Abstract
The increasing demand for low-cost space-borne Earth observation missions has led to small satellite constellation systems development. CubeSat platforms can provide a cost-effective multiple-mission space system using state-of-the-art technology. This paper presents a new approach to CubeSat constellation design for multiple missions using a multi-objective genetic algorithm (MOGA). The CubeSat constellation system is proposed to perform multi-missions that should satisfy global Earth observation and regional disaster monitoring missions. A computational approach using a class of MOGA named non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II is implemented to optimize the proposed system. Pareto optimal solutions are found that can minimize the number of satellites and the average revisit time (ART) for both regional and global coverage while maximizing the percentage coverage. As a result, the study validates the feasibility of implementing the CubeSat constellation design with an acceptable level of performance in terms of ART and percentage coverage. Moreover, the study demonstrates CubeSat’s ability to perform a multi-missions.
1. Introduction
The demand for space-based Earth observation data has increased in recent years. Earth observation missions are vital for understanding and monitoring global change. Small satellites, especially CubeSats [1,2,3], have gained most attention for performing these missions. In the past decade, the space industry has shifted towards developing small satellites, with CubeSats leading the way due to modular and standardized design. CubeSats are becoming a popular option for implementing large constellation systems and are a great starting point for developing countries looking to establish a space industry. The low cost and fast development cycle of CubeSats make them particularly attractive for Earth observation applications. Several missions have proven the capability of CubeSat for Earth observation missions [4,5,6].
Recently, disaster monitoring and management systems have become a necessity with the frequent occurrence of natural disasters. Early forecasting is critical in disaster management because many climate-related disasters can be predicted ahead of time. The early forecast allows an action to be taken ahead of time, reducing the risks and consequences of the disaster. Rapid and continuous data collection is essential for disaster monitoring and management systems. For regions with limited infrastructure, a CubeSat constellation can be used as an alternative to increasing the data collection rate for remote places spread across a large area [7,8]. This study proposes a multi-mission CubeSat constellation system for Earth observation and climate data collection from regional data centers. Multi-mission refers to implementing a single system to perform optimized multiple mission objectives.
Based on the literature review, there have been few studies on the design and optimization of CubeSat constellation systems. Santilli et al. [7] conducted a case study for a CubeSat constellation system for disaster management in remote areas. Furthermore, Lazreg et al. [1] studied the analysis and design of a CubeSat constellation for continuous monitoring of the South Mediterranean Sea. Goncharenko et al. [9] developed a CubeSat constellation to observe the temporal variability of the atmosphere. The study compares different orbital configurations for a CubeSat constellation to minimize revisit time for global coverage. However, none of these studies used optimization techniques in the design of CubeSat constellations. Chadalavada et al. [8] developed an optimization-based framework to design a CubeSat constellation to monitor hurricanes. The study used a two-step optimization method to design a constellation for a selected region of interest.
Other studies proposed multi-objective optimization for satellite constellation optimization. Meziane-Tani et al. [10] studied the optimization of small satellite constellations using a multi-objective genetic algorithm (MOGA) for continuous mutual regional coverage. However, the optimization focused on optimizing a constellation for a single purpose, whereas our study proposes a new approach for multi-mission optimization. Han et al. [11] employed multi-objective optimization approaches to design low Earth orbit (LEO) navigation augmentation constellations. The study modeled the LEO constellation and used the multi-objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO) algorithm. Yan et al. [12] studied the multi-objective optimization design of an extended Walker constellation for global coverage. The main focus of the research was on the optimization design of a Walker constellation configuration by using multi-objective evolutionary algorithms.
However, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, there have been no studies to optimize a CubeSat constellation system for a multi-mission design. Therefore, in this study, we propose an optimized CubeSat constellation system to satisfy global Earth observation and regional disaster monitoring goals. A single system in the CubeSat constellation will perform both Earth observation and disaster monitoring missions. Global and regional missions share conflicting requirements that need optimization to be satisfied by a single system. A computational approach using a modified non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II (NSGA-II) algorithm is implemented using MATLAB®.
Therefore, the main contribution of this paper is the design of a CubeSat constellation capable of performing multiple missions. Additionally, the optimization of the CubeSat constellation design to efficiently perform missions by minimizing the number of satellites and average revisit time (ART) while maximizing total coverage.
2. Mission Design
2.1. CubeSat Design
CubeSats, in general, have a standardized size and form factor. The CubeSat standard size uses one unit (1U) measuring 10 × 10 × 10 cm in volume, which is extendable to larger sizes. In response to the need to conduct broader and more reliable missions, CubeSat platforms larger than 3U have been developed. Furthermore, the significant advancements in CubeSat platform technology and capabilities make them suitable to perform these missions [13,14]. Larger CubeSats, such as 6U and 12U, will be able to perform multiple missions with improved reliability, which was previously limited by the size of smaller platforms. The first 12U CubeSat Star of AOXiang (SAOX) was developed by Northwestern Polytechnical University (NPU) in China. The SAOX project, launched in 2016, was able to test the 12U CubeSat platform in orbit. SAOX demonstrated the larger CubeSat platform’s ability to perform reliable missions at a low cost [14].
A CubeSat constellation system will be designed to meet the demand for global Earth observation and regional disaster monitoring and management missions. A 12U CubeSat platform with two payloads will be designed to satisfy these missions. The first mission, global Earth observation, uses an electro-optical camera (EOC) payload with a 30° field of view (FOV) conic sensor. The second mission, regional disaster monitoring and management, collects data from regional target area data centers using UHF receiver. A standard commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) UHF receiver at 436 MHz frequency with a 0.17 m dipole antenna is assumed for the second payload. High-level specifications for the 12U CubeSat are given in Table 1 based on CubeSat standards and developed systems [14,15].

Table 1.
High-level 12U CubeSat system specifications.
2.2. Target Areas
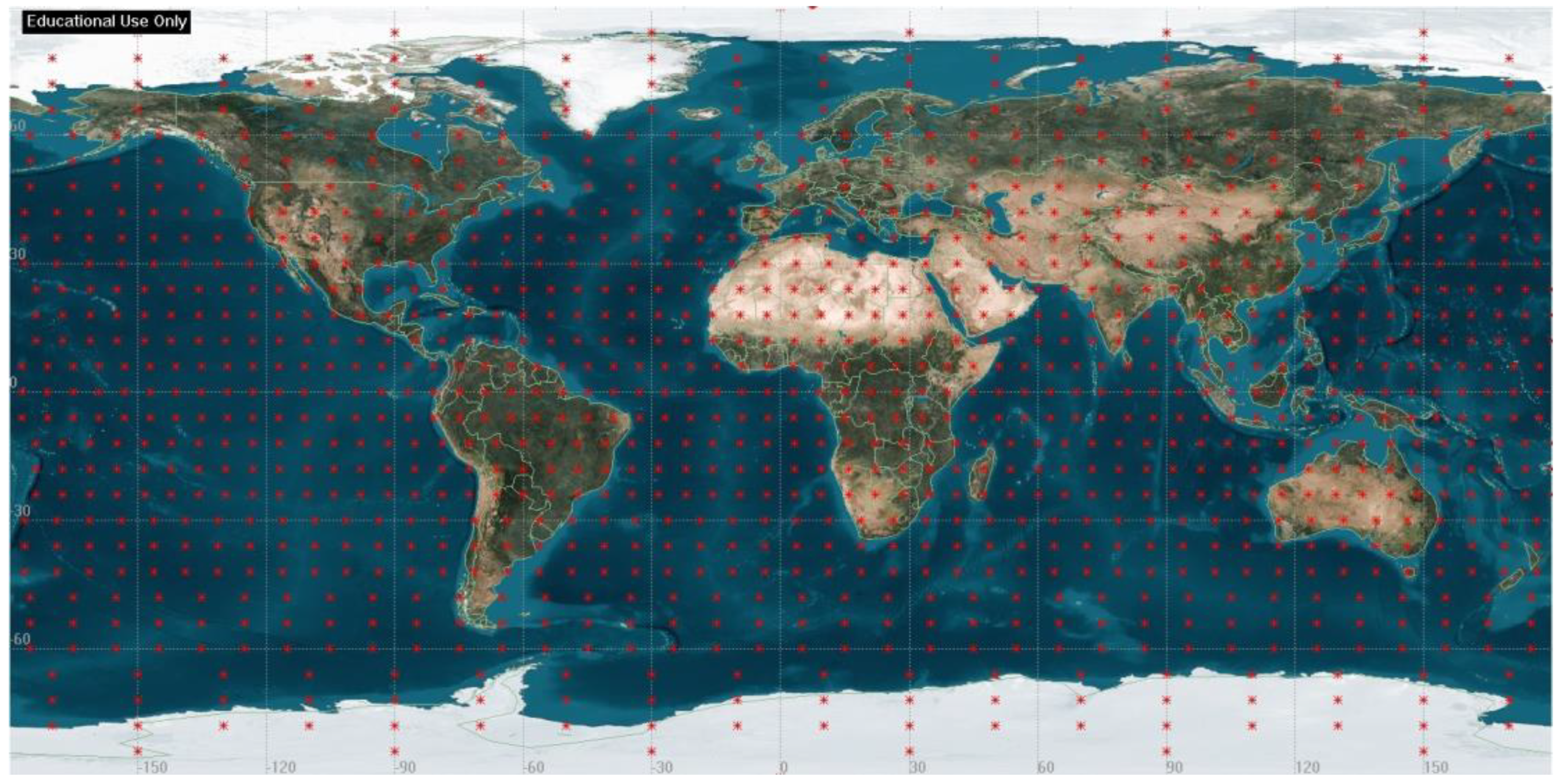
Two target areas are defined to evaluate mission success for the global and regional mission objectives. The study uses a 6° grid in latitude and longitude for global coverage. This results in 1148 target points evenly distributed throughout the world, forming the target area shown in Figure 1. The global coverage analysis is calculated using these grid points.
