Prediction of Grassland Biodiversity Using Measures of Spectral Variance: A Meta-Analytical Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search and Selection of Studies for Meta-Analysis
- Explicitly tested whether plant species richness or diversity was correlated with a measure of spectral variance in space.
- Included a Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient that resulted from a bivariate model or an r2 value with an indication of the relationship direction.
- Did not deal with environments such as in savannahs or mixed planned countryside.
2.2. Extraction and Description of Likely Moderators
2.2.1. Spectral Moderators
2.2.2. Species Moderators
2.2.3. Sampling Design
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Extraction of Effect and Sample Sizes
2.3.2. Three-Level Meta-Analytical Models
2.3.3. Sensitivity Analysis and Publication Bias
3. Results
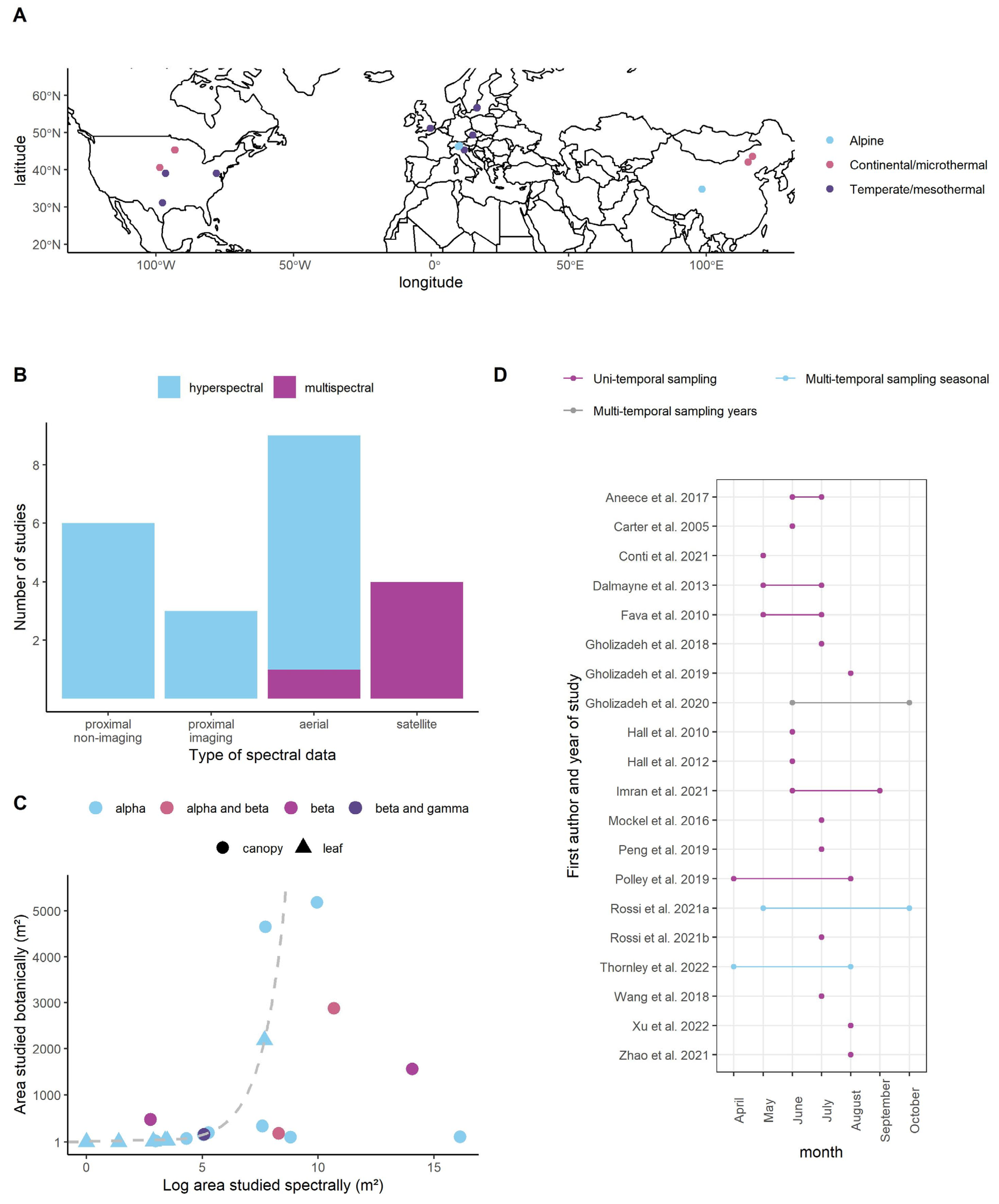
3.1. Overview of Studies
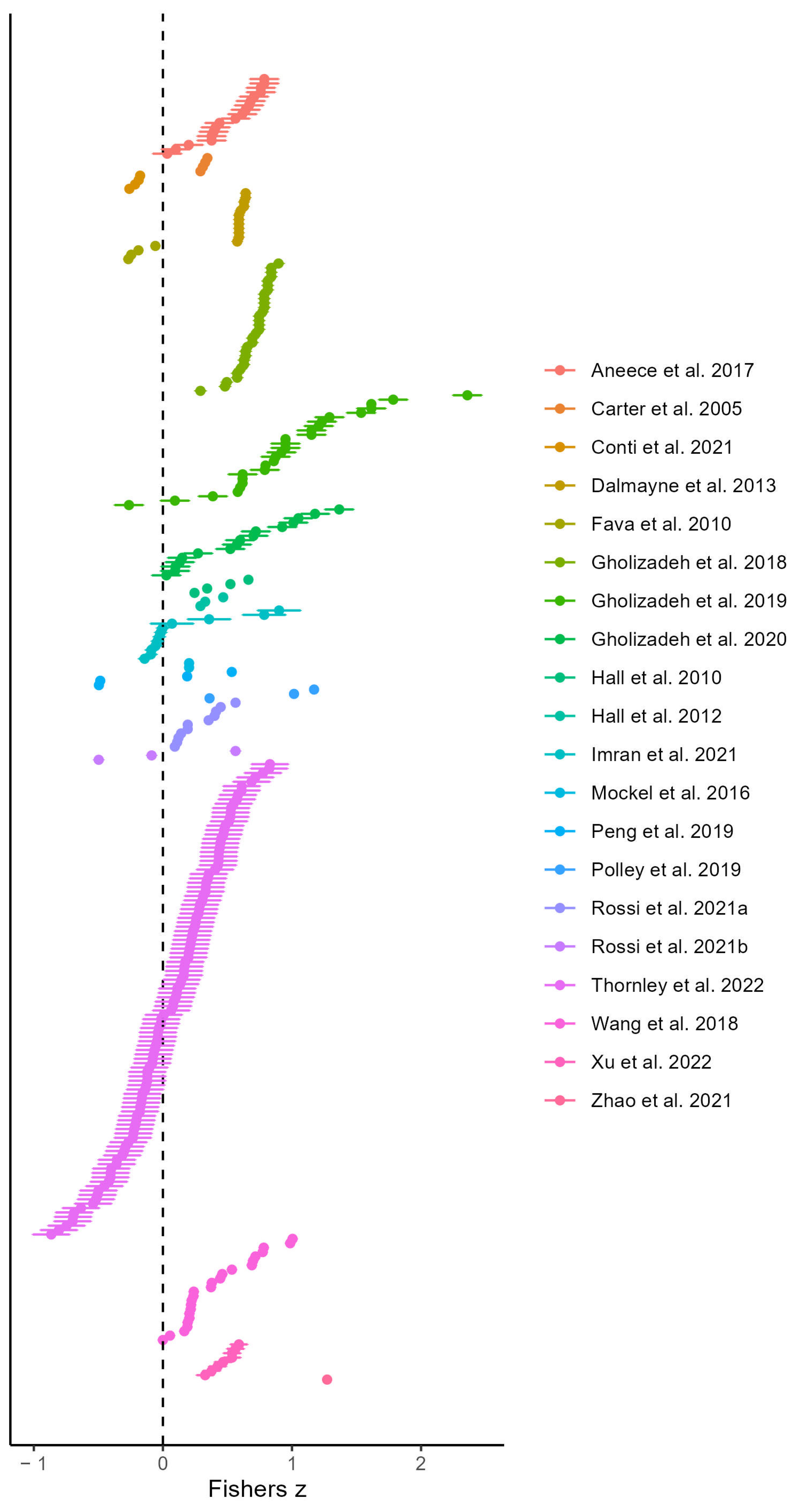
3.2. Results of the Multi-Level Models
4. Discussion
4.1. The Spectral Variation Hypothesis across Studies and Moderator Impact
4.2. Limitation in the Scope of Studies
4.3. Spectral Variation as a Covariate in More Complex Models
4.4. Approaches to the Spectral Variation Hypothesis Outside This Meta-Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gibson, D.J. Ecosystem Ecology. In Grasses and Grassland Ecology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Veldman, J.W.; Buisson, E.; Durigan, G.; Fernandes, G.W.; Le Stradic, S.; Mahy, G.; Negreiros, D.; Overbeck, G.; Veldman, R.G.; Zaloumis, N.P.; et al. Toward an old-growth concept for grasslands, savannas, and woodlands. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 13, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bengtsson, J.; Bullock, J.M.; Egoh, B.; Everson, C.; Everson, T.; O’Connor, T.; O’Farrell, P.J.; Smith, H.G.; Lindborg, R. Grasslands-more important for ecosystem services than you might think. Ecosphere 2019, 10, e02582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Bullock, J.M.; Lavorel, S.; Manning, P.; Schaffner, U.; Ostle, N.; Chomel, M.; Durigan, G.; Fry, E.L.; Johnson, D.; et al. Combatting global grassland degradation. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahama, N.; Uchida, K.; Ushimaru, A.; Isagi, Y. Timing of mowing influences genetic diversity and reproductive success in endangered semi-natural grassland plants. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 221, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piipponen, J.; Jalava, M.; de Leeuw, J.; Rizayeva, A.; Godde, C.; Cramer, G.; Herrero, M.; Kummu, M. Global trends in grassland carrying capacity and relative stocking density of livestock. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 3902–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boeck, H.; Lemmens, C.; Gielen, B.; Bossuyt, H.; Malchair, S.; Carnol, M.; Merckx, R.; Ceulemans, R.J.; Nijs, I. Combined effects of climate warming and plant diversity loss on above- and below-ground grassland productivity. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 60, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Liang, C.; Tang, Y.; He, J.-S.; Fang, J. Climate change alters interannual variation of grassland aboveground productivity: Evidence from a 22-year measurement series in the Inner Mongolian grassland. J. Plant Res. 2010, 123, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borer, E.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Lind, E.M.; Adler, P.B.; Alberti, J.; Anderson, T.M.; Bakker, J.D.; et al. Herbivores and nutrients control grassland plant diversity via light limitation. Nature 2014, 508, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagendra, H. Using remote sensing to assess biodiversity. