Preliminary Estimations of Mars Atmospheric and Ionospheric Profiles from Tianwen-1 Radio Occultation One-Way, Two-Way, and Three-Way Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Three Observation Modes for Tianwen-1
3. Radio Occultation Inversion Technique for Tianwen-1
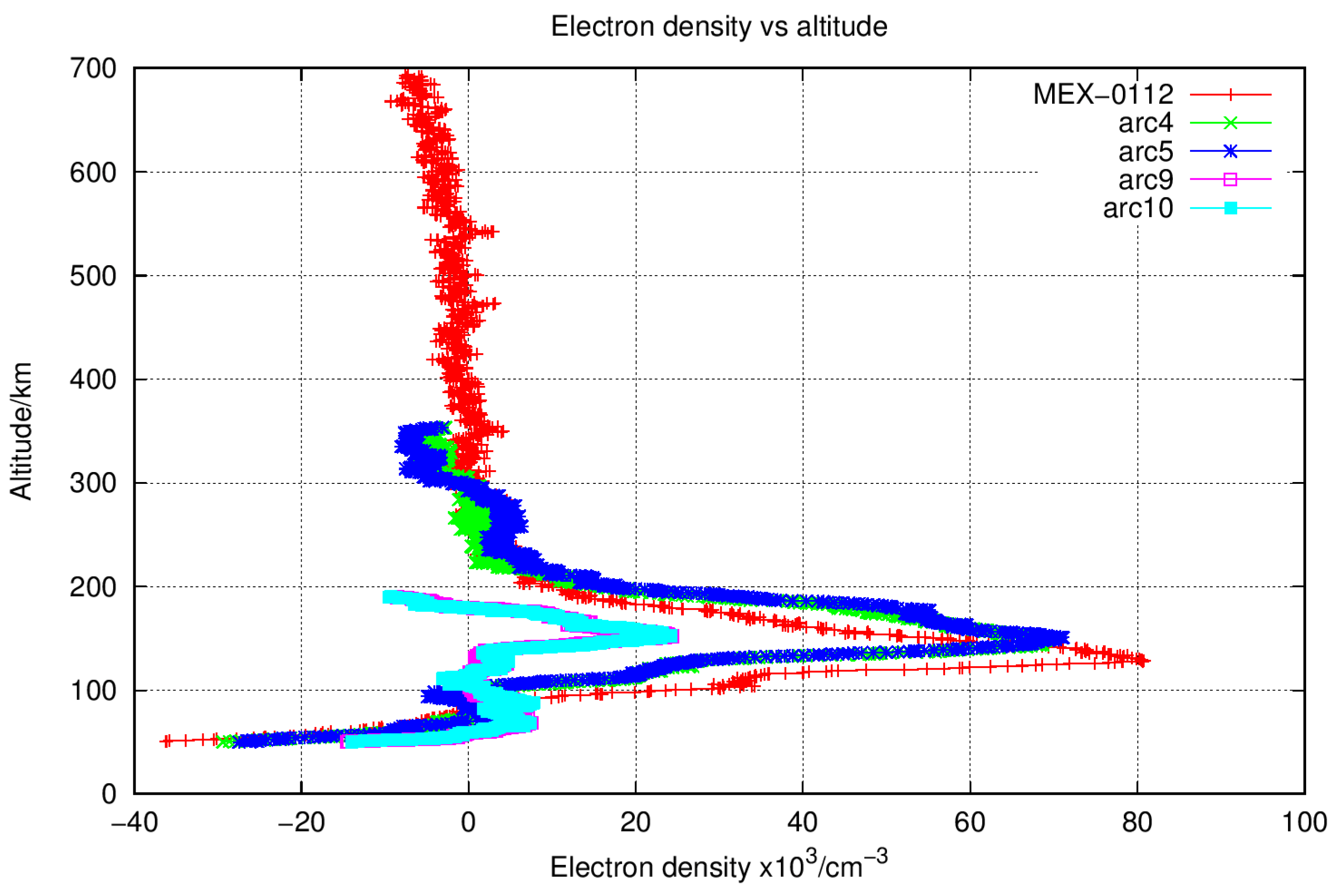
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. Observation Data from Tianwen-1
4.1.1. Tianwen-1 Working Orbit
4.1.2. Zero-Level Data Processing
4.2. Evaluation of Doppler Observation Accuracy
4.2.1. Accuracy Verification of Theoretical Values
4.2.2. Doppler Residual Evaluation
4.3. Inversion Results of the Neutral Atmosphere and Ionosphere from Tianwen-1
4.3.1. Results from One-Way Observation
4.3.2. Results from Two-Way and Three-Way Observation Modes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kliore, A.; Cain, D.L.; Levy, G.S.; Eshleman, V.R.; Fjeldbo, G.; Drake, F.D. Occultation experiment: Results of the first direct measurement of Mars’s atmosphere and ionosphere. Science 1965, 149, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fjeldbo, G.; Eshleman, V.R. The atmosphere of Mars analyzed by integral inversion of the Mariner IV occultation data. Planet. Space. Sci. 1968, 16, 1035–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmar, S.W.; Renzetti, N.A. The Deep Space Network as an Instrument for Radio Science Research; JPL Publication: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 80–93. [Google Scholar]
- Hinson, D.P.; Simpson, R.A.; Twicken, J.D.; Tyler, G.L.; Flasar, F.M. Initial results from radio occultation measurements with Mars Global Surveyor. