Back-Analysis of Slope GNSS Displacements Using Geographically Weighted Regression and Least Squares Algorithms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
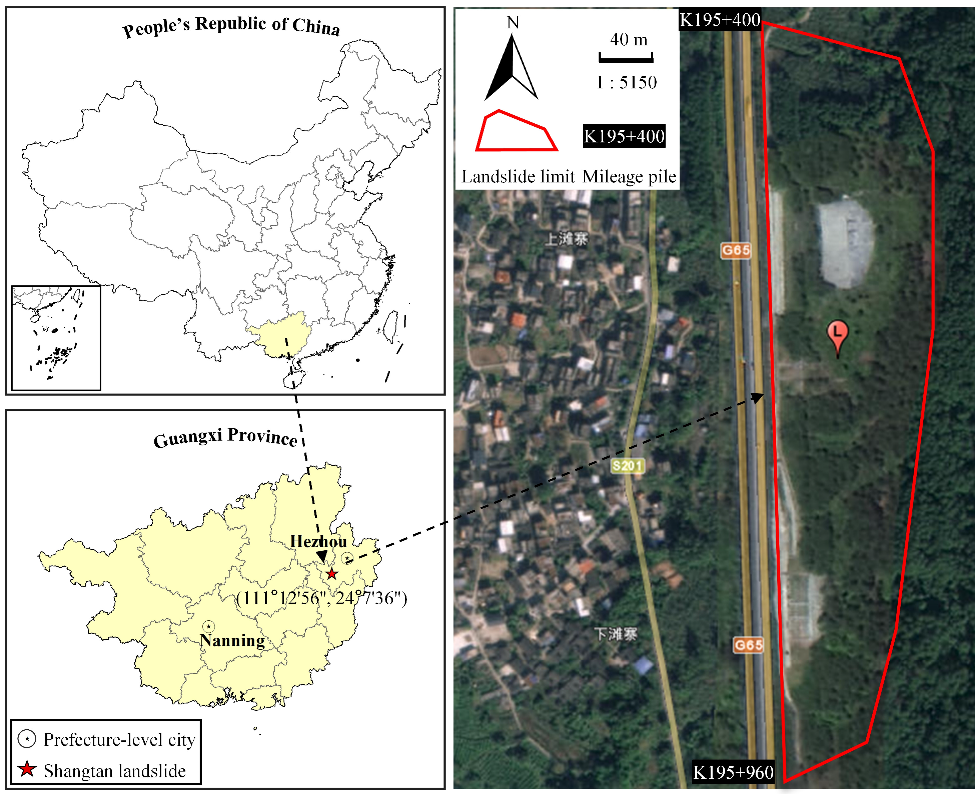
2.1. Study Area
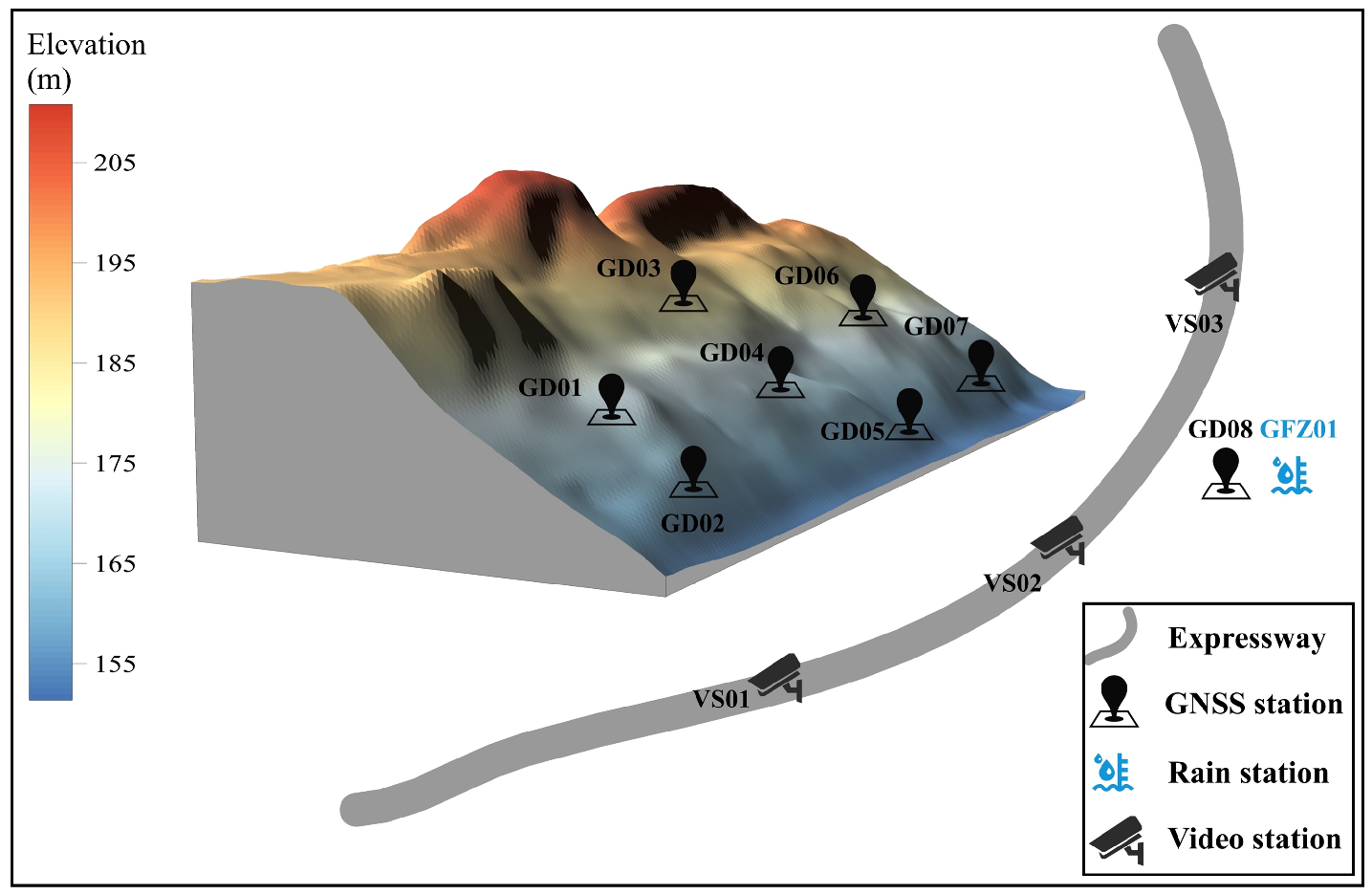
2.2. Numerical Model and Monitoring System
2.3. GWR for Slope Physical Modelling
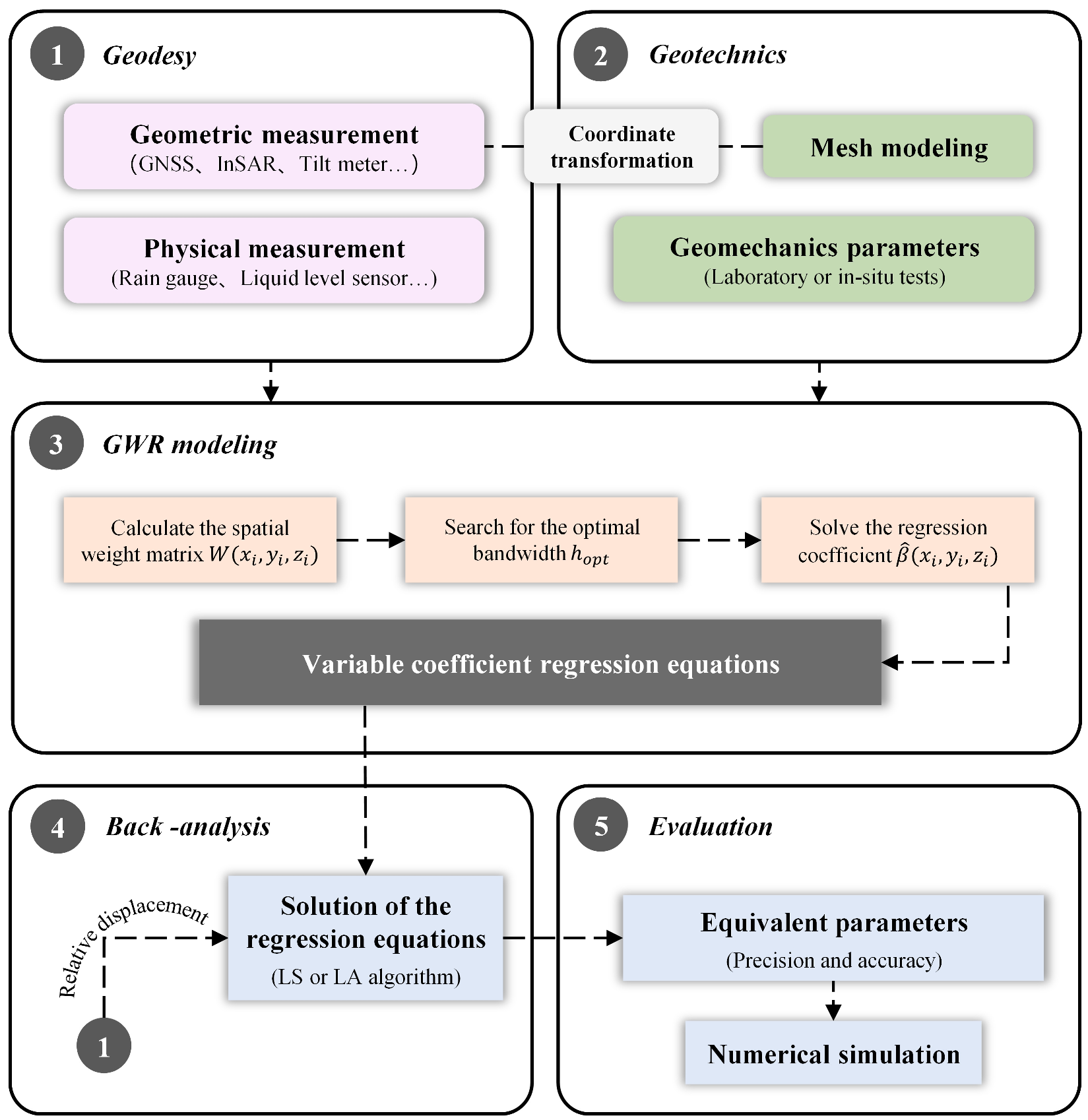
2.4. Displacement Back-Analysis Method Based on GWR
2.5. Instructions on Implementation of the Back-Analysis Method
3. Results
3.1. Simulation Experiments
3.1.1. GWR Modelling
3.1.2. Back-Analysis Based on GWR
3.2. Real Data Experiments
3.2.1. Monitoring Data
3.2.2. Modelling and Back-Analysis
3.2.3. Stability Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kocaman, S.; Gokceoglu, C. A CitSci app for landslide data collection. Landslides 2019, 16, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaron, J.; Loew, S.; Forrer, M. Recharge response and kinematics of an unusual earthflow in Liechtenstein. Landslides 2021, 18, 2383–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peternel, T.; Janza, M.; Segina, E.; Bezak, N.; Macek, M. Recognition of Landslide Triggering Mechanisms and Dynamics Using GNSS, UAV Photogrammetry and In Situ Monitoring Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyazmensky, A.; Stead, D.; Elmo, D.; Moss, A. Numerical analysis of block caving-induced instability in large open pit slopes: A finite element/discrete element approach. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2010, 43, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Sun, P.; Zhang, M.; Li, B. Mechanism on apparent dip sliding of oblique inclined bedding rockslide at Jiweishan, Chongqing, China. Landslides 2011, 8, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Mei, G.; Xu, N. A statistics-based discrete element modeling method coupled with the strength reduction method for the stability analysis of jointed rock slopes. Eng. Geol. 2020, 264, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, S.; Wang, R.; Xiao, M. Stability analysis of a typical landslide mass in the Three Gorges Reservoir under varying reservoir water levels. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Ma, G.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, W.