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2001, 22, 2377–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, W.; Spector, S.; Gardiner, N.; Fladeland, M.; Sterling, E.; Steininger, M. Remote sensing for biodiversity science and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Cawkwell, F.; Dwyer, E.; Barrett, B.; Green, S. Satellite remote sensing of grasslands: From observation to management. J. Plant Ecol. 2016, 9, 649–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinermann, S.; Asam, S.; Kuenzer, C. Remote Sensing of Grassland Production and Management—A Review. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, J. Review of Remote Sensing Applications in Grassland Monitoring. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irisarri, J.G.N.; Oesterheld, M.; Verón, S.R.; Paruelo, J.M. Grass species differentiation through canopy hyperspectral reflectance. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2009, 30, 5959–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthoka, J.; Salakpi, E.; Ouko, E.; Yi, Z.-F.; Antonarakis, A.; Rowhani, P. Mapping Opuntia stricta in the Arid and Semi-Arid Environment of Kenya Using Sentinel-2 Imagery and Ensemble Machine Learning Classifiers. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.B.; Peet, R.K.; Dengler, J.; Pärtel, M. Plant species richness: The world records. J. Veg. Sci. 2012, 23, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelikova, T.J.; Williams, D.G.; Hoenigman, R.; Blumenthal, D.M.; Morgan, J.A.; Pendall, E. Seasonality of soil moisture mediates responses of ecosystem phenology to elevated CO 2 and warming in a semi-arid grassland. J. Ecol. 2015, 103, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavender-Bares, J.; Gamon, J.A.; Hobbie, S.E.; Madritch, M.D.; Meireles, J.E.; Schweiger, A.K.; Townsend, P.A. Harnessing plant spectra to integrate the biodiversity sciences across biological and spatial scales. Am. J. Bot. 2017, 104, 966–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillan, J.K.; Karl, J.W.; van Leeuwen, W.J.D. Integrating drone imagery with existing rangeland monitoring programs. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librán-Embid, F.; Klaus, F.; Tscharntke, T.; Grass, I. Unmanned aerial vehicles for biodiversity-friendly agricultural landscapes—A systematic review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 732, 139204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Gamon, J.A.; Cavender-Bares, J.; Townsend, P.A.; Zygielbaum, A.I. The spatial sensitivity of the spectral diversity–biodiversity relationship: An experimental test in a prairie grassland. Ecol. Appl. 2018, 28, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palmer, M.W.; Earls, P.G.; Hoagland, B.W.; White, P.S.; Wohlgemuth, T. Quantitative tools for perfecting species lists. Environmetrics 2002, 13, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Martin, R.E. Spectranomics: Emerging science and conservation opportunities at the interface of biodiversity and remote sensing. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2016, 8, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Baret, F. PROSPECT: A model of leaf optical properties spectra. Remote. Sens. Environ. 1990, 34, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Verhoef, W.; Baret, F.; Bacour, C.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Asner, G.P.; François, C.; Ustin, S.L. PROSPECT + SAIL models: A review of use for vegetation characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113 (Suppl. S1), S56–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassnacht, F.E.; Müllerová, J.; Conti, L.; Malavasi, M.; Schmidtlein, S. About the link between biodiversity and spectral variation. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2022, 25, e12643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidtlein, S.; Fassnacht, F.E. The spectral variability hypothesis does not hold across landscapes. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gholizadeh, H.; Gamon, J.A.; Helzer, C.J.; Cavender-Bares, J. Multi-temporal assessment of grassland α- and β-diversity using hyperspectral imaging. Ecol. Appl. 2020, 30, e02145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornley, R.; Gerard, F.F.; White, K.; Verhoef, A. Intra-annual taxonomic and phenological drivers of spectral variance in grasslands. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2022, 271, 112908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, M.A.; Rosa, S.; Sicard, A. Mechanisms Underlying the Environmentally Induced Plasticity of Leaf Morphology. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 1–25,. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chavana-Bryant, C.; Prohaska, N.; Serbin, S.P.; Guan, K.; Albert, L.P.; Yang, X.; van Leeuwen, W.J.D.; Garnello, A.J.; Martins, G.; et al. Convergence in relationships between leaf traits, spectra and age across diverse canopy environments and two contrasting tropical forests. New Phytol. 2016, 214, 1033–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cleland, E.E.; Chiariello, N.R.; Loarie, S.R.; Mooney, H.A.; Field, C.B. Diverse responses of phenology to global changes in a grassland ecosystem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13740–13744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastin, G.; Scarth, P.; Chewings, V.; Sparrow, A.; Denham, R.; Schmidt, M.; O’Reagain, P.; Shepherd, R.; Abbott, B. Separating grazing and rainfall effects at regional scale using remote sensing imagery: A dynamic reference-cover method. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, M.G.; de Jong, R.; Della Peruta, R.; Keller, A.; Schaepman, M.E. Determination of grassland use intensity based on multi-temporal remote sensing data and ecological indicators. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, M.E.; Ustin, S.L. The role of environmental context in mapping invasive plants with hyperspectral image data. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4301–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, K.; Mutanga, O.; Everson, T.; Adam, E. Discriminating indicator grass species for rangeland degradation assessment using hyperspectral data resampled to AISA Eagle resolution. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2012, 70, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, S.; Bendoula, R.; Hadoux, X.; Féret, J.-B.; Gorretta, N. A physically-based model for retrieving foliar biochemistry and leaf orientation using close-range imaging spectroscopy. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 220–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Féret, J.-B.; Asner, G.P. Spectroscopic classification of tropical forest species using radiative transfer modeling. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2415–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, H.M.; Muraoka, H.; Nasahara, K.N. Phenology of leaf optical properties and their relationship to mesophyll development in cool-temperate deciduous broad-leaf trees. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 297, 108236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tang, J.; Mustard, J.F.; Wu, J.; Zhao, K.; Serbin, S.; Lee, J.-E. Seasonal variability of multiple leaf traits captured by leaf spectroscopy at two temperate deciduous forests. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2016, 179, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, H.M.; Muraoka, H.; Nasahara, K.; Saigusa, N.; Murayama, S.; Koizumi, H. Phenology of leaf morphological, photosynthetic, and nitrogen use characteristics of canopy trees in a cool-temperate deciduous broadleaf forest at Takayama, central Japan. Ecol. Res. 2014, 30, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesketh, M.; Sánchez-Azofeifa, G.A. The effect of seasonal spectral variation on species classification in the Panamanian tropical forest. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Gamon, J.A.; Cavender-Bares, J. Seasonal patterns of spectral diversity at leaf and canopy scales in the Cedar Creek prairie biodiversity experiment. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.; Sollmann, R.; Wilting, A.; Bohmann, K.; Cole, B.; Balzter, H.; Martius, C.; Zlinszky, A.; Calvignac-Spencer, S.; Cobbold, C.A.; et al. Connecting Earth observation to high-throughput biodiversity data. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavender-Bares, J.; Schneider, F.D.; Santos, M.J.; Armstrong, A.; Carnaval, A.; Dahlin, K.M.; Fatoyinbo, L.; Hurtt, G.C.; Schimel, D.; Townsend, P.A.; et al. Integrating remote sensing with ecology and evolution to advance biodiversity conservation. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 6, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausch, A.; Bannehr, L.; Beckmann, M.; Boehm, C.; Feilhauer, H.; Hacker, J.; Heurich, M.; Jung, A.; Klenke, R.; Neumann, C.; et al. Linking Earth Observation and taxonomic, structural and functional biodiversity: Local to ecosystem perspectives. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 70, 317–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairota, P.; Cafarelli, B.; Didham, R.K.; Lovergine, F.P.; Lucas, R.M.; Nagendra, H.; Rocchini, D.; Tarantino, C. Challenges and opportunities in harnessing satellite remote-sensing for biodiversity monitoring. Ecol. Inform. 2015, 30, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettorelli, N.; Safi, K.; Turner, W. Satellite remote sensing, biodiversity research and conservation of the future. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachendorf, M.; Fricke, T.; Möckel, T. Remote sensing as a tool to assess botanical composition, structure, quantity and quality of temperate grasslands. Grass Forage Sci. 2017, 73, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Gamon, J.A. Remote sensing of terrestrial plant biodiversity. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchini, D.; Hernández-Stefanoni, J.L.; He, K.S. Advancing species diversity estimate by remotely sensed proxies: A conceptual review. Ecol. Inform. 2015, 25, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevitch, J.; Koricheva, J.; Nakagawa, S.; Stewart, G. Meta-analysis and the science of research synthesis. Nature 2018, 555, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koricheva, J.; Gurevitch, J. Uses and misuses of meta-analysis in plant ecology. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 828–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, G. Meta-analysis in applied ecology. Biol. Lett. 2009, 6, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wei, C.; Zhang, Y.; Blackburn, G.A.; Wang, X.; Wei, C.; Wang, J. Meta-Analysis of the Detection of Plant Pigment Concentrations Using Hyperspectral Remotely Sensed Data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Cleemput, E.; Vanierschot, L.; Fernández-Castilla, B.; Honnay, O.; Somers, B. The functional characterization of grass- and shrubland ecosystems using hyperspectral remote sensing: Trends, accuracy and moderating variables. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 747–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirici, G.; Mura, M.; McInerney, D.; Py, N.; Tomppo, E.O.; Waser, L.T.; Travaglini, D.; McRoberts, R.E. A meta-analysis and review of the literature on the k-Nearest Neighbors technique for forestry applications that use remotely sensed data. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Jacob, F.; Duveiller, G. Remote sensing for agricultural applications: A meta-review. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2019, 236, 111402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, R.; Mountrakis, G.; Stehman, S.V. A meta-analysis of remote sensing research on supervised pixel-based land-cover image classification processes: General guidelines for practitioners and future research. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, F.A.; Lefkoff, A.B.; Boardman, J.W.; Heidebrecht, K.B.; Shapiro, A.T.; Barloon, P.J.; Goetz, A.F.H. The spectral image processing system (SIPS)—Interactive visualization and analysis of imaging spectrometer data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 44, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchini, D.; Marcantonio, M.; Ricotta, C. Measuring Rao’s Q diversity index from remote sensing: An open source solution. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feret, J.-B.; Asner, G.P. Tree Species Discrimination in Tropical Forests Using Airborne Imaging Spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2012, 51, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, Y. The Potential of Mapping Grassland Plant Diversity with the Links among Spectral Diversity, Functional Trait Diversity, and Species Diversity. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornley, R.H.; Verhoef, A.; Gerard, F.F.; White, K. The Feasibility of Leaf Reflectance-Based Taxonomic Inventories and Diversity Assessments of Species-Rich Grasslands: A Cross-Seasonal Evaluation Using Waveband Selection. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.J.; Willis, K.J.; Field, R. Scale and Species Richness: Towards a General, Hierarchical Theory of Species Diversity. J. Biogeogr. 2001, 28, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beck, H.E.; Zimmermann, N.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Wood, E.F. Present and future Köppen-Geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huwaldt, J.A. Plot Digitizer. Available online: http://plotdigitizer.sourceforge.net/ (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Walker, D.A. JMASM9: Converting Kendall’s Tau For Correlational Or Meta-Analytic Analyses. J. Mod. Appl. Stat. Methods 2003, 2, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedges, L.V.; Olkin, I. Statistical Methods for Meta-Analysis; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Borenstein, M. Effect sizes for continuous data. In The Handbook of Research Synthesis and Meta-Analysis; Cooper, H., Hedges, L., Valentine, J.C., Eds.; Russell Sage Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 221–235. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, M.W.-L. A Guide to Conducting a Meta-Analysis with Non-Independent Effect Sizes. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2019, 29, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van den Noortgate, W.; López-López, J.A.; Marín-Martínez, F.; Sánchez-Meca, J. Three-level meta-analysis of dependent effect sizes. Behav. Res. Methods 2013, 45, 576–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assink, M.; Wibbelink, C.J.M. Fitting three-level meta-analytic models in R: A step-by-step tutorial. Quant. Methods Psychol. 2016, 12, 154–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W.; Cheung, M.W.-L. Outlier and influence diagnostics for meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 2010, 1, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Lagisz, M.; Jennions, M.D.; Koricheva, J.; Noble, D.W.A.; Parker, T.H.; Sánchez-Tójar, A.; Yang, Y.; O’Dea, R.E. Methods for testing publication bias in ecological and evolutionary meta-analyses. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2021, 13, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 23 June 2022).
