Mapping Diverse Paddy Rice Cropping Patterns in South China Using Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Materials
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 (HLS) Data
2.3. Vegetation Indices Derived from HLS Data
2.4. Field Samples
2.5. Land Cover Map and Slope Data
3. Methods
3.1. Cropping Intensity Identification
3.2. Feature Selection
3.3. DT Model Development for Mapping Diverse PRCPs
3.4. Performance Evaluations
4. Results
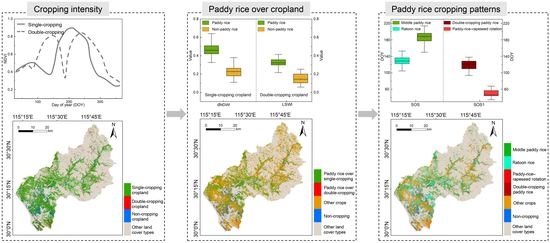
4.1. Derived Cropping Intensity Map
4.2. Optimal Features for Identifying Various PRCPs
4.3. The Developed DT Model Based on the Optimal Feature Analyses
4.4. Evaluation of the PRCP Map
5. Discussion
5.1. Specific Advantages of the Proposed FSHC Method
5.2. Implications, Limitations, and Future Improvements
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuenzer, C.; Knauer, K. Remote sensing of rice crop areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 34, 2101–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Min, J.; Wang, S.; Shi, W.; Xing, G. Further understanding of nitrous oxide emission from paddy fields under rice/wheat rotation in south China. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, G02016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J.; Xin, F.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Doughty, R.B.; Moore, B., 3rd. Fingerprint of rice paddies in spatial-temporal dynamics of atmospheric methane concentration in monsoon Asia. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisseler, D.; Linquist, B.A.; Lazicki, P.A. Effect of fertilization on soil microorganisms in paddy rice systems—A meta-analysis. Soil Boil. Biochem. 2017, 115, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xie, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Yan, X.; Xing, G.; Zhu, Z. Nitrogen fate and environmental consequence in paddy soil under rice-wheat rotation in the Taihu lake region, China. Plant Soil 2009, 319, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qin, Y.; Zou, J.; Liu, Q. Effects of water regime during rice-growing season on annual direct N(2)O emission in a paddy rice-winter wheat rotation system in southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Jiao, X.; Wu, F. Effects of continuous cucumber cropping and alternative rotations under protected cultivation on soil microbial community diversity. Plant Soil 2006, 284, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Fan, F.; Ma, X.; Yin, H.; Zhang, C.; Feng, K.; Deng, Y. Thirty-one years of rice-rice-green manure rotations shape the rhizosphere microbial community and enrich beneficial bacteria. Soil Boil. Biochem. 2017, 104, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, P.; Pellerin, S.; Seufert, V.; Nesme, T. Changes in crop rotations would impact food production in an organically farmed world. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremen, C.; Iles, A.; Bacon, C. Diversified Farming Systems: An Agroecological, Systems-based Alternative to Modern Industrial Agriculture. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-P.; Potapov, P.V.; Krylov, A.; King, L.; Di Bella, C.M.; Hudson, A.; Khan, A.; Adusei, B.; Stehman, S.V.; Hansen, M.C. National-scale soybean mapping and area estimation in the United States using medium resolution satellite imagery and field survey. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X. Evolution of regional to global paddy rice mapping methods: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 119, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschetti, M.; Busetto, L.; Manfron, G.; Laborte, A.; Asilo, S.; Pazhanivelan, S.; Nelson, A. PhenoRice: A method for automatic extraction of spatio-temporal information on rice crops using satellite data time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Li, W.; Tang, Z.; Chen, C.; Qi, W. Mapping paddy rice areas based on vegetation phenology and surface moisture conditions. Ecol. Indic 2015, 56, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, F.; Zhuang, H.; Zhang, J.; Tao, F. NESEA-Rice10: High-resolution annual paddy rice maps for Northeast and Southeast Asia from 2017 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 5969–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Dong, J.; Liao, X.; Sun, L.; Wang, Z.; You, N.; Li, Z.; Fu, P. Examining rice distribution and cropping intensity in a mixed single- and double-cropping region in South China using all available Sentinel 1/2 images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 101, 102351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, D.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Salas, W.; Moore, B. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in southern China using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; Ma, M. Mapping Paddy Rice with Satellite Remote Sensing: A Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Xu, S.; He, T. Mapping Paddy Rice with Sentinel-1/2 and Phenology-, Object-Based Algorithm—A Implementation in Hangjiahu Plain in China Using GEE Platform. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the blending of the Landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily Landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, C.M.; García-Haro, F.J. A comparison of STARFM and an unmixing-based algorithm for Landsat and MODIS data fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Li, A.; Jin, H.; Zhao, W.; Bian, J.; Qu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, B. Derivation of temporally continuous LAI reference maps through combining the LAINet observation system with CACAO. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 233, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, X.; Liu, L.; Wu, X.; Qin, Y.; Steiner, J.L.; Dong, J. Mapping sugarcane plantation dynamics in Guangxi, China, by time series Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2 and Landsat images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, J. Developing a New Method to Identify Flowering Dynamics of Rapeseed Using Landsat 8 and Sentinel-1/2. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claverie, M.; Ju, J.; Masek, J.G.; Dungan, J.L.; Vermote, E.F.; Roger, J.-C.; Skakun, S.V.; Justice, C. The Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 surface reflectance data set. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, K.; Li, Z.; Rao, L.N.; Gao, F.; Xie, D.; Hien, N.T.; Zeng, Z. Mapping paddy rice area and yields over Thai Binh Province in Viet Nam from MODIS, Landsat, and ALOS-2/PALSAR-2. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2238–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Chen, S.; Ye, T. Mapping Crop Rotation by Using Deeply Synergistic Optical and SAR Time Series. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Xu, B.; Yin, H.; Tang, H.; Yang, P.; Wu, W. A phenology-based spectral and temporal feature selection method for crop mapping from satellite time series. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 80, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; You, N.; Zhang, G.; Huang, J.; Dong, J. Optimizing Feature Selection of Individual Crop Types for Improved Crop Mapping. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Zhu, W.; Li, N. An automated rice mapping method based on flooding signals in synthetic aperture radar time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso, A.; Mermoz, S.; Bouvet, A.; Le Toan, T.; Planells, M.; Dejoux, J.-F.; Ceschia, E. Understanding the temporal behavior of crops using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2-like data for agricultural applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vittorio, C.A.; Georgakakos, A.P. Land cover classification and wetland inundation mapping using MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huete, A.R.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, G.; Zhang, X. Analysis of NDVI and scaled difference vegetation index retrievals of vegetation fraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvor, D.; Jonathan, M.; Meirelles, M.S.P.; Dubreuil, V.; Durieux, L. Classification of MODIS EVI time series for crop mapping in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 7847–7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.; Sangermano, F.; Machado, E.; Rogan, J.; Anyamba, A. Global Trends in Seasonality of Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), 1982–2011. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4799–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Babu, J.Y.; Salas, W.; Moore, B. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in South and Southeast Asia using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhang, G.; Qin, Y.; Thau, D.; Biradar, C.; Moore, B. Mapping paddy rice planting area in northeastern Asia with Landsat 8 images, phenology-based algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A Study on Information Extraction of Water Body with the Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI). J. Remote Sens. 2005, 9, 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q.; Liu, M.; Cheng, J.; Ke, Y.; Chen, X. Mapping Paddy Rice Planting Area in Northeastern China Using Spatiotemporal Data Fusion and Phenology-Based Method. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cao, X.; Peng, S.; Ren, H. Analysis and Applications of GlobeLand30: A Review. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2017, 6, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Wu, W.; Zhang, L.; Liao, A.; Peng, S.; Tang, H. A comparative analysis of five global cropland datasets in China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 2307–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tao, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W. Comparing different smoothing methods to detect double-cropping rice phenology based on LAI products—A case study in the Hunan province of China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 6405–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tao, F. The effect of terrain factors on rice production: A case study in Hunan Province. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 1792–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, M.; Crippen, R.; Fujisada, H. ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model (GDEM) and ASTER Global Water Body Dataset (ASTWBD). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumma, M.K.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Maunahan, A.; Islam, S.; Nelson, A. Mapping seasonal rice cropland extent and area in the high cropping intensity environment of Bangladesh using MODIS 500m data for the year 2010. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 91, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Tang, H.; Chen, Z.; Yu, L.; Wu, M. High resolution crop intensity mapping using harmonized Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 data. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 2883–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Roy, D.P.; Vermote, E.; Masek, J.; Kovalskyy, V. Continental-scale validation of MODIS-based and LEDAPS Landsat ETM+ atmospheric correction methods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensholt, R.; Sandholt, I.; Stisen, S. Evaluating MODIS, MERIS, and VEGETATION vegetation indices using in situ measurements in a semiarid environment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1774–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Qiao, Z. Mapping cropping intensity in China using time series Landsat and Sentinel-2 images and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, P.; Eklundh, L. Seasonality Extraction by Function Fitting to Time-Series of Satellite Sensor Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, P.; Eklundh, L. TIMESAT—A program for analyzing time-series of satellite sensor data. Comput. Geosci. 2004, 30, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Xia, H.; Yang, J.; Niu, W.; Wang, R.; Song, H.; Guo, Y.; Qin, Y. Mapping cropping intensity in Huaihe basin using phenology algorithm, all Sentinel-2 and Landsat images in Google Earth Engine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yin, H.; Friedl, M.A.; You, L.; Li, Z.; Tang, H.; Wu, W. Integrating coarse-resolution images and agricultural statistics to generate sub-pixel crop type maps and reconciled area estimates. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Dubayah, R.; Defries, R. Classification trees: An alternative to traditional land cover classifiers. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 17, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Barragán, J.M.; Ngugi, M.K.; Plant, R.E.; Six, J. Object-based crop identification using multiple vegetation indices, textural features and crop phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1301–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, R.; Tian, J.; Li, X.; Yin, D.; Li, J.; Gong, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Wu, D. An enhanced pixel-based phenological feature for accurate paddy rice mapping with Sentinel-2 imagery in Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 178, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhang, M. Mapping paddy rice by the object-based random forest method using time series Sentinel-1/Sentinel-2 data. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 64, 2233–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, H.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, J.; Tao, F. Annual paddy rice planting area and cropping intensity datasets and their dynamics in the Asian monsoon region from 2000 to 2020. Agric. Syst. 2022, 200, 103437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Hu, Q.; Cai, Z.; Yang, J.; Song, Q.; Yin, G.; Xu, B. An Object- and Topology-Based Analysis (OTBA) Method for Mapping Rice-Crayfish Fields in South China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hu, Q.; You, L.; Cai, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wei, H.; Xu, Z.; He, Z.; Yin, G.; Xu, B. Mapping the potential northern limits and promotion extent of ratoon rice in China. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 150, 102822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Band Name | HLS L30 Band | HLS S30 Band | Wavelength Range (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coastal aerosol | B1 | B1 | 0.43–0.45 |
| Blue | B2 | B2 | 0.45–0.51 |
| Green | B3 | B3 | 0.53–0.59 |
| Red | B4 | B4 | 0.64–0.67 |
| Red-edge 1 | – | B5 | 0.69–0.71 |
| Red-edge 2 | – | B6 | 0.73–0.75 |
| Red-edge 3 | – | B7 | 0.77–0.79 |
| Near infrared (NIR) broad | – | B8 | 0.78–0.88 |
| NIR narrow | B5 | B8A | 0.85–0.88 |
| Short wave infrared (SWIR) 1 | B6 | B11 | 1.57–1.65 |
| SWIR 2 | B7 | B12 | 2.11–2.29 |
| Water vapor | – | B9 | 0.93–0.95 |
| Cirrus | B9 | B10 | 1.36–1.38 |
| Thermal infrared 1 | B10 | – | 10.60–11.19 |
| Thermal infrared 2 | B11 | – | 11.50–12.51 |
| Vegetation Index (VI) | Equation | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | [33] | |
| Land surface water index (LSWI) | [17] | |
| Flooding signal vegetation index (FSVI) | [40] | |
| Normalized difference water index (NDWI) | [38] | |
| Modified normalized difference water index (MNDWI) | [39] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Z.; Wei, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.; You, L.; Xu, B. Mapping Diverse Paddy Rice Cropping Patterns in South China Using Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041034
Hu J, Chen Y, Cai Z, Wei H, Zhang X, Zhou W, Wang C, You L, Xu B. Mapping Diverse Paddy Rice Cropping Patterns in South China Using Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(4):1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041034
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jie, Yunping Chen, Zhiwen Cai, Haodong Wei, Xinyu Zhang, Wei Zhou, Cong Wang, Liangzhi You, and Baodong Xu. 2023. "Mapping Diverse Paddy Rice Cropping Patterns in South China Using Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 Data" Remote Sensing 15, no. 4: 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041034
APA StyleHu, J., Chen, Y., Cai, Z., Wei, H., Zhang, X., Zhou, W., Wang, C., You, L., & Xu, B. (2023). Mapping Diverse Paddy Rice Cropping Patterns in South China Using Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sensing, 15(4), 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041034