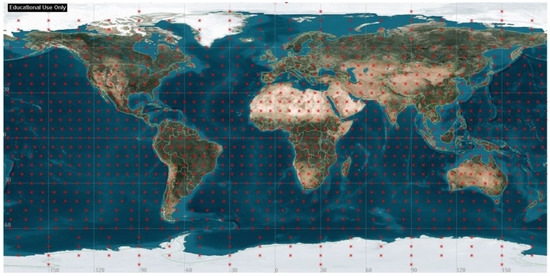
Figure 1.
Distribution of global target area with 6° grid in latitude and longitude.
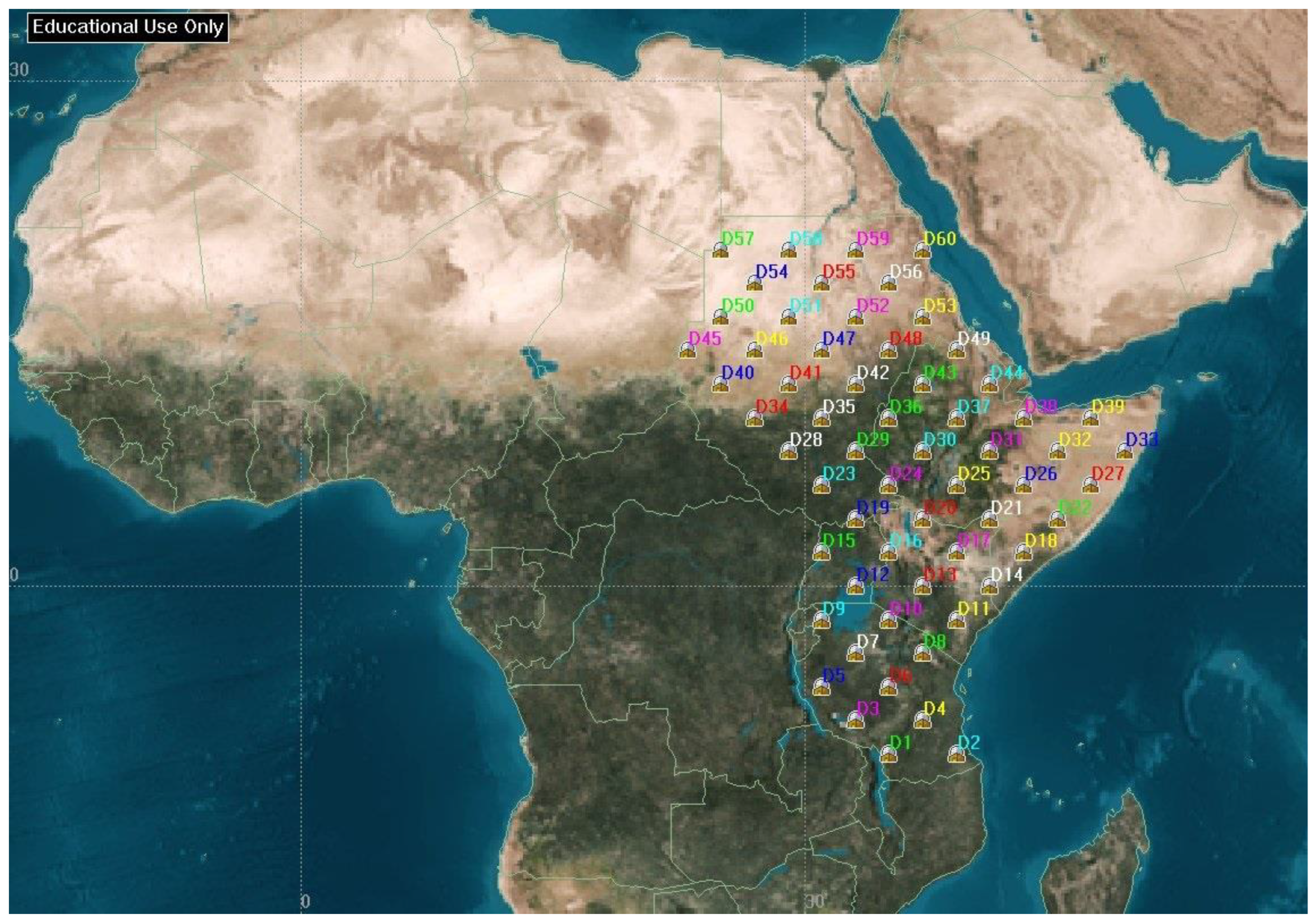
The East African region is selected as the regional disaster monitoring target area, as it is often affected by natural disasters related to climate change [16]. Because the region has limited disaster management and monitoring systems, it will benefit from the development of such systems to mitigate the impact of natural disasters. This study proposes disaster monitoring centers to report the data through a CubeSat constellation link. It will increase the speed of data transmission from rural and remote areas to a central disaster management facility, resulting in a faster response time to act on the disaster. Figure 2 shows the distribution of 60 data collection centers across the regional target area, composed of 11 countries. The data transmitted from these centers will contain climate and emergency reports. Each data transmission center is assumed to have an elevation angle of 30°.
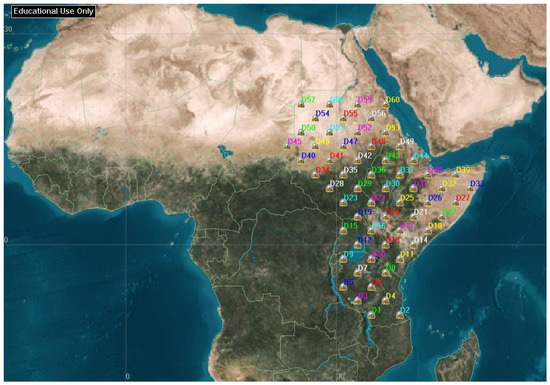
Figure 2.
Regional data collection centers, evenly distributed over the target area.