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Z.; Cheng, X. Displacement back analysis of reservoir landslide based on multi-source monitoring data: A case study of the Cheyiping landslide in the Lancang River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zheng, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, C. Parameter inversion and deformation mechanism of Sanmendong landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir region under the combined effect of reservoir water level fluctuation and rainfall. Eng. Geol. 2016, 205, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, S. A new displacement back analysis to identify mechanical geo-material parameters based on hybrid intelligent methodology. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2004, 28, 1141–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, T.; Dias, D.; Eclaircy-Caudron, S.; Correia, A.G.; Costa, L. Back analysis of geomechanical parameters by optimisation of a 3D model of an underground structure. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2011, 26, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, H.; Ru, Z.; Sun, Q. Probabilistic back analysis based on Bayesian and multi-output support vector machine for a high cut rock slope. Eng. Geol. 2016, 203, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Hong, Y.; Chen, Q.; Karekal, S. A modified optimization algorithm for back analysis of properties for coupled stress-seepage field problems. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 94, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yin, S. Geomechanical parameters identification by particle swarm optimization and support vector machine. Appl. Math. Model. 2009, 33, 3997–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Cheng, L.; Bao, T.; Lv, B. Integrated parameter inversion analysis method of a CFRD based on multi-output support vector machines and the clonal selection algorithm. Comput. Geotech. 2013, 47, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. A reduced order model based on machine learning for numerical analysis: An application to geomechanics. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 100, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Bao, T.; Gu, C.; Jiang, M.; Wang, T.; Shi, Z. Parameter sensitivity and inversion analysis of a concrete faced rock-fill dam based on HS-BPNN algorithm. Sci. China-Technol. Sci. 2016, 59, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Ge, M. Back analysis of rock mass parameters and initial stress for the Longtan tunnel in China. Eng. Comput. 