ultimately determining target positions through threshold segmentation.
2. Proposed Method
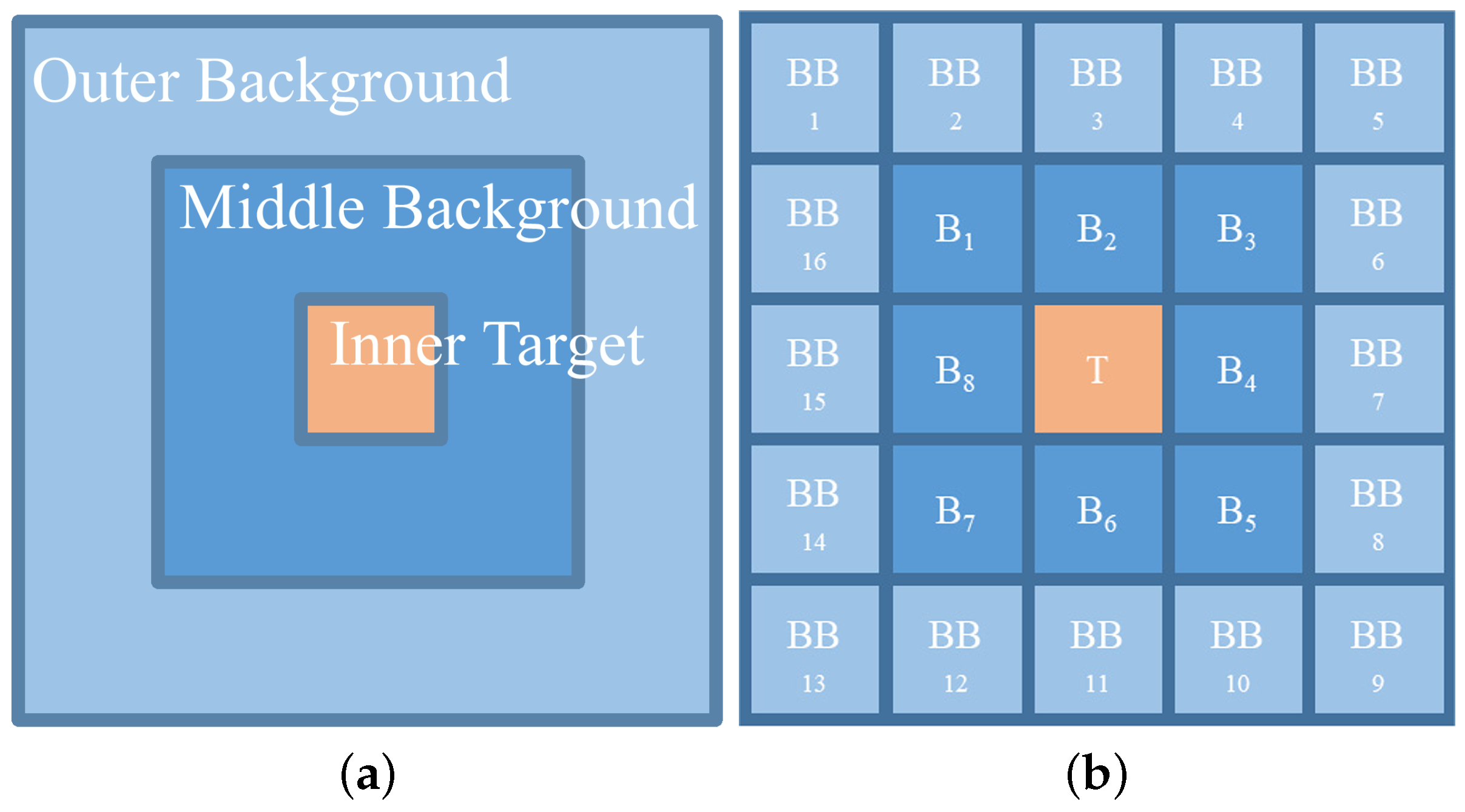
2.1. Target Enhancement and Filtering
2.2. Calculation of MLCF
2.3. Calculate Abnormal Motion
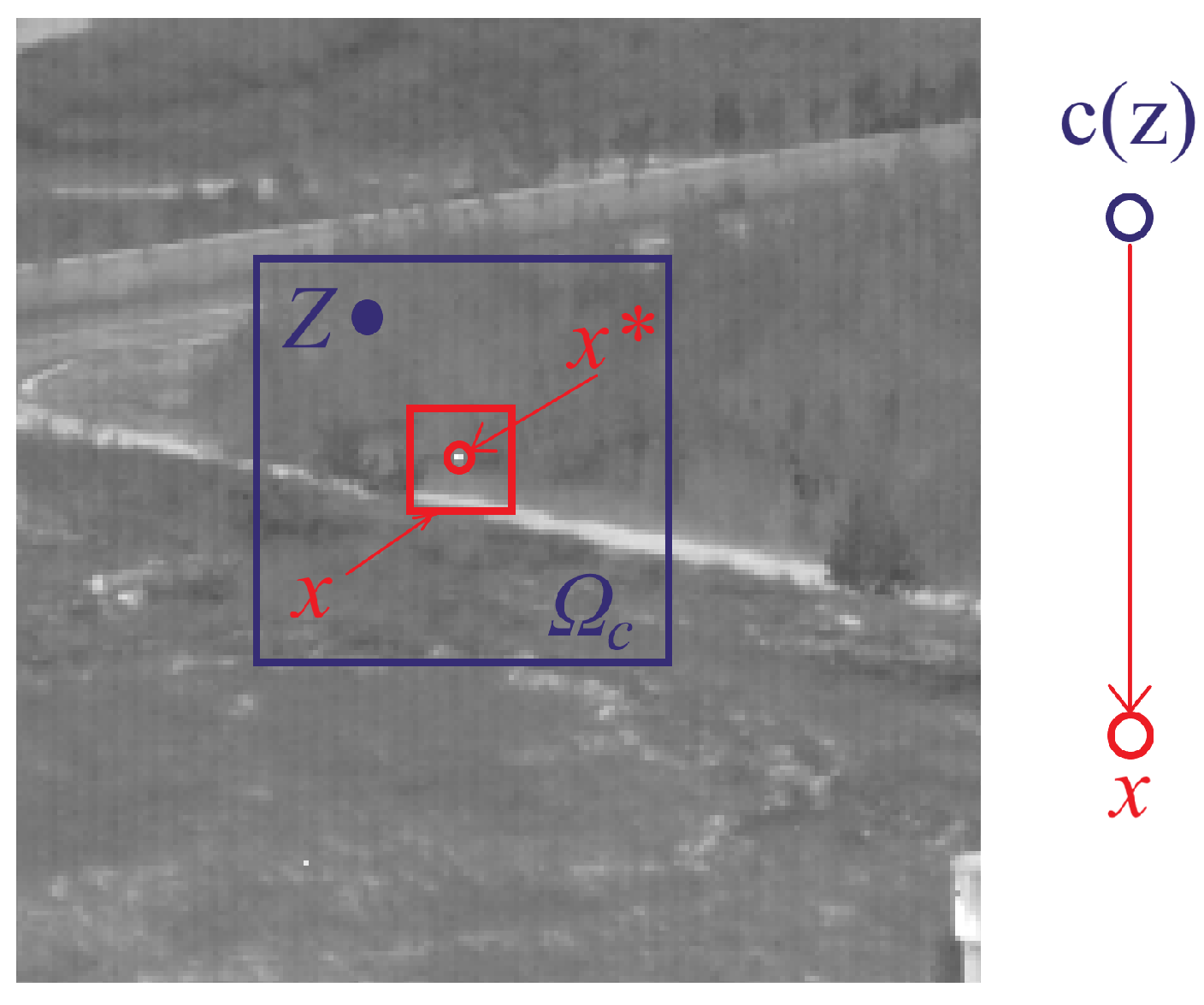
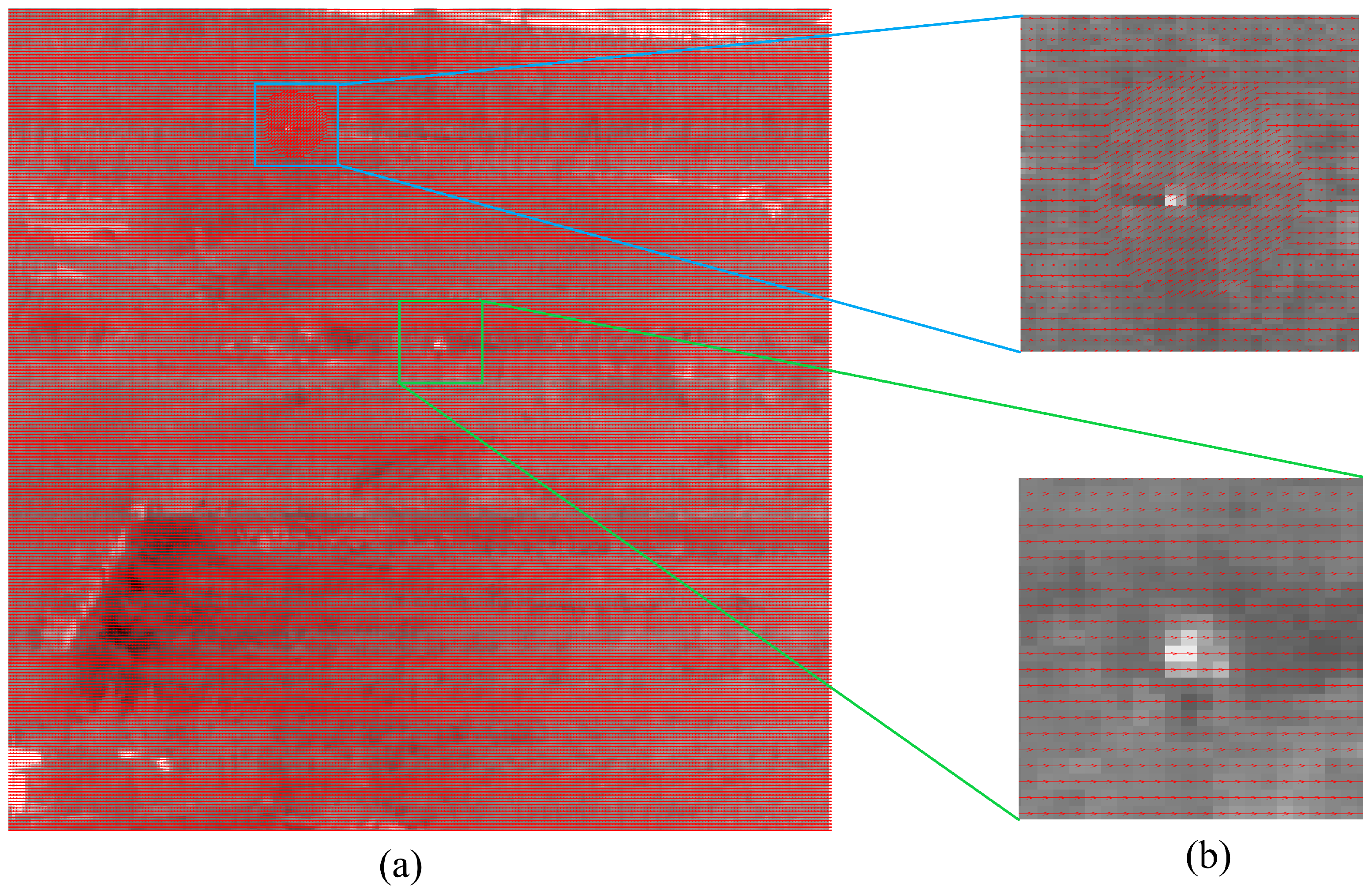
2.3.1. Spatio-Temporal Context
2.3.2. Filtering Motion Based on Statistical Features
2.3.3. Calculation of Target Feature Map
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
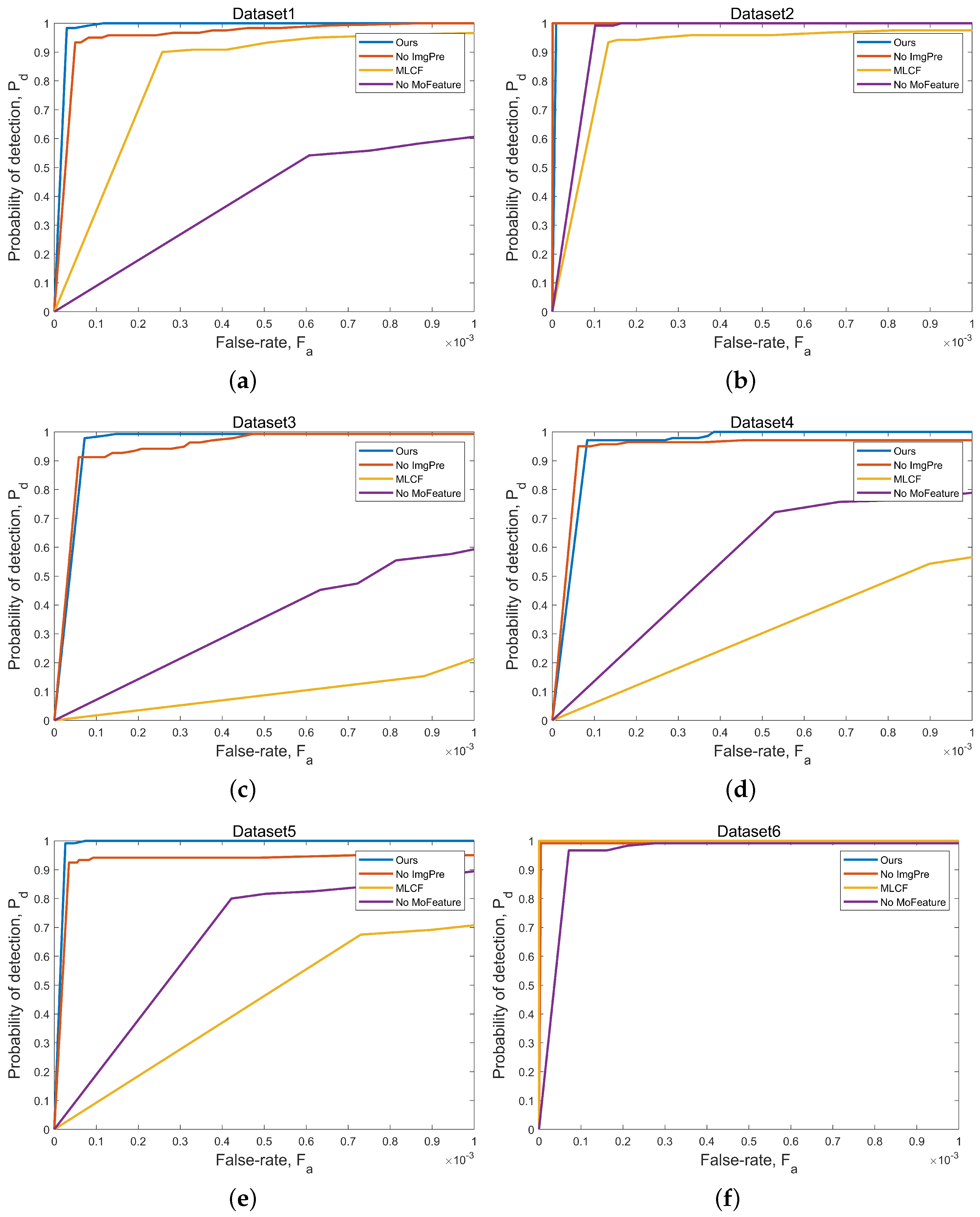
3.1. Ablation Experiments
3.2. Algorithm Performance Evaluation
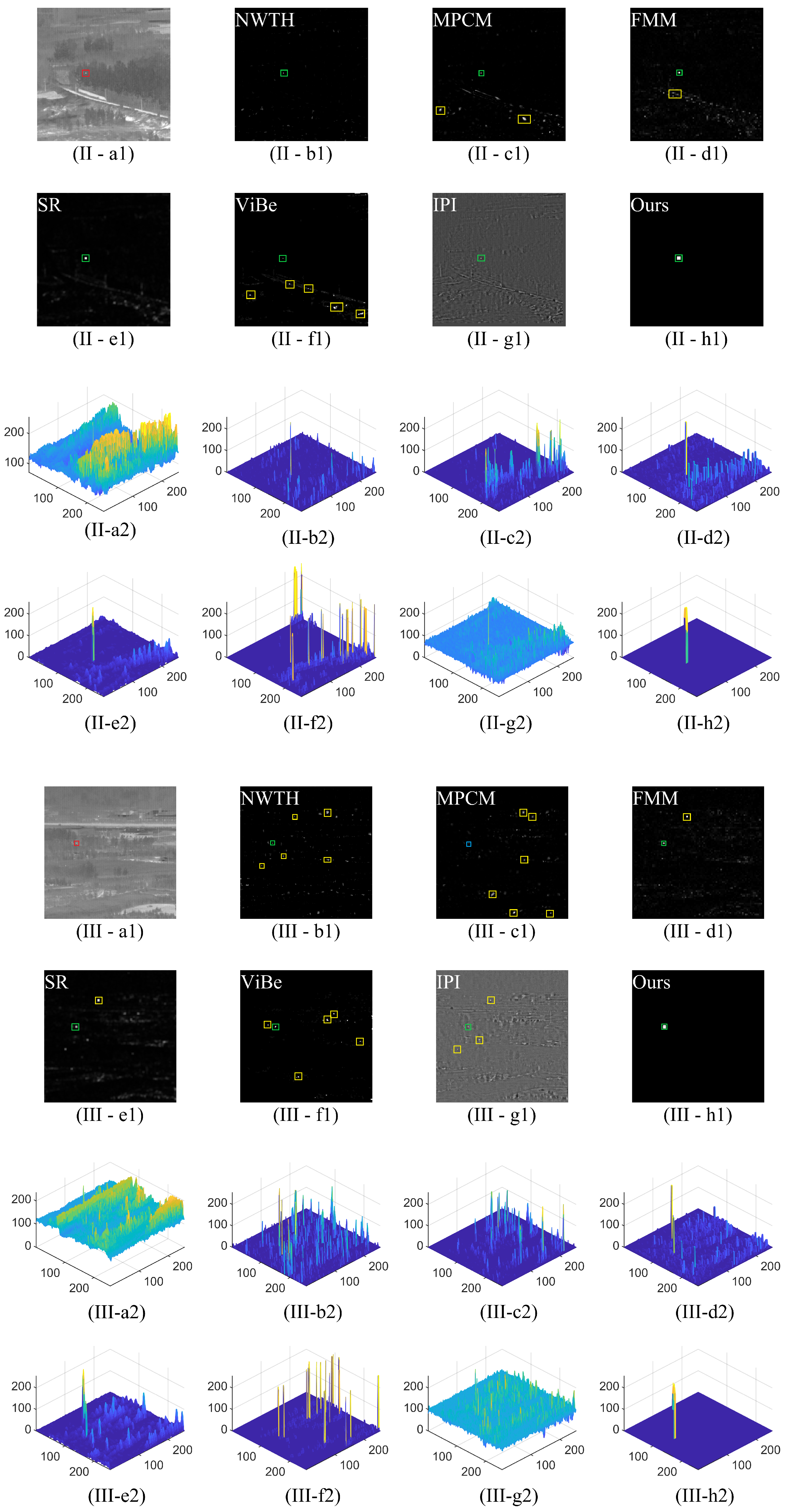
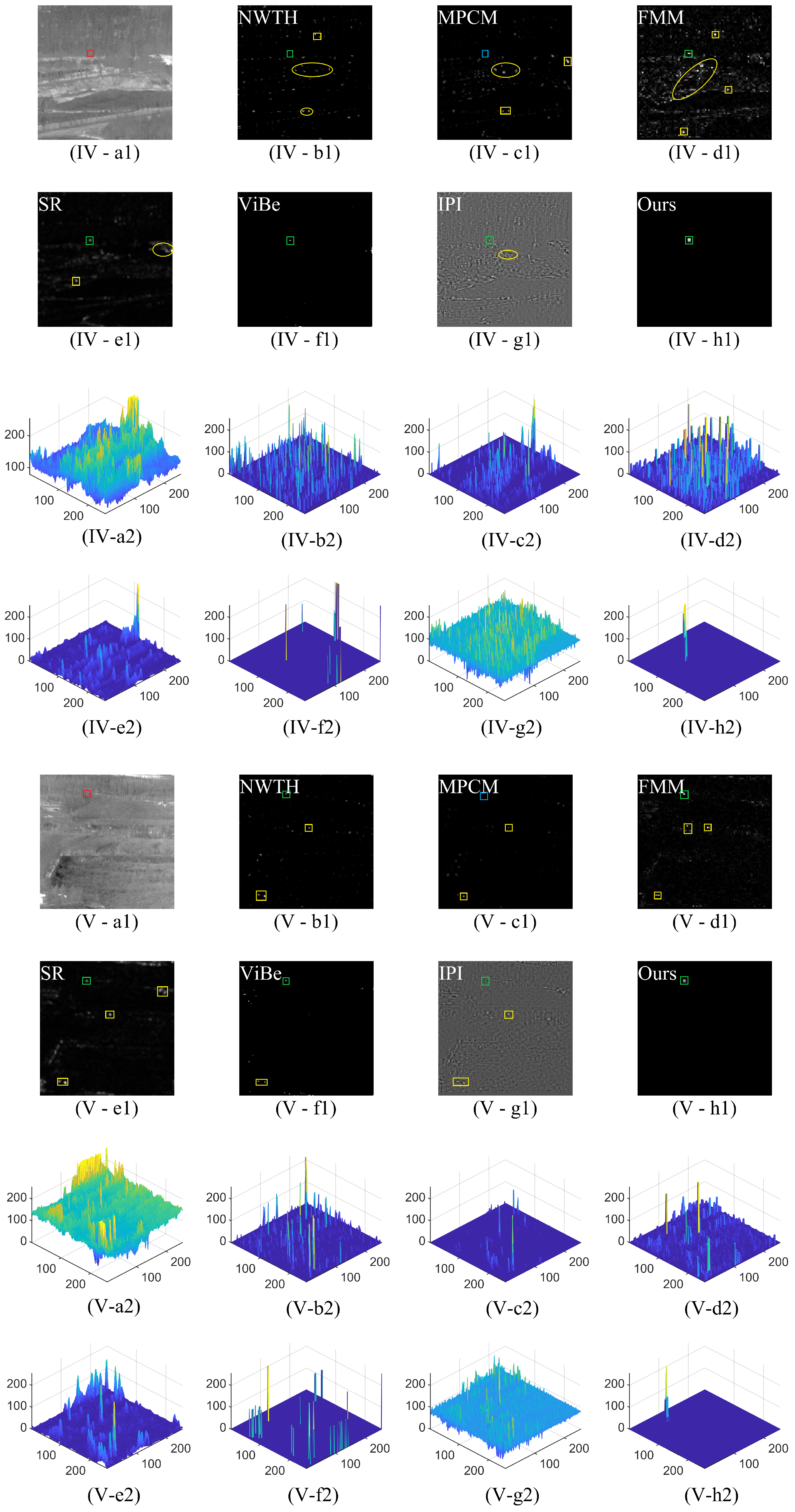
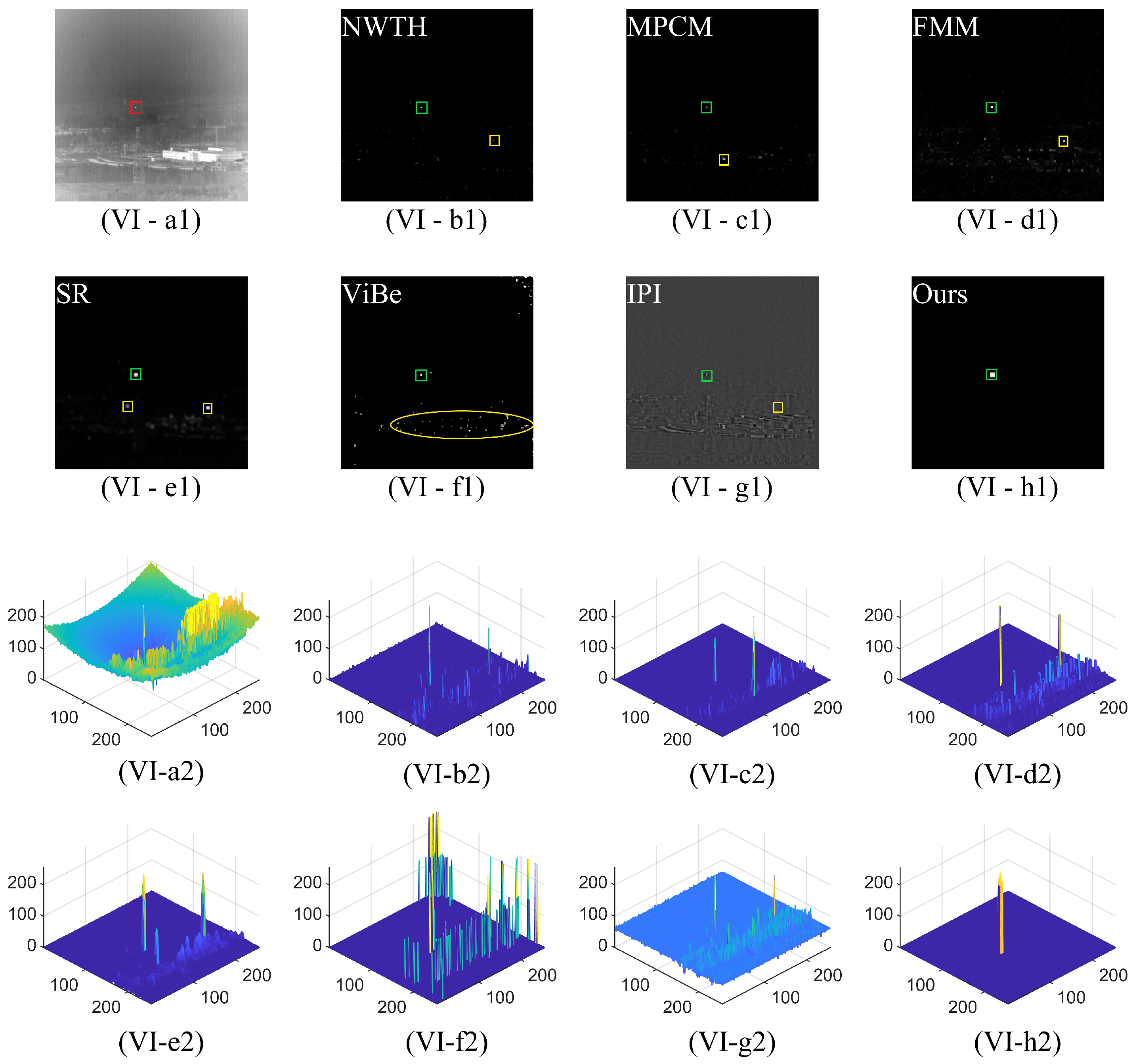
3.2.1. Subjective Evaluation
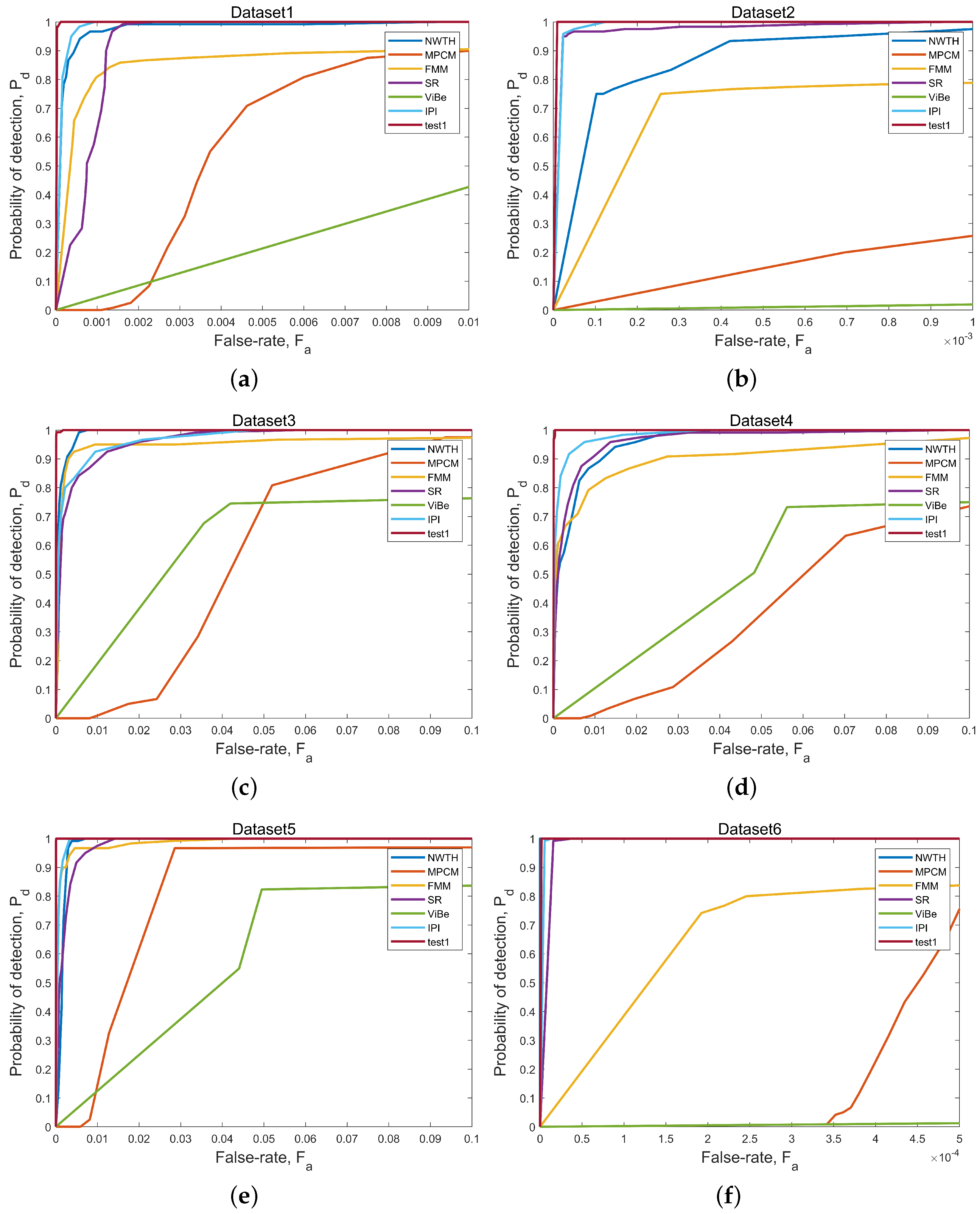
3.2.2. Objective Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, F.; Wu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wang, P.; Kang, N. Graph-regularized Laplace approximation for detecting small infrared target against complex backgrounds. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 85354–85371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, T.; Zhu, X.; Bai, K.; Wang, J. Review on Infrared dim and small target detection technology. J. Zhengzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 52, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Bi, Y. Derivative Entropy-based Contrast Measure for Infrared Small-target Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2452–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Huang, S. Infrared Small-target Detection Algorithms: A Survey. J. Image Graph. 