2.3. Constellation Design
Satellite constellations are typically designed with similar altitude, eccentricity, and inclination so that the effect of perturbations will be approximately the same on each satellite. Such a design will preserve the geometry of the constellation, especially in CubeSat, where there is limited fuel onboard for station keeping. Another advantage is that satellites at constant altitude will have the same resolution and steady signal strength for communication [12,17,18]. The Walker constellation is the most popular type of circular orbit geometry to satisfy the above considerations. The Walker constellation pattern is used in most studies to design a global coverage problem [19,20].
Given the mission requirements, a Walker constellation will be well-suited for our constellation system design. A Walker constellation consists of a total number of satellites () in circular orbits with the same period and inclination. The pattern of the constellation consists of evenly spaced satellites () in each of the orbital planes () specified so that . The ascending nodes of the orbital planes are also evenly spaced over a range of right ascensions of the ascending node (RAAN). The study implemented a Walker Delta constellation pattern with one interplane spacing and 360° RAAN spread.
3. Problem and Optimization Formulation
3.1. Problem Statement
CubeSats are becoming capable of multi-objective missions due to advancements in their platforms. An optimized CubeSat constellation system can perform multiple missions, including global Earth observation and regional disaster monitoring. However, these missions have conflicting requirements that must be addressed by the system. The optimization problem aims to improve system performance by reducing ART for global and regional missions while maximizing total area coverage and minimizing the number of satellites, reducing cost and development time.
Inclination and the number of satellites in terms of orbital planes and satellites per plane are chosen as optimization parameters. This multi-objective optimization problem can be solved using different techniques, with evolutionary algorithms, such as NSGA-II, commonly used for non-linear global optimization problems. NSGA-II algorithms have been modified to handle integer optimization variables, such as the number of orbital planes and satellites per plane.
3.2. Objective Functions Formulation
The main goal of this optimization design is to minimize ART for both missions, minimize the number of satellites, and maximize the total global coverage. The optimization variables are inclination , the number of orbital planes , and the number of satellites in each orbital plane . In this study, a total of four objective functions are formulated.
The first objective is to minimize the total number of satellites in the constellation given as:
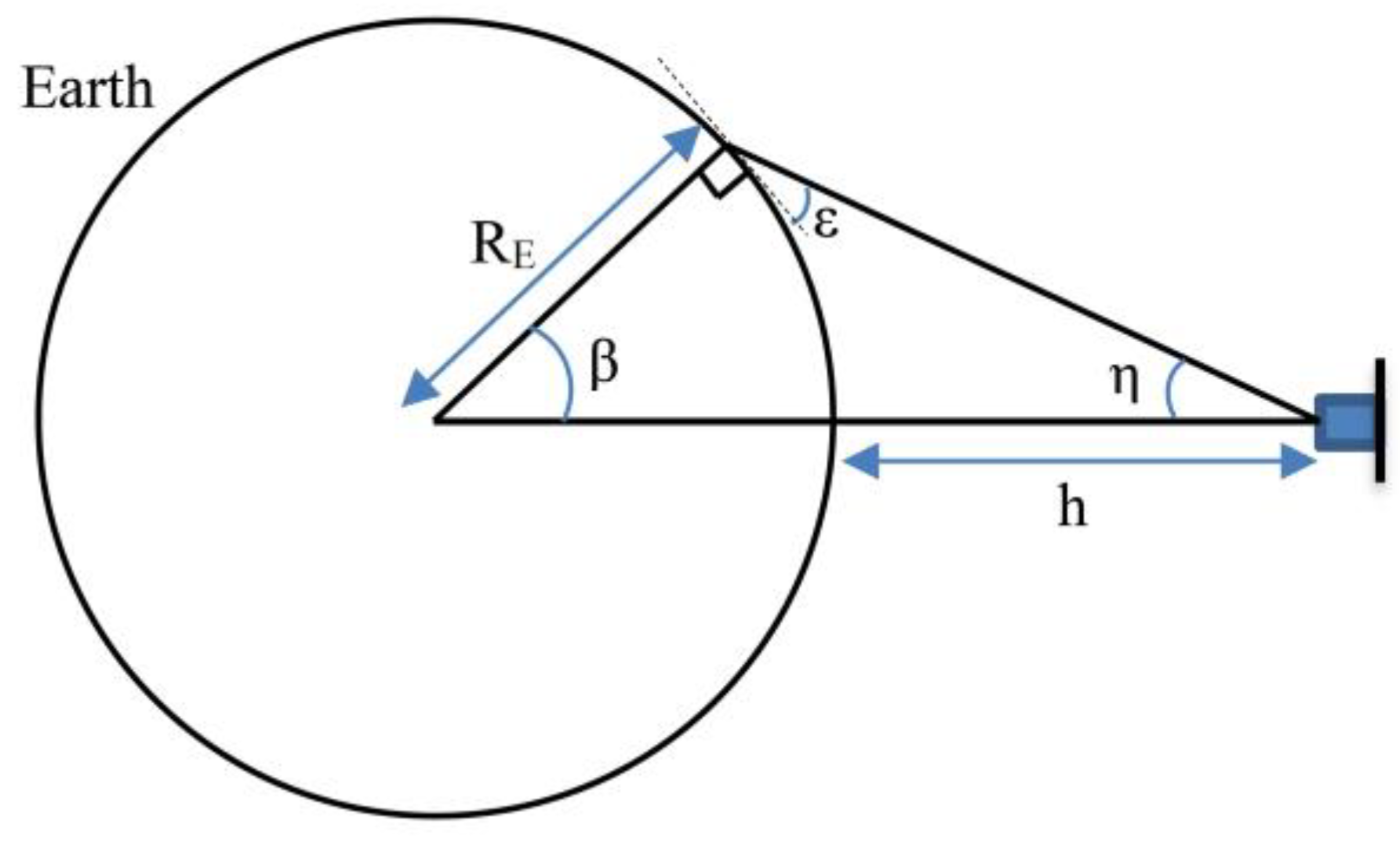
The second and third objectives are to minimize the ART for global and regional coverage, respectively. These two objective functions are formulated using target areas defined in Section 2.2. CubeSat sensors FOV geometry is used to calculate the coverage of a given target point. The payload in the CubeSat design has a nadir FOV that points directly beneath the CubeSat. Figure 3 shows the general FOV geometry of the sensors where represents the Earth radius, while represents the altitude of the CubeSat. The CubeSat elevation angle ε, measured between the local horizontal and coverage end zone, can be calculated from the payload half-angle η as:
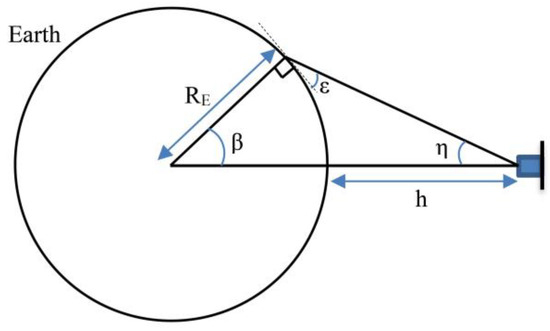
Figure 3.
Geometry representation of the sensor FOV assuming spherical Earth with constant radius .
The angle , which indicates the effective coverage angle of the CubeSat, measured at the center of the Earth from the nadir point to the end of coverage:
Let and represent the position vectors in the Earth-centered, Earth-fixed (ECEF) coordinate system of the CubeSat and target, respectively. Where, represents a CubeSat from the total of CubeSats in the constellation. Furthermore, represents a target point form given number of target area points. Then, the angle between the two vectors is:
From the geometry of the FOV, the criteria for judging if the target is covered by the CubeSat will be . When we have coverage for a given target, we will save the corresponding coverage start time as . The coverage criteria will be continuously checked for every time interval of the given calculation period, saving the start time for each access to the target. ART is calculated for a given target per CubeSat that has two or more accesses. Therefore, the ART of target for a total number of accesses by the CubeSat is given as:
When calculating the ART for the target by the constellation, the access start time of all CubeSats in the constellation will be considered. Therefore, the ART for the target by the constellation with a total number of accesses will be given as:
For global coverage, ART is calculated for total number of grid points accessed by the constellation from global target points. The second objective function is given as:
For regional coverage, ART is calculated for number of grid points accessed by the constellation from regional data centers. The third objective function is given as:
The fourth objective is to maximize the total percentage coverage of the global grid points. It is given in terms of the number of accessed points by the constellation from the total number of grid points.