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 1999, 104, 26997–27012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougher, S.W.; Engel, S.; Hinson, D.P.; Murphy, J.R. MGS Radio Science electron density profiles: Interannual variability and implications. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, E03010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellmann, S.; Pätzold, M.; Häusler, B.; Hinson, D.P.; Tyler, G.L. The structure of Mars lower atmosphere from Mars Express Radio Science (MaRS) occultation measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Planets. 2013, 118, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, D.P.; Asmar, S.W.; Kahan, D.S.; Akopian, V.; Haberle, R.M.; Spiga, A.; Schofield, J.T.; Kleinböhl, A.; Abdou, W.A.; Lewis, S.R.; et al. Initial results from radio occultation measurements with the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter: A nocturnal mixed layer in the tropics and comparisons with polar profiles from the Mars Climate Sounder. Icarus 2014, 243, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakosky, B.M.; Lin, R.P.; Grebowsky, J.M.; Luhmann, J.G.; Beutelschies, G.; Priser, T.; Acuna, M.; Andersson, L.; Baird, D.; Baker, D.; et al. Grebowsky. The Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) Mission. Space Sci. Rev. 2015, 195, 3–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, D.P. Radio occultation measurements of transient eddies in the northern hemisphere of Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, E05002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, D.; Pätzold, M.; Wilson, R.; Häusler, B.; Tellmann, S.; Tyler, G. Radio occultation measurements and MGCM simulations of Kelvin waves on Mars. ICARUS 2008, 193, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjeldbo, G.; Kliore, A.J.; Eshleman, V.R. The neutral atmosphere of Venus as