2020, 25, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Sun, X.; Zhou, X. A Multiscale Fuzzy Metric for Detecting Small Infrared Targets Against Chaotic Cloudy/Sea-Sky Backgrounds. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 45, 1694–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S. Target attribute-based false alarm rejection in small infrared target detection. Proc. SPIE 2012, 8537, 85370G. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Shen, Z. Preprocessing Technology for Small Target Detection in Infrared Image Sequences. Infrared Laser Eng. 1998, 27, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Suyog, D.D.; Meng, H.E.; Ronda, V.; Philip, C. Max-mean and max-median filters for detection of small targets. Proc. SPIE 1999, 3809, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, T.W.; Sohng, K.I. Small Target Detection Using Bilateral Filter Based on Edge Component. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2010, 31, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Yang, J.; Liu, R. Detecting Infrared Small Target By Using TDLMS Filter Baesd on Neighborhood Analysis. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2009, 28, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Wei, Y.; Peng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Qin, Y.; Li, N. Infrared dim and small target detection: A review. Infrared Laser Eng. 2022, 51, 20210393. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Yang, J.; Yang, K. Adaptive detection for infrared small target under sea-sky complex background. Electron. Lett. 2004, 40, 1083–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, D.; Li, J.; Huang, C. A review of infrared single frame dim small target detection algorithms. Laser Infrared 2022, 52, 154–162. [Google Scholar]