2016, 32, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Fourie, A. A real-time back-analysis technique to infer rheological parameters from field monitoring. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2018, 51, 3029–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, G.; Wei, B.; Zhong, Y.; Zhan, L. Dynamic inversion method for the material parameters of a high arch dam and its foundation. Appl. Math. Model. 2019, 71, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Yang, D.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Lu, X.; Pei, L.; Kou, Q. Monitoring-data mechanism-driven dynamic evaluation method for slope safety. Comput. Geotech. 2022, 148, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Fourie, A.; Zhao, X. Back-analysis method for stope displacements using gradient-boosted regression tree and firefly algorithm. J. Comput. Civil. Eng. 2018, 32, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, E.; Moosavi, M.; Hossaini, M.F.; Assary, M.; Golabchi, Y. Determination of initial stress state and rock mass deformation modulus at Lavarak HEPP by back analysis using ant colony optimization and multivariable regression analysis. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Su, H.; Wen, Z. Improved PLS and PSO methods-based back analysis for elastic modulus of dam. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2019, 131, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, G.; Li, Y.; Wei, M.; Liu, B. Displacement back-analysis of rock mass parameters for underground caverns using a novel intelligent optimization method. Int. J. Geomech. 2020, 20, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Yin, T.; Zhou, C. A back-analysis method using an intelligent multi-objective optimization for predicting slope deformation induced by excavation. Eng. Geol. 2018, 239, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, J.; Jin, W.; Sloan, S.; Jiang, Q. Bayesian updating for progressive excavation of high rock slopes using multi-type monitoring data. Eng. Geol. 2019, 252, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, J.; Yu, Y. Multi-objective probabilistic inverse analysis of rainfall-induced landslide based on time-varied data. Rock Soil Mech. 2017, 38, 3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gong, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L. Multi-objective probabilistic back analysis for selecting the optimal updating strategy based on multi-source observations. Comput. Geotech. 