studied with the Mariner V radio occultation experiments. Astron. J. 1971, 76, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, D.P.; Twicken, J.D.; Karayel, E.T. Jupiter’s ionosphere: New results from the first Voyager 2 radio occultation measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 9505–9520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pätzold, M.; Tellmann, S.; Häusler, B.; Bird, M.K.; Tyler, G.L.; Christou, A.A.; Withers, P. A sporadic layer in the Venus lower ionosphere of meteoric origin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L05203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, D.P.; Flasar, F.M.; Kliore, A.J.; Schinder, P.J.; Twicken, J.D.; Herrera, R.G. Jupiter’s ionosphere: Results from the first Galileo radio occultation experiment. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 2107–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, M.; Asmar, S.; Edenhofer, P.; Funke, O.; Pätzold, M.; Volland, H. The structure of Jupiter’s Io plasma torus inferred from Ulysses radio occultation observations. Planet. Space Sci. 1993, 41, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindal, G.F. The atmosphere of Neptune: An analysis of radio occultation data acquired with Voyager 2. Astron. J. 1992, 103, 967–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, G.L. Radio propagation experiments in the outer solar system with Voyager. Proc. IEEE 1987, 75, 1404–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, P. Assimilation Technique of GPS/LEO Occultation Date. Prog. Astron. 2006, 24, 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, P. GPS Radio Occultation Technique and CHAMP Occultation Data Retrieval. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanghai Astronomical Observatory of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Ping, J.; Han, T.; Mao, X.; Hong, Z. Implementation of the Earth-based planetary radio occultation inversion technique. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2011, 54, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cui, J.; Guo, P.; Li, J.; Ping, J.; Jian, N.; Zhang, K. Martian electron density profiles retrieved from Mars Express dual-frequency radio occultation measurements. Adv. Sci. Res. 2015, 55, 2177–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-J.; Jian, N.-C.; Li, J.-L.; Ping, J.-S.; Chen, C.-Y.; Zhang, K.-F. Ionospheric inversion of the Venus Express radio occultation data observed by Shanghai 25 m and New Norcia 35 m antennas. Research in Astron. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 15, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.F.; Zou, H.; Ye, Y.G. Study of Mars’ upper atmosphere based on radio occultation observations. Spacecr. Environ. Eng. 2020, 36, 571–583. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Ping, J.; Cao, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, P.; Wang, M.; Man, H.; Fan, F.; et al. Retrieving Doppler frequency via local correlation method of segmented modeling. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, M.; Jian, N.C.; Han, S.T.; Kong, J.; Guo, P.; Ping, J.S. Tianwen-1 radio occultation observation experiment and feature analysis. J. Deep Space Explor. 2023, 10, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.; Xu, D.; Li, H.; Zhou, H. Initial result of the Chinese Deep Space Stations’ coordinates from Chinese domestic VLBI experiments. Sci. China Inform. Sci. 2017, 60, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, P.; Dehant, V. Mars geodesy, rotation and gravity. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 10, 713–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.W. Astrophysical Quantities, 4th ed.; The Athlone Press: London, UK, 1999; pp. 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Fjeldbo, G.; Eshleman, V.R.; Garriott, O.K.; Smith, F.L. The Two-Frequency bistatic radio-occulation method for the study of planetary ionospheres. J. Geophys. Res. 1965, 70, 3701–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahoy, K.L.; Hinson, D.P.; Tyler, G.L. Radio science measurements of atmospheric refractivity with Mars Global Surveyor. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, E05003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ping, J.; Han, T.; Mao, X.; Hong, Z. Detection of the martian atmosphere and ionosphere using spacecraft-earth radio occultation. Physics 2009, 38, 467–473. [Google Scholar]
- Moyer, T.D. Mathematical Formulation of the Double Precision Orbit Determination Program/dpodp; No. JPL-TR-32-1527; NASA Technical Reports Server (NTRS): Washington, DC, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Withers, P. A review of observed variability in the dayside ionosphere of Mars. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 44, 277–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, K.; Yu, Z.; Jian-Feng, D.; Lue, C.; Hong, W.; Min, F. Orbit determination of Tianwen-1 with one-way Doppler. ACTA Geod. ET Cartogr. Sin. 2023, 52, 588–595. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R. China’s First Mars Exploration Program; China Astronautic Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Schunk, R.W.; Nagy, A.F. Ionospheres—Physics, Plasma Physics and Chemistry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hantsch, M.H.; Bauer, S.J. Solar control of the Mars ionosphere. Planet. Space Sci. 1990, 38, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, E.; Zou, H.; Gurnett, D.A.; Kirchner, D.L.; Morgan, D.D.; Huff, R.; Orosei, R.; Safaeinili, A.; Plaut, J.J.; Picardi, G. Observations of vertical reflections from the topside Martian ionosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 2006, 126, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, F.L.; Smith, C. Numerical evaluation of Chapman’s grazing incidence integral ch (X, χ). JGR 1972, 77, 3592–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
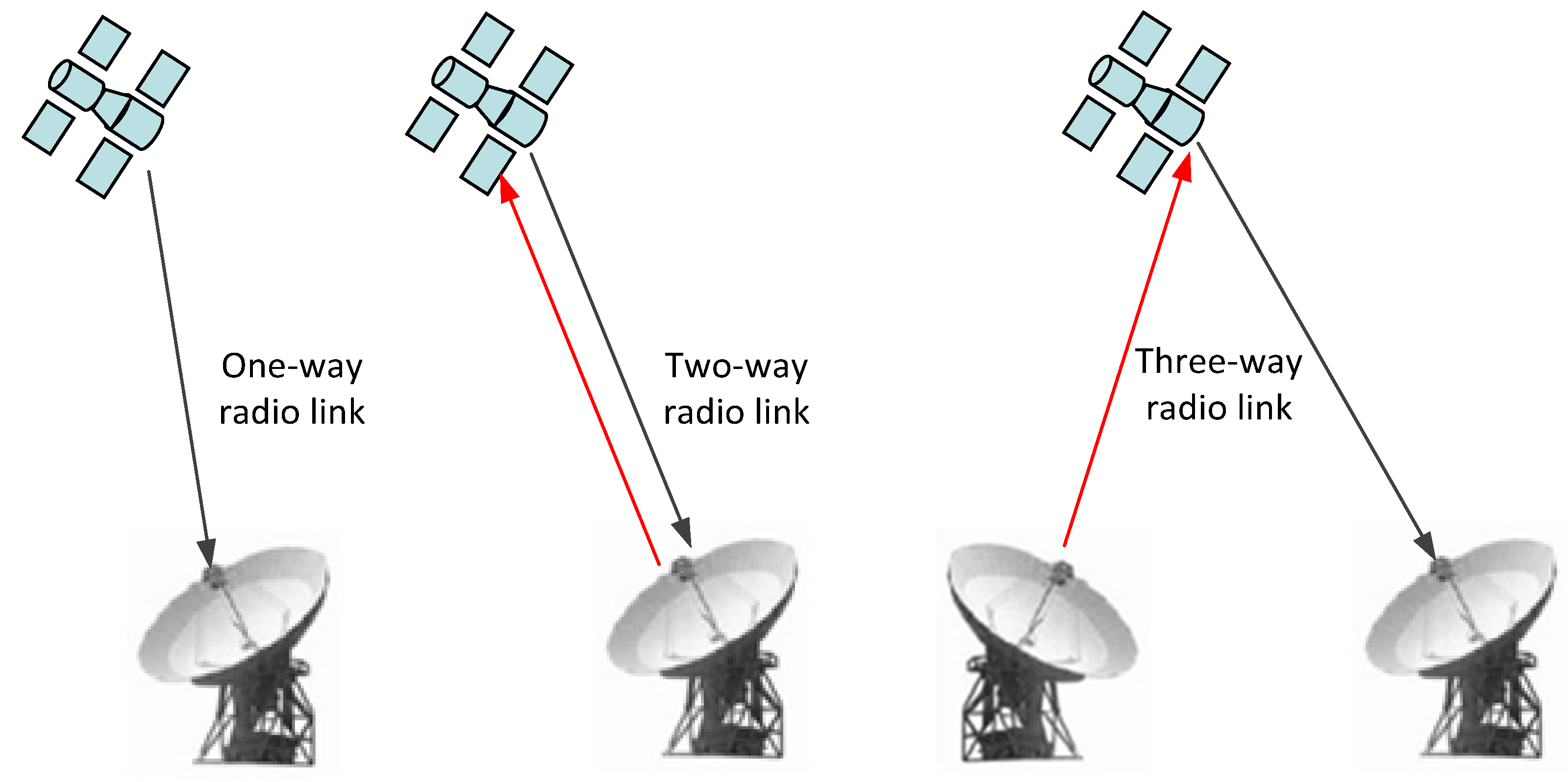

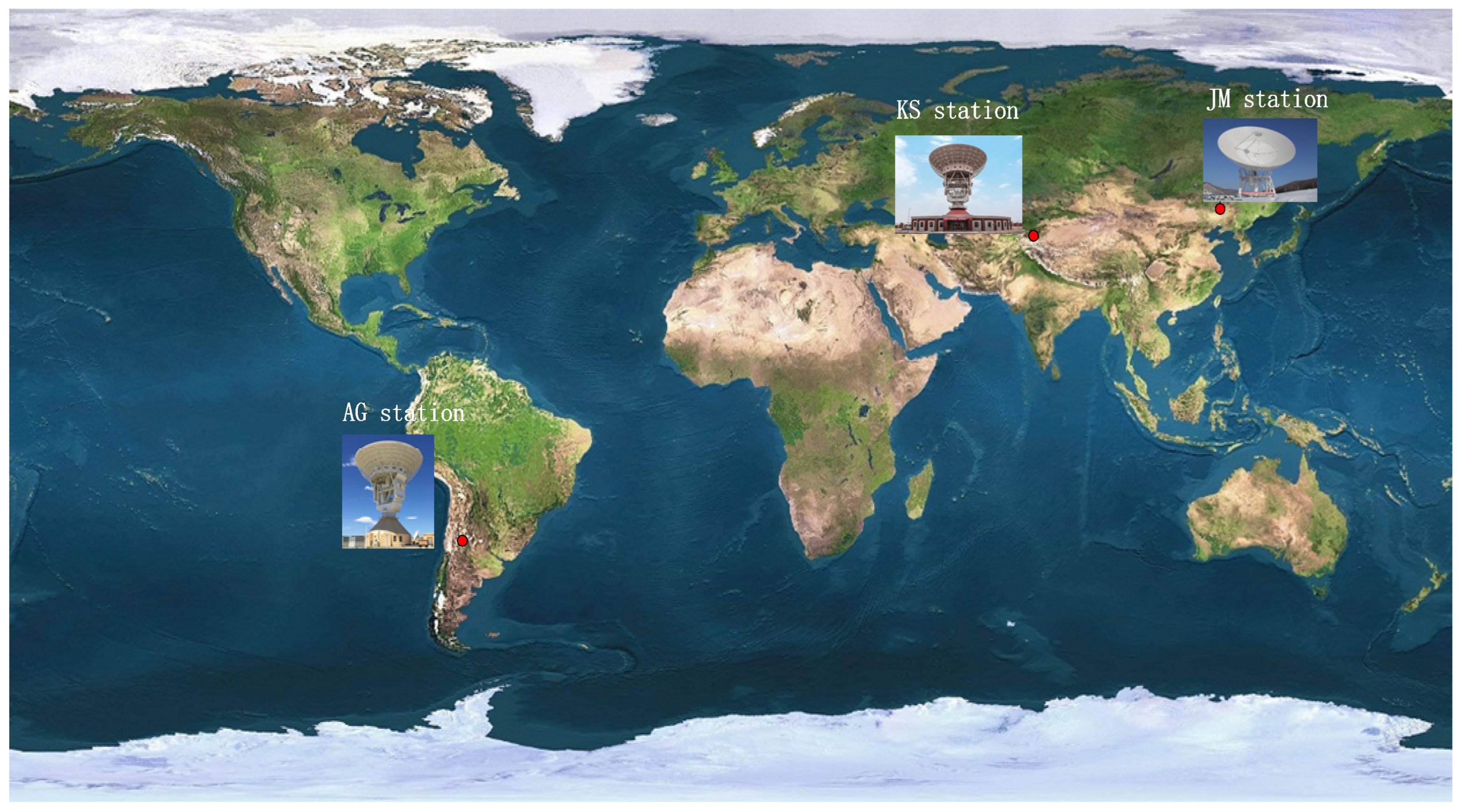

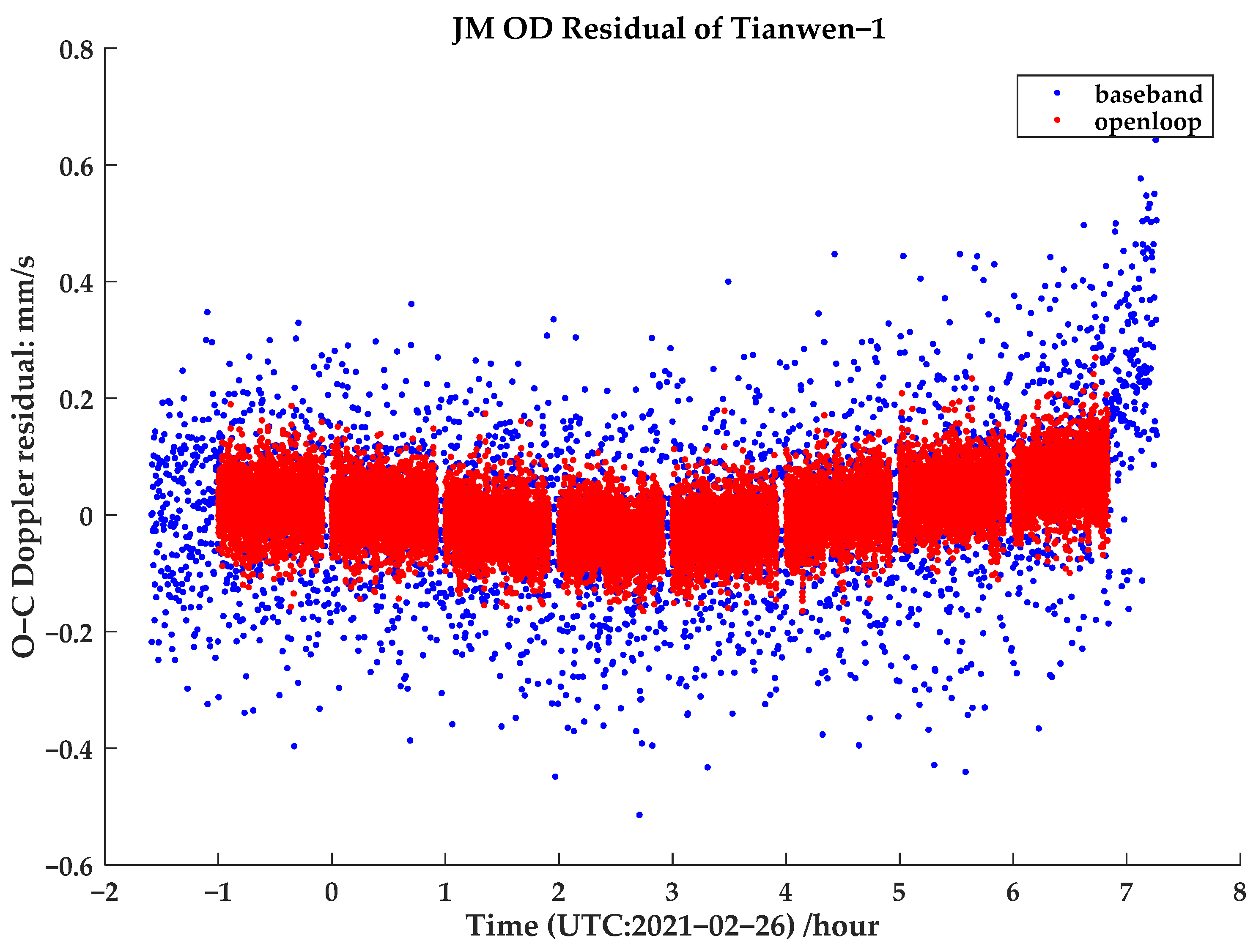

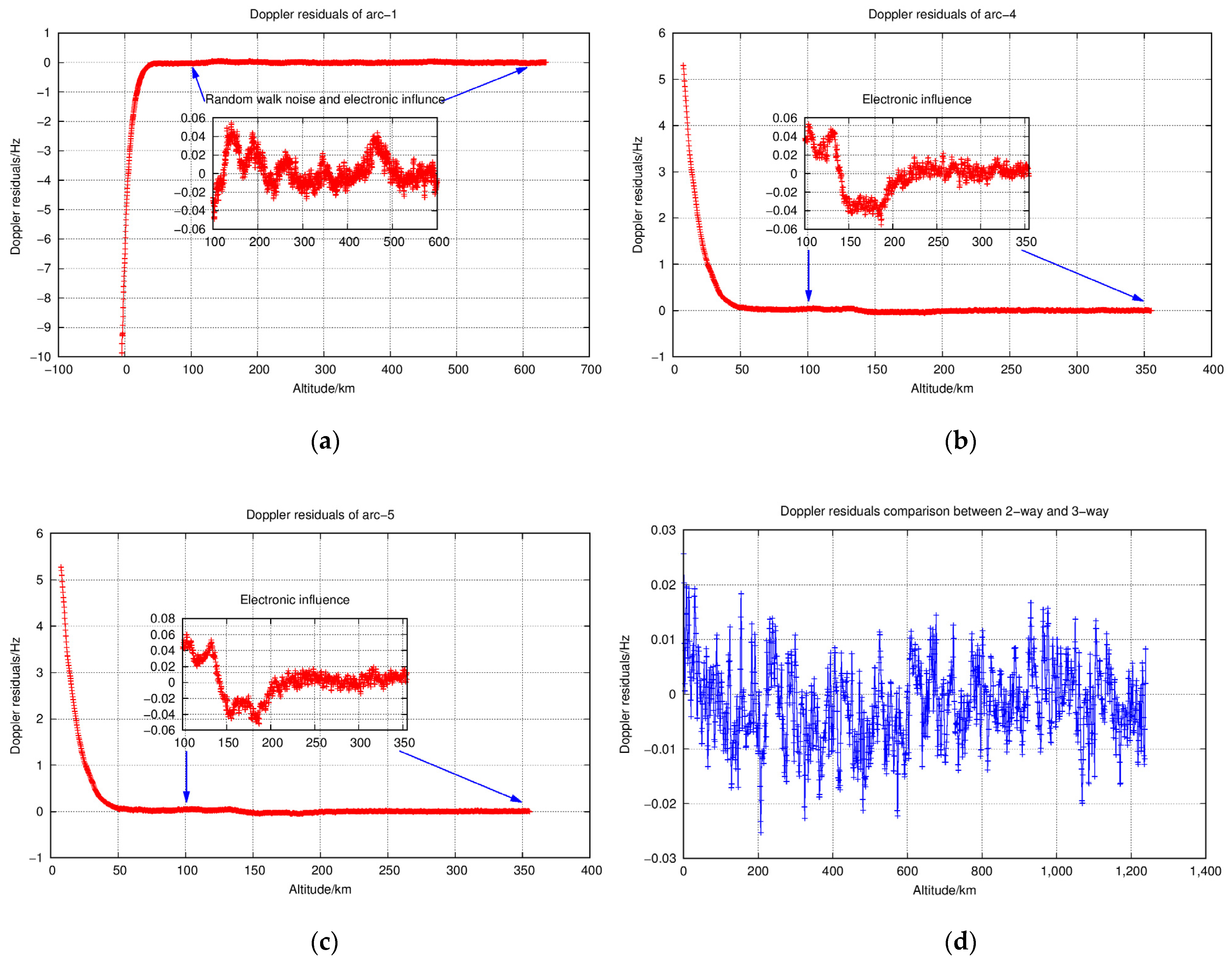
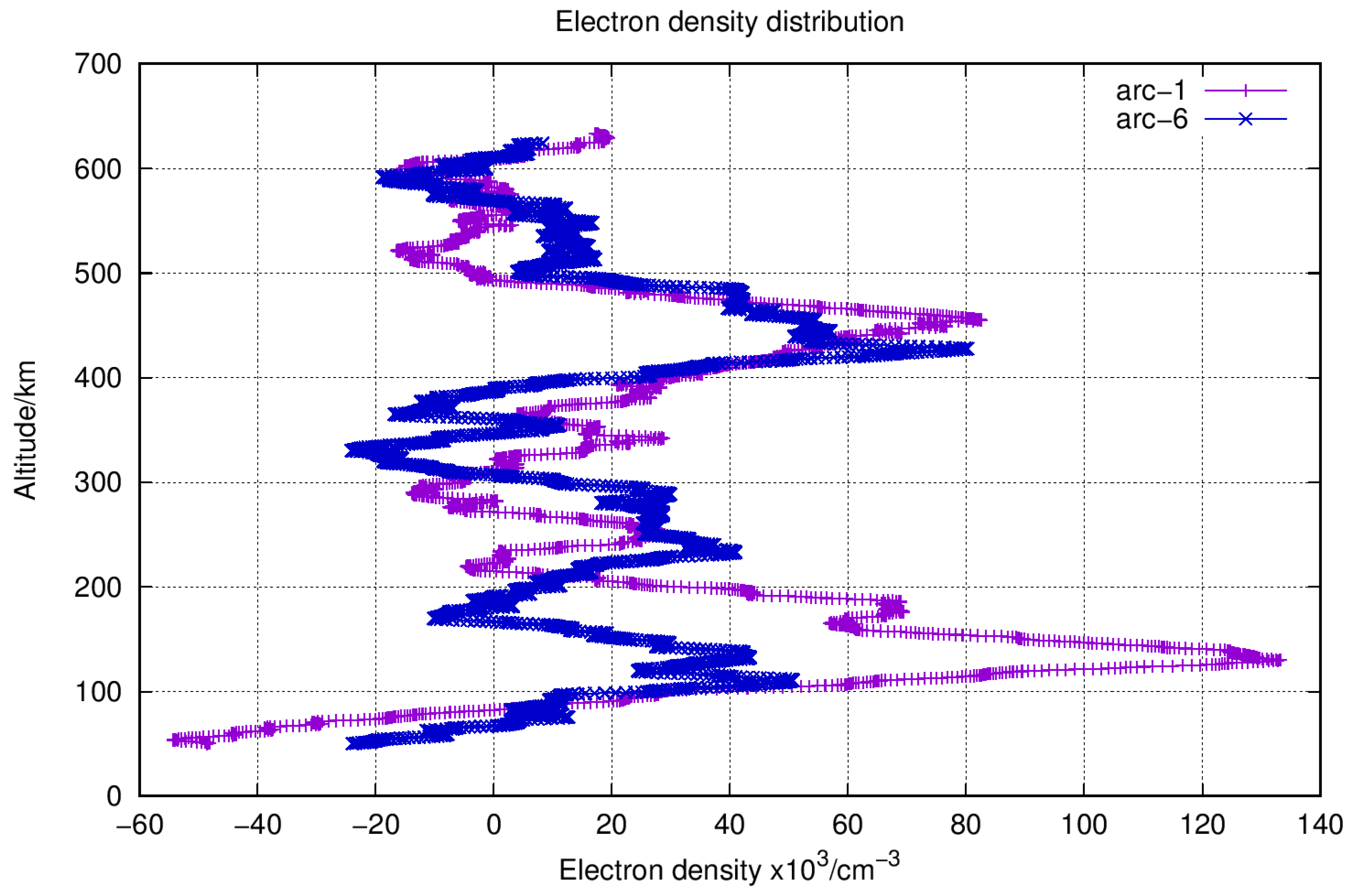
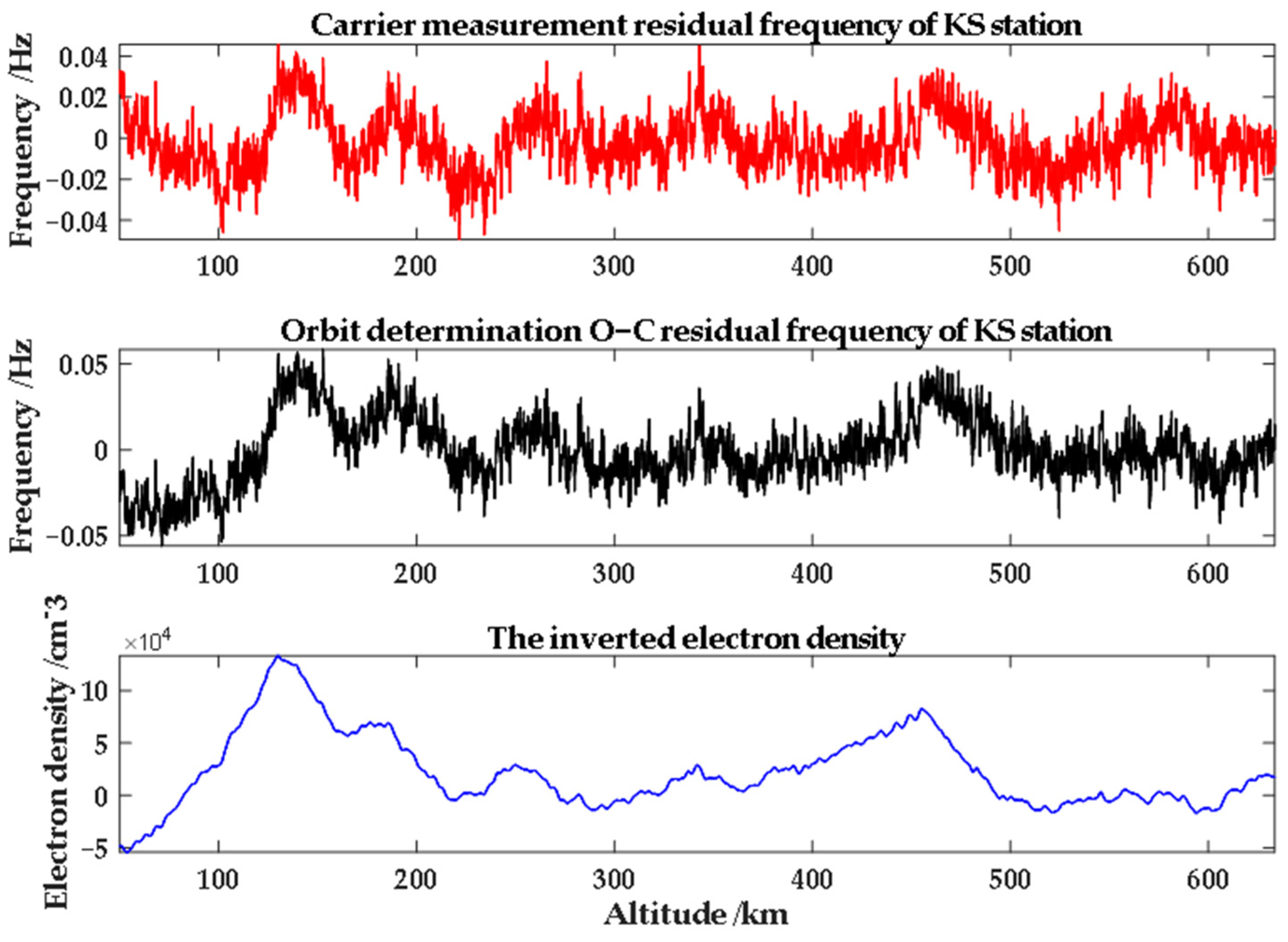
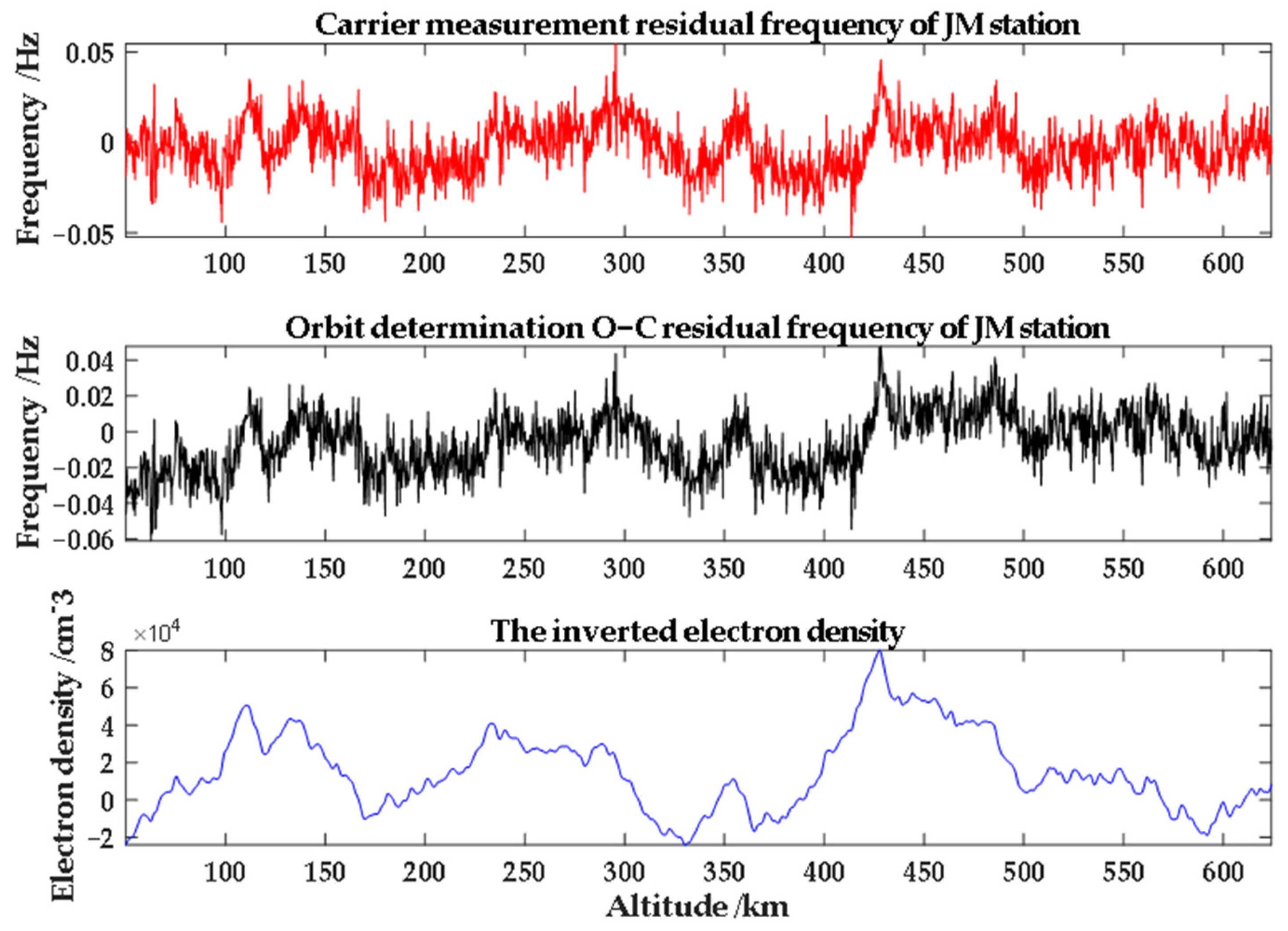

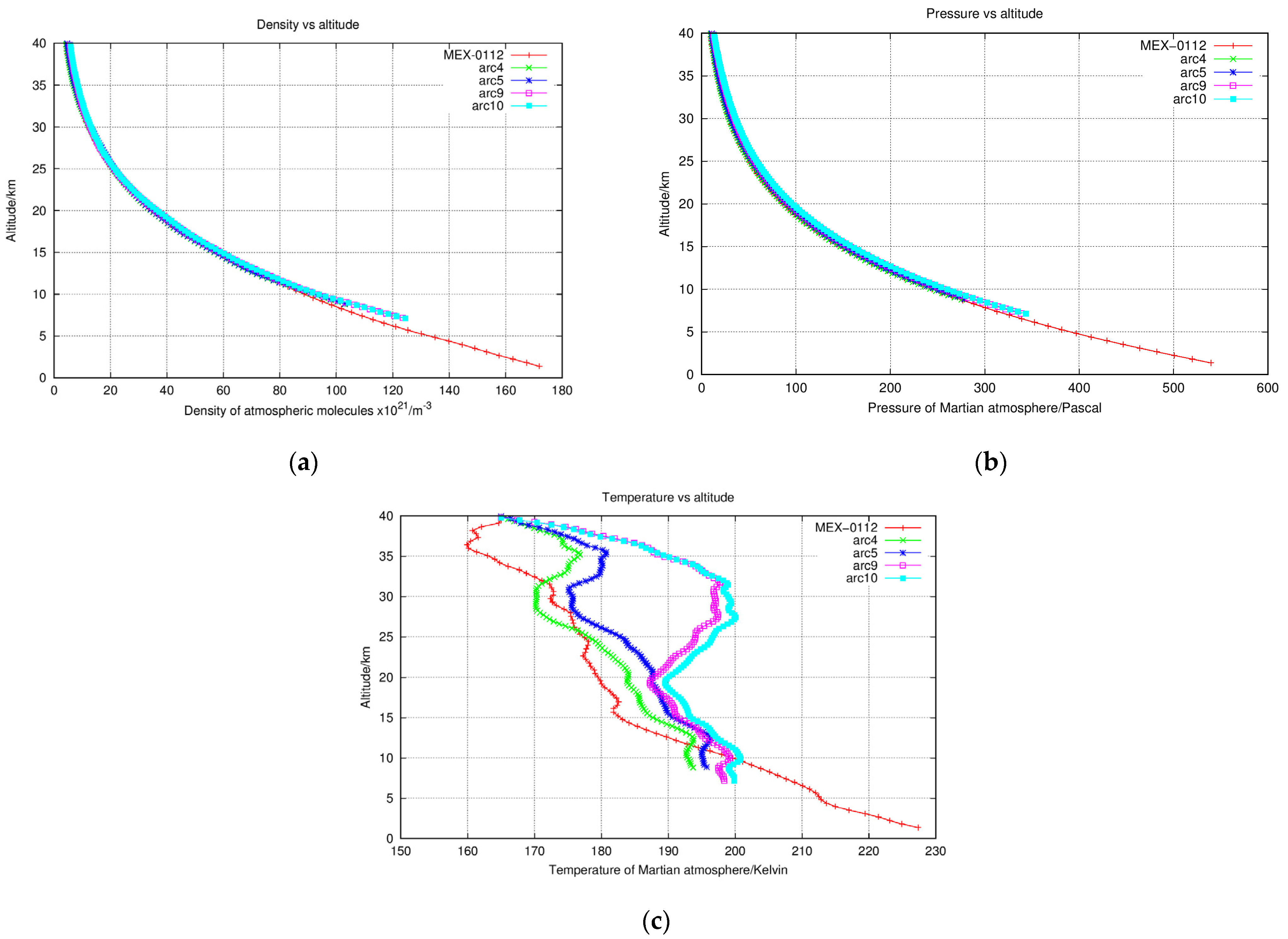
| Arc No. | Time (UTC) | Up/Down | Occultation Type | Link Type | Band |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| arc-1 | 22 March, 02:25:01–02:35:38 | KS | ingress | 1-way | X |
| arc-2 | 22 March, 03:59:01–03:59:10 | ||||
| arc-3 | 22 March, 03:59:01–03:59:10 | ||||
| arc-4 | 22 March, 03:59:11–04:04:21 | KS/KS | egress | 2-way | X |
| arc-5 | 22 March, 03:59:11–04:04:21 | KS/JM | egress | 3-way | X |
| arc-6 | 25 March, 01:13:40–01:23:52 | JM | ingress | 1-way | X |
| arc-7 | 25 March, 02:52:12–02:52:19 | ||||
| arc-8 | 25 March, 02:52:12–02:52:19 | ||||
| arc-9 | 25 March, 02:52:20–02:55:00 | JM/JM | egress | 2-way | X |
| arc-10 | 25 March, 02:52:20–02:55:00 | JM/KS | egress | 3-way | X |
| MEX-0112 (2004) | 15 July, 15:23:00–15:35:23 | DSS-65/DSS-65 | ingress | 2-way | X |