- Aneece, I.P.; Epstein, H.; Lerdau, M. Correlating species and spectral diversities using hyperspectral remote sensing in early-successional fields. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 3475–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.A.; Knapp, A.K.; Anderson, J.E.; Hoch, G.A.; Smith, M.D. Indicators of plant species richness in AVIRIS spectra of a mesic grassland. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, L.; Malavasi, M.; Galland, T.; Komárek, J.; Lagner, O.; Carmona, C.P.; de Bello, F.; Rocchini, D.; Šímová, P. The relationship between species and spectral diversity in grassland communities is mediated by their vertical complexity. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2021, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmayne, J.; Möckel, T.; Prentice, H.C.; Schmid, B.C.; Hall, K. Assessment of fine-scale plant species beta diversity using WorldView-2 satellite spectral dissimilarity. Ecol. Inform. 2013, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, F.; Parolo, G.; Colombo, R.; Gusmeroli, F.; Della Marianna, G.; Monteiro, A.; Bocchi, S. Fine-scale assessment of hay meadow productivity and plant diversity in the European Alps using field spectrometric data. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 137, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, H.; Gamon, J.A.; Zygielbaum, A.I.; Wang, R.; Schweiger, A.K.; Cavender-Bares, J. Remote sensing of biodiversity: Soil correction and data dimension reduction methods improve assessment of α-diversity (species richness) in prairie ecosystems. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, H.; Gamon, J.A.; Townsend, P.A.; Zygielbaum, A.I.; Helzer, C.J.; Hmimina, G.Y.; Yu, R.; Moore, R.M.; Schweiger, A.K.; Cavender-Bares, J. Detecting prairie biodiversity with airborne remote sensing. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2018, 221, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.; Johansson, L.; Sykes, M.; Reitalu, T.; Larsson, K.; Prentice, H. Inventorying management status and plant species richness in semi-natural grasslands using high spatial resolution imagery. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2010, 13, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.; Reitalu, T.; Sykes, M.T.; Prentice, H.C. Spectral heterogeneity of QuickBird satellite data is related to fine-scale plant species spatial turnover in semi-natural grasslands. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2011, 15, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, H.; Gianelle, D.; Scotton, M.; Rocchini, D.; Dalponte, M.; Macolino, S.; Sakowska, K.; Pornaro, C.; Vescovo, L. Potential and Limitations of Grasslands α-Diversity Prediction Using Fine-Scale Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möckel, T.; Dalmayne, J.; Schmid, B.C.; Prentice, H.C.; Hall, K. Airborne Hyperspectral Data Predict Fine-Scale Plant Species Diversity in Grazed Dry Grasslands. Remote. Sens. 2016, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Fan, M.; Bai, L.; Sang, W.; Feng, J.; Zhao, Z.; Tao, Z. Identification of the Best Hyperspectral Indices in Estimating Plant Species Richness in Sandy Grasslands. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polley, H.W.; Yang, C.; Wilsey, B.J.; Fay, P.A. Spectral Heterogeneity Predicts Local-Scale Gamma and Beta Diversity of Mesic Grasslands. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, C.; Kneubühler, M.; Schütz, M.; Schaepman, M.E.; Haller, R.M.; Risch, A.C. Remote sensing of spectral diversity: A new methodological approach to account for spatio-temporal dissimilarities between plant communities. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.; Kneubühler, M.; Schütz, M.; Schaepman, M.E.; Haller, R.M.; Risch, A.C. Spatial resolution, spectral metrics and biomass are key aspects in estimating plant species richness from spectral diversity in species-rich grasslands. Remote. Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 8, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zeng, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, D.; Liu, W.; Ma, Z.; Wu, B. Assessing the Impact of Soil on Species Diversity Estimation Based on UAV Imaging Spectroscopy in a Natural Alpine Steppe. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Du, Q. Hyperspectral Band Selection: A Review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2019, 7, 118–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Rothstein, H.R. When Does It Make Sense to Perform a Meta-Analysis? In Introduction to Meta-Analysis, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2009; pp. 357–364. [Google Scholar]