3.3. Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm
A given multi-objective problem will rise to a set of optimal solutions known as Pareto optimal solutions. These are a set of optimal solutions to the problem. If there is no additional information, one of these Pareto optimal solutions is not better than the others [21]. There are various algorithms for finding Pareto optimal solution sets. Evolutionary algorithms are frequently used to solve these problems as they can keep a diverse solution set. The genetic algorithm (GA) is a widely used global optimization method, among evolutionary algorithms, due to its ability to locate a global optimum solution for a set of nonlinear multi-objective problems [10,22,23].
The multi-objective genetic algorithm is a robust multi-objective optimization technique that results in a set of Pareto optimal solutions. To solve the optimization problem with the four objectives given in Equations (1) and (7)–(9), the class of MOGA, named NSGA-II, is used. The NSGA-II algorithm can find a near-true Pareto optimal front through a fast non-dominated sorting algorithm, diversity preservation, and elitist principles [21,22]. Because of these properties, the NSGA-II algorithm is widely used to solve multi-disciplinary nonlinear multi-objective problems. NSGA-II calculates the nondominated solution set at each generation until the maximum generation or a given convergence criterion is achieved. Several studies have used NSGA-II for constellation design optimization problems, resulting in a good performance [12,22,23,24].
4. Simulation Results and Discussion
4.1. Simulation Setup
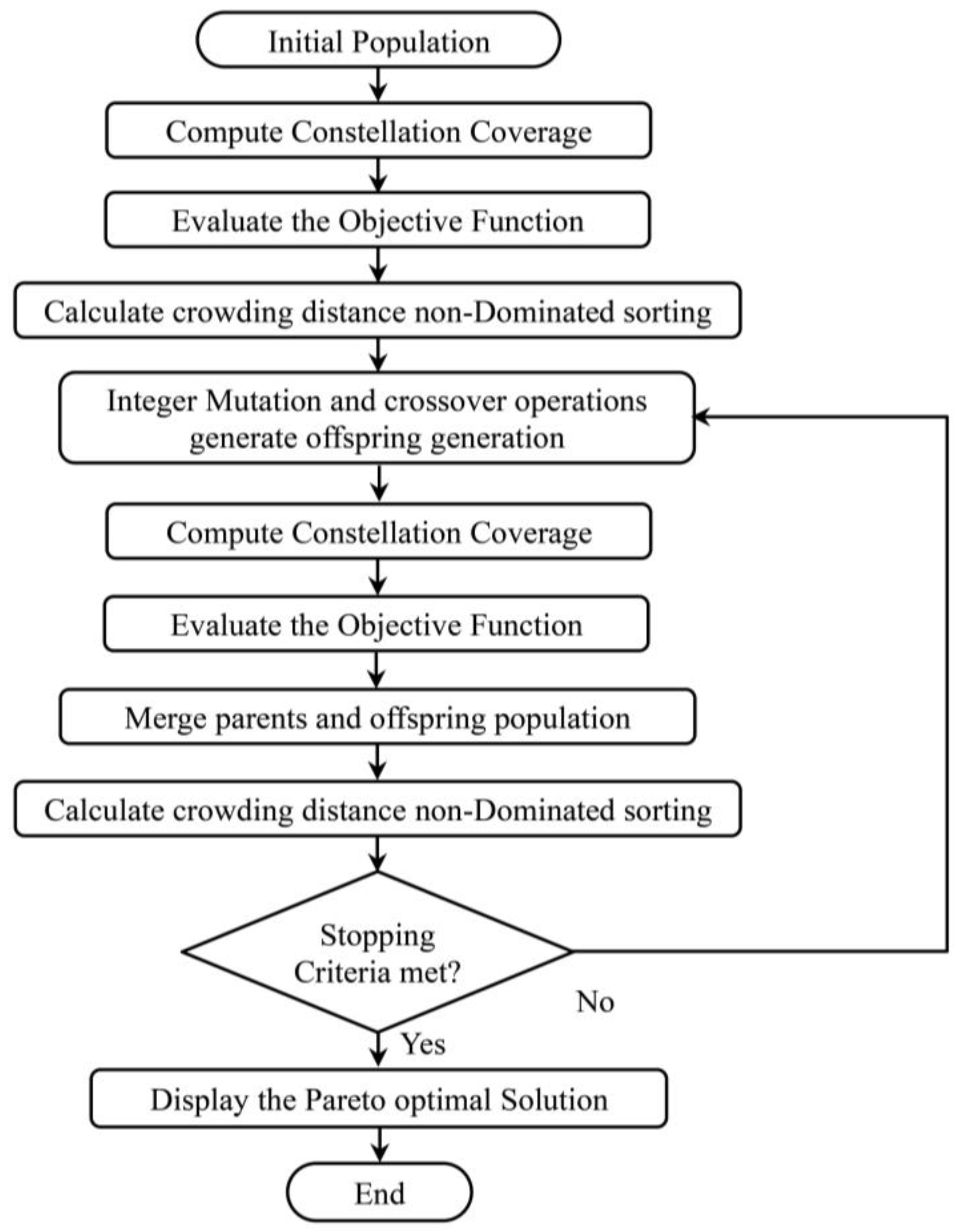
The study implemented a modified MATLAB® function that uses a controlled elitist genetic algorithm variant of NSGA-II. This algorithm is a commonly used optimization algorithm for non-linear optimization problems. In this study, two of the optimization variables, the number of orbital planes and the number of satellites in each orbital plane, are integer variables. We must customize the algorithm to handle integer optimization variables. Due to these integer variables, the initial population and offspring generation functions, namely the mutation and crossover functions, are modified in the library implementation of the algorithm. The NSGA-II population size is set to 100, with a maximum generation of 500. Figure 4 shows the overall system simulation flow chart. The simulation time is assumed for three days starting from 1 April 2020 at 00:00:00.000.
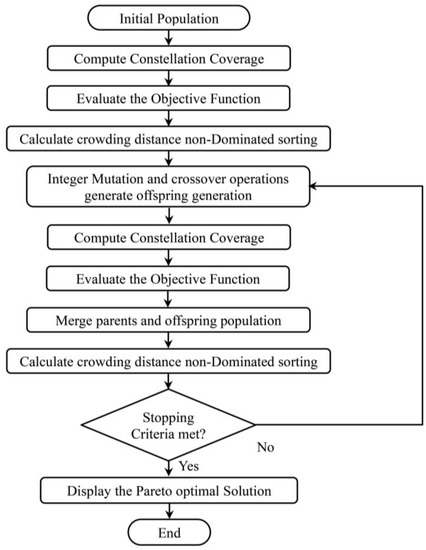
Figure 4.
Overall system flow chart for simulation.
Various perturbation sources can affect the trajectory of the low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite. A perturbation can be defined as a deviation from normal or expected motion. Perturbation sources in LEO include Earth’s nonspherical symmetry, atmospheric drag, Sun and Moon gravity, and solar radiation. The J2 perturbation value in Earth’s nonspherical perturbation is much larger than other perturbations in magnitude [25,26]. As the constellation is in lower Earth orbit, the J2 propagator model is used for the satellite propagator.
This study considers two simulation cases, regional and multi-mission. For the first simulation case, regional optimization, the inclination is assumed to be 40° considering the target area. Moreover, three altitude values at 400 km, 450 km, and 500 km were considered for the constellation to see the effect of altitude change. The second multi-mission optimization simulation case includes both regional and global optimization objectives. The altitude is kept at 450 km for this simulation case to simplify the optimization problem. Table 2 shows the optimization parameters used for the regional and multi-mission simulation cases.