| Arc No. | Latitude (Deg.) | Longitude (Deg.) | SZA (Deg.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| arc-1 | 68.7–70.5 (N) | 204.8–219.2 | 74.6–76.8 |
| arc-4 | 55.1–57.0 (S) | 327.2–330.9 | 80.1–81.3 |
| arc-5 | 55.2–57.0 (S) | 327.3–330.9 | 80.1–81.3 |
| arc-6 | 70.2–70.7 (N) | 146.2–156.4 | 77.7–78.9 |
| arc-9 | 62.8–63.3 (S) | 295.2–297.1 | 88.4–88.8 |
| arc-10 | 62.8–63.4 (S) | 295.3–297.1 | 88.4–88.8 |
| MEX-0112 (2004) | 21.7–26.2 (N) | 243.3–240.5 | 77.9–78.0 |
| Parameter | Source/Value |
|---|---|
| Coordinate System | MEME2000 |
| Central body | Mars |
| Mars Gravity Model | JGMRO120, 120 × 120 |
| N-body perturbation | Sun, major planets, and the Moon |
| Solar and Planetary GM | DE-436 |
| Solar radiation pressure model | Fixed area-mass ratio |
| Solar Radiation Coefficient, CR | The nominal value of the coefficient of SRP is 1.4 |
| Atmospheric correction model | MCD 5.2 |
| Relativity perturbation | Schwarzschild |
| Parameters to solve | Position and velocity, SRP coefficient, Systematic error of range data Empirical acceleration |
| Data weights | Range: 3 m Doppler: 1 mm/s VLBI delay: 0.3 ns VLBI delay rate: 0.3 ps/s |
| Sub Arcs | Orbit Determination Arcs | Overlap Arcs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start (MJD) | End (MJD) | Length (Day) | O−C (mm/s) | Length (Day) | Position Difference (m) | Velocity Difference (m/s) | |
| 1 | 59,369.44 | 59,371.98 | 2.54 | 0.41 | - | - | - |
| 2 | 59,371.35 | 59,373.87 | 2.52 | 0.42 | 0.63 | 25.06 | 0.015 |
| 3 | 59,373.00 | 59,375.92 | 2.92 | 0.53 | 0.87 | 35.14 | 0.027 |
| 4 | 59,375.10 | 59,377.99 | 2.89 | 0.77 | 0.82 | 17.24 | 0.012 |