- Senior, A.M.; Grueber, C.E.; Kamiya, T.; Lagisz, M.; O’Dwyer, K.; Santos, E.S.A.; Nakagawa, S. Heterogeneity in ecological and evolutionary meta-analyses: Its magnitude and implications. Ecology 2016, 97, 3293–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, A.; Mooers, A.O.; Miller, D.C.; Nibbelink, N.; Redding, D.; Kuhn, T.S.; Roberts, J.T.; Gittleman, J.L. Targeting global conservation funding to limit immediate biodiversity declines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12144–12148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gessner, U.; Machwitz, M.; Conrad, C.; Dech, S. Estimating the fractional cover of growth forms and bare surface in savannas. A multi-resolution approach based on regression tree ensembles. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Brandt, M.; Wang, Q.; Prishchepov, A.V.; Tucker, C.J.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Fensholt, R. From woody cover to woody canopies: How Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data advance the mapping of woody plants in savannas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 234, 111465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirguey, P. Simple correction of multiple reflection effects in rugged terrain. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2009, 30, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, D. Negative results are disappearing from most disciplines and countries. Scientometrics 2011, 90, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, S.J.; Gross, R.A. Reporting null results and advancing science. Neurology 2019, 92, 827–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakowska, K.; MacArthur, A.; Gianelle, D.; Dalponte, M.; Alberti, G.; Gioli, B.; Miglietta, F.; Pitacco, A.; Meggio, F.; Fava, F.; et al. Assessing Across-Scale Optical Diversity and Productivity Relationships in Grasslands of the Italian Alps. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, L.T.; Timmermans, J.; van der Windt, N.; Sil, F.; de Sá, N.C.; Soudzilovskaia, N.A.; van Bodegom, P.M. Explaining discrepancies between spectral and in-situ plant diversity in multispectral satellite earth observation. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.A.; Mathieu, R.; Asner, G.P.; Naidoo, L.; Van Aardt, J.; Ramoelo, A.; Debba, P.; Wessels, K.; Main, R.; Smit, I.P.J.; et al. Mapping tree species composition in South African savannas using an integrated airborne spectral and LiDAR system. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 125, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauvel, M.; Lopes, M.; Dubo, T.; Rivers-Moore, J.; Frison, P.-L.; Gross, N.; Ouin, A. Prediction of plant diversity in grasslands using Sentinel-1 and -2 satellite image time series. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2019, 237, 111536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.; Fauvel, M.; Ouin, A.; Girard, S. Spectro-Temporal Heterogeneity Measures from Dense High Spatial Resolution Satellite Image Time Series: Application to Grassland Species Diversity Estimation. Remote. Sens. 2017, 9, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rapinel, S.; Panhelleux, L.; Lalanne, A.; Hubert-Moy, L. Combined use of environmental and spectral variables with vegetation archives for large-scale modeling of grassland habitats. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2021, 46, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, A.K.; Cavender-Bares, J.; Townsend, P.A.; Hobbie, S.E.; Madritch, M.D.; Wang, R.; Tilman, D.; Gamon, J.A. Plant spectral diversity integrates functional and phylogenetic components of biodiversity and predicts ecosystem function. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, H.A.; Aiello-Lammens, M.E.; Euston-Brown, D.; Jones, C.S.; Mollmann, H.K.; Merow, C.; Slingsby, J.A.; van der Merwe, H.; Wilson, A.M.; Silander, J.A. Plant spectral diversity as a surrogate for species, functional and phylogenetic diversity across a hyper-diverse biogeographic region. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2021, 30, 1403–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireles, J.E.; Cavender-Bares, J.; Townsend, P.A.; Ustin, S.; Gamon, J.A.; Schweiger, A.K.; Schaepman, M.E.; Asner, G.P.; Martin, R.E.; Singh, A.; et al. Leaf reflectance spectra capture the evolutionary history of seed plants. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Paper Number | Paper | Botanical Diversity Metrics | Scale Diversity Measured | Temporal Stability | Spectral Diversity Metric | Grassland Types | Shared Experimental Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aneece et al. 2017 [81] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | Carter et al. 2005 [82] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 3 | Conti et al. 2021 [83] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| 4 | Dalmayne et al. 2013 [84] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 5 | Fava et al. 2010 [85] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 6 | Gholizadeh et al. 2018 [86] | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| 7 | Gholizadeh et al. 2019 [87] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 7 |