2022, 151, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J. An advanced Bayesian parameter estimation methodology for concrete dams combining an improved extraction technique of hydrostatic component and hybrid response surface method. Eng. Struct. 2022, 267, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Yao, D. Comprehensive monitoring of talus slope deformation and displacement back analysis of mechanical parameters based on back-propagation neural network. Landslides 2021, 18, 1889–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Dai, W.; Yu, W.; Bai, D. Determination of landslide displacement warning thresholds by applying DBA-LSTM and numerical simulation algorithms. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. Study of uniqueness of multi-parameter inverse analysis of elastic displacement of concrete gravity dam. Eng. Optimiz. 2020, 52, 2033–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupfer, J.; Farris, C. Incorporating spatial non-stationarity of regression coefficients into predictive vegetation models. Landsc. Ecol. 2007, 22, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmann, G.S.; Fogg, G.E. Multi-scale alluvial fan heterogeneity modeled with transition probability geostatistics in a sequence stratigraphic framework. J. Hydrol. 1999, 226, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaske, B. Anastomosing rivers: A review of their classification, origin and sedimentary products. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2001, 53, 149–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Tang, J.; Lu, G.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, T.; Fang, J. The design and application of landslide monitoring and early warning system based on microservice architecture. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2020, 11, 928–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Satirapod, C.; Rizos, C. Stochastic assessment of GPS carrier phase measurements for precise static relative positioning. J. Geod. 2002, 76, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Brunsdon, C. Local forms of spatial analysis. Geogr. Anal. 1999, 31, 340–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Jensen, J.; Weng, Q.; Weaver, R. A geographically weighted regression analysis of the underlying factors related to the surface urban heat island phenomenon. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Mei, C.; Yan, X. Local linear estimation of spatially varying coefficient models: An improvement on the geographically weighted regression technique. Environ. Plan. A 2008, 40, 986–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioda, G.; Locatelli, L. Back analysis of the measurements performed during the excavation of a shallow tunnel in sand. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 1999, 23, 1407–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palancz, B.; Awange, J.L. Application of Pareto optimality to linear models with errors-in-all-variables. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.Z.; Mirjalili, S.; Saremi, S.; Faris, H.; Aljarah, I. Grasshopper optimization algorithm for multi-objective optimization problems. Appl. Intell. 2018, 48, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Oshan, T.M. Geographically weighted regression and multicollinearity: Dispelling the myth. J. Geogr. Syst. 2016, 18, 303–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wu, B.; Barry, M. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in house prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Dai, W.; Yu, W.; Shi, Q.; Santerre, R. Mixed geographically and temporally weighted regression for spatio-temporal deformation modelling. Surv. Rev. 2022, 54, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, G.; Liu, B.; Li, T. A novel displacement back analysis method considering the displacement loss for underground rock mass engineering. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 95, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Feng, S. Back analysis of surrounding rock parameters of tunnel considering displacement loss and space effect. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 5675–5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Jin, A.; Zhao, Y. Application of UAV oblique photogrammetry in the field of geology survey at the high and steep slope. Rock Soil Mech. 2018, 39, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshiri, R.; Motagh, M.; Baes, M.; Sharifi, M.A. Deformation analysis of the Lake Urmia causeway (LUC) embankments in northwest Iran: Insights from multi-sensor interferometry synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) data and finite element modeling (FEM). J. Geod. 2014, 88, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, A.; Neri, A.; De Martino, P.; Isaia, R.; Novellino, A.; Tramparulo, F.D.; Vitale, S. Radial interpolation of GPS and leveling data of ground deformation in a resurgent caldera: Application to Campi Flegrei (Italy). J. Geod. 2020, 94, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qian, S.; Zhu, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Yu, J. An approach for retrieving complete three-dimensional ground displacement components from two parallel-track InSAR measurements. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, D. A quaternion-based geodetic datum transformation algorithm. J. Geod. 2006, 80, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shen, Y.; Li, W. The seamless model for three-dimensional datum transformation. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 2099–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Jia, N. More efficient methods among commonly used robust estimation methods for GPS coordinate transformation. Surv. Rev. 2013, 45, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itasca, F. Fast Lagrangian Analysis of Continua; Itasca Consulting Group Inc.: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, S.; Toll, D.G.; Rosser, N.J.; Brain, M.J. An investigation of the combined effect of rainfall and road cut on landsliding. Eng. Geol. 2022, 307, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Hack, R. Some new pre-warning criteria for creep slope failure. Sci. China-Technol. Sci. 2011, 54, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbeheshti, N.; Featherstone, W.E. Non-stationary covariance function modelling in 2D least-squares collocation. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Q.; Dai, W.; Santerre, R.; Li, Z.; Liu, N. Spatially heterogeneous land surface deformation data fusion method based on an enhanced spatio-temporal random effect model. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Dai, W.; Xie, L.; Xu, W. Fusion of GNSS and InSAR time series using the improved STRE model: Applications to the San Francisco Bay Area and Southern California. J. Geod. 2022, 96, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Ding, C.; Wang, Y. A geographically and temporally weighted regression model to explore the spatiotemporal influence of built environment on transit ridership. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2018, 70, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hong, S. Urban expansion patterns and their driving forces based on the center of gravity-GTWR model: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Ji, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Van Oort, N.; Jin, Y.; Hoogendoorn, S. A comparison in travel patterns and determinants of user demand between docked and dockless bike-sharing systems using multi-sourced data. Transp. Res. Pt. A-Policy Pract. 2020, 139, 148–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Ji, Q. Regional differences and driving factors analysis of carbon emission intensity from transport sector in China. Energy 2021, 224, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Wang, X.; Pei, L.; Su, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Identifying the spatiotemporal dynamic of PM2.5 concentrations at multiple scales using geographically and temporally weighted regression model across China during 2015–2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, R.; Huang, J. Bayesian updating for one-dimensional consolidation measurements. Can. Geotech. J. 2015, 52, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
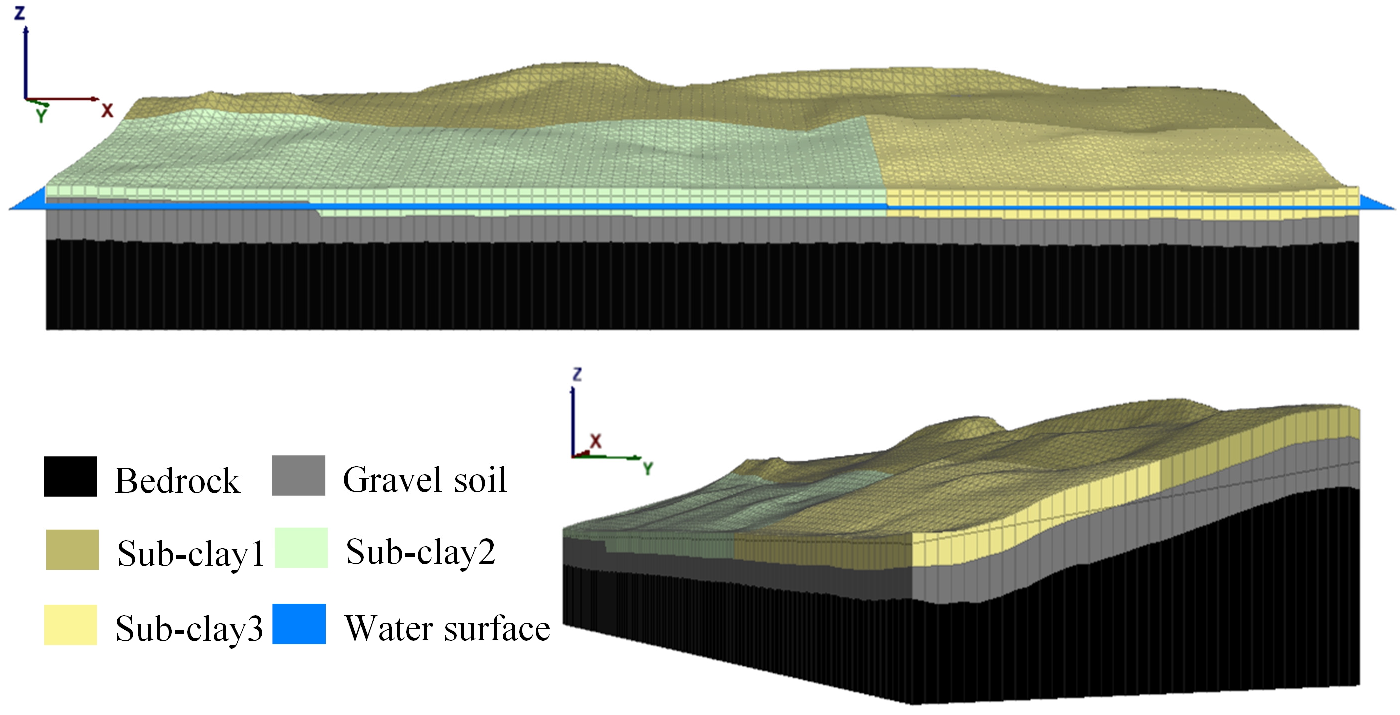


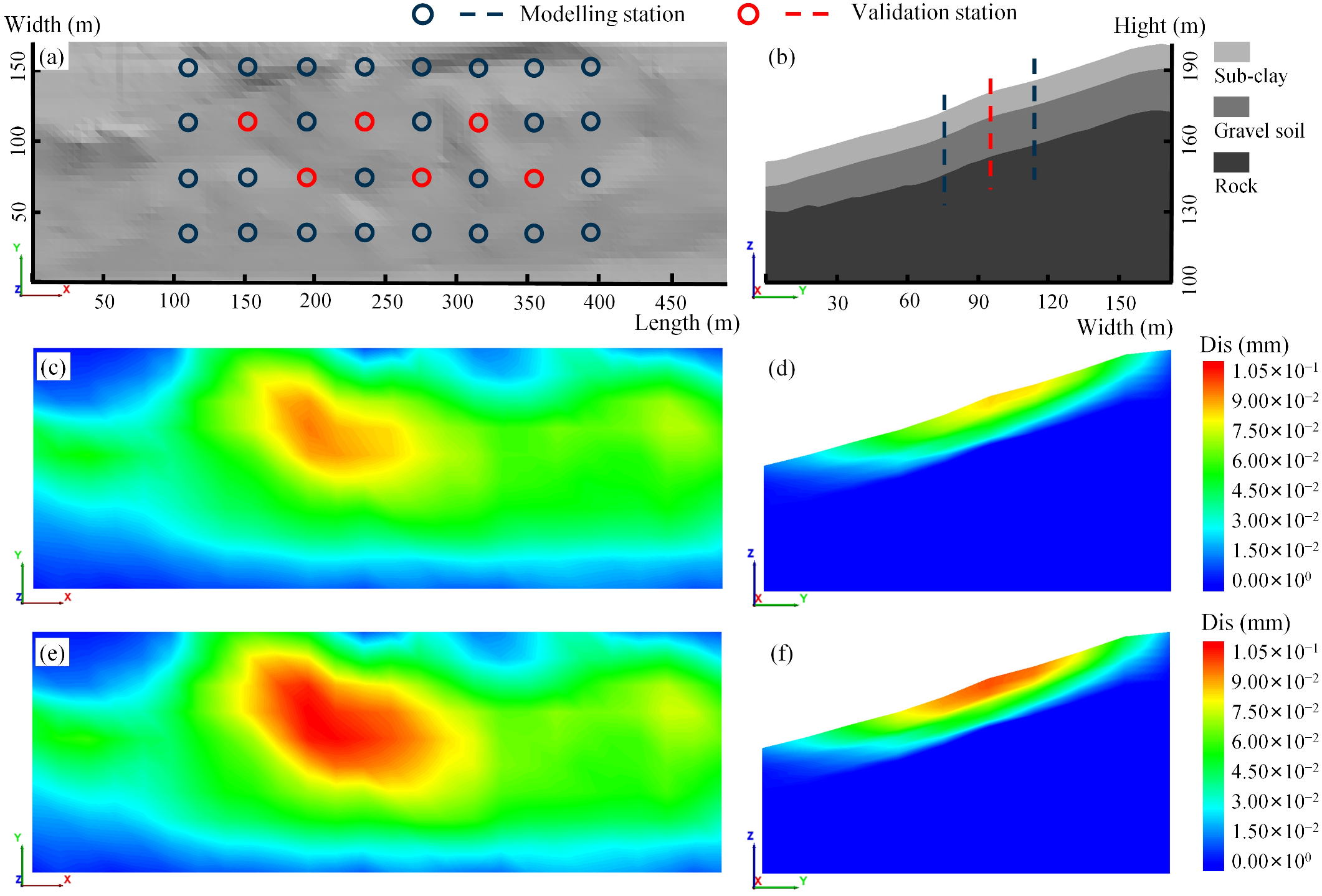
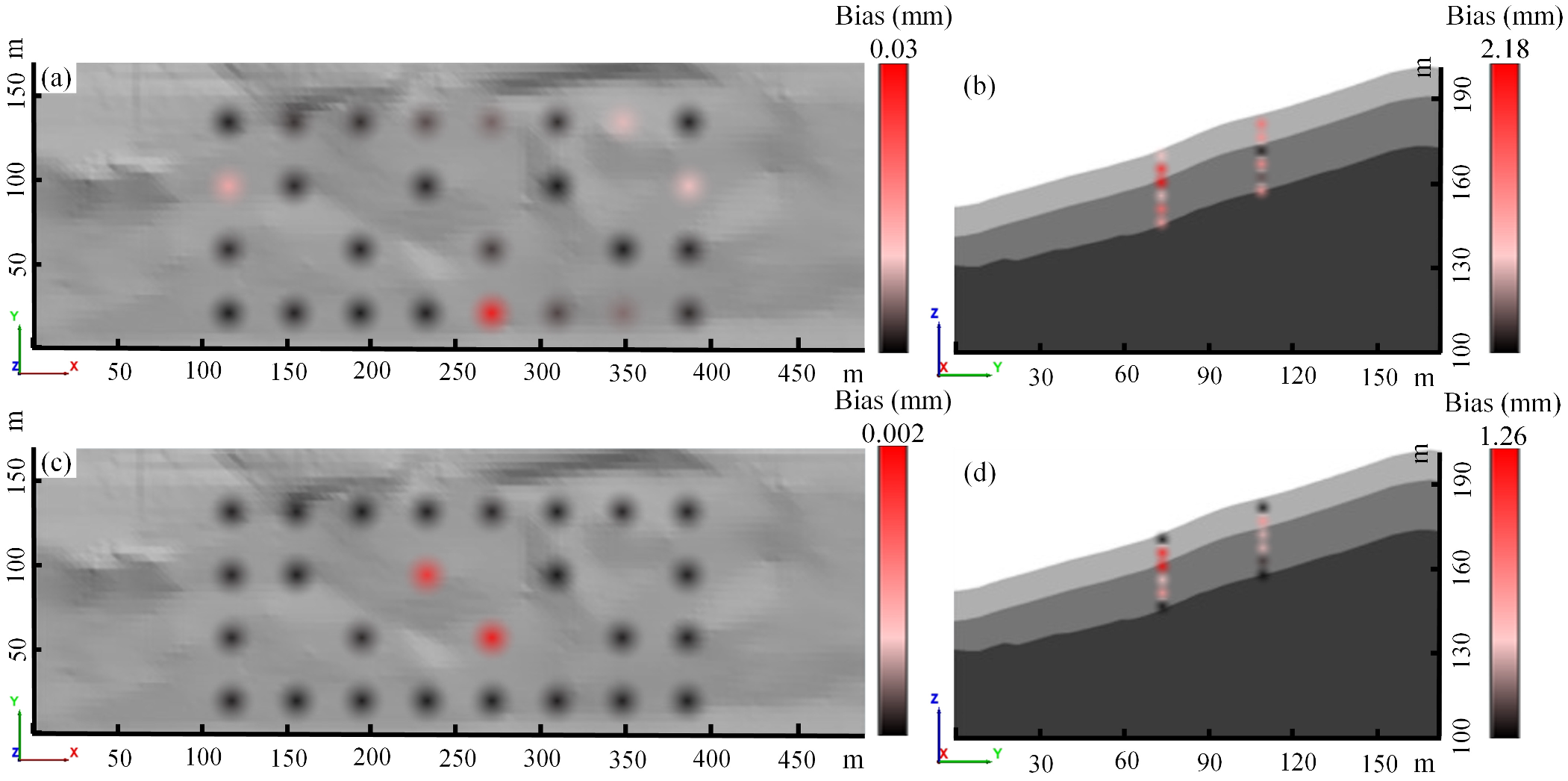

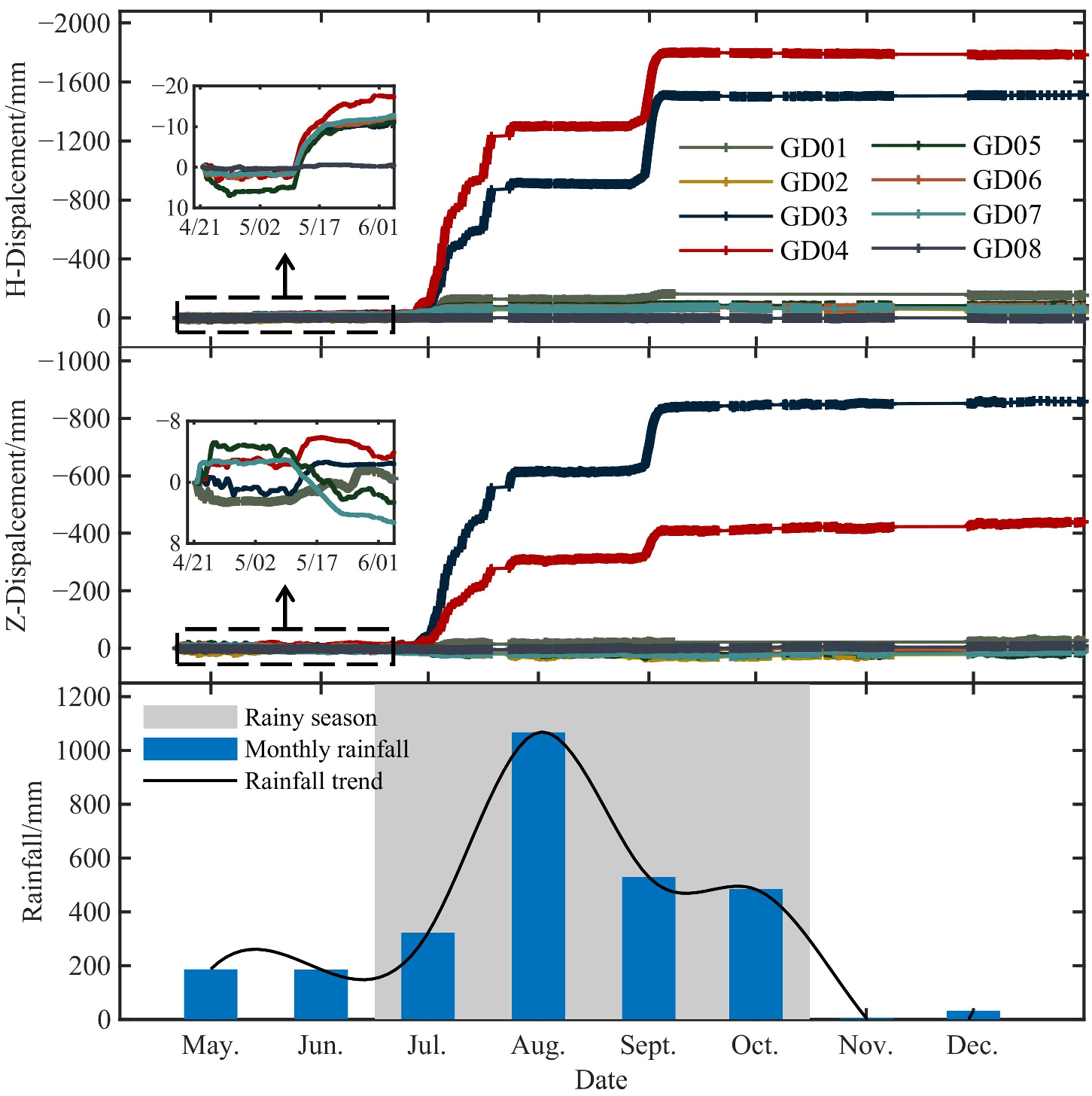
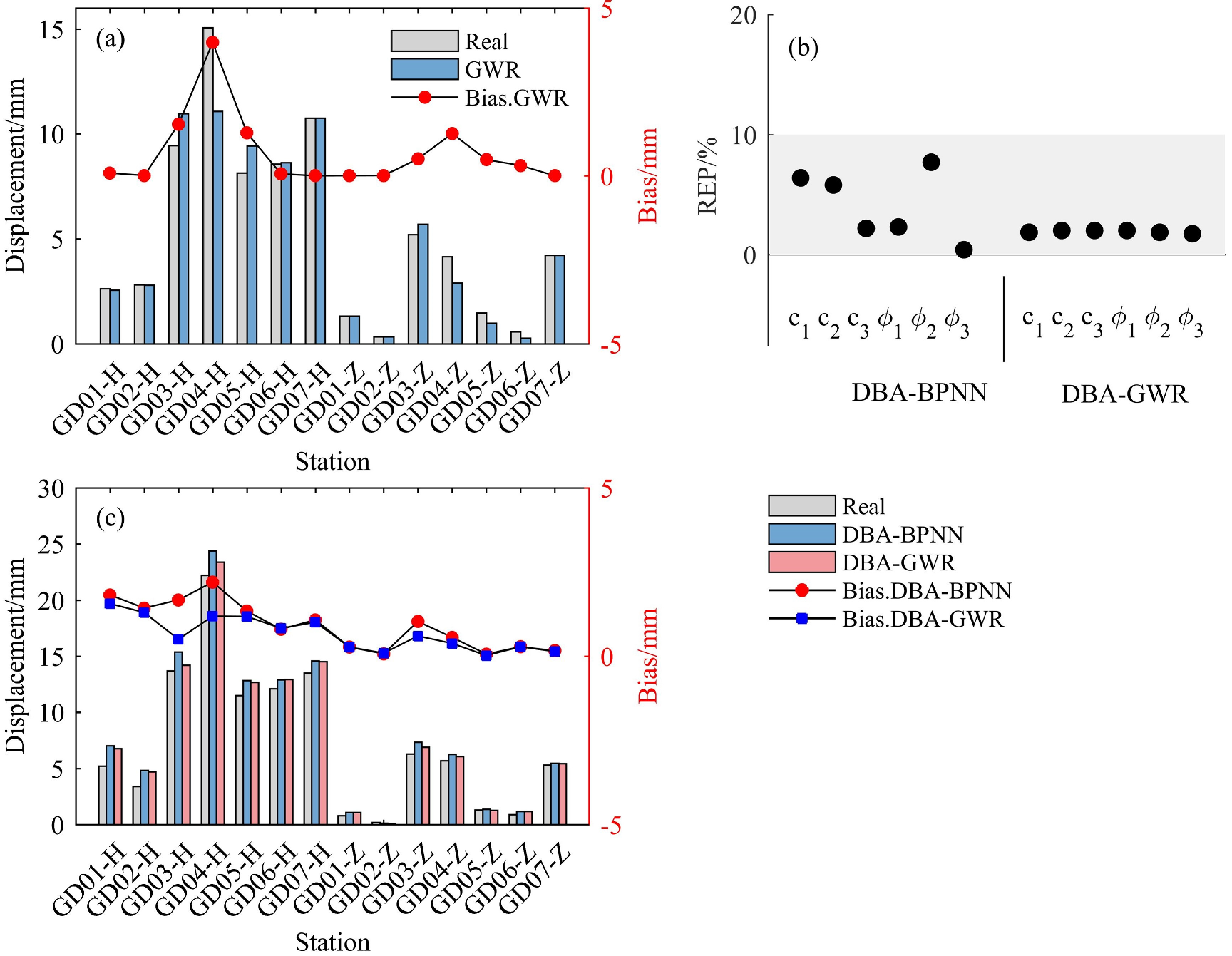

| Parameter | Symbol | Unity | Sub-Clay 1–3 | Gravel Soil | Rock |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry volumetric weight | 2200 | 2200 | 2900 | ||
| Bulk modulus | 20 | 60 | 1300 | ||
| Shear modulus | 13 | 36 | 800 | ||
| Cohesion | 10–16 | 18 | 48 | ||
| Angle of friction | 10–14.5 | 16 | 40,000 | ||
| Biot modulus | 400 | 1000 | - | ||
| Infiltration coefficient | 50 | 50 | - |
| No. | Content | Method | Monitoring Instrument | Monitoring Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Displacement | GNSS | Huace H3 GNSS Receiver | 1 h |