- Candès, E.J.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; John, L. Robust principal component analysis. J. ACM 2011, 58, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Gao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, L. Detection Algorithm of Single Frame Infrared Small Target Based on RPCA. J. Ordnance Equip. Eng. 2018, 39, 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Meng, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Alexander, G.H. Infrared patch-image model for small target detection in a single image. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 4996–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Peng, L.; Yang, C.; Peng, Z. Infrared Small Target Detection Based on Non-Convex Optimization with Lp-Norm Constraint. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Wu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wang, P. Detection of Small Target Using Schatten 1/2 Quasi-Norm Regularization with Reweighted Sparse Enhancement in Complex Infrared Scenes. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, B.; Hong, D.; Yao, J.; Jocelyn, C. LRR-Net: An Interpretable Deep Unfolding Network for Hyperspectral Anomaly Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5513412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itti, L.; Koch, C.; Niebur, E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yang, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, Y. Small target detection utilizing robust methods of the human visual system for IRST. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2009, 30, 994–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lv, G.; Xu, L. Infrared dim target detection based on visual attention. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2012, 55, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ma, Y.; Huang, J.; Mei, X.; Ma, J. An infrared small target detecting algorithm based on human visual system. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Tian, X.; Yuan, Y. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, B.; Fan, F.; Kun, L.; Yu, F. A robust infrared small target detection algorithm based on human visual system. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 2168–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Li, B. Effective infrared small target detection utilizing a novel local contrast method. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1890–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hong, D.; Jocelyn, C. UIU-Net: U-Net in U-Net for Infrared Small Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 32, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Ma, F.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, F. A Sidelobe-Aware Small Ship Detection Network for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5205516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hong, D.; Tian, J.; Jocelyn, C.; Li, W.; Ran, T. ORSIm Detector: A Novel Object Detection Framework in Optical Remote Sensing Imagery Using Spatial-Frequency Channel Features. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5146–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Sun, S.G.; Kim, K.T. Highly efficient supersonic small infrared target detection using temporal contrast filter. Electron. Lett. 2014, 50, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Chuang, J.; Liu, T. Regularized background adaptation: A novel learning rate control scheme for Gaussian mixture modeling. Image Process. IEEE Trans. 