Table 2.
Optimization parameters with their boundary value for two simulation cases.
4.2. Results and Discussion
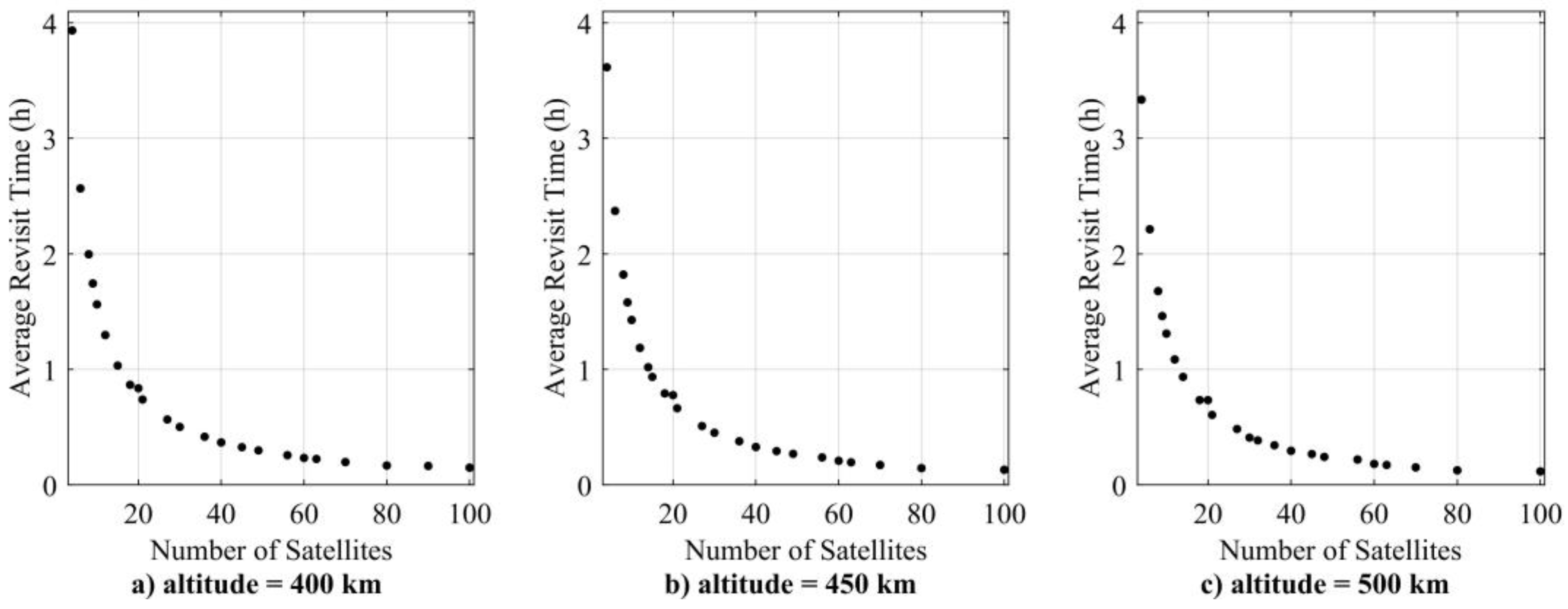
For the regional coverage optimization case, the optimization parameters used are the number of orbital planes and the number of satellites in each orbital plane . The objective functions for this case are to minimize the number of satellites and the regional target ART as given in Equations (1) and (8), respectively. The results in Figure 5, for three cases of altitude, show that ART decreases as the number of satellites increases. For the four satellites, the ART is 3.93 h, 3.62 h, and 3.34 h for 400 km, 450 km, and 500 km altitudes, respectively. Whereas for 100 satellites, the ART is 0.15 h, 0.13 h, and 0.12 h for 400 km, 450 km, and 500 km altitudes, respectively. ART decreases with an increase in altitude, but the relative change in ART is small as the number of satellites increases.
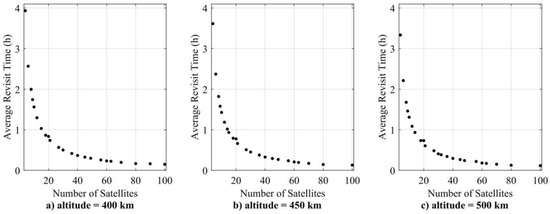
Figure 5.
Pareto front for regional target coverage simulation case at different altitudes.
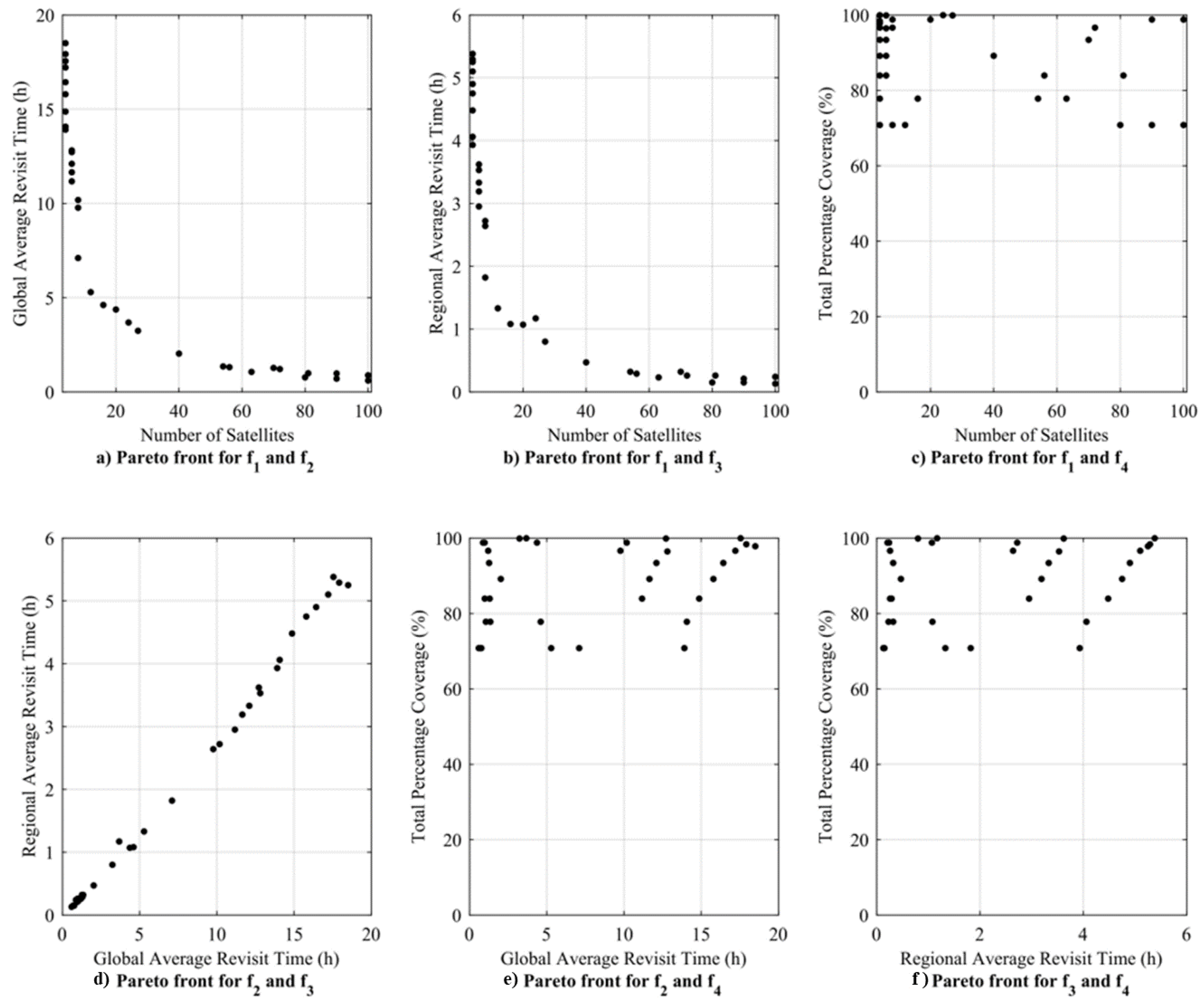
The second simulation case considers the inclination , the number of orbital planes and the number of satellites in each orbital plane as the optimization variables. The altitude is kept constant at 450 km because varying the altitude results in a relatively slight change in the objective function, as demonstrated by the first simulation case. Table 3 shows Pareto optimal solution sets for the multi-mission simulation case by considering four objective functions (, , , and ) as given in Equations (1), (7), (8), and (9), respectively.