| 2 | Rainfall | Rain gauge | GFZ01 digital rain gauge | 20 min |
| 3 | Environment | Video | Hikvision surveillance camera | Real time |
| Plan | Cohesion (kPa) | Angle of Friction (°) | Water (m) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 13 | 14.5 | 17 | 16.5 | 13 | 14 | A face |
| Situation 1 | 12 | 13.5 | 16 | 16 | 12.25 | 13 | ↑0.5 |
| Situation 2 | 11 | 12.5 | 15 | 15.5 | 11.5 | 12 | ↑0.5 |
| Sets | Cohesion (kPa) | Angle of Friction (°) | Water (m) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 11.5 | 14 | 15 | 10.75 | 11 | ↑0.5 |
| 2 | 9.5 | 11 | 13.5 | 14.5 | 10.25 | 10.5 | ↑0.5 |
| 3 | 9 | 10.5 | 13 | 14 | 9.75 | 10 | ↑0.5 |
| 4 | 8.5 | 10 | 12.5 | 13.5 | 9.25 | 9.5 | ↑0.5 |
| Time | Cohesion (kPa) | Angle of Friction (°) | Water (m) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original data | 16 | 15 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 17 | A face |
| 5/21 | 15.1 | 14.1 | 14.1 | 14.0 | 15.3 | 16.2 | ↑0.4 |
| 6/21 | 14.2 | 13.2 | 13.2 | 13.1 | 14.2 | 15.2 | ↑0.9 |
| Method | Precision (mm) | Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | Bias (max) | Accuracy Rate | REP (max) | |
| Optimal back-analysis | 0.9 | 2.3 | 83.3% | 10.2% |
| DBA-BPNN | 1.1 | 2.2 | 100.0% | 7.7% |
| DBA-GWR | 0.8 | 1.6 | 100.0% | 2.0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, W.; Dai, Y.; Xie, J. Back-Analysis of Slope GNSS Displacements Using Geographically Weighted Regression and Least Squares Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030759
Dai W, Dai Y, Xie J. Back-Analysis of Slope GNSS Displacements Using Geographically Weighted Regression and Least Squares Algorithms. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(3):759. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030759
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Wujiao, Yue Dai, and Jiawei Xie. 2023. "Back-Analysis of Slope GNSS Displacements Using Geographically Weighted Regression and Least Squares Algorithms" Remote Sensing 15, no. 3: 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030759
APA StyleDai, W., Dai, Y., & Xie, J. (2023). Back-Analysis of Slope GNSS Displacements Using Geographically Weighted Regression and Least Squares Algorithms. Remote Sensing, 15(3), 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030759