2011, 20, 822–836. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Thanarat, H.C.; David, H.; Larry, D. Real-time Foreground-Background Segmentation using Codebook Model. Real-Time Imaging 2005, 11, 167–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Hui, K.; Zhan, Y.; Qi, M. A novel improved ViBe algorithm to accelerate the ghost suppression. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, Changsha, China, 13–15 August 2016; pp. 1692–1698. [Google Scholar]
- Berthold, K.P.H.; Brian, G.S. Determining optical flow. Artif. Intell. 1981, 1, 185–203. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, D.L.; Takeo, K. An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision. In Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence—Volume 2 (IJCAI’81), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 August 1981; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1981; pp. 674–679. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Hu, Y. Method of Infrared Small Moving Target Detection Based on Coarse-to-Fine Structure in Complex Scenes. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Dong, L.; Yang, C.; Xu, W. An infrared small target detection algorithm based on peak aggregation and Gaussian discrimination. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 106214–106225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ma, Y.; Fan, F.; Wu, M.; Huang, J. A Double-Neighborhood Gradient Method for Infrared Small Target Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 1476–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.; Zhang, D. Fast Tracking via Spatio-Temporal Context Learning. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1311.1939. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, B.; Song, Z.; Fan, H.; Zhong, P.; Hu, W.; Zhang, X.; Ling, J.; Su, H.; Jin, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A dataset for infrared image dim-small aircraft target detection and tracking under ground/air background. Sci. Data Bank 2019, 5, 291–302. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Zhou, F. Analysis of new top-hat transformation and the application for infrared dim small target detection. Pattern Recognit. 2010, 43, 2145–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; You, X.; Li, H. Multiscale patch-based contrast measure for small infrared target detection. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 58, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, L. Saliency Detection: A Spectral Residual Approach. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Olivier, B.; Marc, V.D. ViBe:A universal background subtraction algorithm for video sequences. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 1709–1724. [Google Scholar]
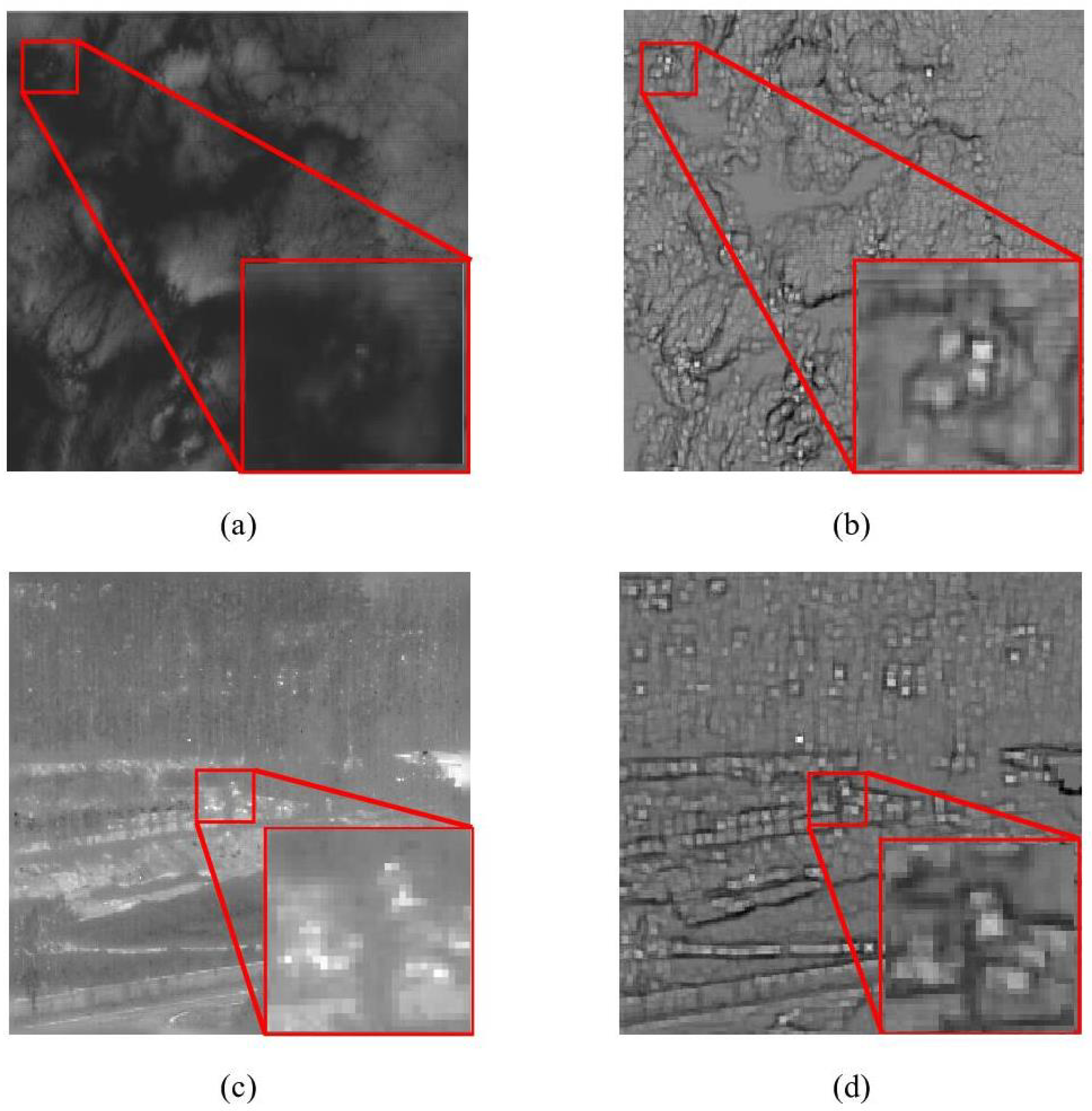

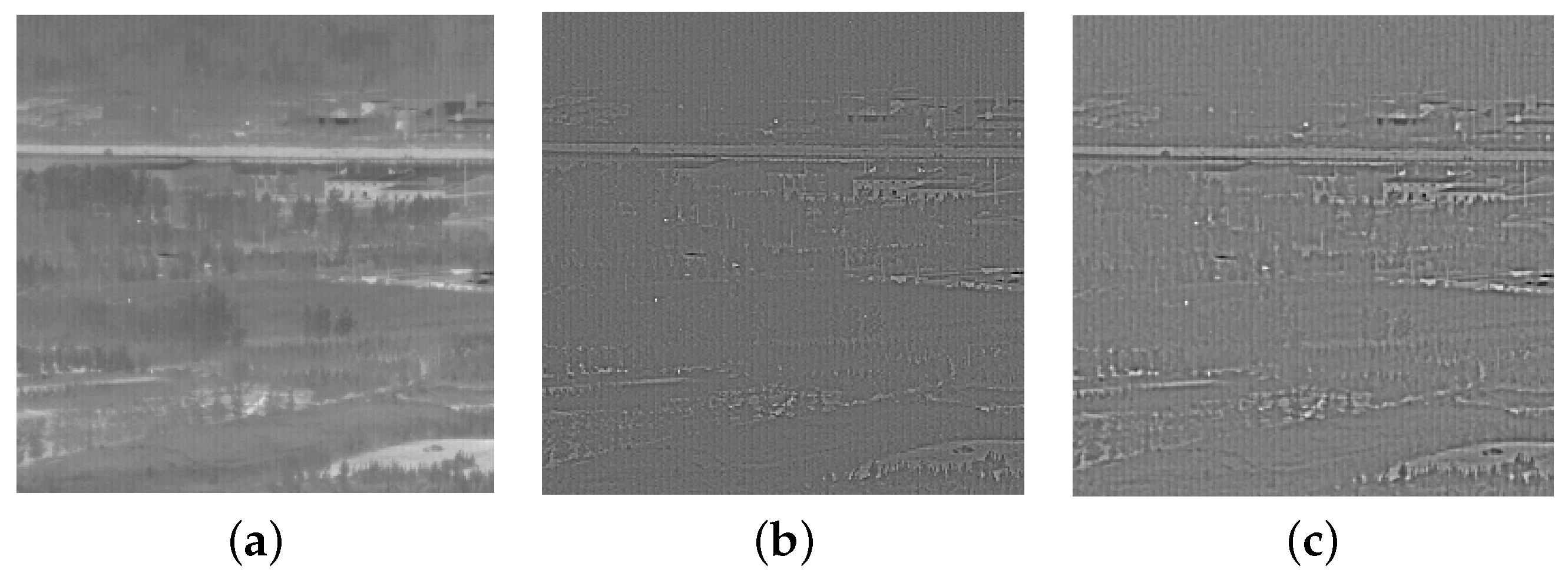
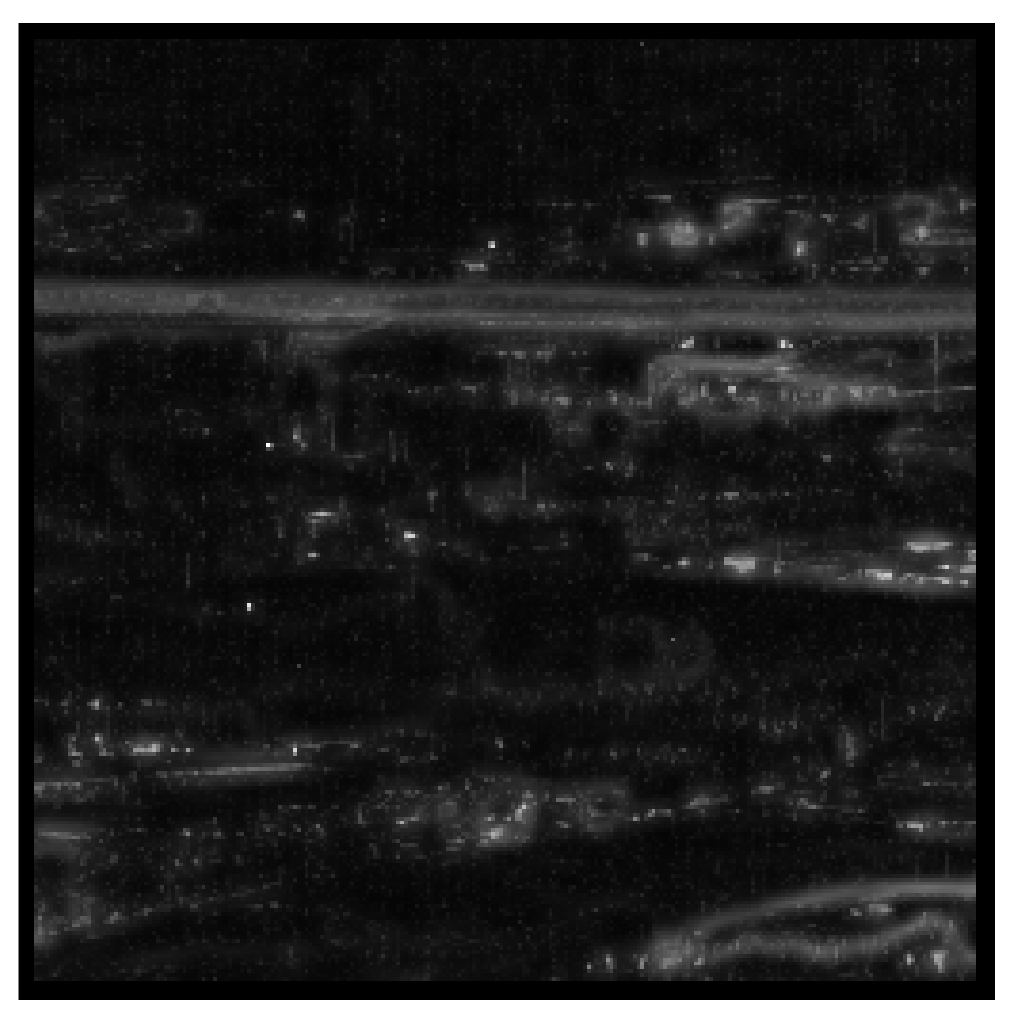





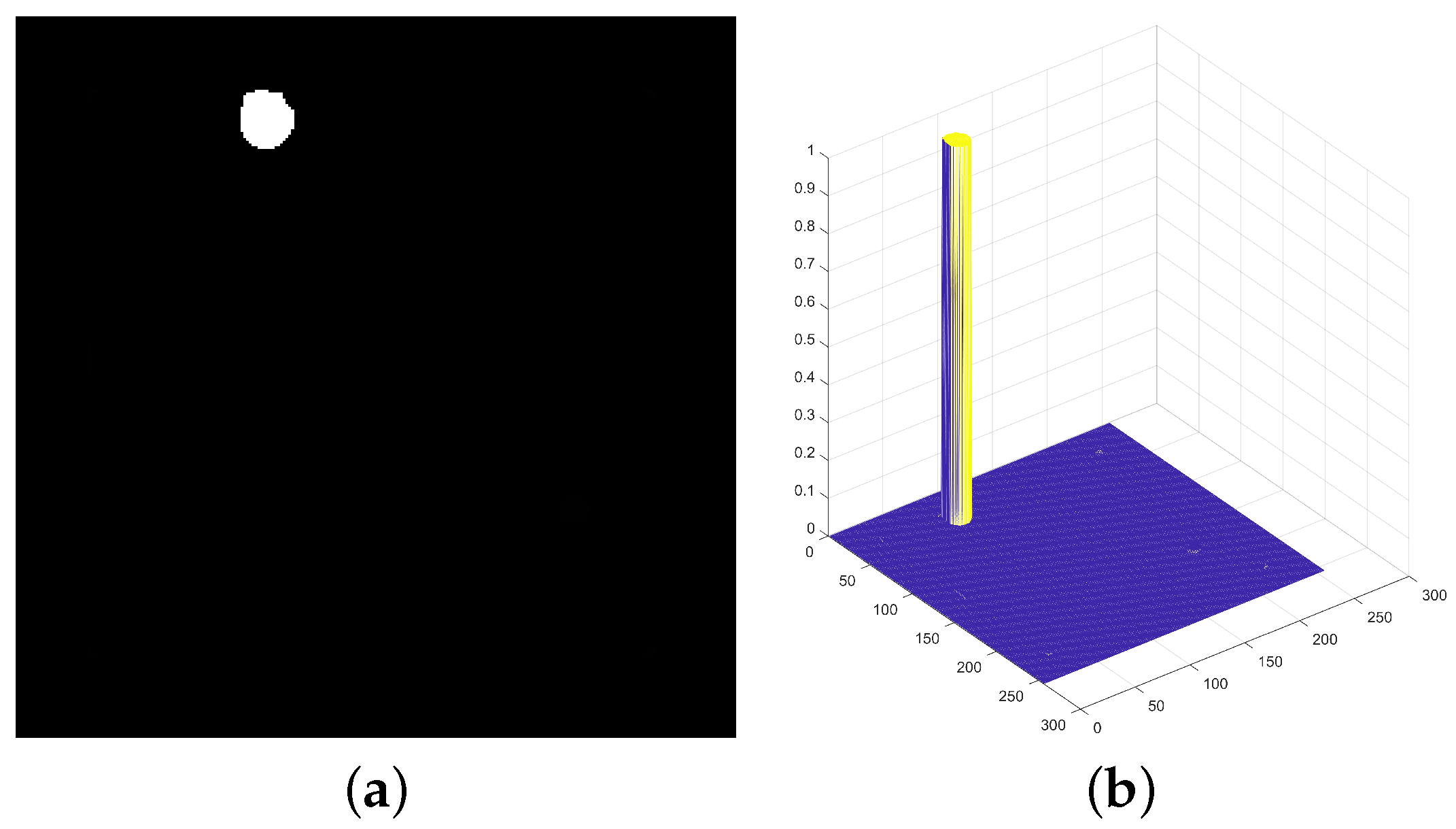

| Datasets | Frames | Size | Target Size | Background |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset 1 | 120 | 256 × 256 | 2 × 2 | Roads and buildings, with camera spots and obvious performance |
| Dataset 2 | 100 | 256 × 256 | 2 × 2 | Woods and Roads |
| Dataset 3 | 120 | 256 × 256 | 1 × 1–2 × 2 | Woods and roads, presence of background interference from suspected target |