Table 3.
Pareto front solution for multi-mission optimization.
Figure 6a,b show a decrease in regional and global ART as the number of satellites increases. Moreover, we can see an increase in the ART at the same number of satellites as the inclination increases. Consider solutions 1 and 9 in Table 3, which have the same number of satellites at 40° and 89° inclination, respectively. Global and regional ART increases as inclination increases. However, for the same solution, the total percentage coverage increases from 70.79% to 99.93%. Figure 6c shows the plot of the number of satellites versus the total percentage coverage, showing that the same number of satellites can have different coverage. Figure 6e,f show the global and regional ART plots with the total percentage coverage.
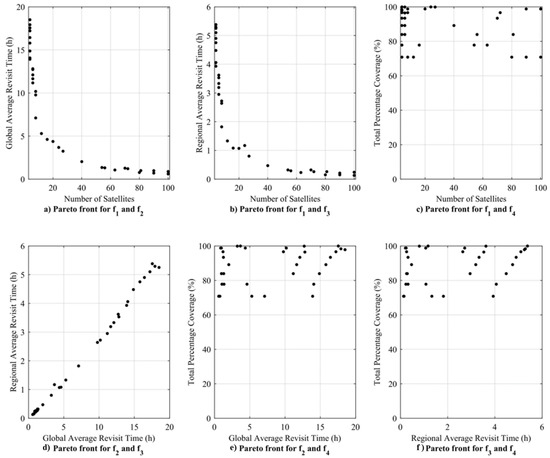
Figure 6.
Plot of Pareto front for multi-mission simulation case.
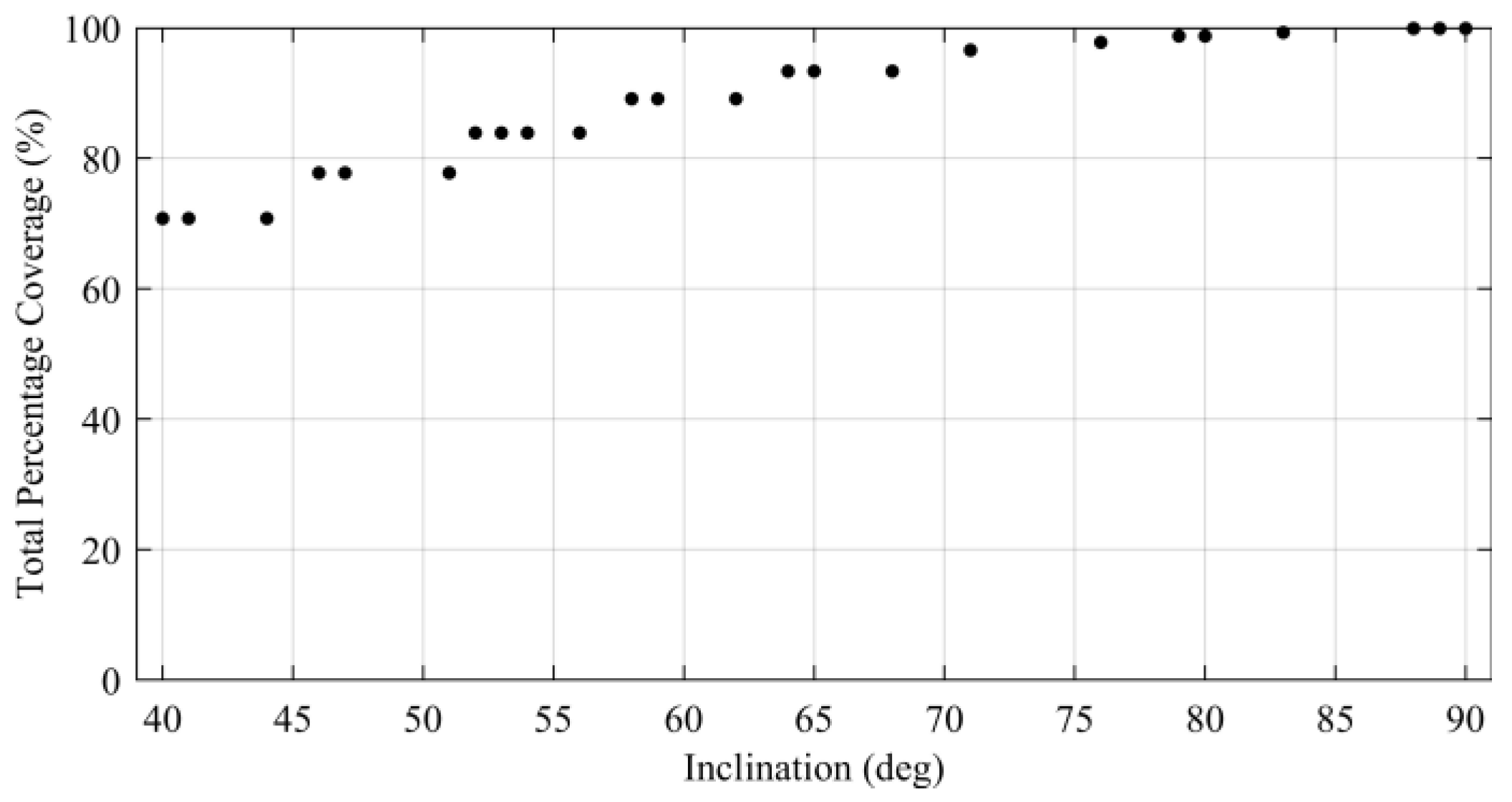
This result indicates that the number of satellites is not the main parameter affecting the total percentage coverage for the assumed simulation period. Furthermore, we can see that both global and regional ARTs depend on the number and pattern of CubeSats in the constellation. Figure 7 shows the relationship between the inclination and the total percentage coverage. The result shows that the total percentage coverage is mainly dependent on the inclination of the constellation rather than on the other constellation parameters.
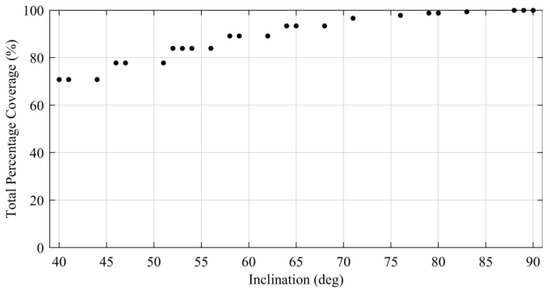
Figure 7.
Relationship between inclination and total coverage in the optimal solution.