| 8 | Gholizadeh et al. 2020 [29] | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 7 |
| 9 | Hall et al. 2010 [88] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 10 | Hall et al. 2012 [89] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 11 | Imran et al. 2021 [90] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 |
| 12 | Möckel et al. 2016 [91] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 13 | Peng et al. 2019 [92] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 9 |
| 14 | Polley et al. 2019 [93] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 10 |
| 15 | Rossi et al. 2021a [94] | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| 16 | Rossi et al. 2021b [95] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 12 |
| 17 | Thornley et al. 2022a [31] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 13 |
| 18 | Wang et al. 2018 [23] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 19 | Xu et al. 2022 [96] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 14 |
| 20 | Zhao et al. 2021 [66] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| Model Type | Cluster Variable | Moderators | Total Number of Effect Sizes (studies) | Number of Effect Sizes Per Group of Moderator | Pooled Correlation (Fisher’s Z) with 95% CI | Pooled Correlation (r) with 95% CI | Significance Test of Pooled Correlation | Estimates for Moderators (if Significant) (r) | Significance Tests of Moderator Based Estimates | Random Effect Variance % (Sampling Error) | Random Effect Variance % (τ2level 2) | Random Effect Variance % (τ2level 3) | Multi-Level Variance % (I2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | 3 -level model | Study | - | 297(20) | - | 0.3741 (±0.162) | 0.358 (±0.161) | 8.3 × 10 −6 | - | - | 16.5 | 21.9 | 61.6 | 83.5 |
| 3-level model | Site | - | 297(20) | - | 0.333 (±0.2) | 0.32 (±0.197) | 0.0012 | - | - | 14.6 | 22.2 | 63.1 | 85.4 | |
| Spectral data | 3-level moderator model | Study | Pixel Size | 297(20) | - | - | - | - | - | 0.18 (n. s.) | 17.88 | 22.31 | 59.81 | 82.12 |
| 3-level moderator model | Study | Leaf or Canopy | 297(20) | Leaf = 53; Canopy = 244 | - | - | - | Leaf = 0.49 (±0.128); Canopy = 0.3111 (±0.146) | 0.0036 (**) | 16.01 | 18.76 | 65.22 | 83.99 | |
| 3-level moderator model | Study | Spectral Region | 297(20) | Single = 153; Cross = 144 | - | - | - | - | 0.154 (n. s.) | 17.13 | 22.76 | 60.12 | 82.87 | |
| 3-level moderator model | Study | Spectral Resolution | 297(20) | Multi-spectral = 38; Hyperspectral = 259 | - | - | - | 0.2094 (n. s.) | 16.8 | 22.29 | 60.9 | 83.2 | ||
| 3-level moderator model | Study | Spectral Diversity Metric | 297(20) | Complex = 97; Simple = 200 | - | - | - | - | 0.7448 (n. s.) | 16.29 | 21.61 | 62.09 | 83.71 | |
| Species data | 3-level moderator model | Study | Level of Diversity | 296(20) | Alpha = 269; Beta = 27 | - | - | - | - | 0.24 (n. s.) | 16.2 | 19.2 | 64.6 | 83.8 |
| 3-level moderator model | Study | Species Diversity Metric | 232(18) | Richness = 133; Diversity = 99 | - | - | - | - | 0.86 (n. s.) | 13.9 | 23.8 | 62.2 | 86.1 | |
| 3-level moderator model | Study | Richness Level | 247(15) | - | - | - | - | 0.0161 ± 0.0015 | 0.0433 (*) | 15.82 | 13.95 | 70.2 | 84.2 | |
| Sampling Design | 3-level moderator model | Study | Spatial Matching | 297(20) | - | - | - | - | - | 0.3199 (n. s.) | 16.9 | 22.41 | 60.69 | 83.1 |
| 3-level moderator model | Study | Climate | 297(20) | Alpine = 26; Continental = 101; Temperate = 170 | - | - | - | - | 0.0878 (n. s.) | 17.99 | 23.78 | 58.23 | 82.01 | |
| 3-level moderator model | Study | Sampling Season | 297(20) | Summer= 252; Other = 45 | - | - | - | - | 0.8065 (n. s.) | 16.4 | 21.89 | 61.71 | 83.6 | |
| 3-level moderator model | Study | Site Type | 297(20) | Experimental = 175; Natural = 122 | - | - | - | - | 0.3122 (n. s.) | 15.75 | 20.8 | 63.46 | 84.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thornley, R.H.; Gerard, F.F.; White, K.; Verhoef, A. Prediction of Grassland Biodiversity Using Measures of Spectral Variance: A Meta-Analytical Review. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030668
Thornley RH, Gerard FF, White K, Verhoef A. Prediction of Grassland Biodiversity Using Measures of Spectral Variance: A Meta-Analytical Review. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(3):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030668
Chicago/Turabian StyleThornley, Rachael H., France F. Gerard, Kevin White, and Anne Verhoef. 2023. "Prediction of Grassland Biodiversity Using Measures of Spectral Variance: A Meta-Analytical Review" Remote Sensing 15, no. 3: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030668
APA StyleThornley, R. H., Gerard, F. F., White, K., & Verhoef, A. (2023). Prediction of Grassland Biodiversity Using Measures of Spectral Variance: A Meta-Analytical Review. Remote Sensing, 15(3), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030668