| Dataset 4 | 120 | 256 × 256 | 2 × 2 | Mountains and roads, camera spots exist |
| Dataset 5 | 100 | 256 × 256 | 2 × 2–3 × 3 | Woods and buildings, the presence of background interference from suspected targets |
| Dataset 6 | 120 | 256 × 256 | 2 × 2 | Sky and buildings, there are camera spots and mostly fall in the construction area |
| Method | Parameters |
|---|---|
| NWTH [37] | = 6, |
| MPCM [38] | Size = 3 × 3, 5 × 5, 7 × 7 |
| FMM [5] | Size = 3 × 3 |
| SR [39] | Filter size = 3 × 3 |
| ViBe [40] | Sample size N = 20, threshold min = 2, distance decision threshold R = 20 |
| IPI [16] | Window = 20 × 20, step = 10 |
| Ours | Size = 3 × 3, 5 × 5, 7 × 7, sz = 55 × 55 |
| Data 1 | Data 2 | Data 3 | Data 4 | Data 5 | Data 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NWTH | 5.5903 | 8.1547 | 2.1314 | 1.4806 | 3.4384 | 7.1288 |
| MPCM | 6.3444 | 13.7679 | 2.8051 | 1.3986 | 4.1912 | 38.3163 |
| FMM | 15.0151 | 23.3408 | 8.4642 | 7.7013 | 11.658 | 26.1281 |
| SR | 46.545 | 78.3005 | 20.6858 | 18.9573 | 41.3178 | 64.6102 |
| ViBe | 26.9869 | 26.3032 | 3.9963 | 6.8403 | 6.5531 | 0.9571 |
| IPI | 0.363 | 0.4214 | 0.3461 | 0.3064 | 0.2383 | 0.3972 |
| Ours | 450.3183 | 557.0121 | 278.7068 | 263.6374 | 180.7475 | 160.8375 |
| Data 1 | Data 2 | Data 3 | Data 4 | Data 5 | Data 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NWTH | 3.7615 | 4.78 | 2.409 | 2.5365 | 3.7806 | 18.0906 |
| MPCM | 3.2747 | 3.1213 | 2.4737 | 3.0158 | 6.6757 | 13.0021 |
| FMM | 2.357 | 1.9951 | 1.8506 | 1.6132 | 2.2914 | 5.7597 |
| SR | 3.1152 | 3.8647 | 1.6985 | 1.644 | 2.095 | 6.8911 |
| ViBe | 2.6948 | 3.2421 | 3.4688 | 3.1747 | 4.847 | 2.9726 |
| IPI | 2.0986 | 2.2984 | 1.5215 | 1.5729 | 2.0606 | 5.3225 |