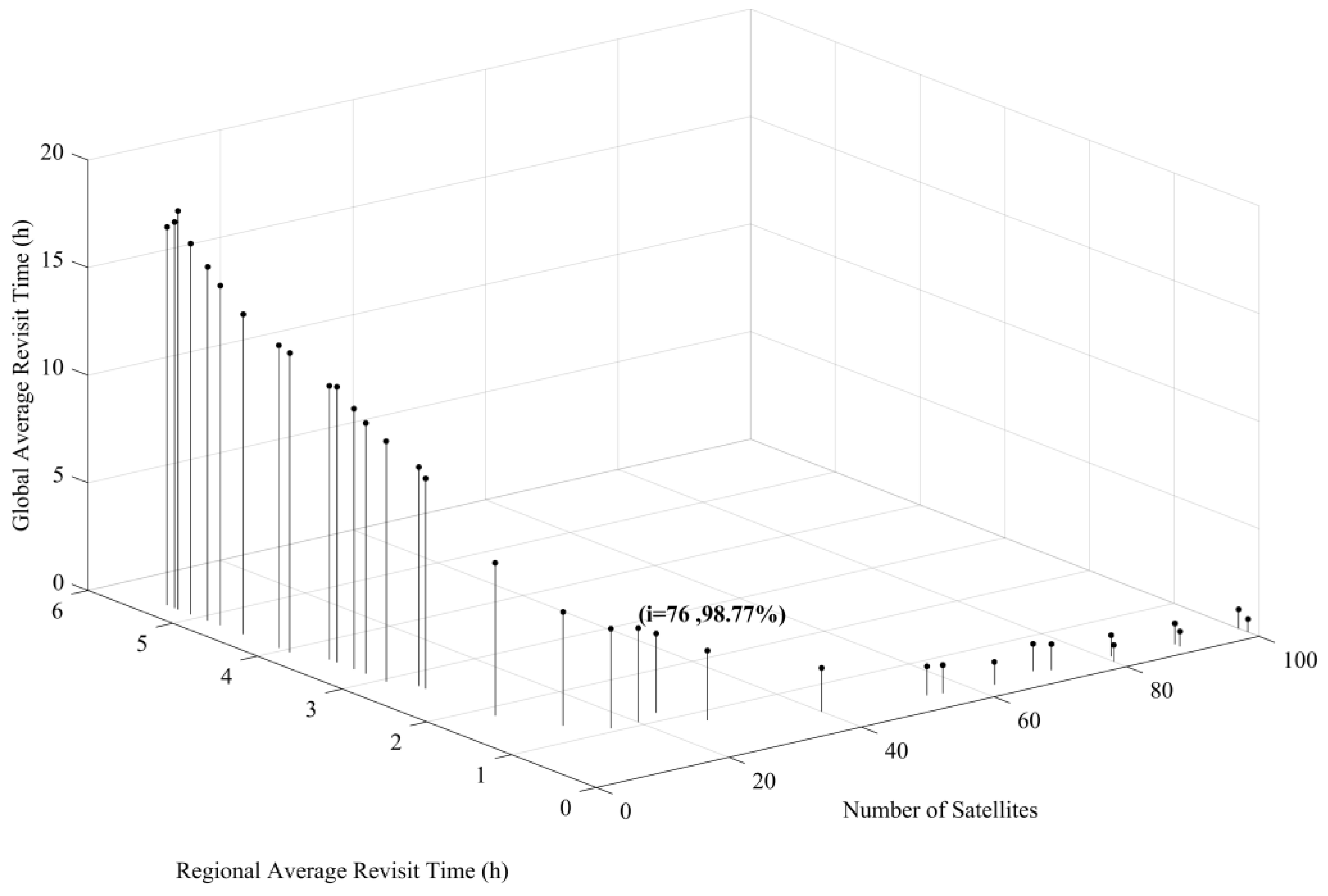
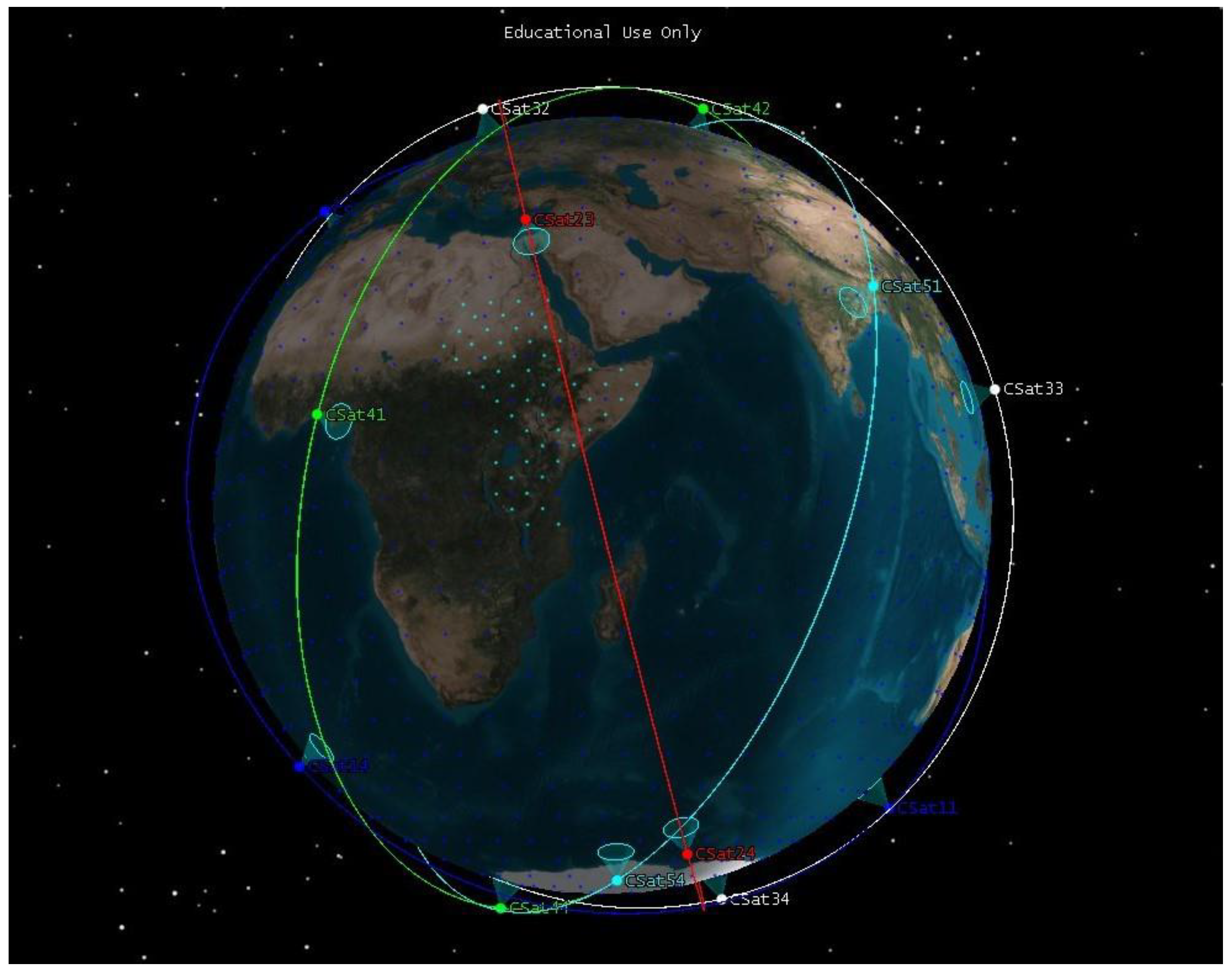
Figure 8 shows a 3D plot of the objective functions , , and . The result shows the conflicting nature of the selected objectives, showing that there is no single solution to satisfy these objectives. Let us consider one solution from all possible feasible solutions in the Pareto optimal solution sets that can compromise all objectives. Solution number 20 in Table 3 has a total of 20 satellites, making it less costly to design, launch, and operate compared to the other solutions with a higher number of satellites. The solution also has a regional ART of 1.07 h, sufficient to monitor and manage most of the natural disasters in the target area [7]. The solution provides 98.77% of global coverage with 4.37 h of ART. Figure 9 shows the CubeSat constellation model for solution number 20.
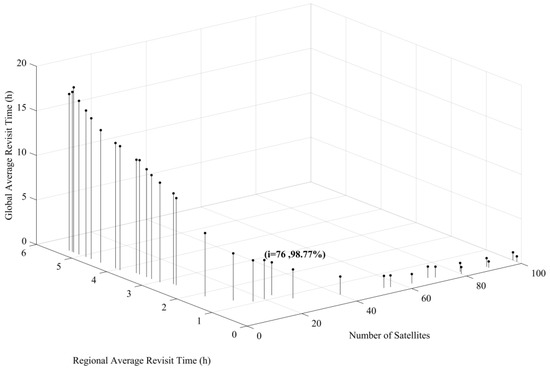
Figure 8.