| Arc No. | Mean SZA (Degree) | Theoretical Density () and Altitude | Observed Density () and Altitude | Density Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| arc-4 | 80.7 | 70,770/138 km | 69,272/148 km | 2% |
| arc-5 | 80.7 | 70,770/138 km | 71,100/150 km | 1% |
| arc-9 | 88.7 | 23,111/150 km | 24,388/152 km | 5% |
| arc-10 | 88.7 | 23,111/150 km | 24,219/152 km | 5% |
| MEX-0112 | 78.0 | 81,670/136 km | 80,791/128 km | 1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Chen, L.; Jian, N.; Guo, P.; Kong, J.; Wang, M.; Han, Q.; Ping, J.; Wu, M. Preliminary Estimations of Mars Atmospheric and Ionospheric Profiles from Tianwen-1 Radio Occultation One-Way, Two-Way, and Three-Way Observations. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235506
Liu M, Chen L, Jian N, Guo P, Kong J, Wang M, Han Q, Ping J, Wu M. Preliminary Estimations of Mars Atmospheric and Ionospheric Profiles from Tianwen-1 Radio Occultation One-Way, Two-Way, and Three-Way Observations. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(23):5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235506
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Min, Lue Chen, Nianchuan Jian, Peng Guo, Jing Kong, Mei Wang, Qianqian Han, Jinsong Ping, and Mengjie Wu. 2023. "Preliminary Estimations of Mars Atmospheric and Ionospheric Profiles from Tianwen-1 Radio Occultation One-Way, Two-Way, and Three-Way Observations" Remote Sensing 15, no. 23: 5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235506
APA StyleLiu, M., Chen, L., Jian, N., Guo, P., Kong, J., Wang, M., Han, Q., Ping, J., & Wu, M. (2023). Preliminary Estimations of Mars Atmospheric and Ionospheric Profiles from Tianwen-1 Radio Occultation One-Way, Two-Way, and Three-Way Observations. Remote Sensing, 15(23), 5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235506