| Ours | 89.2149 | 329.1653 | 29.1149 | 35.6475 | 60.3617 | 185.2471 |
| Datum 1 | Datum 2 | Datum 3 | Datum 4 | Datum 5 | Datum 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NWTH | 0.9764 | 0.8553 | 0.9915 | 0.9603 | 0.9847 | 1 |
| MPCM | 0.5568 | 0.1411 | 0.5554 | 0.3825 | 0.8128 | 0.1125 |
| FMM | 0.8526 | 0.6727 | 0.9510 | 0.9012 | 0.9875 | 0.6439 |
| SR | 0.9218 | 0.9743 | 0.9647 | 0.9642 | 0.9804 | 0.9839 |
| ViBe | 0.3366 | 0.4755 | 0.6723 | 0.5506 | 0.6189 | 0.3824 |
| IPI | 0.9870 | 0.9859 | 0.9703 | 0.9848 | 0.9943 | 0.9944 |
| Ours | 0.9984 | 0.9954 | 0.9995 | 0.9995 | 0.9999 | 0.9983 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Cao, L.; Su, K.; Dai, D.; Li, N.; Wu, D. Infrared Moving Small Target Detection Based on Space–Time Combination in Complex Scenes. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5380. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225380
Wang Y, Cao L, Su K, Dai D, Li N, Wu D. Infrared Moving Small Target Detection Based on Space–Time Combination in Complex Scenes. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(22):5380. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225380
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yao, Lihua Cao, Keke Su, Deen Dai, Ning Li, and Di Wu. 2023. "Infrared Moving Small Target Detection Based on Space–Time Combination in Complex Scenes" Remote Sensing 15, no. 22: 5380. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225380
APA StyleWang, Y., Cao, L., Su, K., Dai, D., Li, N., & Wu, D. (2023). Infrared Moving Small Target Detection Based on Space–Time Combination in Complex Scenes. Remote Sensing, 15(22), 5380. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225380