Relationship between the number of satellites, Regional ART, and Global ART in the optimal solution.
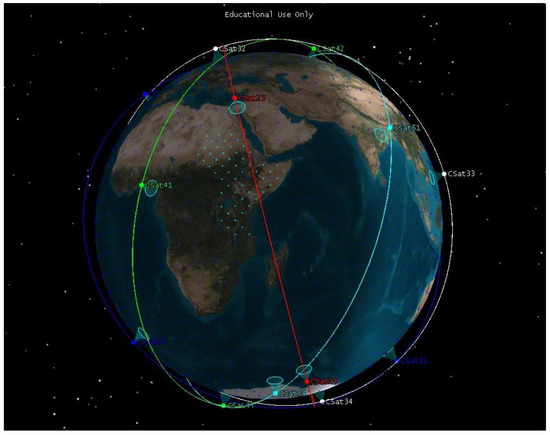
Figure 9.
CubeSat constellation model for solution number 20.
5. Conclusions
This paper presents a computational approach for designing an optimized multi-mission CubeSat constellation system. We have two mission objectives: global Earth observation and regional disaster management. The East African region is selected as the regional target area because it is frequently affected by natural disasters. The objective functions and optimization parameters are chosen by considering the constellation’s requirements and design variables. We propose a modified NSGA-II algorithm to find Pareto optimal solutions.
The study performs two simulation cases, regional and multi-mission, to see the effect on the constellation parameters’ design. The results of the regional simulation case showed a decrease in ART with increasing altitude, but a relative change in ART is small as the number of satellites increases. The second simulation results have shown the capability of CubeSats constellations to perform multiple missions with an acceptable level of performance. The Pareto optimal solution presents all possible feasible solutions. The paper also presents a new mission design approach for the future CubeSat constellation design.
This study can be further extended by developing the communication architecture and protocol for better regional data collection. Furthermore, the mission operation, control, and economic aspects can be further investigated for CubeSat constellation missions. The other consideration is the deployment of the CubeSat constellation. CubeSats are usually launched as a secondary payload, which may not offer the desired launch date and orbit. Several initiatives for a new micro-launch vehicle have recently been underway to change this issue. However, these initiatives face challenges such as competitive pricing, complexity, and scale-down [27].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.D.M. and H.-D.K.; methodology, S.D.M. and H.-D.K.; software, S.D.M.; validation, S.D.M. and H.-D.K.; formal analysis, S.D.M.; investigation, S.D.M. and H.-D.K.; resources, S.D.M.; data curation, S.D.M.; writing—original draft preparation, S.D.M.; writing—review and editing, S.D.M. and H.-D.K.; visualization, S.D.M.; supervision, H.-D.K.; project administration, S.D.M.; funding acquisition, H.-D.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT under Grant 2022M1A3C2074536, Future Space Education Center.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lazreg, N.; Ben Bahri, O.; Besbes, K. Analysis and design of Cubesat constellation for the Mediterranean south costal monitoring against illegal immigration. Adv. Sp. Res. 2018, 61, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti, C.; Robson, D. 2—CubeSat Missions and Applications. In Cubesat Handbook; Cappelletti, C., Battistini, S., Malphrus, B.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villela, T.; Costa, C.A.; Brandão, A.M.; Bueno, F.T.; Leonardi, R. Towards the Thousandth CubeSat: A Statistical Overview. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2019, 2019, 5063145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzi, P.G.; Selva, D.; Hitomi, N.; Blackwell, W.J. Assessment of Constellation Designs for Earth Observation: Application to the TROPICS Mission. Acta Astronaut. 2019, 161, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Chen, W.; Cao, C.; Zhang, C.; Mu, Z. A Multiple-CubeSat Constellation for Integrated Earth Observation and Marine/Air Traffic Monitoring. Adv. Sp. Res. 2021, 67, 3712–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, N.; Elzanaty, A.; Almorad, H.; Dahrouj, H.; Al-Naffouri, T.Y.; Alouini, M.-S. CubeSat Communications: Recent Advances and Future Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tut. 2020, 22, 1839–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santilli, G.; Vendittozzi, C.; Cappelletti, C.; Battistini, S.; Gessini, P. CubeSat constellations for disaster management in remote areas. Acta Astronaut. 2018, 145, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadalavada, P.; Dutta, A. Regional CubeSat Constellation Design to Monitor Hurricanes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2022, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharenko, Y.v.; Berg, W.; Reising, S.C.; Iturbide-Sanchez, F.; Chandrasekar, V. Design and Analysis of CubeSat Microwave Radiometer Constellations to Observe Temporal Variability of the Atmosphere. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth. Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 11728–11736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meziane-Tani, I.; Métris, G.; Lion, G.; Deschamps, A.; Bendimerad, F.T.; Bekhti, M. Optimization of small satellite constellation design for continuous mutual regional coverage with multi-objective genetic algorithm. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2016, 9, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, L.; Fu, W.; Zhou, H.; Li, T.; Xu, B.; Chen, R. LEO Navigation Augmentation Constellation Design with the Multi-Objective Optimization Approaches. Chinese J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Liu, C.; You, P.; Shaowei, Y. Multi-objective optimization design of extended Walker constellation for global coverage services. In Proceedings of the 2016 2nd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 14–17 October 2016; pp. 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poghosyan, A.; Golkar, A. CubeSat evolution: Analyzing CubeSat capabilities for conducting science missions. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2017, 88, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, P.; Guo, J. Star of AOXiang: An innovative 12U CubeSat to demonstrate polarized light navigation and microgravity measurement. Acta Astronaut. 2018, 147, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, R.; López, R.; Ocerin Martínez, E.; Davis, S.; Hernani, J.T.; Brennan-Craddock, R.; Kellerman, N.; Pastena, M.; Melega, N.; Mariani, F. A compact multispectral imager for the MANTIS mission 12U CubeSat. In Proceedings of the CubeSats and SmallSats for Remote Sensing IV; Norton, C.D., Pagano, T.S., Babu, S.R., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2020; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- IFRC World Disasters Report—Leaving No One Behind; International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 9782970128908.
- Cornara, S.; Beech, T.W.; Belló-Mora, M.; Janin, G. Satellite constellation mission analysis and design. Acta Astronaut. 2001, 48, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.M.; Hong, Z.C.; Lee, T.H.; Chang, B.J. Design of a micro-satellite constellation for communication. Acta Astronaut. 2013, 82, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittecar, W.R.; Ferringer, M.P. Global coverage constellation design exploration using evolutionary algorithms. AIAA/AAS Astrodyn. Spec. Conf. 2014, 2014, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kak, A.; Akyildiz, I.F. Designing Large-Scale Constellations for the Internet of Space Things With CubeSats. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 1749–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferringer, M.P.; Spencer, D.B. Satellite constellation design tradeoffs using multiple-objective evolutionary computation. J. Spacecr. Rockets 2006, 43, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitri, T.; Kim, Y.; Jo, S.; Bang, H. Satellite Constellation Orbit Design Optimization with Combined Genetic Algorithm and Semianalytical Approach. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2017, 2017, 1235692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Jia, Q.; Shao, X. Optimal small satellite orbit design based on robust multi-objective optimization method. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 70, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallado, D.A.; MacClain, W.D. Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications; Kluwer Academic Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bate, R.R.; Mueller, D.D.; White, J.E. Fundamentals of Astrodynamics; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Wekerle, T.; Pessoa Filho, J.B.; da Costa, L.E.V.L.; Trabasso, L.G. Status and Trends of Smallsats and Their Launch Vehicles—An Up-to-Date Review. J. Aerosp. Technol. Manag. 2017, 9, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).